Abstract
Hydrothermal processes have played a significant role in rare earth element (REE) precipitation in the Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit. The poor preservation of primary fluid inclusions and superposition or modification by multiphase hydrothermal activities have made identification of physico-chemical conditions of ore-forming fluids extremely difficult. Fortunately, with more and more reliable thermodynamic properties of aqueous REE species and REE minerals reported in recent years, a series of thermodynamic calculations are conducted in this study to provide constraints on REE precipitation in hydrothermal solutions, and provide an explanation of typical paragenesis of REE and gangue minerals at Bayan Obo. During the competition between fluocerite and monazite for LREE in the modelled solution (0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF and 0.1 M trichloride of light rare earth elements (LREE) from La to Sm), all LREE would eventually be hosted by monazite at a temperature over 300 °C, with continuous introduction of H3PO4. Additionally, monazite of heavier LREE would precipitate earlier, indicating that the Ce- and La-enriched monazite at Bayan Obo was crystallized from Ce and La pre-enriched hydrothermal fluids. The fractionation among LREE occurred before the ore-forming fluids infiltrating ore-hosting dolomite. When CO2 (aq) was introduced to the aqueous system (model 1), bastnaesite would eventually and completely replace monazite-(Ce). Cooling of hot hydrothermal fluids (>400 °C) would significantly promote this replacement, with only about one third the cost of CO2 for the entire replacement when temperature dropped from 430 °C to 400 °C. Sole dolomite addition (model 2) would make bastnaesite replace monazite and then be replaced by parisite. The monazite-(Ce) replaced by associated bastnaesite and apatite is an indicator of very hot hydrothermal fluids (>400 °C) and specific dolomite/fluid ratios (e.g., initial dolomite at 1 kbar: 0.049–0.068 M and 0.083–0.105 M at 400 °C and 430 °C). In hot solution (>430 °C) that continuously interacts with dolomite, apatite precipitates predating the bastnaesite, but it behaves oppositely at <400 °C. The former paragenesis is in accord with petrography observed in this study. Some mineral pairs, such as monazite-(Ce)-fluorite and monazite-(Ce)-parisite would never co-precipitate at any calculated temperature or pressure. Therefore, their association implies multiphase hydrothermal activities. Pressure variation would have rather limited influence on the paragenesis of REE minerals. However, temperature and fluid composition variation (e.g., CO2 (aq), dolomite, H3PO4) would cause significantly different associations between REE and gangue minerals.
1. Introduction
The Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit is a typical carbonatite-related deposit, which indicates the rare earth element (REE) resources originated from local carbonatite magma [1,2]. However, there is still controversy about whether the abnormal REE enrichment was initiated during the intrusion of dolomitic carbonatite melt, or during hydrothermal metasomatism which overlapped a sedimentary carbonate formation [3,4]. Regardless of the origin of the ore-hosting dolomite, it is widely accepted that carbonatite-related hydrothermal processes are critical to the ultimate REE enrichment [5]. Some recent studies have even proposed that most of the REE-bearing minerals precipitated during hydrothermal processes at Bayan Obo [6,7]. There is a fundamental problem about the physico-chemical conditions of the ore-forming fluids and REE precipitation. Unfortunately, the primary fluid inclusions were poorly preserved at Bayan Obo. Although a few fluid inclusions with fluorocarbonate daughter minerals reach homogenization at over 400 °C [8], most of the fluid inclusions trapped in the megacrysts of gangue minerals from the vein-type ores display a homogenization temperature <340 °C, which is far lower than the highest temperature of the Bayan Obo carbonatite and ore-hosting dolomite calculated by dolomite–calcite geothermometry [5,9,10]. Therefore, it is difficult to analyze the Mesoproterozoic ore-forming fluids directly.
Thermodynamic modelling provides an alternative approach to the physico-chemical conditions of the ore-forming fluids and REE precipitation. Additionally, these semi-quantitative calculations are able to explain the paragenesis or sequent formation of various REE minerals qualitatively, which is vital to exploring the theoretical mechanism of Bayan Obo REE mineralization. In recent years, the fluorine and chlorine complexes of REE have been demonstrated to be the most important REE carriers during transportation, and more accurate thermodynamic properties of these species at higher temperature were also extrapolated accordingly [11]. The standard thermodynamic properties (lattice parameters, heat capacity and entropy of formation) of bastnaesite and parisite have been experimentally determined [12]. Several studies have provided general thermodynamic explanation of REE transportation and precipitation [13,14,15]. However, there has been no specific thermodynamic modelling based on the mineralogy and petrography of the Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit yet. Considering that the dominating REE-bearing minerals at Bayan Obo are monazite and fluorocarbonate (bastnaesite, parisite and so on), it is time to perform thermodynamic calculations about the precipitation of REE minerals when all the requirements have been met.
2. Geological Setting
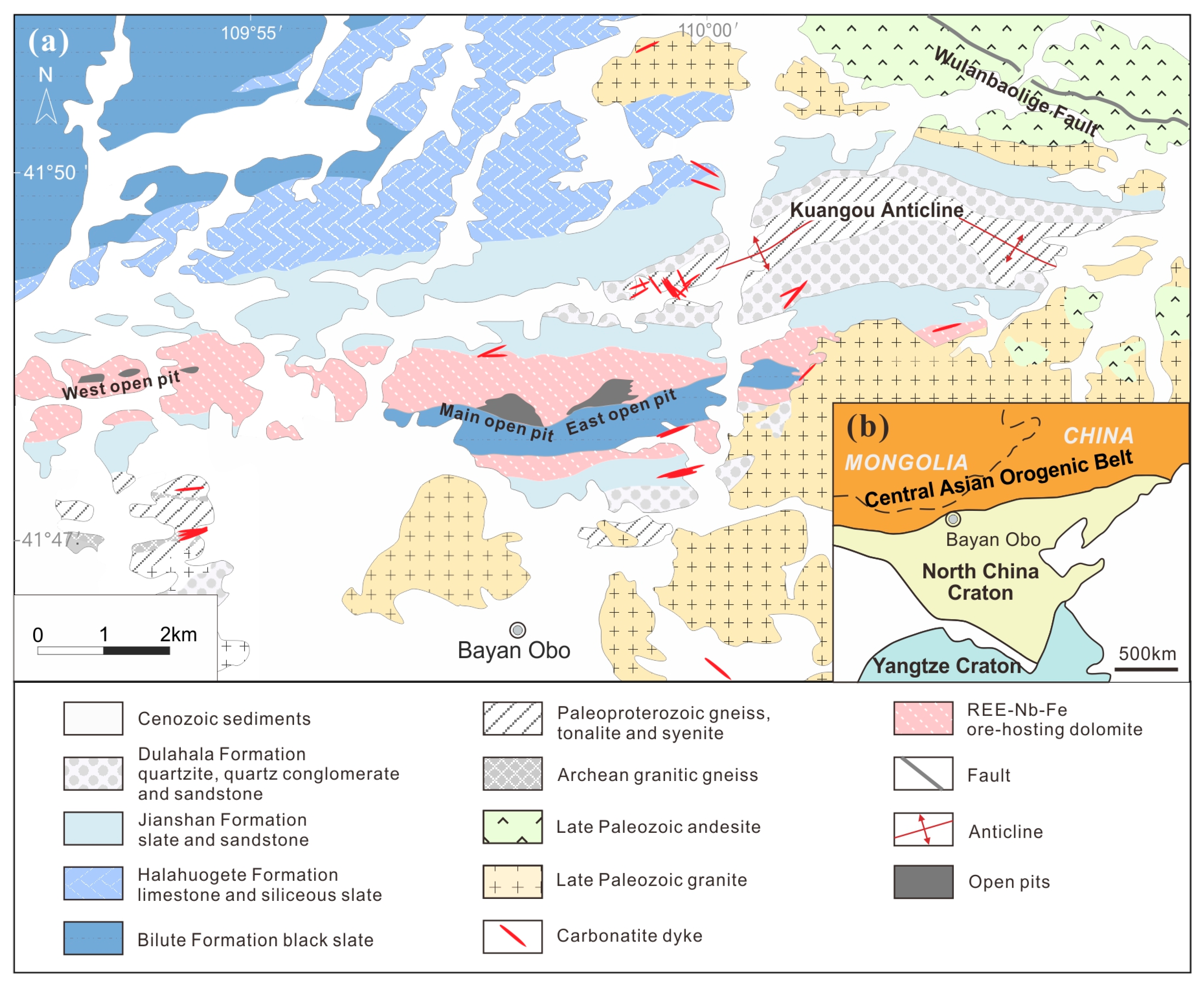
The geological setting of the Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit is well-known and described in dozens of articles in detail [2,16,17]. There will only be a concise summary here. The Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit is located on the north margin of the North China Craton (Figure 1b). At the age of 1.4–1.3 Ga [18], the Mesoproterozoic carbonatite intruded the Archean-Paleoproterozoic metamorphic basement rocks (2.4 Ga and 2.0 Ga of granitic gneiss and 2.0 Ga tonalite) [19,20,21] and the Paleoproterozoic-Mesoproterozoic metasedimentary cover, named as Lower Bayan Obo Group (1.8–1.4 Ga) [22,23,24,25]. The wall rock of some Bayan Obo carbonatite dykes suffered alkali metasomatism (fenitization) caused by hydrothermal fluids derived from these carbonatite dykes [26]. Meanwhile, the Bayan Obo ore-hosting dolomite, where most REE and Nb resources are host, also suffered extensive alkali and fluorine metasomatism. The ore-hosting dolomite is a nearly W-E-trending dolomite unit, enveloping a layer of black slate of Bayan Obo Group with similar trending (Figure 1a). Extensive alkali metasomatism also occurred in the slate in contact with the surrounding ore-hosting dolomite [27,28].
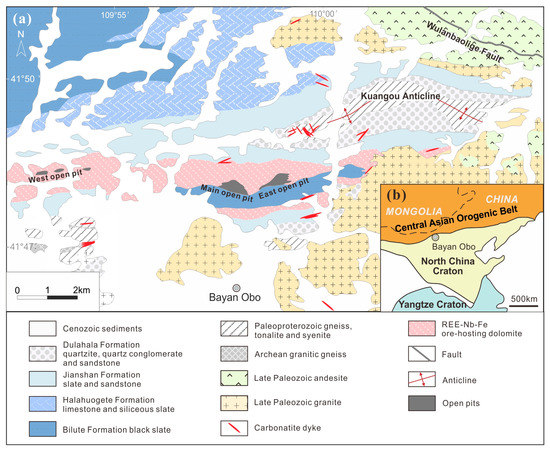
Figure 1.
The geological setting of the Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit (adapted from Yang et al. [18]) has been plotted in (a). The location of the Bayan Obo deposit in China is marked in the interior plot (b).
The carbonatite dykes at Bayan Obo were classified into magnesio-ferro-carbonatite dykes and calcio-carbonatite dykes, according to their major components. There are barely any REE-bearing minerals in the Mg-Fe-carbonatite dykes, except discrete monazite grains [7]. In contrast, the Ca-carbonatite dykes contain abundant bastnaesite and parisite, so that this kind of dyke may contain REE oxides even up to nearly 20 wt% [29]. The ore-hosting dolomite consists of coarse-grained dolomite on the margin of open pits, with only a few interstitial monazite grains, and extensively-altered fine-grained dolomite that is interior to the whole dolomite unit, containing the majority of the monazite and fluorocarbonates. Partial fine-grained dolomite was altered into diverse ores with certain grades of REE, Nb or Fe.
3. Methods
The backscatter electron imaging and energy-dispersive spectrum analyses were conducted on a FEI Nova Nano SEM 450 scanning electron microscope, at the State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Northwest University, China. The acceleration voltage was set as 20.0 kV, with a probe diameter of 4 μm. X-ray mapping was performed for monazite-bastnaesite associated thin section, because various REE minerals are indistinguishable in BSE imaging.
