Structural Assessment of Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, and Hydroxide Substitutions in Lead Arsenate Apatites (Mimetites)–Pb5(AsO4)3X
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Analytical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Characteristics of the Synthesized Products
3.2. Rietveld Refinement from High-Resolution Synchrotron Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elliott, J.C.; Wilson, R.M.; Dowker, S.E.P. Apatite structures. Adv. X Ray Anal. 2002, 45, 172–181. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J.; Dong, Z. Structural derivation and crystal chemistry of apatites. Acta Cryst. B 2003, 59, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.; Ferraris, C.; Kim, J.; Madhavi, S. Apatite–An adaptive framework structure. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2005, 57, 307–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasero, M.; Kampf, A.R.; Ferraris, C.; Pekov, I.V.; Rakovan, J.; White, T.J. Nomenclature of the apatite supergroup minerals. Eur. J. Miner. 2010, 22, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptáček, P. Apatites and Their Synthetic Analogues—Synthesis, Structure, Properties and Applications; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.C. Structure and Chemistry of the Apatites and Other Calcium Phosphates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; ISBN 0-444-81582-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, J.M.; Rakovan, J.F. Structurally robust, chemically diverse: Apatite and apatite supergroup minerals. Elements 2015, 11, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, P.E.; Elliot, J.C.; Young, R.A. Monoclinic structure of synthetic Ca5(PO4)3Cl, chlorapatite. Acta Cryst. B 1972, 28, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, M.; Marumo, F.; Iwai, S.; Aoki, H. Structure of barium chlorapatite. Acta Cryst. B 1979, 35, 2382–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, H.; Matsumoto, T. Structure refinements of two natural pyromorphites, Pb5(PO4)3Cl, and crystal chemistry of chloroapatite group, M5(PO4)3Cl. Z. Kristallogr. 1998, 213, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Fenton, R.R.; Hunter, B.A.; Kennedy, B.J. Powder diffraction studies of synthetic calcium and lead apatites. Aust. J. Chem. 2000, 53, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audubert, F.; Savariault, J.M.; Lacout, J.L. Pentalead tris (vanadate) iodide, a defect vanadinite-type compound. Acta Cryst. C 1999, 55, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Maddrell, E.R.; Abraitis, P.K.; Salje, E.K.H. Impact of leach on lead vanado-iodoapatite [Pb5(VO4)3I]: An infrared and Raman spectroscopic study. Mat. Sci. Eng. B Adv. 2007, 137, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stennett, M.C.; Pinnock, I.J.; Hyatt, N.C. Rapid synthesis of Pb5(VO4)3I, for the immobilisation of iodine radioisotopes, by microwave dielectric heating. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 414, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetsugu, Y. Synthesis of lead vanadate iodoapatite utilizing dry mechanochemical process. J. Nucl. 2014, 454, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merker, L.; Wondratschek, H. Bleiverbindungen mit Apatitstruktur, insbesondere Blei–Jod–und Blei–Brom-Apatite. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1959, 300, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, C.M.B.; Bell, A.M.T.; Charnock, J.M.; Knight, K.S.; Wendlandt, R.F.; Plant, D.A.; Harrison, W.J. Synchrotron X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray powder diffraction studies of the structure of johnbaumite [Ca10(AsO4)6(OH,F)2] and synthetic Pb-, Sr- and Ba-arsenate apatites and some comments on the crystal chemistry of the apatite structure type in general. Miner. Mag. 2009, 73, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epp, T.; Marks, M.A.; Ludwig, T.; Kendrick, M.A.; Eby, N.; Neidhardt, H.; Oelmann, Y.; Markl, G. Crystallographic and fluid compositional effects on the halogen (Cl, F, Br, I) incorporation in pyromorphite-group minerals. Am. Miner. 2019, 104, 1673–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zeng, Y.Z.; Wang, C.M. Prediction of apatite lattice constants from their constituent elemental radii and artificial intelligence methods. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markl, G.; Marks, M.A.; Holzäpfel, J.; Wenzel, T. Major, minor, and trace element composition of pyromorphite-group minerals as recorder of supergene weathering processes from the Schwarzwald mining district, SW Germany. Am. Miner. 