Abstract
A novel adsorbent material based on microaggregates of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with succinic acid has been developed. The magnetic aggregates (MA) were characterized in terms of the size distribution (master sizer analysis), morphology (TEM), chemical structure (IR-spectroscopy and XRD), magnetic properties (VSM), and Z-Potential. The effects of various parameters such as contact time, dosage of magnetic aggregates, the amount of succinic acid on the magnetic aggregates on the adsorption capacity, as well as the efficiency of the treatment in the adsorption of two transition metals, copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn) from real wastewater, were investigated. The kinetic behavior was analyzed by using the Lagergren pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and Elovich and intra-particle diffusion models. Langmuir and Freundlich’s models were applied to simulate the adsorption equilibrium. The magnetic aggregates reached the equilibrium condition relatively fast, within 10 min. Magnetic aggregates with a higher amount of succinic acid in their formulation showed a higher adsorption capacity of the two metals in all the experiments. This is consistent with the adsorption mechanism mainly based on electrostatic interaction between the metal ions and the negative charges on the surface of magnetic aggregates. A higher adsorption capacity for the removal of copper compared to zinc was found. Additionally, the electrochemical characterization of the magnetic aggregates was done as a preliminary study for proposing a regeneration method of the MA along with the extraction metals adsorbed based on an electrochemical process.
1. Introduction
Transition metal removal from industrial wastewater is of paramount importance due to the harmful effects of heavy metals on human health and the environment. For such reasons, water treatment for the removal of heavy metals has engaged numerous applications and technologies over the last decades, although more research is required to improve such technologies. Treatment methods are classified as chemical, physical, and biological and their selection takes into consideration several features as well as their limitations [1]. The most-used methods for the removal of transition metals from industrial wastewater include adsorption, cementation, membrane filtration, electrodialysis, and photocatalysis, although the selection of the most suitable method depends on a series of parameters: cost, environmental impact, metal concentrations, and pH values [1,2].
Two of the most common transition metals used by the electrical and the electroplating industry are copper and zinc. In this regard, it is important to consider that copper, even in small amounts, is highly toxic for humans and it has the ability to accumulate in the food chain. Despite this, copper is worth recovering from wastewater because of its high price and market demand [3]. Up-to-date, various methods have been employed for recovering copper ions from wastewater, including traditional methods such as co-precipitation and electrochemical processes and more alternative technologies such as membrane filtration and ion exchange technologies [3]. Interestingly, such methods pose some significant limitations to their use due to the high cost, high energy consumption, expensive equipment, and incomplete metal removal [2]. On the other hand, zinc is frequently used in industrial processes such as in the steel, batteries, and paint production chains as well as in the plating industry, which generates wastewater with a high concentration of zinc [4,5]. Despite the fact that zinc is essential for several metabolic processes, in high concentrations, it is harmful to both human health and the environment [5,6]. In the case of zinc, absorption is one of the most effective methods for removing heavy metal ions from wastewater, although there is still need for improvement in the development of absorbent materials [5].
In recent years, great effort has been dedicated to the development of magnetic nano-particles that can efficiently capture transition metals from industrial wastewater. Several studies have demonstrated the efficiency of different types of magnetic materials in water treatment and, in particular, in the removal of toxic metal ions [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Specifically for the removal of metals, different types of MA and magnetic bead functionalized with polymers have been used [8,18,19,20,21]. However, such materials usually require a multi-step process for their production and functionalization is done after the formation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles [9,19,20]. Here, functionalized magnetic aggregates composed of magnetic nanoparticles that have been functionalized with succinic acid in a one-step process have been used in order to study the capture of copper and zinc ions from real wastewater samples. Contrary to what has been reported by Singh et al. [17], the nanoparticles in the present study form micro-sized aggregates, which, in a possible large-scale industrial application, could be handled easier with fewer health and safety and environmental concerns in respect to nano-sized particles [22,23]. Magnetic aggregates were synthesized and functionalized by co-precipitation of Fe(II) chloride and Fe(III) chloride in an alkaline solution containing succinic acid. The ferromagnetic core has superparamagnetic-like properties that can be used for the separation of the magnetic aggregates from the treated solution. Succinic acid acts both as a stabilizer and as a selective anionic coating bonded through a covalent bond and is thus selective for the metal cations used in this study. MA were characterized and tested for Cu2+ and Zn2+ removal from aqueous solutions. Important factors affecting absorption efficiency such as coating percentage and contact time as well as desorption for ion recovery were investigated. Lastly, preliminary experiments were conducted to explore the possibility to regenerate the magnetic aggregates through an electrochemical process, extracting at the same time the pollutants that can be used again as raw materials.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
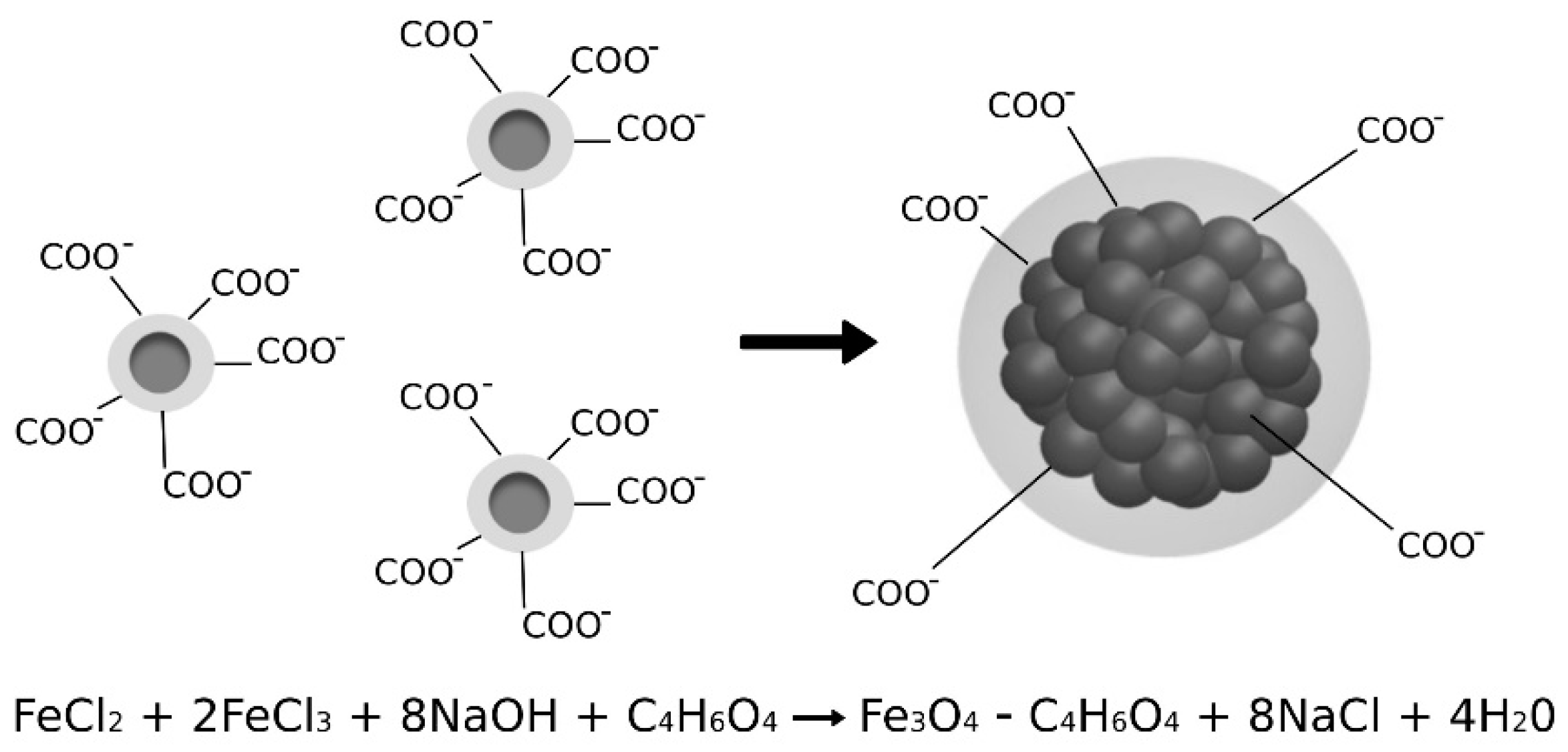
Magnetite nanoparticles and their aggregates were synthesized according to the recipe provided by Captive Systems. The magnetic aggregates were produced according to a one-step co-precipitation reaction in a basic environment following the method previously reported [24]. A solution of Fe(II) chloride (commercial grade, p.c. FER008000000, Brenntag) and Fe(III) chloride (commercial grade, p.c. FER006000000, Brenntag) in molar ratio 1:2 was prepared. According to the stoichiometry of the reaction, sodium hydroxide was dissolved in water to obtain the basic solution. Functionalized magnetic aggregates with negatively charged surfaces (Figure 1) were obtained by adding succinic acid (commercial grade, p.c. 203-740-4, Brenntag) into the basic solution. Two different percentages of succinic acid with respect to the weight of MA were used to obtain MA with 5% w/w and 10% of the coating compared to the magnetite core.
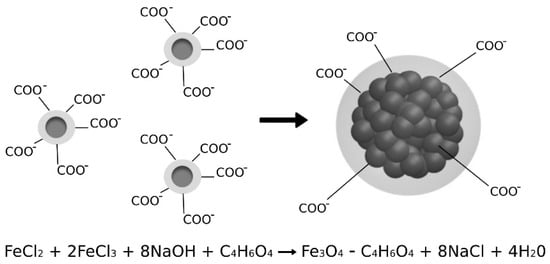
Figure 1.
Formation reaction and structure of aggregated nanoparticles coated with succinic acid.
The Fe(II-III) chloride and the sodium hydroxide solutions containing succinic acid were pumped through two syringe pumps with a flow rate of 25 mL min−1, into a mixing device that guarantees a turbulent flow. The co-precipitation reaction takes place in the mixing device, resulting in the formation of magnetic aggregates of functionalized nanoparticles. The MA were collected into a beaker and then aged for 30 min under low stirring to stabilize the aggregates. The excess sodium hydroxide and sodium chloride produced during the co-precipitation reaction was removed through a series of washing cycles with distilled water and centrifugation (Sorvall™ ST 8 Benchtop Centrifuge, Fisher Scientific, Munich, Germany) until the pH of the solution resulted neutral.
2.2. Sample Characterization
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis was performed to check the effective presence of the coating on the surface of the MA with succinic acid. The measurements were done on dried MA supported on HBr support using an FTIR spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Nicolet 380, Fisher Scientific, Munich, Germany) in a wave range of 4000–0 cm−1 with a resolution of 5 cm−1 according to the transmittance method.
A transmission scanning microscope (TEM) (PHILIPS CM200, Philips Electron Optrics) was used to determine the dimension and morphology of the produced magnetite aggregates. X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) (Philips model PW1830. Kα1Cu = 1.54058 Å, Fei Electron Optics Bv, Eindhoven, Netherlands) was used to define the microstructure of the oxide. The particle size distribution of the aggregates was measured using MasterSizer 3000 (Malvern Panalytical, Monza, Italy) while the Z-potential was obtained by using Zetasizer Nano ZS DLS (Malvern Panalytical, Monza, Italy). Magnetic properties were measured using VS) M (EZ9, MicroSense). B Brunauer, Emmett, and Telle analysis (BET) was used to determine the skeletal density and the specific surface area (NovaTouch, AntonPaar).
2.3. Adsorption Test
The synthesized MA were used to remove and recover copper ions from industrial wastewaters. The wastewaters were provided by Gaser Group, an Italian electroplating company. The first wastewater sample (sample 1) was contaminated only with copper in a concentration of 350 mg/L at pH 6.9, and the second sample (sample 2) containing both copper and zinc in a concentration of 138 mg/L and 126 mg/L, respectively, at pH 7.2. The adsorption tests were conducted in batch mode using 100 mL of wastewater and adding to the sample the solution containing the MA and stirring with a magnetic stirrer. The stirring was stopped at different time points during the test (from 1 min to 120 min) and the MA were collected on the bottom of the beaker using a neodymium magnet. The resulting solution was analyzed through Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry, ICP-MS, (Optima 8300, Perkin Elmer, Milan, Italy), to evaluate the residual amount of metal ions after the treatment. The effect of contact time on the efficiency of the MA in removing metal ions was tested. Two different amounts of MA were employed with a maximum contact time of 2 h. The efficiency (η) was calculated as in Equation (1):
where Ci and Cf represent the initial and the final concentration of the metal ions in the supernatant (mg L−1).
η = (Ci − Cf)/Ci × 100
At a fixed contact time, the mass balance reported in Equation (2) was used to determine the adsorbed amount of metal ions per gram of MA (Q, mg of metal ion g−1 of MA):
where Ci and Cf represent the initial and the final concentration of the metal ions in the supernatant (mg L−1), mMA is the amount of MA used in the test (g), and V is the volume of the sample (L). When the adsorption process reaches the equilibrium, Q indicates the maximum adsorption capacity, Qmax, and Cf, the equilibrium concentration, Ce.