Thermodynamic calculations were conducted on the software GEM Selektor v.3.4, which is designed for thermodynamic modelling of an aqueous system by Gibbs energy minimization [30,31]. The database PSI/Nagra 12-07, embedded in the GEMS [32], and a third-party database named MINES 2017, packaged by Gysi and Williams-Jones [33] and Gysi [34], were adopted during the calculations. The MINES database includes revised SUPCRT92 data for aqueous species in addition to data on common ore and gangue minerals. Due to the limited data in these databases, the properties of some species were manually entered into the modified MINES 2017. The standard thermodynamic properties of fluocerite of LREE (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm) were cited from Konings and Kovács [35] (S0, Cp0) and Migdisov et al. [11,15] (G0, V0). The data on phosphates of LREE (LnPO4, Ln=La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm) were collected from Ni et al. [36] (V0), Ushakov et al. [37] (H0), Thiriet et al. [38] (S0, G0) and Popa et al. [39,40,41] (Cp0). The standard thermodynamic properties of apatite-(F) (Ca10(PO4)6F2) are sourced from Jemal [42] (G0), Cruz et al. [43,44] (H0, V0) and Dachs et al. [45] (Cp0, S0). Even though the data for bastnaesite (Ce0.50La0.25Nd0.20Pr0.05CO3F), parisite, and parisite-(Ce) (CaCe0.95La0.60Nd0.35Pr0.10(CO3)3F2) have been included in MINES by default, their properties would be summarized in Table 1, because of their significance to the calculation of REE precipitation [33]. The standard thermodynamic properties of all manually entered species and minerals entered species and minerals have been collected in Table 1. In addition, it is noticeable that the thermodynamic properties of bastnaesite and parisite were measured from natural minerals with a complex but fixed composition, while there were only properties of end members of the phosphate and fluocerite of each light lanthanide, instead of a solid solution of monazite or fluocerite, because these properties were only measured from artificially synthetic materials with simple compositions (REEPO4 or REEF3).

Table 1.
Standard thermodynamic properties of REE minerals that are added into the modified MINES database.
To set the initial composition of the modelled REE-bearing ore-forming fluids, the composition of orthomagmatic carbonatitic fluids trapped in fluid inclusion from Kalkfeld carbonatite (Namibia) [46] and the composition of hydrothermal fluids derived from alkali and silica-oversaturated intrusive and volcanic rocks (Capitan Pluton, U.S.) were taken into consideration [47] (Table 2). Although the LREE content of Banks et al. [47] has been adopted by Migdisov et al. [14] to calculate the transport and deposition of REE, the LREE content in fluids derived from alkali silicate magma is lower than that of carbonatitic fluids derived from Ca-carbonatite by 1 or 2 orders of magnitude [46]. The Bayan Obo REE mineralization became extensive after the carbothermal stage, when Ca-carbonatite dykes were formed by Ca-CO2-rich carbonatite-derived fluids [7]. The fenitization occurred in both the wall rock of Ca-carbonatite dykes and the ore-hosting dolomite at Bayan Obo, and, thus, the ore-forming fluids were believed to be derived from Ca-carbonatite [48]. Therefore, as the only available composition of natural Ca-carbonatite-derived fluids, the analytical results of Kalkfeld carbonatite were chosen as the compositional benchmark of the Bayan Obo ore-forming fluids. Since the chloride of LREE has been demonstrated as the stable host of LREE at diverse pH and temperature [14,49], the LREE were introduced into the aqueous system in form of trichlorides. The initial composition of aqueous solution was set to 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF, 0.1 M LaCl3, 0.1 M CeCl3, 0.1 M PrCl3 and 0.1 M NdCl3. Another 0.1 M of SmCl3 and 0.001–0.1 M H3PO4 were added when calculating the LREE fractionation during monazite precipitation. The equal content of LREEs was chosen to assess their precipitation order, or fractionation order, avoiding influence from differentiated composition. The HCl was added to the modelled solution to help maintain an acid environment because real carbonatitic fluids may contain cations like Ca2+ and react with HF to form insoluble fluoride during REE transport. When monitoring the replacement of bastnaesite by monazite in the hydrothermal solution (model 1), 0.1 M of SmCl3 and 0.001–0.6 M CO2 (aq) were introduced to the aqueous system. On the other hand, there was an addition of 0.1 M SmCl3, 0.1 M H3PO4 and 0.001–0.3 M dolomite when simulating the replacement of bastnaesite by monazite (model 2) and replacement of parisite by bastnaesite when neutralization occurred between the ore-hosting dolomite and the acid hydrothermal solution. In the above calculations, the amount of H3PO4, CO2 and dolomite remained undetermined in fluid inclusions. Therefore, they were introduced to the system stepwise in rather wide ranges. The detailed species composition in the modelled solution at each step is displayed in Supplementary Tables S1–S5. P, T and X (composition of CO2, dolomite and H3PO4) were set as independent variables, while the pH and pe of the aqueous system were dependent variables. The initial pH and pe states of each calculation in this study are summarized in Table S6.

Table 2.
Composition of several vital elements in fluids derived from alkali igneous rock and carbonatite, and the initial composition of the modelled solution in this study.
4. Petrographic Conditions of REE and Gangue Minerals Related to Thermodynamic Calculation
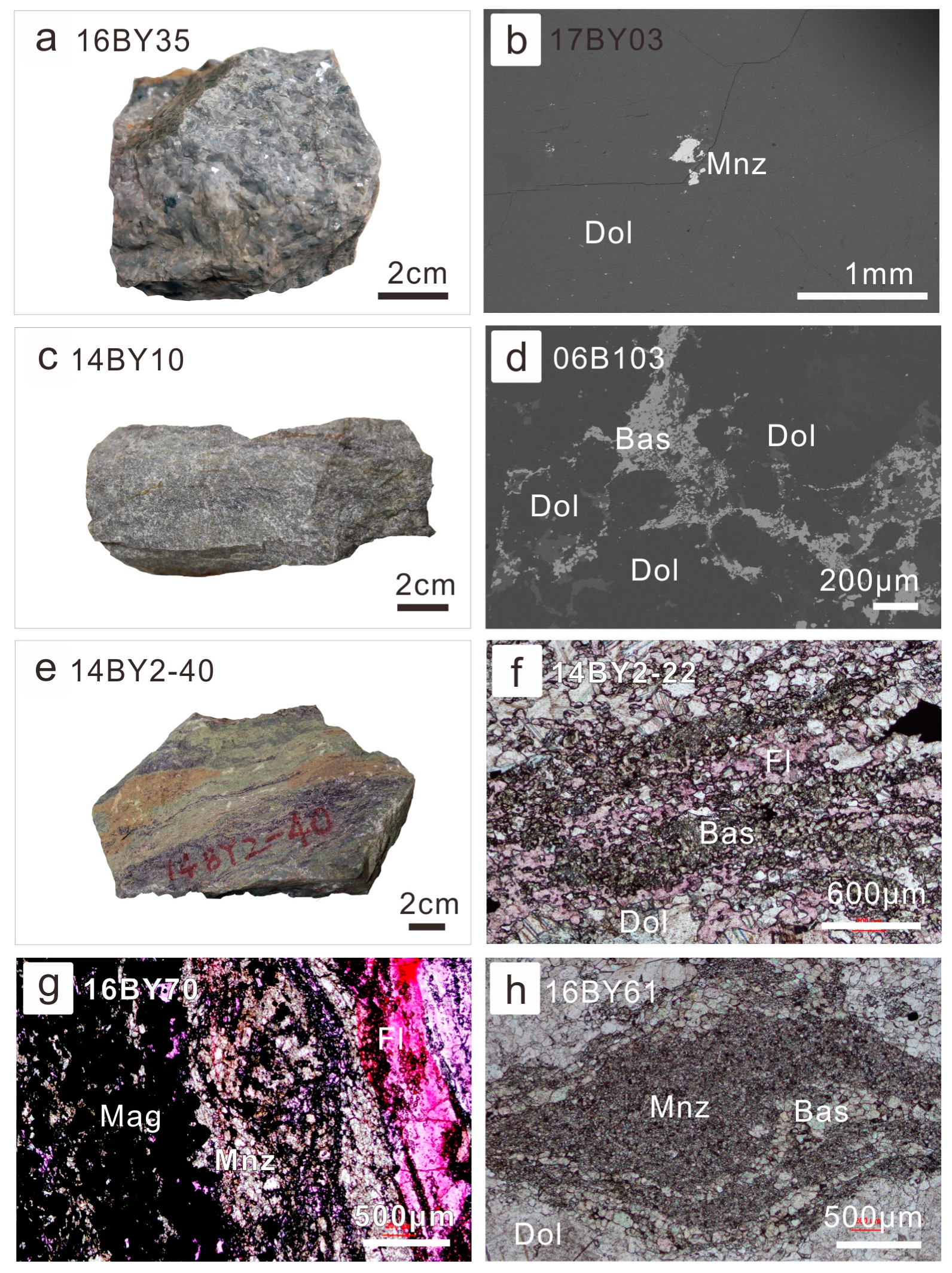
Similar to the Bayan Obo Mg-Fe carbonatite dykes, the least-altered coarse-grained ore-hosting dolomite barely contained REE minerals, except a few monazite grains (Figure 2a,b). Based on moderate ΣREE in the fresh coarse-grained ore-hosting dolomite, similar to Mg-Fe carbonatite dykes, they were regarded as a product of the magmatic stage of Bayan Obo carbonatite evolution [7]. When the ore-forming fluids began to interact with dolomite grains from their boundaries, bastnaesite began to precipitate (Figure 2c,d). In extensively-altered ore-hosting dolomite or ores, it is common for abundant bastnaesite to associate with fluorite (Figure 2e,f). Occasionally, monazite would coprecipitate with fluorite in diverse types of ores (Figure 2g) or be associated with bastnaesite (Figure 2h).
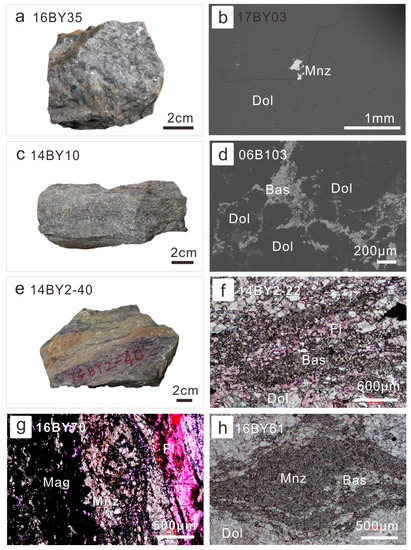
Figure 2.
Petrography of ore-hosting dolomite with diverse degrees of alteration: (a) photography of the coarse-grained ore-hosting dolomite (sample No. 16BY35); (b) discrete monazite grain in the coarse-grained ore-hosting dolomite (backscatter electron (BSE) image of sample 17BY03); (c) photography of the slightly-altered fine-grained ore-hosting dolomite (sample No. 14BY10); (d) interstitial bastnaesite aggregates among relatively fine-dolomite grains (BSE of 06B103); (e) photography of the extensively-altered fine-grained ore-hosting dolomite (sample No. 16BY35); this sample was also called fluorite-aegirine-rich ore; (f) bastnaesite in the fluorite-rich ores under plane polarized light (14BY2-22); (g) monazite associated with fluorite and iron oxide in the aegirine-rich ores under plane polarized light (16BY70); (h) the association of monazite (fine-grained) and bastnaesite (coarser-grained) in the fine-grained ore-hosting dolomite (16BY61). Abbreviation of minerals: Dol—dolomite; Mnz—monazite; Bas—bastnaesite; Fl—fluorite; Mag—magnetite.
