Abstract
Diatomitic and clastic-volcanoclastic marly samples from the Paranisia area of Limnos Island, were studied mineralogically by X-ray diffraction (XRD), chemically by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF) and morphologically by scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDS), together with some physical properties such as the insulation block density, specific surface area and porosity. The diatomaceous samples were classified as porcelaneous or clayey (moler type) diatomite. Opal-CT forms microplates disseminated in the groundmass and are diagenetically formed in expense of opal-A dissolution. The purest diatomaceous beds have been transformed into opaline beds (opal-CT-rich rocks), whereas the clayey beds were not influenced by diagenetic transformations. The studied diatomites from Limnos Island are suitable materials for environmental uses, as an absorbent, for the production of insulation bricks or as lightweight aggregates.
1. Introduction
Diatomite is a friable, earthy, very fine-grained, siliceous sedimentary rock resulting from the accumulation of fossil frustules of diatoms. They consist of porous siliceous algae skeletons with Si-O tetrahedral interconnection nets. [1,2]. Pure diatomites are usually light in colour, with low thermal conductivity and a high fusion point. Besides the silica polymorphs, diatomitic rocks may also contain clay minerals, carbonates, feldspars, volcanic glass, silica sand, iron oxides and organic matter [3,4].
The general term diatomite may reflect, besides the pure opal-A deposits, the calcareous and clayey diatomites. The diagenetically transformed opal-A to opal-CT rocks called porcelanites [1,2,3].
Diatomite deposits exist in many countries all over the world: USA (especially California), Canada, Belgium, Denmark, Germany, USSR, Canada, South Korea, Romania, Japan, South Africa, Ireland, etc. They also appear in Mediterranean countries such as Greece, Italy, Spain, France, Morocco, Algeria and Cyprus [5].
Worldwide diatomite production has increased by 4% from previous years, more specifically, 2.6 million tones in 2019. The USA is the dominant country, with 38% of global production. China follows with 16%, Turkey 9%, Denmark, Peru, Mexico, France and Argentina, 4% each. Denmark produces mostly moler-type diatomite (a diatomite with high percentage of clays). More specifically, in 2019 the USA produced 980 thousand tons of diatomite, China 420 thousand tons, Turkey 243 thousand tons and Denmark 108 thousand tons. Total world production amounts to 2.6 million tons (BGS, World Mineral Production 2019).
There are several locations in Greece where diatomaceous formations can be found. Greek diatomite is related to Tertiary marine and continental basins. The most significant diatomite deposits of all types are those of Kleidi in the Florina region, Komninon in the Ptolemaida region, Eani in the Kozani region, Elasona, Megalopoli and the basin of Mitilinion in Samos Island, which are continental deposits, as well as Milos, Gavdos, Zakinthos and the basins of Kastelli and Heraclium in Crete, which are shallow marine or deep sea deposits [6,7,8,9].
Diatomites have several uses after treatment and calcination. For example, diatomite is used as a water filtering agent, as agro-foods, as oil absorbents, as lightweight aggregates, in insulation bricks, as catalyst supports and electrode material for energy conversion and storage [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25].
In the present study, a new deposit of diatomaceous-rich sediments from Limnos Island, Greece, were studied mineralogically and geochemically in order to classify them, while some physical parameters, such as insulation block density, porosity and specific surface area were measured in order to ascertain their possible environmental uses.
2. Materials and Methods
Limnos Island is located in the NE Aegean Sea and is part of the broader Tertiary sedimentary basin located on the Rhodope metamorphic unit. The basin’s sedimentary rocks can be delineated into two discrete units: the upper unit that consists of Oligocene marine and continental sedimentary rocks and tuffs and the lower sedimentary sequence that is comprised of Eocene-Oligocene sandstones, conglomerates and flysch.
