Tests of Strength Parameters of Hydro-Mixtures Based on Ashes from a Fluidized Bed Boiler in the In-Situ Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The possibility of using sludge from coal enrichment installations as fuel;
- Simple preparation of fuel for combustion and simple fuel supply to the combustion chamber;
- Significant (80%) reduction of SO2 emissions to the atmosphere by supplying sulfur-binding compounds to the bed;
- Low nitrogen dioxide emissions due to low temperature of bed (850 °C);
- High combustion efficiency due to turbulent mixing and long residence time of particles in the circulating fluidized bed.
- Long start-up from the cold state due to sizeable ceramic mass (6.5–7 h);
- Much higher air pressure needed for combustion than in pulverized coal boilers, due to higher flow resistance and the need to maintain a fluidized bed.
- A significant range of penetration;
- The smallest possible amount of seepage (excess) water;
- Binding properties and strength properties in the low range;
- Resistance to water (impact of groundwater).
2. Characteristics of the Filled Dog Heading: Materials and Methods
2.1. Filling Process of the Incline
2.2. Sampling Points of the Bound Hydro-Mixture
3. Methodology and Research Results
- Methodology of making fine-fraction hydro-mixtures in laboratory conditions and their testing;
- Methodology of in situ sampling and strength tests carried out in the laboratory.
3.1. Methodology of Making and Testing Hydro-Mixtures in Laboratory Conditions
- The mass ratio of S/W (dry ash/water) and density;
- Amount of excess water;
- Compressive strength;
- Water resistance.
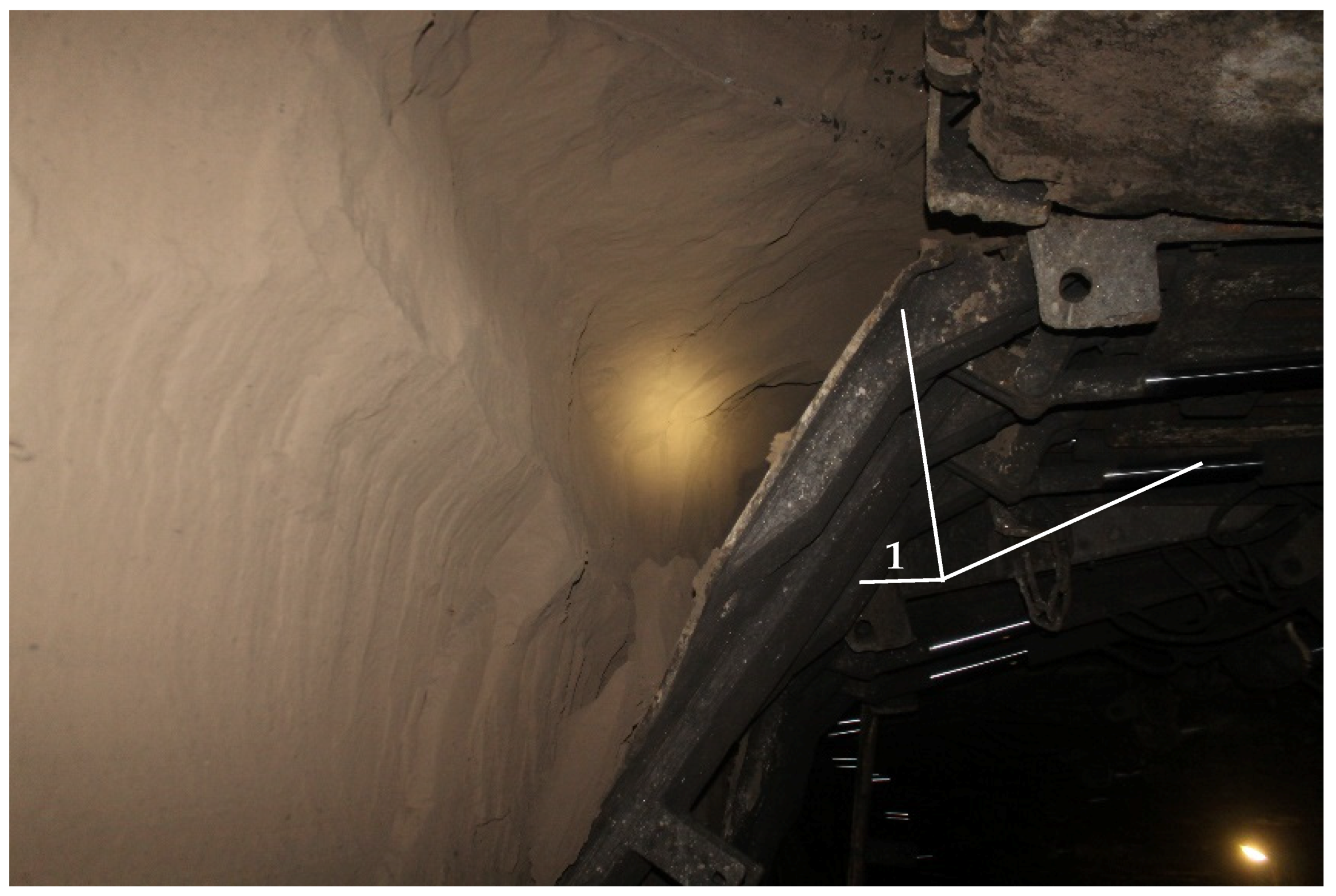
3.2. Methodology of Sampling and In-Situ Testing
4. Discussion
- With the rise of water share in the mixture, its density decreases. In the table spread range from 160 to 260 mm, the density was respectively from 1450 to 1380 kg/m3;
- With the increase of water share in the hydro-mixture, the amount of excess water grows. In the table spread range from 160 to 260 mm, the amount of excess water was 2.5% to 17.6%, respectively;
- With the increase of water content in the hydro-mixture, uniaxial compression strength Rc decreases. As shown in Table 2, after 28 days of seasoning in the table spread range from 160 to 260 mm, the strength drops from 1.08 to 0.68 MPa and after 60 days from 1.35 to 0.84 MPa;