Q = [(Ci − Cf)/mMA]V
2.4. Electrochemical Characterization
Electrochemical characterization of the MA was done by a cyclic voltammetry test. A standard three-electrode setup was employed, which consisted of a platinum wire counter electrode (CE), an Ag/AgCl reference electrode (RE), and a working electrode (WE), i.e., MA deposited on an inert substrate. The latter, a fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) coated glass, assured the electrical contact with the magnetite particles, deposited through drop-casting method, allowing to investigate the activity of Fe3O4 particles. A typical working electrode fabrication comprised the drop-casting of 20 μL of an aqueous solution containing 20 g/L Fe3O4 particles onto a 1 cm2 substrate area, the geometrical area in direct contact with the electrolyte solution. The ink was dried at 40 °C on a hotplate until the complete evaporation of the solvent occurred. To limit the ohmic contribution, the reference electrode was placed in the proximity of the working electrode, allowing a proper measurement of the electrochemical signal. The voltammetric investigation was carried out in a 0.1 M NaSO4 solution, at pH 5.5. Before the test, the MA were immersed in two control solutions containing zinc or copper ions, and thoroughly washed.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MA Characterization
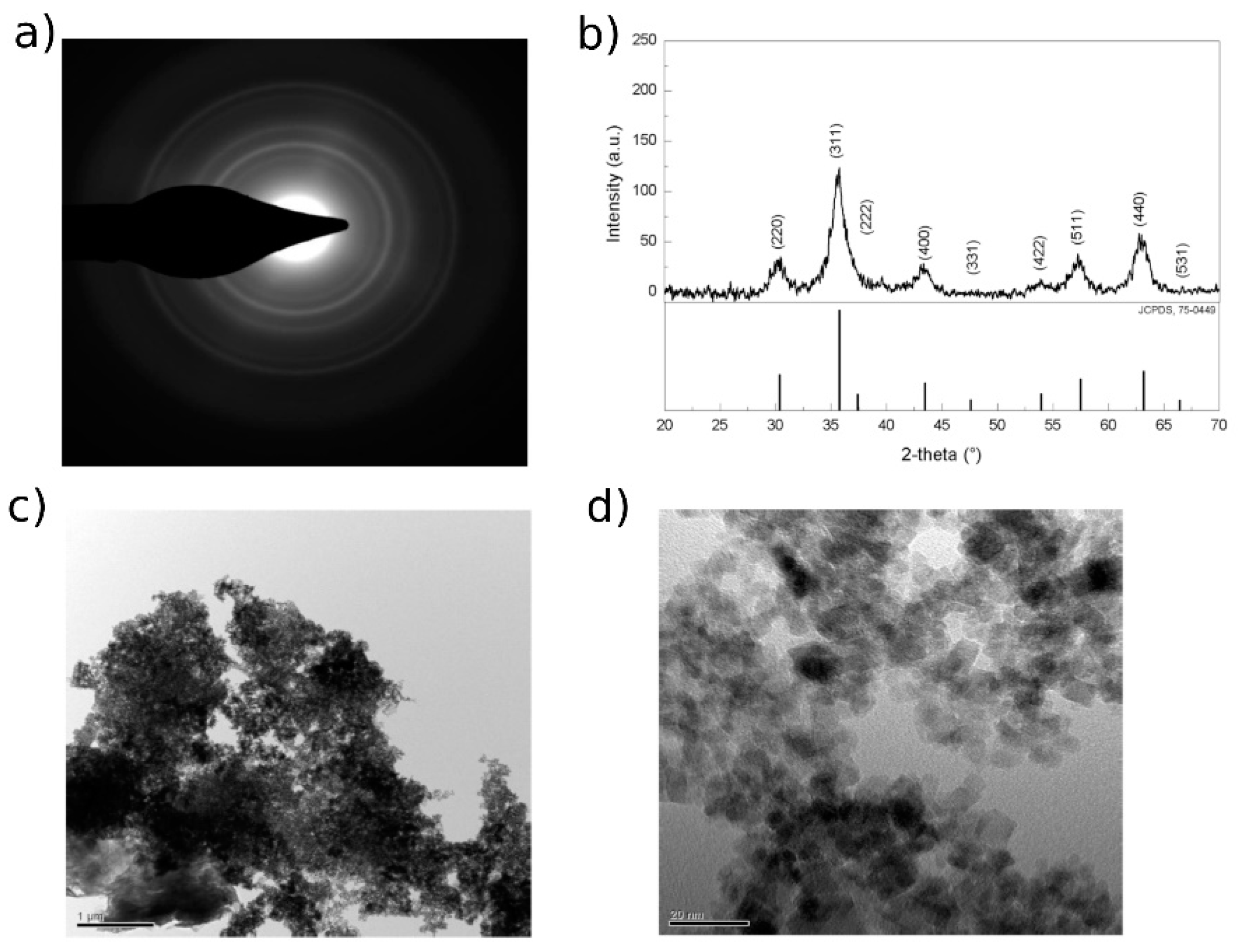
The synthesis conditions selected resulted in the formation of stable micron-sized aggregates of unitary nanoparticles with an average diameter of 10–15 nm. Figure 2c,d show TEM images of MA with 10% w/w of coating. This specific geometry allows maintaining the advantages in terms of the extremely high surface area of the nanomaterials, avoiding the problem of the separation of nano-sized compounds thanks to the micron-size of the aggregates. Comparing the diffraction pattern (Figure 2a) obtained with TEM measurements to those collected with a conventional XRD apparatus (Figure 2b), it is possible to notice that only characteristic reflection peaks corresponding to pure magnetite (Fe3O4) are present and not peaks belonging to other iron oxide forms such as maghemite (Fe2O3).
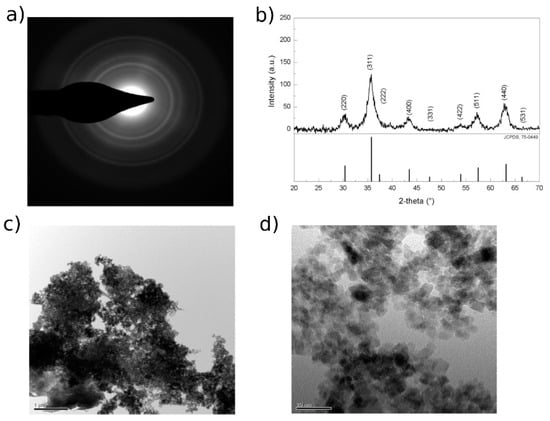
Figure 2.
MA (a) TEM diffraction pattern. (b) Diffraction pattern collected with XRD apparatus for succinic-coated magnetite nano-aggregates and XRD reference pattern of Fe3O4 from the Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS), no. 75-0449. (c,d) TEM images. Scale bars: 1 μm (c), 20 nm (d).
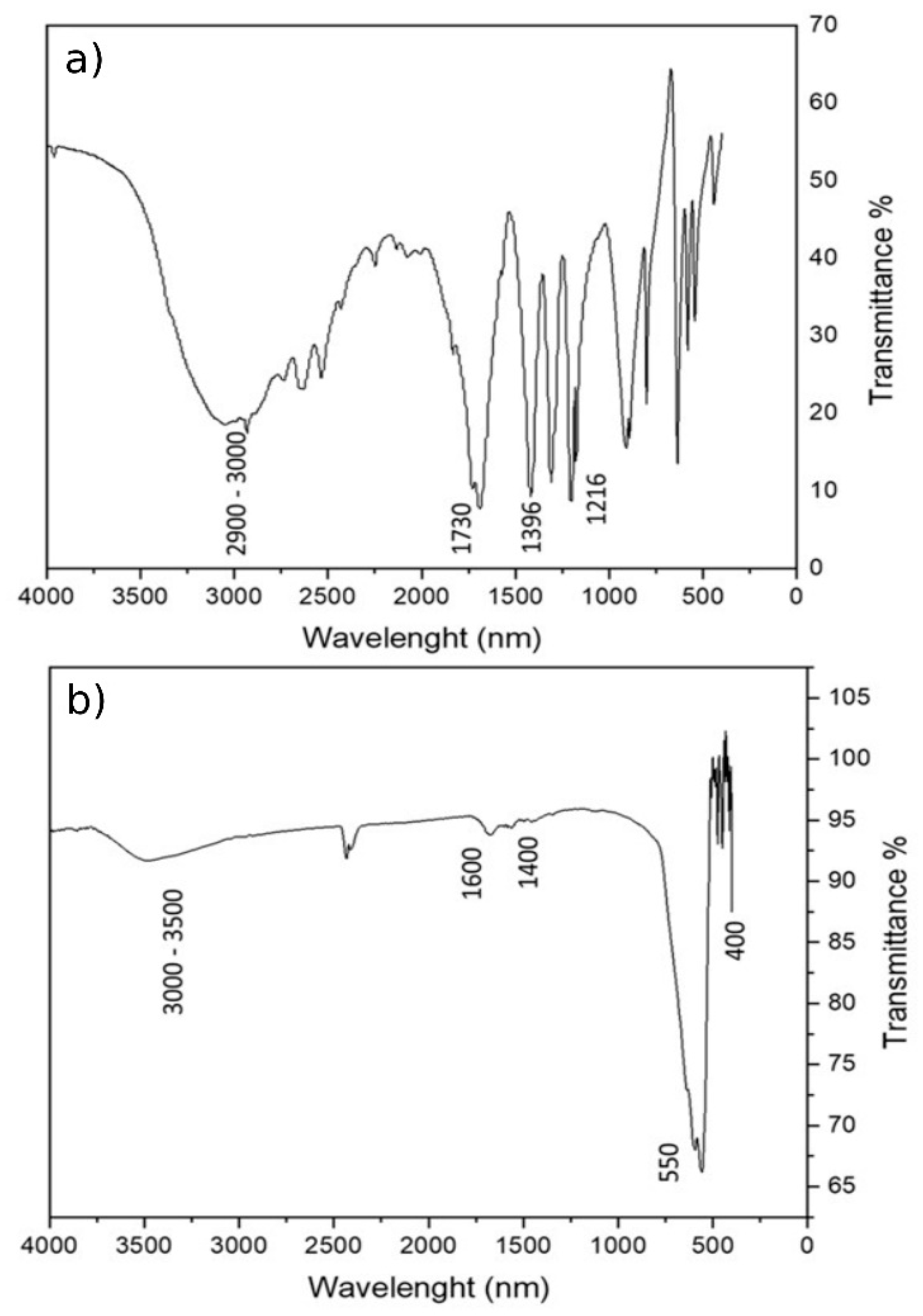
The effective formation of the organic coating on the magnetite particles was evaluated through Fourier Transformed Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The spectrum of succinic acid (Figure 3a) was taken as reference. Figure 3b shows the FTIR spectrum of the MA coating with succinic acid, where it is possible to observe the characteristic peaks of the succinic acid at about 1633 cm−1. The peak related to symmetric stretching of the carboxylate group is at 1537 cm−1 and at about 1400 cm−1 that of the C–H2 scissoring. The characteristic peaks of the O–H of carboxylic groups are present between 3000 and 3500 cm−1. The characteristic peaks of magnetite appear at 400 and 550 cm−1. The small peak at 1025 cm−1 is related to the C–O stretch. The peak representing the C=O bond of saturated carboxylic acids, which is usually located at 1700 cm−1, is no longer present, supporting the fact that the coating binds the Fe–O of the MA through carboxylate groups. The results confirmed the effective functionalization of the magnetite surface.
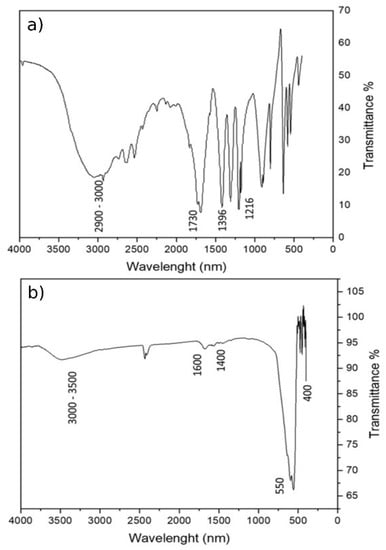
Figure 3.
FTIR analysis (a) spectrum of succinic acid, and (b) MA coated with succinic acid.
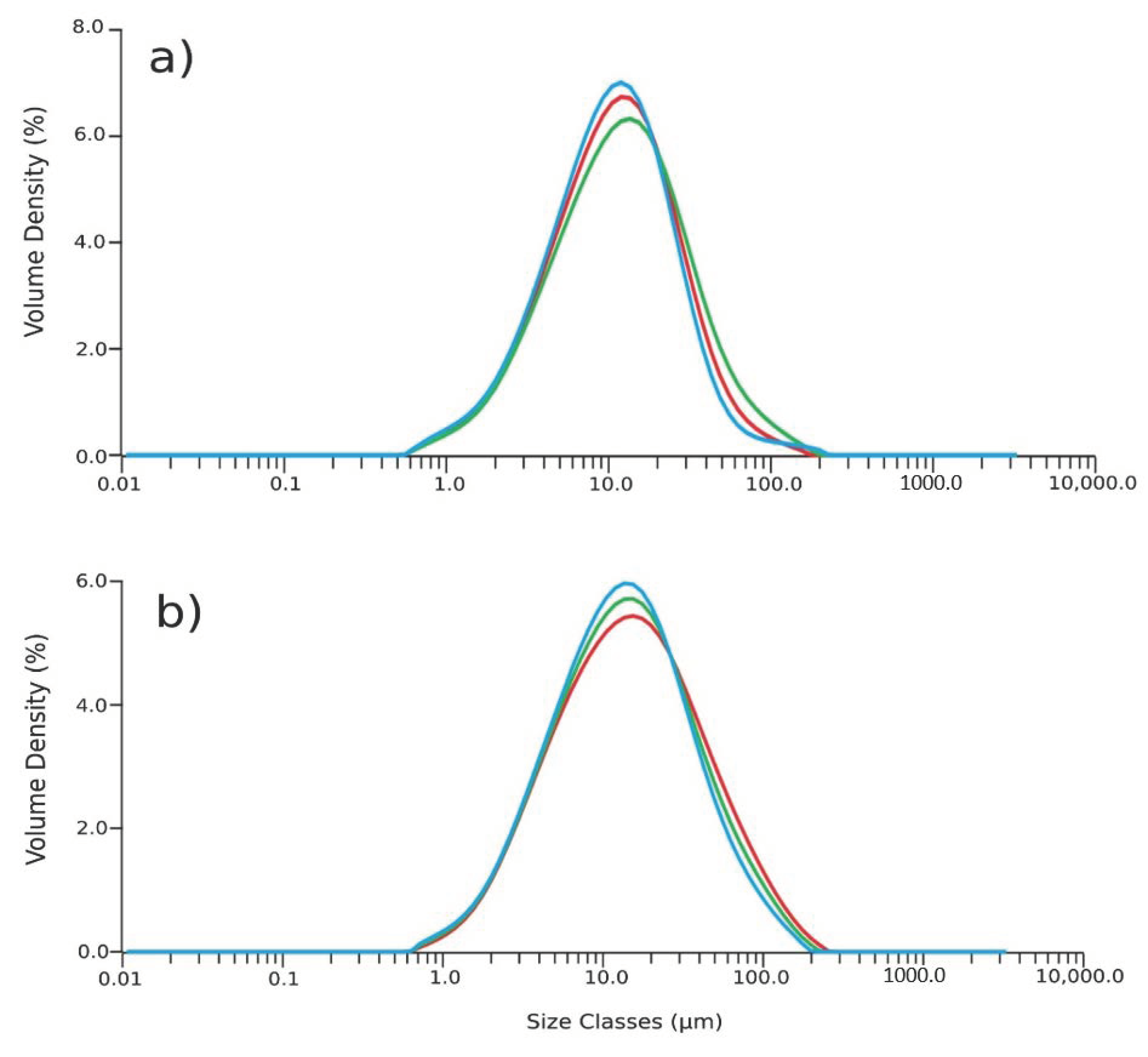
The effect of the concentration of the succinic acid on the size distribution of the coated nanoparticle aggregates was evaluated. Figure 4a,b report the results of the analysis of the aggregates obtained with two different percentages w/w of succinic acid compared to the weight of magnetite core. Using 10% w/w of succinic acid results in aggregates with an average diameter of 30 µm (Figure 4a). Decreasing the coating to a percentage of 5% w/w leads to aggregates with a dimension of 50 µm (Figure 4b) due to the effect of the succinic acid acting as a stabilizer. The coating is expected to cover the surface of the nanoparticles, preventing aggregation. Succinic acid guarantees a negative charge on the surface of nanoparticles and this negative charge acts as a repulsive force, preventing the agglomeration [25,26].
