The Influence of REE β-Diketone Complexes on the Corrosion Behaviour of Mild Steel and 304 SS in 3.5% NaCl Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Test and Inhibitor Solutions
2.2. Material Preparation
2.3. Weight-Loss Tests
2.4. Potentiodynamic Polarisation Experiments
2.5. Surface Analysis of the Specimens
2.5.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5.2. Optical Microscopy
2.5.3. Raman Spectroscopy (RS)
2.5.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Corrosion Measurements via Weight-Loss Tests
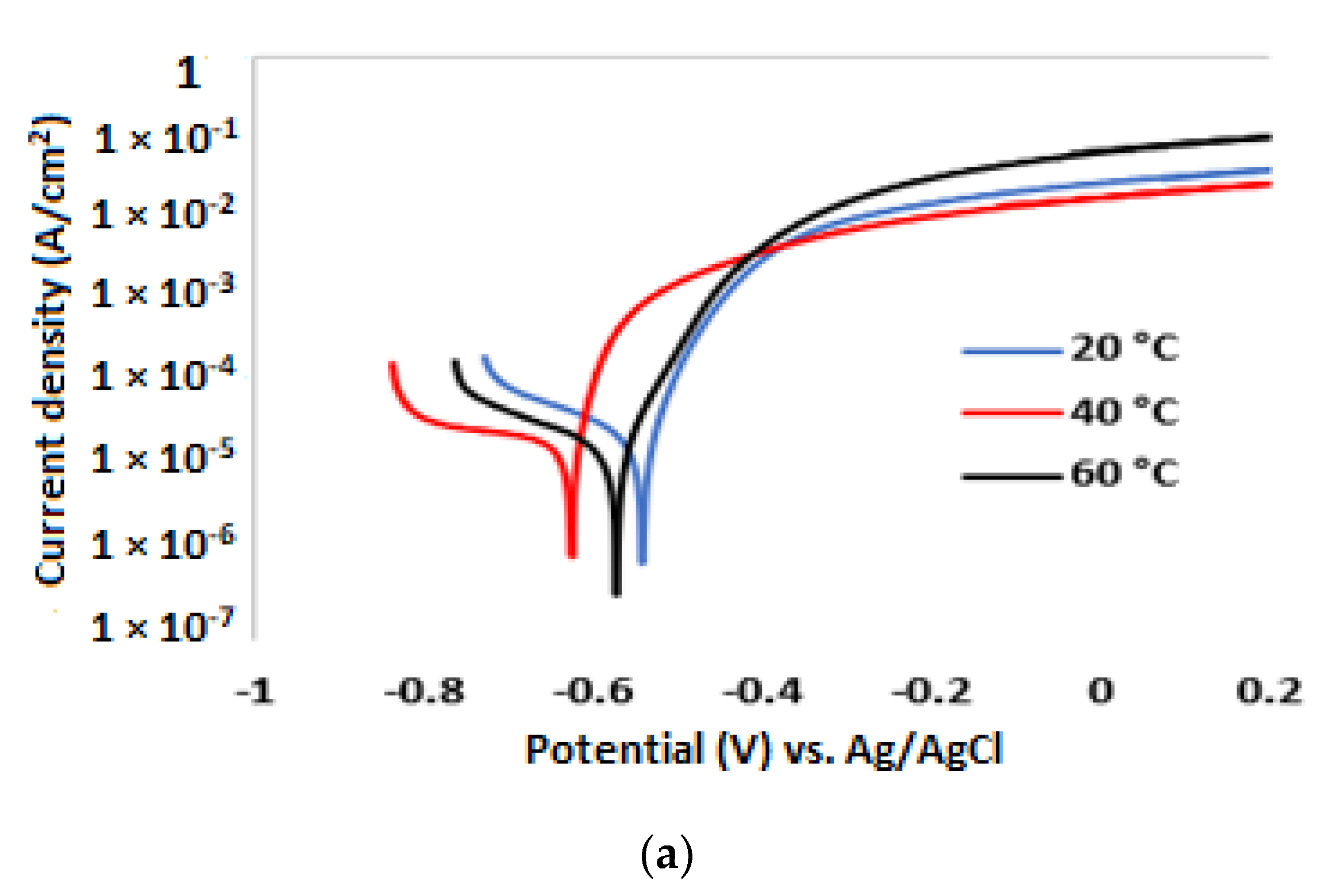
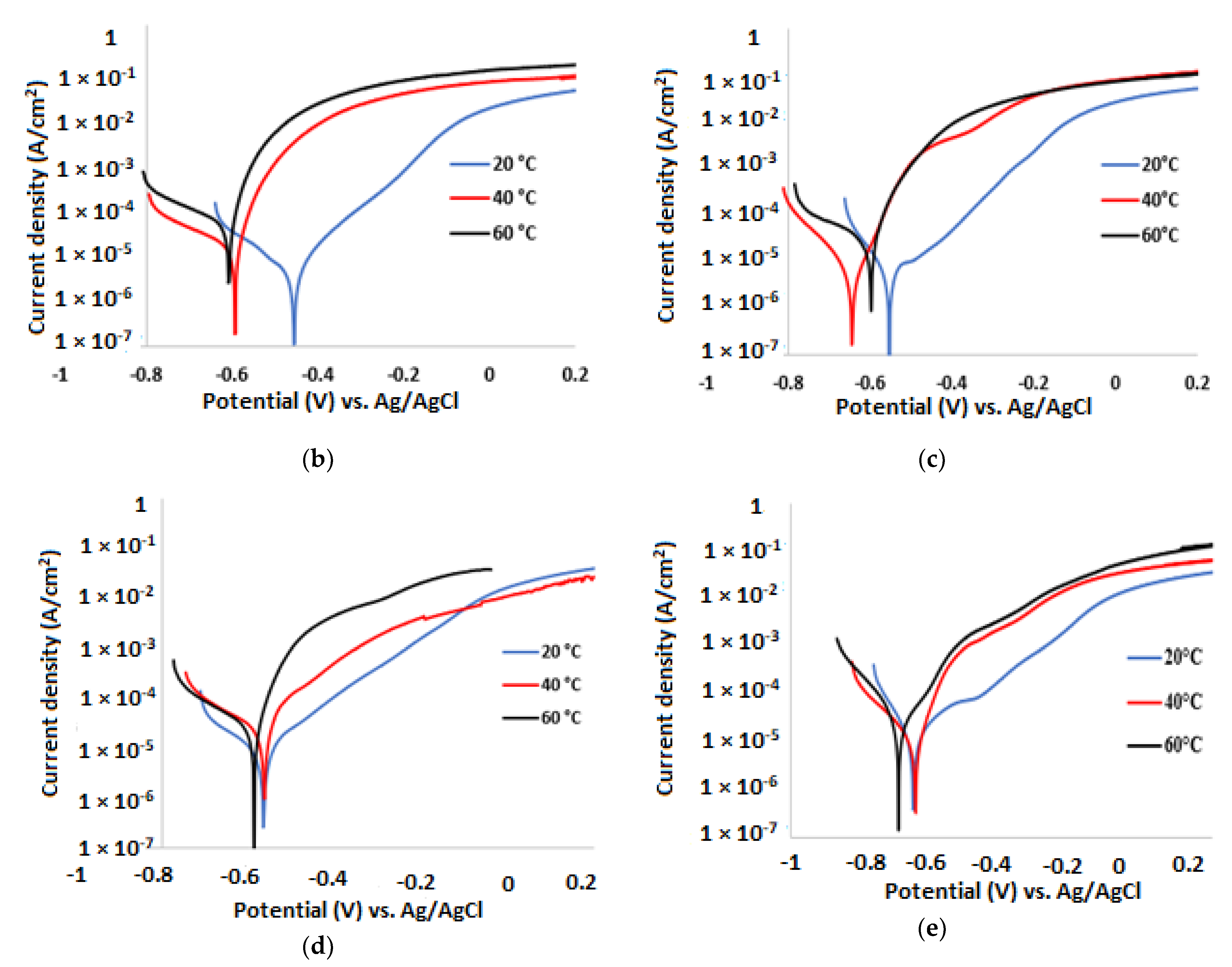
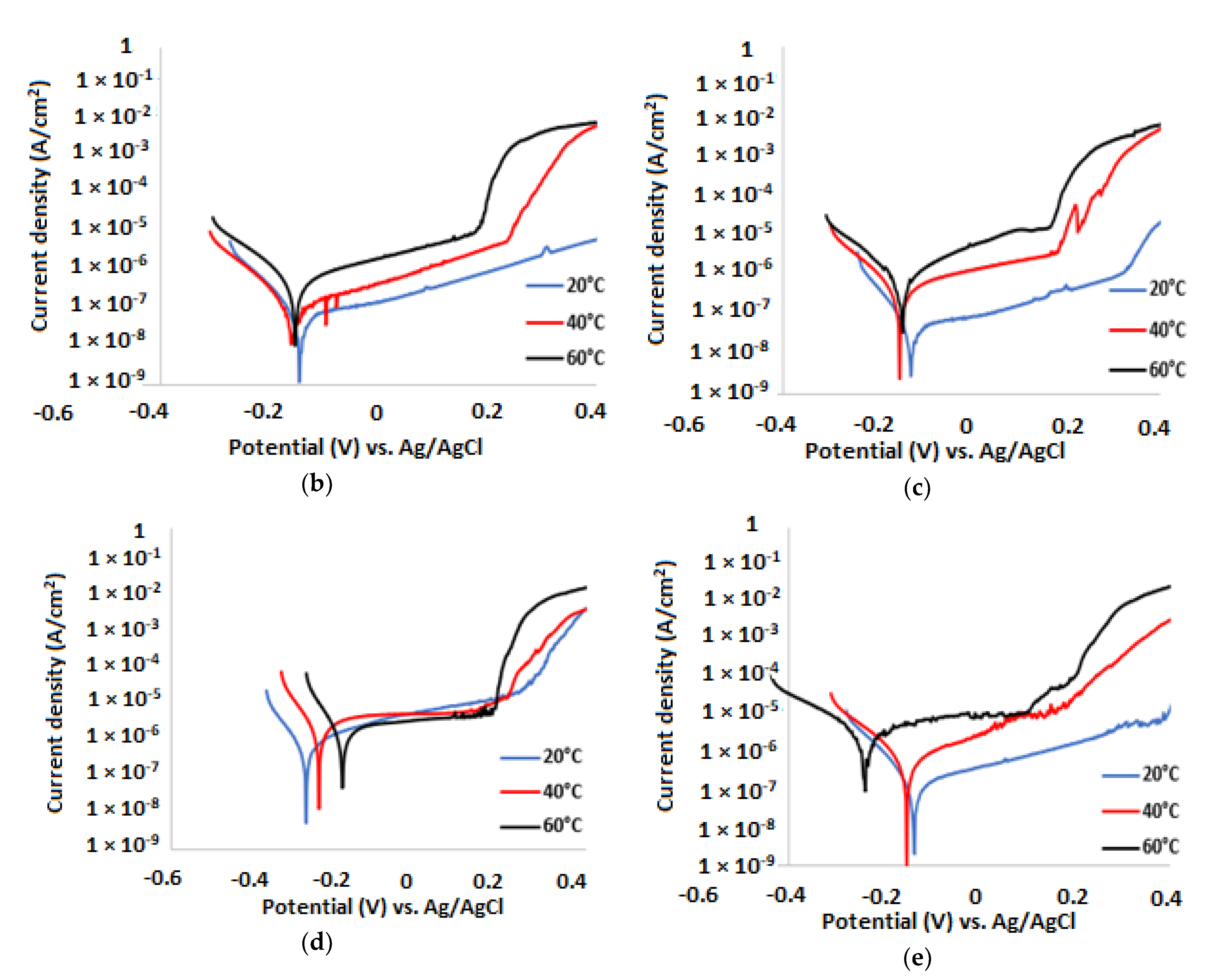
3.2. Potentiodynamic Polarisation Measurements
4. Surface Analyses of the Specimen
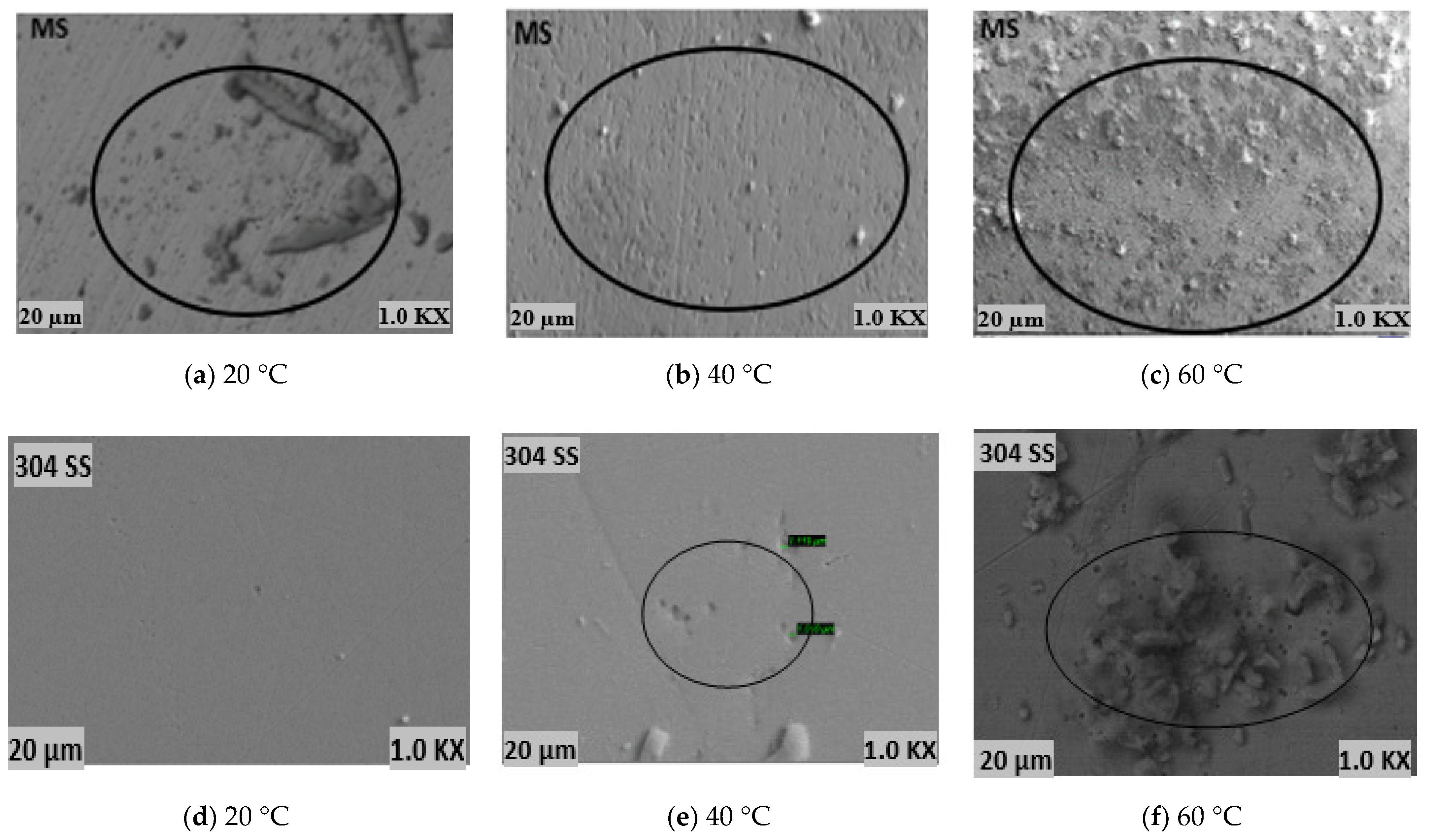
4.1. Optical Microscopy
4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy Analysis (SEM/EDS)
4.3. Surface Mapping of the Mild Steel and 304 Stainless Steel
4.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
4.3.2. Raman Spectroscopy
5. Conclusions
- The four tested REE β-diketone inhibitors were found to be reasonably effective corrosion inhibitors against localised corrosion for mild steel and 304 SS in 3.5% NaCl solution and decreased the overall corrosion rates at the concentration of 0.5% in comparison to when the same samples were tested without inhibitors.
- Surface analysis results obtained from Raman spectra confirmed the formation of a protective film layer containing a rare earth element oxide and iron oxide/iron oxyhydroxide on the mild steel and 304 SS. As expected, an increase in temperature did lead to an increase in corrosion rate.
- As the temperature increased, there was a consistent decrease in the value of cathodic Tafel constants compared to when no inhibitors were used under the same conditions and environment. This decrease in the trend of the cathodic Tafel constant confirmed that the tested REE β-diketone complexes acted as cathodic corrosion inhibitors. With the stainless-steel samples exposed to 3.5% NaCl, there was a definitive shift in the corrosion potential to more noble values in the presence of all four corrosion inhibitors, hinting that they act as anodic-type inhibitors. One can, therefore, conclude that the inhibitors are probably mixed corrosion inhibitors whose mode of action depends on the environment and material present when they are used.
