Chronic Lead Exposure Alters Mineral Properties in Alveolar Bone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Micro-CT Analyses
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
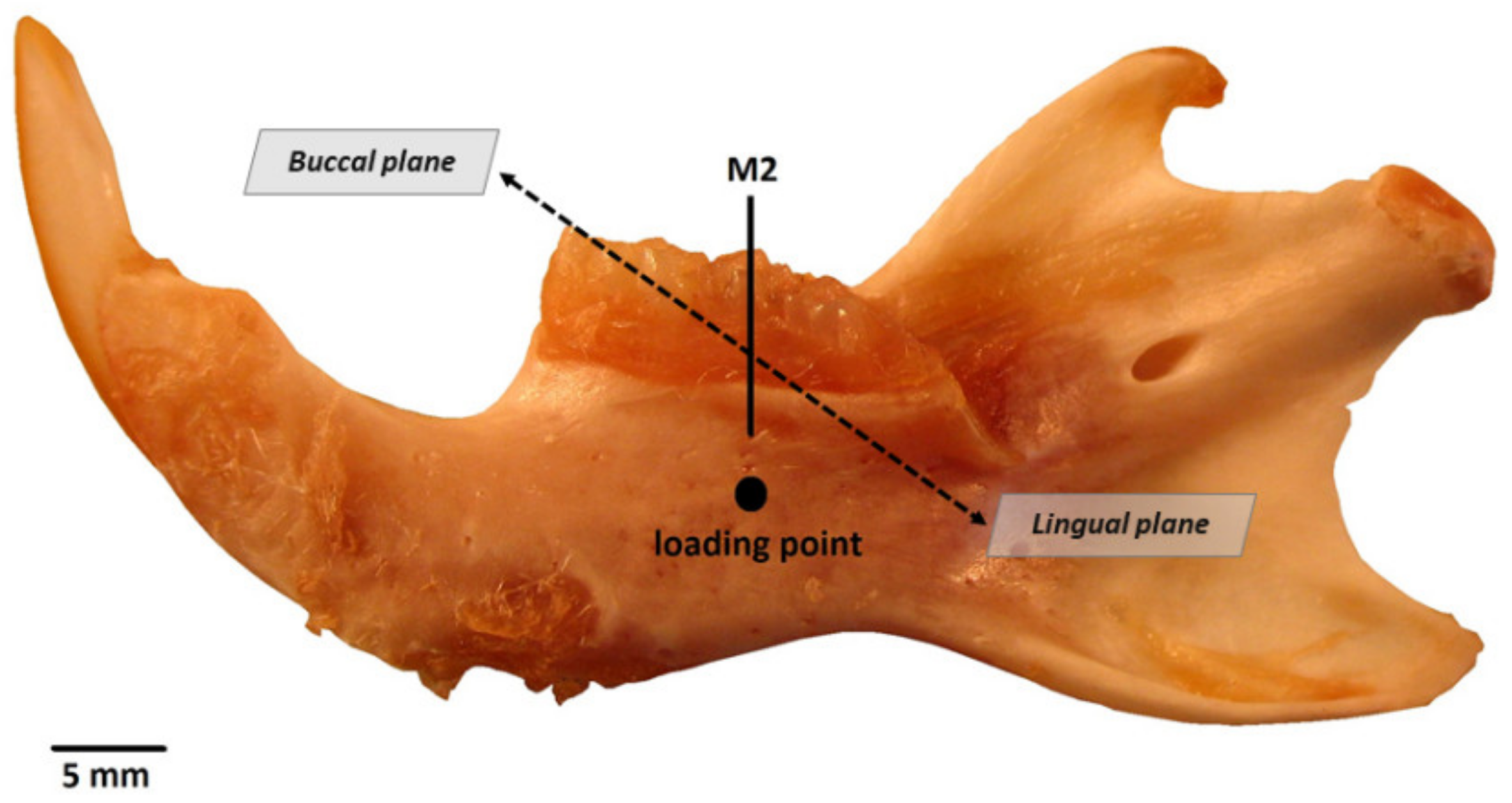
2.4. Three-Point Bending Test
2.5. Elemental Analyses
2.6. Attenuated Total Reflectance Infrared Spectrometry Analyses
2.7. X-ray Diffraction Analyses
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Micro-Architectural Characteristics
3.2. Mechanical Properties (Three-Point Bending Test)
3.3. Bone Mineral Composition
3.4. Crystalline Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, T.-M.G.; Liu, S.S.Y.; Babler, W.J. Craniofacial biology, orthodontics, and implants. In Basic and Applied Bone Biology; Burr, D.B., Allen, M.R., Eds.; Elsevier-Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almela, T.; Brook, I.M.; Moharamzadeh, K. Bone tissue engineering in maxillofacial region. In Biomaterials for Oral and Dental Tissue Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, E.F.; Vesterby, A.; Kassem, M.; Melsen, F.; Mosekilde, L. Bone remodeling and bone structure. In Physiology and Pharmacology of Bone; Mundy, G.R., Martin, T.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1993; pp. 67–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeGeros, R.Z. Calcium phosphates in oral biology and medicine. Monogr. Oral Sci. 1991, 15, 1–201. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Lloret, P.; Lee, C.M.; Conti, M.I.; Terrizzi, A.R.; González-López, S.; Martínez, M.P. Effects of chronic lead exposure on bone mineral properties in femurs of growing rats. Toxicology 2017, 37, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, M.; Akesson, A.; Bjellerup, P.; Vahter, M. Metal-bone interactions. Toxicol. Lett. 2000, 112–113, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, K.; Gerhardsson, L.; Börjesson, J.; Lindh, E.; Lundström, N.; Schütz, A.; Skerfving, S.; Edling, C. Lead intoxication caused by skeletal disease. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 1995, 21, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronis, M.J.J.; Aronson, J.; Gao, G.G.; Hogue, W.; Skinner, R.A.; Badger, T.M.; Lumpkin, C.K., Jr. Skeletal effects of developmental lead exposure in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 62, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gangoso, L.; Álvarez-Lloret, P.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A.B.; Mateo, R.; Hiraldo, F.; Donázar, J.A. Long-term effects of lead poisoning on bone mineralization in vultures exposed to ammunition sources. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monir, A.U.; Gundberg, C.M.; Yagerman, S.E.; van der Meulen, M.C.; Budell, W.C.; Boskey, A.L.; Dowd, T.L. The effect of lead on bone mineral properties from female adult C57/BL6 mice. Bone 2010, 47, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Estival, J.; Álvarez-Lloret, P.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A.B.; Mateo, R. Chronic effects of lead (Pb) on bone properties in red deer and wild boar: Relationship with vitamins A and D3. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 174, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskey, A.L.; Mendelsohn, R. Infrared spectroscopic characterization of mineralized tissues. Vib. Spectrosc. 2005, 38, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rey, C.; Combes, C.; Drouet, C.; Glimcher, M.J. Bone mineral: Update on chemical composition and structure. Osteoporosis Int. 2009, 20, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Rodriguez, E.; Benavides-Reyes, C.; Torres, C.; Dominguez-Gasca, N.; Garcia-Ruiz, A.I.; Gonzalez-Lopez, S.