- After 60 days of seasoning in a climatic chamber and after 24-h soaking in water, all tested samples showed a drop in strength. The lowest water-resistance of 5.2% was recorded for the hydro-mixture with the table spread of 160 mm, while the highest water resistance of 15.5% for the hydro-mixture with the table spread of 260 mm.
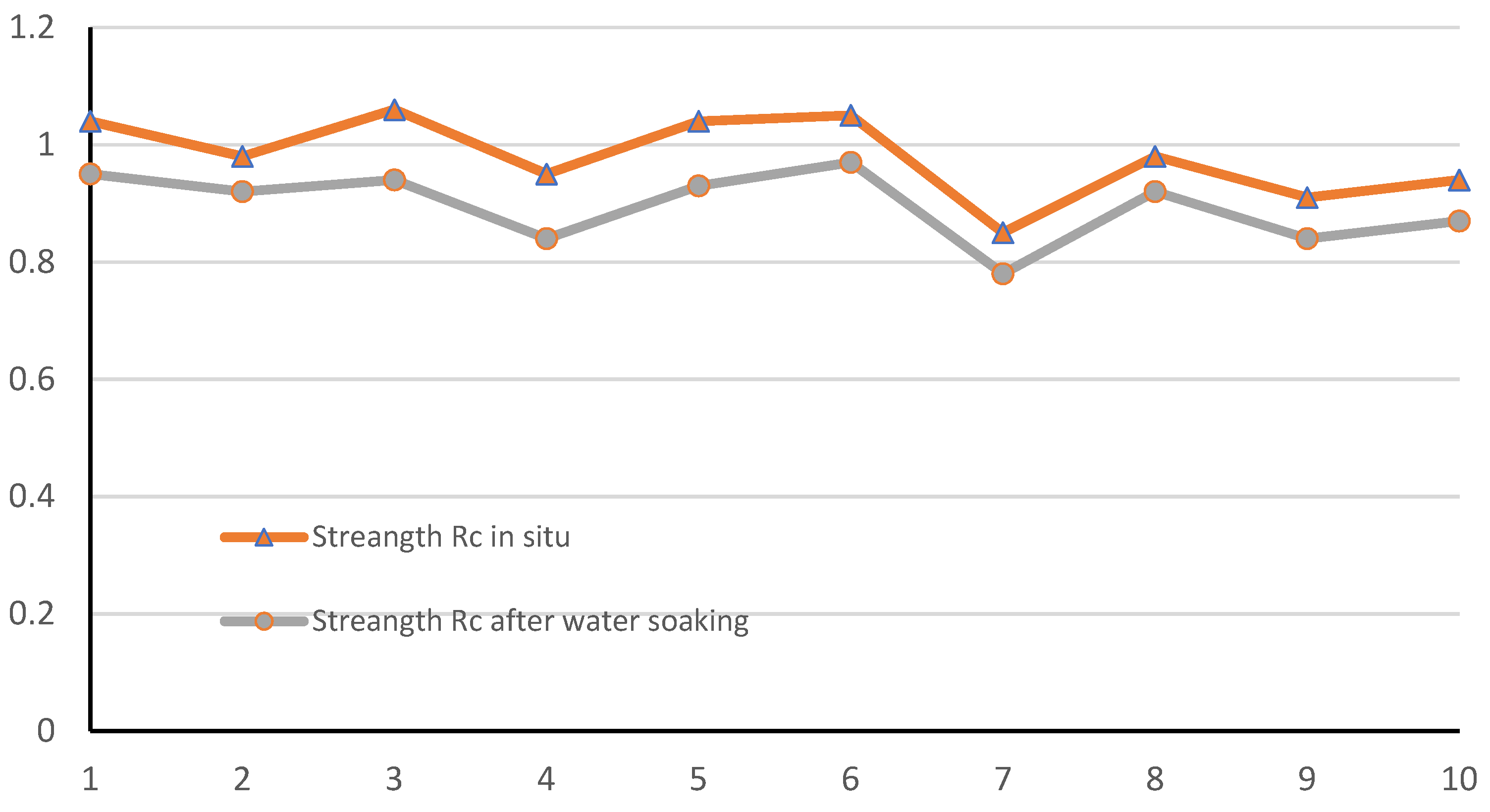
- The uniaxial compressive strength of samples collected in situ 60 days after their placement in the incline ranged from 0.91 to 1.06 MPa;
- The water resistance tests showed that all tested samples were characterized by some loss of strength Rc in the range from 6.1% to 11.6%.
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plewa, F.; Mysłek, Z. Zagospodarowanie Odpadów Przemysłowych w Podziemnych Technologiach Górniczych; Politechniki Śląskiej Poland: Gliwice, Poland, 2001; pp. 107–128. [Google Scholar]
- Plewa, F.; Kleta, H. Zastosowanie odpadów energetycznych do likwidacji wyrobisk górniczych w kopalniach metanowych. Zeszyty Naukowe Pol. Śl. Górnictwo 2001, 250, 120–131. [Google Scholar]
- Plewa, F.; Popczyk, M.; Mysłek, Z. Rodzaj produktów wytwarzanych w energetyce zawodowej i możliwość ich wykorzystania w podziemnych technologiach górniczych. Polityka Energetyczna 2007, 10, 391–402. [Google Scholar]
- ISAP. Rozporządzenie Ministra Środowiska z Dnia 11 Maja 2015r w Sprawie Odzysku lub Unieszkodliwiania Odpadów Poza Instalacjami i Urządzeniami. Polish Government Regulation of the Minister, Dz.U. 2015 poz. 796. Available online: http://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=wdu20150000796 (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- ISAP. Ustawa z Dnia 14 Grudnia 2012r o Odpadach. Polish Government Regulation of the Minister, Dz.U. 2013 poz. 21. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20130000021 (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Polish Standardization Committee. PN-G-11011: 1998—Materiały do Podsadzki Zestalanej i Doszczelniania Zrobów—Wymagania i Badania; Polish Standardization Committee: Warsaw, Poland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- ISAP. Rozporządzenie Ministra Środowiska z Dnia 9 Grudnia 2014r w Sprawie Katalogu Odpadów. Polish Government Regulation of the Minister, Dz.U. 2014 poz; 1923. Available online: http://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20140001923 (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Popczyk, M. Analysis of physico-mechanical properties of hydromixtures prepared based on ashes from fluidized bed boilers regarding possibilities of liquidation of the underground excavations and cavities. Syst. Wspomagania Inżynierii Produkcji. Górnictwo Perspekt. Zagrożenia 2016, 1, 228–238. [Google Scholar]