- The applied concentration of 0.5% was not sufficient to afford a 100% inhibitor efficiency for either the stainless steel (except at room temperature in the mass loss tests) or the mild steel, especially as the testing temperature increased. It is recommended that a range of higher concentrations be further investigated.
- While one incidence of slight evidence that the type of rare earth element metal present in the corrosion inhibitor could be important was observed, no conclusive evidence could be obtained that either the β-diketone or rare earth element metal played a significant role in the performance of the corrosion inhibitors. Further work with similar inhibitors, in which either or both the β-diketone component or rare earth element in the corrosion inhibitor are varied, should be undertaken in the future.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fouda, A.S.; Abd El-Wahab, S.M.; Attia, M.S.; Youssef, A.O.; Elmoher, H.O. Rare earth metals as eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in produced water. Der Pharma Chem. 2015, 7, 74–87. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Amiery, A.A.; Binti Kassim, F.A.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Mohamad, A.B. Synthesis and characterization of a novel eco-friendly corrosion inhibition for mild steel in 1 M hydrochloric acid. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, A.; Singh, B.; Verma, C.; Ebenso, E.E. Synthesis, characterization and corrosion inhibition potential of two novel Schiff bases on mild steel in acidic medium. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 47148–47163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esmailzadeh, S.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Sarlak, H. Interpretation of Cyclic Potentiodynamic Polarization Test Results for Study of Corrosion Behavior of Metals: A Review. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2018, 54, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volarič, B.; Milošev, I. Rare earth chloride and nitrate salts as individual and mixed inhibitors for aluminium alloy 7075-T6 in chloride solution. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, O.; Thomas, S.; Smith, C.; Birbilis, N. Chromate replacement: What does the future hold? NPJ Mater. Degrad. 2018, 2, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, F.; Leary, S.G.; Wilson, K.; Deacon, G.B.; Junk, P.C.; Forsyth, M. Corrosion mitigation of mild steel by new rare earth cinnamate compounds. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2004, 34, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, A.E.; Hinton, B.R.W.; De Bruin-dickason, C.; Deacon, G.B.; Junk, P.C.; Forsyth, M. New, environmentally friendly, rare earth carboxylate corrosion inhibitors for mild steel. Corros. Sci. 2018, 139, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoza-Mar, L.; Olivares-Xometl, O.; Domínguez-Aguilar, M.A.; Flores, E.A.; Arellanes-Lozada, P.; Jiménez-Cruz, F. Corrosion inhibitor activity of 1,3-diketone malonates for mild steel in aqueous hydrochloric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2012, 61, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.D.; Ha, P.T.N.; Anh, H.T.; Hoai, N.T.; Hien, P.V. Role of hydroxyl group in cerium hydroxycinnamate on corrosion inhibition of mild steel in 0.6 M NaCl solution. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2019, 23, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, F.; Leary, S.G.; Deacon, G.B.; Junk, P.C.; Forsyth, M. The nature of the surface film on steel treated with cerium and lanthanum cinnamate based corrosion inhibitors. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.I.; Heredia, A.; Botella, J.; Odriozola, J.A. Study of the reaction of lanthanum nitrate with metal oxides present in the scale formed at high temperatures on stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 1995, 30, 5146–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, T.A.; Forsyth, M.; Hughes, A.E. Corrosion protection of AA2024-T3 using rare earth diphenyl phosphates. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 4024–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.D.; Thang, V.Q.; Hoai, N.T.; Hien, P. Van Yttrium 3-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-propenoate used as inhibitor against copper alloy corrosion in 0.1 M NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2016, 112, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Hughes, A.E.; Deacon, G.B.; Junk, P.C.; Hinton, B.R.W.; Forsyth, M.; Mardel, J.I.; Somers, A.E. A study of rare-earth 3-(4-methylbenzoyl)-propanoate compounds as corrosion inhibitors for AS1020 mild steel in NaCl solutions. Corros. Sci. 2018, 145, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudellioua, H.; Hamlaoui, Y.; Tifouti, L.; Pedraza, F. Effects of polyethylene glycol (PEG) on the corrosion inhibition of mild steel by cerium nitrate in chloride solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotting, F.; Aoki, I.V. Octylsilanol and Ce(III) ions—Alternative corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in chloride neutral solutions. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 8723–8734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, I.; Shahrabi, T.; Mahdavian, M.; Izadi, M. Cerium/diethyldithiocarbamate complex as a novel corrosion inhibitive pigment for AA2024-T3. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horiguchi, M.; Sawamura, K.; Saito, I.; Hayakawa, Y. β-Diketones as Corrosion Inhibitors for Aluminum in Alkaline Media. J. Electrochem. Soc. Jpn. 1968, 36, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desa, M.N.; Desai, M.B. Carbonyl compounds as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in HCl solutions. Corros. Sci. 1984, 24, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Weng, Y.; Salitanate; Feng, L.; Yue, H. Corrosion inhibition of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds on steel in acid medium. Pet. Sci. 2009, 6, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avdeev, Y.G.; Kuznetsov, Y.I.; Buryak, A.K. Inhibition of steel corrosion by unsaturated aldehydes in solutions of mineral acids. Corros. Sci. 2013, 69, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, A.; Attar, M.M.; Mahdavian, M. Acetylacetonate complexes as new corrosion inhibitors in phosphoric acid media: Inhibition and synergism study. Prog. Color Color. Coat. 2009, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Okawara, T.; Ishihama, K.; Takehara, K. Redetermination of diaquatris(4-oxopent-2-en-2-olato-κ2O,O′)lanthanum(III). Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E Struct. Rep. Online 2014, 70, m258–m259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastri, V.S.; Ghali, E.; Elboujdaini, M. Corrosion Prevention and Protection: Practical Solutions; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2007; ISBN 047002402X. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, B.R. Corrosion Inhibition with Rare Earth Metal Salts. J. Alloys Compd. 1992, 180, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.S.; Li, W.J. Corrosion resistance of cerium-conversion coated AZ31 magnesium alloys in cerium nitrate solutions. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forsyth, M.; Seter, M.; Hinton, B.; Deacon, G.; Junk, P. New “Green” corrosion inhibitors based on rare earth compounds. Aust. J. Chem. 2011, 64, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.; Tedim, J.; Fernandes, S.C.M.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Gandini, A.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Chitosan-based self-healing protective coatings doped with cerium nitrate for corrosion protection of aluminum alloy 2024. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 75, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, E.A.; Kozhukharov, S.; Machkova, M.; Kozhukharov, V. Comparison between the inhibition efficiencies of Ce(III) and Ce(IV) ammonium nitrates against corrosion of AA2024 aluminum alloy in solutions of low chloride concentration. Corros. Sci. 2012, 62, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobara, M.; Baraka, A.; Akid, R.; Zorainy, M. Corrosion protection mechanism of Ce4+/organic inhibitor for AA2024 in 3.5% NaCl. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 2227–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forsyth, M.; Wilson, K.; Behrsing, T.; Forsyth, C.; Deacon, G.B.; Phanasgoankar, A. Effectiveness of rare-earth metal compounds as corrosion inhibitors for steel. Corrosion 2002, 58, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, L.C.; Depan, D.; Holmes, W.E.; Gallo, A.; Knierim, K.; Bertrand, T.; Hernandez, R. Kinetic and thermodynamic analyses of the corrosion inhibition of synthetic extracellular polymeric substances. PeerJ Mater. Sci. 2020, 2, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, M.; Markley, T.; Ho, D.; Deacon, G.B.; Junk, P.; Hinton, B.; Hughes, A. Inhibition of Corrosion on AA2024-T3 by New Environmentally Friendly Rare Earth Organophosphate Compounds. Corros. Sci. 2008, 64, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudellioua, H.; Hamlaoui, Y.; Tifouti, L.; Pedraza, F. Effect of the temperature of cerium nitrate–NaCl solution on corrosion inhibition of mild steel. Mater. Corros. 2020, 71, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasakau, K.A.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Lamaka, S.V.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Mechanism of corrosion inhibition of AA2024 by rare-earth compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 5515–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amadeh, A.; Allahkaram, S.R.; Hosseini, S.R.; Moradi, H.; Abdolhosseini, A. The use of rare earth cations as corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel in aerated NaCl solution. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 2008, 55, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.K.; Khan, F. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid using extract of glycine max leaves. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 3489–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Gu, R.; Tian, Z. Electrochemical and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Studies on Inhibition of Iron Corrosion by Benzotriazole. Langmuir 2002, 18, 7609–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldona, E.B.; Zhang, M.; Liang, G.; Hollis, T.K.; Webster, C.E.; Smith, D.W.; Wipf, D.O. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic medium by simple azole-based aromatic compounds. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 880, 114858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudellioua, H.; Hamlaoui, Y.; Tifouti, L.; Pedraza, F. Comparison Between the Inhibition Efficiencies of Two Modification Processes with PEG–Ceria Based Layers Against Corrosion of Mild Steel in Chloride and Sulfate Media. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 4402–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Faria, D.L.A.; Venâncio Silva, S.; De Oliveira, M.T. Raman microspectroscopy of some iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1997, 28, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubb, A.M.; Allen, H.C. Vibrational spectroscopic characterization of hematite, maghemite, and magnetite thin films produced by vapor deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2804–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babouri, L.; Belmokre, K.; Abdelouas, A.; Bardeau, J.F.; El Mendili, Y. The inhibitive effect of cerium carbonate on the corrosion of brass in 3% NaCl solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 7818–7839. [Google Scholar]
- Criado, M.; Martínez-Ramirez, S.; Bastidas, J.M. A Raman spectroscopy study of steel corrosion products in activated fly ash mortar containing chlorides. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, B.; Zuo, Y. Corrosion inhibition of carboxylate inhibitors with different alkylene chain lengths on carbon steel in an alkaline solution. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 7065–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

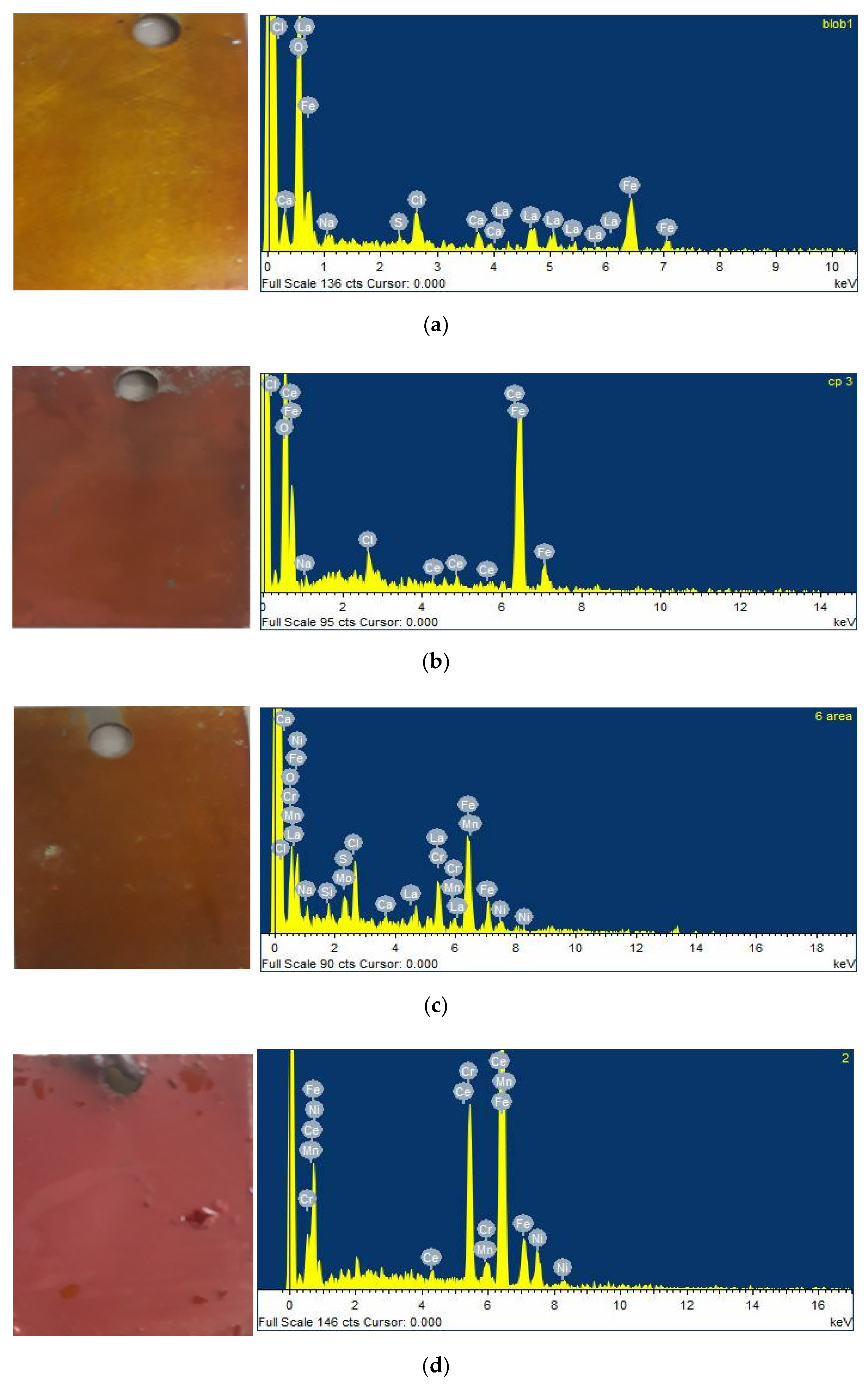










| Nominal Composition (wt.%) | C | S | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild steel | 0.12 | 0.040 | 0.015 | 0.8 | - | - | Balance | |
| Stainless steel (type 304) | 0.05 | 0.019 | 0.320 | 1.5 | 18.5 | 9.0 | 0.46 | Balance |
| REE Inhibitor | CR with Inhibitor (μm/y) | CR without Inhibitor (μm/y) | IE (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild steel | Ce(acac)3 | 42 | 156 | 74 |
| Ce(hfac)3 | 41 | 166 | 75 | |
| La(acac)3 | 43 | 180 | 76 | |