2014, 99, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manecki, M.; Maurice, P.A.; Traina, S.J. Uptake of aqueous Pb by Cl−, F−, and OH− apatites: Mineralogic evidence for nucleation mechanisms. Am. Miner. 2000, 85, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajda, T. Solubility of mimetite Pb5(AsO4)3Cl at 5–55 °C. Env. Chem. 2010, 7, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkiewicz, O.; Rakovan, J.; Cahill, C.L. Time-resolved in situ studies of apatite formation in aqueous solutions. Am. Miner. 2010, 95, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flis, J.; Borkiewicz, O.; Bajda, T.; Manecki, M.; Klasa, J. Synchrotron-based X-ray diffraction of the lead apatite series Pb10(PO4)6Cl2–Pb10(AsO4)6Cl2. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2010, 17, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajda, T.; Mozgawa, W.; Manecki, M.; Flis, J. Vibrational spectroscopic study of mimetite–pyromorphite solid solutions. Polyhedron 2011, 30, 2479–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicka, U.; Bajda, T.; Manecki, M. Synthesis and solubility of brompyromorphite Pb5(PO4)3Br. Miner. Pol. 2012, 43, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaśniak-Kominek, M.; Matusik, J.; Bajda, T.; Manecki, M.; Rakovan, J.; Marchlewski, T.; Szala, B. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic study of hydroxylpyromorphite Pb10(PO4)6OH2 –hydroxylmimetite Pb10(AsO4)6(OH)2 solid solution series. Polyhedron 2015, 99, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzio, B.; Manecki, M.; Kwaśniak-Kominek, M. Transition from Endothermic to Exothermic Dissolution of Hydroxyapatite Ca5(PO4)3OH–Johnbaumite Ca5(AsO4)3OH Solid Solution Series at Temperatures Ranging from 5 to 65 °C. Minerals 2018, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.Y.; Traina, S.J.; Logan, T.J.; Ryan, J.A. In situ lead immobilization by apatite. Env. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Schwartz, F.W. Lead immobilization by hydroxyapatite in aqueous solutions. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1994, 15, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.Y.; Logan, T.J.; Traina, S.J. Lead immobilization from aqueous solutions and contaminated soils using phosphate rocks. Env. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Q. Factors influencing the effectiveness and stability of aqueous lead immobilization by hydroxyapatite. J. Env. Qual. 1996, 25, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laperche, V.; Traina, S.J.; Gaddam, P.; Logan, T.J. Chemical and mineralogical characterizations of Pb in a contaminated soil: Reactions with synthetic apatite. Env. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 3321–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laperche, V.; Logan, T.J.; Gaddam, P.; Traina, S.J. Effect of apatite amendments on plant uptake of lead from contaminated soil. Env. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2745–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpiene, J.; Lagerkvist, A.; Maurice, C. Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments–a review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhao, L.; Arellano, E. Biochar- and phosphate-induced immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated soil and water: Implication on simultaneous remediation of contaminated soil and groundwater. Env. Sci. Pollut. 2014, 21, 4665–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.; Wan, J.; Huang, D.; Hu, L.; Huang, C.; Cheng, M.; Xue, W.; Gong, X.; Wang, R.; Jiang, D. Precipitation, adsorption and rhizosphere effect: The mechanisms for phosphate-induced Pb immobilization in soils—a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manecki, M. Lead in Water and Soil: Speciation, Toxicity, and Treatment Technologies. In Encyclopedia of Water: Science, Technology, and Society; Maurice, P.A., Ed.; Willey: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1713–1727. ISBN 978-1-119-30075-5. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, W.J.; Wendlandt, R.F.; Wendlandt, A.E. Low temperature aqueous solubility and stability of apatite-structure arsenates of lead, barium, and strontium and uptake of arsenic by hydroxylapatite. In Proceedings of the 18th General Meeting of the International Mineralogical Association, Edinburgh, Scotland, 1–6 September 2002; p. 185, Programme with Abstracts, Abstract A18-10. [Google Scholar]
