Top-Down Synthesis of NaP Zeolite from Natural Zeolite for the Higher Removal Efficiency of Cs, Sr, and Ni
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of NaP Zeolite
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Batch Sorption Tests
2.5. Kinetics, Isotherms, and Cation Exchange Capacity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and characterization of NaP Zeolite and Natural Zeolite
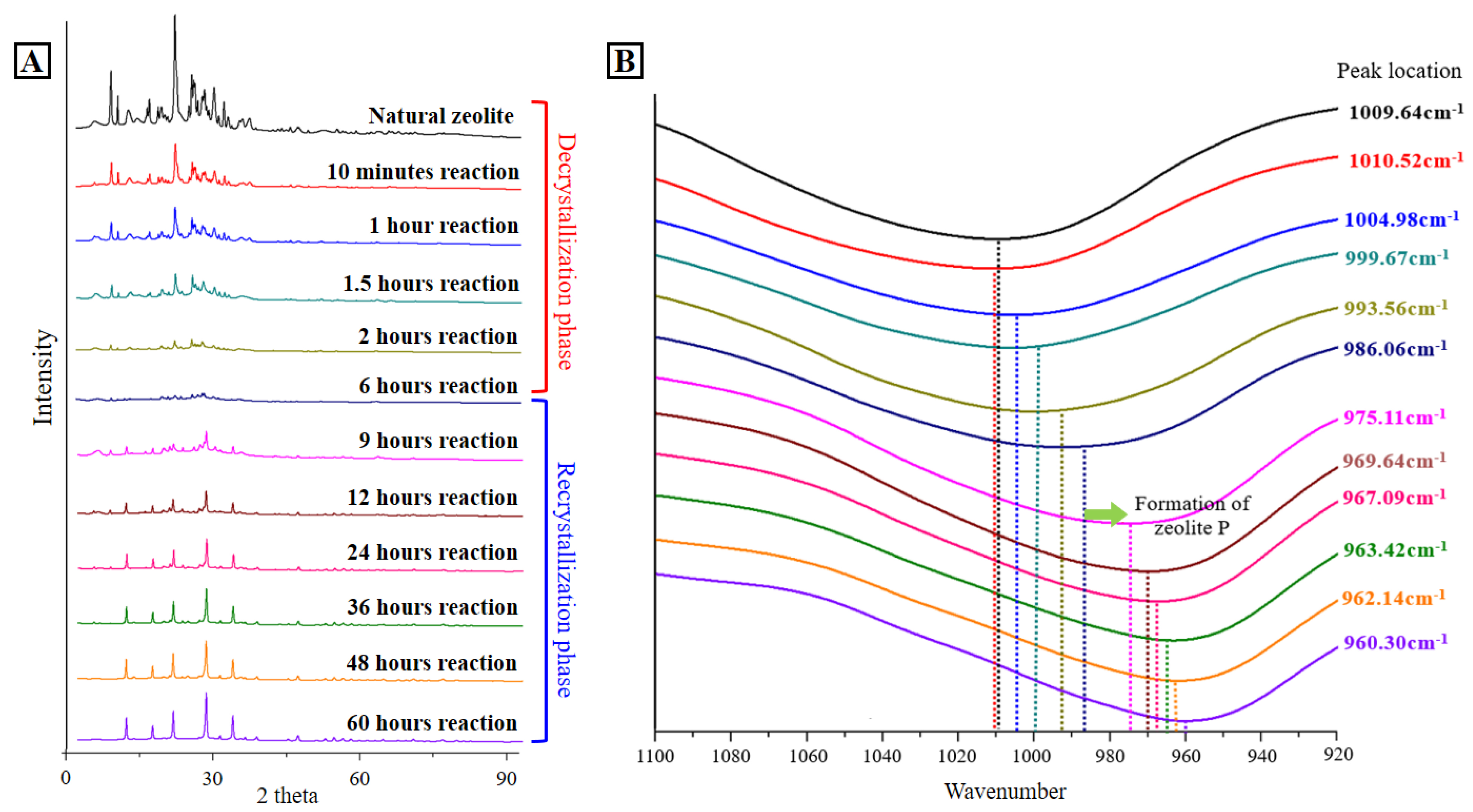
3.2. Mechanism of NaP Zeolite Formation
3.3. Visualization of NaP Zeolite Formation Process
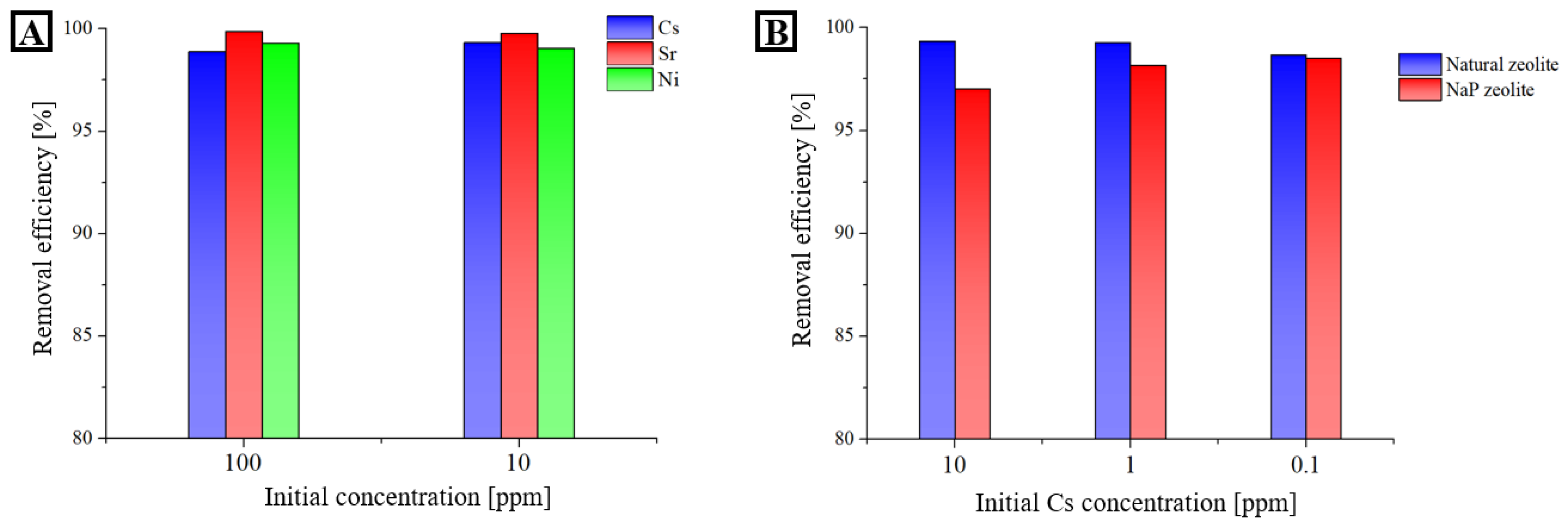
3.4. Removal of Cs+, Ni2+, and Sr2+ Using the Natural and NaP Zeolites
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- NaP zeolite was synthesized from natural zeolite, mainly consisting of clinoptilolite and mordenite. The NaP zeolite showed three times higher specific surface area and had a smaller pore size distribution than the original natural zeolite.
- (2)
- The synthesis process was observed with time-dependent XRD, FT-IR, XRF, and SEM analysis. The desilication is the main mechanism of phase transition, and the whole synthesis process consists of decrystallization followed by a recrystallization phase.