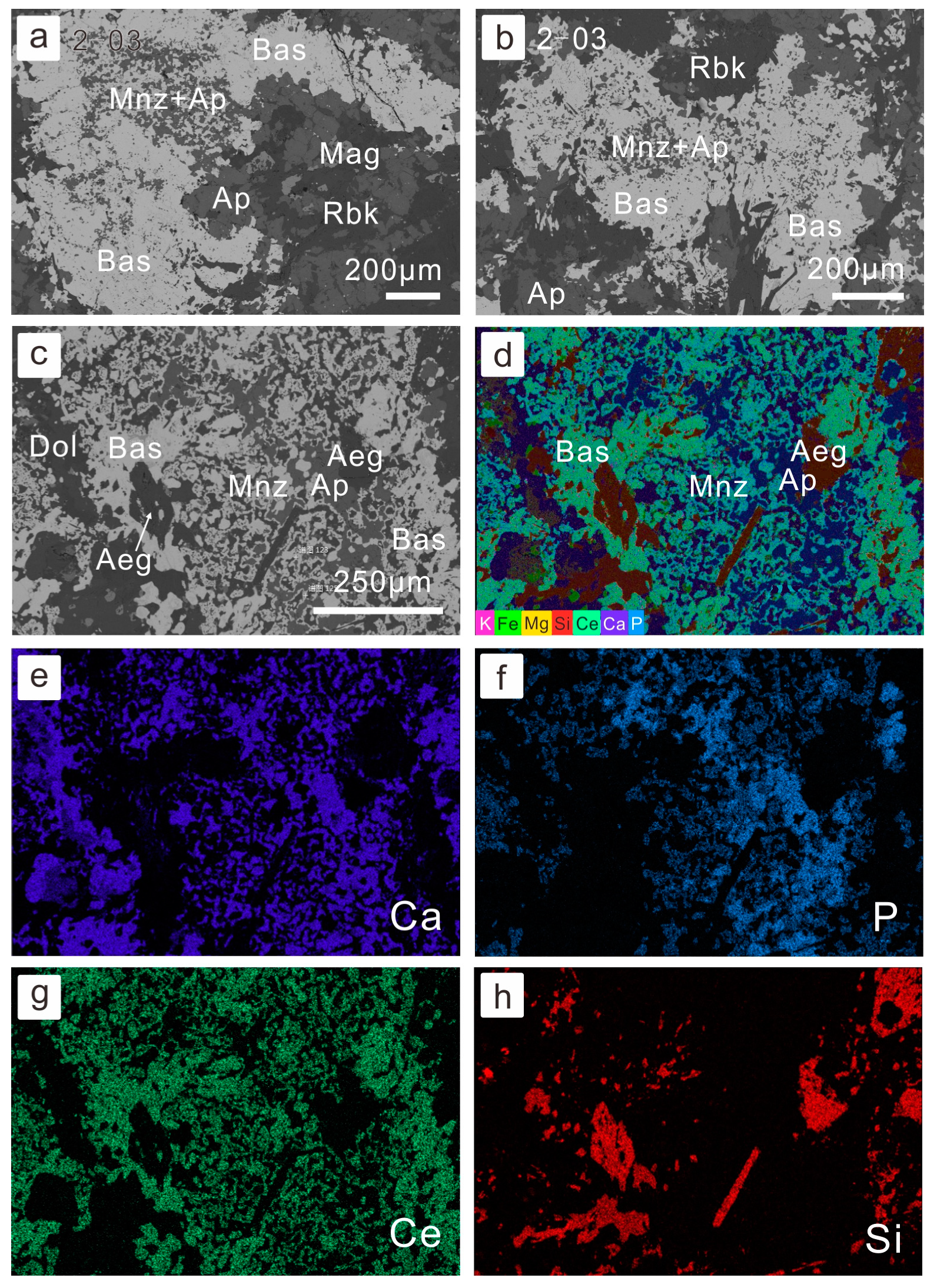
There are complex paragenesis relationships among various REE minerals and gangue minerals. For example, fine-gained monazite is often surrounded and replaced by coarser-grained bastnaesite and apatite association (Figure 3). A similar phenomenon was also observed by Smith et al. [50]. The monazite gradually dissolved and then apatite was formed subsequently at the cost of phosphate anions. Meanwhile, the REE in the hydrothermal fluids precipitated in the form of bastnaesite. As a result, monazite was gradually corroded by the ore-forming fluids, while the precipitation of bastnaesite took place. It is common for bastnaesite to be associated with apatite (Figure 4a,b), even without monazite, which may be because formerly formed monazite was completely dissolved. The paragenesis of apatite and bastnaesite was often indistinguishable (Figure 4a), but occasionally it is evident that apatite precipitates predating the bastnaesite (Figure 4b). Fluorite also often coexists with bastnaesite, especially in fluorite-rich banded or massive ores (Figure 4c). It is also possible that monazite is associated with interstitial apatite and calcite, indicating the dissolution of the former (Figure 4d).
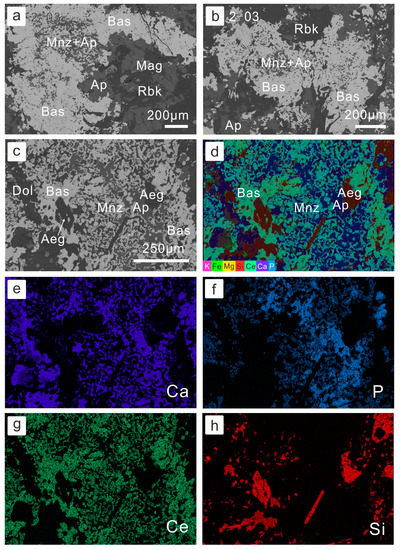
Figure 3.
Petrography of replacement of bastnaesite by monazite: (a,b) monazite associated with apatite and replaced by bastnasite–apatite association (BSE image for sample 14BY-2-03, sodium-amphibole-rich ore); (c) coarser-grain bastnaesite replaced and associated with monazite and apatite (BSE image for sample BY-4, fluorite-rich REE-Nb ore); (d) compiled multi-element x-ray mapping, where monazite displays as light blue and bastnaesite has a green color; (e–h) single-element x-ray mapping of (c). Abbreviation of minerals: Dol—dolomite; Mnz—monazite; Bas—bastnaesite; Mag—magnetite; Rbk—riebeckite; Ap—apatite; Aeg—aegirine.
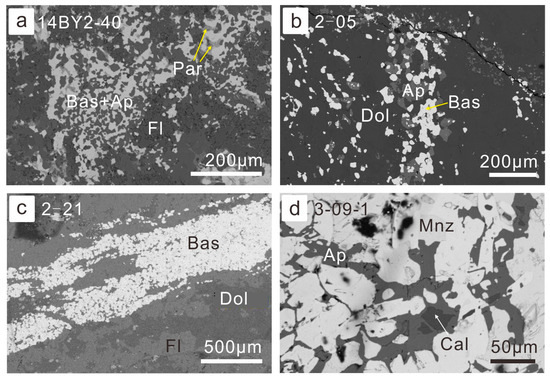
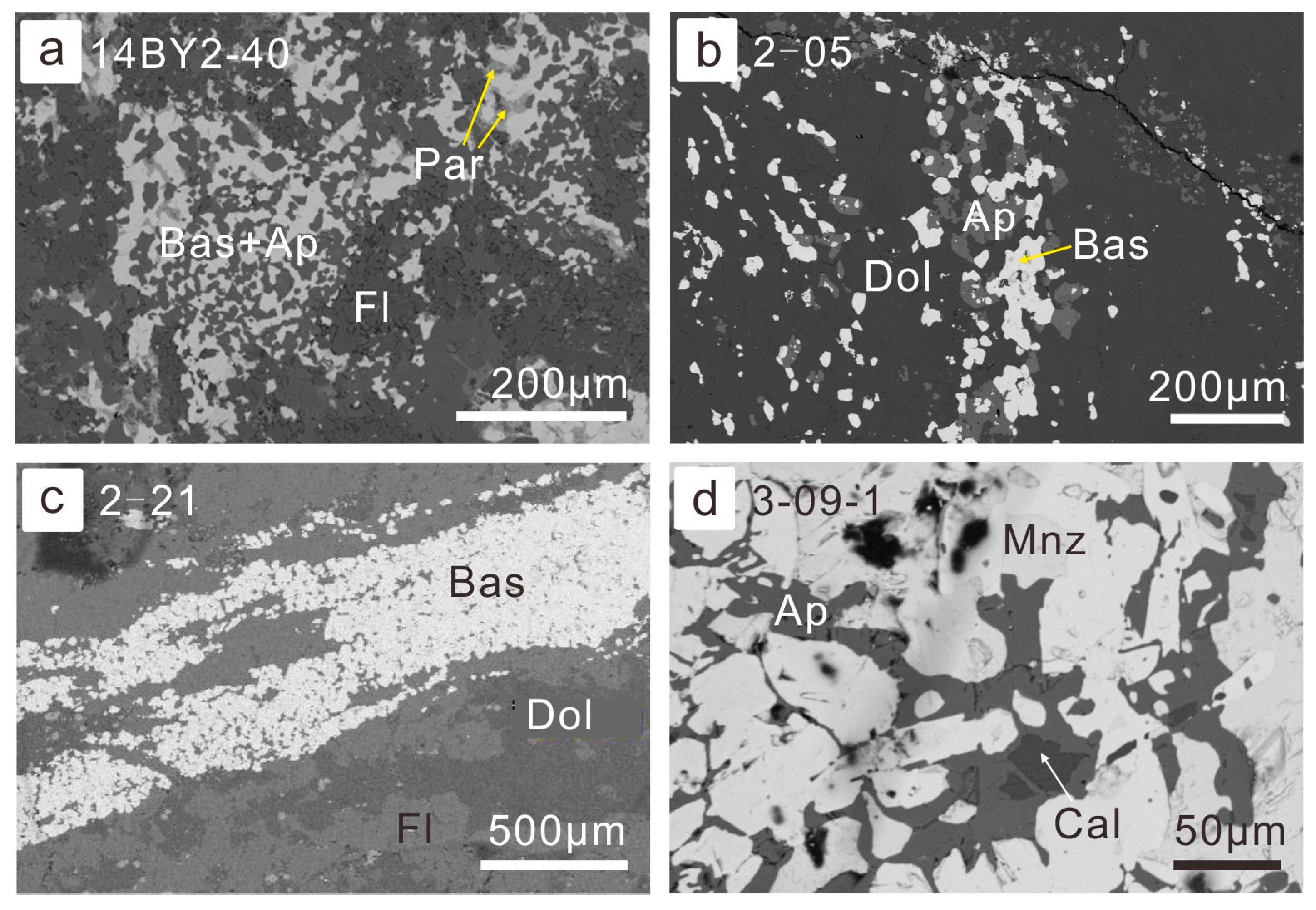
Figure 4.
Petrography of association of REE minerals and gangue minerals: (a) the association of bastnaesite with apatite was replaced by fluorite and parisite (BSE image for sample 14BY2-40, fluorite-aegirine-rich ores); (b) bastnaesite association with apatite in the matrix of dolomite (BSE image for sample 14BY2-05, fine-grained ore-hosting dolomite); (c) banded bastnaesite aggregates in the fluorite-rich REE-Nb ores (BSE image for sample 14BY2-21); (d) monazite was corroded from grain boundaries and replaced by apatite and calcite (BSE image for sample 14BY3-09-1, banded REE-Fe ore). Abbreviation of minerals: Bas—bastnaesite; Ap—apatite; Par—parisite; Fl—fluorite; Dol—dolomite; Mnz—monazite; Cal—calcite. Hereinafter in the caption signatures, these abbreviations of mineral names will be used.
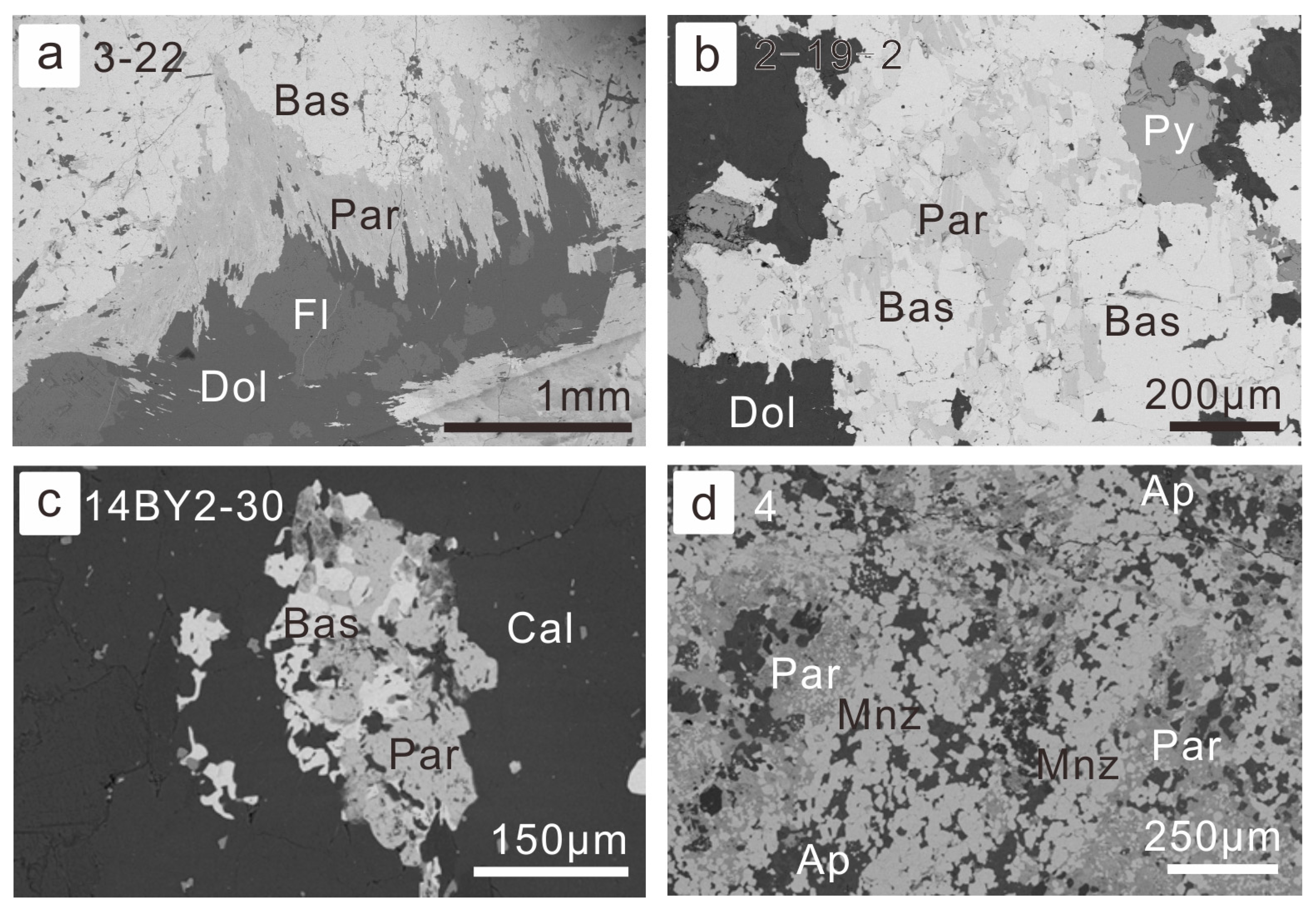
The replacement of parisite by bastnaesite and monazite was common in the Ca-carbonatite dykes and various type of ores. Megacryst of bastnaesite in the vein-type of ores was able to be altered into parisite at the margin (Figure 5a), and those bastnaesites in the fluorite-rich altered ore-hosting dolomite were replaced by parisite from grain boundaries or cleavages with the grains (Figure 5b). The parisite would corrode and replace the bastnaesite gradually, with relics of the latter inside the aggregates of parisite (Figure 5c). Occasionally, there are fine-grained monazite aggregates that were replaced by parisite from their grain boundaries. Both the parisite and apatite were crystallized interstitially (Figure 5d).