- Wendlandt, A.E.; Harrison, W.J.; Wendlandt, R.F. Investigation of hydroxylapatite as a means of removing dissolved arsenic from potable water. In Proceedings of the Geological Society of America Annual Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 27–31 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, W.J.; Wendlandt, R.F.; Charnock, J.M.; Henderson, C.M.B. Spectroscopic investigations of the adsorption of As onto bovine bone. In Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69, Proceedings of the 15th Annual Goldschmidt Conference, Moscow, ID, USA, 21–25 May 2005; Elsvier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; p. A65. [Google Scholar]
- Bundschuh, J.; Holländer, H.M.; Ma, Q. In-Situ Remediation of Arsenic-Contaminated Sites; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; p. 208. ISBN 9781138747753. [Google Scholar]
- Rakovan, J.F.; Hughes, J.M. Strontium in the apatite structure: Strontian fluorapatite and belovite-(Ce). Can. Miner. 2000, 38, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.C. The design and evaluation of nuclear-waste forms: Clues from mineralogy. Can. Miner. 2001, 39, 697–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Fleet, M.E. Compositions of the apatite-group minerals: Substitution mechanisms and controlling factors. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2002, 48, 13–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakovan, J.; Reeder, R.J.; Elzinga, E.J.; Cherniak, D.J.; Tait, C.D.; Morris, D.E. Structural characterization of U(VI) in apatite by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Env. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3114–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Hughes, J.M.; Rakovan, J.; Pan, Y. Site preference of U and Th in Cl, F, and Sr apatites. Am. Miner. 2009, 94, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audubert, F.; Carpena, J.; Lacout, J.L.; Tetard, F. Elaboration of an iodine-bearing apatite iodine diffusion into a Pb3(VO4)2 matrix. Solid State Ion. 1997, 95, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, M.; Kosuga, A.; Masuo, S.; Imamura, M.; Yamanaka, S. Thermal and mechanical properties of AgPb9(VO4)6I and AgBa9(VO4)6I. J. Alloy. Compd. 2004, 384, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campayo, L.; Grandjean, A.; Coulon, A.; Delorme, R.; Vantelon, D.; Laurencin, D. Incorporation of iodates into hydroxyapatites: A new approach for the confinement of radioactive iodine. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 17609–17611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Lu, F.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Ewing, R.C.; Lian, J. Bulk iodoapatite ceramic densified by spark plasma sintering with exceptional thermal stability. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 2409–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, P.H.; Le Page, Y.; Whitfield, P.S.; Mitchell, L.D.; Davidson, I.J.; White, T.J. Geometrical parameterization of the crystal chemistry of P63/m apatites: Comparison with experimental data and ab initio results. Acta Cryst. B 2005, 61, 635–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegas, A.; Jansen, M. Structural relationships between cations and alloys; an equivalence between oxidation and pressure. Acta Cryst. B 2002, 58, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, P.H.; Le Page, Y.; Whitfield, P.S.; Mitchell, L.D. Geometrical parameterization of the crystal chemistry of P63/m apatite. II. Precision, accuracy and numerical stability of the crystal-chemical Rietveld refinement. J. Appl. Cryst. 2006, 39, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, W.E. An X-ray diffraction study of synthetic members of the pyromorphite series. Am. Miner. 1966, 51, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak, H.; Diduszko, R.; Kozak, M. XRAYAN Program do Rentgenowskiej Analizy Fazowej, Wersja 4.0.1; Koma: Warszawa, Poland, 2006. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Holland, T.J.B.; Redfern, S.A.T. UNITCELL: A nonlinear least-squares program for cell-parameter refinement and implementing regression and deletion diagnostics. J. App. Cryst. 1997, 30, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.C.; Von Dreele, R.B. General Structure Analysis System; Report LAUR 86-748; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Almos, NM, USA, 1994.
