Spatial Contamination and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soil around Nonferrous Metal Smeltery in North China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
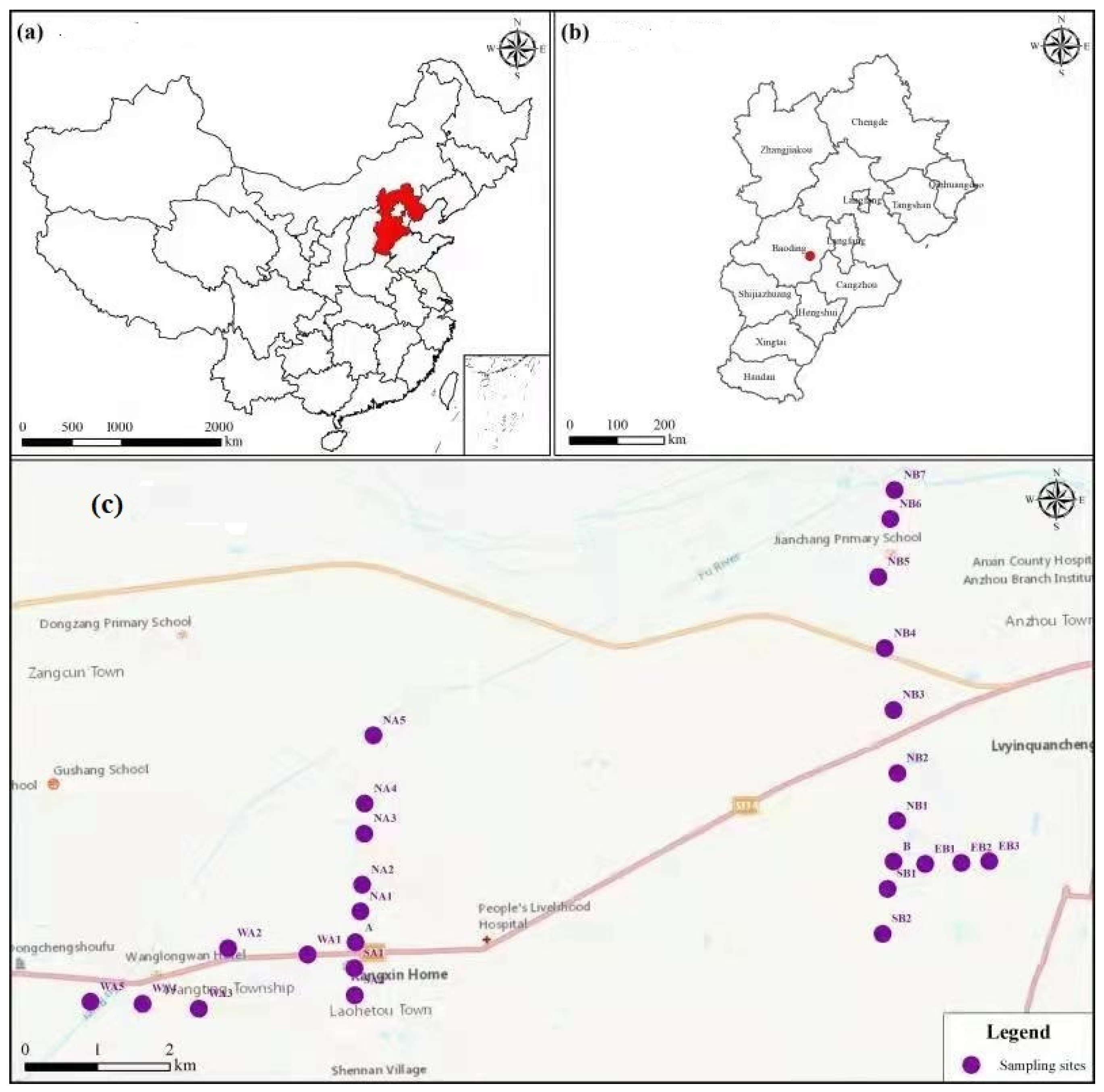
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Analysis of Heavy Metals and Quality Control
2.3. Spatial Distribution
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Contents Analysis of Seven Toxic Elements in the Soil
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Seven Toxic Elements
3.3. Homology and Principal Component Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soil
3.4. Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.; Peng, S.; Mao, X.; Zeng, G.M. Source apportionment and spatial and quantitative ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from a typical Chinese agricultural county. Process Saf. Environ. 2019, 126, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, L. Spatial Distribution and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soils Influenced by Industrial Enterprise Distribution: Case Study in Jiangsu Province. Sci Total Environ. 2020, 710, 134953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Shi, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, Q.; Chen, X.C.; Chen, Y.X. The influence of soil heavy metals pollution on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity, and community composition near a copper smelter. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 67, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Feng, X.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, G.; Li, G.; Li, F.; Liu, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Z. Environmental contamination of heavy metals from zinc smelting areas in Hezhang County, western Guizhou, China. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pelt, R.S.V.; Shekhter, E.G.; Barnes, M.A.W.; Duke, S.E.; Gill, T.E.; Pannell, K.H. Spatial and temporal patterns of heavy metal deposition resulting from a smelter in El Paso, Texas. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 210, 106414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, S.; Schröder, W.; Wosniok, W.; Harmens, H.; Frontasyeva, M.V.; Alber, R. Modelling and mapping heavy metal and nitrogen concentrations in moss in 2010 throughout Europe by applying Random Forests models. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 156, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, S.Y.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhang, S.L.; Liu, G.J.; Chen, F. Spatial assessment of farmland soil pollution and its potential human health risks in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Chao, S.H.; Liu, J.W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.J. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burges, A.; Epelde, L.; Garbisu, C. Impact of repeated single-metal and multi-metal pollution events on soil quality. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.M.; Wang, Q.S.; Luo, J.; Chen, L.G.; Zhu, R.L.; Wang, S.; Tang, C.H. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment for children near a large Cu-smelter in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Ippolito, J.A.; Xing, W.Q.; Qiu, K.Y.; Yang, H. Lead smelting effects heavy metal concentrations in soils, wheat, and potentially humans. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 257, 113641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.M.; Zhou, J.; Du, B.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Zhang, W.T. Health risks to local residents from the exposure of heavy metals around the largest copper smelter in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, H.T.; Aelion, C.M.; McDermott, S.; Lawson, A.B. Identifying natural and anthropogenic sources of metals in urban and rural soils using GIS-based data, PCA, and spatial interpolation. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2378–2385. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Liao, R.; Ali, A.; Mahar, A.; Guo, D.; Li, R.; Sun, X.; Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil near a Pb/Zn smelter in Feng County, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borůvka, L.; Vacek, O.; Jehlička, J. Principal component analysis as a tool to indicate the origin of potentially toxic elements in soils. Geoderma 2005, 128, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Wu, S.H.; Xia, Z.; Cui, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhou, S. Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of the Lihe River Watershed, East China: Spatial Distribution, Ecological Risk, and Pollution Source. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Z.W.; Zhang, L.Z.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y.F.; Nie, Z.Q.; Cheng, J.L.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.W.; Chai, M. Contamination and risk of heavy metals in soils and sediments from a typical plastic waste recycling area in North China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Environmental Monitoring Station. The Background Value of Soil Elements in China; China Environmental Monitoring Station: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- MEE of China. Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (GB 35500-2018); Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kicińska, A. Environmental risk related to presence and mobility of As, Cd and Tl in soils in the vicinity of a metallurgical plant—Long-term observations. