Analysis of Spatial Variability of River Bottom Sediment Pollution with Heavy Metals and Assessment of Potential Ecological Hazard for the Warta River, Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
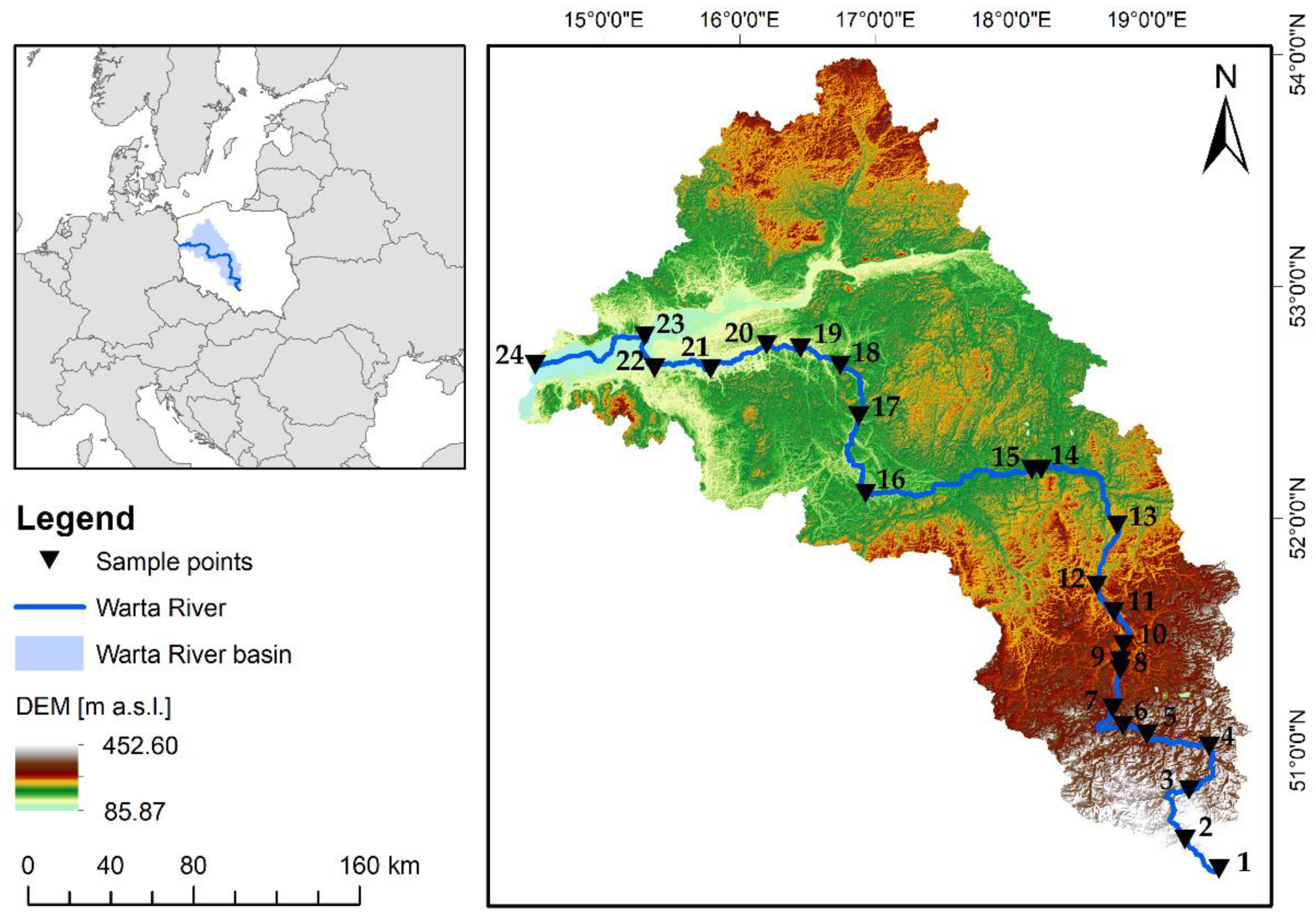
2.1. Study Site Description
2.2. Materials
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. General Characterization of the Content of Heavy Metals in the Warta River Bottom Sediments
2.3.2. Geoaccumulation Index
2.3.3. Enrichment Factor
2.3.4. Pollution Load Index
2.3.5. Metal Pollution Index