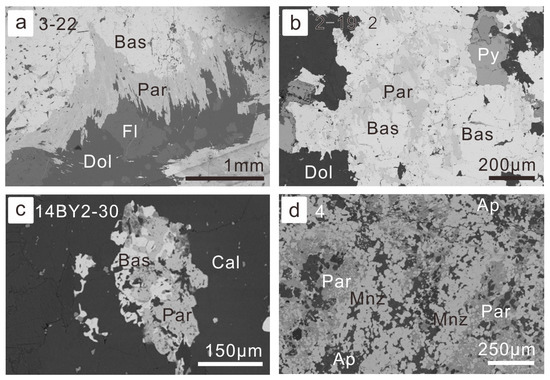
Figure 5.
Petrography of replacement of parisite by bastnaesite and monazite: (a) bastnaesite megacryst in the vein type of ore with its margin altered into parisite (BSE image for sample 14BY3-22, vein-type of ore); (b) bastnaesite was replaced by parisite from the grain boundaries and cleavages within the grains (BSE image for sample 14BY2-19, fluorite-rich altered ore-hosting dolomite); (c) bastnaesite grains were almost replaced by parisite (BSE image for sample 14BY2-30, vein-type of ore); (d) fine-grained monazite aggregates were altered into parisite from grain boundaries (BSE image for sample BY-4, fluorite-rich REE-Nb ore). Abbreviation of minerals have been listed in former figures, except Par for parisite and Py for pyrite.
5. Results
5.1. LREE Fractionation during Precipitation of Monazite
In the modelled solution with 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF and 0.1 M trichloride of each LREE (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm), phosphoric acid was added stepwise into the aqueous solution, with 0.001 M H3PO4 at each step. Only LREE was taken into consideration because monazite at Bayan Obo was LREE-enriched. In these calculations, under different temperatures and pressures, there is competition between the fluocerite and phosphate of LREE in the modelled solution.
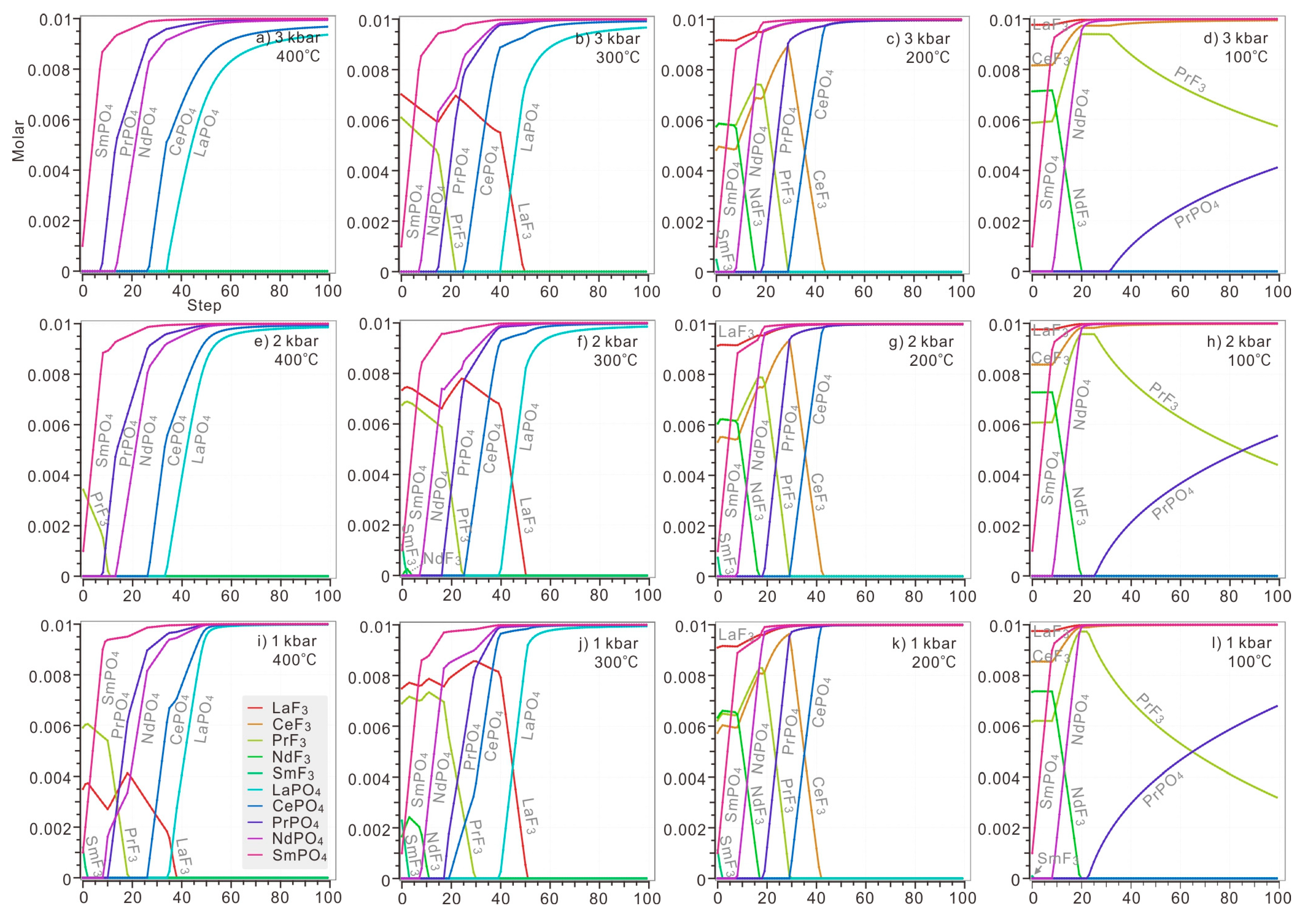
Under the pressure of 3 kbar, LREE would only precipitate as monazite at a temperature of 400 °C, in the order of heavier LREEs Sm, Pr and Nd to lighter LREEs Ce and La (Figure 6a). Fluocerites of La and Pr became stable when H3PO4 was instantly added to the solution at 300 °C under the same pressure (Figure 6b), but these fluocerites would be completely replaced by corresponding monazite with continuous addition of H3PO4 (0.021 M and 0.049 M H3PO4 for fluocerite-(Pr) and –(La)). At 200 °C, fluocerite of all LREE would appear when H3PO4 was instantly added, but only LaF3 remained stable in the whole range of added H3PO4 (Figure 6c). The monazite of Sm, Nd, Pr and Ce began to dissolve and the corresponding fluocerite was crystalized when 0.001, 0.008, 0.019 and 0.030 M H3PO4 was added to the solution. At 100 °C, the stability of not only LaF3 but CeF3 also significantly increased (Figure 6d). In contrast, Sm and Nd prefers to precipitate in the form of monazite. SmPO4 crystalized instantly when H3PO4 was added. NdF3 dissolved and NdPO4 began to form when 0.009 M H3PO4 was added. Pr were stored in PrF3 until 0.033 M H3PO4 was introduced, and then PrPO4 began to replace corresponding fluocerite.
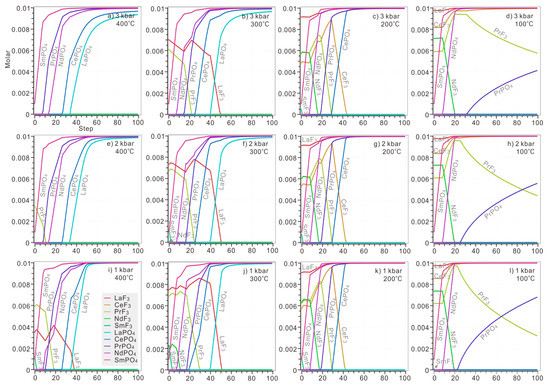
Figure 6.
The precipitation of fluocerite and monazite in solution with 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF, 0.1 M LaCl3, 0.1 M CeCl3, 0.1 M PrCl3, 0.1 M NdCl3, 0.1 M SmCl3 and 0.001–0.1 M H3PO4. The H3PO4 was added stepwise with 0.001 M at each step. The calculation was conducted at diverse temperatures (ranging from 400 °C to 100 °C) and pressures (ranging from 3 kbar to 1 kbar). The P-T condition of each plot: (a) 3 kbar, 400 °C; (b) 3 kbar, 300 °C; (c) 3 kbar, 200 °C; (d) 3 kbar, 10 °C; (e) 2 kbar, 400 °C; (f) 2 kbar, 300 °C; (g) 2 kbar, 200 °C; (h) 2 kbar, 100 °C; (i) 1 kbar, 400 °C; (j) 1 kbar, 300 °C; (k) 1 kbar, 200 °C; (l) 1 kbar, 100 °C.
Under a lower pressure of 2 kbar, PrF3 would exist as the only fluocerite when H3PO4 was introduced at 400 °C (Figure 6e). At 300 °C, the fluocerite of Sm and Nd became more unstable when a trace amount of H3PO4 was added (Figure 6f). The precipitation order remains the same below 200 °C (Figure 6g,h).
Under the pressure of 1 kbar, the fluocerite of La, Pr and Sm appeared once H3PO4 was added at 400 °C (Figure 6i). In solution below 300 °C, the precipitation order would remain similar to that of solution under lower pressure (Figure 6j–l). At 300 °C, all fluocerite of LREE completely dissolved when a certain amount of H3PO4 was added. LREE tends to precipitate as monazite (Figure 6j). At 200 °C, Only LaF3 would be preserved all the way; SmPO4, NdPO4, PrPO4 and CePO4 were formed subsequently, with increasing addition of H3PO4 accompanying dissolution of fluocerite in the order of SmF3, NdF3, PrF3 and CeF3 (Figure 6k). La and Ce tended to be stored in corresponding fluocerite no matter how much H3PO4 was added at 100 °C (Figure 6l). In contrast, Sm and Nd prefer to precipitate in the form of monazite eventually. SmPO4 crystalized instantly when H3PO4 was added. NdF3 dissolved and NdPO4 began to form when 0.01 M H3PO4 was added. Pr was stored in PrF3 until 0.024 M H3PO4 was introduced, and then PrPO4 began to replace the corresponding fluocerite.
These calculations indicate that increasing temperature or pressure would destabilize fluocerite, but the influence of pressure is rather limited. When the modelled solution was hotter than 300 °C under diverse pressure, all REE would precipitate in monazite eventually. While in a modelled solution hotter than 200 °C, no LaPO4 and CeLO4 would be formed, respectively (Figure 6a,b,e,f,i,j). Among all fluocerite of LREE, LaF3 was the most stable species under 300 °C.
5.2. Replacement of Bastnaesite by Monazite
The precipitation of fluorocarbonates needs a carbonate anion in hydrothermal solution. There are two methods introducing carbonate into the aqueous system that have been considered in this study: adding CO2 (aq) (model 1) or adding dolomite into the acid solution (model 2), which has been proposed by Williams-Jones et al. [13]. Since the natural bastnaesite, whose standard thermodynamic properties were measured by Gysi and Williams-Jones [12], contains four LREEs (La, Ce, Pr, Nd), the modelled solution is composed of 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF, 0.1 M H3PO4 and 0.1 M trichloride of La, Ce, Pr and Nd. Sm was excluded from the system to simplify the calculation. Quantities of 0.001 M CO2 and 0.001 M dolomite were contained in the initial solution of model 1 and model 2, respectively.