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A.B. Changes with age (from 0 to 37 D) in tibiae bone mineralization, chemical composition and structural organization in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5215–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, F.A.; Ruscsák, K.; Palmquist, A. 50 years of scanning electron microscopy of bone—A comprehensive overview of the important discoveries made and insights gained into bone material properties in health, disease, and taphonomy. Bone Res. 2019, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dempster, D.W.; Compston, J.E.; Drezner, M.K.; Glorieux, F.H.; Kanis, J.A.; Malluche, H.; Meunier, P.J.; Ott, S.M.; Recker, R.R.; Parfitt, A.M. Standardized nomenclature, symbols, and units for bone histomorphometry: A 2012 update of the report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamilton, J.D.; O’Flaherty, E.J. Effects of lead exposure on skeletal development in rats. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1994, 22, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouxsein, M.L.; Boyd, S.K.; Christiansen, B.A.; Guldberg, R.E.; Jepsen, K.J.; Müller, R. Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 1468–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou-Yang, H.; Paschalis, E.P.; Mayo, W.E.; Boskey, A.L.; Mendelsohn, R. Infrared microscopic imaging of bone: Spatial distribution of CO3(2−). J. Bone Miner. Res. 2001, 16, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, C.; Collins, B.; Goehl, T.; Dickson, I.R.; Glimcher, M.J. The carbonate environment in bone mineral: A resolution-enhanced fourier transform infrared spectroscopy study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1989, 45, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.S.; Vairavamurthy, V.; Chance, M.R.; Mendelsohn, R.; Paschalis, E.P.; Betts, F.; Boskey, A.L. In situ analysis of mineral content and crystallinity in bone using infrared micro-spectroscopy of the v4 PO4-3 vibration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1527, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, W.N.; Jenkins, T. Profile fitting for quantitative. Analysis in X-ray powder diffraction. Adv. X-ray Anal. 1983, 26, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Klug, H.P.; Alexander, L.E. X-ray Diffraction Procedures; John Willey: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Olchowik, G.; Widomska, J.; Tomaszewski, M.; Gospodarek, M.; Tomaszewska, M.; Jagiełło-Wójtowicz, E. The influence of lead on the biomechanical properties of bone tissue in rats. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2014, 21, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pounds, J.G. Effect of lead intoxication on calcium homeostasis and calcium-mediated cell function: A review. Neurotoxicology 1984, 5, 295–331. [Google Scholar]
- Huja, S.S.; Fernandez, S.A.; Hill, K.J.; Li, Y. Remodeling dynamics in the alveolar process in skeletally mature dogs. Anat. Rec. A. Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 2006, 288, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donnelly, E.; Boskey, A.L.; Baker, S.P.; van der Meulen, M.C. Effects of tissue age on bone tissue material composition and nanomechanical properties in the rat cortex. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 92, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brès, E.F.; Voegel, J.C.; Barry, J.C.; Waddington, W.G.; Frank, R.M. Feasibility study for the detection of lead substitution sites in the hydroxyapatite crystal structure using high-resolution electron microscopy (HREM) at optimum focus. J. Appl. Cryst. 