2.3.6. Ecological Risk Assessment
2.3.7. Toxic Risk Index
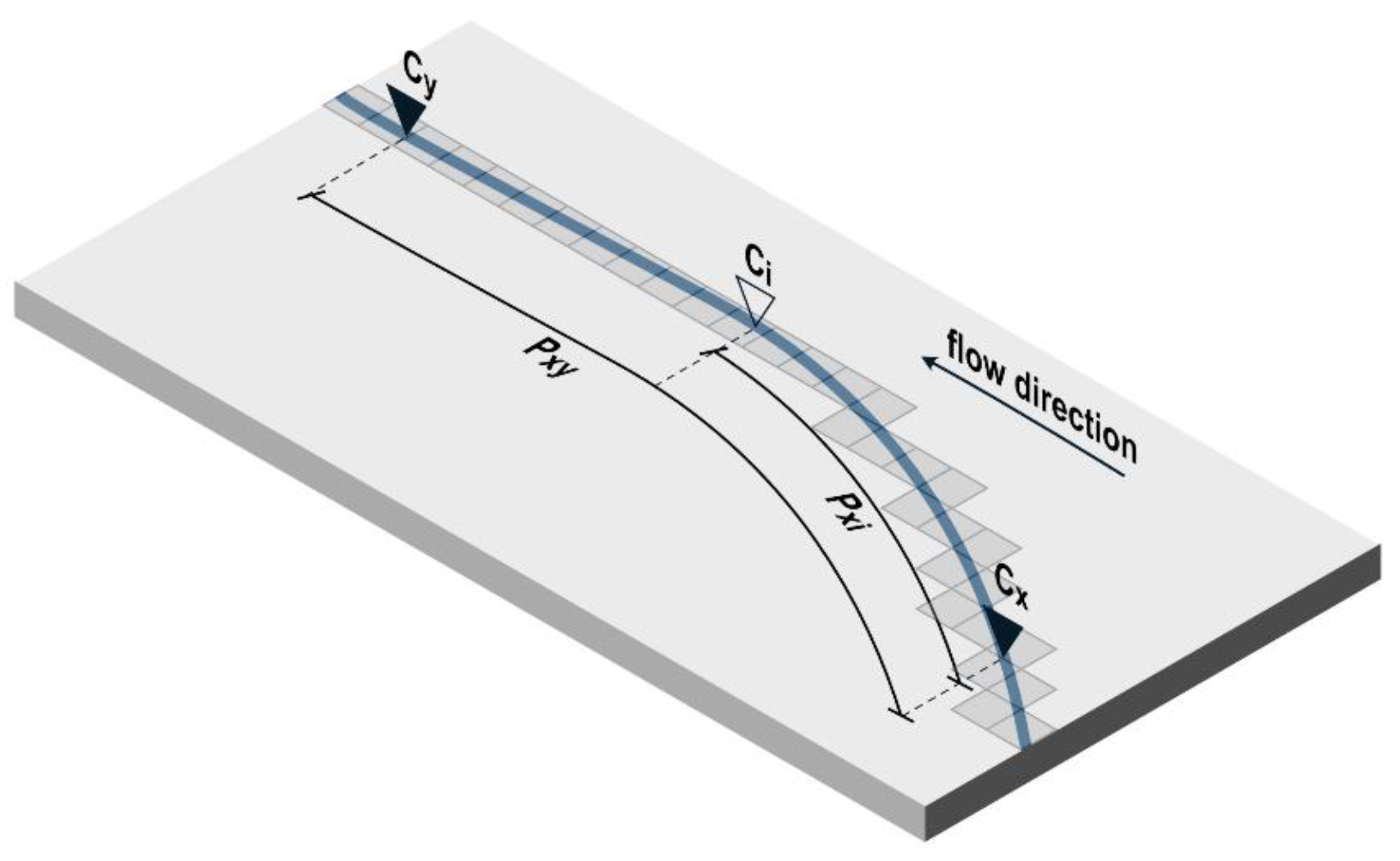
2.3.8. Analysis of Spatial Variability of the Heavy Metal Content in the Warta River Bottom Sediments
2.3.9. Linear Interpolation
3. Results
3.1. General Characterization of Heavy Metal Concentrations
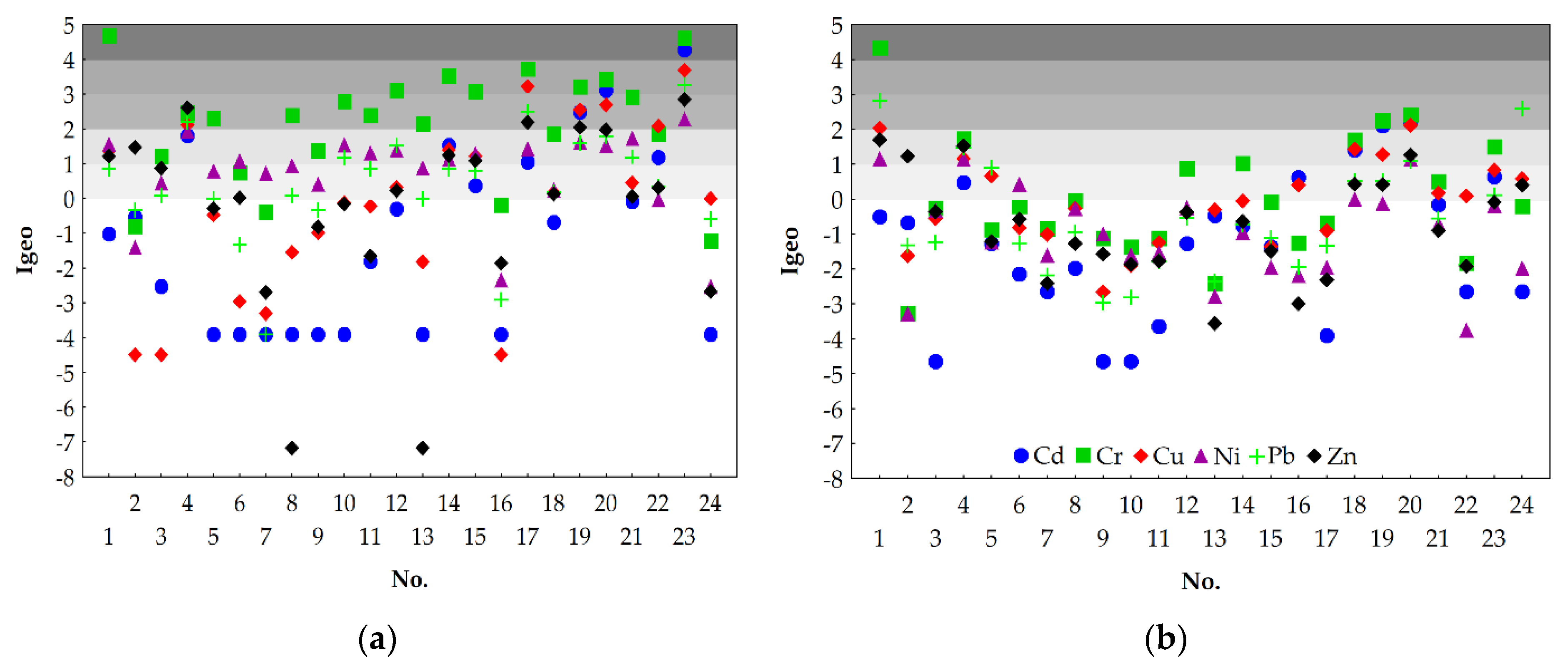
3.2. Assessment of the Contamination of the Warta River Bottom Sediment
3.3. Toxic Effect of Heavy Metals
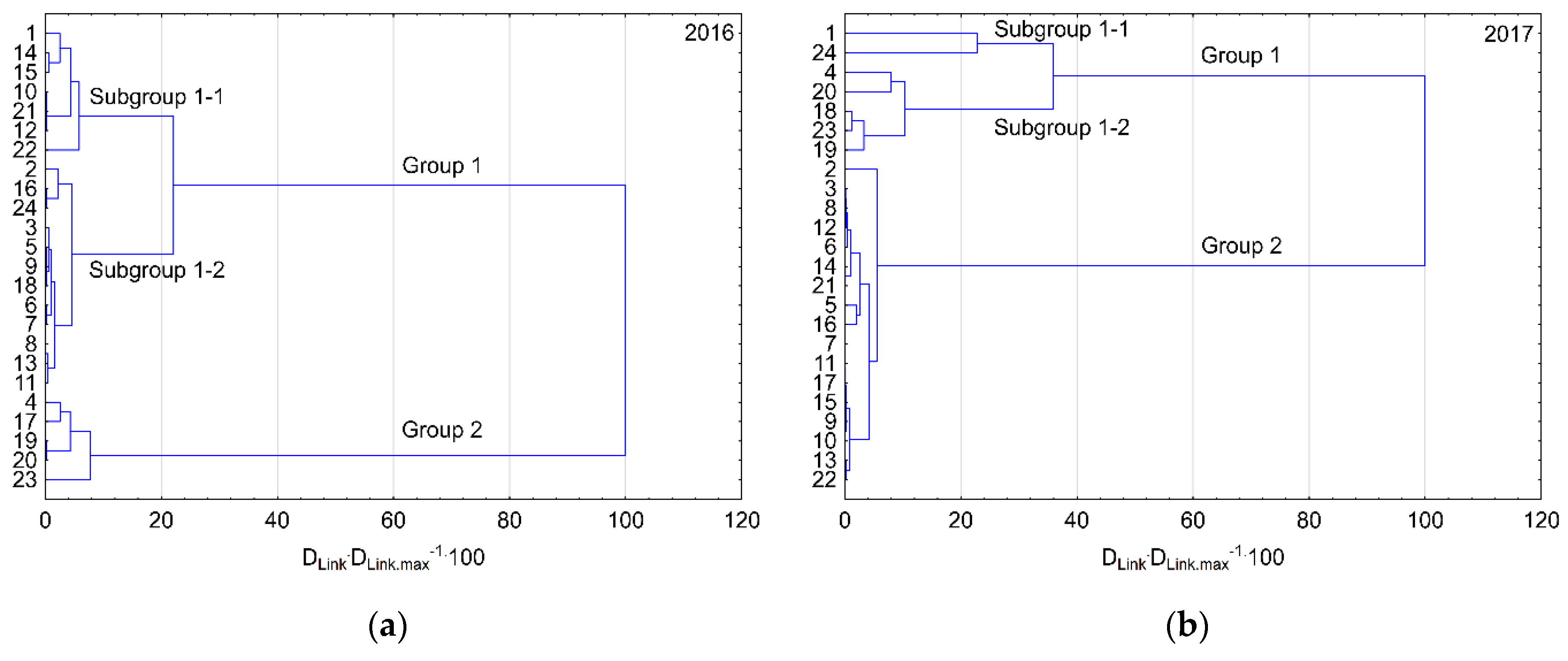
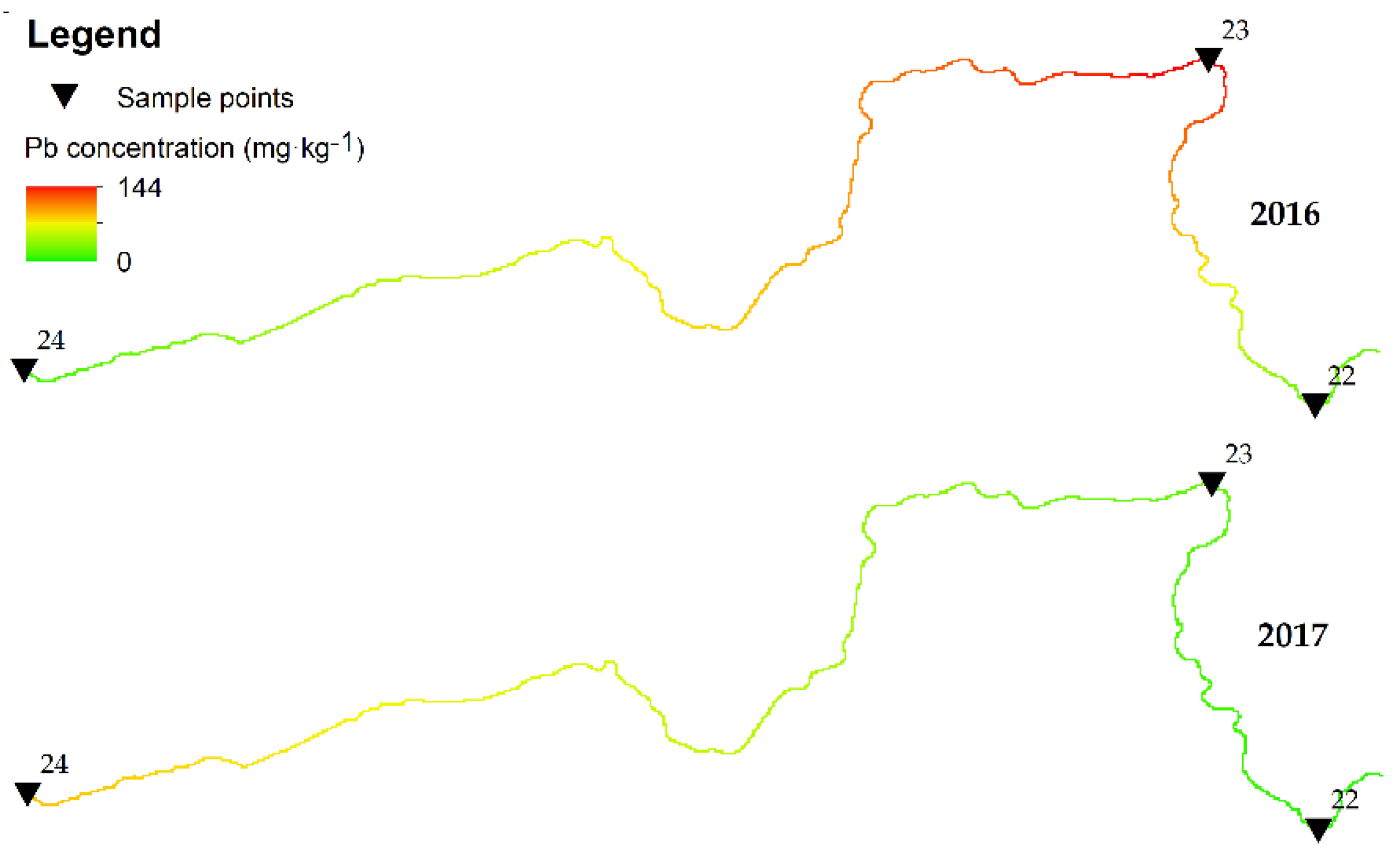
3.4. Spatial Analysis of Contamination of the Warta River Bottom Sediments with Heavy Metals
3.5. Linear Interpolation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- As shown by the results of analysis of Igeo, EF, PLI, and MPI values, the level of contamination of the Warta River bottom sediments with heavy metals was higher in 2016 than in 2017.
- According to the assessment of the potential toxic effects of heavy metals accumulated in bottom sediments made on the basis of TEC, MEC, PEC, and TRI, the ecological risk related to the presence of heavy metals in the river bottom sediments was much lower in 2017 than in 2016.
- Cluster analysis permitted distinction of two groups of the sample collection stations at which bottom sediments showed similar chemical character. Changes in the classification of particular stations to particular groups indicated that the concentration of heavy metals in the Warta river bottom sediments is mainly related to the point sources of contamination in urbanized areas and connected with river fluvial process.
