REE Geochemistry of Neogene–Holocene Sediments of La Fontanilla Cove (Tinto Estuary, SW Spain)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
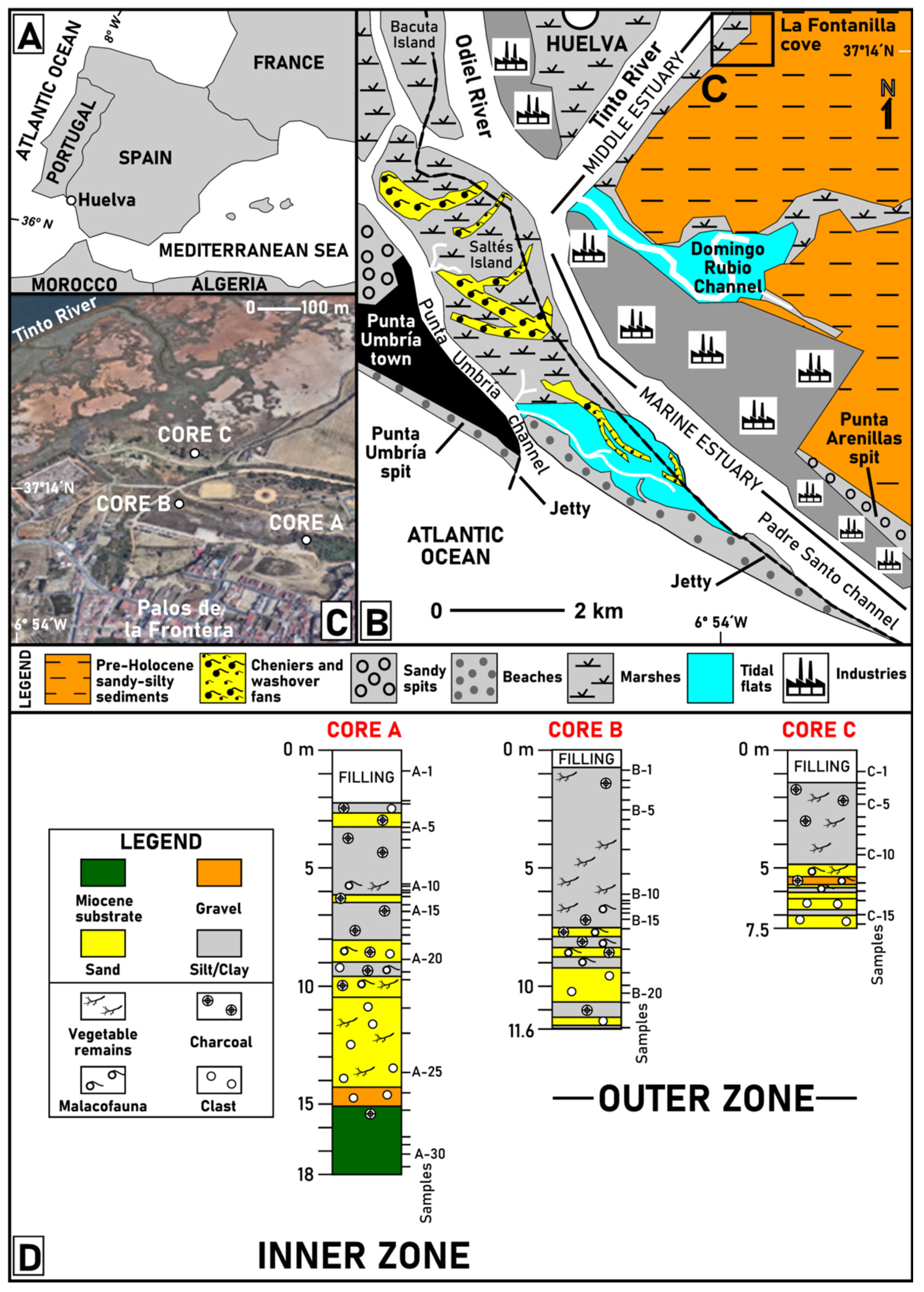
2. Study Area
2.1. The Tinto Estuary
2.2. Historical and Recent Pollution
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Coring and Sampling
3.2. Compositional Analysis
3.3. Textural Analysis
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Core Descriptions and Paleoenvironmental Significance
4.2. REE and Grain Size
4.3. REE Parameters Variation with Depth
4.3.1. LaN/YbN Ratio
4.3.2. LaN/SmN Ratio
4.3.3. Eu Anomaly (Eu/Eu*)
4.3.4. Ce Anomaly (Ce/Ce*)
4.4. REE: Relation with Natural and Anthropogenic Inputs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, D.R.; Whitfield, M.; Dickson, A.G. The equilibrium speciation of dissolved components in freshwater and seawater at 25 °C and 1 atm pressure. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1981, 45, 855–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A. The aqueous geochemistry of the rare-earth elements and yttrium: 1. Review of available low-temperature data for inorganic complexes and the inorganic REE speciation of natural waters. Chem. Geol. 1990, 82, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T. Rare earth element (REE) silicic acid complexes in seawater to explain the incorporation of REEs in opal and the “leftover” REEs in surface water: New interpretation of dissolved REE distribution profiles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 113, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, R.H.; Kim, K.H. Rare earth precipitation and coprecipitation behavior: The limiting role of PO43− on dissolved rare earth concentrations in seawater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R. The geochemistry of rare earth elements in the Amazon River estuary. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks; influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 1989, 21, 169–200. [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Masuda, A. Rare earth elements of Pacific pelagic sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Elderfield, H.; Szymczak, R.; Casey, K. Island weathering: River sources of rare earth elements to the Western Pacific Ocean. Mar. Chem. 1999, 68, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Comparing yttrium and rare earths in hydrothermal fluids from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: Implications for Y and REE behaviour during near-vent mixing and for the Y/Ho ratio of Proterozoic seawater. Chem. Geol. 1999, 155, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verplanck, P.L.; Nordstrom, D.K.; Taylor, H.E.; Kimball, B.A. Rare earth element partitioning between hydrous ferric oxides and acid mine water during iron oxidation. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1339–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolhar, R.; Kamber, B.S.; Moorbath, S.; Fedo, C.M.; Whitehouse, M.J. Characterisation of early Archaean chemical sediments fy trace signatures. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 222, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benes, P.; Stamberg, K.; Vopalka, D.; Siroky, L.; Prochazkova, S. Kinetics of radioeuropium sorption on Gorelben sand from aqueous solutions and groundwater. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2003, 256, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Tang, J.; Daniels, J.M.; Bounds, W.J.; Burdige, D.J. Rare earth element concentrations and speciation in organic-rich black waters of the Great Dismal Swamp, Virginia, USA. Chem. Geol. 2004, 209, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erel, Y.; Stolper, E.M. Modeling of rare-earth element partitioning between particles and solution in aquatic environments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.L.; O′nions, R.K.; Hamilton, P.J. A Sm-Nd isotopic study of atmospheric dusts and particulates from major river systems. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1984, 70, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachikawa, K.; Athias, V.; Jeandel, C. Neodymium budget in the modern ocean and paleo-oceanographic implications. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Upstill-Goddard, R.; Sholkovitz, E.R. The rare earth elements in rivers, estuaries, and coastal seas and their significance to the composition of ocean waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 971–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.; Szymczak, R. The estuarine chemistry of rare earth elements: Comparison of the Amazon, Fly, Sepik and the Gulf of Papua systems. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2000, 179, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacan, F.; Jeandel, C. Tracing Papua New Guinea imprint on the central Equatorial Pacific Ocean using neodymium isotopic compositions and Rare Earth Element patterns. