Geochemistry and Geochronology of Early Paleozoic Intrusive Rocks in the Terra Nova Bay Area, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica
Abstract
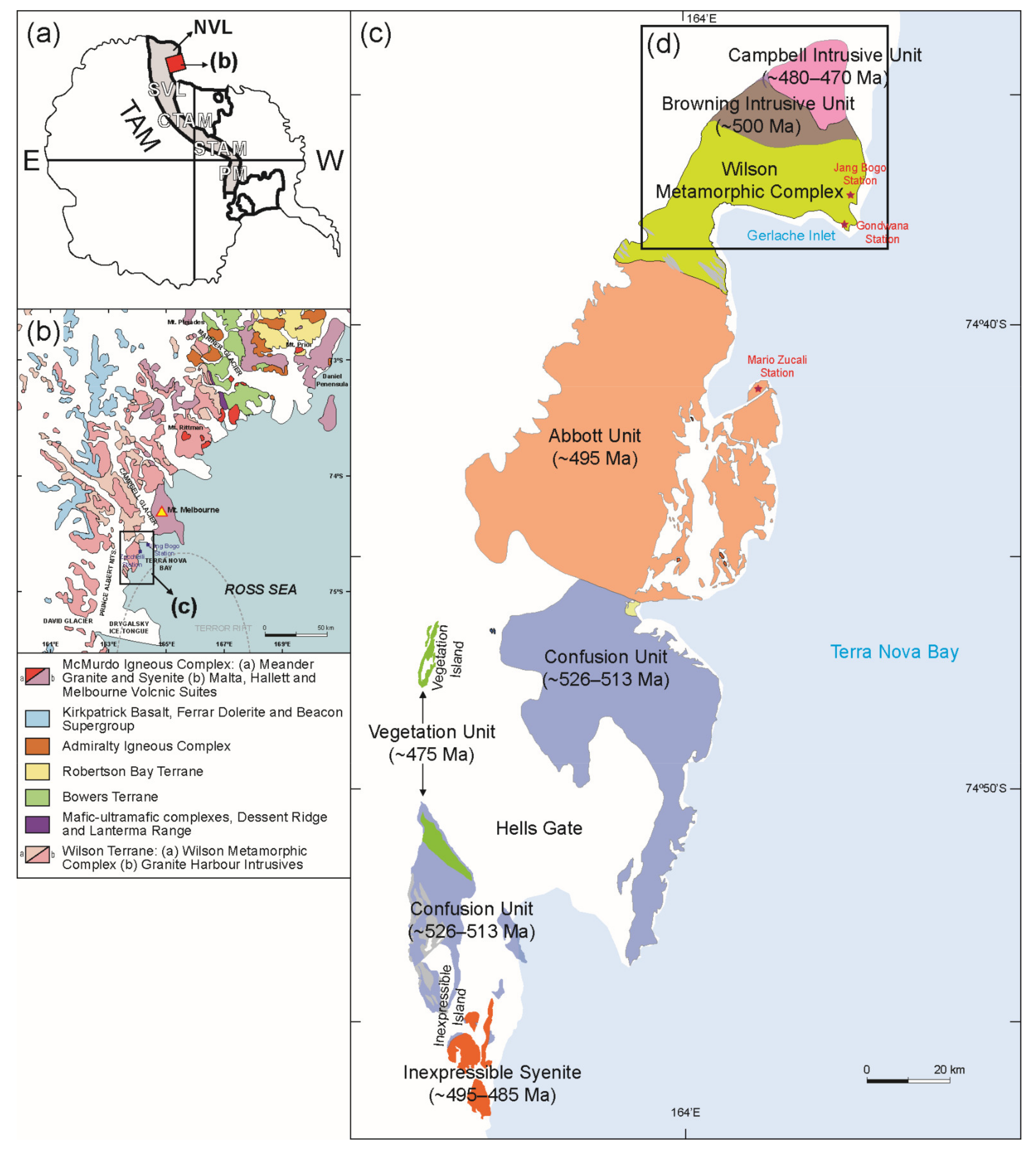
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
3. Field Occurrences and Relationships
3.1. Wilson Metamorphic Complex (Precambrian–Early Cambrian Protoliths)
3.2. Browning Intrusive Unit (Late Cambrian)
3.3. Campbell Intrusive Unit (Early Ordovician)
4. Analytical Methods
5. Results
5.1. U-Pb Geochronology
5.2. Whole-Rock Geochemistry
6. Discussion
6.1. Magma Sources of the BIU–CIU in the TNIC
6.2. Tectonic Environment for the TNIC Magmatism
7. Conclusions
- Two distinct intrusive units are identified in the TNIC. The BIU (Late Cambrian) originates from arc crustal melting, and also is contributed to the migmatization of the WMC. The CIU (Early Ordovician), which comprises later igneous bodies, is attributed to mantle-derived melts intrusions and associated crustal anatexis.