- (3)
- The maximum sorption capacity of natural zeolite and NaP zeolite was determined and showed that both zeolites fit well with Langmuir isotherms. The Cs removal efficiency of natural zeolite and NaP zeolite was not much different, however, for Sr and Ni the removal efficiency of NaP zeolite is much higher than the natural zeolite, showing the high applicability of NaP zeolite.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steinhauser, G.; Brandl, A.; Johnson, T.E. Comparison of the Chernobyl and Fukushima nuclear accidents: A review of the environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 800–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Smolders, E. Plant uptake of radiocaesium: A review of mechanisms, regulation and application. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mähler, J.; Persson, I. A Study of the Hydration of the Alkali Metal Ions in Aqueous Solution. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 51, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboneau, M.L.; Adams, J.P. National Low-Level Waste Management Program Radionuclide Report Series. Volume 10, Nickel-63, DOE/LLW—126; Idaho National Engineering Laboratory: Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, M.M.; Ali, M.; Holiel, M. Preparation of activated carbon from doum stone and its application on adsorption of 60Co and 152+154Eu: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 164, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos-Neskovic, C.; Ayrault, S.; Badillo, V.; Jiménez, B.; Garnier, E.; Fedoroff, M.; Jones, D.; Merinov, B. Structure of copper-potassium hexacyanoferrate (II) and sorption mechanisms of cesium. J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanchuk, A.Y.; Kuzenkova, A.S.; Slesarev, A.S.; Tour, J.M.; Kalmykov, S.N. Cs(I) and Sr(II) Sorption onto Graphene Oxide. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2016, 34, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A. Sorption of the long-lived radionuclides cesium-134, strontium-85 and cobalt-60 on bentonite. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2003, 258, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munthali, M.W.; Johan, E.; Aono, H.; Matsue, N. Cs+ and Sr2+ adsorption selectivity of zeolites in relation to radioactive decontamination. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2015, 3, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanova, I.I.; Knyazeva, E.E. Micro–mesoporous materials obtained by zeoliterecrystallization: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3671–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, H.; Akiba, K. Adsorption Behavior of Cesium and Strontium on Synthetic Zeolite P. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 1993, 30, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-J.; Egashira, K. Modification of different grades of Korean natural zeolites for increasing cation exchange capacity. Appl. Clay Sci. 1997, 12, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, E.; Yamada, T.; Munthali, M.W.; Kabwadza-Corner, P.; Aono, H.; Matsue, N. Natural Zeolites as Potential Materials for Decontamination of Radioactive Cesium. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smičiklas, I.; Dimovic, S.; Plecas, I. Removal of Cs1+, Sr2+ and Co2+ from aqueous solutions by adsorption on natural clinoptilolite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 35, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-S.; Huang, J.; Hu, H.-Q.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y. Determination of kinetic and equilibrium parameters of the batch adsorption of Ni(II) from aqueous solutions by Na-mordenite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argun, M.E. Use of clinoptilolite for the removal of nickel ions from water: Kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrozova, P.; Kynicky, J.; Urubek, T.; Nguyen, V.D. Synthesis and Modification of Clinoptilolite. Molecules 2017, 22, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, Z.; Xu, X.; Lü, Z.; Song, J.; He, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yan, L. Synthesis of zeolite NaP with controllable morphologies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 158, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, K.M.; Karakaya, N.; Bakır, S. Some properties and potential applications of the Na- and Ca-bentonites of ordu (N.E. Turkey). Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 54, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram, H.; Önal, M.; Yılmaz, H.; Sarıkaya, Y. Thermal analysis of a white calcium bentonite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 101, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, T.S.; Burns, R.G. Activity diagrams for clinoptilolite; susceptibility of this zeolite to further diagenetic reactions. Am. Miner. 1990, 75, 601–619. Available online: https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/msa/ammin/article-abstract/75/5-6/601/42378 (accessed on 26 January 2021).