- Toby, B.H. EXPGUI, a graphical user interface for GSAS. J. Appl. Cryst. 2001, 34, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Cryst. 2011, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.A. The Rietveld Method; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; p. 298. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Hughes, J.M. Crystal structure refinements of vanadinite and pyromorphite. Can. Miner. 1989, 27, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Baikie, T.; Ferraris, C.; Klooster, W.T.; Madhavi, S.; Pramana, S.S.; Pring, A.; Schmidt, G.; White, T.J. Crystal chemistry of mimetite, Pb10(AsO4)6Cl1.48O0. 26, and finnemanite, Pb10(AsO3)6Cl2. Acta Cryst. B 2008, 64, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Hughes, J.M.; Moore, P.B. The crystal structure of mimetite and clinomimetite, Pb5(AsO4)3Cl. Can. Miner. 1991, 29, 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Baikie, T.; Schreyer, M.; Wei, F.; Herrin, J.S.; Ferraris, C.; Brink, F.; Topolska, J.; Piltz, R.O.; Price, J.; White, T.J. The influence of stereochemically active lone-pair electrons on crystal symmetry and twist angles in lead apatite-2H type structures. Miner. Mag. 2014, 78, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreidler, E.R.; Hummel, F.A. The crystal chemistry of apatite: Structure fields of fluor- and chlorapatite. Am. Miner. 1970, 55, 170–184. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.J.; Stephens, P.W.; Tang, Y.; Li, W.; Phillips, B.L.; Parise, J.B.; Reeder, R.J. Arsenate substitution in hydroxylapatite: Structural characterization of the Ca5(PxAs1–xO4)3OH solid solution. Am. Miner. 2009, 94, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsanan, K.; Young, R.A. Structure of strontium hydroxide phosphate, Sr5(PO4)3OH. Acta Cryst. B 1972, 28, 3668–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corker, D.L.; Chai, B.H.T.; Nicholls, J.O.H.N.; Loutts, G.B. Neodymium-Doped Sr5(PO4)3F and Sr5(VO4)3F. Acta Cryst. C 1995, 51, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nötzold, D.; Wulff, H.; Herzog, G. Differenzthermoanalyse der Bildung des Pentastrontiumchloridphosphats und röntgenographische Untersuchung seiner Struktur. J. Alloys Compd. 