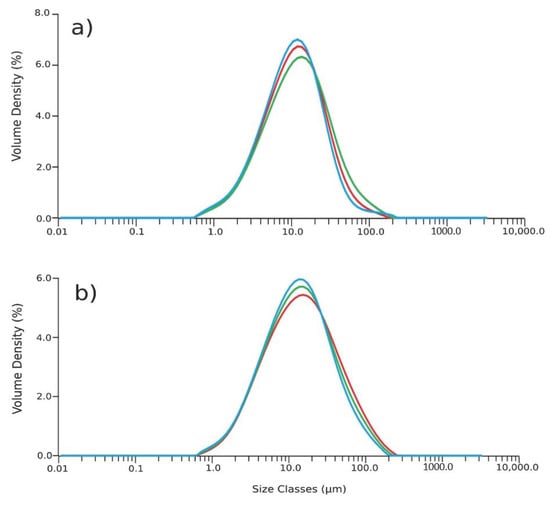
Figure 4.
Particles’ size distribution of aggregates with (a) 10% w/w of coating and (b) 5% w/w of coating.
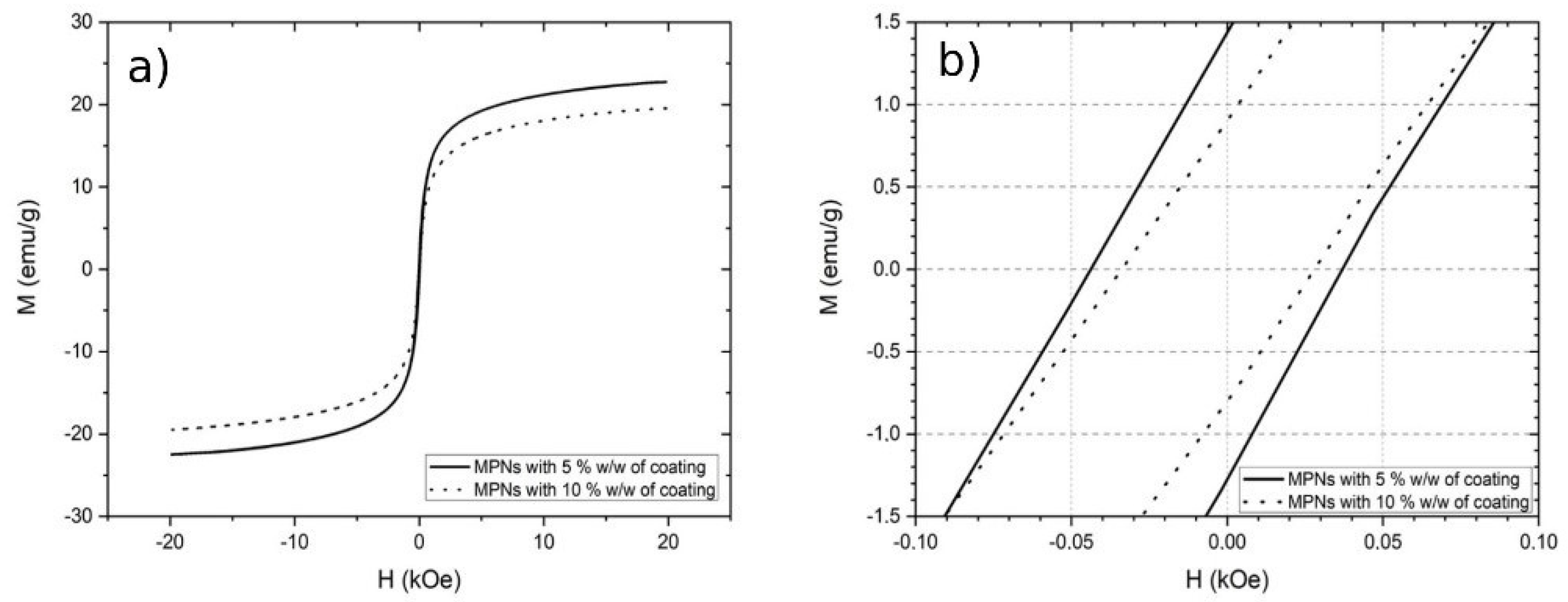
MA show a good magnetic saturation (M) at room temperature and 20KOe (Figure 5a). MA with 5% w/w of coating have a M of 22.7 emu/g, while the those with 10% of coating have an M of 19.5 emu/g. This was expected indeed, since the MA with 10% of coating have more non-magnetic mass on them. The coercivity measured was 28.5 Oe and 37.6 Oe, respectively, for MA with 5% and 10% of coating (Figure 5b); thus, these materials have a superparamagnetic-like behavior.
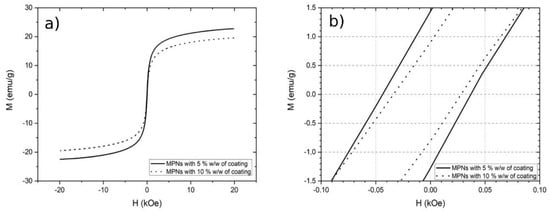
Figure 5.
VSM curve of functionalized MA at room temperature. (a) Magnetic saturation, (b) coercivity behavior.
The BET surface area and the skeletal density were found to be 85.6 m2 g−1 and 6.24 g cm−3 for the MA with 10% of coating and 62.9 m2 g−1 and 4.12 g cm−3 for the MA with 5% of coating. The zeta potential at pH 7 was −31.3 mV and −21.6 mV, respectively, for the MA with 10% of coating and for the MA with 5% of coating, while the Z-potential of bare magnetite is −0.8 mV. These results agree with the type of coating used, which provides negative charges on the surface of the particles.
3.2. Adsorption Tests
Experiments were carried out to establish the contact time needed to reach the adsorption equilibrium. This condition is found when the MA reach their maximum adsorption capacity and efficiency and indicates the contact time needed for performing an efficient treatment. This information is crucial for the correct design of the treatment equipment. Short contact time for reaching the equilibrium means a small size reactor and space needed, thus lower costs. The experiments were carried out in batch mode in 100 mL of each of the wastewater samples (sample 1 and sample 2). MA with different percentages of coating (5–10% w/w) and a dosage of 1000 ppm were used for the experiments that had a duration of 120 min. Samples of treated water were taken for the ICP-MS analysis at different time points. The efficiency was measured as reported in Equation (1).
3.2.1. Single-Ion Adsorption
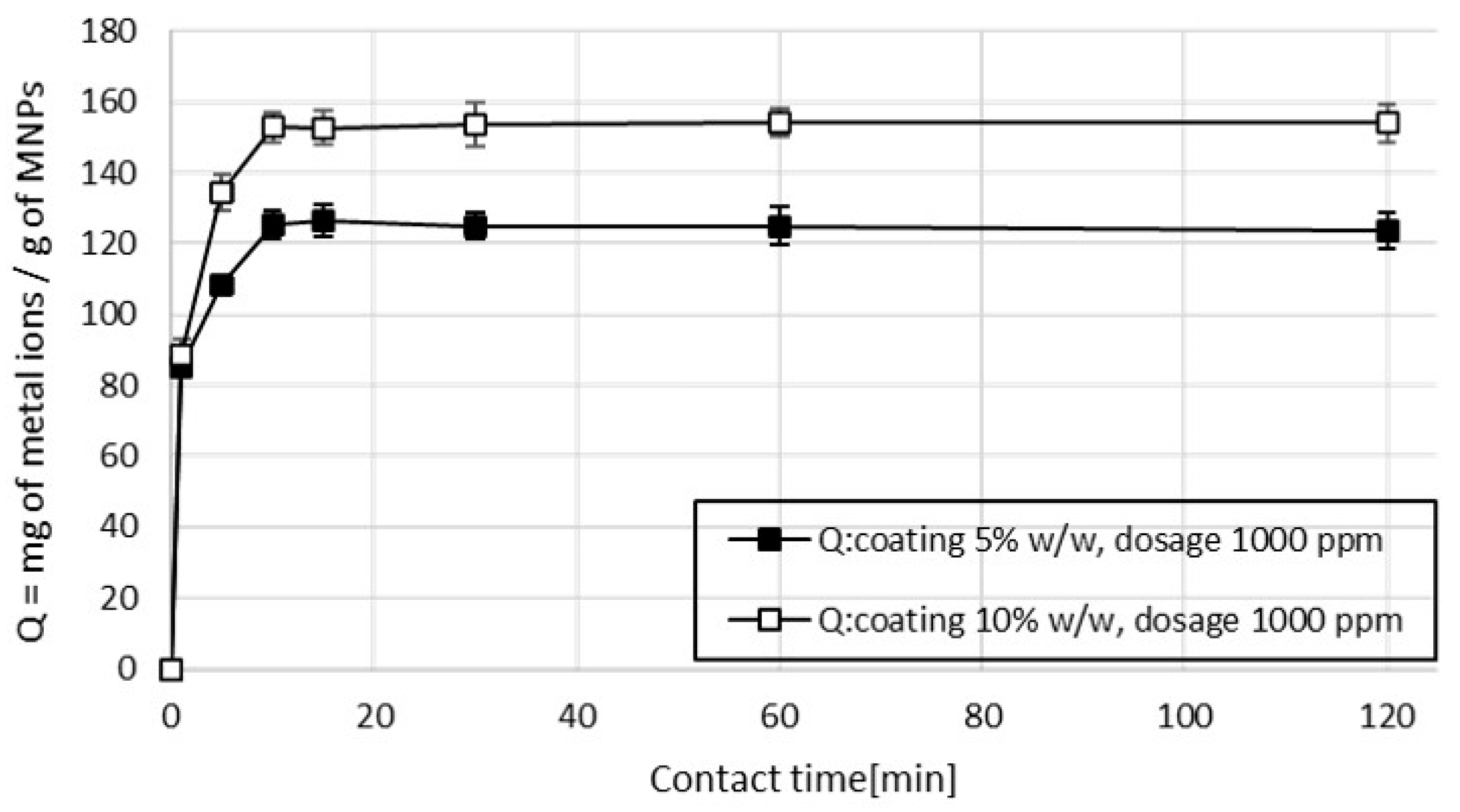
Results obtained from sample 1 measurements (containing only copper ions) show that a short contact time was sufficient to achieve the adsorption equilibrium, as explained by the adsorption mechanism considered [27]. The uptake of metal ions takes place on the surface of MA by monolayer adsorption and the contribution of limitation due to internal diffusion resistance is negligible. At a MA dosage of 1000 ppm, the maximum adsorption capacity (Q) was reached within 10 min of contact time and then reached a plateau (Figure 6), indicating that the adsorption process reached the equilibrium.
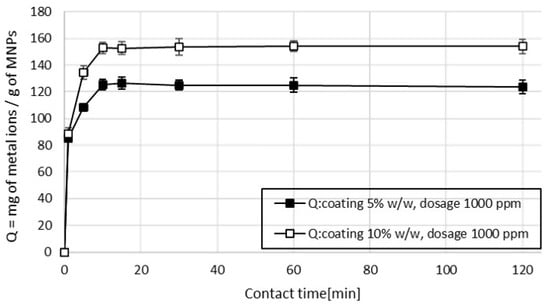
Figure 6.
Effect of contact time and percentage of coating on the adsorption capacity for Cu2+, dosage 1000 ppm, pH 6.9.
It was observed, that, while the time for reaching the adsorption equilibrium is not correlated to the percentage of coating, the value of the maximum adsorption capacity depends strictly on the amount of coating used in the MA. The MA with 5% w/w of succinic acid had a maximum adsorption capacity Qmax of 122 mg of copper (Cu2+) for a gram of MA. Increasing the amount of coating to 10% w/w, the Qmax increased to 153 mg of copper (Cu2+) for a gram of MA. The adsorption mechanism is driven by physio-chemical interactions, mostly represented by electrostatic attractions between the metal ions and the hydroxyl groups present on the surface of the MA. Increasing the amount of coating during the synthesis of the MA resulted in more hydroxyl functional groups available for the adsorption of metal ions; thus, the efficiency of the treatment is enhanced [28,29].
