Shear-Related Gold Ores in the Wadi Hodein Shear Belt, South Eastern Desert of Egypt: Analysis of Remote Sensing, Field and Structural Data
Abstract
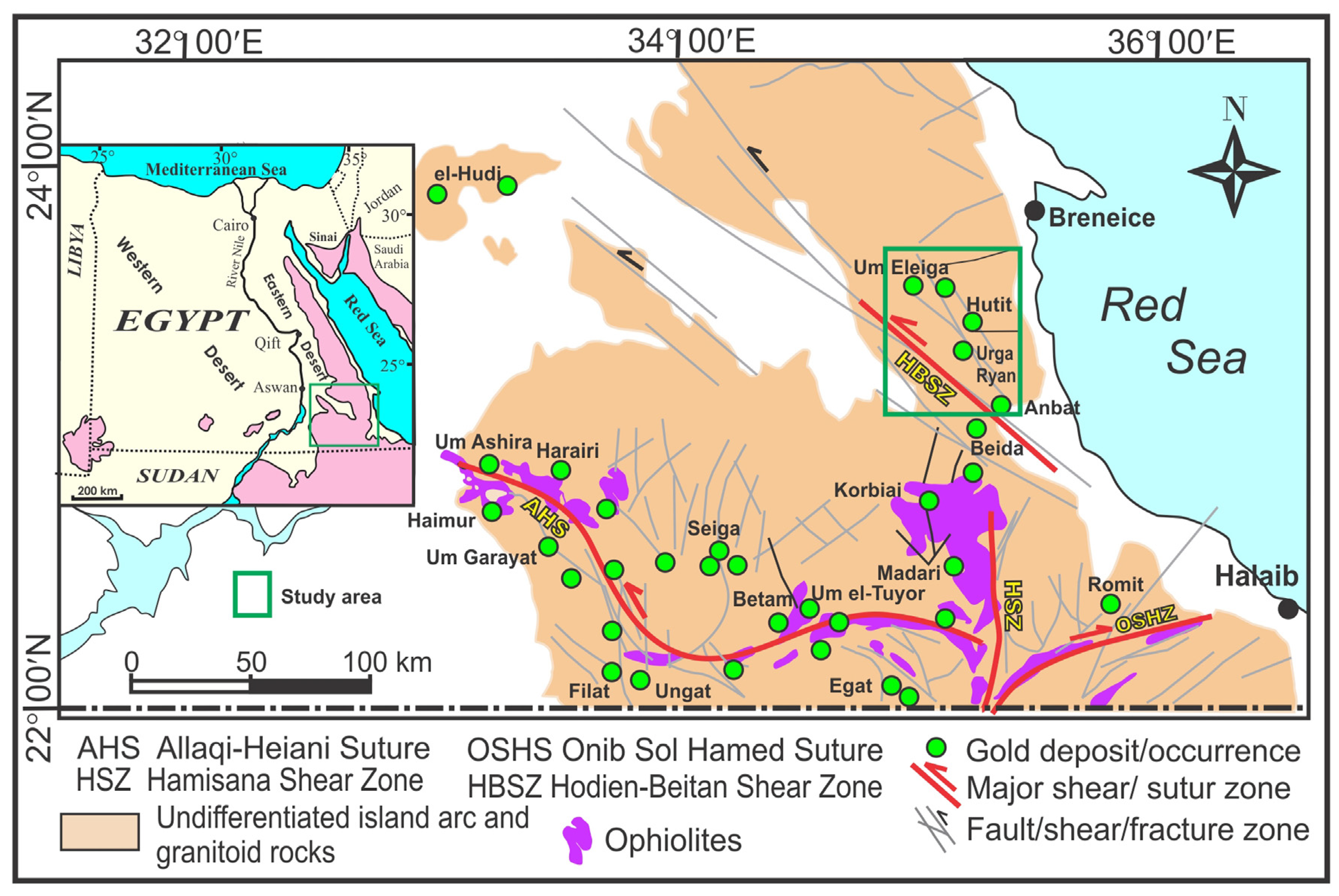
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
3. Remote Sensing Data Characteristics and Analysis
3.1. Data and Processing Techniques
3.2. Landsat-8 OLI and ASTER-Based Lithological Mapping
3.3. Hydrothermal Alteration Zones Detection
3.4. PALSAR-Based Lineaments Extraction
3.5. Geospatial Modelling for Gold Mineralization Zones
4. Structural Setting and Analysis
4.1. The Gold-Mineralized Shear Zones
4.1.1. Wadi Khashab Shear Zone
4.1.2. Wadi Rahaba Shear Zone
4.1.3. Wadi Beitan Fault Zone
4.2. Deformation Events
4.2.1. D1: NNE–SSW Crustal Shortening
4.2.2. D2: NE–SW Oblique Convergence and Transpression
4.2.3. D3: E–W Shortening and Sinistral Shearing
4.2.4. D4: Extension and Terrane Exhumation
5. Gold Occurrences in the Wadi Hodein Shear Belt
5.1. The Wadi Khashab Occurrence
5.2. The El-Anbat Deposit
5.3. The Um Teneidab Deposit
5.4. The Urga El-Ryan Occurrence
5.5. Hutit Deposit
5.6. The Um Eleiga Deposit
6. Discussion
6.1. Remote Sensing Targeting of New Gold Occurrences
6.2. Transpressional Tectonics in the Evolution of the Wadi Hodein Shear Belt
6.3. Structures Controlling Gold Occurrences
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pour, B.A.; Hashim, M.; van Genderen, J. Detection of hydrothermal alteration zones in a tropical region using satellite remote sensing data: Bau gold field, Sarawak, Malaysia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 54, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, B.A.; Hashim, M. Structural geology mapping using PALSAR data in the Bau gold mining district, Sarawak, Malaysia. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, B.A.; Hashim, M.; Marghany, M. Exploration of gold mineralization in a tropical region using Earth Observing-1 (EO1) and JERS-1 SAR data: A case study from Bau gold field, Sarawak, Malaysia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 2393–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, A.B.; Hashim, M.; Makoundi, C.; Zaw, K. Structural Mapping of the Bentong-Raub Suture Zone Using PALSAR Remote Sensing Data, Peninsular Malaysia: Implications for Sedimenthosted/Orogenic Gold Mineral Systems Exploration. Resour. Geol. 2016, 66, 368–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, B.A.; Hashim, M. Structural mapping using PALSAR data in the Central Gold Belt, Peninsular Malaysia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 64, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pour, A.B.; Hashim, M. Application of Landsat-8 and ALOS-2 data for structural and landslide hazard mapping in Kelantan, Malaysia. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoheir, B.; Emam, A. Field and ASTER imagery data for the setting of gold mineralization in Western Allaqi–Heiani belt, Egypt: A case study from the Haimur deposit. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 99, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, A.B.; Park, T.-Y.; Park, Y.; Hong, J.K.; Muslim, A.M.; Läufer, A.; Crispini, L.; Pradhan, B.; Zoheir, B.; Rahmani, O.; et al. Landsat-8, Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer, and WorldView-3 Multispectral Satellite Imagery for Prospecting Copper-Gold Mineralization in the Northeastern Inglefield Mobile Belt (IMB), Northwest Greenland. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusky, T.M.; Ramadan, T.M. Structural controls on Neoproterozoic mineralization in the South Eastern Desert, Egypt: An integrated field, Landsat TM and SIR-C/X SAR approach. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2002, 35, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoheir, B.; Emam, A.; El-Amawy, M.; Abu-Alam, T. Auriferous shear zones in the central Allaqi-Heiani belt: Orogenic gold in post-accretionary structures, SE Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 146, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoheir, B.A.; Emam, A.; Abd El-Wahed, M.; Soliman, N. Gold endowment in the evolution of the Allaqi-Heiani suture, Egypt: A synthesis of geological, structural, and space-borne imagery data. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 110, 102938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoheir, B.; Emam, A.; Abdel-Wahed, M.; Soliman, N. Multispectral and Radar Data for the Setting of Gold Mineralization in the South Eastern Desert, Egypt. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, G.R. Spectral Signatures of Particulate Minerals in The Visible and Near Infrared. Geophysics 1977, 42, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, R.N.; King, T.V.V.; Klejwa, M.; Swayze, G.A.; Vergo, N. High spectral resolution reflectance spectroscopy of minerals. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 12653–12680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, S.M.; Sadek, M.F. Geological mapping and spectral based classification of basement rocks using remote sensing data analysis: The Korbiai-Gerf nappe complex, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 134, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, J.R.; Dwyer, J.L.; Barsi, J.A. The next Landsat satellite: The Landsat Data Continuity Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.A.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Seins. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pour, A.B.; Sekandari, M.; Rahmani, O.; Crispini, L.; Läufer, A.; Park, Y.; Hong, J.K.; Pradhan, B.; Hashim, M.; Hossain, M.S.; et al. Identification of Phyllosilicates in the Antarctic Environment Using ASTER Satellite Data: Case Study from the Mesa Range, Campbell and Priestley Glaciers, Northern Victoria Land. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekandari, M.; Masoumi, I.; Beiranvand Pour, A.; Muslim, A.M.; Rahmani, O.; Hashim, M.; Zoheir, B.; Pradhan, B.; Misra, A.; Aminpour, S.M. Application of Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, ASTER and WorldView-3 Spectral Imagery for Exploration of Carbonate-Hosted Pb-Zn Deposits in the Central Iranian Terrane (CIT). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirmard, H.; Farahbakhsh, E.; Beiranvand Pour, A.; Muslim, A.M.; Müller, R.D.; Chandra, R. Integration of Selective Dimensionality Reduction Techniques for Mineral Exploration Using ASTER Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takodjou Wambo, J.D.; Pour, A.B.; Ganno, S.; Asimow, P.D.; Zoheir, B.; Reis Salles, R.D.; Nzenti, J.P.; Pradhan, B.; Muslim, A.M. Identifying high potential zones of gold mineralization in a sub-tropical region using Landsat-8 and ASTER remote sensing data: A case study of the Ngoura-Colomines goldfield, eastern Cameroon. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 122, 103530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, A.B.; Park, Y.; Crispini, L.; Läufer, A.; Kuk Hong, J.; Park, T.-Y.S.; Zoheir, B.; Pradhan, B.; Muslim, A.M.; Hossain, M.S.; et al. Mapping Listvenite Occurrences in the Damage Zones of Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica Using ASTER Satellite Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abrams, M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Twenty Years of ASTER Contributions to Lithologic Mapping and Mineral Exploration. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abrams, M.; Tsu, H.; Hulley, G.; Iwao, K.; Pieri, D.; Cudahy, T.; Kargel, J. The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) after Fifteen Years: Review of Global Products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 38, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillou, P.; Lopez, S.; Farr, T.; Rosenqvist, A. Mapping subsurface geology in Sahara using L-Band SAR: First results from the ALOS/PALSAR imaging Radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenqvist, A.; Shimada, M.; Watanabe, M.; Tadono, T.; Yamauchi, K. Implementation of systematic data observation strategies for ALOS PALSAR, PRISM andAVNIR-2. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Wahed, M.; Hamimi, Z. The Infracrustal Rocks in the Egyptian Nubian Shield: An Overview and Synthesis. In The Geology of the Egyptian Nubian Shield; Regional Geology, Reviews; Hamimi, Z., Arai, S., Fowler, A.R., El-Bialy, M.Z., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Wahed, M.A. Thrusting and transpressional shearing in the Pan-African nappe southwest El-Sibai core complex, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2008, 50, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Wahed, M.A.; Harraz, H.Z.; El-Behairy, M.H. Transpressional imbricate thrust zones controlling gold mineralization in the Central Eastern Desert of Egypt. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 78, 424–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Wahed, M.A.; Kamh, S.Z.; Ashmway, M.; Shebl, A. Transpressive Structures in the Ghadir Shear Belt, Eastern Desert, Egypt: Evidence for Partitioning of Oblique Convergence in the Arabian Nubian Shield during Gondwana Agglutination. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamimi, Z.; Abd El-Wahed, M.A. Suture(s) and Major Shear Zones in the Neoproterozoic Basement of Egypt. In The Geology of Egypt; Regional Geology Reviews; Hamimi, Z., El-Barkooky, A., Martínez Frías, J., Fritz, H., Abd El-Rahman, Y., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 153–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Wahed, M.A.; Kamh, S.Z. Pan-African dextral transpressive duplex and flower structure in the Central Eastern Desert of Egypt. Gondwana Res. 2010, 18, 315–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, H.; Wallbrecher, E.; Khudeir, A.A.; Abu El Ela, F.; Dallmeyer, D.R. Formation of Neoproterozoic core complexes during oblique convergence (Eastern Desert, Egypt). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 1996, 23, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiling, R.O.; Abdeen, M.M.; Dardir, A.A.; El Akhal, H.; El Ramly, M.F.; Kamal El Din, G.M.; Osman, A.F.; Rashwan, A.A.; Rice, A.H.; Sadek, M.F. A structural synthesis of the Proteorozoic Arabian-Nubian Shield in Egypt. Geol. Rundsch. 1994, 83, 484–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asran, A.M.H.; Kamal El-Din, G.M.; Akawy, A. Petrochemistry and tectonic significance of gneiss amphibolite-migmatite association of Khuda metamorphic core complex, Southeastern Desert, Egypt. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference of the Arab World, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 21–24 February 2000; pp. 15–34. [Google Scholar]
- El Amawy, M.A.; Wetait, M.A.; El Alfy, Z.S.; Shweel, A.S. Geology, geochemistry and structural evolution of Wadi Beida area, south Eastern Desert, Egypt. Egypt J. Geol. 2000, 44, 65–84. [Google Scholar]
- Abdeen, M.M.; Sadek, M.F.; Greiling, R.O. Thrusting and multiple folding in the Neoproterozoic Pan-African basement of Wadi Hodein area, south Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2008, 52, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoheir, B. Transpressional zones in ophiolitic mélange terranes: Potential exploration targets for gold in the South Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 111, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoheir, B.A. Lode-gold mineralization in convergent wrench structures: Examples from South Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 114, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nano, L.; Kontny, A.; Sadek, M.F.; Greiling, R.O. Structural evolution of metavolcanics in the surrounding of the gold mineralization at El Beida, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. Ann. Geol. Surv. Egypt 2002, 25, 1122. [Google Scholar]