1994, 215, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberius-Henning, P.; Mattsson, C.; Lidin, S. Crystal structure of pentastrontium tris(phosphate) bromide, Sr5(PO4)3Br and of pentabarium tris(phosphate) bromide Ba5(PO4)3Br, two bromoapatites. Z. Krist. Ncs 2000, 215, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đordević, T.; Šutović, S.; Stojanović, J.; Karanović, L. Sr, Ba and Cd arsenates with the apatite-type structure. Acta Cryst. C 2008, 64, i82–i86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calos, N.J.; Kennard, C.H.; Davis, R.L. Crystal structure of mimetite, Pb5(AsO4)3Cl. Z. Krist. Cryst. Mater. 1990, 191, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okudera, H. Relationships among channel topology and atomic displacements in the structures of Pb5(BO4)3Cl with B = P (pyromorphite), V (vanadinite), and As (mimetite). Am. Miner. 2013, 98, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






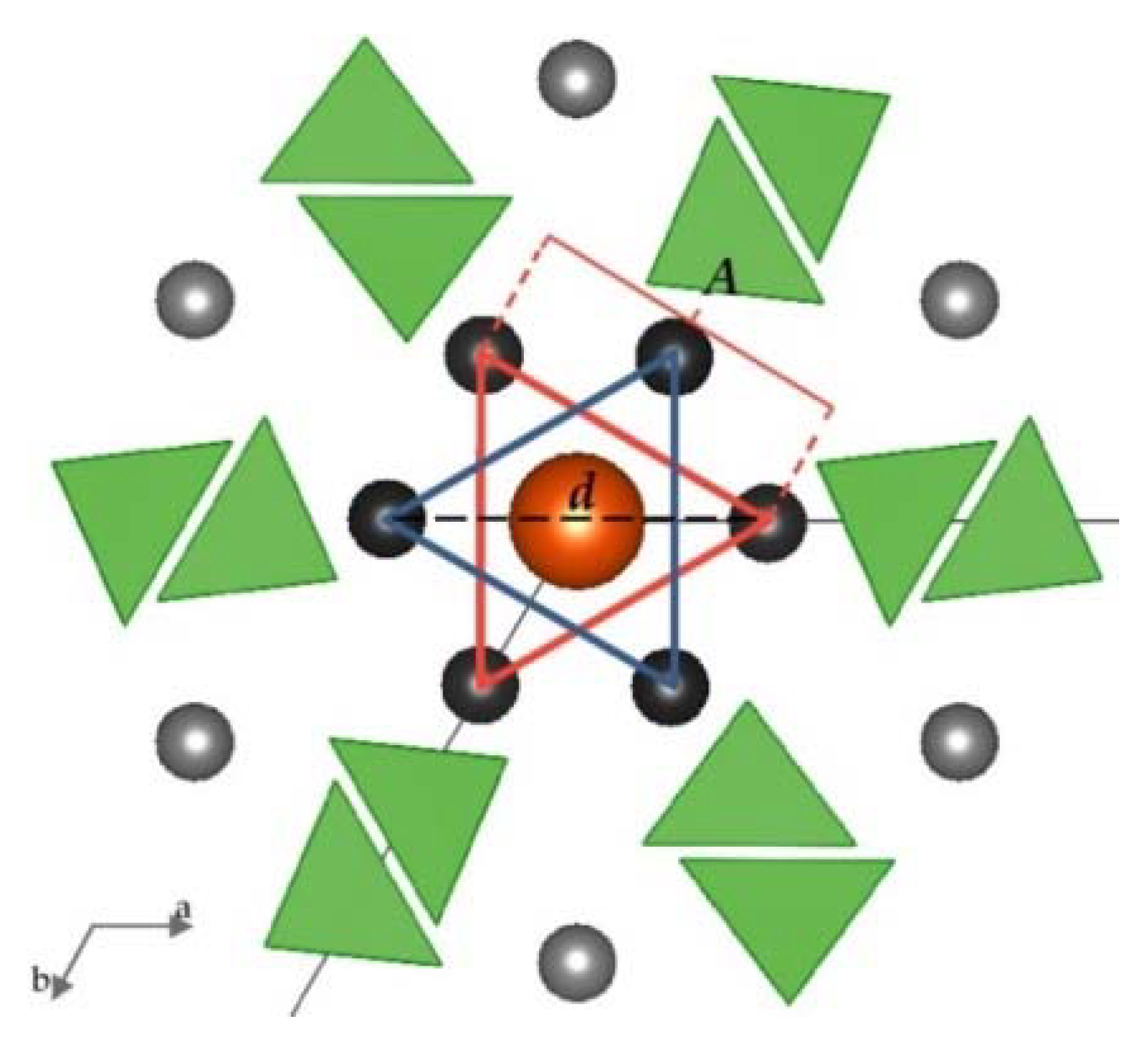


| Intended Chemical Formula | Empirical Chemical Formula | Sample Name |
|---|---|---|
| Pb5(AsO4)3F | Pb5.00(AsO4)2.99F0.98 | mimetite-F |
| Pb5(AsO4)3Cl | Pb5.00(AsO4)2.99Cl1.00 | mimetite-Cl |
| Pb5(AsO4)3Br | Pb5.00(AsO4)2.98Br0.97 | mimetite-Br |
| Pb5(AsO4)3I | Pb5.00(AsO4)3.03I0.60 | mimetite-I |
| Pb5(AsO4)3OH | Pb5.00(AsO4)3.01OH1.00 | mimetite-OH |
| Atom | Parameters | X = F | X = Cl | X = Br | X = I | X = OH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a [Å] | 10.081 | 10.249 | 10.312 | 10.353 | 10.187 | ||
| c [Å] | 7.426 | 7.443 | 7.474 | 7.530 | 7.523 | ||
| V [Å3] | 653.619(8)a | 677.00(4) | 688.320(19) | 699.125(24) | 676.303(13) | ||
| rX [Å]b | 1.33 | 1.81 | 1.96 | 2.20 | 1.37 | ||
| Av CR [Å]c | 1.21 | 1.23 | 1.24 | 1.25 | 1.21 | ||
| Pb(1) | x | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | |
| y | 2/3 | 2/3 | 2/3 | 2/3 | 2/3 | ||
| z | 0.00463(14) | 0.00506 | 0.00577(34) | 0.00706(27) | 0.00357 | ||
| Uiso [Å2] | 0.01415(10) | 0.01967 | 0.02438 | 0.02871 | 0.02292 | ||
| Pb(2) | x | 0.23638(5) | 0.25085 | 0.25530(12) | 0.25888(12) | 0.24762 | |
| y | 1.00391(9) | 1.00362 | 1.00160(20) | 0.99753(19) | 0.99940 | ||
| z | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | ||
| Uiso [Å2] | 0.02296(10) | 0.01971 | 0.02286 | 0.03552 | 0.03163 | ||
