Recovery of Palladium and Gold from PGM Ore and Concentrate Leachates Using Fe3O4@SiO2@Mg-Al-LDH Nanocomposite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instrumentation
2.2. Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2@Mg–Al LDH Nanocomposite
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Extraction and Recovery of Au(III) and Pd(II) from Synthetic Samples
2.4.1. Selection of Eluent Type
2.4.2. Optimization Using Central Composite Design (CCD)
2.5. Determination of Adsorption Capacity
2.6. Regeneration and Reusability Studies
2.7. Effect of Interfering Ions
2.8. Application to Real Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Adsorbents
3.1.1. Powder X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis of Fe3O4@SiO2@Mg–Al-LDH
3.1.2. Structural and Morphological Properties of the Composite
3.1.3. Surface Area and Pore Sizes Analysis
3.1.4. Zeta Potential of Fe3O4@SiO2@Mg–Al-LDH Nanocomposite
3.2. Extraction and Recovery of Au(III) and Pd(II) from Synthetic Samples
3.2.1. Selection of Eluent Type
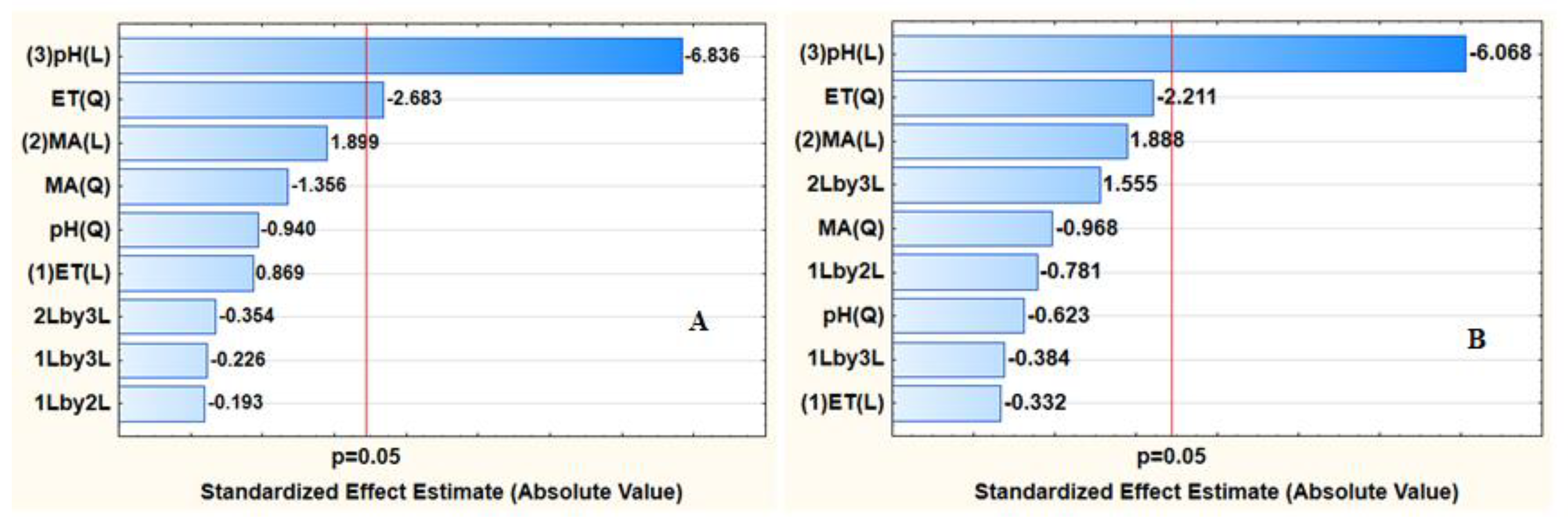
3.2.2. Optimization Using Central Composite Design (CCD)
Statistical Analysis
Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
3.3. Determination of Adsorption of Capacity
3.4. Regeneration and Reusability Studies
3.5. Analytical Figures of Merit
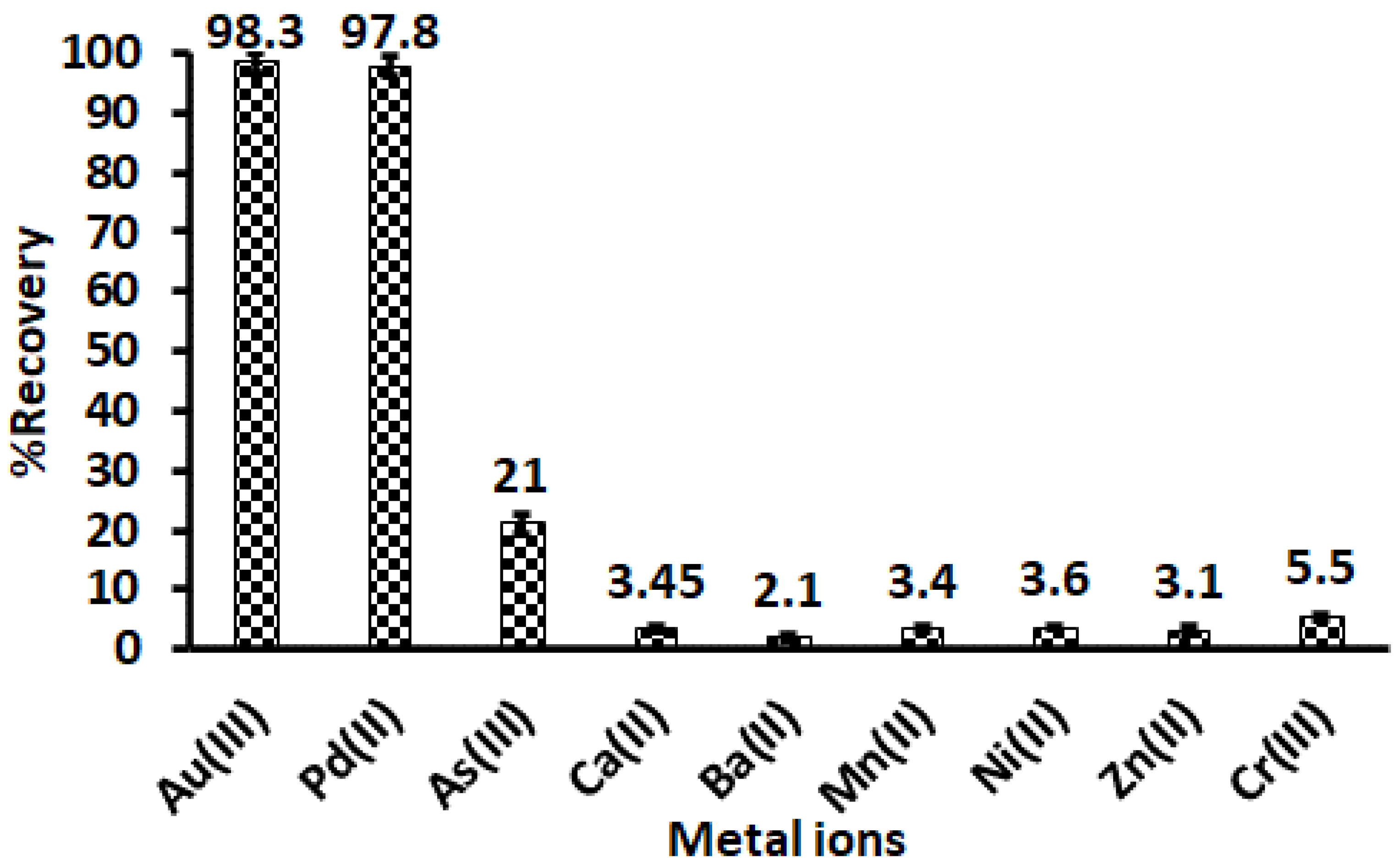
3.6. Effect of Interfering Ions
3.7. Application to Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mpinga, C.N.; Eksteen, J.J.; Aldrich, C.; Dyer, L. Direct leach approaches to Platinum Group Metal (PGM) ores and concentrates: A review. Miner. Eng. 2015, 78, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, E.; Alorro, R.D.; Encila, A.N.; Yoo, K. Magnetic adsorbents for the recovery of precious metals from leach solutions and wastewater. Metals 2017, 7, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jainae, K.; Sanuwong, K.; Nuangjamnong, J.; Sukpirom, N.; Unob, F. Extraction and recovery of precious metal ions in wastewater by polystyrene-coated magnetic particles functionalized with 2-(3-(2-aminoethylthio)propylthio)ethanamine. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzelewska-Piekut, M.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Separation of Pt(IV), Pd(II), Ru(III) and Rh(III) from model chloride solutions by liquid-liquid extraction with phosphonium ionic liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, T.H.; Ouchi, T. Recycling of Critical Metals BT—REWAS 2019; Gaustad, G., Fleuriault, C., Gökelma, M., Howarter, J.A., Kirchain, R., Ma, K., Meskers, C., Neelameggham, N.R., Olivetti, E., Powell, A.C., et al., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Komendova, R. Recent advances in the preconcentration and determination of platinum group metals in environmental and biological samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, J.R.; Parker, H.L.; Muñoz García, A.; Hicken, A.; Asemave, K.; Farmer, T.J.; He, H.; Clark, J.H.; Hunt, A.J. Bio-derived materials as a green route for precious & critical metal recovery and re-use. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1951–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.-J.; Yu, H.; Hong, S.