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Liu, P.H.; Jiang, X.F.; Chen, P.J. Health risk assessment and spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metal pollution in rice samples from a surrounding hydrometallurgy plant area in No. 721 uranium mining, East China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 207, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, R.; Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Gang, Z.; Zhang, H. Heavy metal contents, distribution, and prediction in a regional soil-wheat system. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 422–431. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, Y.G.; Luo, G.P.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.L.; Hall, M.H.P.; Guo, R.; Wang, H.; Cui, J.; et al. Heavy metal contamination of urban soil in an old industrial city (Shenyang) in Northeast China. Geoderma 2013, 192, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, H.; Su, M.; An, P. Spatial network analysis of surface soil pollution from heavy metals and some other elements: A case study of the Baotou region of China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Hong, C.; Tong, W.; Xu, M.X.; Huang, C.; Yin, H.; Lin, Y.; Fu, Q. Health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in a soil-rice system: A case study in the Jin-Qu Basin of China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Potential Ecological Risk of Single Metal ( ) | Comprehensive Potential Ecological Risk Index (RI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Threshold Range | Assessment Criterion | Threshold Range | Assessment Criterion |
| < 40 | Low | RI < 150 | Low |
| 40 ≤ < 80 | Moderate | 150 ≤ < 300 | Moderate |
| 80 ≤ < 160 | Considerable | 300 ≤ < 600 | High |
| 160 ≤ < 320 | High | ≥ 600 | Very high |
| ≥ 320 | Very high | ||
| Smeltery | Content | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smeltery A | Maximum (mg/kg) | 117 | 86 | 156 | 391 | 3 | 503 | 96 |
| Minimum (mg/kg) | 68 | 46 | 64 | 98 | 0.49 | 45 | 49 | |
| Average content (mg/kg) | 88 | 62 | 103 | 200 | 1.4 | 146 | 69 | |
| Standard deviation | 15 | 11 | 29 | 77 | 0.60 | 131 | 15 | |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 15.4 | 15.83 | 24.09 | 25.58 | 34.26 | 76.58 | 20.89 | |
| Smeltery B | Maximum (mg/kg) | 127 | 87 | 190 | 273 | 1.3 | 287 | 101 |
| Minimum (mg/kg) | 63 | 40 | 33 | 65 | 0.26 | 27 | 40 | |
| Average content (mg/kg) | 86 | 59 | 83 | 117 | 0.53 | 57 | 65 | |
| Standard deviation | 18 | 15 | 38 | 60 | 0.23 | 60 | 16 | |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 21.15 | 25.83 | 46.09 | 50.78 | 43.87 | 105.3 | 24.33 | |
| Soil background value (mg/kg) [18,19] | 68 | 31 | 22 | 78 | 0.09 | 22 | 14 | |
| Standard limit (mg/kg) [20] | 250 | 190 | 100 | 300 | 0.6 | 170 | 25 | |
| Smeltery | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | As | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smeltery A | Cr | 1 | ||||||
| Ni | 0.565 * | 1 | ||||||
| Cu | 0.312 | 0.648 ** | 1 | |||||
| Zn | 0.122 | 0.100 | 0.188 | 1 | ||||
| Cd | −0.248 | 0.210 | 0.556 * | 0.459 | 1 | |||