| As | x | 0.40395(11) | 0.40714 | 0.40896(20) | 0.40491(21) | 0.40060 | |
| y | 0.38267(10) | 0.38331 | 0.37815(17) | 0.380001(17) | 0.37689 | ||
| z | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | ||
| Uiso [Å2] | 0.00984(23) | 0.00883 | 0.00838 | 0.01515 | 0.01508 | ||
| O(1) | x | 0.3208(6) | 0.32833 | 0.34000h | 0.3567(18) | 0.33388 | |
| y | 0.4936(5) | 0.49474 | 0.49543h | 0.5111(14) | 0.49738 | ||
| z | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | ||
| Uiso [Å2] | 0.0128(17) | 0.04555 | 0.08219 | 0.09133 | 0.02269 | ||
| O(2) | x | 0.59886(15) | 0.60045 | 0.60049(23) | 0.5960(7) | 0.59424 | |
| y | 0.4962(5) | 0.48128 | 0.4738(12) | 0.4827(12) | 0.48179 | ||
| z | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | ||
| Uiso [Å2] | 0.0158(18) | 0.02689 | 0.03885 | 0.07495 | 0.06533 | ||
| O(3) | x | 0.3518(4) | 0.35298 | 0.3494(10) | 0.3591(10) | 0.35403 | |
| y | 0.2658(4) | 0.27245 | 0.2733(9) | 0.2650(9) | 0.26182 | ||
| z | 0.0689(5) | 0.06819 | 0.0636(8) | 0.0758(9) | 0.07079 | ||
| Uiso [Å2] | 0.0190(13) | 0.04534 | 0.06731 | 0.11329 | 0.03906 | ||
| X | x | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| y | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| z | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 0.37433 | ||
| Uiso [Å2] | 0.138(7) | 0.00555 | 0.01941 | 0.025f | 0.52451 | ||
| Occ.d | 1.012(19) | 0.80446 | 0.797(5) | 0.4629(29) | 0.86556 | ||
| x | 0e | 0e | 0i | 0e | |||
| y | 0e | 0e | 0i | 0e | |||
| z | 1/2e | 1/2e | 1/2i | 0.37182e | |||
| Uiso [Å2] | 0.025e,f | 0.025e,f | 0.025f,i | 0.03003e,f | |||
| Occ. | 0.0535e | 0.044(5)e | 0.6150(29)i | 0.04227e | |||
| x | 0.74971g | 0.796(5)g | 0.59585g | ||||
| y | 0.78630g | 0.828(5)g | 1.10557g | ||||
| z | 0.12045g | 0.102(5)g | 0.12728g | ||||
| Uiso [Å2] | 0.025f,g | 0.025f,g | 0.03003f,g | ||||
| Occ. | 0.18841g | 0.143(14)g | 0.14682g | ||||
| wRp [%] | 9.64 | 7.64 | 8.38 | 7.46 | 9.53 | ||
| Rp [%] | 7.67 | 6.43 | 7.10 | 6.28 | 7.94 | ||
| χ2 | 3.056 | 0.901 | 1.021 | 1.009 | 1.918 |
| Bonds | This Study | Dai et al. [64] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X = F | X = Cl | X = Br | X = I | X = OH | X = Cl | |
| As–O(1) | 1.700 | 1.696 | 1.681 | 1.664(6) | 1.674 | 1.70 |
| As–O(2) | 1.709 | 1.715 | 1.710 | 1.715(6) | 1.710 | 1.72 |