- Gneiss and schist in the WMC exhibit Late Neoproterozoic to Early Paleozoic (Early Cambrian) protolith ages and a metamorphic age of 502 ± 15 Ma. A leucogranite from the BIU reveals the emplacement age of 500 ± 5 Ma which is synchronous with the metamorphism of the WMC. Relatedly, gabbroic diorites and leucogranites from the CIU produce ages of ~480 ± 5 Ma, while biotite granite (later intrusive in the CIU) samples yield igneous ages between ~475–470 Ma.
- Sr-Nd isotopic characteristics of the BIU–CIU display both the Ross orogenic mantle–mafic crust (87Sr/86Sr(500–470 Ma) = 0.7043–0.7049 and εNd(500–470 Ma) = 1.4 to 1.8) and felsic crust (87Sr/86Sr(500–470 Ma) = 0.7189–0.7232 and εNd(500–470 Ma) = −8.7 to −10.8) compositions as well as their mixing combinations.
- The distinct wide range of 87Sr/86Sr(i) and εNd(t) associated with the BIU–CIU are attributed to mantle and mafic crust melting, crustal assimilation, subsequent felsic crust melting, and magma mixing, which are processes typical in continental arcs. These processes well explain the Ross orogenic arc crustal building of the TNIC in NVL.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finn, C.; Moore, D.; Damaske, D.; Mackey, T. Aeromagnetic legacy of early Paleozoic subduction along the Pacific margin of Gondwana. Geology 1999, 27, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godard, G.; Palmeri, R. High-pressure metamorphism in Antarctica from the Proterozoic to the Cenozoic: A review and geodynamic implications. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 844–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, S.D.; Wilson, C.J.L.; Fanning, C.M. Early Paleozoic tectonism within the East Antarctic craton: The final suture between east and west Gondwana? Geology 2001, 29, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meert, J.G. A synopsis of events related to the assembly of eastern Gondwana. Tectonophysics 2003, 362, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, S.D.; Miller, J.M. Terminal suturing of Gondwana and the onset of the Ross–Delamerian Orogeny: The cause and effect of an Early Cambrian reconfiguration of plate motions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 219, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, S.D. Antarctica—Before and after Gondwana. Gondwana Res. 2011, 19, 335–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsvik, T.H.; Cocks, L.R.M. Gondwana from top to base in space and time. Gondwana Res. 2013, 24, 999–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzsimons, I.C.W. A review of tectonic events in the East Antarctic Shield and their implications for Gondwana and earlier supercontinents. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2000, 31, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, S.L. Archaean-Cambrian crustal development of East Antarctica: Metamorphic characteristics and tectonic implications. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2003, 206, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalziel, I.W.D. Overview: Neoproterozoic-Paleozoic geography and tectonics: Review, hypothesis, environmental speculation. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1997, 109, 16–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawood, P.A. Terra Australis Orogen: Rodinia breakup and development of the Pacific and Iapetus margins of Gondwana during the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic. Earth Sci. Rev. 2005, 69, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, G.; Rocchi, S. Origin and interaction of mafic and felsic magmas in an evolving late orogenic setting: The Early Paleozoic Terra Nova Intrusive Complex, Antarctica. Contrib. Mineral. Petr. 1999, 137, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, S.; Di Vincenzo, G.; Ghezzo, C. The Terra Nova Intrusive Complex (Victoria Land, Antarctica); Terra Antarctic Reports; Terra Antarctic Publication: Genova, Italy, 2004; Volume 10, p. 50. [Google Scholar]