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Park, M.S.; Jeong, H.S. Modified tunicate nanocellulose liquid crystalline fiber as closed loop for recycling platinum-group metals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 228, 115424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, B.; Chopin, E.I.B.; Jupinet, B.; Gauthier, D. Comparison of microwave-assisted digestion procedures for total trace element content determination in calcareous soils. Talanta 2008, 77, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.K.; Hassan, H.M.A.; Shahat, A.; Awual, M.R.; Kamel, R.M. A ligand-based conjugate solid sensor for colorimetric ultra-trace gold (III) detection in urban mining waste. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 581, 123842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Gandhi, M.R.; Shibayama, A. Rapid and selective recovery of palladium from platinum group metals and base metals using a thioamide-modified calix[4]arene extractant in environmentally friendly hydrocarbon fluids. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, B. International Journal of Mineral Processing Recovery of platinum group metals from spent catalysts: A review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 145, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Ting, Y.-P. Ultrasound-assisted nitric acid pretreatment for enhanced biorecovery of platinum group metals from spent automotive catalyst. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, C.B.; Rojas, F.S.; Pavón, J.M.C. On-line preconcentration of palladium (II) using a microcolumn packed with a chelating resin, and its subsequent determination by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchim. Acta 2007, 158, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Ramezani, M. Selective determination of ultra trace amounts of gold by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after dispersive liquid--liquid microextraction. Talanta 2008, 75, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Song, N.; Lv, X.; Jia, Q. Magnetic dual task-specific polymeric ionic liquid nanoparticles for preconcentration and determination of gold, palladium and platinum prior to their quantitation by graphite furnace AAS. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3497–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, Y.; Miguel, O.; Rivera-Borroto, J.M.G.D.; la Vega, J.B.D.L.; Torre, I. Determination of Gold in Geological Samples Combining the Fire Assay and Ultraviolet Visible Spectrophotometry Techniques. Acad. J. Sci. Res. 2018, 6, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Jalilian, N.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Molaei, K. Extraction and determination of trace amounts of gold (III), palladium (II), platinum (II) and silver (I) with the aid of a magnetic nanosorbent made from Fe3O4-decorated and silica-coated graphene oxide modified with a polypyrrole-polythiophene copolymer. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Rahman, I.M.M.; Miyaguchi, M.; Mashio, A.S.; Maki, T.; Hasegawa, H. On-site analysis of gold, palladium, or platinum in acidic aqueous matrix using liquid electrode plasma-optical emission spectrometry combined with ion-selective preconcentration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, L.; Yamini, Y.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Nezhadali, A.; Shariati, S.; Nourmohammadian, F. Development of cloud point extraction for simultaneous extraction and determination of gold and palladium using ICP-OES. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenova, E.; Karadjova, I.; Tsalev, D.L. Solid-phase extraction in the determination of gold, palladium, and platinum. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 1249–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, E.J.; dos, S.; do Amaral, C.D.B.; Nagata, N.; Grassi, M.T. Cloud point extractors for simultaneous determination of Pd and Pt in water samples by ICP OES with multivariate optimisation. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulbur-Alfakhoury, E.; Leermakers, M. Elimination of interferences in the determination of platinum, palladium and rhodium by diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP MS) using selective elution. Talanta 2020, 223, 121771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayatian, G.; Sharifi, K. Development of a dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method for determination of palladium in water samples using dicyclohexano-18- crown-6 as extracting agent. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2014, 79, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, C.; Saçmacı, Ş.; Kartal, Ş.; Saçmacı, M. Determination of gold and palladium in environmental samples by FAAS after dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction pretreatment. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 4059–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokya, T.A.; Farhadi, K. Optimization of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the selective determination of trace amounts of palladium by flame atomic absorption spectroscopy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Lu, S.; Chang, X.; Li, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tian, H. Selective solid-phase extraction and separation of trace gold, palladium and platinum using activated carbon modified with ethyl-3-(2-aminoethylamino)-2-chlorobut-2-enoate. Microchim. Acta 2011, 173, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, A.R.M.; Alorro, R.D.; Tadesse, B.; Yoo, K.; Tabelin, C.B. Repurposing of nickeliferous pyrrhotite from mine tailings as magnetic adsorbent for the recovery of gold from chloride solution. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, E.; Yamini, Y. Polythiophene-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a selective adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of silver(I), gold(III), copper(II) and palladium(II). Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyestani, M.R.; Shemirani, F.; Mozaffari, S.; Alvand, M. A magnetized graphene oxide modified with 2-mercaptobenzothiazole as a selective nanosorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction of gold (III), palladium (II) and silver (I). Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2871–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugushe, A.S.; Mpupa, A.; Nomngongo, P.N. Ultrasound-assisted magnetic solid phase extraction of lead and thallium in complex environmental samples using magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes/zeolite nanocomposite. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 103960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biata, N.R.; Jakavula, S.; Mashile, G.P.; Nqombolo, A.; Moutloali, R.M.; Nomngongo, P.N. Recovery of gold (III) and iridium (IV) using magnetic layered double hydroxide (Fe3O4/Mg-Al-LDH) nanocomposite: Equilibrium studies and application to real samples. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 197, 105447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Fei, W.; Gu, Z. Different morphologies of SiO2@Mg-Al-LDH nanocomposites as catalyst for the synthesis of propylene glycol methyl ether. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Du, N.; Zhang, R.; Hou, W. Mechanochemical synthesis of Fe3O4@(Mg-Al-OH LDH) magnetic composite. Powder Technol. 2012, 228, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munonde, T.S.; Maxakato, N.W.; Nomngongo, P.N. Preconcentration and speciation of chromium species using ICP-OES after ultrasound-assisted magnetic solid phase extraction with an amino-modified magnetic nanocomposite prepared from Fe3O4, MnO2 and Al2O3. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, P.; Tang, Z.; Niu, H.; Cai, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, H.; Meng, W.; Giesy, J.P. Surfactant-modified flowerlike layered double hydroxide-coated magnetic nanoparticles for preconcentration of phthalate esters from environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1414, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, D.; Tantai, X.; Jiang, B.; Sun, Y.; Yang, N. Synthesis of Three-Dimensional Hierarchical Flower-Like Mg–Al Layered Double Hydroxides with Excellent Adsorption Performance for Organic Anionic Dyes. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandan, A.; Ozada, N. Bredigite-Magnetite (Ca7MgSi4O16-Fe3O4) nanoparticles: A study on their magnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 726, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munonde, T.S.; Maxakato, N.W.; Nomngongo, P.N. Preparation of magnetic Fe3O4 nanocomposites modified with MnO2, Al2O3, Au and their application for preconcentration of arsenic in river water samples. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wu, J.; Tian, R.; Jiang, W. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic mesoporous core–shell nanocomposites for targeted drug delivery applications. J. Porous Mater. 2017, 24, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Das, A.; Stöckelhuber, K.W.; Wagenknecht, U.; Heinrich, G. Advances in layered double hydroxide (LDH)-based elastomer composites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 594–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi Moaser, A.; Khoshnavazi, R. Facile synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4@MgAl-LDH@STPOM nanocomposites for highly enhanced and selective degradation of methylene blue. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 9472–9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nqombolo, A.; Mpupa, A.; Gugushe, A.S.; Moutloali, R.M.; Nomngongo, P.N. Adsorptive removal of lead from acid mine drainage using cobalt-methylimidazolate framework as an adsorbent: Kinetics, isotherm, and regeneration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3330–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rio, E.; Gaona, D.; Hernández-Garrido, J.C.; Calvino, J.J.; Basallote, M.G.; Fernández-Trujillo, M.J.; Pérez-Omil, J.A.; Gatica, J.M. Speciation-controlled incipient wetness impregnation: A rational synthetic approach to prepare sub-nanosized and highly active ceria--zirconia supported gold catalysts. J. Catal. 2014, 318, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saman, N.; Rashid, M.U.; Lye, J.W.P.; Mat, H. Recovery of Au(III) from an aqueous solution by aminopropyltriethoxysilane-functionalized lignocellulosic based adsorbents. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 123, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Min, H.; Hong, X.; Yi, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Z. Plant tannin immobilized Fe3O4@SiO2 microspheres: A novel and green magnetic bio-sorbent with superior adsorption capacities for gold and palladium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachel, S.R.; Klein, B.P.; Morbec, J.M.; Schöniger, M.; Hutter, M.; Schmid, M.; Kratzer, P.; Meyer, B.; Tonner, R.; Gottfried, J.M. Chemisorption and Physisorption at the Metal/Organic Interface: Bond Energies of Naphthalene and Azulene on Coinage Metal Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 8257–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, E.S.; Dashtian, K.; Ghaedi, M. Fe3O4-FeMoS4: Promise magnetite LDH-based adsorbent for simultaneous removal of Pb (II), Cd (II), and Cu (II) heavy metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, S.; Shao, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, D. Amino-functionalized Fe3O4@ SiO2 core--shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 349, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziarz, P.; Matusik, J.; Strkaczek, T.; Kapusta, C.; Woch, W.M.; Tokarz, W.; Radziszewska, A.; Leiviskä, T. Highly effective magnet-responsive LDH-Fe oxide composite adsorbents for As (V) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komendova, R. The HR-CS-GF-AAS determination and preconcentration of palladium in contaminated urban areas, especially in lichens. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojoudi, H.; Badiei, A.; Banaei, A.; Bahar, S.; Karimi, S.; Mohammadi Ziarani, G.; Ganjali, M.R. Extraction of gold, palladium and silver ions using organically modified silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles and silica gel as a sorbent. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3859–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrowolski, R.; Mróz, A.; Dąbrowska, M.; Olszański, P. Solid sampling high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for gold determination in geological samples after preconcentration onto carbon nanotubes. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2017, 132, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadir, Z.; Bulut, V.N.; Bektaş, H.; Soylak, M. A sensitive method for the determination of gold and palladium based on dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination using N-(6-morpholin-4-ylpyridin-3-yl)-N′-phenylthiourea. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 6896–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameters | Lower Level (−) | Central Point (0) | Higher Level (+) |
|---|---|---|---|
| mass of adsorbent (mg) | 50 | 125 | 200 |
| extraction time (min) | 5.0 | 17.5 | 30 |
| pH | 2.0 | 5.5 | 9.0 |
| Adsorbent | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4 | 85.1 | 0.107 | 4.20 |
| Fe3O4@SiO2 | 235 | 0.149 | 5.75 |
| Mg–Al-LDH | 93.4 | 0.357 | 6.34 |
| Fe3O4@SiO2@Mg–Al-LDH | 220 | 0.294 | 7.85 |
| Isotherm & Equation | Description | Parameters | Au(III) | Pd(II) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe (experimental) | 288 | 312 | ||
| Langmuir | Qmax (mg mg−1) | 289 | 313 | |
| qmax: maximum monolayer adsorption capacity, mg g−1, KL: Langmuir constant, L mg−1 and Ce: concentration of the target analyte at equilibrium, mg L−1 | KL (L·mg−1) | 0.37 | 0.32 | |
| R2 | 0.9924 | 0.9907 | ||
| RL | 0.23–0.73 | 0.25–0.766 | ||
| Freundlich | n | 1.33 | 1.4 | |
| where qe is the target analyte adsorbed at equilibrium (mg g−1), Kf and n are Freundlich constants including the factors affecting the adsorption capacity and adsorption intensity respectively | KF (L·mg−1) | 87.8 | 107 | |
| R2 | 0.9882 | 0.9429 | ||
| Temkin | BT | 122 | 144 | |