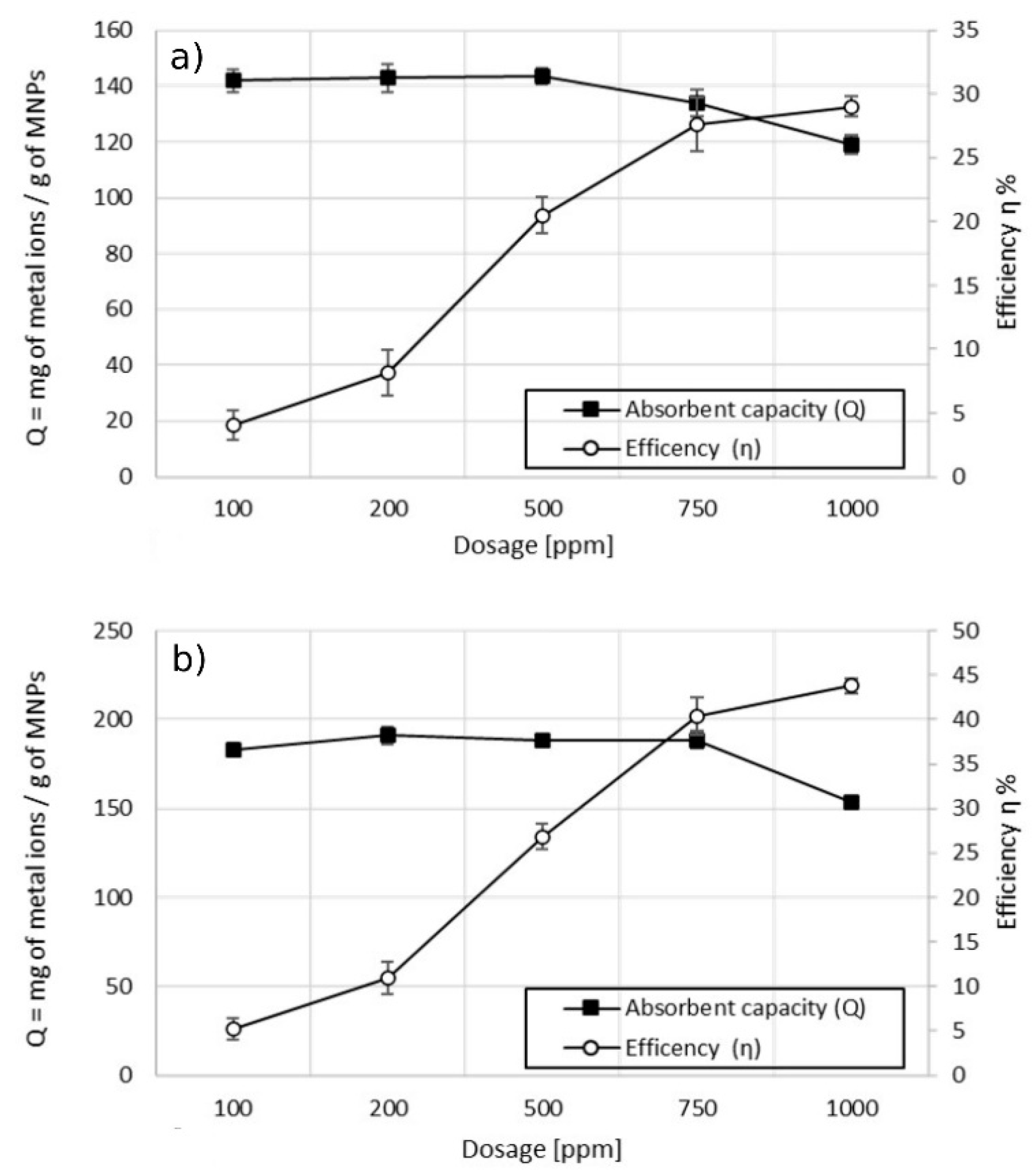
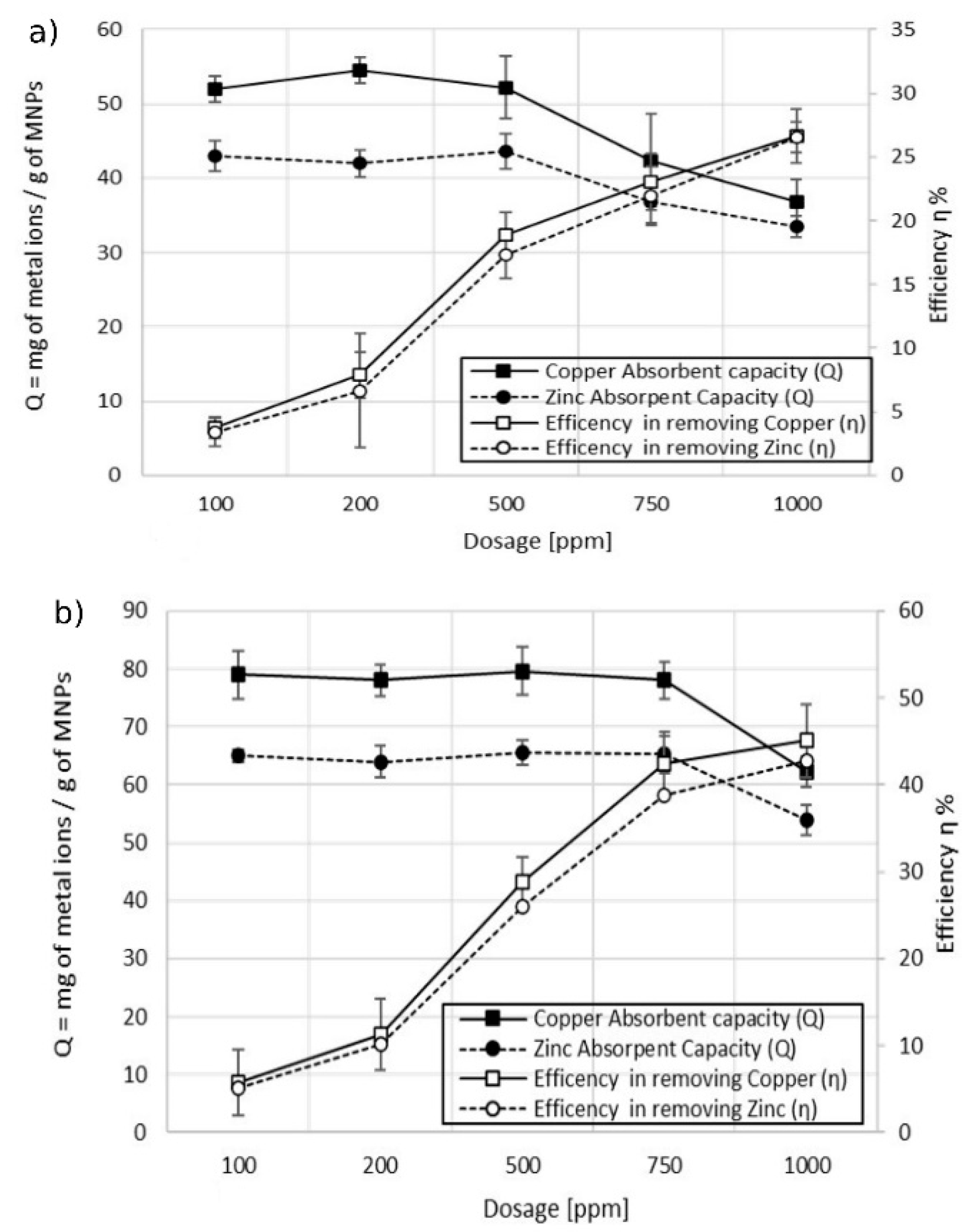
The effect of the dosage of MA on the adsorption capacity of copper (Cu2+) was studied by performing a series of batch experiments in 100 mL of sample 1 using MA with 5% w/w and 10% w/w of coating. Taking into consideration the results from previous experiments, it was decided to use a contact time of 30 min to ensure adsorption equilibrium. Figure 7 shows the behavior of the maximum adsorption capacity Qmax, calculated according to Equation (2), at increasing dosages of MA (from 100 to 1000 ppm). The trend of the treatment efficiency at various dosages, calculated according to Equation (1), is also reported.
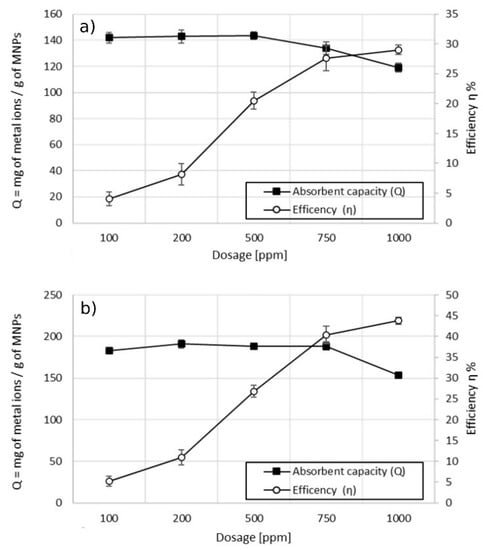
Figure 7.
Effect of the dosage on adsorption capacity vs. efficiency. (a) MA with 5% w/w of coating; (b) MA with 10% w/w of the coating, pH 6.9.
From the results obtained, an optimal dosage to optimize the maximum adsorption capacity related to the efficiency of the treatment can be defined. The ideal dosage would maximize the interactions between metal ions and adsorption sites present on the MA [30,31]. Increasing the dosage of MA led, firstly, to a linear increase of efficiency while the adsorption capacity remained constant. Further increase of the dosage led to a slight increase in the efficiency of the treatment, while the adsorption capacity decreased drastically. In the case of MA with 5% w/w coating (Figure 7a), the maximum Q was 144 mg of Cu2+ per gram of MA at a dosage of 500 ppm with an efficiency of the treatment equal to 20%. Doubling the dosage to 1000 ppm, the adsorption capacity was 30% lower while the efficiency of the treatment increased by 10%. The maximum adsorption capacity, using MA with 10% w/w coating (Figure 7b), was equal to 188 mg of Cu2+ per gram of MA at a dosage of 750 ppm, with a corresponding efficiency of the treatment equal to 40%. Increasing the dosage of the MA to 1000 ppm led to an enhancement of efficiency of 3%, while the adsorption capacity decreased to 150 mg of Cu2+ per gram of MA (18% lower). Increasing the dosage of the MA would raise the number of available adsorption sites, leading to a significant enhancement of the removal efficiency. Over a threshold dosage, the adsorption capacity decreased and the efficiency enhancement became slower. This behavior could be due to a high concentration of MA in water that led to an aggregation of particles during the mixing process. Despite the fact that the concentration of MA in water increased with the higher dosage, the total surface available for the adsorption decreased due to the formation of aggregates of higher dimension, with a consequent reduction in the adsorption capacity [32,33,34]. This explanation may be supported by the fact that MA with 10% w/w of coating presented the decay of adsorption capacity at higher dosage due to the higher stability towards aggregation. Another explanation, reported in other studies, is attributed to induced metal ions desorption from the particles’ surface at higher dosage [35].
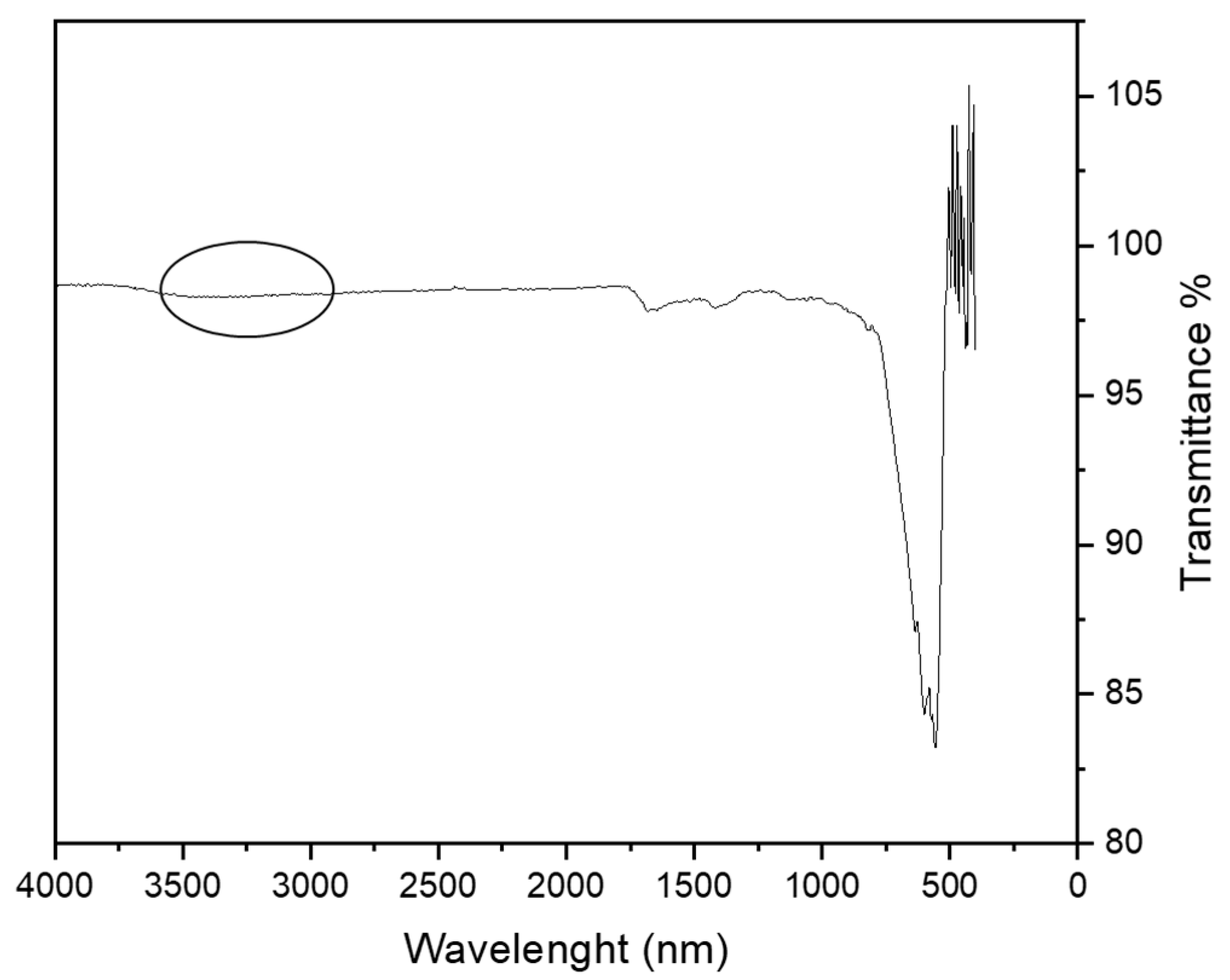
In the FT-IR spectrum of the MA after the adsorption of copper (Figure 8), the characteristic peaks of the O–H of carboxylic groups that are present between 3000 and 3500 cm−1 disappeared, confirming that the metal ions are adsorbed on the MA through these moieties.