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 186, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Burdige, D.J. Balancing the global oceanic neodymium budget: Evaluating the role of groundwater. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 253, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, T.C.; Sonke, J.E.; Chmeleff, J.; Van Beek, P.; Souhaut, M.; Boaventura, G. Rapid neodymium release to marine waters from lithogenic sediments in the Amazon estuary. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Haley, B.A.; Mix, A.C. Neodymium isotopes in authigenic phases, bottom waters and detrital sediments in the Gulf of Alaska and their implications for paleo-circulation reconstruction. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 193, 14–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeandel, C. Overview of the mechanisms that could explain the ‘Boundary Exchange at the land–ocean contact’. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2016, 374, 20150287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Welch, S.A.; Christy, A.G.; Isaacson, L.; Kirste, D. Mineralogical control of rare earth elements in acid sulfate soils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hissler, C.; Hostache, R.; Iffly, J.F.; Pfister, L.; Stille, P. Anthropogenic rare earth element fluxes into floodplains: Coupling between geochemical monitoring and hydrodynamic sediment transport modelling. Compt. Rendus Geosci. 2015, 347, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksız, S.; Bau, M. Contrasting behaviour of anthropogenic gadolinium and natural rare earth elements in estuaries and the gadolinium input into the North Sea. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 260, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksız, S.; Bau, M. Anthropogenic dissolved and colloid/nanoparticle-bound samarium, lanthanum and gadolinium in the hine River and the impending destruction of the natural rare earth element distribution in rivers. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 362, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmyr, L.; Österholm, P.; Åström, M. Estuarine behaviour of metal loads leached from coastal lowland acid sulphate soils. Mar. Environ. Res. 2008, 66, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannigan, R.; Dorval, E.; Jones, C. The rare earth element chemistry of estuarine surface sediments in the Chesapeake Bay. Chem. Geol. 2010, 272, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åström, M.E.; Österholm, P.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Nystrand, M.; Peltola, P.; Nordmyr, L.; Boman, A. Attenuation of rare earth elements in a boreal estuary. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 96, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.G.; Morgan, B.; Burton, E.D. Legacy impacts of acid sulfate soil runoff on mangrove sediments: Reactive iron accumulation, altered sulfur cycling and trace metal enrichment. Chem. Geol. 2016, 427, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, B.; Johnston, S.G.; Burton, E.D.; Hagan, R.E. Aciddic drainage drives anomalous rare earth element signatures in intertidal mangrove sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Job, T.; Penny, D.; Morgan, B. Geochemical signatures of acidic drainage recorded in estuarine sediments after an extreme drought. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, P.; Caetano, M.; Martins, M.D.; Caçador, I. Effects of salt marsh plants on mobility and bioavailability of REE in estuarine sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 144314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellwiga, O.; Watermannb, F.; Brumsacka, H.-J.; Gerdesb, G. High-resolution Reconstruction of a Holocene Coastal Sequence (NW Germany) Using Inorganic Geochemical Data and Diatom Inventories. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1999, 48, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault de Chanvalon, A.; Metzger, E.; Mouret, A.; Knoery, J.; Chiffoleau, J.-F.; Brach-Papa, C. Particles transformation in estuaries: Fe, Mn and REE signatures through the Loire Estuary. J. Sea Res. 2016, 118, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Job, T.; Penny, D.; Hua, Q. Metal enrichment in estuarine sediments proximal to acid sulfate soils as a novel palaeodrought proxy. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ouyang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, C.; Peng, S.; Tang, Z.; Qiuc, Y.; Zhong, H.; Peng, X. Rare earth element fractionations of the northwestern South China Sea sediments, and their implications for East Asian monsoon reconstruction during the last 36 kyr. Quat. Int. 2019, 525, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Zhou, X.P. Origin of middle rare earth element enrichments in acid waters of a Canadian High Arctic lake. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, J.; López-González, N.; Carro, B.; Lozano-Soria, O. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in Holocene sediments of an acidic estuary: Environmental markers (Tinto river estuary, Southwestern Spain). J. Geochem. Explor. 2005, 86, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammons, C.H.; Wood, S.A.; Nimick, D.A. Diel behavior of rare earth elements in a mountain stream with acidic to neutral pH. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 3747–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammons, C.H.; Wood, S.A.; Pedrozo, F.; Varekamp, J.C.; Nelson, B.J.; Shope, C.L.; Baffico, G. Hydrogeochemistry and rare earth element behavior in a volcanically acidified watershed in Patagonia, Argentina. Chem. Geol. 2005, 222, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Gammons, C.H.; Parker, S.R. The behavior of rare earth elements in naturally and anthropogenically acidified waters. J. Alloy. Comp. 2006, 418, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, R.; Delgado, J.; Nieto, J.M.; Márquez-García, B. Rare earth element geochemistry of sulphide weathering in the São Domingos mine area (Iberian Pyrite Belt): A proxy for fluid–rock interaction and ancient mining pollution. Chem. Geol. 2010, 276, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Pérez-López, R.; Galván, L.; Nieto, J.M.; Boski, T. Enrichment of rare earth elements as environmental tracers of contamination by acid mine drainage in salt marshes: A new perspective. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grawunder, A.; Merten, D.; Büchel, G. Origin of middle rare earth element enrichment in acid mine drainage-impacted areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6812–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudêncio, M.I.; Valente, T.; Marques, R.; Sequeira Braga, M.A.; Pamplona, J. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in a passive treatment system built for acid mine drainage remediation. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, P.; Valente, T.; Geraldo, D.; Ribeiro, C. Photosynthetic pigments in acid mine drainage: Seasonal patterns and associations with stressful abiotic characteristics. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarti, G.; Rossi, V.; Amorosi, A. Influence of Holocene stratigraphic architecture on ground surface settlements: A case study from the City of Pisa (Tuscany, Italy). Sediment. Geol. 2012, 281, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Dellapenna, T.; Louchouarn, P.; Lee, G. Historical reconstruction of anthropogenic mercury input from sedimentary records: Yeongsan Estuary, South Korea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 167, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Jalon-Rójas, I.; Wang, X.H.; Liu, Y. Impacts of land reclamation on sediment transport and sedimentary environment in a macro-tidal estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 242, 106861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, M.; Ruiz, F.; Campos, J.M.; Bermejo, J.; González-Regalado, M.L.; Rodríguez Vidal, J.; Cáceres, L.M.; Olías, M.; Abad, M.; Izquierdo, T.; et al. Where did Christopher Columbus start: The estuarine scenario of a historical date. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 250, 107162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Cortizas, A.; López-Merino, L.; Bindler, R.; Mighall, T.; Kylander, M.E. Early atmospheric metal pollution provides evidence for Chalcolithic/Bronze Age mining and metallurgy in Southwestern Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Dupuy, C. Behaviour of rare earth elements at the freshwater-seawater interface of two acid mine rivers: The Tinto and Odiel (Andalucia, Spain). Appl. Geochem. 1999, 14, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, N.; Borrego, J.; Carro, B.; Grande, J.A.; De la Torre, M.L.; Valente, T. Rare-earth-element fractionation patterns in estuarine sediments as a consequence of acid mine drainage: A case study in SW Spain. Bol. Geol. Min. 2012, 123, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mil-Homens, M.; Vale, C.; Naughton, F.; Brito, P.; Drago, T.; Anes, B.; Raimundo, J.; Schmidt, S.; Caetano, M. Footprint of roman and modern mining activities in a sediment core from the southwestern Iberian Atlantic shelf. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, M.; Ruiz, F.; González-Regalado, M.L.; Rodríguez Vidal, J.; Cáceres, L.M.; Olías, M.; Campos, J.M.; Fernández, L.; Abad, M.; Izquierdo, T.; et al. Natural and anthropic pollution episodes during the Late Holocene evolution of the Tinto River estuary (SW Spain). Sci. Mar. 2021, 85, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Vidal, J.; Cáceres, L.M.; Arroyo, M.; González-Regalado, M.L.; Gómez, P.; Ruiz, F. La construcción geológica de la bahía colombina. In La Recuperación Geoarqueológica del Puerto Histórico de Palos de la Frontera (s. XIV-XV); Campos, J.M., Ed.; Universidad de Huelva: Huelva, Spain, 2021; pp. 191–204. [Google Scholar]