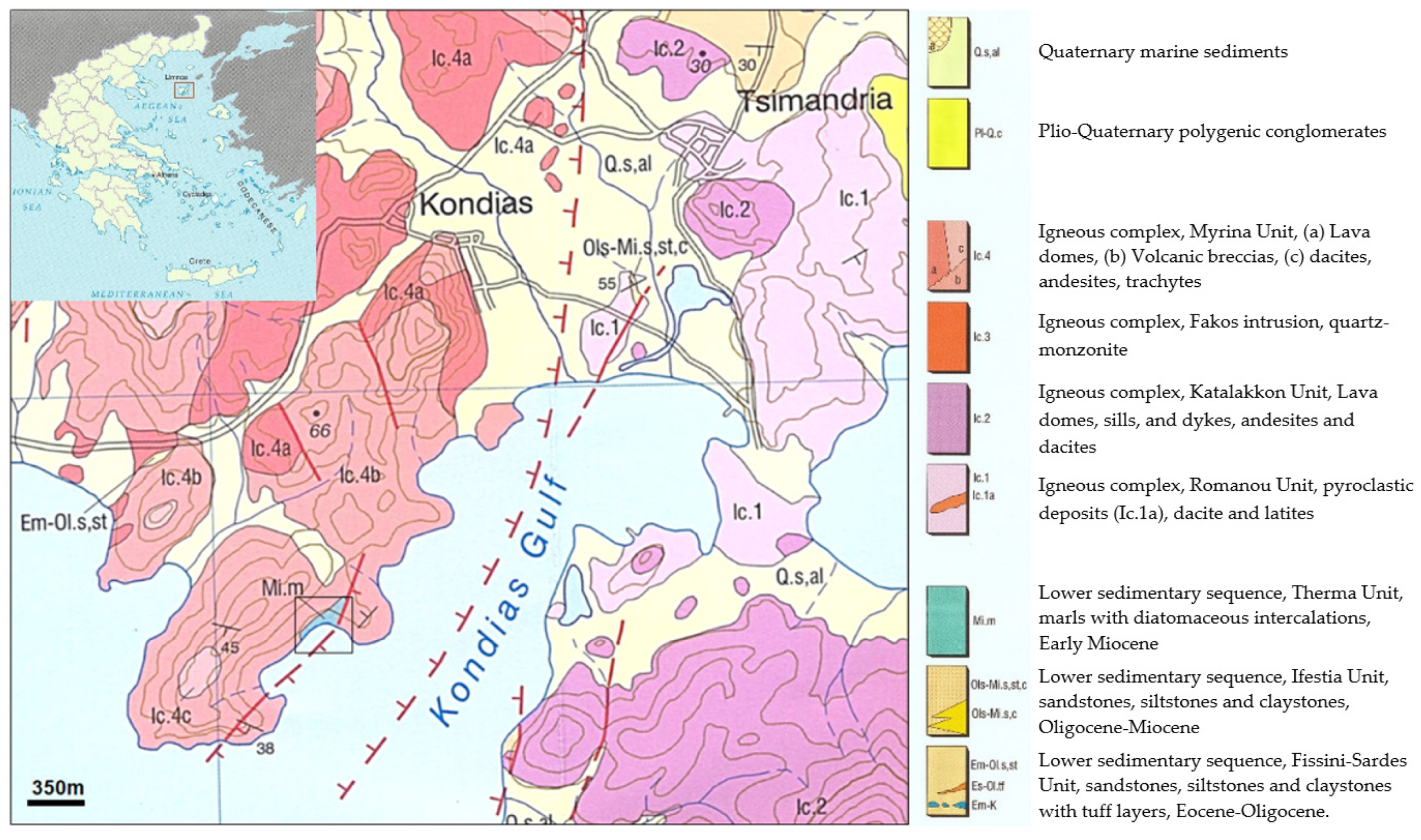
The study area (Figure 1) belongs to the Therma unit (Mi.m), which is part of the lower sedimentary sequence and consists of thinly bedded, whitish-yellow marls with diatomaceous intercalations and abundant plant remains, conglomerate bodies with oxidized pebble and volcanic clasts near the base. The diatomitic beds were found immediately below the volcanic tuffs of the upper unit, with thicknesses varying from 0.5 to 30 m. The average depth of the drilling procedure in the Paranisia area was about 25 m and the main rock types drilled were diatomite, clayey diatomite and tuffs. Most of the samples were altered, except samples from drill A9, where the whole stratigraphic column exists. A total of eight samples from drill A9 were collected and studied.
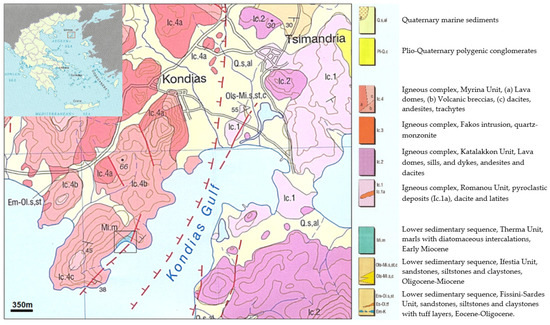
Figure 1.
Geological map of the study area on Limnos Island [26] (Reprinted/adapted with permission from Prof. M. Fyticas).
2.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
A representative amount of the collected diatomite samples were powdered in an agate mortar and analyzed by X-ray diffraction to determine their mineralogical composition. XRD analysis was performed using a Phillips (PW1820/00) diffractometer with Ni-filtered CuKα radiation (PHILLIPS Analytical, Eindhoven, The Netherlands). The counting statistics of the XRD study were, step size: 0.01° 2θ, start angle: 3°, end angle: 63° and scan speed: 0.02° 2θ/s. Quantitative estimates of the abundance of the mineral phases were derived from the XRD data, using the intensity of certain reflections and external standard mixtures of minerals [27,28]. Corrections were made using the MAUD-Material Analysis Using Diffraction software (v. 2.992, Lutterotti L., University of Trento, Trento, Italy) with RIETVELD refinement [29]. Clay mineralogy was identified from air-dried, glycolated and heat-treated oriented samples scanned from 3 to 23° 2θ at a scanning speed of 1.2°/min. From the morphological examination of the background of the XRD patterns, a very broad background hump between 10–30° 2θ clearly indicates the presence of amorphous material. The content of the amorphous phase was calculated according to the methodology proposed by Kantiranis et al. [27]. The detection limit for crystalline and amorphous phases was ±2% w/w.