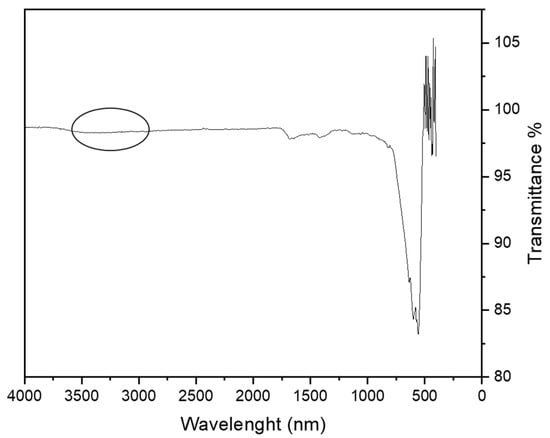
Figure 8.
FTIR spectrum of the MA with 10% of coating after the adsorption of copper ions.
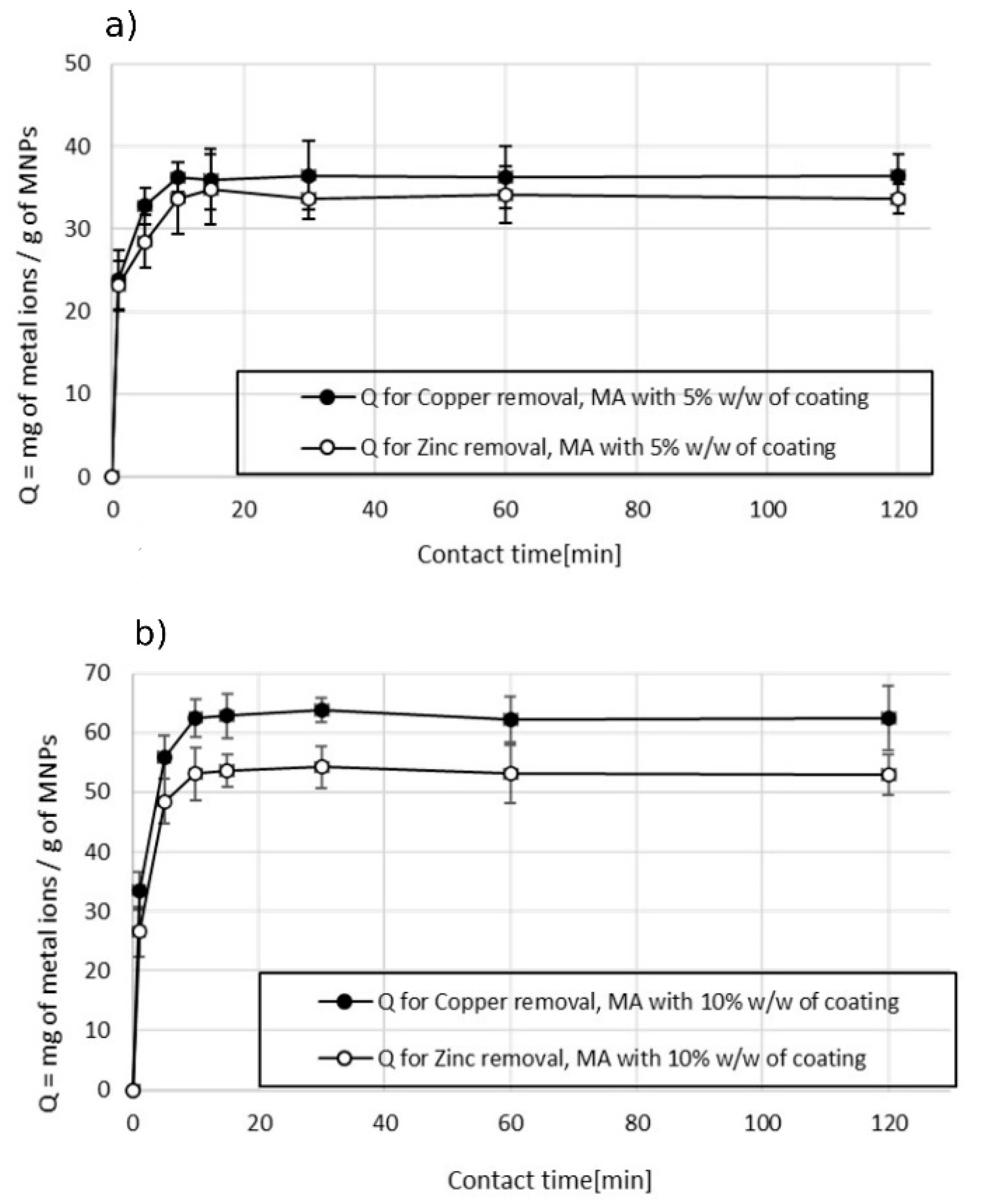
3.2.2. Double-Ion Adsorption
A short contact time to reach the adsorbent equilibrium was observed also in the experiments conducted on sample 2, which contained copper and zinc as pollutants. The experiments were carried out as previously described, using a dosage of 1000 ppm. Figure 9 shows that the maximum adsorption capacity was reached within 10 min and then the value remained stable at longer contact times. These experiments confirmed that the efficiency in the removal of metal ions is higher for the MA with a higher content of succinic acid. The values of Qmax are higher in the case of experiments done with MA with 10% w/w of coating (Figure 9b) in comparison with the ones obtained with MA with 5% w/w of coating (Figure 9a). Of note, a difference in the efficiency was found for the two types of metal ions. The maximum adsorption capacity in the removal of copper was higher than the one of zinc in both the cases of using MA with 10% w/w and 5% w/w of the coating: 62 mg of Cu2+ per gram of MA vs. 53 mg of Zn2+ per gram of MA using MA with 10% w/w of coating, and 37 mg of Cu2+ per gram of MA vs. 33 mg of Zn2+ per gram of MA using MA with 5% w/w of the coating. This behavior was attributed to the dependence of the adsorption mechanism on the electrostatic interactions and the difference in the size of hydrated ionic radii (zinc 4.35 Å > copper 4.19 Å, Qzinc < Qcopper). The higher the hydrated ionic radius, the greater the distance from the adsorption negatively charged sites on the MA, resulting in weaker adsorption and thus a lower adsorption capacity [28,36,37]. The effect of dosage on the adsorption capacity versus the efficiency of the treatment was also studied for sample 2 wastewater. Figure 8 shows the dependence of the adsorption capacity vs. efficiency at different MA dosages. The general trend observed in the treatment of wastewater containing both metal ions was in line with the one observed in the case of wastewater polluted with a single metal ion (sample 1). The adsorption capacity remained constant while the efficiency increased linearly by increasing the dosage of the MA. After a certain dosage, 500 ppm for the experiment conducted with the MA with 5% w/w of coating (Figure 10a), and 750 ppm for the experiment conducted with the MA with 10% w/w of coating (Figure 10b), a decrease in the adsorbent capacity was observed while the efficiency of the treatment rose at a slower rate.
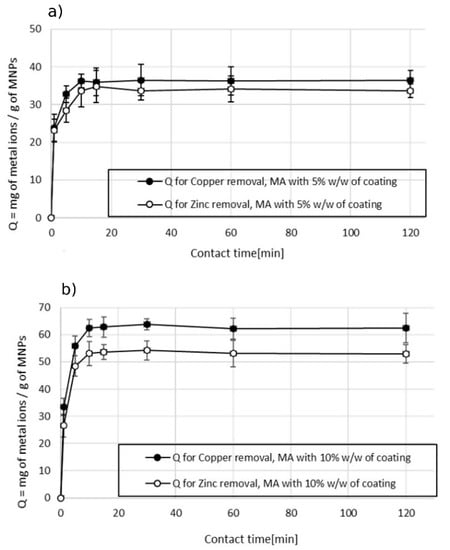
Figure 9.
Effect of contact time on the adsorption capacity in the removal of Cu2+ and Zn2+. (a) MA with 5% w/w coating and (b) MA with 10% w/w coating, pH 7.2.
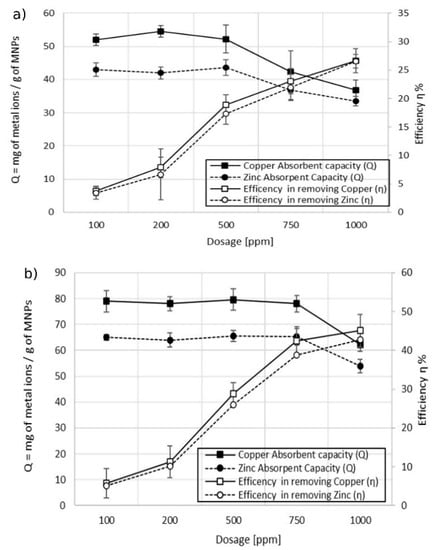
Figure 10.
Effect of contact time on the adsorption capacity in the removal of Cu2+ and Zn2+. (a) MA with 5% w/w coating and (b) MA with 10% w/w coating, pH 7.2.
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
Langmuir and Freundlich’s adsorption isotherm models were used to understand the adsorption mechanism of the Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions on the functionalized MA. This analysis is crucial to understand how the adsorbed compounds interact with the surface of the MA.
Langmuir’s model assumes that the adsorption process takes place at specific homogeneous sites within the adsorbent and all sorption sites are identical and energetically equivalent. According to Langmuir’s model, once the sites of the adsorbent are filled, there is no possibility of further adsorption. The surface of the adsorbent reaches a saturation point corresponding to a maximum adsorption capacity Qmax. This model is commonly used in monolayer adsorption processes. The linear form of the Langmuir isotherm is expressed by the following equation:
where Qmax is the maximum amount of adsorption with complete monolayer coverage on the adsorbent surface (mg g−1), KL is the Langmuir constant related to the energy of adsorption (L mg−1), and Qe and Ce Q indicate, respectively, the adsorption capacity at equilibrium and the equilibrium concentration. The Langmuir constants KL and Qmax were calculated from the linear plot of 1/Ce versus 1/Qe. The KL parameter is used for predicting the affinity between the sorbate species and sorbent compound, thus when adsorption is favorable or unfavorable, through a dimensionless constant called separation factor or equilibrium parameter (RL).
where C0 (mg L−1) is the initial concentration of the ions. The value of RL indicates if the absorption process is irreversible (RL = 0), linear (RL = 1), unfavorable (RL > 1), or favorable (0 < RL < 1).
1/Qe = 1/Qmax + 1 (KL Qmax Ce)−1
RL = 1/(1 + KLC0)
The Freundlich isotherm is commonly used to describe heterogeneous systems and reversible adsorption, which is not always related to monolayer formations. It gives information about the heterogeneity of the adsorbent surface. The linear form of the Freundlich adsorption isotherm is expressed as:
where KF is the Freundlich constant and it indicates the adsorption capacity, n is an empirical parameter related to the intensity of adsorption. The value of n is correlated to the heterogeneity of the adsorbent and, for favorable adsorption processes, the value of n is comprised in the range of 1–10. The value of KF and n were calculated from the intercept and slope of the linear plot of log Ce vs. ln Qe. Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14 represent plots of the experimental data based on the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models for all the series of experiments performed in this work.
Log(Qe) = log(KF) + 1/n log(Ce)
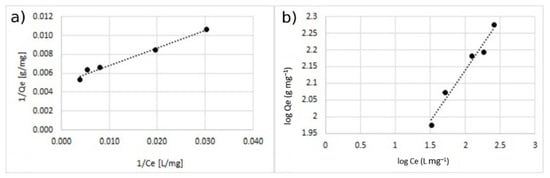
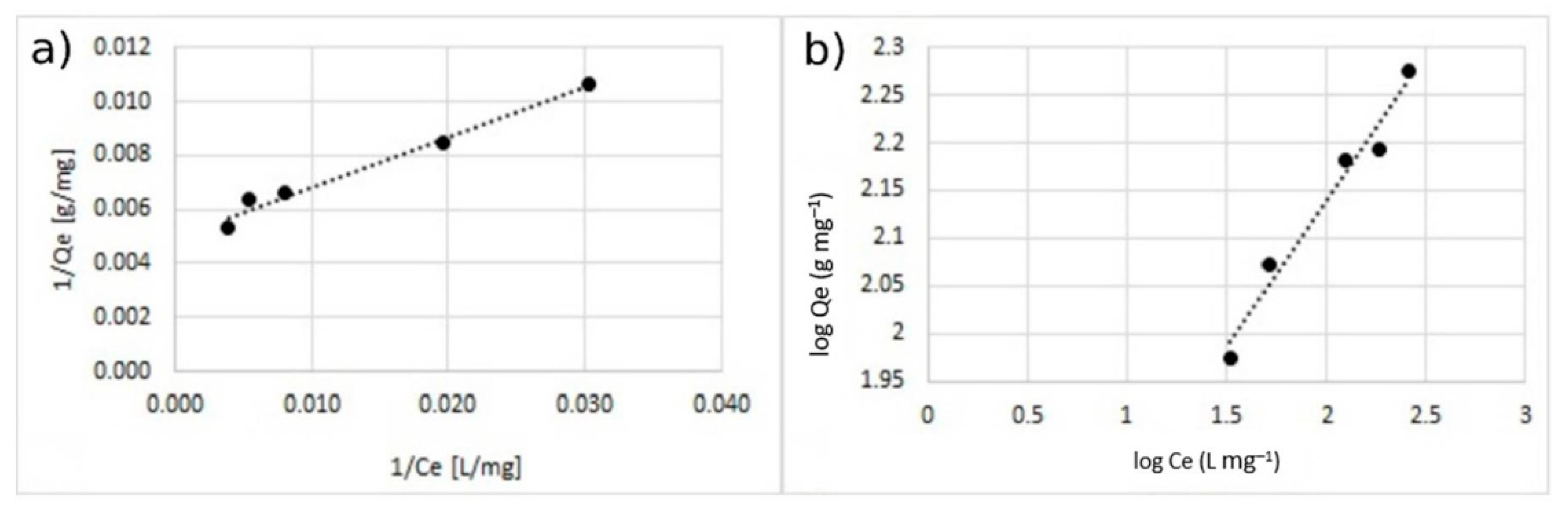
Figure 11.