- Zoheir, B.A.; Qaoud, N.N. Hydrothermal alteration geochemistry of the Betam gold deposit, south Eastern Desert, Egypt: Mass-volume-mineralogical changes and stable isotope systematics. Appl. Earth Sci. 2008, 117, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlan, H.A.; Mokhles, K.; Azer, M.K.; Khalil, A.E.S. The Neoproterozoic Abu Dahr ophiolite, South Eastern Desert, Egypt: Petrological characteristics and tectonomagmatic evolution. Min. Pet. 2015, 109, 611–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, M.Z.; Arai, S. Chemical variations of mineral inclusions in Neoproterozoic high-Cr chromitites from Egypt: Evidence of fluids during chromitite genesis. Lithos 2016, 240–243, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H. Highly depleted harzburgite-dunite-chromitite complexes from the Neoproterozoic ophiolite, south Eastern Desert, Egypt: A possible recycled upper mantle lithosphere. Precambrian Res. 2013, 233, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, M.F.; Lebda, E.M.; Nasr, B.B.; Khedr, M.Z. Geology and Tectonic Evolution of the Area around Wadi Arais, Southern Eastern Desert, Egypt. In Proceedings of the Six International Conference on Geology of the Arab World, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 11–14 February 2002; Volume 1, pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Raslan, M.F.; Ali, M.A.; El-Feky, M.G. Mineralogy and radioactivity of pegmatites from South Wadi Khuda area, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Chin. J. Geochem. 2010, 29, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asran, A.M.; Hassan, S. Remote sensing-based geological mapping and petrogenesis of Wadi Khuda Precambrian rocks, South Eastern Desert of Egypt with emphasis on leucogranite. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baraga, M.H. Geological and Mineralogical and Geochemical Studies on the Precambrian Rocks around Wadi Rahaba, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Geology Department, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt, 1993; 247p. [Google Scholar]
- Sabins, F.F. Remote Sensing Principles and Interpretation; W. H. Freeman Company: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 366–371. [Google Scholar]
- Segal, D.B. Use of Landsat Multispectral Scanner Data for Definition of Limonitic Exposures in Heavily Vegetated Areas. Econ. Geol. 1983, 78, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbaz, O.; Gürsoy, Ö.; Gökce, A. Detecting Clay Minerals in Hydrothermal Alteration Areas with Integration of ASTER Image and Spectral Data in Kösedag-Zara (Sivas), Turkey. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 91, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Harrison, A. Standardized principal components. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1985, 6, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.P.; Tiwari, R.K.; Saini, V.; Srivastava, N.A. Simplified approach for interpreting principal component images. Adv. Remote Sens. 2013, 2, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loughlin, W.P. Principal components analysis for alteration mapping. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1991, 57, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Crosta, A.P.; Souza Filho, C.R.; Azevedo, F.; Brodie, C. Targeting key alteration 648 minerals in epithermal deposits in Patagonia, Argentina, using ASTER imagery and principal component analysis. Inter. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4233–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, Y.; Fu, B.; Cudhy, T.J. Detecting lithology with Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Refection Radiometer (ASTER) multispectral thermal infrared “radiance-at-sensor” data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 99, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, S.; Kusky, T.M. ASTER spectral ratioing for lithological mapping in the Arabian-Nubian Shield, the Neoproterozoic Wadi Kid area, Sinai, Egypt. Gondwana Res. 2007, 11, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, S.; Kusky, T.M. Lithological mapping in the Eastern Desert of Egypt, the Barramiya area, using Landsat thematic mapper (TM). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2006, 44, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.M.; Sadek, M.F.; Greiling, R.O. Spectral analyses of basement rocks in El-Sibai-Umm Shaddad area, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt using ASTER thermal infrared data. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 8, 6853–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, S.S.; Hassan, S.M.; Sadek, M.F. Prospecting for new gold-bearing alteration zones at El-Hoteib area, South Eastern Desert, Egypt, using remote sensing data analysis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 71, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, M.F.; Ali-Bik, M.W.; Hassan, S.M. Late Neoproterozoic basement rocks of Kadabora-Suwayqat area, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt: Geochemical and remote sensing characterization. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 10459–10479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, Y. A Stabilized Vegetation Index and Several Mineralogic Indices Defined for ASTER VNIR and SWIR Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2003 International Geosciences and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS ’03), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1552–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Bannari, A.; El-Battay, A.; Saquaque, A.; Miri, A. PALSAR-FBS L-HH Mode and Landsat-TM Data Fusion for Geological Mapping. Adv. Remote Sens. 2016, 5, 246–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mars, J.C.; Rowan, L.C. Mapping Phyllic and Argillic-Altered Rocks in Southeastern Afghanistan Using Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) Data. USGS Open-File Rep. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Yang, J.; Li, D. Adaptive-window polarimetric SAR image speckle filtering based on a homogeneity measurement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5435–5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnous, M.; El-Rayes, A.; Geriesh, M.; Ghodeif, K.; Al-Oshari, F. Groundwater potentiality mapping of tertiary volcanic aquifer in IBB basin, Yemen by using remote sensing and GIS tools. J. Coast. Conserv. 2020, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzied, S.; Kaiser, M.; Shendi, E.; Abdel-Fattah, M. Multi-criteria decision support for geothermal resources exploration based on remote sensing, GIS and geophysical techniques along the Gulf of Suez coastal area, Egypt. Geothermics 2020, 88, 101893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzied, S.M.; Alrefaee, H.A. Spatial prediction of landslide-susceptible zones in El-Qaá area, Egypt, using an integrated approach based on GIS statistical analysis. Bull. Int. Assoc. Eng. Geol. 2018, 78, 2169–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, S.A.