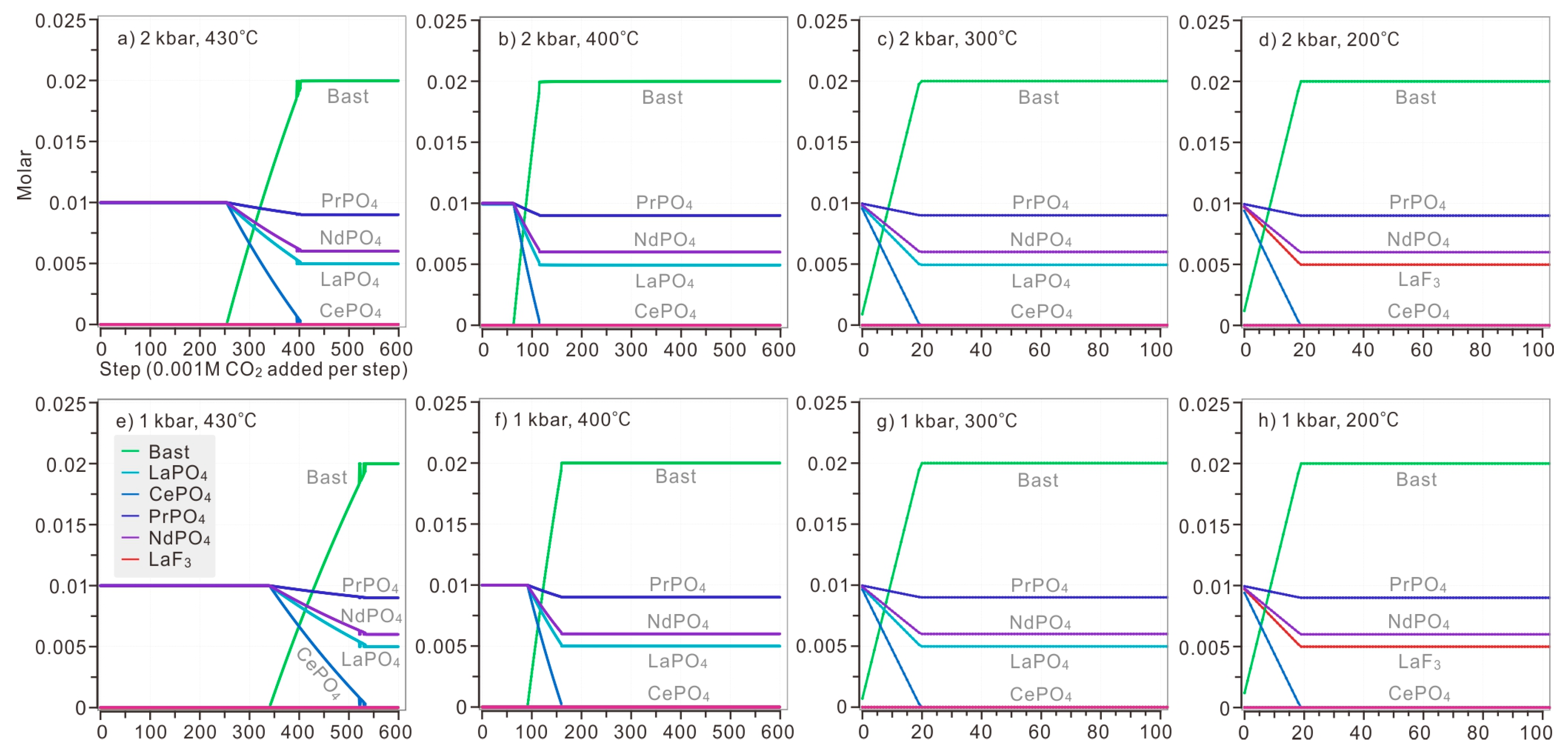
Model 1: When CO2 (aq) was introduced to the solution, bastnaesite began to replace monazite precipitated from the solution. Under the pressure of 2 kbar, at 430 °C, the amount of CO2 necessary to initiate the formation of bastnaesite was 0.339 M (Figure 7a). At 400 °C, monazite of LREE remained stable until over 0.09 M CO2 was added (Figure 7b). At 300 °C, when 0.02 M CO2 were added to the solution, bastnaesite reached its maximum amount, 0.02 M, as well (Figure 7c). At 200 °C, LaPO4 would not exist and, in turn, LaF3 stored all of the La before CO2 was introduced. Once CO2 was introduced, fluocerite-(La) phosphate of Ce, Pr and Nd began to dissolve, until CePO4 completely dissolved and all Ce were consumed by bastnaesite (Ce0.50La0.25Nd0.20Pr0.05CO3F) (Figure 7d). With decreasing temperature, complete replacement of bastnaesite by monazite requires less CO2 (aq): 0.53 M CO2 at 430 °C, 0.16 M CO2 at 400 °C, 0.02 M CO2 at 300 °C, and 0.019 M CO2 at 200 °C. At temperatures over 400 °C, the cooling of the hydrothermal solution significantly promoted the formation of bastnaesite (Figure 7a,b), as the amount of CO2 necessary for complete replacement decreases rapidly.
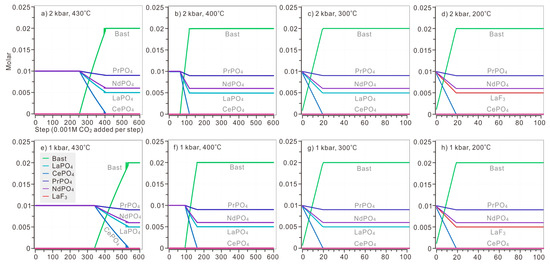
Figure 7.
The replacement of bastnaesite by monazite when CO2 (aq) was introduced stepwise (0.001 M CO2 each step). The modelled solution contains 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF, 0.1 M H3PO4, 0.1 M LaCl3, 0.1 M CeCl3, 0.1 M PrCl3, 0.1 M NdCl3, and 0.001–0.6 M CO2. The calculation was conducted on diverse temperature (ranging from 430 °C to 200 °C) and pressure (ranging from 2 kbar to 1 kbar). The P-T condition of each plot: (a) 2 kbar, 430 °C; (b) 2 kbar, 400 °C; (c) 2 kbar, 300 °C; (d) 2 kbar, 200 °C; (e) 1 kbar, 430 °C; (f) 1 kbar, 400 °C; (g) 1 kbar, 300 °C; (h) 1 kbar, 200 °C.
Under the pressure of 1 kbar, the precipitation order is similar to that of the solution under the pressure of 2 kbar. At above 400 °C, it took slightly less CO2 to initiate formation of bastnaesite compared with a solution under 1 kbar (Figure 7e,f). LaF3 was still stable at 200 °C, storing La when bastnaesite could no longer take it (Figure 7h). The decreased pressure would hinder the replacement of bastnaesite by monazite, but the influence was rather limited in solution below 300 °C.
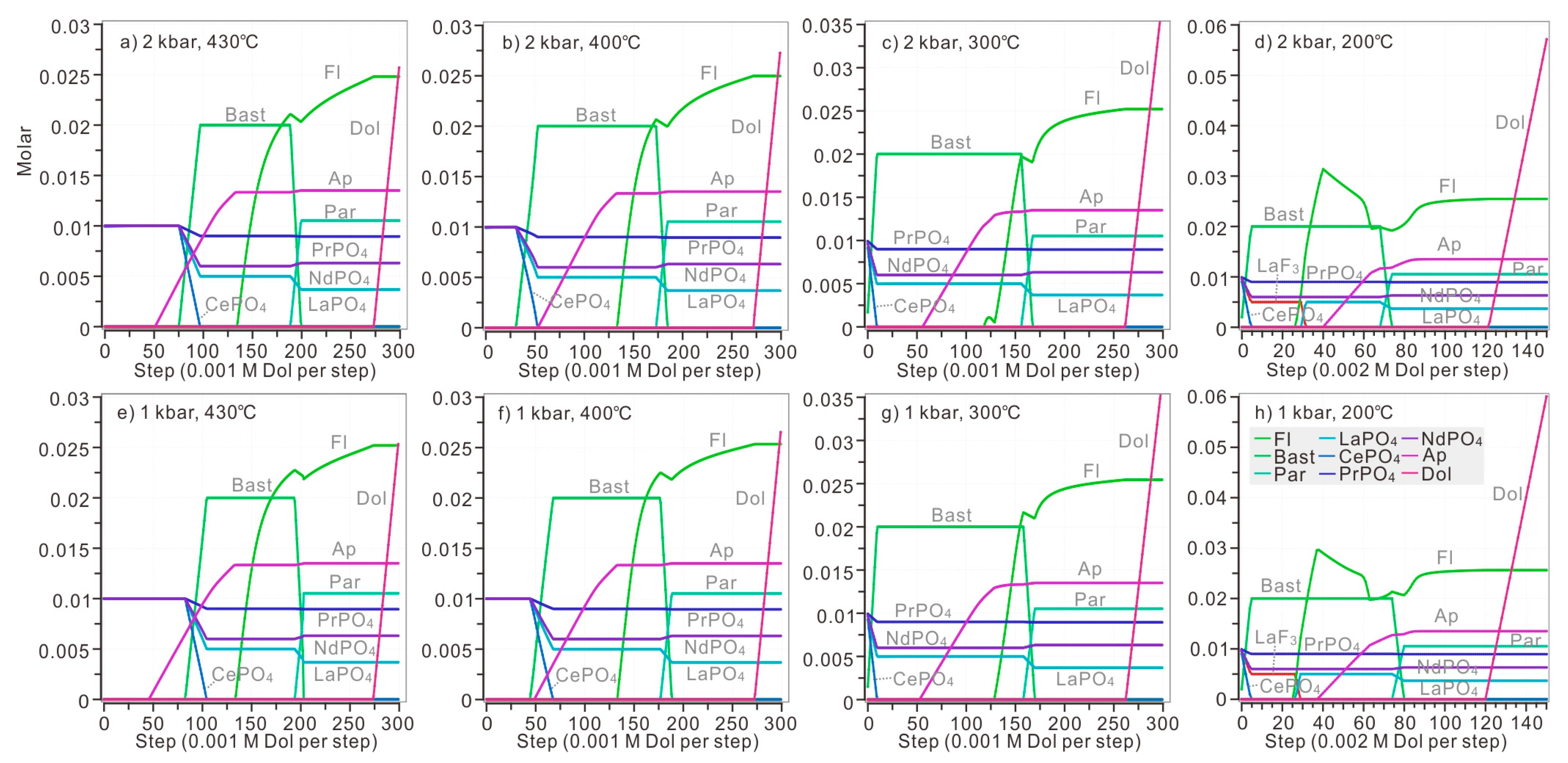
Model 2: If dolomite, rather than CO2, was added into the system, the neutralization reaction between dolomite and acid model solution would produce both CO32− and Ca2+ in the system. Therefore, it is possible to monitor the precipitation of fluorite and apatite. Under the pressure of 2 kbar and temperature of 430 °C, when 0.052 M dolomite was introduced to the system, apatite began to precipitate (Figure 8a). 0.077 M dolomite was needed for the initiation of monazite dissolution and bastnaesite formation. Apatite was able to coexist with CePO4 and bastnaesite when a specific amount of dolomite was introduced to the modelled solution (added dolomite was in the range of 0.076–0.096 M at 430 °C).
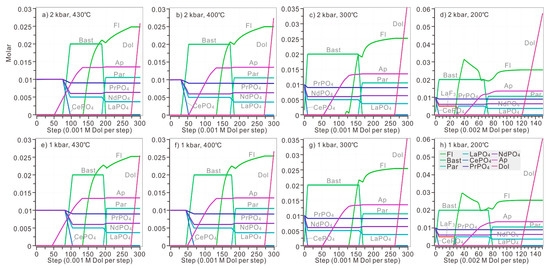
Figure 8.
The replacement of bastnaesite by monazite when dolomite was introduced stepwise. Different amounts of dolomite were added in the calculations under different P and T: 0.001 M dolomite was added for each step in calculations above 300 °C, while 0.002 M dolomite was added for each step when calculating at 200 °C (Figure 8d,h). The modelled solution contains 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF, 0.1 M H3PO4, 0.1 M LaCl3, 0.1 M CeCl3, 0.1 M PrCl3, 0.1 M NdCl3, and 0.001 M-0.3 M dolomite. The calculation was conducted at diverse temperatures (ranging from 430 °C to 200 °C) and pressures (ranging from 2 kbar to 1 kbar). The P-T condition of each plot: (a) 1 kbar, 200 °C; (b) 1 kbar, 300 °C; (c) 1 kbar, 400 °C; (d) 1 kbar, 430 °C; (e) 2 kbar, 200 °C; (f) 2 kbar, 300 °C; (g) 2 kbar, 400 °C; (h) 2 kbar, 430 °C.