| La(hfac)3 | 45 | 159 | 72 | |
| 304 SS | Ce(acac)3 | 0.0 | 0.7498 | 100 |
| Ce(hfac)3 | 0.0 | 0.6722 | 100 | |
| La(acac)3 | 0.0 | 0.5430 | 100 | |
| La(hfac)3 | 0.0 | 0.6378 | 100 |
| 3.5% NaCl solution without inhibitor | ||||||
| Temp. (°C) | (V) | (A/cm2) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | CR (µm/y) | IE (%) |
| 20 | −0.552 | 1.62 × 10−5 | 54 | 360 | 191 | |
| 40 | −0.626 | 2.41 × 10−5 | 42 | 314 | 284 | |
| 60 | −0.591 | 2.89 × 10−5 | 64 | 284 | 340 | |
| Temp. (°C) | (V) | (A/cm2) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | CR (µm/y) | IE (%) |
| 20 | −0.434 | 1.01 × 10−5 | 109 | 186 | 118 | 38.0 |
| 40 | −0.604 | 1.54 × 10−5 | 69 | 207 | 181 | 36.0 |
| 60 | −0.630 | 1.60 × 10−5 | 47 | 215 | 188 | 33.5 |
| Temp. (°C) | (V) | (A/cm2) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | CR (µm/y) | IE (%) |
| 20 | −0.554 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 135 | 81 | 104 | 46.0 |
| 40 | −0.643 | 1.57 × 10−5 | 54 | 120 | 163 | 43.0 |
| 60 | −0.597 | 1.94 × 10−5 | 46 | 301 | 200 | 41.0 |
| Temp. (°C) | (V) | (A/cm2) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | CR (µm/y) | IE (%) |
| 20 | −0.575 | 1.04 × 10−5 | 126 | 211 | 109 | 36.0 |
| 40 | −0.592 | 1.61 × 10−5 | 125 | 182 | 169 | 33.0 |
| 60 | −0.584 | 2.09 × 10−5 | 66 | 151 | 219 | 28.0 |
| Temp. (°C) | (V) | (A/cm2) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | CR (µm/y) | IE (%) |
| 20 | −0.650 | 1.01 × 10−5 | 212 | 116 | 119 | 38.0 |
| 40 | −0.637 | 1.58 × 10−5 | 69 | 164 | 186 | 34.0 |
| 60 | −0.691 | 2.04 × 10−5 | 92 | 127 | 240 | 29.0 |
| 3.5% NaCl solution without inhibitor | ||||||
| Temp. (°C) | (V) | (A/cm2) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | CR (µm/y) | IE (%) |
| 20 | −0.287 | 3.66 × 10−7 | 351 | 67 | 3.79 | |
| 40 | −0.359 | 1.40 × 10−6 | 76 | 49 | 14.50 | |
| 60 | −0.370 | 4.47 × 10−6 | 123 | 57 | 56.66 | |
| Temp.(°C) | (V) | (A/cm2) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | CR (µm/y) | IE (%) |
| 20 | −0.134 | 5.84 × 10−8 | 243 | 79 | 0.60 | 84 |
| 40 | −0.157 | 3.5 × 10−7 | 206 | 86 | 3.63 | 75 |
| 60 | −0.190 | 2.14 × 10−6 | 391 | 100 | 22.17 | 52 |
| Temp. (°C) | (V) | (A/cm2) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | CR (µm/y) | IE (%) |
| 20 | −0.122 | 4.07 × 10−8 | 482 | 70 | 0.42 | 89 |
| 40 | −0.132 | 3.73 × 10−7 | 345 | 93 | 3.49 | 76 |
| 60 | −0.135 | 2.11 × 10−6 | 323 | 102 | 11.50 | 53 |
| Temp. (°C) | (V) | (A/cm2) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | CR (µm/y) | IE (%) |