- Rocchi, S.; Tonarini, S.; Armienti, P.; Innocenti, F.; Manetti, P. Geochemical and isotopic structure of the early Palaeozoic active margin of Gondwana in northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Tectonophysics 1998, 284, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.I.; Woo, J.; Koh, H.J.; Lee, S.-R. Geologic Map around the Jang Bogo Station, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica 1:20,000; Project Publication of the Korea Polar Research Institute and Ministry of Ocean and Fisheries: Seoul, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Elliot, D.H. The geological and tectonic evolution of the Transantarctic Mountains: A review. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2013, 381, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodge, J.W. Geological and tectonic evolution of the Transantarctic Mountains, from ancient craton to recent enigma. Gondwana Res. 2020, 80, 50–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stump, E. The Ross Orogen of the Transantarctic Mountains; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Armienti, P.; Ghezzo, C.; Innocenti, F.; Manetti, P.; Rocchi, S.; Tonarini, S. Isotope geochemistry and petrology of granitoid suites from Granite Harbour Intrusives of the Wilson Terrane, North Victoria Land, Antarctica. Eur. J. Mineral. 1990, 2, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomparola, R.M.; Ghezzo, C.; Belousova, E.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y. Resetting of the U–Pb Zircon System in Cambro-Ordovician Intrusives of the Deep Freeze Range, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. J. Petrol. 2007, 48, 327–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradshaw, J.D.; Laird, M.G. The pre-Beacon Geology of Northern Victoria Land; Australian Academy of Science: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, S.D.; Bradshaw, J.D.; Laird, M.G. Geochemistry of Cambrian volcanics of the Bowers Supergroup and implications for the Early Palaeozoic tectonic evolution of northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 68, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y. Constraints on early Paleozoic magmatic processes and tectonic setting of Inexpressible Island, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Adv. Polar Sci. 2019, 30, 52–69. [Google Scholar]
- Peccerillo, A.; Taylor, S.R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1976, 58, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagini, R.; Cappelli, B.; Di Vincenzo, G. P-T Estimates of the Mt. Abbott Intrusives and Enclosed Metamorphic “Septa” at Terra Nova Bay (North Victoria Land, Antarctica); Vulcanismo Potassico: Ischia, Italy, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo, B.; Cappelli, B.; Carmignani, L.; Gosso, G.; Memmi, I.; Montrasio, A.; Palmeri, R.; Pannuti, F.; Pertusati, P.C.; Ricci, C.A.; et al. The metamorphic rocks of the Wilson Terrane between David and Mariner Glaciers, North Victoria Land, Antarctica. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1987, 33, 99–130. [Google Scholar]
- Palmeri, R. P-T paths and migmatite formation: An example from Deep Freeze Range, northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Lithos 1997, 42, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Park, M.; Park, Y.; Qi, C.; Kim, H.; Lee, M.J.; Michibayashi, K. Upper mantle seismic anisotropy beneath the Northern Transantarctic Mountains inferred from peridotite xenoliths near Mt. Melbourne, northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. J. Struct. Geol. 2021, 143, 104237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GANOVEX. Geological Map of North Victoria Land, Antarctica, 1:500,000-Explanetory Notes; GANOVEX III; Geologisches Jahrbuch: Hannover, Germany, 1987; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Pertusati, P.C.; Musumeci, G.; Colombo, F.; Meccheri, M.; Baroni, C.; Capponi, G.; Carmignani, L.; Castelli, D.; Colombo, F.; Crispini, L.; et al. Mount Melbourne Quadrangle (Victoria Land), Geological 1:250,000 Map Series; GIGAMAP, Pertusati, P.C., Tessenshon, F.C., Eds.; Museo Nazionale Dell’Antartide: Siena, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Capponi, G.; Castelli, D.; Fioretti, A.M.; Oggiano, G. Geological Mapping and Field Relationships of the Eclogites from the Lanterman Range, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica; Terra Antarctica Publications: Siena, Italy, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paces, J.B.; Miller, J.D., Jr. Precise U-Pb ages of Duluth Complex and related mafic intrusions, northeastern Minnesota: Geochronological insights to physical, petrogenetic, paleomagnetic, and tectonomagmatic processes associated with the 1.1 Ga Midcontinent Rift System. J. Geophys. Res. Sol. Earth 1993, 98, 13997–14013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, M.; Allé, P.; Corfu, F.; Griffin, W.L.; Meier, M.; Oberli, F.; Quadt, A.V.; Roddick, J.C.; Spiegel, W. Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace element and REE analyses. Geostand. Newsl. 1995, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, T.R.; Williams, I.S. Considerations in Zircon Geochronology by SIMS; Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry; Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 2003; Volume 53. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, K.R. User’s Manual for SQUID 2; Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, K.R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.6: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel; Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kuno, H. Lateral variation of basalt magma type across continental margins and Island Arcs. Bull. Volcanol. 1966, 29, 195–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, T.N.; Baragar, W.R.A. A Guide to the Chemical Classification of the Common Volcanic Rocks. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1971, 8, 523–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, G.A.; Katsura, T. Chemical Composition of Hawaiian Lavas. J. Petrol. 1964, 5, 82–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, G.A. Composition and Origin of Hawaiian Lavas. In Studies in Volcanology; Coats, R.R., Hay, R.L., Anderson, C.A., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1968; Volume 116. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, D.A. The application of a Th-Hf-Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary Volcanic Province. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1980, 50, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J. Sources and settings of granitic rocks. Int. Union Geol. Sci. 1996, 19, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, T. The Chemical Composition of Subducting Sediments; Elsevier-Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the Continental Crust; Elsevier-Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserburg, G.J.; Jacobsen, S.B.; DePaolo, D.J.; McCulloch, M.T.; Wen, T. Precise determination of Sm/Nd ratios, Sm and Nd isotopic abundances in standard solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1981, 45, 2311–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePaolo, D.J. Neodymium Isotope Geochemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, G. Origin of Igneous Rocks: The Isotopic Evidence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Steiger, R.H.; Jäger, E. Subcommission on geochronology: Convention on the use of decay constants in geo- and cosmochronology. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1977, 36, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begemann, F.; Ludwig, K.R.; Lugmair, G.W.; Min, K.; Nyquist, L.E.; Patchett, P.J.; Renne, P.R.; Shih, C.Y.; Villa, I.M.; Walker, R.J. Call for an improved set of decay constants for geochronological use. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, T.; Plank, T.; Zindler, A.; White, W.; Bourdon, B. Element transport from slab to volcanic front at the Mariana arc. J. Geophys. Res. Sol. Earth 1997, 102, 14991–15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesworth, C.J.; Turner, S.P.; McDermott, F.; Peate, D.W.; van Calsteren, P. U-Th Isotopes in Arc Magmas: Implications for Element Transfer from the Subducted Crust. Science 1997, 276, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spandler, C.; Pirard, C. Element recycling from subducting slabs to arc crust: A review. Lithos 2013, 170, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-F. Subduction zone geochemistry. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1223–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, P.B.; Hanghøj, K.; Greene, A.R. One View of the Geochemistry of Subduction-Related Magmatic Arc, with an Emphasis on Primitive Andesite and Lower Crust; Elsevier-Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.C.; Plank, T. Dehydration and melting experiments constrain the fate of subducted sediments. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2000, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, M.T.; Jaques, A.L.; Nelson, D.R.; Lewis, J.D. Nd and Sr isotopes in kimberlites and lamproites from Western Australia: An enriched mantle origin. Nature 1983, 302, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, K.J.; Hawkesworth, C.J.; Erlank, A.J.; Mitchell, R.H.; Scott-Smith, B.H. Sr, Nd and Pb isotope and minor element geochemistry of lamproites and kimberlites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1985, 76, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conticelli, S.; Peccerillo, A. Petrology and geochemistry of potassic and ultrapotassic volcanism in central Italy: Petrogenesis and inferences on the evolution of the mantle sources. Lithos 1992, 28, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F. Temporal and spatial distribution of Mesozoic mafic magmatism in the North China Craton and implications for secular lithospheric evolution. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2007, 280, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pe-Piper, G.; Zhang, Y.; Piper, D.J.W.; Prelević, D. Relationship of Mediterranean type lamproites to large shoshonite volcanoes, Miocene of Lesbos, NE Aegean Sea. Lithos 2014, 184–187, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.-B.; Oh, C.W.; Lee, S.-Y.; Choi, S.-G.; Kim, T.; Yi, K. Triassic mafic and intermediate magmatism associated with continental collision between the North and South China Cratons in the Korean Peninsula. Lithos 2016, 246, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.M.; Abbruzzi, J.M. Magmatic evidence for Neogene lithospheric evolution of the central Andean “flat-slab” between 30°S and 32°S. Tectonophysics 1996, 259, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.B.; Ducea, M.N.; Kapp, P.; Gehrels, G.E.; DeCelles, P.G. Spatial and temporal radiogenic isotopic trends of magmatism in Cordilleran orogens. Gondwana Res. 2017, 48, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wodzicki, A.; Robert Jr, R. Geology of the Bowers Supergroup, Central Bowers Mountains, Northern Victoria Land. Geol. Investig. North. Vic. Land 1986, 39–68. [Google Scholar]
- Borg, S.G.; Stump, E.; Chappell, B.W.; McCulloch, M.T.; Wyborn, D.; Armstrong, R.L.; Holloway, J.R. Granitoids of northern Victoria Land, Antarctica; implications of chemical and isotopic variations to regional crustal structure and tectonics. Am. J. Sci. 1987, 287, 127–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.M.; Wright, T.O. Importance of thrust faulting in the tectonic development of northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Nature 1985, 315, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.O.; Ross, R.J., Jr.; Repetski, J.E. Newly discovered youngest Cambrian or oldest Ordovician fossils from the Robertson Bay terrane (formerly Precambrian), northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Geology 1984, 12, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt, G.; Tessensohn, F. Early Paleozoic Westward Directed Subduction at the Pacific Margin of Antartica. In Gondwana Six: Structure, Tectonics, and Geophysics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987; pp. 89–105. [Google Scholar]
- Federico, L.; Crispini, L.; Capponi, G.; Bradshaw, J.D. The Cambrian Ross Orogeny in northern Victoria Land (Antarctica) and New Zealand: A synthesis. Gondwana Res. 2009, 15, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, L.; Capponi, G.; Crispini, L. The Ross orogeny of the transantarctic mountains: A northern Victoria Land perspective. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2006, 95, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, S.; Bracciali, L.; Di Vincenzo, G.; Gemelli, M.; Ghezzo, C. Arc accretion to the early Paleozoic Antarctic margin of Gondwana in Victoria Land. Gondwana Res. 2011, 19, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, G.; Horton, F.; Palmeri, R. Protracted (~30Ma) eclogite-facies metamorphism in northern Victoria Land (Antarctica): Implications for the geodynamics of the Ross/Delamerian Orogen. Gondwana Res. 2016, 40, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, Y.; Cho, M.; Lee, J.I. P–T evolution and episodic zircon growth in barroisite eclogites of the Lanterman Range, northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2019, 37, 509–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, T.; Lee, J.I.; Kim, S.J. SHRIMP U-Pb ages of zircon from banded gneisses and a leucocratic dyke in the Wilson Terrane, northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2017, 53, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.-B.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, J.I.; Kim, H. Timing and metamorphic evolution of the Ross Orogeny in and around the Mountaineer Range, northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Minerals 2020, 10, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, S.; Di Vincenzo, G.; Dini, A.; Petrelli, M.; Vezzoni, S. Time–space focused intrusion of genetically unrelated arc magmas in the early Paleozoic Ross–Delamerian Orogen (Morozumi Range, Antarctica). Lithos 2015, 232, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen-Peter, G.; Cottle, J.M.; Smit, M.; Cooper, A.F. Coupled garnet Lu–Hf and monazite U–Pb geochronology constrain early convergent margin dynamics in the Ross orogen, Antarctica. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2016, 34, 293–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Rock Type | Lithologic Unit | 87Rb/86Sr | 87Sr/86Sr | 2σ | 87Sr/86Sr(i) | 147Sm/144Nd | 143Nd/144Nd | 2σ | 143Nd/144Nd(i) | εNd(t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J-43-5 | Biotite granite | CIU | 1.80495 | 0.717245 | 0.000012 | 0.705158 | 0.10093 | 0.512138 | 0.000007 | 0.511827 | −4.01 |
| J-44-1 | 0.41780 | 0.707084 | 0.000009 | 0.704286 | 0.09378 | 0.512393 | 0.000007 | 0.512104 | 1.40 | ||
| J-45-1 | Gabbroic diorites | CIU | 0.21733 | 0.706200 | 0.000009 | 0.704714 | 0.11081 | 0.512449 | 0.000006 | 0.512101 | 1.58 |
| J-46-1 | 0.79927 | 0.715014 | 0.000008 | 0.709548 | 0.12345 | 0.512024 | 0.000007 | 0.511636 | −7.49 | ||
| J-57 | 0.26677 | 0.705749 | 0.000010 | 0.704900 | 0.09269 | 0.512401 | 0.000008 | 0.512110 | 1.76 | ||
| J-58 | Foliated porphyritic granite | BIU | 2.70148 | 0.732299 | 0.000010 | 0.713050 | 0.11659 | 0.511921 | 0.000007 | 0.511539 | −8.88 |
| J-7-3 | Leucogranite | BIU–CIU | 1.50378 | 0.719052 | 0.000009 | 0.708767 | 0.11344 | 0.512045 | 0.000006 | 0.511688 | −6.47 |
| J-12-2 | 1.72002 | 0.735458 | 0.000010 | 0.723202 | 0.16922 | 0.512104 | 0.000012 | 0.511550 | −8.67 | ||
| J-26-2 | Migmatitic gneiss | WMC | 2.75044 | 0.738528 | 0.000009 | 0.718930 | 0.10899 | 0.511811 | 0.000007 | 0.511454 | −10.54 |
| J-28 | 2.29805 | 0.736266 | 0.000010 | 0.719892 | 0.11170 | 0.511808 | 0.000007 | 0.511442 | −10.77 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.; Yi, S.-B.; Kim, H.; Kim, T.; Kim, T.; Lee, J.I. Geochemistry and Geochronology of Early Paleozoic Intrusive Rocks in the Terra Nova Bay Area, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Minerals 2021, 11, 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070787
Kim D, Yi S-B, Kim H, Kim T, Kim T, Lee JI. Geochemistry and Geochronology of Early Paleozoic Intrusive Rocks in the Terra Nova Bay Area, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Minerals. 2021; 11(7):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070787
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Daeyeong, Sang-Bong Yi, Hyeoncheol Kim, Taehwan Kim, Taehoon Kim, and Jong Ik Lee. 2021. "Geochemistry and Geochronology of Early Paleozoic Intrusive Rocks in the Terra Nova Bay Area, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica" Minerals 11, no. 7: 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070787
APA StyleKim, D., Yi, S.-B., Kim, H., Kim, T., Kim, T., & Lee, J. I. (2021). Geochemistry and Geochronology of Early Paleozoic Intrusive Rocks in the Terra Nova Bay Area, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Minerals, 11(7), 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070787