Adsorption isotherm for adsorption of Cu2+ using MA with 10% w/w of the coating. (a) Langmuir model and (b) Freundlich model.
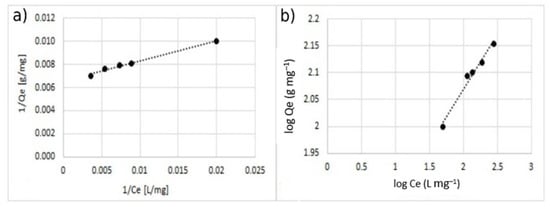
Figure 12.
Adsorption isotherm for adsorption of Cu2+ using MA with 5% w/w of the coating. (a) Langmuir model and (b) Freundlich model.
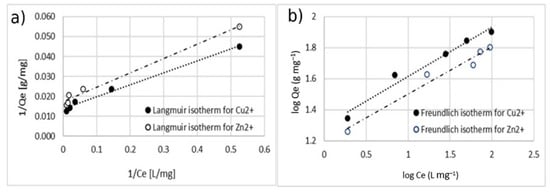
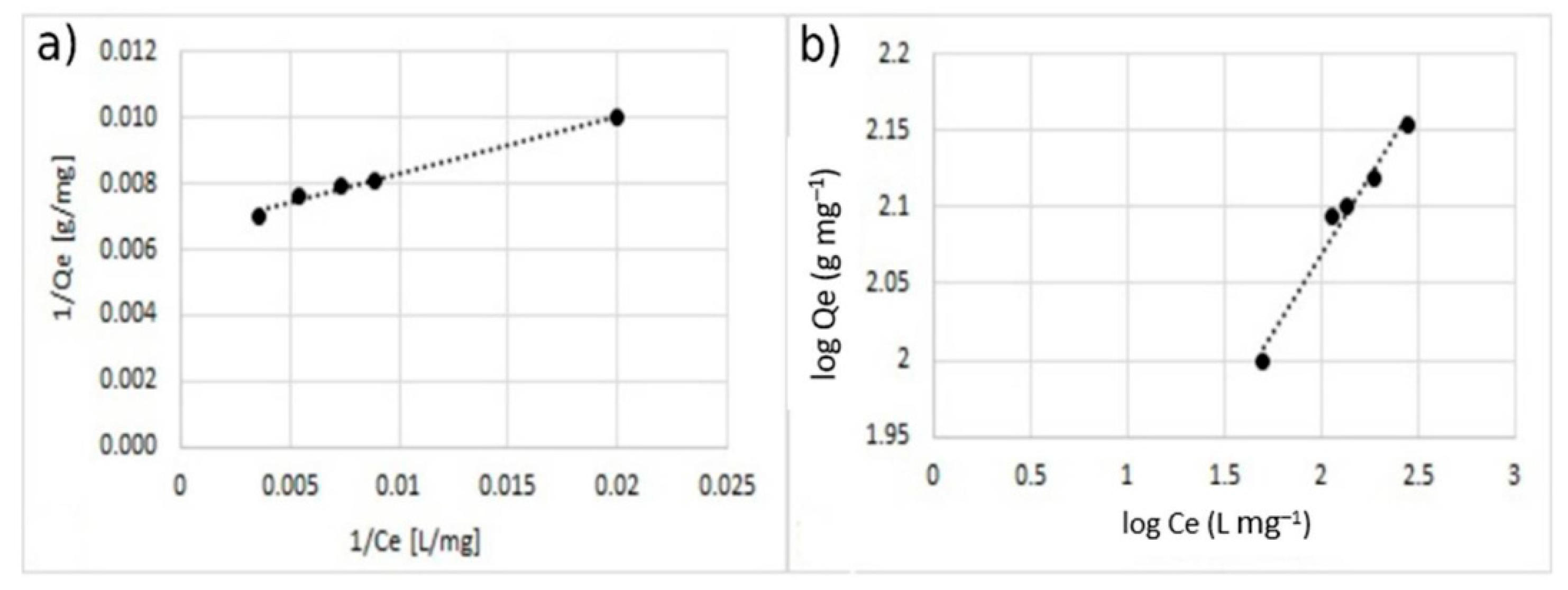
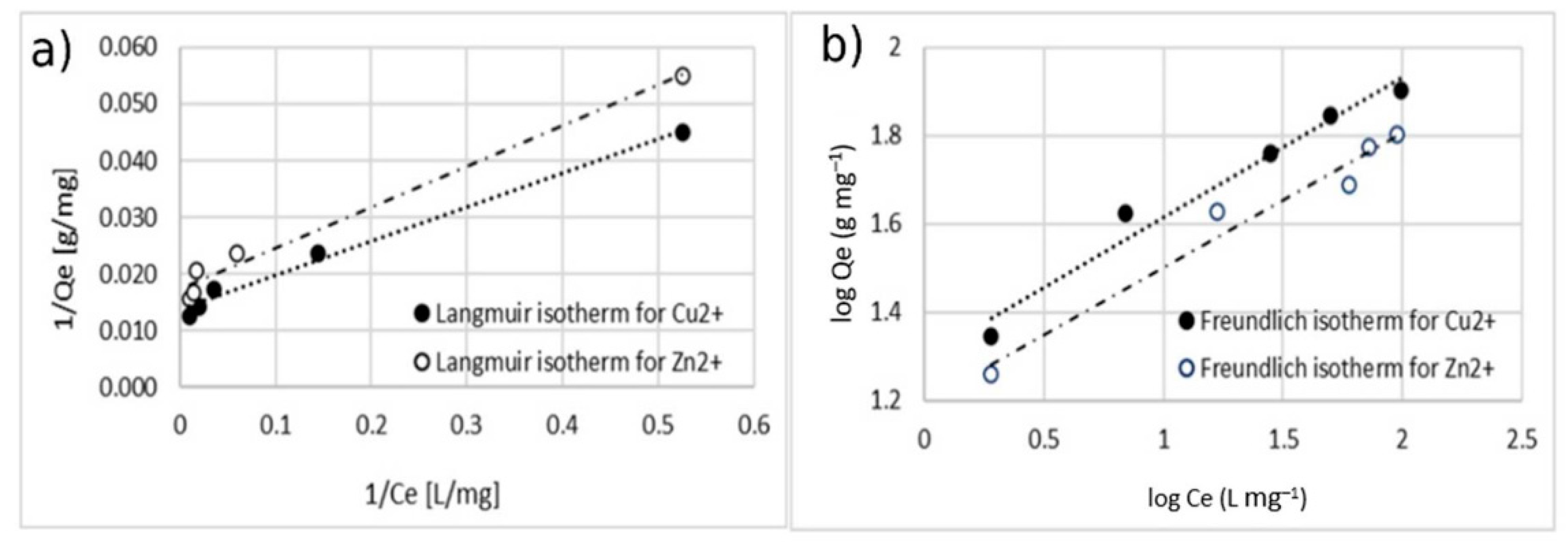
Figure 13.
Adsorption isotherm for adsorption of Cu2+ and Zn 2+ using MA with 10% w/w of coating. (a) Langmuir model and (b) Freundlich model.
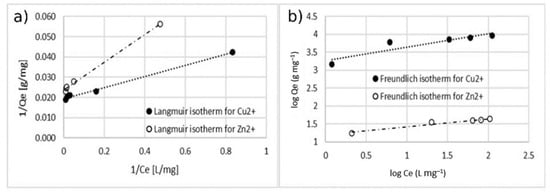
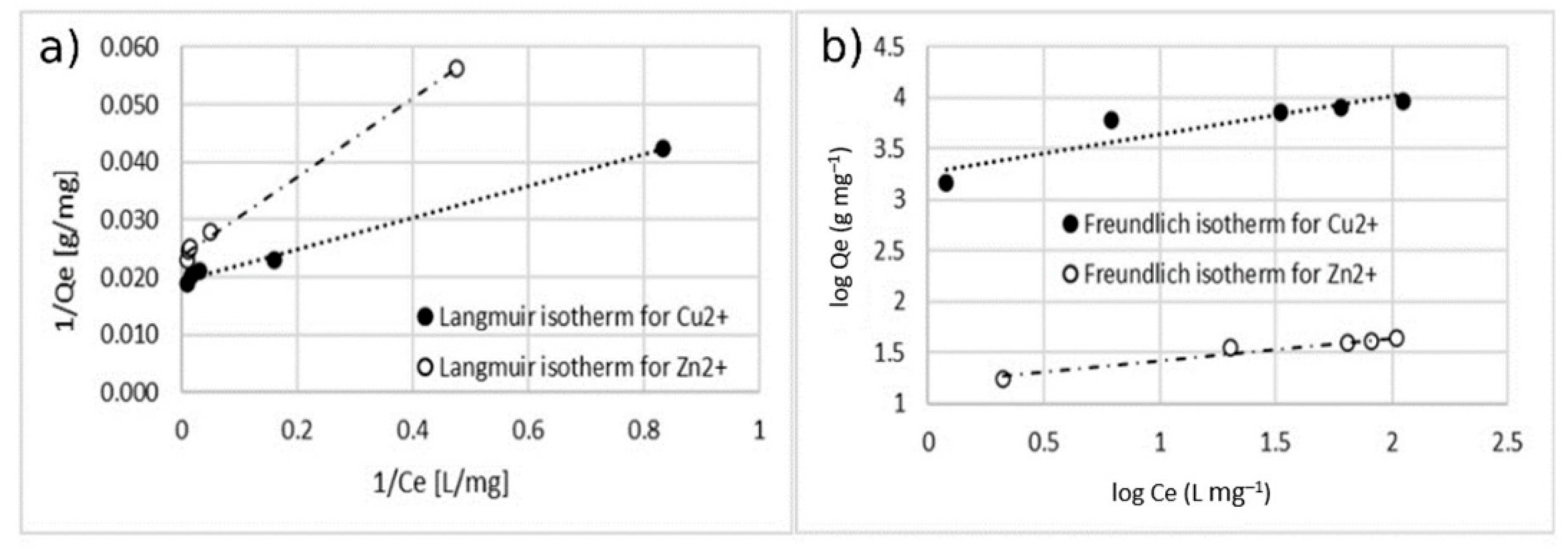
Figure 14.
Adsorption isotherm for adsorption of Cu2+ and Zn2+ using MA with 5% w/w of coating. (a) Langmuir model and (b) Freundlich model.
Table 1 and Table 2 report all the models’ parameters obtained by fitting the experimental data within both the isotherm models. Table 1 collects the results belonging to single-ion adsorption experiments; Table 2 collects the results regarding the double-ion adsorption experiment.

Table 1.
Isotherm constants for the adsorption of Cu2+.

Table 2.
Isotherm constants for the adsorption of Cu2+ and Zn2+.
The comparison between the values of the correlation coefficient (r2) of the linearized isotherm models suggested that the Langmuir model fitted the experimental data better for both the cases of single- and double-ion adsorption. The value of the Qmax calculated with Langmuir model was similar to the one obtained with experimental data. The value of KL was in the range of 0–1, indicating that the adsorption of Cu2+ and Zn2+ on the surface of coated MA was favorable. This is also confirmed by the n-parameter, calculated by using the Freundlich model which was in the range of 0–10.
3.4. Kinetic Studies
The adsorption kinetics of metal ions on the coated MA were analyzed by four kinetic models: Lagergren pseudo-first-order kinetic (Equation (6)), pseudo-second-order kinetic (Equation (7)), Elovich model (Equation (8)), and the Weber and Morris model (Equation (9)).
where Qt (mg g−1) is the adsorption at time t (min); Qe (mg g−1) indicates the adsorption capacity at adsorption equilibrium; and K1 (min−1) and K2 (g mg−1 min−1) represent the kinetic constants for the pseudo-first-order and the pseudo-second-order models, respectively. The Elovich model (Equation (8)) is used to describe the adsorption process on adsorbent material with a heterogeneous surface. From its linear model, is it possible to calculate the initial adsorption rate α (mg g−1 min−2) and the desorption constant β (g mg−1 min−1).
Ln(Qe − Qt) = ln(Qe) − K1 t
t/Qt = 1 (K2 Qe2)−1 + t/Qe
Qt = 1/β ln (αβ) + 1/β ln(t)
An intra-particle diffusion mechanism was explored by using the Weber and Morris model (Equation (9)).
where Kintra is the intra-particle diffusion rate constant (mg g−1 min−1/2) and C is a constant related to the thickness of the boundary layer (mg g−1). Figure 15, Figure 16 and Figure 17 represent plots of the experimental data based on the four kinetic models adopted.
3Qt = (Kintra t 1/2) + C
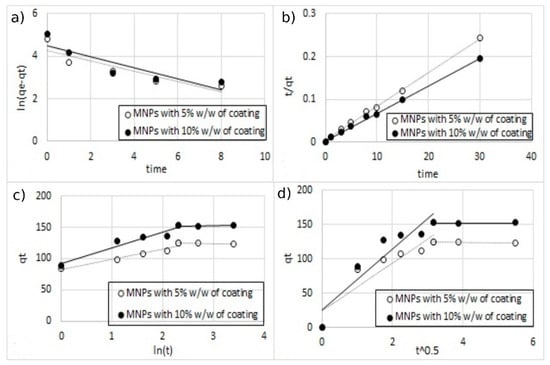
Figure 15.
The fitting of different kinetic models for single-ion adsorption (Cu2+) onto MA functionalized with 5% and 10% w/w of coating, (a) pseudo-first-order, (b) pseudo-second-order, (c) Elovich model, and (d) intra-particle diffusion model.