1986, 19, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, D. Apatite, Its Crystal Chemistry, Mineralogy and Utilisation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciotti, I. Cationic and Anionic Substitutions in Hydroxyapatite. In Handbook of Bioceramics and Biocomposites; Antoniac, I., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 145–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Fenton, R.R.; Hunter, B.A.; Kennedy, B.J. Powder diffraction studies of synthetic calcium and lead apatites. Aust. J. Chem. 2000, 53, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappard, D.; Baslé, M.-F.; Legrand, E.; Audran, M. Trabecular bone microarchitecture: A review. La microarchitecture de l’os trabéculaire: Une revue. Morphologie 2008, 92, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Long-Term Exposure to Low-Dose Lead Induced Deterioration in Bone Microstructure of Male Mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 195, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Matsumoto, H.; Fujii, A. Mandible bone loss in osteoporosis rats. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2003, 21, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, Y.; Ito, K.; Murai, S. Effects of experimental osteoporosis on alveolar bone loss in rats. J. Oral Sci. 1998, 40, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Matsumoto, H.; Hori, M.; Gunji, A.; Hakozaki, K.; Akimoto, Y.; Fujii, A. Correlation among geometric, densitometric, and mechanical properties in mandible and femur of osteoporotic rats. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2008, 26, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.B.; Reinhardt, R.A.; Nummikoski, P.V.; Patil, K.D. Longitudinal alveolar bone loss in postmenopausal osteoporotic/osteopenic women. Osteoporos Int. 1999, 10, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R.M.; Peacock, M.; Marshall, D.H.; Horsman, A.; Aaron, J.E. Spinal osteoporosis in men. Bone Miner. 1989, 5, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaron, J.E.; Johnson, D.R.; Paxton, S.; Kanis, J.A. Secondary osteoporosis and the microanatomy of trabecular bone. Clin. Rheumatol. 1989, 8, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, J.A.A.; Costa, I.M.; Maia e Silva, A.; Marques, J.M.S.; Zagalo, C.M.; Cavaleiro, I.I.B.; Fernandes, T.A.P.; Goncalves, L.L. Changes in bone Pb accumulation: Cause and effect of altered bone turnover. Bone 2014, 64, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferretti, J.L. Biomechanical Properties of Bone. In Bone Densitometry and Osteoporosis; Genant, H.K., Guglielmi, G., Jergas, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, M.I.; Bozzini, C.; Facorro, G.B.; Lee, C.M.; Mandalunis, P.M.; Piehl, L.L.; Piñeiro, A.E.; Terrizzi, A.R.; Martínez, M.P. Lead bone toxicity in growing rats exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.I.; Terrizzi, A.R.; Lee, C.M.; Mandalunis, P.M.; Bozzini, C.; Piñeiro, A.E.; Martínez, M.P. Effects of lead exposure on growth and bone biology in growing rats exposed to simulated high altitude. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterhoff, G.; Morgan, E.F.; Shefelbine, S.J.; Karim, L.; McNamara, L.M.; Augat, P. Bone mechanical properties and changes with osteoporosis. Injury 2016, 47 (Suppl. 2), S11–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, E.F.; Unnikrisnan, G.U.; Hussein, A.I. Bone Mechanical Properties in Healthy and Diseased States. Ann. Rev. Biomed. 2018, 20, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pounds, J.G.; Long, G.J.; Rosen, J.F. Cellular and molecular toxicity of lead in bone. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 91, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, N.; Cauley, J.A.; Wilson, J.W.; Talbott, E.O.; Morrow, L.; Hochberg, M.C.; Hillier, T.A.; Muldoon, S.B.; Cummings, S.R. Relationship of blood lead levels to incident non spine fractures and falls in older women: The study of osteoporotic fractures. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2008, 23, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Very high blood lead levels among adults—United States, 2002–2011. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep 2013, 62, 967–971. [Google Scholar]