- Plewa, F.; Popczyk, M.; Piontek, P. Zastosowanie ubocznych produktów spalania z kotłów fluidalnych energetyki zawodowej w podsadzce hydraulicznej. Polityka Energetyczna 2009, 12, 485–495. [Google Scholar]
- Plewa, F.; Popczyk, M. Wyznaczanie wybranych parametrów hydromieszanin wykorzystywanych w technologiach górniczych w funkcji rozlewności. In Proceedings of the Międzynarodowa Konferencja VIII Szkoła Geomechaniki, Ustroń, Poland, 16–19 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Palarski, J. Fill transportation and sedimentation mechanisms for stope filling. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Transport and Sedimentation of Solid Particles, Kraków, Poland, 2–5 September 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Popczyk, M. The impact of changes in the rheological parameters of fine-grained hydromixtures on the efficiency of a selected industrial gravitational hydraulic transport system. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. Bristol Inst. Phys. 2017, 268, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popczyk, M. Optimization of the composition of fly ashwater mixture in terms of minimizing seepage water and the possibility of gravitational hydrotransport into the underground workings. Miner. Resour. Manag. 2018, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popczyk, M. Badania wodorządności hydromieszanin wykonanych na bazie wybranych odpadów energetycznych stosowanych w podziemnych technologiach górniczych. In Bezpieczne i Efektywne Górnictwo Wybrane Zagadnienia; Monograph; Silesian University of Technology Publishing House: Gliwice, Poland, 2020; pp. 130–143. [Google Scholar]
- Popczyk, M. The influence of increased proportion of mixing water in a hydromixture made on the basis of selected energy waste on the gravity performance of a transport installation. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 261, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popczyk, M. Perspective directions of the development of hydrotransport gravity mixers installations in the light of existing industrial solutions. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 174, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| S/W Ratio | Density [kg/m3] | Table Spread [mm] | Amount of Excess Water [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1:0.75 | 1450 | 160 | 2.5 |