- In view of the necessity of taking up measures aimed at protection of water resources, it is vital to find methods providing the possibly most accurate information on the status of the whole courses of the rivers not only at their certain points. The solution proposed in this paper permits analysis of the changes in the river bottom sediments along the whole course of the river, which is essential for identification of potential sources of contamination and for taking up actions aimed at limitation of the effect of such sources. The main drawback of the method proposed is the fact that it is based on point measurements, disregarding a variable related to the land use, e.g., the effect of urbanized areas.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dąbrowska, J.; Dąbek, P.B.; Lejcuś, I. A GIS based approach for the mitigation of surface runoff to a shallow lowland reservoir. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2018, 18, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowska, J.; Pawęska, K.; Dąbek, P.B.; Stodolak, R. The implications of economic development, climate change and European water policy on surface water quality threats. Acta Sci. Pol. Formatio Circumiectus 2017, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, T.M.; Yaseen, Z.M. A survey on river water quality modelling using artificial intelligence models: 2000–2020. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124670. [Google Scholar]
- Sojka, M.; Jaskuła, J.; Wicher-Dysarz, J. Assessment of Biogenic Compounds elution from the Główna River catchment in the Years 1996–2009. Annu. Set Environ. Prot. 2016, 18, 815–830. [Google Scholar]
- Kuriata-Potasznik, A.; Szymczyk, S.; Skwierawski, A. Influence of cascading river–lake systems on the dynamics of nutrient circulation in catchment areas. Water 2020, 12, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Siepak, M.; Jaskuła, J.; Wicher-Dysarz, J. Heavy metal transport in a river-reservoir system: A case study from central Poland. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriata-Potasznik, A.; Szymczyk, S.; Skwierawski, A.; Glińska-Lewczuk, K.; Cymes, I. Heavy metal contamination in the surface layer of bottom sediments in a flow-through lake: A case study of Lake Symsar in Northern Poland. Water 2016, 8, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Yin, J.; Chen, L.; Peng, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, K. Ecological risk of human health posed by sediments in a karstic river basin with high longevity population. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskuła, J.; Sojka, M.; Wicher-Dysarz, J. Analysis of the vegetation process in a two-stage reservoir on the basis of satellite imagery—a case study: Radzyny Reservoir on the Sama River. Annu. Set Environ. Prot. 2018, 20, 203–220. [Google Scholar]
- Jaskuła, J.; Sojka, M. Assessment of spectral indices for detection of vegetative overgrowth of reservoirs. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 4199–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dysarz, T.; Wicher-Dysarz, J.; Sojka, M.; Jaskuła, J. Analysis of extreme flow uncertainty impact on size of flood hazard zones for the Wronki gauge station in the Warta river. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicher-Dysarz, J.; Szałkiewicz, E.; Jaskuła, J.; Dysarz, T.; Rybacki, M. Possibilities of controlling the river outlets by weirs on the example of Noteć Bystra River. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Hu, Z.; Fan, D. Accumulation and transformation of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Yangtze River estuary to the East China Sea shelf. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.K.; Sharma, M.K. Distribution of trace metals in the Hindon River system, India. J. Hydrol. 2001, 253, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot, N.; Wojciechowska, E.; Rezania, S.; Walkusz-Miotk, J.; Pazdro, K. The effects of urban vehicle traffic on heavy metal contamination in road sweeping waste and bottom sediments of retention tanks. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandeng, E.P.B.; Bidjeck, L.M.B.; Bessa, A.Z.E.; Ntomb, Y.D.; Wadjou, J.W.; Doumo, E.P.E.; Dieudonné, L.B. Contamination and risk assessment of heavy metals, and uranium of sediments in two watersheds in Abiete-Toko gold district, Southern Cameroon. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Fan, D.; Liu, M.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Liao, H. Source identification, geochemical normalization and influence factors of heavy metals in Yangtze River Estuary sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, G.O.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G.A. Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal in Brisbane River sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatis, N.; Kamidis, N.; Pigada, P.; Sylaios, G.; Koutrakis, E. Quality Indicators and Possible Ecological Risks of Heavy Metals in the Sediments of three Semi-closed East Mediterranean Gulfs. Toxics 2019, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Li, F.; Dominech, S.; Wen, X.; Yang, S. Heavy metals of surface sediments in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary: Distribution, speciation and environmental risks. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 198, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, J.P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Martens, W.N.; Goonetilleke, A. Enrichment, distribution and sources of heavy metals in the sediments of Deception Bay, Queensland, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Qi, J.; Xia, X. Long-term variations in sediment heavy metals of a reservoir with changing trophic states: Implications for the impact of climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Jaskuła, J.; Siepak, M. Heavy metals in bottom sediments of reservoirs in the lowland area of western Poland: Concentrations, distribution, sources and ecological risk. Water 2019, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doležalová Weissmannová, H.; Mihočová, S.; Chovanec, P.; Pavlovský, J. Potential ecological risk and human health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in industrial affected soils by coal mining and metallurgy in Ostrava, Czech Republic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Shan, J.; Chen, J.; Tang, C.; Yi, M.; Zhao, X. Distribution characteristics and sources of trace metals in sediment cores from a trans-boundary watercourse: An example from the Shima River, Pearl River Delta. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2016, 134, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, M.I.; Song, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Mehmood, M.S.; Sajid, M.; Khan, A.J. Contamination level, ecological risk, and source identification of heavy metals in the hyporheic zone of the Weihe River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvandi, H. Preliminary evaluation of heavy metal contamination in the Zarrin-Gol River sediments, Iran. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Wu, M.; Liao, S.; Zhang, D.; Pan, B. The sorption of heavy metals on thermally treated sediments with high organic matter content. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cymes, I.; Glińska-Lewczuk, K.; Szymczyk, S.; Sidoruk, M.; Potasznik, A. Distribution and potential risk assessment of heavy metals and arsenic in sediments of a dam reservoir: A case study of the Łoje retention reservoir, NE Poland. J. Elementol. 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Do, D.D.; Nguyen, T.X.; Nguyen, V.N.; Nguyen, D.T.P.; Nguyen, M.H.; Bach, Q.V. Seasonal, spatial variation, and pollution sources of heavy metals in the sediment of the Saigon River, Vietnam. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Liu, E.; Zhang, E.; Li, K.; Shen, J. Spatial distribution, contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, a large eutrophic plateau lake in southwest China. Catena 2016, 145, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, M.H.; Ahmed, F.; Ishiga, H. Assessment of metal concentrations in lake sediments of southwest Japan based on sediment quality guidelines. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha-D’Mello, C.A.; Nayak, G.N. Assessment of metal enrichment and their bioavailability in sediment and bioaccumulation by mangrove plant pneumatophores in a tropical (Zuari) estuary, west coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.S.; Huang, J.J.S.; Burr, G.; Kao, L.C.; Wei, K.Y.; Liou, S.Y.H. High resolution record of heavy metals from estuary sediments of Nankan River (Taiwan) assessed by rigorous multivariate statistical analysis. Quat. Int. 2019, 527, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geol. J. 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Mar. Res. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Berger, T.A. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojakowska, I.; Sokołowska, G. Geochemiczne klasy czystości osadów wodnych. Przegląd Geologiczny 1998, 46, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Sakan, S.M.; Đorđević, D.S.; Manojlović, D.D.; Predrag, P.S. Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza river sediments. J. Environ. Manage. 2009, 90, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, K.; Ram Mohan, V.; Szefer, P. Evaluation of metal contamination in coastal sediments of the Bay of Bengal, India: Geochemical and statistical approaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, S.; Moore, F. Assessment of heavy metal concentration in the Khoshk River water and sediment, Shiraz, Southwest Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 164, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rashdi, S.; Arabi, A.A.; Howari, F.M.; Siad, A. Distribution of heavy metals in the coastal area of Abu Dhabi in the United Arab Emirates. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 97, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.M.; Meybeck, M. Elemental mass-balance of material carried by major world rivers. Mar. Chem. 1979, 7, 173–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singovszka, E.; Balintova, M.; Demcak, S.; Pavlikova, P. Metal pollution indices of bottom sediment and surface water affected by acid mine drainage. Metals 2017, 7, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Q.; Jia, J.; Wen, X. Heavy metals in wetland soils along a wetland-forming chronosequence in the Yellow River Delta of China: Levels, sources and toxic risks. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Bi, C.; Jia, J.; Deng, L.; Chen, Z. Impact of intensive land use on heavy metal concentrations and ecological risks in an urbanized river network of Shanghai. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H. Spatial variation of heavy metal contamination in the riparian sediments after two-year flow regulation in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptak, M.; Sojka, M.; Choiński, A.; Nowak, B. Effect of environmental conditions and morphometric parameters on surface water temperature in Polish lakes. Water 2018, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrame, M.O.; De Marco, S.G.; Marcovecchio, J.E. Dissolved and particulate heavy metals distribution in coastal lagoons. A case study from Mar Chiquita Lagoon, Argentina. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 85, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Sun, B.; Zeng, D.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B. Vertical distribution of trace elements in the sediment cores from major rivers in east China and its implication on geochemical background and anthropogenic effects. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, M.; Ayrault, S.; Evrard, O.; Laceby, J.P.; Gateuille, D.; Lefevre, I.; Mouchel, J.M.; Meybeck, M. Investigating the metal contamination of sediment transported by the 2016 Seine River flood (Paris, France). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Teng, Y. Source apportionment and source-oriented risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of an urban river-lake system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custodio, M.; Cuadrado, W.; Peñaloza, R.; Montalvo, R.; Ochoa, S.; Quispe, J. Human risk from exposure to heavy metals and arsenic in water from rivers with mining influence in the Central Andes of Peru. Water 2020, 12, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, A.; Li, M.; Zhang, X. Effect of pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and flow rate of overlying water on heavy metals release from storm sewer sediments. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Iqbal, J.; Akhter, G.; Shah, M.H. Fractionation, bioavailability, contamination and environmental risk of heavy metals in the sediments from a freshwater reservoir, Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 184, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Class | Value | Sediment Pollution |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Igeo ≤ 0 | no enrichment |
| 1 | 0 < Igeo ≤ 1 | minor enrichment |
| 2 | 1 < Igeo ≤ 2 | moderate enrichment |
| 3 | 2 < Igeo ≤ 3 | moderately severe enrichment |
| 4 | 3 < Igeo ≤ 4 | severe enrichment |
| 5 | 4 < Igeo ≤ 5 | very severe enrichment |
| 6 | 5 < Igeo | extremely severe enrichment |
| Class | Value | Sediment Pollution |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | EF ≤ 1 | no enrichment |
| 1 | 1 < EF ≤ 3 | minor enrichment |
| 2 | 3 < EF ≤ 5 | moderate enrichment |
| 3 | 5 < EF ≤ 10 | moderately severe enrichment |
| 4 | 10 < EF ≤ 25 | severe enrichment |
| 5 | 25 < EF ≤ 50 | very severe enrichment |
| 6 | 50 < EF | extremely severe enrichment |
| HMs | Level I (≤ TEC) | Level II (>TEC ≤ MEC) | Level III (>MEC ≤ PEC) | Level IV (>PEC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | ≤0.99 | 0.99–3.0 | 3.0–5.0 | >5.0 |
| Cr | ≤43 | 43–76.5 | 76.5–110 | >110 |
| Cu | ≤32 | 32–91 | 91–150 | >150 |
| Ni | ≤23 | 23–36 | 36–49 | >49 |
| Pb | ≤36 | 36–83 | 83–130 | >130 |
| Zn | ≤120 | 120–290 | 290–460 | >460 |
| Class | Value | Toxic Risk |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | TRI ≤ 5 | no toxic risk |
| 1 | 5 < TRI ≤ 10 | low |
| 2 | 10 < TRI ≤ 15 | moderate |
| 3 | 15 < TRI ≤ 20 | considerable |
| 4 | 20 < TRI | very high |
| No. | HMs | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | |||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| 1 | 0.37 | 0.53 | 193.00 | 152.00 * | 23.20 | 36.98 | 22.20 | 16.80 | 27.00 | 106.00 * | 168.00 | 234.00 |
| 2 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 4.32 | 0.78 | 0.40 | 2.93 | 2.84 | 0.77 | 12.00 | 5.99 | 200.00 | 168.50 |
| 3 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 17.40 | 6.26 | 0.40 | 6.12 | 10.30 | 5.99 | 16.00 | 6.32 | 132.00 | 55.79 |
| 4 | 2.62 | 1.04 | 41.40 | 25.05 | 39.10 | 20.07 | 28.60 | 16.66 | 69.00 | 41.66 | 440.00 | 207.50 |
| 5 | 0.05 | 0.31 | 37.00 | 4.12 | 6.50 | 14.30 | 13.10 | 3.21 | 15.00 | 27.90 | 58.90 | 31.20 |
| 6 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 12.60 | 6.57 | 1.16 | 5.12 | 15.90 | 10.11 | 6.00 | 6.26 | 73.10 | 48.48 |
| 7 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 5.75 | 4.20 | 0.91 | 4.49 | 12.40 | 2.47 | 1.00 | 3.32 | 11.10 | 13.52 |
| 8 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 39.30 | 7.33 | 3.09 | 7.48 | 14.40 | 6.23 | 16.00 | 7.72 | 0.50 | 29.84 |
| 9 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 19.60 | 3.46 | 4.55 | 1.42 | 9.96 | 3.76 | 12.00 | 1.91 | 40.80 | 24.31 |
| 10 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 52.20 | 2.90 | 8.28 | 2.40 | 21.90 | 2.47 | 34.00 | 2.13 | 64.60 | 19.62 |
| 11 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 39.40 | 3.46 | 7.74 | 3.79 | 18.60 | 2.58 | 27.00 | 4.35 | 22.80 | 21.11 |