At 400 °C, when 0.032 M dolomite was added, the monazite began to be replaced by bastnaesite (Figure 8b). More than 0.054 M dolomite was needed for the precipitation of apatite. In addition, it is impossible for apatite to coexist with CePO4 and bastnaesite because bastnaesite reached its maximum value when 0.053 M dolomite was introduced to the modelled solution, and monazite-(Ce) disappeared simultaneously.
At 300 °C, once the dolomite was introduced, bastnaesite replaced monazite instantly until CePO4 was completely consumed (Figure 8c). Bastnaesite reached its maximum content after 0.01 M dolomite was added. Slightly more dolomite (0.056 M) was necessary for apatite crystallization. The replacement of bastnaesite by monazite required less dolomite in a cooler solution.
At 200 °C (Figure 8d), once dolomite was introduced into the system, LaF3, CePO4, PrPO4 and NdPO4 dissolved and bastnaesite began to precipitate. Bastnaesite reached its maximum content after 0.01 M dolomite was added. When 0.031 M dolomite was added, fluocerite-(La) lost stability and fluorite began to act as the major host of fluorine, and LaPO4 was formed simultaneously. Apatite suddenly appeared when 0.040 M dolomite was added to the solution. Dolomite became saturated when 0.122 M dolomite was added. In general, the decreasing temperature would promote the replacement of bastnaesite by monazite with the continuous addition of dolomite.
The decreased pressure slightly influenced REE precipitation by increasing the dolomite necessary for replacement of bastnaesite by monazite (Figure 8e–h). Under the pressure of 1 kbar, only 0.045 M and 0.084 M dolomite was need for the initiation of bastnaesite formation at 400 °C and 430 °C, respectively. Under the pressure of 1 kbar, apatite was able to coexist with CePO4 and bastnaesite when a specific amount of dolomite was introduced to the modelled solution (added dolomite was in the range of 0.049–0.068 M and 0.083–0.105 M at 400 °C and 430 °C).
5.3. Replacement of Parisite by Bastnaesite
When sufficient dolomite was added into the system, parisite would eventually replace the bastnaesite. In the last model, under the same pressure, the parisite began to replace bastnaesite with an increasing amount of dolomite at higher temperatures (Figure 8). In the modelled solution at 2 kbar, a little bit less dolomite was needed: 0.189 M, 0.173 M, 0.156 M and 0.136 M dolomite for the modelled solution at 430 °C, 400 °C, 300 °C and 200 °C, respectively (Figure 8a–d). Under the pressure of 1 kbar, the initiation of this replacement requires 0.194 M, 0.177 M, 0.159 M and 0.150 M dolomite at 430 °C, 400 °C, 300 °C and 200 °C, respectively (Figure 8e–h).
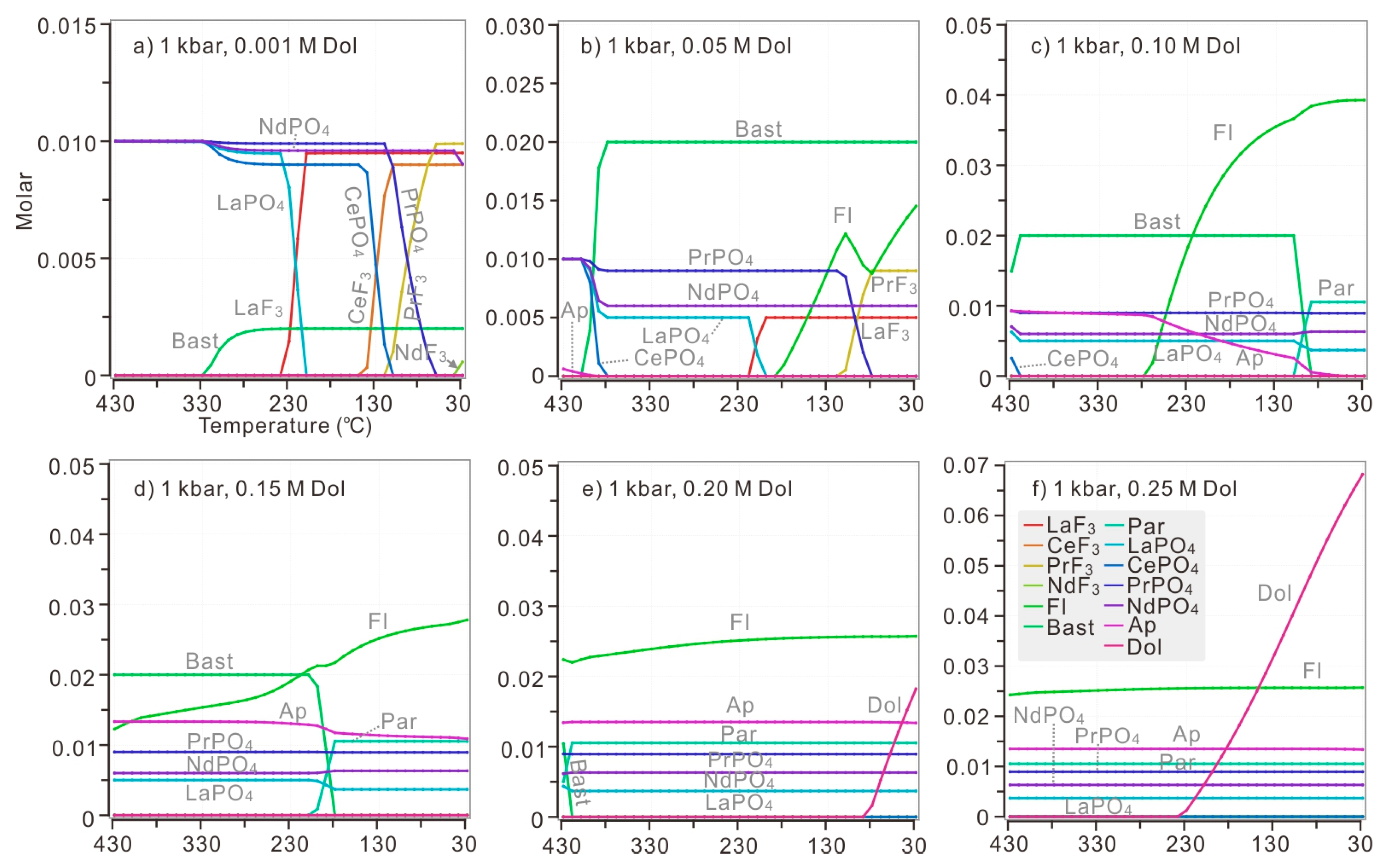
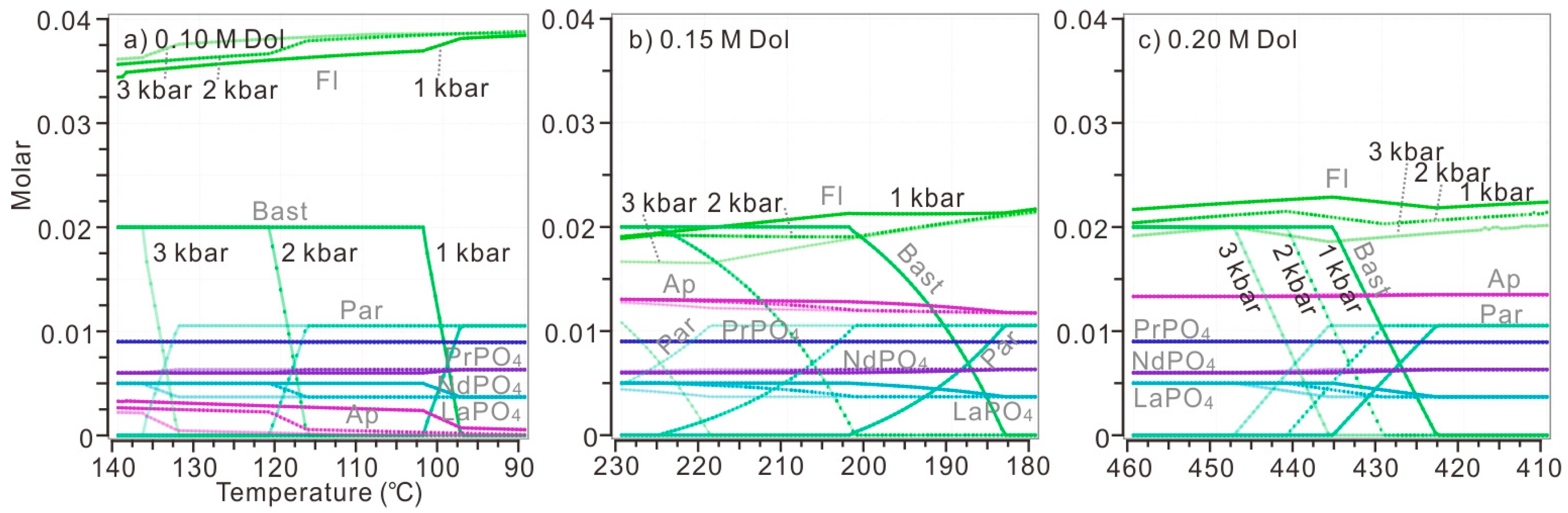
In order to evaluate the influence of temperature on the replacement of parisite by bastnaesite, a series of calculations was conducted in a continuous range of temperatures from 30 to 430 °C, with several discrete and specific amounts of added dolomite (Figure 9). When 0.001 M dolomite was introduced, there is only competition between monazite and fluocerite as the major hosts of LREE (Figure 9a). The parisite would only precipitate when over 0.10 M dolomite was added (Figure 9c–f). Specifically, when 0.10 M dolomite was introduced, parisite was able to replace bastnaesite below 100 °C (Figure 9c). When 0.15 M dolomite was added, the replacement would be initiated below 200 °C, and apatite stayed stable in the whole range of calculated temperatures (Figure 9d). When over 0.20 M dolomite was added, parisite became the dominated REE host at any calculated temperature (Figure 9e,f). Besides, dolomite turned out to be saturated when the temperature of solution dropped to 80 °C and 230 °C in the case of 0.20 M and 0.25 M dolomite addition (Figure 9e,f). In the above calculations, with several discrete initial amounts of dolomite, the replacement of bastnaesite and apatite-(F) by CePO4 was possible only when 0.10 M dolomite was added into a solution at over 420 °C (Figure 9c).
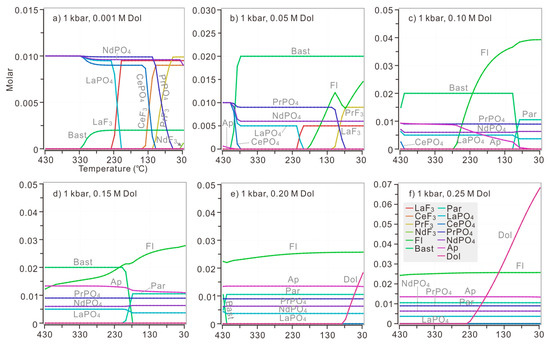
Figure 9.
The precipitation of REE minerals in a continuous range of temperatures (30–430 °C) when discrete amounts of dolomite were added into a modelled solution, with 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF, 0.1 M H3PO4, 0.1 M LaCl3, 0.1 M CeCl3, 0.1 M PrCl3 and 0.1 M NdCl3. All calculations were performed under the pressure of 1 kbar. The discrete amount of dolomite added into the initial fluids include (a) 0.001 M; (b) 0.05 M; (c) 0.10 M; (d) 0.15 M; (e) 0.20 M; and (f) 0.25 M. The temperature decreased 10 °C per step.
The influence of pressure on the replacement of parisite by bastnaesite was also verified by calculations (Figure 10). Based on the above calculations with discrete dolomite addition, the replacement of parisite by bastnaesite was possible when 0.10 M, 0.15 M and 0.20 M dolomite was introduced to the system (Figure 9c–e). Each condition was calculated under various pressures from 1 kbar to 3 kbar. In a cooling solution, the increase of pressure would generally elevate the onset temperature of the above replacement. When 0.10 M dolomite was added, parisite began to precipitate at 102 °C, 116 °C and 137 °C under the pressures of 1 kbar, 2 kbar and 3 kbar (Figure 10a). When 0.15 M and 0.20 M dolomite were added, the onset temperature of this replacement was increased from 202 °C to 225 °C and 436 °C to 441 °C if the pressure increased from 1 kbar to 2 kbar (Figure 10b,c). In general, increasing pressure promoted the replacement of parisite by bastnaesite at higher temperatures. However, the significant variation of pressure only caused replacement onset temperature to vary within 35 °C.