- Civis, J.; Sierro, F.J.; González-Delgado, J.A.; Flores, J.A.; Andrés, I.; Porta, J.; Valle, M.F. El Neógeno marino de la provincial de Huelva: Antecedentes y definición de las unidades litoestratigráficas. In Paleontología del Neógeno de Huelva; Universidad de Salamanca: Salamanca, Spain, 1987; pp. 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mayoral, E.; Pendón, J.G. Icnofacies y sedimentación en zona costera. Plioceno Superior (?), litoral de Huelva. Acta Geol. Hisp. 1986, 21–22, 507–513. [Google Scholar]
- Pendón, J.G.; Rodríguez Vidal, J. Caracteres sedimentógicos y geomorfológicos del Alto Nivel Aluvial cuaternario en el litoral de Huelva. Acta Geol. Hisp. 1986, 21–22, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Borrego, J.; Morales, J.A.; Pendón, J.G. Holocene flling of an estuarine lagoon along the mesotidal coast of Huelva: The Piedras River mouth, southwestern Spain. J. Coast. Res. 1993, 9, 242–254. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R., Jr.; Welty, A.; Borrego, J.; Morales, J.A.; Pendon, J.G.; Ryan, J.G. Rio Tinto estuary (Spain): 5000 years of pollution. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEDEX (Centro de Estudios y Experimentación de Obras Públicas). Dinámica Litoral de la Flecha de El Rompido (Huelva); Ministerio de Obras Públicas: Madrid, Spain, 1991; p. 100. [Google Scholar]
- CEEPYC (Centro de Estudios y Experimentacion de Puertos y Costas ‘Ramon Iribarren’). Plan de Estudio de la Dinámica Litoral de la Provincia de Huelva; Informe Direccion General de Puertos y Costas: Madrid, Spain, 1979; p. 37. [Google Scholar]
- Cuena, G.J. Proyecto de Regeneración de las Playas de Isla Cristina. Informe del Servicio de Costas; Ministerio de Obras Publicas y Turismo: Madrid, Spain, 1991; p. 100. [Google Scholar]
- Galán, E.; González, I. Contribución de la mineralogía de arcillas a la interpretación de la evolución paleogeográfica del sector occidental de la cuenca del Guadalquivir. Estud. Geológicos 1993, 49, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, A.; Cáceres, L.M.; Rodríguez Vidal, J.; Carretero, M.I.; Abad, M.; Olías, M.; Pozo, M. Evidence of high-energy events in the geological record: Mid-Holocene evolution of the southwestern Doñana National Park (SW Spain). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2005, 229, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, E.; Requena, A.; Fernández Caliani, J.C. Provenance and evolution of clay minerals in the Tinto river, SW Spain. Geol. Carphat. 1996, 5, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández Caliani, J.C.; Ruiz, F.; Galán, E. Clay minerals and heavy metal distributions in the lower estuary of Huelva and adjacent Atlantic shelf, SW Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 198, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, C.; Fernández-Caliani, J.C.; Miras, A.; Galán, E. Mineralogía de los suelos y sedimentos actuales del estero Domingo Rubio (estuario de Huelva). Macla 2007, 7, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Requena, A.; Claus, F.L.; Fernandez-Caliani, J.C. Mineralogy and geochemical features of the recent sediments in the Odiel river (Huelva). Cuad. Lab. Xeol. De Laxe Coruña 1991, 16, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Tornos, F. La Geología y Metalogenia de la Faja Pirítica Ibérica. Macla 2008, 10, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Olías, M.; Cánovas, C.R.; Macías, F.; Basallote, M.D.; Nieto, J.M. The evolution of pollutant concentrations in a river severely affected by acid mine drainage: Río Tinto (SW Spain). Minerals 2020, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.H.; Lamothe, P.J. Heavy metal anomalies in the Tinto and Odiel River and estuary system, Spain. Estuaries 1993, 16, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F. Trace metals in estuarine sediments from the southwestern Spanish coast. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2000, 42, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, G.; Ruiz, F.; Rodríguez Vidal, J.; González-Regalado, M.L.; Cáceres, L.M.; Gómez, P.; Abad, M.; Izquierdo, T.; Toscano, A.; Arroyo, M.; et al. Miocene-Late Quaternary environmental changes and mollucs as proxies of MIS-1 transgression in the Tinto-Odiel estuary, SW Spain. J. Iber. Geol. 2022, 48, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1985; p. 312. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, K.J.M.; Groenewoud, H.; Dorten, W.; Kramer, G.N.; Muntaun, H.; Quevauvillert, P.H. Certified reference materials for the quality control of rare earth element determinations in the environment. Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Jung, H.S.; Choi, M.S.; Li, C.X. The rare earth element compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze) and Huanghe (Yellow) river sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 201, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbidge, C.I.; Trindade, M.J.; Dias, M.I.; Oosterbeek, L.; Scarre, C.; Rosina, P.; Cruz, A.; Cura, S.; Cura, P.; Caron, L.; et al. Luminescence dating and associated analyses in transition landscapes of the Alto Ribatejo, central Portugal. Quat. Geochron. 2014, 20, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.; Prudêncio, M.I.; Waerenborgh, J.C.; Rocha, F.; Ferreira da Silva, E.; Dias, M.I.; Madeira, J.; Vieira, B.J.C.; Marques, J.G. Geochemical fingerprints in topsoils of the volcanic Brava Island, Cape Verde. Catena 2016, 147, 522–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, J.; López-González, N.; Carro, B.; Lozano-Soria, O. Origin of the anomalies in light and middle REE in sediments of an estuary affected by phosphogypsum wastes (south-western Spain). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, H.L.; Myerr, R.A.; O′Connor, G.A. Soil Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2002; p. 320. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, S.A.L.; Haeckel, M.; Bau, M.; Bajracharva, R.; Koschinsky, A. Small-scale heterogeneity of trace metals including rare earth elements and yttrium in deep-sea sediments and porewaters of the Peru Basin, southeastern equatorial Pacific. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 4829–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Q.; Xue, Z.G.; Chu, F. Rare Earth Element distributions in continental shelf sediment, Northern South China Sea. Water 2020, 12, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhassan, A.B.; Aljahdali, M.O. Fractionation and Distribution of Rare Earth Elements in Marine Sediment and Bioavailability in Avicennia marina in Central Red Sea Mangrove Ecosystems. Plants 2021, 10, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, B.; Rate, A.W.; Burton, E.D.; Smirk, M.N. Enrichment and fractionation of rare earth elements in FeS- and organic-rich estuarine sediments receiving acid sulfate soil drainage. Chem. Geol. 2012, 308, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edzwald, J.K.; Upchurch, J.B.; O′Melia, C.R. Coagulation in estuaries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1974, 8, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E. Chemical evolution of Rare Earth Elements: Fractionation between colloidal and solution phases of filtered river water. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1992, 114, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M. Scavenging of disolved yttrium and rare earth elements by precipitating iron oxyhydroxide experimental evidence for Ce-oxidation, Y-Jo fractionation and lanthanide tetrad effect. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, R.; Ramanathan, A.; Ramesh, S.; Purvaja, R.; Subramanian, V. Distribution of rare earth elements and heavy metals in the surficial sediments of the Himalayan river syste. Geochem. J. 2000, 34, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, P.; Prego, R.; Mil-Homens, M.; Caçador, I.; Cartano, M. Sources and distribution of yttrium and rare elements in surface sediments from Tagus estuary, Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblanc, M.; Morales, J.A.; Borrego, J.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F. 4500-year-old pollution in southwestern Spain: Long-term implications for modern mining pollution. Econ. Geol. 2000, 95, 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Pourret, O.; Guo, H.; Bonhoure, J. Rare earth elements sorption to iron oxyhydroxide; Model development and application to groundwater. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 87, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| CORE | SAMPLE | DEPTH | PALEOEN. | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Y | Yb | Lu | ∑ REE | LaN/YbN | LaN/SmN | Ce/Ce* | Eu/Eu* | Y/Ho |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | Error: 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.03 | 0.01 | |||||||||
| CORE A | A-1 | 1.0 | Filling | 14 | 28.9 | 3.54 | 12.9 | 2.46 | 0.56 | 2.15 | 0.32 | 1.71 | 0.34 | 1.03 | 0.13 | 8.4 | 0.87 | 0.13 | 77.44 | 1.22 | 0.84 | 0.94 | 1.14 | 24.71 |
| A-2 | 2.1 | Filling | 16 | 32.3 | 4.1 | 15.1 | 2.83 | 0.63 | 2.34 | 0.33 | 1.71 | 0.33 | 1.07 | 0.13 | 8.4 | 0.85 | 0.13 | 86.25 | 1.39 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 1.14 | 25.45 | |
| A-3 | 2.3 | Marsh | 20.3 | 41.1 | 5.05 | 18.2 | 3.35 | 0.74 | 2.87 | 0.43 | 2.28 | 0.43 | 1.41 | 0.17 | 11.6 | 1.13 | 0.17 | 109.23 | 1.35 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 1.11 | 26.98 | |