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Pourtaghi, Z.S.; Rezaei, A. Groundwater qanat potential mapping using frequency ratio and Shannon’s entropy models in the Moghan watershed, Iran. Earth Sci Inf. 2015, 8, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirubakaran, M.; Johnny, J.C.; Ashokraj, C.; Arivazhagan, S. A geostatistical approach for delineating the potential groundwater recharge zones in the hard rock terrain of Tirunelveli taluk, Tamil Nadu, India. Arab J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnous, M.O. Groundwater potentiality papping of hard-rock terrain in arid regions using geospatial modelling: Example fromWadi Feiran basin, South Sinai, Egypt. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 1375–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Gupta, A.; Ghosh, S. Exploring groundwater potential zones using MIF technique in semi-arid region: A case study of Hingoli district, Maharashtra. Spat. Inf. Res. 2018, 25, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, O.A.E.; Laftouhi, N. Combination of a geographic system and remote sensing data to map groundwater recharge potential in arid and semi-arid areas: The Haouz plain, Morocco. Earth Sci. Inf. 2016, 9, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamimi, Z.; Abd El-Wahed, M.; Gahlan, H.A.; Kamh, S.Z. Tectonics of the Eastern Desert of Egypt: Key to understanding the Neoproterozoic evolution of the Arabian-Nubian Shield (East African Orogen). In Geology of the Arab World—An Overview; Bendaoud, A., Hamimi, Z., Hamoudi, M., Djemai, S., Zoheir, B., Eds.; Springer Geology: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Karim, A.M.; El-Mahallawi, M.M.; Finger, F. The ophiolite mélange of Wadi Dunqash and Arayis, Eastern Desert of Egypt: Petrogenesis and tectonic evolution. Acta Miner. Petrogr. Szeged 1996, 36, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadan, T.M.; Kontny, A. Mineralogical and structural characterization of alteration zones detected by orbital remote sensing at Shalatein District, SE Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2004, 40, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Abdelsalam, M.G. Tracing along-strike structural continuity in the Neoproterozoic Allaqi-Heiani Suture, southern Egypt using principal component analysis (PCA), fast Fourier transform (FFT), and redundant wavelet transform (RWT) of ASTER data. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2006, 44, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, M.A.; Hussein, A.M.; Abdallah, M.A. Shear zone-hosted goldmineralization in the Late Proterozoic rocks of El Beida area, south Eastern Desert, Egypt. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. (Sect. B Appl. Earth Sci.) 2001, 110, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, T.M. Geological and Geochemical Studies on some Basement Rocks at Wadi Hodein Area, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Geology Department, Faculty of Science, Cairo, Egypt, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Obeid, M.A. The Pan-African arc-related volcanism of the Wadi Hodein area, south Eastern Desert, Egypt: Petrological and geochemical constraints. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2006, 44, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamimi, Z.; Sakran, S. Boudinage structures in Um Teneidbah area, southern Eastern Desert, Egypt: Dynamic and paleostrain analysis. Egypt J. Geol. 2001, 45, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, O.A.; El-Manakhly, M.M. Gold deposits in the southern Eastern Desert, Egypt. In A Commodity Package; Egyptian Geological Survey and Mining Authority: Cairo, Egypt, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, R.; Klemm, D. Gold and Gold Mining in Ancient Egypt and Nubia, Geoarchaeology of the Ancient Gold Mining Sites in the Egyptian and Sudanese Eastern Deserts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; 663p. [Google Scholar]
- Gabra, S.Z. Gold in Egypt: A Commodity Package; Geological Survey of Egypt: Cairo, Egypt, 1986; 86p.