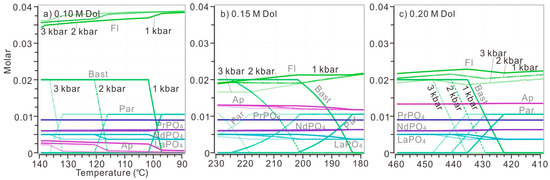
Figure 10.
The replacement of parisite by bastnaesite at diverse temperatures and pressures. The initial model solution is the same as fluids in Figure 10. Discrete amounts of dolomite were introduced to the aqueous system: (a) 0.10 M; (b) 0.15 M; (c) 0.20 M. For each plot, the precipitation of REE minerals and gangue minerals have been calculated under the pressure from 1 kbar (solid lines) to 2 kbar (dash lines) then to 3 kbar (transparent lines with spots) and at temperature of 90–140°C for (a), 180–230 °C for (b) and 410–460 °C for (c). These temperature ranges were selected to cover the replacement processes. The temperature decreased 0.5 °C per step.
6. Discussion
6.1. REE Fractionation Indicated by Monazite Precipitation
According to our calculation, with increasing concentration of H3PO4, monazite of heavier LREE tends to crystalize from the aqueous solution earlier (Figure 6). However, monazite at Bayan Obo is characterized by Ce enrichment. For example, monazite collected from ore-hosting dolomite contains Ce (23.7–43.5 wt%, ave. 29.8 wt%, n = 12) and La (13.0–28.8 wt%, ave. 18.4 wt%), much more than the sum of other REEs [51]. This indicates that the hydrothermal fluid forming the monazite is Ce-and La-enriched, and extreme LREE enrichment was accomplished ahead of the extensive precipitation of monazite. Since monazite is one of the earliest hydrothermal minerals in the ore-hosting dolomite, the fractionation among LREEs was unlikely to be caused by fractionated crystallization during the hydrothermal process, but played as a geochemical characteristic of the initial ore-forming fluid infiltrating the ore-hosting dolomite, which conforms to the proposal that the ore-forming fluids originated from carbonatite [48]. These calculations have provided thermodynamic support. In addition, fluocerite has never been discovered and reported at Bayan Obo in the past 30 years. Thus, REE precipitation is very likely to occur when temperatures of hydrothermal fluids are over 300 °C, when LaF3 would not be persistent in a wide range of H3PO4 compositions (0.001–0.1 M), and LaPO4 would host all of the La eventually. Meanwhile, the concentration of H3PO4 in the solution should exceed 0.05 M when fluocerites remain absent under variant pressure, even though analytical measurement was unable to provide this constraint. Despite all of this, the pressure of ore-forming fluids is not easy to judge due to its limited influence on the precipitation of fluocerite and monazite in the modelled solution. On the other hand, the stability of fluocerite decreases significantly along with increasing temperature.
6.2. Replacement of Bastnaesite by Monazite
The modelled solution (model 1) contains the same amount of La, Ce, Pr and Nd. Actually, as proved above, the real ore-forming fluids are extremely La- and Ce-enriched. Therefore, PrPO4 and NdPO4 would be unstable in real hydrothermal fluids because limited Pr and Nd would be definitely consumed by bastnaesite. The replacement of bastnaesite by monazite would be continuous until either La or Ce was exhausted. Monazite was more likely to remain stable in hydrothermal fluids hotter than 400 °C (Figure 7a,b). In a cooling hydrothermal system hotter than 400 °C, the temperature decrease would influence the stability of monazite and promote replacement of bastnaesite to monazite more significantly. The amount of CO2 needed for the complete replacement of bastnaesite by monazite at 400 °C was less than one third of the CO2 needed at 430 °C. Therefore, extensive replacement of bastnaesite by monazite might begin to occur when hydrothermal fluid was cooled to about 400 °C or a little bit above, which is in accord with the complete dissolution temperature (420–480 °C) of the few discovered fluorocarbonate crystals trapped in Bayan Obo fluid inclusions [8]. However, it is still uncertain whether these few fluorocarbonate-bearing fluid inclusions are primary. Combined with the calculation of model 2, the addition of dolomite would also promote the replacement of bastnaesite by monazite. However, the neutralization reaction is not a must for the replacement if the ore-forming fluids contain sufficient CO2 (aq) as shown in model 1, and precipitation of apatite and fluorite may need extra calcium cations in this condition. Therefore, significant pH shifting is not a fundamental requirement for the occurrence of replacement among REE minerals. However, the dolomite definitely participates in REE precipitation at Bayan Obo, as almost all REE resources are hosted in a dolomite unit.
The monazite-(Ce) would be replaced by associated apatite and bastnaesite when the hydrothermal solution was hot enough (>400 °C) (Figure 3; Figure 8a,b,e,f). Meanwhile, in a cooler modelled solution of 200 °C or 300 °C, when bastnaesite finished replacing all of the CePO4, the apatite-(F) was unable to crystallize yet. As these results have shown, a certain amount of dolomite was also necessary for the coexistence of monazite-(Ce), bastnaesite and apatite-(F) (the range of dolomite necessary at 1 kbar: 0.049–0.068 M and 0.083–0.105 M at 400 °C and 430 °C; 2 kbar: 0.077 –0.097 M at 430 °C). With added dolomite less than the specific range, monazite would remain stable while bastnaesite would be unlikely to appear. When introduced dolomite exceeds the specific range, bastnaesite and apatite would remain stable while CePO4 would dissolve completely. Considering that Bayan Obo monazite is Ce-enriched, the condition that monazite-(Ce) dissolves completely is inappropriate for crystallization of Bayan Obo monazite.
It is interesting that, in our calculation of model 2, monazite-(Ce) would never co-precipitate with fluorite. If there is any association of these two minerals, as in Figure 2g, according to the above results, the fluorite and monazite should crystallize subsequently, or overlap each other as products of two hydrothermal activities. Other associated relationships, such as bastnaesite with fluorite or bastnaesite with apatite, are likely to occur from the perspective of thermodynamic modelling. Generally, with continuous addition of dolomite into solution with constant temperature, bastnaesite would precipitate earlier than fluorite (Figure 8), as in the paragenesis in Figure 4c, where fluorite crystallizes from the grain boundaries of bastnaesite aggregates. For the same reason, the bastnaesite and associated apatite were replaced by fluorite in Figure 4a. Bastnaesite would be associated with apatite at any calculated temperature. At 430 °C, apatite would crystalize earlier than bastnaesite with increasing introducing of dolomite, as shown in Figure 4b. At 400 °C, bastnaesite would nearly co-precipitate with apatite. At lower temperatures, the precipitation of bastnaesite would predate the apatite. Therefore, all above petrography observed in this study supports a very-high-temperature REE precipitation.
6.3. Replacement of Parisite by Bastnaesite
Based on a series of calculations, decreasing temperature, increasing the addition of dolomite and increasing pressure are beneficial to the replacement of parisite by bastnaesite. In a real hydrothermal solution, the temperature keeps dropping when it is infiltrating and interacting with the cold ore-hosting dolomite. The replacement of parisite by bastnaesite was more likely to occur in the peripheral veinlets of the fluid passage, because this high-rock/fluid-ratio environment, as well as quenched fringe of the hydrothermal fluids, meets favorable conditions of both increasing dolomite addition and decreasing temperature. The pressure of the hydrothermal fluids is difficult to assess, as the pressure would drop in an open system but keep rather stable in a closed or semi-closed system. However, the significant variation in pressure would only affect the onset temperature of replacement slightly, according to calculations in this study. Therefore, regardless of the shift of pressure, the parisite was observed replacing the bastnaesite (or monazite occasionally as in Figure 5d) in the ore-hosting dolomite from the narrow space of their grain boundaries (Figure 5b,c). Alternatively, if the hydrothermal fluids have interacted with enough dolomite, the replacement of parisite by bastnaesite would also occur in veins or extensional fractures in the ore-hosting dolomite, instead of in a high-dolomite/fluid-ratio environment, as in the condition shown in Figure 5a.
According to the calculation in Figure 8 and Figure 9, parisite would not directly replace monazite-(Ce) in modelled solution at any temperature. The paragenesis in Figure 5d was possibly caused by multi-phase hydrothermal activities, or parisite completely replaced interstitial bastnaesite among monazite grains.
There are mainly two REE mineralization events at Bayan Obo that have been recognized by former researchers [1,2,3]. The Mesoproterozoic and Paleozoic mineralization events produce similar mineral assemblages, including similar REE minerals (monazite and fluorocarbonates) and similar gangue minerals (fluorite, apatite, aegirine, sodium amphibole, phlogopite). The Paleozoic mineralization also contains some unique gangue minerals, including barite and various sulfides. Besides mineral composition, these two mineralization events caused different occurrences of the above minerals: disseminated grains, banded or massive aggregates in the Mesoproterozoic ores and altered ore-hosting dolomite, and megacrysts or veinlets of the above minerals in the vein-breccia types of ores. The similar mineral assemblage of two mineralization events indicates that their corresponding ore-forming fluids contained similar bulk composition (except sulfur-bearing species in the Paleozoic ore-forming fluids). According to former research on the Bayan Obo Sm-Nd isotopic system, there is no external REE introduced to the Paleozoic hydrothermal fluids [1,52]. This implies that the Paleozoic REE ores were product of local dissolution–reprecipitation. Therefore, thermodynamic calculations in this study are also able to provide an explanation of the Paleozoic REE precipitation process (Figure 5a,b), as if the vein-type of ores could be regarded as the product of a geochemically closed-system, except for the addition of dolomite or CO2 (aq). The variation of pressure would not influence the paragenesis of REE minerals significantly. Therefore, modelling in this study could be applied to aqueous systems at diverse depths.
7. Conclusions
(1) During the precipitation of monazite in REE-rich fluids, heavier LREE tends to precipitate earlier and be fractionated from the fluids earlier. The Ce- and La-enriched monazite at Bayan Obo was caused by La and Ce pre-enriched hydrothermal fluids, supporting the carbonatitic fluids as ore-forming fluids from the perspective of thermodynamic calculation.
(2) With continuous introduction of sole CO2 (aq), bastnaesite would eventually replace CePO4 entirely. If dolomite is introduced solely to the acid hydrothermal fluids, bastnaesite replaces all monazite-(Ce) and is then replaced by parisite. The drop in temperature in hot hydrothermal fluids (>400 °C) would significantly promote the replacement of parisite by bastnaesite by decreasing CO2 or dolomite demands.
(3) Based on our calculation of the modelled solution, the association of bastnaesite, monazite-(Ce) and apatite-(F) is a characteristic texture of hydrothermal fluids over 400 °C, which provides a constraint on the temperature of Bayan Obo REE mineralization. It is possible that post-magmatic hydrothermal fluids (carbonatitic fluids), or hot-magma-induced local recrystallization triggered the Bayan Obo REE mineralization.
(4) The association of REE minerals and gangue minerals have the potential to provide further constraints on the physico-chemical conditions of Bayan Obo hydrothermal fluids. Based on this study, apatite is often associated with bastnaesite at any temperature, but only crystallizes earlier, at temperatures as high as ~430 °C. The association of monazite-(Ce)-fluorite and monazite-parisite indicates multi-phase hydrothermal activities, as they were unlikely to co-precipitate in the modelled solution at any calculated temperature from 200 °C to 430 °C.