| Pb | 0.053 | 0.498 * | 0.545 * | 0.189 | 0.679 ** | 1 | ||
| As | 0.407 | 0.629 ** | 0.190 | 0.179 | −0.047 | 0.217 | 1 | |
| Smeltery B | Cr | 1 | ||||||
| Ni | 0.773 ** | 1 | ||||||
| Cu | 0.344 | 0.707 ** | 1 | |||||
| Zn | 0.610 ** | 0.658 ** | 0.536 * | 1 | ||||
| Cd | −0.174 | −0.160 | 0.249 | 0.113 | 1 | |||
| Pb | −0.276 | −0.157 | 0.184 | 0.190 | 0.839 ** | 1 | ||
| As | 0.632 ** | 0.690 ** | 0.334 | 0.536 * | −0.370 | −0.288 | 1 | |
| Smeltery | Parameter | Component | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total variance interpretation of Smeltery A | Initial eigenvalues | % of variance | 2.978 | 1.758 | 0.95 | 0.673 | 0.365 | 0.155 | 0.12 |
| Cumulative % | 42.549 | 25.114 | 13.575 | 9.609 | 5.218 | 2.219 | 1.716 | ||
| Total | 42.549 | 67.664 | 81.239 | 90.847 | 96.065 | 98.284 | 100 | ||
| Extraction sums of squared loadings | % of variance | 2.978 | 1.758 | ||||||
| Cumulative % | 42.549 | 25.114 | |||||||
| Total | 42.549 | 67.664 | |||||||
| Component matrix a of Smeltery A | Component | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | As | |
| 1 | 0.451 | 0.843 | 0.816 | 0.409 | 0.603 | 0.755 | 0.545 | ||
| 2 | 0.71 | 0.392 | −0.124 | −0.284 | −0.752 | −0.37 | 0.549 | ||
| Total variance interpretation of Smeltery B | Initial eigenvalues | % of variance | 3.4 | 2.106 | 0.586 | 0.404 | 0.301 | 0.144 | 0.059 |
| Cumulative % | 48.565 | 30.088 | 8.376 | 5.767 | 4.305 | 2.052 | 0.847 | ||
| Total | 48.565 | 78.653 | 87.029 | 92.796 | 97.101 | 99.153 | 100 | ||
| Extraction sums of squared loadings | % of variance | 3.4 | 2.106 | ||||||
| Cumulative % | 48.565 | 30.088 | |||||||
| Total | 48.565 | 78.653 | |||||||
| Component matrix a of Smeltery B | Component | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | As | |
| 1 | 0.851 | 0.942 | 0.645 | 0.773 | −0.227 | −0.226 | 0.82 | ||
| 2 | −0.09 | 0.072 | 0.489 | 0.372 | 0.916 | 0.91 | −0.221 |
| Site | RI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | Cd | Pb | As | ||
| A0 | 3.30 | 11.96 | 20.73 | 1.25 | 156.09 | 10.55 | 62.22 | 266.10 |
| A1 | 2.13 | 13.97 | 35.80 | 2.84 | 947.31 | 116.95 | 64.15 | 1183.15 |
| A2 | 3.42 | 11.78 | 29.13 | 2.44 | 433.22 | 107.60 | 59.41 | 647.01 |
| A3 | 2.86 | 11.47 | 34.80 | 2.96 | 354.95 | 20.20 | 50.67 | 477.91 |
| A4 | 2.63 | 9.58 | 33.15 | 2.28 | 482.98 | 21.38 | 51.76 | 603.77 |
| A5 | 2.66 | 9.33 | 22.41 | 1.54 | 335.66 | 11.32 | 47.44 | 430.37 |
| A6 | 3.05 | 10.35 | 18.75 | 4.99 | 394.84 | 21.77 | 70.80 | 524.57 |
| A7 | 2.09 | 8.77 | 15.86 | 1.83 | 308.80 | 18.48 | 60.20 | 416.04 |
| A8 | 2.17 | 7.94 | 19.89 | 2.13 | 525.85 | 39.95 | 39.56 | 637.48 |
| A9 | 2.06 | 7.42 | 16.44 | 2.03 | 239.36 | 20.34 | 37.54 | 325.19 |
| A10 | 1.98 | 8.05 | 14.65 | 1.71 | 309.47 | 17.79 | 35.67 | 389.33 |
| A11 | 3.06 | 12.45 | 28.19 | 1.47 | 312.01 | 21.27 | 54.93 | 433.39 |
| A12 | 2.24 | 9.08 | 27.59 | 2.85 | 653.59 | 50.15 | 40.28 | 785.77 |