| A-4 | 3.2 | Alluvial | 18.3 | 37.1 | 4.69 | 17.1 | 3.21 | 0.71 | 2.68 | 0.4 | 2.11 | 0.4 | 1.38 | 0.16 | 10.9 | 1.08 | 0.16 | 100.38 | 1.29 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 1.13 | 27.25 | |
| A-5 | 3.4 | Marsh | 28 | 56.4 | 6.74 | 25.6 | 5.06 | 1.24 | 4.45 | 0.6 | 3.44 | 0.62 | 1.82 | 0.26 | 14.4 | 1.68 | 0.26 | 150.57 | 1.22 | 0.82 | 0.94 | 1.22 | 23.23 | |
| A-6 | 3.6 | Marsh | 35.7 | 74.3 | 9.01 | 33.2 | 6.72 | 1.48 | 5.83 | 0.87 | 4.58 | 0.87 | 2.71 | 0.35 | 21.3 | 2.3 | 0.35 | 199.57 | 1.15 | 0.78 | 0.95 | 1.10 | 24.48 | |
| A-7 | 3.9 | Marsh | 36.9 | 75.4 | 9.4 | 35 | 6.98 | 1.72 | 6.17 | 0.82 | 4.5 | 0.85 | 2.44 | 0.35 | 18.8 | 2.31 | 0.36 | 202 | 1.16 | 0.78 | 0.93 | 1.22 | 22.12 | |
| A-8 | 4.2 | Marsh | 35.7 | 73.6 | 8.92 | 32.7 | 6.51 | 1.41 | 5.5 | 0.82 | 4.25 | 0.78 | 2.48 | 0.31 | 19.8 | 2.06 | 0.31 | 195.15 | 1.30 | 0.81 | 0.95 | 1.10 | 25.38 | |
| A-9 | 5.7 | Lagoon | 26.7 | 54.9 | 6.79 | 25 | 4.97 | 1.05 | 4.14 | 0.6 | 3.04 | 0.56 | 1.78 | 0.22 | 14 | 1.47 | 0.22 | 145.44 | 1.37 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 1.08 | 25.00 | |
| A-10 | 5.85 | Lagoon | 29.9 | 59.8 | 7.14 | 27.3 | 5.37 | 1.23 | 4.48 | 0.59 | 3.03 | 0.59 | 1.69 | 0.24 | 13.3 | 1.58 | 0.25 | 156.49 | 1.35 | 0.82 | 0.94 | 1.17 | 22.54 | |
| A-11 | 6.0 | Lagoon | 26.3 | 53.8 | 6.64 | 24.3 | 4.84 | 1.08 | 4.13 | 0.62 | 3.19 | 0.6 | 1.88 | 0.24 | 14.6 | 1.55 | 0.23 | 144 | 1.29 | 0.80 | 0.93 | 1.13 | 24.33 | |
| A-12 | 6.15 | Lagoon | 33.4 | 67 | 8.29 | 30.6 | 6.17 | 1.48 | 5.42 | 0.69 | 3.76 | 0.71 | 2.06 | 0.3 | 16 | 1.94 | 0.3 | 178.12 | 1.26 | 0.80 | 0.93 | 1.19 | 22.54 | |
| A-13 | 6.3 | Lagoon | 23.2 | 47.4 | 5.9 | 21.4 | 4.23 | 0.91 | 3.56 | 0.51 | 2.68 | 0.5 | 1.53 | 0.19 | 12.8 | 1.32 | 0.19 | 126.32 | 1.38 | 0.81 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 25.60 | |
| A-14 | 6.6 | Ebb-Tide Channel | 26.6 | 51.4 | 6.26 | 23.6 | 4.66 | 1.16 | 4.09 | 0.54 | 2.88 | 0.55 | 1.57 | 0.24 | 12.8 | 1.5 | 0.23 | 138.08 | 1.31 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 1.24 | 23.27 | |
| A-15 | 6.9 | Ebb-Tide Channel | 24.7 | 48.6 | 5.89 | 22.5 | 4.43 | 1.1 | 3.79 | 0.53 | 2.81 | 0.54 | 1.51 | 0.22 | 11.8 | 1.39 | 0.21 | 130.02 | 1.33 | 0.82 | 0.93 | 1.25 | 21.85 | |
| A-16 | 7.3 | Ebb-Tide Channel | 23.4 | 47.1 | 5.84 | 21.4 | 4.24 | 0.94 | 3.59 | 0.53 | 2.78 | 0.53 | 1.68 | 0.21 | 13.1 | 1.37 | 0.21 | 126.92 | 1.26 | 0.81 | 0.93 | 1.12 | 24.72 | |
| A-17 | 7.6 | Ebb-Tide Channel | 23.7 | 46.4 | 5.7 | 21.5 | 4.25 | 1.05 | 3.73 | 0.49 | 2.61 | 0.49 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 11.3 | 1.34 | 0.2 | 124.36 | 1.34 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 1.23 | 23.06 | |
| A-18 | 7.9 | Ebb-Tide Channel | 16.2 | 30.5 | 3.91 | 14.5 | 2.76 | 0.64 | 2.31 | 0.29 | 1.48 | 0.29 | 0.79 | 0.11 | 6.7 | 0.75 | 0.12 | 81.35 | 1.53 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 1.18 | 23.10 | |
| A-19 | 8.3 | MIS-1 Flood | 17 | 36 | 4.51 | 16.3 | 3.3 | 0.69 | 2.67 | 0.37 | 1.82 | 0.33 | 1.12 | 0.13 | 8.3 | 0.88 | 0.13 | 93.55 | 1.48 | 0.76 | 0.94 | 1.08 | 25.15 | |
| A-20 | 8.9 | MIS-1 Flood | 20.5 | 42.1 | 5.08 | 18.3 | 3.41 | 0.69 | 2.82 | 0.39 | 1.95 | 0.35 | 1.14 | 0.14 | 8.9 | 0.93 | 0.14 | 106.84 | 1.66 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 1.04 | 25.43 | |
| A-21 | 9.5 | MIS-1 Flood | 28.3 | 59.1 | 7.15 | 26.3 | 5.25 | 1.09 | 4.33 | 0.61 | 3.14 | 0.59 | 1.91 | 0.25 | 14.6 | 1.57 | 0.23 | 154.42 | 1.39 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 1.07 | 24.75 | |
| A-22 | 9.8 | MIS-1 Flood | 25.7 | 53.1 | 6.4 | 22.6 | 4.43 | 0.9 | 3.61 | 0.5 | 2.53 | 0.46 | 1.52 | 0.18 | 10.9 | 1.19 | 0.18 | 134.2 | 1.62 | 0.85 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 23.70 | |
| A-23 | 11 | Alluvial | 20.6 | 42.5 | 5.22 | 19.4 | 3.87 | 0.81 | 3.27 | 0.45 | 2.25 | 0.42 | 1.33 | 0.17 | 10.3 | 1.07 | 0.16 | 111.82 | 1.46 | 0.78 | 0.94 | 1.06 | 24.52 | |
| A-24 | 12 | Alluvial | 18.1 | 37.3 | 4.63 | 17.2 | 3.48 | 0.7 | 2.77 | 0.39 | 1.94 | 0.36 | 1.14 | 0.14 | 8.5 | 0.9 | 0.13 | 97.68 | 1.58 | 0.77 | 0.94 | 1.05 | 23.61 | |
| A-25 | 13.7 | Alluvial | 18 | 36.2 | 4.43 | 15.8 | 3.12 | 0.66 | 2.56 | 0.37 | 1.93 | 0.35 | 1.2 | 0.14 | 9 | 0.96 | 0.14 | 94.86 | 1.45 | 0.85 | 0.93 | 1.09 | 25.71 | |
| A-26 | 14.6 | Alluvial | 29.6 | 60 | 7.32 | 26.6 | 5.13 | 1.09 | 4.38 | 0.66 | 3.48 | 0.67 | 2.14 | 0.27 | 17.4 | 1.84 | 0.26 | 160.84 | 1.29 | 0.85 | 0.94 | 1.07 | 25.97 | |
| A-27 | 15.3 | Alteration Miocene | 29.1 | 59.1 | 7.22 | 26 | 4.83 | 1.05 | 4.19 | 0.63 | 3.39 | 0.65 | 2.08 | 0.26 | 17 | 1.76 | 0.27 | 157.53 | 1.22 | 0.89 | 0.94 | 1.09 | 26.15 | |
| A-28 | 16.5 | Alteration Miocene | 29.4 | 59.2 | 7.29 | 26.6 | 4.92 | 1.04 | 4.16 | 0.62 | 3.31 | 0.63 | 1.99 | 0.25 | 16.5 | 1.7 | 0.26 | 157.87 | 1.28 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 1.07 | 26.19 | |