- Terrizzi, A.R.; Fernandez-Solari, J.; Lee, C.M.; Bozzini, C.; Mandalunis, P.M.; Elverdin, J.C.; Conti, M.I.; Martínez, M.P. Alveolar bone loss associated to periodontal disease in lead intoxicated rats under environmental hypoxia. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2013, 58, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tort, B.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, E.K.; Jung, Y.S.; Ha, M.; Song, K.B.; Lee, Y.E. Lead exposure may affect gingival health in children. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Control | Lead | p Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TV (mm3) | 24.173 | ± | 2.065 | 17.546 | ± | 2.223 | N.S. |
| BV (mm3) | 11.189 | ± | 1.279 | 6.427 | ± | 0.995 | 0.019 |
| BV/TV (%) | 46.056 | ± | 3.030 | 35.945 | ± | 2.394 | 0.028 |
| BMD (mg/cm3) | 1142.60 | ± | 7.68 | 1093.01 | ± | 12.49 | 0.014 |
| Tb.Th (mm) | 0.111 | ± | 0.005 | 0.102 | ± | 0.004 | N.S. |
| Tb.Sp (mm) | 0.247 | ± | 0.0167 | 0.227 | ± | 0.0139 | N.S. |
| Tb.N (1/mm) | 4.128 | ± | 0.206 | 3.504 | ± | 0.168 | 0.045 |
| Conn.Dn (1/mm3) | 157.07 | ± | 30.26 | 138.54 | ± | 18.85 | N.S. |
| Control | Lead | p Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bend displacement (mm) | 2.28 | ± | 0.20 | 1.30 | ± | 0.15 | 0.008 |
| Maximal bending Load (N) | 85.90 | ± | 2.25 | 87.04 | ± | 5.28 | N.S. |
| Control | Lead | p Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICP-OES analyses | |||||||
| Pb μg/g | L.O.D. | 1.33 | ± | 0.08 | |||
| Ca (% d.w.) | 24.26 | ± | 0.94 | 24.25 | ± | 0.12 | N.S. |
| P (% d.w.) | 11.06 | ± | 4.26 | 11.03 | ± | 1.47 | N.S. |
| Ca/P | 2.20 | ± | 0.04 | 2.19 | ± | 0.01 | N.S. |
| ATR-FTIR analyses | |||||||
| Degree mineralization | 3.96 | ± | 0.12 | 4.14 | ± | 0.11 | N.S. |
| Carbonate in bone mineral | 0.31 | ± | 0.008 | 0.28 | ± | 0.006 | 0.004 |
| Crystallinity index | 0.71 | ± | 0.01 | 0.76 | ± | 0.03 | N.S. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez-Lloret, P.; Benavides-Reyes, C.; Lee, C.M.; Martínez, M.P.; Conti, M.I.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A.B.; González-López, S.; Perez-Huerta, A.; Terrizzi, A.R. Chronic Lead Exposure Alters Mineral Properties in Alveolar Bone. Minerals 2021, 11, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060642
Álvarez-Lloret P, Benavides-Reyes C, Lee CM, Martínez MP, Conti MI, Rodríguez-Navarro AB, González-López S, Perez-Huerta A, Terrizzi AR. Chronic Lead Exposure Alters Mineral Properties in Alveolar Bone. Minerals. 2021; 11(6):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060642
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez-Lloret, Pedro, Cristina Benavides-Reyes, Ching Ming Lee, María Pilar Martínez, María Inés Conti, Alejandro B. Rodríguez-Navarro, Santiago González-López, Alberto Perez-Huerta, and Antonela Romina Terrizzi. 2021. "Chronic Lead Exposure Alters Mineral Properties in Alveolar Bone" Minerals 11, no. 6: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060642
APA StyleÁlvarez-Lloret, P., Benavides-Reyes, C., Lee, C. M., Martínez, M. P., Conti, M. I., Rodríguez-Navarro, A. B., González-López, S., Perez-Huerta, A., & Terrizzi, A. R. (2021). Chronic Lead Exposure Alters Mineral Properties in Alveolar Bone. Minerals, 11(6), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11060642