| A13 | 2.17 | 9.07 | 18.40 | 2.39 | 379.41 | 16.35 | 64.64 | 492.44 |
| A14 | 2.47 | 10.66 | 20.85 | 3.56 | 381.52 | 26.38 | 47.47 | 492.91 |
| A15 | 2.54 | 8.11 | 24.90 | 3.78 | 751.06 | 32.70 | 36.65 | 859.75 |
| A16 | 2.83 | 9.68 | 17.85 | 1.97 | 364.75 | 16.69 | 43.50 | 457.25 |
| A17 | 2.94 | 11.44 | 27.71 | 3.85 | 560.96 | 39.70 | 51.91 | 698.50 |
| B0 | 2.22 | 6.91 | 7.56 | 0.94 | 82.10 | 6.35 | 39.67 | 145.76 |
| B1 | 1.98 | 6.65 | 10.38 | 1.11 | 128.91 | 7.53 | 49.40 | 205.97 |
| B2 | 1.86 | 6.55 | 9.53 | 1.03 | 153.22 | 9.45 | 33.11 | 214.74 |
| B3 | 1.84 | 6.68 | 21.44 | 1.77 | 419.02 | 66.73 | 29.36 | 546.84 |
| B4 | 2.41 | 10.19 | 14.08 | 1.05 | 106.84 | 16.45 | 69.75 | 220.77 |
| B5 | 3.16 | 11.73 | 26.17 | 3.48 | 143.88 | 11.75 | 63.29 | 263.47 |
| B6 | 2.82 | 9.03 | 24.02 | 0.86 | 170.53 | 7.08 | 47.87 | 262.22 |
| B7 | 3.72 | 14.12 | 26.32 | 3.12 | 175.96 | 12.24 | 74.18 | 309.64 |
| B8 | 2.23 | 10.76 | 21.15 | 1.55 | 111.20 | 10.74 | 45.66 | 203.29 |
| B9 | 2.35 | 8.31 | 15.92 | 0.83 | 162.79 | 6.91 | 45.95 | 243.06 |
| B10 | 3.52 | 12.73 | 22.09 | 1.81 | 146.97 | 11.02 | 45.10 | 243.24 |
| B11 | 2.45 | 8.15 | 13.18 | 1.30 | 175.74 | 10.00 | 40.60 | 251.42 |
| B12 | 2.23 | 6.78 | 11.29 | 1.04 | 156.10 | 7.08 | 39.27 | 223.81 |
| B13 | 2.67 | 9.52 | 13.91 | 0.97 | 152.34 | 7.15 | 47.88 | 234.44 |
| B14 | 2.65 | 9.68 | 18.14 | 1.11 | 254.20 | 8.67 | 46.82 | 341.26 |
| B15 | 2.59 | 12.55 | 23.77 | 1.80 | 156.06 | 13.80 | 49.53 | 260.11 |
| B16 | 2.21 | 12.17 | 43.53 | 1.69 | 187.85 | 14.12 | 50.59 | 312.16 |
| Average of Smeltery A | 2.59 | 10.06 | 23.73 | 2.55 | 438.44 | 33.86 | 51.05 | 562.27 |
| Average of Smeltery B | 2.52 | 9.56 | 18.97 | 1.50 | 169.63 | 13.36 | 48.12 | 263.66 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, D.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Liang, S. Spatial Contamination and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soil around Nonferrous Metal Smeltery in North China. Minerals 2021, 11, 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121357
Han D, Li X, Wang M, Liang S. Spatial Contamination and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soil around Nonferrous Metal Smeltery in North China. Minerals. 2021; 11(12):1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121357
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Dongmei, Xiliang Li, Menglu Wang, and Shuxuan Liang. 2021. "Spatial Contamination and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soil around Nonferrous Metal Smeltery in North China" Minerals 11, no. 12: 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121357
APA StyleHan, D., Li, X., Wang, M., & Liang, S. (2021). Spatial Contamination and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soil around Nonferrous Metal Smeltery in North China. Minerals, 11(12), 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11121357