| where qe is the amount of adsorbate adsorbed at equilibrium (mg g−1); Ce is the concentration of adsorbate in solution at equilibrium (mg L−1)). B is a constant related to the heat of adsorption and A is the Temkin isotherm constant (L g−1)) | KT (L mg−1) | 2.14 | 2.03 | |
| R2 | 0.9538 | 0.8823 | ||
| Dubinin-Radushkevich | Qs (mg g−1) | 292 | 302 | |
| | where qe is the amount of target analyte adsorbed at equilibrium (mg g−1)), qs is the maximum adsorption capacity, β is the activity coefficient useful in obtaining the mean sorption energy E (kJ mol−1) and ε is the Polanyi potential. | β (×10−9) | −1.0 | −1.2 |
| E (kJ mol−1) | 22.4 | 20.4 | ||
| R2 | 0.9779 | 0.9256 |
| Deionised Water | Real Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | Pd | Au | Pd | ||
| Linearity (µg L−1) | 0.4–500 | 0.5–550 | Linearity (µg g−1) | 0.7–450 | 1.0–500 |
| R2 | 0.9989 | 0.9969 | R2 | 0.9912 | 0.9923 |
| LOD (µg L−1) | 0.10 | 0.13 | LOD (µg g−1) | 0.21 | 0.27 |
| LOQ (µg L−1) | 0.34 | 0.45 | LOQ (µg g−1) | 0.68 | 0.90 |
| Intraday (%RSD) | 1.3 | 1.6 | Intraday (%) | 2.3 | 2.5 |
| Interday (%RSD) | 3.5 | 4.3 | Interday (%) | 4.7 | 5.1 |
| PF | 55.0 | 46.6 |
| Analyte | Adsorbent | Detection Techniques | LOD (μg L−1) | PF | %RSD | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au, Pd, Pt | LEP-OES | 0.8, 3.1, 57.3 | 250 | ≤5 | [19] | |
| Au(III), Pd(II) and Pt(IV) | Fe3O4@SiO2@MPS | graphite furnace AAS | 0.197, 0.223 and 1.070 | 197, 174 and 168 | 2.1, 1.4 and 1.5 | [16] |
| Pd | C18 modified silica | HR-CS-GF-AAS | 1.110 | 100 | 1.5 | [51] |
| Au3+, Pd2+ and Ag+ | mag-GO@MBT/SDS NPs | ICP-OES | 0.045–0.076 | 160, 160 and 140 | 3.1 | [30] |
| Au(III), Pd(II) and Ag(I) | 2,3-Bis(2-formylphenoxy)-propan-1-ol | FAAS | 0.12, 0.28 and 0.17 | - | - | [52] |
| Au(III) | CNT | HR CS GF AAS | 2.24 | 264 | 8 | [53] |
| Au(III) and Pd(II) | N-(6-morpholin-4-ylpyridin-3-yl)-N′-phenylthiourea | 1.75 and 1.65 μg L−1 | 2.8 | [54] | ||
| Au(III) and Pd(II) | Fe3O4@SiO2@Mg–Al-LDH | ICP-OES | 0.10–0.13 | 47–55 | 2.3–5.1 | This work |
| Au(III) | Pd(II) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Certified value | Recovered | %R | Certified value | Recovered | %R | |
| SARM 186 | 2.58 ± 0.8 | 2.21 ± 0.15 | 85.6 | 28.1 ± 1.4 | 28.0 ± 0.22 | 99.6 |
| SARM 107 | 0.046 ± 0.010 | 0.040 ± 0.020 | 87.7 | 0.926 ± 0.036 | 0.758 ± 0.050 | 81.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biata, N.R.; Jakavula, S.; Moutloali, R.M.; Nomngongo, P.N. Recovery of Palladium and Gold from PGM Ore and Concentrate Leachates Using Fe3O4@SiO2@Mg-Al-LDH Nanocomposite. Minerals 2021, 11, 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11090917
Biata NR, Jakavula S, Moutloali RM, Nomngongo PN. Recovery of Palladium and Gold from PGM Ore and Concentrate Leachates Using Fe3O4@SiO2@Mg-Al-LDH Nanocomposite. Minerals. 2021; 11(9):917. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11090917
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiata, Nkositetile Raphael, Silindokuhle Jakavula, Richard Motlhaletsi Moutloali, and Philiswa Nosizo Nomngongo. 2021. "Recovery of Palladium and Gold from PGM Ore and Concentrate Leachates Using Fe3O4@SiO2@Mg-Al-LDH Nanocomposite" Minerals 11, no. 9: 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11090917
APA StyleBiata, N. R., Jakavula, S., Moutloali, R. M., & Nomngongo, P. N. (2021). Recovery of Palladium and Gold from PGM Ore and Concentrate Leachates Using Fe3O4@SiO2@Mg-Al-LDH Nanocomposite. Minerals, 11(9), 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11090917