| 12 | 0.61 | 0.31 | 64.50 | 13.79 | 11.20 | 6.91 | 19.70 | 6.36 | 43.00 | 10.30 | 84.20 | 55.35 |
| 13 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 33.30 | 1.41 | 2.54 | 7.30 | 13.80 | 1.09 | 15.00 | 2.94 | 0.50 | 6.09 |
| 14 | 2.16 | 0.44 | 86.30 | 15.23 | 23.80 | 8.69 | 16.60 | 3.88 | 27.00 | 9.12 | 170.00 | 46.45 |
| 15 | 0.96 | 0.29 | 63.10 | 7.11 | 21.00 | 3.52 | 18.40 | 1.94 | 26.00 | 6.90 | 153.00 | 25.67 |
| 16 | 0.05 | 1.15 | 6.60 | 3.17 | 0.40 | 11.92 | 1.48 | 1.65 | 2.00 | 3.90 | 19.80 | 9.05 |
| 17 | 1.56 | 0.05 | 100.00 | 4.68 | 83.80 | 4.82 | 20.20 | 1.93 | 85.00 | 5.95 | 327.00 | 14.44 |
| 18 | 0.47 | 2.00 | 27.40 | 24.40 | 10.20 | 24.34 | 8.92 | 7.49 | 17.00 | 21.38 | 78.60 | 97.10 |
| 19 | 4.22 * | 3.23 | 69.60 | 35.89 | 52.60 | 21.77 | 23.20 | 6.86 | 45.00 | 21.39 | 296.00 | 95.61 |
| 20 | 6.46 * | 3.52 | 81.30 | 40.26 | 58.30 | 39.00 | 21.60 | 16.60 | 52.00 | 31.81 | 283.00 | 173.50 |
| 21 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 56.90 | 10.66 | 12.30 | 10.17 | 24.90 | 4.58 | 34.00 | 10.18 | 74.70 | 38.67 |
| 22 | 1.70 | 0.12 | 27.00 | 2.12 | 38.20 | 9.60 | 7.36 | 0.56 | 19.00 | 4.12 | 88.90 | 19.02 |
| 23 | 14.50 * | 1.17 | 184.00 * | 21.33 | 116.00 | 16.11 | 36.70 | 6.61 | 144.00 * | 16.22 | 519.00 | 67.95 |
| 24 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 3.20 | 6.56 | 9.00 | 13.55 | 1.30 | 1.91 | 10.00 | 90.47* | 11.30 | 95.45 |
| Period | 2016 | 2017 | 2016/2017 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMs | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
| Minimum | 0.05 | 3.20 | 0.40 | 1.30 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.03 | 0.78 | 1.42 | 0.56 | 1.91 | 6.09 | 0.03 | 0.78 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 1.00 | 0.50 | |
| Mean | 1.57 | 52.7 | 22.3 | 16.0 | 31.4 | 138 | 0.69 | 16.8 | 11.8 | 5.52 | 18.7 | 66.6 | 1.13 | 34.7 | 17.0 | 10.8 | 25.0 | 102 | |
| Maximum | 14.5 | 193 | 116 | 36.7 | 144 | 519 | 3.5 | 152 | 39.0 | 16.8 | 106 | 234 | 14.5 | 193 | 116 | 36.7 | 144 | 519 | |
| Percentile | 1% | 0.05 | 3.20 | 0.40 | 1.30 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.03 | 0.78 | 1.42 | 0.56 | 1.91 | 6.09 | 0.03 | 0.78 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 1.00 | 0.50 |
| 5% | 0.05 | 4.32 | 0.40 | 1.48 | 2.00 | 0.50 | 0.03 | 1.41 | 2.40 | 0.77 | 2.13 | 9.05 | 0.03 | 2.12 | 0.40 | 1.09 | 2.00 | 6.09 | |
| 10% | 0.05 | 5.75 | 0.40 | 2.84 | 6.00 | 11.1 | 0.03 | 2.12 | 2.93 | 1.09 | 2.94 | 13.5 | 0.05 | 3.17 | 1.16 | 1.48 | 2.94 | 11.1 | |
| 25% | 0.05 | 18.5 | 2.82 | 10.1 | 13.5 | 31.8 | 0.12 | 3.46 | 4.66 | 1.94 | 4.24 | 20.4 | 0.05 | 5.22 | 4.14 | 2.71 | 6.13 | 22.0 | |
| 50% | 0.42 | 39.3 | 9.60 | 16.3 | 22.5 | 81.4 | 0.31 | 6.57 | 8.09 | 3.82 | 7.31 | 42.6 | 0.34 | 18.5 | 8.85 | 8.21 | 15.5 | 61.7 | |
| 75% | 1.63 | 67.1 | 31.0 | 21.8 | 38.5 | 185 | 0.86 | 18.3 | 15.2 | 6.74 | 21.4 | 95.5 | 1.10 | 40.8 | 21.4 | 16.7 | 29.9 | 161 | |
| 90% | 4.22 | 100 | 58.3 | 24.9 | 69.0 | 327 | 2.00 | 35.9 | 24.3 | 16.6 | 41.7 | 174 | 3.23 | 86.3 | 39.1 | 22.2 | 69.0 | 283 | |
| 95% | 6.46 | 184 | 83.8 | 28.6 | 85.0 | 440 | 3.23 | 40.3 | 37.0 | 16.7 | 90.5 | 208 | 4.22 | 152 | 58.3 | 24.9 | 90.5 | 327 | |
| 99% | 14.5 | 193 | 116 | 36.7 | 144 | 519 | 3.52 | 152 | 39.0 | 16.8 | 106 | 234 | 14.5 | 193 | 116 | 36.7 | 144 | 519 | |
| Range | 14.5 | 190 | 116 | 35.4 | 143 | 519 | 3.5 | 151 | 37.6 | 16.2 | 104 | 228 | 14.5 | 192 | 116 | 36.1 | 143 | 519 | |
| IQR | 1.58 | 48.6 | 28.2 | 11.6 | 25.0 | 153 | 0.74 | 14.8 | 10.6 | 4.80 | 17.2 | 75.2 | 1.05 | 35.6 | 17.2 | 14.0 | 23.7 | 139 | |
| MAD | 0.37 | 24.5 | 8.95 | 5.80 | 11.0 | 70.2 | 0.24 | 3.88 | 4.43 | 2.29 | 3.70 | 24.5 | 0.29 | 15.0 | 5.84 | 6.27 | 11.3 | 42.0 | |
| QCD | 0.94 | 0.57 | 0.83 | 0.36 | 0.48 | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.68 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.65 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 0.66 | 0.76 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaskuła, J.; Sojka, M.; Fiedler, M.; Wróżyński, R. Analysis of Spatial Variability of River Bottom Sediment Pollution with Heavy Metals and Assessment of Potential Ecological Hazard for the Warta River, Poland. Minerals 2021, 11, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030327
Jaskuła J, Sojka M, Fiedler M, Wróżyński R. Analysis of Spatial Variability of River Bottom Sediment Pollution with Heavy Metals and Assessment of Potential Ecological Hazard for the Warta River, Poland. Minerals. 2021; 11(3):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030327
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaskuła, Joanna, Mariusz Sojka, Michał Fiedler, and Rafał Wróżyński. 2021. "Analysis of Spatial Variability of River Bottom Sediment Pollution with Heavy Metals and Assessment of Potential Ecological Hazard for the Warta River, Poland" Minerals 11, no. 3: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030327
APA StyleJaskuła, J., Sojka, M., Fiedler, M., & Wróżyński, R. (2021). Analysis of Spatial Variability of River Bottom Sediment Pollution with Heavy Metals and Assessment of Potential Ecological Hazard for the Warta River, Poland. Minerals, 11(3), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11030327