| A-29 | 16.8 | Miocene | 30.2 | 61.2 | 7.5 | 27.3 | 5.01 | 1.07 | 4.28 | 0.64 | 3.46 | 0.63 | 2.08 | 0.26 | 17.1 | 1.73 | 0.26 | 162.72 | 1.31 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 1.08 | 27.14 | |
| A-30 | 17.2 | Miocene | 29.2 | 59.1 | 7.25 | 26.2 | 4.94 | 1.05 | 4.2 | 0.62 | 3.32 | 0.63 | 2.05 | 0.25 | 16.3 | 1.74 | 0.26 | 157.11 | 1.27 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 1.08 | 25.87 | |
| A-31 | 17.7 | Miocene | 22.3 | 46.2 | 5.71 | 20.7 | 3.82 | 0.79 | 3.25 | 0.47 | 2.49 | 0.47 | 1.48 | 0.19 | 12.2 | 1.28 | 0.19 | 121.54 | 1.33 | 0.86 | 0.94 | 1.05 | 25.96 | |
| CORE B | B-1 | 0.8 | Freshwater Pond | 32.7 | 67.4 | 8.2 | 33.5 | 6.64 | 1.59 | 5.77 | 0.82 | 4.6 | 0.87 | 2.52 | 0.34 | 23.1 | 2.26 | 0.34 | 190.65 | 1.09 | 0.73 | 0.95 | 1.20 | 26.55 |
| B-2 | 1.2 | Freshwater Pond | 30.2 | 62.4 | 7.46 | 29.7 | 5.51 | 1.29 | 4.93 | 0.69 | 3.9 | 0.75 | 2.18 | 0.29 | 20 | 1.98 | 0.3 | 171.58 | 1.14 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 1.15 | 26.67 | |
| B-3 | 1.6 | Marsh | 34.8 | 74.1 | 8.38 | 33.6 | 6.53 | 1.44 | 5.65 | 0.79 | 4.54 | 0.88 | 2.52 | 0.36 | 21.3 | 2.34 | 0.36 | 197.59 | 1.09 | 0.79 | 1.00 | 1.11 | 24.20 | |
| B-4 | 2 | Marsh | 33.6 | 69.3 | 8.16 | 32.2 | 6.21 | 1.36 | 5.31 | 0.74 | 4.1 | 0.77 | 2.27 | 0.32 | 19.3 | 2.09 | 0.32 | 186.05 | 1.19 | 0.80 | 0.96 | 1.10 | 25.06 | |
| B-5 | 2.4 | Marsh | 31.6 | 66.9 | 7.65 | 30.2 | 5.92 | 1.32 | 5.05 | 0.72 | 3.91 | 0.74 | 2.18 | 0.3 | 18.4 | 2 | 0.31 | 177.2 | 1.15 | 0.79 | 0.99 | 1.13 | 24.86 | |
| B-6 | 2.8 | Marsh | 32.6 | 69.4 | 7.85 | 31.6 | 6 | 1.33 | 4.93 | 0.69 | 3.73 | 0.71 | 2.08 | 0.28 | 17.4 | 1.93 | 0.29 | 180.82 | 1.27 | 0.80 | 1.00 | 1.14 | 24.51 | |
| B-7 | 3.2 | Marsh | 32.8 | 69.3 | 7.83 | 31.1 | 6.12 | 1.35 | 5.14 | 0.71 | 3.89 | 0.73 | 2.17 | 0.3 | 18 | 1.97 | 0.3 | 181.71 | 1.24 | 0.79 | 0.99 | 1.12 | 24.66 | |
| B-8 | 4 | Marsh | 31.4 | 63.9 | 7.48 | 29.5 | 5.71 | 1.25 | 4.75 | 0.64 | 3.57 | 0.66 | 1.92 | 0.27 | 16.9 | 1.82 | 0.28 | 170.05 | 1.27 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 1.12 | 25.61 | |
| B-9 | 5 | Marsh | 31.2 | 63.9 | 7.43 | 29.7 | 5.58 | 1.22 | 4.76 | 0.66 | 3.56 | 0.67 | 1.93 | 0.27 | 16.7 | 1.78 | 0.27 | 169.63 | 1.31 | 0.82 | 0.96 | 1.10 | 24.93 | |
| B-10 | 5.8 | Marsh | 27.1 | 55.4 | 6.57 | 25.8 | 5.06 | 1.13 | 4.35 | 0.58 | 3.23 | 0.6 | 1.77 | 0.25 | 15 | 1.61 | 0.25 | 148.7 | 1.23 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 1.12 | 25.00 | |
| B-11 | 6 | Marsh | 33.6 | 69.2 | 8.22 | 30.6 | 6.07 | 1.49 | 5.34 | 0.71 | 3.75 | 0.71 | 2.04 | 0.3 | 17 | 1.95 | 0.3 | 181.28 | 1.27 | 0.82 | 0.96 | 1.22 | 23.94 | |
| B-12 | 6.2 | Ebb-Tide Channel | 32.9 | 67 | 7.85 | 31.3 | 6.11 | 1.31 | 5.02 | 0.69 | 3.82 | 0.71 | 2.03 | 0.28 | 17.7 | 1.89 | 0.29 | 178.9 | 1.28 | 0.79 | 0.96 | 1.10 | 24.93 | |
| B-13 | 6.4 | Ebb-Tide Channel | 30.5 | 62.4 | 7.43 | 27.6 | 5.47 | 1.32 | 4.72 | 0.62 | 3.36 | 0.65 | 1.87 | 0.26 | 15.5 | 1.77 | 0.27 | 163.74 | 1.28 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 1.21 | 23.85 | |
| B-14 | 6.6 | Ebb-Tide Channel | 27.9 | 57 | 6.65 | 26.8 | 5.03 | 1.11 | 4.32 | 0.59 | 3.32 | 0.61 | 1.78 | 0.25 | 15.8 | 1.66 | 0.25 | 153.07 | 1.26 | 0.82 | 0.96 | 1.11 | 25.90 | |
| B-15 | 6.8 | Ebb-Tide Channel | 31.5 | 63 | 7.55 | 28.4 | 5.65 | 1.38 | 4.95 | 0.66 | 3.54 | 0.68 | 1.99 | 0.28 | 17 | 1.84 | 0.29 | 168.71 | 1.23 | 0.82 | 0.94 | 1.22 | 25.00 | |
| B-16 | 7 | Ebb-Tide Channel | 32.2 | 64 | 7.75 | 29.3 | 5.8 | 1.42 | 5.13 | 0.67 | 3.6 | 0.77 | 2.02 | 0.29 | 16.1 | 1.88 | 0.29 | 171.22 | 1.26 | 0.82 | 0.93 | 1.21 | 20.91 | |
| B-17 | 7.2 | MIS-1 Flood | 32 | 65.4 | 7.66 | 30.4 | 6.02 | 1.3 | 5.09 | 0.71 | 3.98 | 0.74 | 2.21 | 0.3 | 18.9 | 2.01 | 0.31 | 177.03 | 1.17 | 0.78 | 0.96 | 1.10 | 25.54 | |
| B-18 | 8 | MIS-1 Flood | 30.6 | 61.5 | 7.26 | 28.9 | 5.49 | 1.18 | 4.61 | 0.64 | 3.5 | 0.65 | 1.89 | 0.26 | 17 | 1.74 | 0.27 | 165.49 | 1.28 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 1.09 | 26.15 | |
| B-19 | 9 | Alluvial | 31 | 65.4 | 7.41 | 29.4 | 5.63 | 1.27 | 4.81 | 0.66 | 3.67 | 0.68 | 1.95 | 0.27 | 16.7 | 1.8 | 0.27 | 170.92 | 1.30 | 0.81 | 0.99 | 1.14 | 24.56 | |
| B-20 | 9.5 | Alluvial | 27.4 | 56.3 | 6.61 | 25.5 | 4.91 | 1.07 | 4.13 | 0.56 | 3.03 | 0.58 | 1.69 | 0.23 | 15 | 1.53 | 0.23 | 148.77 | 1.35 | 0.82 | 0.96 | 1.11 | 25.86 | |
| B-21 | 9.8 | Alluvial | 32.1 | 61.7 | 7.43 | 29.7 | 5.77 | 1.26 | 5 | 0.68 | 3.68 | 0.7 | 1.94 | 0.26 | 17.6 | 1.7 | 0.25 | 169.77 | 1.45 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 1.09 | 25.14 | |
| B-22 | 11.2 | Marsh | 34.2 | 71.3 | 8.17 | 32.1 | 6.33 | 1.36 | 5.24 | 0.72 | 3.98 | 0.77 | 2.14 | 0.31 | 18.6 | 2.03 | 0.31 | 187.56 | 1.25 | 0.80 | 0.98 | 1.10 | 24.16 | |
| CORE C | C-1 | 0.9 | Filling | 18.8 | 37 | 4.67 | 17.8 | 3.45 | 0.88 | 2.95 | 0.39 | 2.13 | 0.4 | 1.14 | 0.17 | 9.3 | 1.11 | 0.17 | 100.36 | 1.25 | 0.80 | 0.91 | 1.29 | 23.25 |