| 1:0.85 | 1430 | 180 | 4.5 |
| 1:1.00 | 1420 | 200 | 7.9 |
| 1:1.05 | 1410 | 220 | 10.2 |
| 1:1.12 | 1400 | 240 | 14.3 |
| 1:1.20 | 1380 | 260 | 17.6 |
| Table Spread Value of Hydro-Mixture | Strength Rc [MPa] | Water Resistance k [%] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 days | 14 days | 28 days | 60 days | Rc60 + 24 h Soaking with Water | ||
| 160 | 0.48 | 0.85 | 1.08 | 1.35 | 1.28 | 5.2 |
| 180 | 0.42 | 0.75 | 0.95 | 1.25 | 1.17 | 6.4 |
| 200 | 0.32 | 0.62 | 0.88 | 1.18 | 1.09 | 7.6 |
| 220 | 0.26 | 0.52 | 0.82 | 1.06 | 0.95 | 10.4 |
| 240 | 0.19 | 0.42 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 13.4 |
| 260 | 0.15 | 0.36 | 0.68 | 0.84 | 0.71 | 15.5 |
| Marked Sampling Points | Time of Sample Collection since the Placement of the Mixture [days] | Strength Rc on Average after 60 days [MPa] | Rc60 + 24 h Water Soaking [MPa] | Water Resistance k [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 57 | 1.04 | 0.95 | 8.7 |
| 2 | 57 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 6.1 |
| 3 | 57 | 1.06 | 0.94 | 11.3 |
| 4 | 58 | 0.95 | 0.84 | 11.6 |
| 5 | 58 | 1.04 | 0.93 | 10.6 |
| 6 | 58 | 1.05 | 0.97 | 7.6 |
| 7 | 59 | 0.85 | 0.78 | 8.2 |
| 8 | 59 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 6.1 |
| 9 | 59 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 7.7 |
| 10 | 59 | 0.94 | 0.87 | 7.4 |
| Average | - | 0.98 | - | 8.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popczyk, M. Tests of Strength Parameters of Hydro-Mixtures Based on Ashes from a Fluidized Bed Boiler in the In-Situ Approach. Minerals 2021, 11, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070770
Popczyk M. Tests of Strength Parameters of Hydro-Mixtures Based on Ashes from a Fluidized Bed Boiler in the In-Situ Approach. Minerals. 2021; 11(7):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070770
Chicago/Turabian StylePopczyk, Marcin. 2021. "Tests of Strength Parameters of Hydro-Mixtures Based on Ashes from a Fluidized Bed Boiler in the In-Situ Approach" Minerals 11, no. 7: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070770
APA StylePopczyk, M. (2021). Tests of Strength Parameters of Hydro-Mixtures Based on Ashes from a Fluidized Bed Boiler in the In-Situ Approach. Minerals, 11(7), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070770