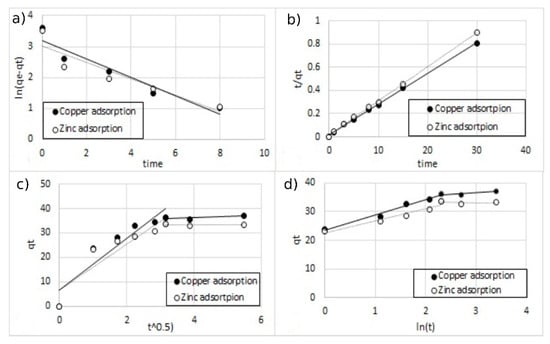
Figure 16.
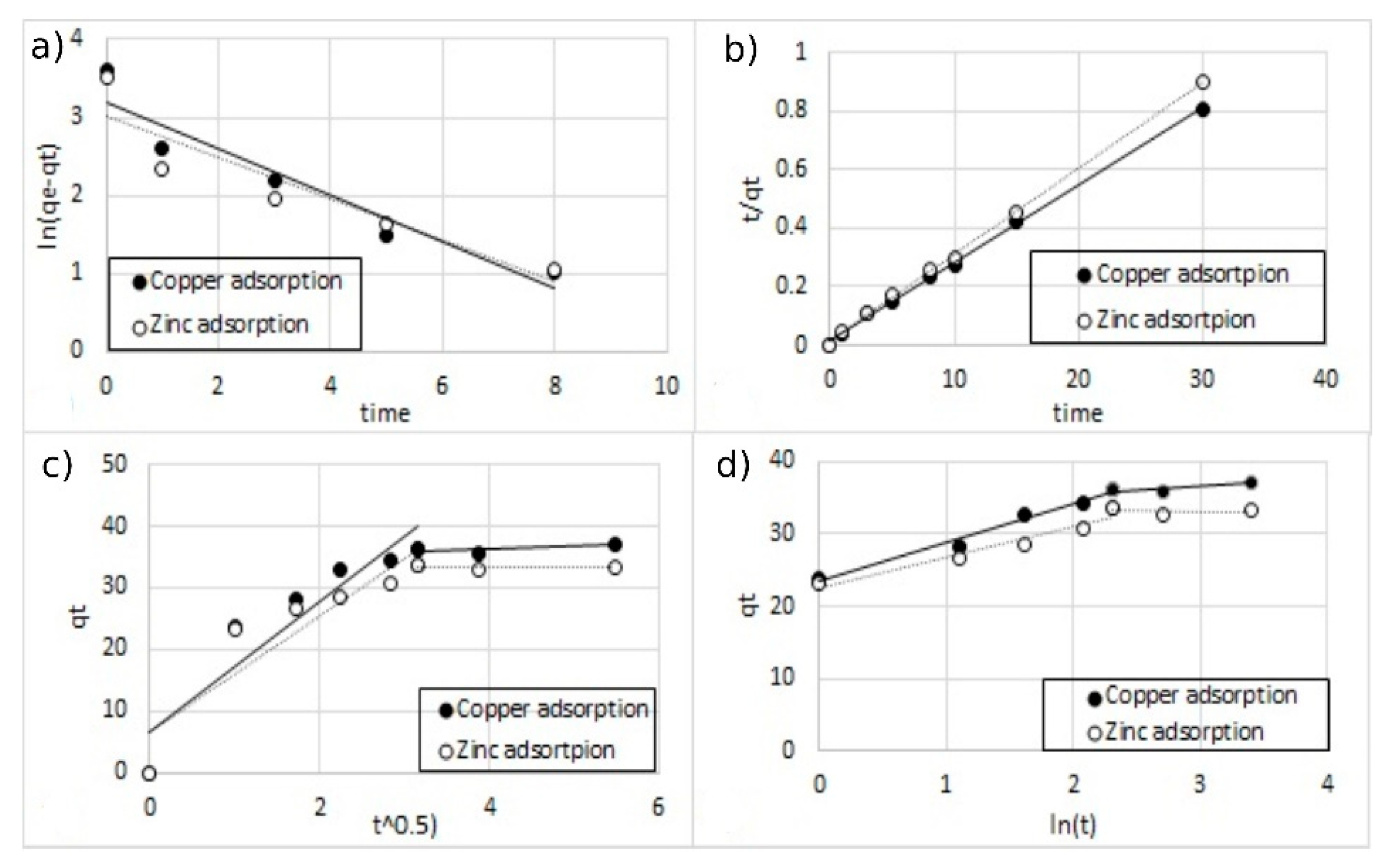
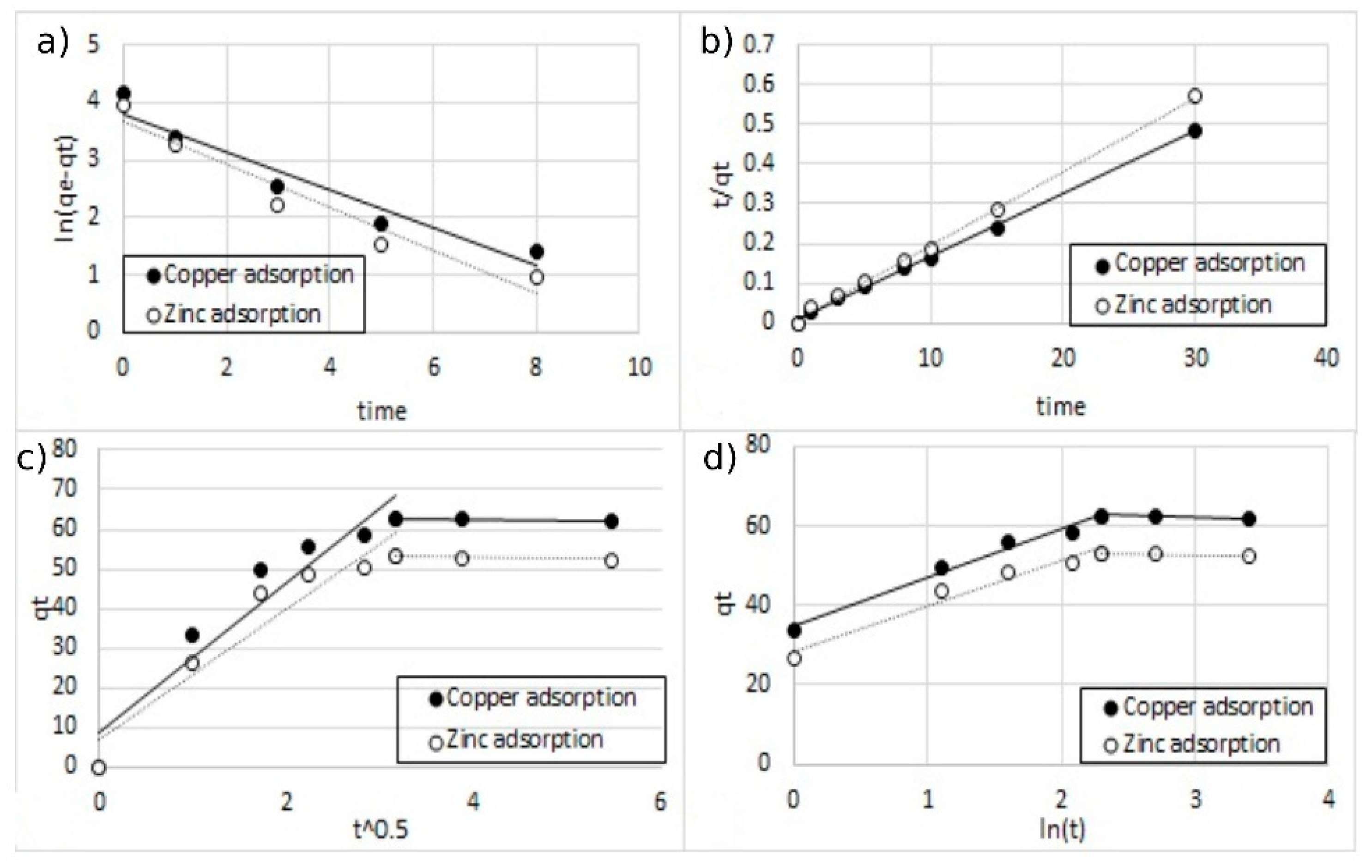
The fitting of different kinetic models for double-ion adsorption (Cu2+ and Zn2+) onto MA functionalized with 5% of coating, (a) pseudo-first-order, (b) pseudo-second-order, (c) Elovich model, and (d) intra-particle diffusion model.
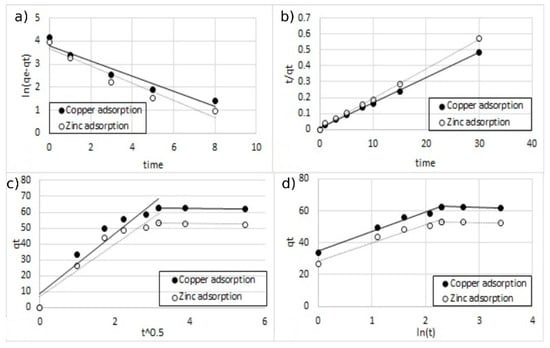
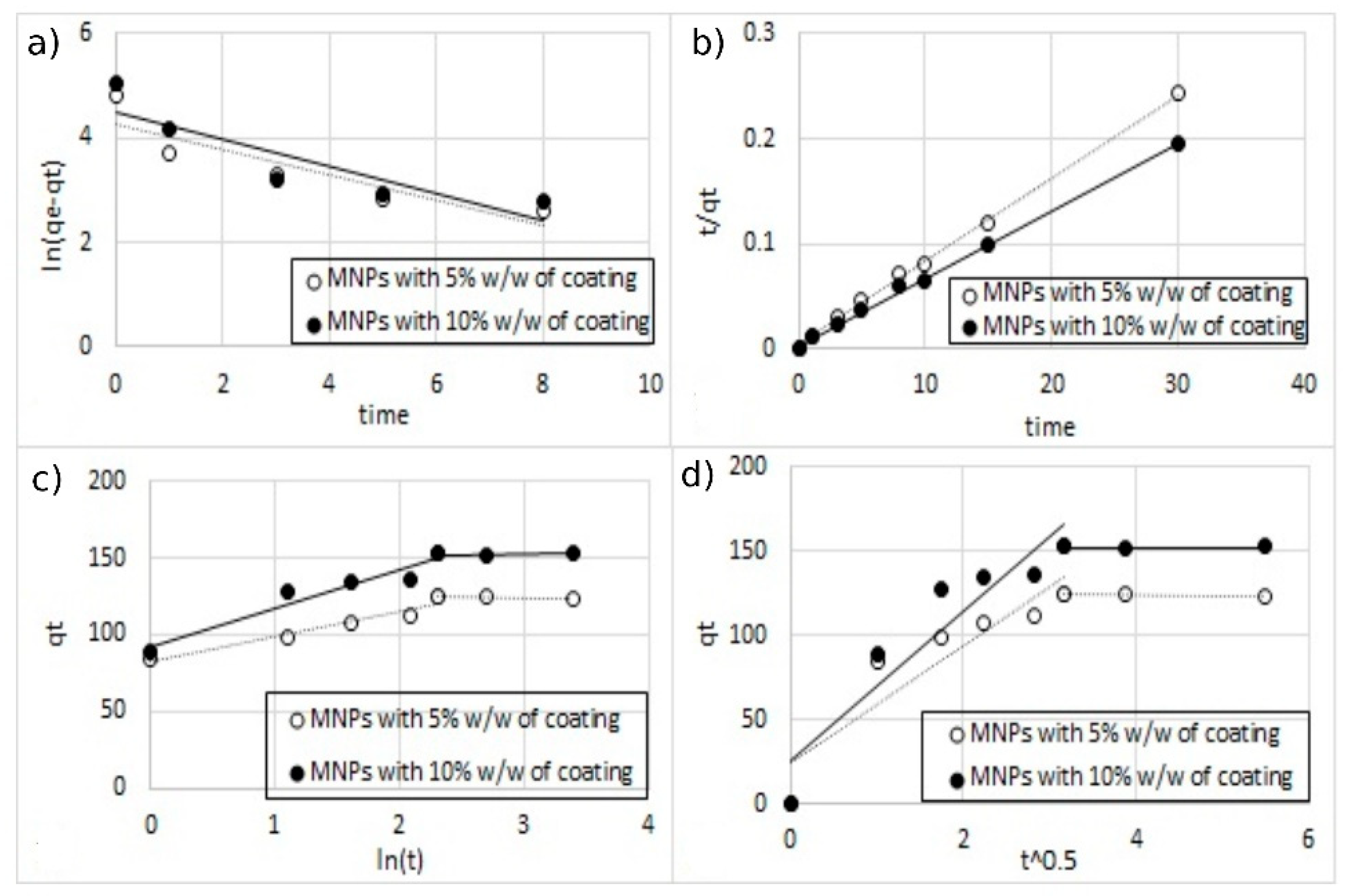
Figure 17.
The fitting of different kinetic models for double-ion adsorption (Cu2+ and Zn2+) onto MA functionalized with 10% of coating, (a) pseudo-first-order, (b) pseudo-second-order, (c) Elovich model, and (d) intra-particle diffusion model.
All the parameters of the different models calculated from the regressions are reported in Table 3. For all the regression, the sum of error squared (SSE) between the predicted values and the experimental data was measured. The best results in terms of higher correlation coefficients (R2) with low SSE values were obtained, with the pseudo-second-order kinetic model indicating that the adsorption mechanism is dependent on the adsorbate and the adsorbent [12,38]. This result was indeed expected since the adsorption model is based on the interaction between the negative charges present on the surface of the MA and the positive charges of metal ions.

Table 3.
Kinetic parameters of the different models for single-ion and double-ion adsorption onto functionalized MA.