| C-2 | 1.4 | Marsh | 29.3 | 62.7 | 7.47 | 27.7 | 5.5 | 1.18 | 4.8 | 0.7 | 3.65 | 0.7 | 2.21 | 0.27 | 17.2 | 1.79 | 0.26 | 165.43 | 1.28 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 1.07 | 24.57 | |
| C-3 | 1.6 | Marsh | 32.9 | 68.6 | 8.33 | 30.4 | 6.2 | 1.36 | 5.34 | 0.78 | 4.09 | 0.78 | 2.49 | 0.31 | 18.7 | 2.03 | 0.3 | 182.61 | 1.24 | 0.78 | 0.95 | 1.10 | 23.97 | |
| C-4 | 1.9 | Marsh | 32.6 | 67.4 | 8.15 | 29.8 | 5.97 | 1.31 | 5.18 | 0.78 | 4.07 | 0.78 | 2.49 | 0.3 | 19.5 | 2 | 0.3 | 180.63 | 1.23 | 0.80 | 0.95 | 1.10 | 25.00 | |
| C-5 | 2.3 | Marsh | 33 | 67.7 | 8.15 | 30.4 | 6.15 | 1.51 | 5.39 | 0.72 | 3.97 | 0.79 | 2.18 | 0.32 | 18 | 2.1 | 0.31 | 180.69 | 1.20 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 1.22 | 22.78 | |
| C-6 | 2.8 | Marsh | 32.1 | 66.8 | 8.07 | 29.5 | 5.77 | 1.3 | 5 | 0.72 | 3.9 | 0.74 | 2.36 | 0.29 | 18.4 | 1.97 | 0.29 | 177.21 | 1.25 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 1.13 | 24.86 | |
| C-7 | 3.3 | Marsh | 19.9 | 39.8 | 5 | 19.3 | 3.89 | 0.96 | 3.5 | 0.48 | 2.67 | 0.54 | 1.6 | 0.22 | 12.2 | 1.45 | 0.22 | 111.73 | 1.02 | 0.75 | 0.92 | 1.21 | 22.59 | |
| C-8 | 3.6 | Marsh | 35.1 | 73.4 | 8.84 | 33.1 | 6.59 | 1.59 | 5.72 | 0.76 | 4.07 | 0.78 | 2.24 | 0.32 | 18.4 | 2.15 | 0.32 | 193.38 | 1.24 | 0.78 | 0.96 | 1.21 | 23.59 | |
| C-9 | 4.2 | Marsh | 33.4 | 69.4 | 8.28 | 30.2 | 6.09 | 1.35 | 5.27 | 0.78 | 4.03 | 0.76 | 2.45 | 0.3 | 18.8 | 2.03 | 0.3 | 183.44 | 1.26 | 0.81 | 0.96 | 1.11 | 24.74 | |
| C-10 | 4.5 | Marsh | 30.6 | 64 | 7.75 | 28.4 | 5.65 | 1.22 | 4.82 | 0.7 | 3.67 | 0.67 | 2.17 | 0.27 | 16.7 | 1.78 | 0.27 | 168.67 | 1.28 | 0.80 | 0.95 | 1.09 | 24.93 | |
| C-11 | 5 | MIS-1 Flood | 24.3 | 50.3 | 6.08 | 22.5 | 4.5 | 0.94 | 3.77 | 0.55 | 2.77 | 0.52 | 1.63 | 0.21 | 12.4 | 1.37 | 0.21 | 132.05 | 1.31 | 0.80 | 0.95 | 1.06 | 23.85 | |
| C-12 | 5.7 | MIS-1 Flood | 22 | 45.8 | 5.57 | 20.2 | 3.7 | 0.74 | 3.04 | 0.43 | 2.22 | 0.4 | 1.29 | 0.16 | 10.3 | 1.06 | 0.16 | 117.07 | 1.56 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 1.03 | 25.75 | |
| C-13 | 6 | MIS-1 Flood | 34.7 | 71.5 | 8.65 | 31.8 | 6.25 | 1.36 | 5.43 | 0.79 | 4.04 | 0.77 | 2.44 | 0.3 | 18.5 | 2.06 | 0.3 | 188.89 | 1.31 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 1.09 | 24.03 | |
| C-14 | 6.4 | Alluvial | 23.2 | 46.9 | 5.87 | 21.3 | 4.12 | 0.83 | 3.28 | 0.45 | 2.25 | 0.42 | 1.32 | 0.16 | 10.1 | 1.12 | 0.17 | 121.49 | 1.54 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 1.05 | 24.05 | |
| C-15 | 7 | Alluvial | 23.7 | 60.3 | 6.25 | 22.5 | 4.56 | 0.9 | 3.58 | 0.5 | 2.53 | 0.46 | 1.47 | 0.19 | 10.2 | 1.3 | 0.19 | 138.63 | 1.41 | 0.77 | 1.14 | 1.04 | 22.17 | |
| C-16 | 7.4 | Alluvial | 24.2 | 48 | 5.85 | 22.9 | 4.18 | 0.86 | 3.35 | 0.44 | 2.37 | 0.42 | 1.24 | 0.17 | 10.5 | 1.18 | 0.18 | 125.84 | 1.52 | 0.85 | 0.93 | 1.07 | 25.00 |
| LaN/YbN | LaN/SmN | Ce/Ce* | Eu/Eu* | Σ REE | Clay | Silt | Sand | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LaN/YbN | 1 | |||||||
| LaN/SmN | 0.42 | 1 | ||||||
| Ce/Ce* | −0.13 | −0.34 | 1 | |||||
| Eu/Eu* | −0.46 | −0.21 | −0.29 | 1 | ||||
| Σ REE | −0.56 | −0.34 | 0.37 | 0.11 | 1 | |||
| Clay | −0.37 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.43 | 1 | ||
| Silt | −0.50 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.57 | 0.82 | 1 | |
| Sand | 0.47 | −0.03 | −0.17 | −0.16 | −0.55 | −0.93 | −0.98 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prudêncio, M.I.; Ruiz, F.; Marques, R.; Dias, M.I.; Vidal, J.R.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Cáceres, L.M.; González-Regalado, M.L.; Muñoz, J.M.; Pozo, M.; et al. REE Geochemistry of Neogene–Holocene Sediments of La Fontanilla Cove (Tinto Estuary, SW Spain). Minerals 2022, 12, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12040417
Prudêncio MI, Ruiz F, Marques R, Dias MI, Vidal JR, Rodrigues AL, Cáceres LM, González-Regalado ML, Muñoz JM, Pozo M, et al. REE Geochemistry of Neogene–Holocene Sediments of La Fontanilla Cove (Tinto Estuary, SW Spain). Minerals. 2022; 12(4):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12040417
Chicago/Turabian StylePrudêncio, Maria Isabel, Francisco Ruiz, Rosa Marques, Maria Isabel Dias, Joaquín Rodríguez Vidal, Ana Luísa Rodrigues, Luis Miguel Cáceres, María Luz González-Regalado, Juan Manuel Muñoz, Manuel Pozo, and et al. 2022. "REE Geochemistry of Neogene–Holocene Sediments of La Fontanilla Cove (Tinto Estuary, SW Spain)" Minerals 12, no. 4: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12040417
APA StylePrudêncio, M. I., Ruiz, F., Marques, R., Dias, M. I., Vidal, J. R., Rodrigues, A. L., Cáceres, L. M., González-Regalado, M. L., Muñoz, J. M., Pozo, M., Gómez, P., Toscano, A., Abad, M., Izquierdo, T., Arroyo, M., Romero, V., & Gómez, G. (2022). REE Geochemistry of Neogene–Holocene Sediments of La Fontanilla Cove (Tinto Estuary, SW Spain). Minerals, 12(4), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12040417