| As–O(3) | 1.689 | 1.673 | 1.679 | 1.673(4) | 1.691 | 1.67 |
| Average As–O | 1.698(9) | 1.689(20) | 1.687(15) | 1.68(1) | 1.691(12) | 1.69 |
| Distortion index | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.010 | 0.005 | |
| Pb(1)–O(1) | 2.482 | 2.518 | 2.564 | 2.528(5) | 2.534 | 2.52 |
| Pb(1)–O(2) | 2.803(4) | 2.718 | 2.685(9) | 2.793(9) | 2.754 | 2.78 |
| Pb(1)–O(3) | 2.946(4) | 3.002 | 3.054 | 2.963(9) | 2.944 | 2.94 |
| Pb(2)–O(1) | 3.005(5) | 3.063 | 3.137 | 3.264 | 3.058 | 3.07 |
| Pb(2)–O(2) | 2.362(4) | 2.385 | 2.421(11) | 2.322(10) | 2.398 | 2.33 |
| Pb(2)–O(3) | 2.605 | 2.567 | 2.514(6) | 2.643(7) | 2.617 | 2.63 |
| Pb(2)–O(3) | 2.657(4) | 2.762 | 2.831(10) | 2.755(10) | 2.691 | 2.73 |
| Pb(2)–X | 3.005 | 3.158 | 3.222 | 3.286 | 2.693 | 3.16 |
| Twist angle (φ)° | 20.34(20) | 19.04(26) | 16.38(05) | 11.42(16) | 18.60(26) | 18 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sordyl, J.; Puzio, B.; Manecki, M.; Borkiewicz, O.; Topolska, J.; Zelek-Pogudz, S. Structural Assessment of Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, and Hydroxide Substitutions in Lead Arsenate Apatites (Mimetites)–Pb5(AsO4)3X. Minerals 2020, 10, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10060494
Sordyl J, Puzio B, Manecki M, Borkiewicz O, Topolska J, Zelek-Pogudz S. Structural Assessment of Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, and Hydroxide Substitutions in Lead Arsenate Apatites (Mimetites)–Pb5(AsO4)3X. Minerals. 2020; 10(6):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10060494
Chicago/Turabian StyleSordyl, Julia, Bartosz Puzio, Maciej Manecki, Olaf Borkiewicz, Justyna Topolska, and Sylwia Zelek-Pogudz. 2020. "Structural Assessment of Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, and Hydroxide Substitutions in Lead Arsenate Apatites (Mimetites)–Pb5(AsO4)3X" Minerals 10, no. 6: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10060494
APA StyleSordyl, J., Puzio, B., Manecki, M., Borkiewicz, O., Topolska, J., & Zelek-Pogudz, S. (2020). Structural Assessment of Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, and Hydroxide Substitutions in Lead Arsenate Apatites (Mimetites)–Pb5(AsO4)3X. Minerals, 10(6), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10060494