- Takla, M.A.; El Dougdoug, A.A.; Gad, M.A.; Rasmay, A.H.; El Tabbal, H.K. Gold-bearing quartz veins in mafic and ultramafic rocks, Hutite and Um Tenedba, south Eastern Desert, Egypt. Ann. Geol. Surv. Egypt 1995, 20, 411–432. [Google Scholar]
- Ashmawy, M.H. The Ophiolitic Me’lange of the South Eastern Desert of Egypt: Remote Sensing Fieldwork and Petrographic Investigations. Ph.D. Thesis, Berliner Geowiss. Abh., Berlin, Germany, 1987; 135p. [Google Scholar]
- Kokaly, R.F.; Clark, R.N.; Swayze, G.A.; Livo, K.E.; Hoefen, T.M.; Pearson, N.C.; Klein, A.J. USGS Spectral Library Version 7 (No. 1035); US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Tavarnellia, E.; Holdsworthb, R.E.; Cleggb, P.; Jonesc, R.R.; McCaffrey, K.J.W. The anatomy and evolution of a transpressional imbricate zone, Southern Uplands, Scotland. J. Struct. Geol. 2004, 26, 1341–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, G.; Giese, J.; Berger, A.; Gnos, E. A new perspective on the significance of the Ranotsara shear zone in Madagascar. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 99, 1827–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, E.; Pedrosa-Soares, A.C.; Alkmim, F.F.; Dussin, I.A. A suture–related accretionary wedge formed in the Neoproterozoic Araçuaí orogen (SE Brazil) during Western Gondwanaland assembly. Gondwana Res. 2015, 27, 878–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]















| Landsat-8 (OLI/TIRS) | Wavelength (µm) | ASTER | Wavelength (µm) | Band | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Band | Resolution (m) | Resolution (m) | |||
| Band 1 | 30 Costal/Aerosol | 0.435–0.451 | 15 | 0.52–0.6 | Band1 |
| Band 2 | 30 Blue | 0.452–0.512 | 15 | 0.63–0.69 | Band 2 |
| Band 3 | 30 Green | 0.533–0.590 | 15 | 0.76–0.86 | Band 3 |
| Band 4 | 30 Red | 0.636–0.673 | 30 | 1.60–1.70 | Band 4 |
| Band 5 | 30 NIR | 0.851–0.879 | 30 | 2.145–2.185 | Band 5 |
| Band 6 | 30 SWIR-1 | 1.566–1.651 | 30 | 2.185–2.225 | Band 6 |
| Band 7 | 30 SWIR-2 | 2.107–2.294 | 30 | 2.235–2.285 | Band 7 |
| Band 8 | 15 Pan | 0.503–0.676 | 30 | 2.295–2.365 | Band 8 |
| Band 9 | 30 Circus | 1.363–1.384 | 30 | 2.360–2.430 | Band 9 |
| band10 | 100 TIR-1 | 10.60–11.19 | 90 | 8.125–8.475 | Band 10 |
| band11 | 100 TIR-2 | 11.50–12.51 | 90 | 8.475–8.825 | Band 11 |
| - | - | - | 90 | 8.925–8.275 | Band 12 |
| - | - | - | 90 | 10.25–10.95 | Band 13 |
| - | - | - | 90 | 10.95–11.65 | Band 14 |
| Fine Resolution | ScanSAR | Polarimetric | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beam Mode | FBS, DSN | FBD | WB1, WB2 | PLR |
| Center Frequency | L-Band (1.27 GHz) | |||
| Polarization | HH or VV | HH + HV or VV + VH | HH or VV | HH + HV + VV + VH |
| Spatial Resolution | 10 m | 20 m | 100 m | 30 m |
| Swath Width | 70 km | 70 km | 250–350 km | 30 km |
| Off-Nadir Angle | 34.3° (default) | 27.1° (default) | 21.5° (default) | |
| Thematic Layer | Class Ranges | Layer Weight | Influence (%) | Class Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithology map | Gn/Pgb/NSS/WD | 0.38 | 38 | 1 |