| 20 | −0.243 | 1.02 × 10−7 | 379 | 72 | 1.07 | 72 |
| 40 | −0.198 | 1.01 × 10−6 | 344 | 77 | 10.46 | 25 |
| 60 | −0.177 | 3.53 × 10−6 | 185 | 80 | 36.56 | 21 |
| Temp. (°C) | (V) | (A/cm2) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | CR (µm/y) | IE (%) |
| 20 | −0.126 | 8.13 × 10−8 | 301 | 78 | 0.84 | 78 |
| 40 | −0.156 | 3.85 × 10−7 | 369 | 105 | 3.99 | 73 |
| 60 | −0.162 | 2.05 × 10−6 | 306 | 164 | 21.23 | 54 |
| Inhibitor Used | Inhibitor Only | Corrosion Product | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (cm−1) | Assignment | Frequency (cm−1) | Assignment | |
| 1584 | C=O | 1576 | C=O | |
| 3134 | O-H | 2967 | OH | |
| 1595 | C=O | 1408 | C=O | |
| 3335 | O-H | 2967 | OH | |
| 1644 | C=O | 1632 | C=O | |
| 3041 | O-H | 2921 | OH | |
| 1648 | C=O | 1615 | C=O | |
| 3041 | O-H | 2920 | OH | |
| Inhibitor Used | Inhibitor Only | Corrosion Product | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (cm−1) | Assignment | Frequency (cm−1) | Assignment | |
| 1583 | C=O | 1311, 248 | Fe–O | |
| 455 | REE–O | 524 | REE–O | |
| 2931 | O-H | 377 | γ-FeOOH | |
| 1598 | C=O | 1316, 244 | Fe–O | |
| 492 | REE–O | 524 | REE–O | |
| 3069 | O-H | 377 | γ-FeOOH | |
| 1654 | C=O | 1306, 250 | Fe–O | |
| 445 | REE–O | 530 | REE–O | |
| 3157 | O-H | 377 | γ-FeOOH | |
| 1681 | C=O | 1308, 246 | Fe–O | |
| 455 | REE–O | 526 | REE–O | |
| 3152 | O-H | 377 | γ-FeOOH | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lawal, O.J.; Potgieter, J.H.; Billing, C.; Whitefield, D.J. The Influence of REE β-Diketone Complexes on the Corrosion Behaviour of Mild Steel and 304 SS in 3.5% NaCl Solution. Minerals 2022, 12, 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12040416
Lawal OJ, Potgieter JH, Billing C, Whitefield DJ. The Influence of REE β-Diketone Complexes on the Corrosion Behaviour of Mild Steel and 304 SS in 3.5% NaCl Solution. Minerals. 2022; 12(4):416. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12040416
Chicago/Turabian StyleLawal, Olatunde J., Johannes H. Potgieter, Caren Billing, and David J. Whitefield. 2022. "The Influence of REE β-Diketone Complexes on the Corrosion Behaviour of Mild Steel and 304 SS in 3.5% NaCl Solution" Minerals 12, no. 4: 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12040416
APA StyleLawal, O. J., Potgieter, J. H., Billing, C., & Whitefield, D. J. (2022). The Influence of REE β-Diketone Complexes on the Corrosion Behaviour of Mild Steel and 304 SS in 3.5% NaCl Solution. Minerals, 12(4), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12040416