- Hillier, S.; Lumsdon, D.G. Distinguishing opaline silica from cristobalite in bentonites: A practical procedure and perspective based on NaOH dissolution. Clay Miner. 2008, 43, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Yamasaki, N.; Muratani, M.; Hino, R. Structure and formation process of (K,Na)-clinoptilolite. Mater. Res. Bull. 2003, 38, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.O.; El-Sheikh, S.M.; Salama, T.M.; Bakr, M.F.; Fodial, M.H. Controllable synthesis of NaP zeolite and its application in calcium adsorption. Sci. China Mater. 2015, 58, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynne, B.Y.; Campbell, K.A. Morphologic and Mineralogic Transitions From Opal-A to Opal-CT in Low-Temperature Siliceous Sinter Diagenesis, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand. J. Sediment. Res. 2004, 74, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, B.; Cheetham, A.; Stuart, J.; Adams, C. Investigations on P zeolites: Synthesis, characterisation, and structure of highly crystalline low-silica NaP. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1998, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cui, X.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Synthesis of SAPO-34/ZSM-5 Composite and Its Catalytic Performance in the Conversion of Methanol to Hydrocarbonsc. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2014, 26, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, M.; Aranovich, G. Classification of Gibbs adsorption isotherms. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Song, J.-S.; Han, M.H.; Cho, C.-H. GIS-NaP1 zeolite microspheres as potential water adsorption material: Influence of initial silica concentration on adsorptive and physical/topological properties. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.M.K.; Thompsett, D.; Tsang, S.C. Ultra-thin porous silica coated silver–platinum alloy nano-particle as a new catalyst precursor. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1522–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marage, P.; Langlet, M.; Joubert, J. A new route for the deposition of SiO2 sol-gel coatings. Thin Solid Films 1994, 238, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermida, L.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Mohamed, A.R. Synthesis and Characterization of Mesostructured Cellular Foam (MCF) Silica Loaded with Nickel Nanoparticles as a Novel Catalyst. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2013, 4, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rimsza, J.; Jones, R.; Criscenti, L. Interaction of NaOH solutions with silica surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 516, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, B.; Smith, D.K.; Straub, C.P. Determination of low concentrations of radioactive cesium in water. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Type | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe,exp (mg/g) | k1 (1/h) | Qe,cal (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/mg⋅h) | Qe,cal (mg/g) | R2 | |
| Natural zeolite—Cs | 49.51 | 0.2431 | 0.1094 | 0.9024 | 0.2721 | 49.50 | 0.9999 |
| Natural zeolite—Sr | 13.22 | 0.0298 | 0.2811 | 0.0133 | 0.0562 | 13.37 | 0.9996 |
| Natural zeolite—Ni | 5.21 | 0.1774 | 0.7238 | 0.8881 | 0.1126 | 5.27 | 0.9997 |
| NaP zeolite—Cs | 51.52 | 0.1220 | 0.0179 | 0.1522 | 0.3421 | 51.55 | 0.9999 |
| NaP zeolite—Sr | 27.93 | 0.1934 | 0.2206 | 0.9068 | 0.1677 | 28.01 | 0.9999 |
| NaP zeolite—Ni | 24.51 | 0.2044 | 0.3209 | 0.9697 | 0.1288 | 24.63 | 0.9999 |
| Type | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | 1/n | KF (L/mg) | R2 | |
| Natural zeolite—Cs | 40.00 | 1.968 | 0.9543 | 0.1909 | 18.58 | 0.9095 |
| Natural zeolite—Sr | 12.75 | 4.962 | 0.9606 | 0.2089 | 7.360 | 0.8865 |
| Natural zeolite—Ni | 6.09 | 7.139 | 0.9832 | 0.1864 | 2.732 | 0.6386 |
| NaP zeolite—Cs | 58.82 | 0.178 | 0.9842 | 0.2766 | 16.19 | 0.7329 |
| NaP zeolite—Sr | 25.32 | 1.716 | 0.9329 | 0.1537 | 11.26 | 0.9235 |
| NaP zeolite—Ni | 24.57 | 7.017 | 0.9994 | 0.0933 | 15.56 | 0.8027 |
| Type | Ca | Na | K | Mg | Total CEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cmol/kg | |||||
| Natural zeolite | 61.90 | 47.63 | 5.94 | 3.72 | 119.19 |
| NaP zeolite | 105.63 | 174.32 | 2.09 | 28.85 | 310.89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.; Um, W. Top-Down Synthesis of NaP Zeolite from Natural Zeolite for the Higher Removal Efficiency of Cs, Sr, and Ni. Minerals 2021, 11, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030252
Hong S, Um W. Top-Down Synthesis of NaP Zeolite from Natural Zeolite for the Higher Removal Efficiency of Cs, Sr, and Ni. Minerals. 2021; 11(3):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030252
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Seokju, and Wooyong Um. 2021. "Top-Down Synthesis of NaP Zeolite from Natural Zeolite for the Higher Removal Efficiency of Cs, Sr, and Ni" Minerals 11, no. 3: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030252
APA StyleHong, S., & Um, W. (2021). Top-Down Synthesis of NaP Zeolite from Natural Zeolite for the Higher Removal Efficiency of Cs, Sr, and Ni. Minerals, 11(3), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030252