(5) Pressure variation has a rather limited influence on the paragenesis of REE minerals, whereas temperature and composition variation cause significantly different associations of REE minerals and gangue minerals.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2075-163X/10/6/495/s1, Table S1: The composition of REE-bearing minerals (fluocerite and monazite) in solution with 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF, 0.1 M LaCl3, 0.1 M CeCl3, 0.1 M PrCl3, 0.1 M NdCl3, 0.1 M of SmCl3 and 0.001–0.1 M H3PO4. The H3PO4 was added stepwise with 0.001 M of each step. Table S2: The composition of REE minerals and gangue minerals when CO2 (aq) was introduced stepwise (0.001 M CO2 each step). The modelled solution contains 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF, 0.1 M H3PO4, 0.1 M LaCl3, 0.1 M CeCl3, 0.1 M PrCl3, 0.1 M NdCl3, and 0.001 M–0.6 M CO2. Table S3: The composition of REE minerals and gangue minerals when dolomite was introduced stepwise (0.002 M for each step of 1 kbar-200 °C and 2 kbar–200 °C; 0.001 M for the rest of plots). The modelled solution contains 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF, 0.1 M H3PO4, 0.1 M LaCl3, 0.1 M CeCl3, 0.1 M PrCl3, 0.1 M NdCl3, and 0.001 M–0.3 M dolomite. Table S4: The composition of REE minerals and gangue minerals in a continuous range of temperature (30–430 °C) when discrete amount of dolomite was added into a modelled solution, with 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HF, 0.1 M H3PO4, 0.1 M LaCl3, 0.1 M CeCl3, 0.1 M PrCl3, 0.1 M NdCl3. The temperature increased 10 °C per step. Table S5: The composition of REE minerals and gangue minerals have been calculated under the pressure from 1 kbar to 3 kbar when 0.10 M, 0.15 M and 0.20 M dolomite was added into the system (the same initial composition as in table S4) and replacement of parisite to bastnaesite occurred. The temperature increased 0.5 °C per step. Table S6: The initial pH and per of calculated solutions in this study. (Automatically calculated by GEMS).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L.; resources, S.L., L.D. and H.-R.F.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L.; writing—review and editing, L.D. and H.-R.F.; funding acquisition, S.L. and L.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41902066; 41930430) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Grant No. Lzujbky-2019-pd06; 2022019zr106).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Kai-Yi Wang, Yong-Gang Zhao and Wen-Liang Ma for their kindly contribution during the field work. Pang Yun-Long was appreciated for his help during the operation of SEM.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhu, X.K.; Sun, J.; Pan, C.X. Sm–Nd isotopic constraints on rare-earth mineralization in the Bayan Obo ore deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 64, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.R.; Yang, K.F.; Hu, F.F.; Liu, S.; Wang, K.Y. The giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit, China: Controversy and ore genesis. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 335–344. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.Y.; Lai, X.D.; Pirajno, F.; Liu, Y.L.; Ling, M.X.; Sun, W.D. The Bayan Obo (China) giant REE accumulation conundrum elucidated by intense magmatic differentiation of carbonatite. Precambrian Res. 2017, 288, 39–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.F.; Fan, H.R.; Pirajno, F.; Li, X.C. The Bayan Obo (China) giant REE accumulation conundrum elucidated by intense magmatic differentiation of carbonatite. Geology 2019, 47, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.P.; Henderson, P. Preliminary Fluid Inclusion Constraints on Fluid Evolution in the Bayan Obo Fe-REE-Nb Deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Econ. Geol. 2000, 95, 1371–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Y.L.; Lu, J.; Jiang, S.Y.; Simonetti, A.; Xu, C.; Zhang, W. The formation of the ore-bearing dolomite marble from the giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit, Inner Mongolia: Insights from micron-scale geochemical data. Miner. Deposita 2020, 55, 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Fan, H.R.; Groves, D.I.; Yang, K.F.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, Q.W. Multiphase carbonatite-related magmatic and metasomatic processes in the genesis of the ore-hosting dolomite in the giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit. Lithos 2020, 354–355, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.R.; Xie, Y.H.; Wang, K.Y.; Tao, K.J. REE Daughter Minerals Trapped in Fluid Inclusions in the Giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe Deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2004, 46, 638–645. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, C.J.; Qiu, Y.Z.; Zhou, G.F.; Wang, Z.G.; Zhang, T.R.; Xiao, G.R. Fluid inclusion study of carbonatite dykes/veins and ore-hosted dolostone at the Bayan Obo deposit. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.Y.; Fan, H.R.; Yang, K.F.; Hu, F.F.; Wu, C.M.; Hu, F.Y. Calcite-dolomite geothermometry of Bayan Obo carbonatites. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 1141–1149, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Migdisov, A.A.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Wagner, T. An experimental study of the solubility and speciation of the Rare Earth Elements (III) in fluoride- and chloride-bearing aqueous solutions at temperatures up to 300 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 7087–7109. [Google Scholar]
- Gysi, A.P.; Williams-Jones, A.E. The thermodynamic properties of bastnäsite-(Ce) and parisite-(Ce). Chem. Geol. 2015, 392, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Jones, A.E.; Migdisov, A.A.; Samson, I.M. Hydrothermal mobilization of the rare earth elements-a tale of “Ceria” and “Yttria”. Elements 2012, 8, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdisov, A.A.; Williams-Jones, A.E. Hydrothermal transport and deposition of the rare earth elements by fluorine-bearing aqueous liquids. Mineral. Deposita 2014, 49, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdisov, A.A.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Brugger, J.; Caporiscio, F.A. Hydrothermal transport, deposition, and fractionation of the REE: Experimental data and thermodynamic calculations. Chem. Geol. 2016, 439, 13–42. [Google Scholar]
- Drew, L.J.; Meng, Q.R.; Sun, W.J. The Bayan Obo iron-rare-earth-niobium deposits, Inner Mongolia, China. Lithos 1990, 26, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, E.C.T.; Back, J.M.; Minkin, J.A. Host-rock controlled epigenetic, hydrothermal metasomatic origin of the Bayan Obo REE-Fe-Nb ore deposit, Inner Mongolia, P.R.C. Appl. Geochem. 1992, 7, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.F.; Fan, H.R.; Santosh, M.; Hu, F.F.; Wang, K.Y. Mesoproterozoic mafic and carbonatitic dykes from the northern margin of the North China Craton: Implications for the final breakup of Columbia supercontinent. Tectonophysics 2011, 498, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.Y.; Fan, H.R.; Xie, Y.H.; Li, H.M. The zircon U-Pb dating of basement complex of the giant Bayan Obo REE-Fe-Nb deposit. Chin. Sci. B 2001, 46, 1390–1394. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.R.; Yang, K.F.; Hu, F.F.; Wang, K.Y.; Zhai, M.G. Zircon geochronology of basement rocks from the Bayan Obo area, Inner Mongolia, and tectonic implications. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 1342–1350, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Ling, M.X.; Sun, W.D. Chronology and geological significance of the basement rock of the giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe ore deposit. Geochimica 2011, 40, 209–222, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhai, M.G.; Peng, P.; Santosh, M.; Ma, X.D. Detrital zircon U–Pb dating and whole-rock geochemistry from the clastic rocks in the northern marginal basin of the North China Craton: Constraints on depositional age and provenance of the Bayan Obo Group. Precambrian Res. 2015, 258, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Bagas, L.; Nie, F.J.; Jiang, S.H.; Li, C. Re–Os system of black schist from the Mesoproterozoic Bayan Obo Group, Central Inner Mongolia, China and its geological implications. Lithos 2016, 261, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Zhao, G.C.; Liu, F.L.; Shi, J.R. Detrital zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic and whole-rock geochemical study of the Bayan Obo Group, northern margin of the North China Craton: Implications for Rodinia reconstruction. Precambrian Res. 2017, 303, 372–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.G.; Hu, M.M.; Wu, C.; Wang, G.S.; Liu, C.F.; Cai, A.R.; Jiang, T. Coupled U–Pb dating and Hf isotopic analysis of detrital zircons from Bayan Obo Group in Inner Mongolia: Constraints on the evolution of the Bayan Obo rift belt. Geol. J. 2017, 53, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bas, M.J.; Keller, J.; Tao, K.J.; Wall, F.; Williams, C.T.; Zhang, P.S. Carbonatite dykes at Bayan Obo, Inner Mongolia, China. Mineral. Petrol. 1992, 46, 195–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.G.; Fei, H.C.; Wang, A.J.; Yang, F.; Yan, K. Formation and geochemistry of the ore-bearing alkaline volcanic rocks in the Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2012, 86, 735–751, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.Y.; Fang, A.M.; Zhang, J.E.; Yu, L.J.; Dong, C.; Zan, J.F.; Hao, M.Z. Genetic relationship between fenitized ores and hosting dolomite carbonatite of the Bayan Obo REE deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 174, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Yang, X.Y.; Chen, T.H.; Zhang, P.S.; Le Bas, M.J.; Henderson, P. Geochemical constraints on the genesis of the Bayan Obo Fe-Nb-REE deposit in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Chin. Rare Earths Soc. 1999, 17, 289–295, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Kulik, D.A.; Hingerl, F.F.; Dmytrieva, S.V. GEM-Selektor geochemical modeling package: TSolMod library and data interface for multicomponent phase models. Can. Mineral. 2012, 50, 1173–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, D.A.; Wagner, T.; Dmytrieva, S.V.; Kosakowski, G.; Hingerl, F.F.; Chudnenko, K.V.; Berner, U. GEM-Selektor geochemical modeling package: Revised algorithm and GEMS3K numerical kernel for coupled simulation codes. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 17, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoenen, T.; Hummel, W.; Berner, U.; Curti, E. The PSI/Nagra Chemical Thermodynamic Database 12/07; Paul Scherrer Institut, Villigen PSI: Villigen, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–445. [Google Scholar]
- Gysi, A.P.; Williams-Jones, A.E. Hydrothermal mobilization of pegmatite-hosted Zr and REE at Strange Lake, Canada: A reaction path model. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 122, 324–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysi, A.P. Numerical simulations of CO2 sequestration in basaltic rock formations: Challenges for optimizing mineral-fluid reactions. Pure Appl. Chem. 2017, 89, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konings, R.J.M.; Kovács, A. Thermodynamic properties of the lanthanide (III) halides. Handb. Phys. Chem. Rare Earths 2003, 33, 147–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.X.; Hughes, M.; Mariano, A.N. Crystal chemistry of the monazite and xenotime. Am. Mineral. 1995, 80, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushakov, S.V.; Helean, K.B.; Navrotsky, A.; Boatner, L.A. Thermochemistry of rare-earth orthophosphates. J. Mater. Res. 2001, 16, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiriet, C.; Konings, R.J.M.; Jovorský, P.; Magnani, N.; Wastin, F. The low temperature heat capacity of LaPO4 and GdPO4, the thermodynamic functions of the monazite-type LnPO4 series. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2005, 37, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, K.; Sedmidubský, D.; Beneš, O.; Thiriet, C.; Konings, R.J.M. The high-temperature heat capacity of LnPO4 (Ln = La, Ce, Gd) by drop calorimetry. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2006, 38, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, K.; Jutier, F.; Wastin, F.; Konings, R.J.M. The heat capacity of NdPO4. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2006, 38, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, K.; Konings, R.J.M. High-temperature heat capacities of EuPO4 and SmPO4 synthetic monazites. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 445, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, M. Thermochemistry and relative stability of apatite phosphates. Phosphorus Res. B 2004, 15, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, F.J.A.L.; Minas da Piedade, M.E.; Calado, J.C.G. Standard molar enthalpies of formation of hydroxy-, chlor-, and bromapatite. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2005, 37, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, F.J.A.L.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Calado, J.C.G.; Minas da Piedade, M.E. A Molecular Dynamics Study of the Thermodynamic Properties of Calcium Apatites. 1. Hexagonal Phases. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 24473–24479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dachs, E.; Harlov, D.; Benisek, A. Excess heat capacity and entropy of mixing along the chlorapatite–fluorapatite binary join. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2010, 37, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühn, B.; Rankin, A.H. Composition of natural, volatile-rich Na-Ca-REE-Sr carbonatitic fluids trapper in fluid inclusions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 3781–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, D.A.; Yardley, B.W.D.; Campbell, A.R.; Jarvis, K.E. REE composition of an aqueous magmatic fluid: A fluid inclusion study from the Capitan Pluton, New Mexico, U.S.A. Chem. Geol. 1994, 113, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fan, H.R.; Yang, K.F.; Hu, F.F.; Rush, B.; Liu, X.; Li, X.C.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, Q.W.; Wang, K.Y. Fenitization in the Giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe Deposit: Implication for REE Mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 94, 290–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krneta, S.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Cook, N.J.; Ehrig, K.J. Numerical Modeling of REE Fractionation Patterns in Fluorapatite from the Olympic Dam Deposit (South Australia). Minerals 2018, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.P.; Henderson, P.; Zhang, P.S. Reaction relationships in the Bayan Obo Fe-REE-Nb deposit Inner Mongolia, China: Implications for the relative stability of rare-earth element phosphates and fluorocarbonates. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1999, 134, 294–310. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.L.; Chen, J.F.; Li, H.M.; Qian, H.; Xiao, G.W.; Zhang, T.R. Single-grain U-Th-Pb-Sm-Nd dating of monazite from dolomite type ore of the Bayan Obo deposit. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2005, 21, 881–888, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Fan, H.R.; Yang, K.F.; Hu, F.F.; Wang, K.Y.; Chen, F.K.; Yang, Y.H.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, Q.W. Mesoproterozoic and Paleozoic hydrothermal metasomatism in the giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit: Constrains from trace elements and Sr-Nd isotope of fluorite and preliminary thermodynamic calculation. Precambrian Res. 2018, 311, 228–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).