3.5. Evaluation of the Electrochemical Activity
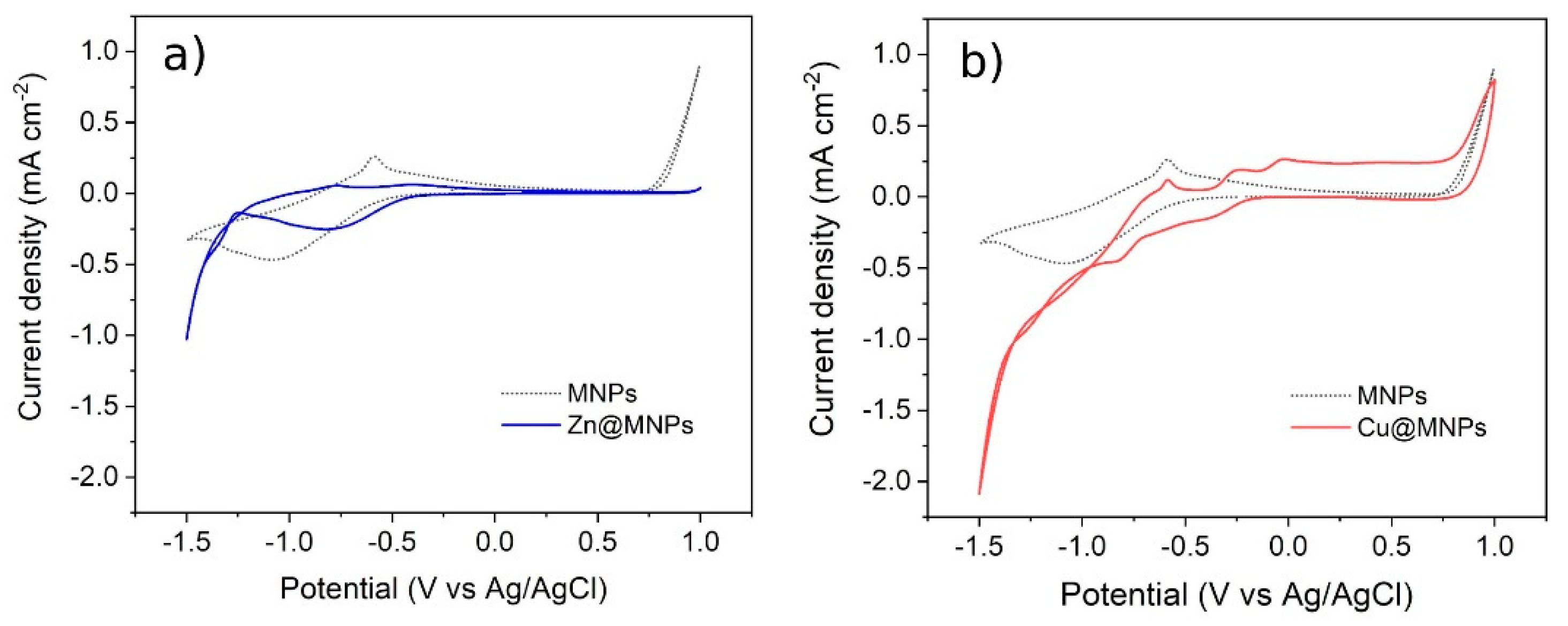
Electrochemical characterization tests were conducted to observe the variation in the electrochemical activity of the magnetite particles with absorbed metal cations. These preliminary tests were carried out on the hypothesis of desorbing the metal ion from the surface of the MA, applying a polarization. The electrochemical activity of the functionalized particles can be observed from the CV curves (Figure 18). The presence of redox peaks indicated the coated particles to be active, i.e., taking part in the electrochemical reactions. At high cathodic bias, the oxide surface may be reduced to metallic iron, as indicated by the broad cathodic peak at about −1 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The position of the oxidation peak in the backward scan, associated with the oxidation of the surface metallic iron back into magnetite, suggested good reversibility of the reaction. The results suggested the coated-MA to be electrochemically active.
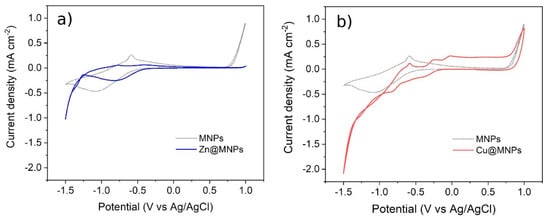
Figure 18.
Cyclic voltammetry on MA used in the treatment of wastewater samples, (a) Zn2+-absorbed MA. (b) Cu2+-absorbed MA. (Dotted curve: functionalized MA with no ions absorbed).
Eventally, the tests were carried out on the magnetite aggregates after the absorption of metallic cations, i.e., Zn and Cu. The electrochemical activity of the Zn@MA signicantly changed with respect to the reference sample. In particular, even if the redox reactions related to Fe3O4 were still present, the peaks associated with zinc reduction (−1.3 V vs. Ag/AgCl) and oxidation (−0.8 V vs. Ag/AgCl) reactions were observed. In analogy to the zinc case, the magnetite particles were immersed in a solution containing copper ions, to promote their absorption. The Cu@MA particles showed additional redox peaks with respect to the reference sample. In particular, the anodic peaks close to 0 V vs. Ag/AgCl may be ascribed to the oxidation of copper, suggesting its reduction during the cathodic scan. These results suggest that ions absorbed on the MA effectively interact electrochemically with the electrode surface, suggesting the possibility to recover the absorbed metal cations by applying a polarization. To verify the reduction of the absorbed metals on the electrode surface, allowing the recovery of this material through this method, further experiments and characterization need to be performed.
4. Conclusions
In this work, aggregates of Fe3O4 nanoparticles functionalized with succinic acid were synthesized by a single-step co-precipitation method. Their capacity in adsorbing transition metals was proved by treating two samples of industrial wastewater contaminated with transition metals, Cu2+ and Zn2+. Adsorption measurements showed that MA need a short contact time to reach the equilibrium, which was reached within 10 min in all experiments. The maximum adsorption capacity was 188 mg of Cu2+ per gram of MA in the case of wastewater contaminated with a single ion, and 62 mg of Cu2+ per gram of MA and 53 mg of Zn2+ per gram of MA in the case of wastewater contaminated with both ions. The percentage of MA coating was 10% w/w in both cases. The adsorption mechanism was driven mainly by electrostatic attraction between metal ions and MA and this process was influenced by the hydrated ionic radius of the metal. From the two adsorption isotherm models used here, the Langmuir isotherm adsorption model better fitted the adsorption data. The adsorption process follows a pseudo-second-order kinetic mechanism. In conclusion, it was demonstrated that MA with a magnetite core and an outer coating made by succinic acid could be a promising material for efficient and fast removal and recovery of transition metals from wastewater. Moreover, the electrochemical activity of the MA was proved, showing that an electrochemical process for recycling the MA and extracting the transition metals is worth being investigated.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M.; methodology, R.P., G.P. and A.A.; software, J.I. and C.K.; validation, formal analysis, investigation R.P., C.J.P., G.P. and A.A.; resources, L.M.; data curation R.P., G.P., J.I., C.K. and A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, R.P., C.K., G.P.; writing—review and editing, C.K., G.P.; visualization, L.M.; supervision, L.M.; project administration, L.M.; funding acquisition, L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 821431.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy issues of the involved company.
Acknowledgments
We thank Captive Systems srl for providing the materials used for the experiments and Gaser Group for providing the samples used in the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Al-Saydeh, S.A.; El-Naas, M.; Zaidi, S.J. Copper removal from industrial wastewater: A comprehensive review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 56, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbabi, M.; Golshani, N. Removal of copper ions Cu (II) from industrial wastewater: A review of removal methods. Int. J. Epidemiol. Res. 2016, 3, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Ma, J.; Liang, P. Effective removal and selective capture of copper from salty solution in flow electrode capacitive deionization. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 6, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gakwisiri, C.; Raut, N.; Al-Saadi, A.; Al-Aisri, S.; Al-Ajmi, A. A Critical Review of Removal of Zinc from Wastewater. Proc. World Congr. Eng. 2012, 1, 627–630. [Google Scholar]
- Emadi, M.; Shams, E.; Amini, M.K. Removal of zinc from aqueous solutions by magnetite silica core-shell nanoparticles. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 787682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plum, L.M.; Rink, L.; Haase, H. The Essential Toxin: Impact of Zinc on Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1342–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şenel, S.; Uzun, L.; Kara, A.; Denizli, A. Heavy Metal Removal from Synthetic Solutions with Magnetic Beads Under Magnetic Field. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2008, 45, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, L.; Kara, A.; Osman, B.; Yılmaz, E.; Beşirli, N.; Denizli, A. Removal of heavy-metal ions by magnetic beads containing triazole chelating groups. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnamawati, F.; Sembiring, R. Preparation of Magnetic Chitosan Beads for Heavy Metal Ions Removal from Water. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 276, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Johar, R.; Jassal, P.S. Adsorption of nickel (II) ions from wastewater using glutaraldehyde cross-linked magnetic chitosan beads: Isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamad, T.; Naushad, M.; Eldesoky, G.E.; Alqadami, A.A.; Khan, A. Synthesis and characterization of egg-albumen-formaldehyde based magnetic polymeric resin (MPR): Highly efficient adsorbent for Cd(II) ion removal from aqueous medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 286, 110951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Naushad, M.; Abdalla, M.A.; Ahamad, T.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alshehri, S.M.; Ghfar, A.A. Efficient removal of toxic metal ions from wastewater using a recyclable nanocomposite: A study of adsorption parameters and interaction mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Naushad, M.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alsuhybani, M.; Algamdi, M. Excellent adsorptive performance of a new nanocomposite for removal of toxic Pb(II) from aqueous environment: Adsorption mechanism and modeling analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naushad, M.; Alqadami, A.A.; Ahamad, T. Removal of Cd(II) ion from aqueous environment using triaminotriethoxysilane grafted oxidized activated carbon synthesized via activation and subsequent silanization. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumaimess, M.S.; Alsohaimi, I.H.; Alqadami, A.A.; Kamel, M.M.; Naushad, M.; Ahamad, T.; Alshammari, H. Synthesis of phosphorylated raw sawdust for the removal of toxic metal ions from aqueous medium: Adsorption mechanism for clean approach. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 89, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Alqadami, A.A.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Jeon, B.-H.; Alshareef, S.A.; Alothman, Z.A.; Hamedelniel, A.E. Oil industry waste based non-magnetic and magnetic hydrochar to sequester potentially toxic post-transition metal ions from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Barick, K.; Bahadur, D. Surface engineered magnetic nanoparticles for removal of toxic metal ions and bacterial pathogens. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kalita, P.; Senapati, K.K.; Garg, A. Study on Magnetic Materials for Removal of Water Pollutants. In Emerging Pollutants-Some Strategies for the Quality Preservation of Our Environment; IntechOpen Limite: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Lei, X.; Cai, N.; Xie, X.; Xue, Y.; Yu, F. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water by Magnetic Cellulose-Based Beads with Embedded Chemically Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles and Activated Carbon. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3960–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baresel, C.; Schaller, V.; Jonasson, C.; Johansson, C.; Bordes, R.; Chauhan, V.; Sugunan, A.; Sommertune, J.; Welling, S. Functionalized magnetic particles for water treatment. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.K.; Sung, T.I.; Cho, E.S.; Namkung, K.C.; Bae, D.J.; Park, I.H. Magnetic Separation for Contaminants in Wastewater Using Magnetic Micro Bead. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3768–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, T.; Dutta, J. Applications of Nanotechnology in Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Innov. Emerg. Res. Eng. 2015, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.C.; Yu, H.; Fu, P.P. Toxicity and Environmental Risks of Nanomaterials: Challenges and Future Needs. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2009, 27, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscatelli, D.; Masi, M.; Pesce, R.M. Amphiphilic Magnetic Nanoparticles and Aggregates to Remove Hydrocarbons and Metal Ions and Synthesis Thereof. U.S. Patent No. 10,418,159, 17 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Prozorov, T.; Kataby, G.; Gedanken, A. Effect of surfactant concentration on the size of coated ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Thin Solid Films 1999, 340, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puentes-Vara, L.A.; Gregorio-Jauregui, K.M.; Bolarín, A.M.; Navarro-Clemente, M.E.; Dorantes, H.J.; Corea, M. Effects of surfactant and polymerization method on the synthesis of magnetic colloidal polymeric nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2016, 18, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-H.; Chen, D.-H. Rapid removal of heavy metal cations and anions from aqueous solutions by an amino-functionalized magnetic nano-adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo, L.; Erto, A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C. Magnetite nanoparticles for removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: Synthesis and characterization. Adsorption 2013, 19, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almomani, F.; Bhosale, R.; Khraisheh, M.; Kumar, A.; Almomani, T. Heavy metal ions removal from industrial wastewater using magnetic nanoparticles (MNP). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Abbood, H.A.; He, F.; Peng, H.; Huang, K. Magnetic EDTA-modified chitosan/SiO2/Fe3O4 adsorbent: Preparation, characterization, and application in heavy metal adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.-M.; Man, C.; Hu, Z.-B. Effective removal of Cu (II) ions from aqueous solution by amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, J.; Shafique, U.; Zaman, W.-U.; Salman, M.; Dar, A.; Anwar, S. Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from water by adsorption on peels of banana. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1752–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Balasubramanian, R.; Iyer, C. Evaluation of the marine algae Ulva fasciata and Sargassum sp. for the biosorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsuhybani, M.; Alshahrani, A.; Algamdi, M.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; Alqadami, A.A. Highly efficient removal of Pb(II) from aqueous systems using a new nanocomposite: Adsorption, isotherm, kinetic and mechanism studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erentürk, S.; Malkoç, E. Removal of lead(II) by adsorption onto Viscum album L.: Effect of temperature and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 4727–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predescu, A.; Matei, E.; Berbecaru, A.; Vidu, R. Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewaters. ARA Annu. Congr. Proc. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasherpour, I.; Salahi, E.; Pazouki, M. Comparative of the removal of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ by nano crystallite hydroxyapatite from aqueous solutions: Adsorption isotherm study. Arab. J. Chem. 2012, 5, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, L. Water-soluble Fe3O4 nanoparticles with high solubility for removal of heavy-metal ions from waste water. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 4544–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).