| Sg/Pg | 2 | |||
| Gt | 3 | |||
| Ms/Mv | 4 | |||
| S/Omg | 5 | |||
| Alteration Zone image (threshold) | Clay minerals | 0.19 | 19 | 5 |
| OH-bearing rocks | 4 | |||
| Calcite-bearing rocks | 3 | |||
| Quartz-bearings rocks | 2 | |||
| Sedimentary rocks | 1 | |||
| Proximity to gold mines (km) | <10 | 0.12 | 12 | 3 |
| 10–20 | 2 | |||
| >20 | 1 | |||
| Proximity to favorable contacts (km) | <2 | 0.10 | 10 | 3 |
| 2–10 | 2 | |||
| >10 | 1 | |||
| Proximity to major faults (km) | <1 | 0.08 | 8 | 3 |
| 1–3 | 2 | |||
| >3 | 1 | |||
| Major faults density (km/km2) | 0–0.28 | 0.07 | 7 | 1 |
| 0.29–0.56 | 2 | |||
| 0.57–0.84 | 3 | |||
| 0.85–1.12 | 4 | |||
| 1.13–1.4 | 5 | |||
| Lineaments density (km/km2) | 0–0.55 | 0.06 | 6 | 1 |
| 0.56–1.11 | 2 | |||
| 1.12–1.66 | 3 | |||
| 1.67–2.21 | 4 | |||
| 2.22–2.76 | 5 |
| (A) Landsat-8 Alteration Map | Field Data | |||||
| Classes | Iron Oxide/Hydroxides | OH-Bearing and Carbonate Minerals | Totals User’s Accuracy | |||
| Iron oxide/hydroxides | 52 | 8 | 60–87% | |||
| OH-bearing and carbonate minerals | 6 | 54 | 60–90% | |||
| Totals | 58 | 62 | 120 | |||
| Producer’s accuracy | 89.65% | 87.10% | - | |||
| Overall accuracy = 88.33% | Kappa Coefficient = 0.77 | |||||
| (B)ASTER Alteration Map | Field Data | |||||
| Iron Oxide/Hydroxides | OHI | KLI | CLI | Totals | User’s Accuracy | |
| Iron oxide/hydroxides | 22 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 30 | 73% |
| OHI | 3 | 20 | 6 | 1 | 30 | 67% |
| KLI | 1 | 4 | 24 | 1 | 30 | 80% |
| CLI | 1 | 4 | 2 | 23 | 30 | 77% |
| Totals | 27 | 34 | 33 | 26 | 120 | - |
| Producer’s accuracy | 81% | 59% | 73% | 88% | - | - |
| Overall accuracy = 74.10% | Kappa Coefficient = 0.65 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abd El-Wahed, M.; Zoheir, B.; Pour, A.B.; Kamh, S. Shear-Related Gold Ores in the Wadi Hodein Shear Belt, South Eastern Desert of Egypt: Analysis of Remote Sensing, Field and Structural Data. Minerals 2021, 11, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050474
Abd El-Wahed M, Zoheir B, Pour AB, Kamh S. Shear-Related Gold Ores in the Wadi Hodein Shear Belt, South Eastern Desert of Egypt: Analysis of Remote Sensing, Field and Structural Data. Minerals. 2021; 11(5):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050474
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbd El-Wahed, Mohamed, Basem Zoheir, Amin Beiranvand Pour, and Samir Kamh. 2021. "Shear-Related Gold Ores in the Wadi Hodein Shear Belt, South Eastern Desert of Egypt: Analysis of Remote Sensing, Field and Structural Data" Minerals 11, no. 5: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050474
APA StyleAbd El-Wahed, M., Zoheir, B., Pour, A. B., & Kamh, S. (2021). Shear-Related Gold Ores in the Wadi Hodein Shear Belt, South Eastern Desert of Egypt: Analysis of Remote Sensing, Field and Structural Data. Minerals, 11(5), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11050474