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM-EDS)
The morphological study and microanalysis of representative diatomaceous samples was performed using scanning electron microscopy on a Jeol JSM-840: a scanning electron microprobe equipped with a LINK 10,000 energy dispersion analyzer (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). The instrument operating conditions were voltage 15 kV, electron beam intensity < 3 nA and 1 mm diameter, while the measurement time was 60 s. Corrections were made using the ZAF-4/FLS software provided by LINK. Fragments of the studied samples were sprinkled onto double-sided aluminum tape mounted on a SEM stub, carbon-coated and viewed through randomly selected fields of view.
2.3. X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)
Bulk analyses of the studied samples were determined by a Bruker S4-Pioneer X-Ray Fluorescence wavelength dispersive spectrometer (Brucker AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany). The spectrometer was fitted with a Rh tube, six analyzing crystals, namely: LIF200, LIF220, LIF420, PE, TLAP and PX1 and the detectors were a gas-flow proportional counter, a scintillation detector or a combination of the two. The gas-flow proportional counter uses P10 gas, which is a mixture of 90% argon and 10% methane. Major elements were analyzed on a fused glass bead at 60 kV and 45 mA tube-operating conditions. Matrix effects in the samples were corrected for by applying theoretical alpha factors and measured line overlap factors to the raw intensities measured. The standards that were used in the calibration procedures for major element analyses were: AGV-1 (Andesite) (USGS), JG-1 (Granodiorite) (GSJ), JB-1 (Granodiorite) (GSJ), NIM-G (Granite) (MINTEK), GA (Granite) (CRPG) and GH (Granite) (CRPG).
2.4. Physical Parameters
2.4.1. Insulation Block Density
According to ASTM D4404-84 (2004), the dry unit weight is defined as the quotient of the weight of a unit to the volume of the unit: d = w/v (g/cm3). Where W is the total weight of the unit including the pores with their content (air) and V is the total volume of the unit. When a material is to be used as an insulation agent, the measured dry unit weight represents the insulation block density of the material. According to their insulation density, the studied diatomite rocks were evaluated as possible materials in the cement and insulation bricks industry.
2.4.2. Specific Surface Area
Specific surface measurement is used in various science and technology fields. The most important method, among others, is the absorption of low thermal nitrogen of Brunauer, Emmett and Teller [29,30]. For the analyses, two glass bottles with the same volume are required. The first bottle is filled with the examined sample and the other is empty. In room temperature conditions, the two bottles are filled with nitrogen gas (pressure 1 atm). After that, the bottles are frozen by immersing them in liquid nitrogen (circa −190 °C). The absorbed nitrogen gas by the sample leads to a difference between the two bottles. The equilibrium pressure in the bottle with the material is stabilized by itself, in the field of the B.E.T. method, under low temperature conditions and can be determined without additional pressure measurements. The specific surface area of a sample (Sg) is calculated by the following equation [30]: Sg = A*Δh/m (m2/g), where A is a coefficient obtained from a special nomogram using the pressure difference of the manometer (Δh) in mm and the atmospheric pressure in mmHg, while m is the mass in g of the material used.
2.4.3. Porosity
Lightweight materials are characterized by the presence of pores in their structure. Porosity is described as the quotient of the pore volume of a sample to the total volume of the sample. The propagation speed of elastic waves through a sample is defined by the porosity. According to Wyllie et al. (1958) [31], the velocity of the P-waves (Vp) is related to the porosity (φ) by the following equation: 1/Vp = (φ/Vpf) + (1 − φ/Vpm), where Vpf is the velocity of P-waves through the pores of a rock sample filled with fluid (liquid or gas). The velocity of P-waves in the water is 1450 m/s, while in the air it is 330 m/s [32]. Vpm is the P-waves velocity through a rock sample without pores. From the previous equation it can be concluded that samples with high porosity values lead to a decrease P-wave velocity.
A special portable ultrasound speed measuring device Pundit Lab+ (Proceq, Switzerland) was used for the porosity measurement of the studied bulk samples. Since the dimension of the specimens are known, the accuracy of the method depends on the precise measure of the P-wave propagation time. In this device, the recording range of the propagation time of the ultrasound ranges from 0.1 to 9999 μs, while the accuracy of the measurement is 0.1 μs. For the precise operation of the instrument, special 54 kHz cylindrical transducers were used, which are fitted diametrically to the ends of the studied samples. To improve the acoustic contact between the samples and the transducers, plasticine was used as the contact medium [33,34], while a cylindrical standard of synthetic material was used to adjust the accuracy of the instrument.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mineralogical Composition
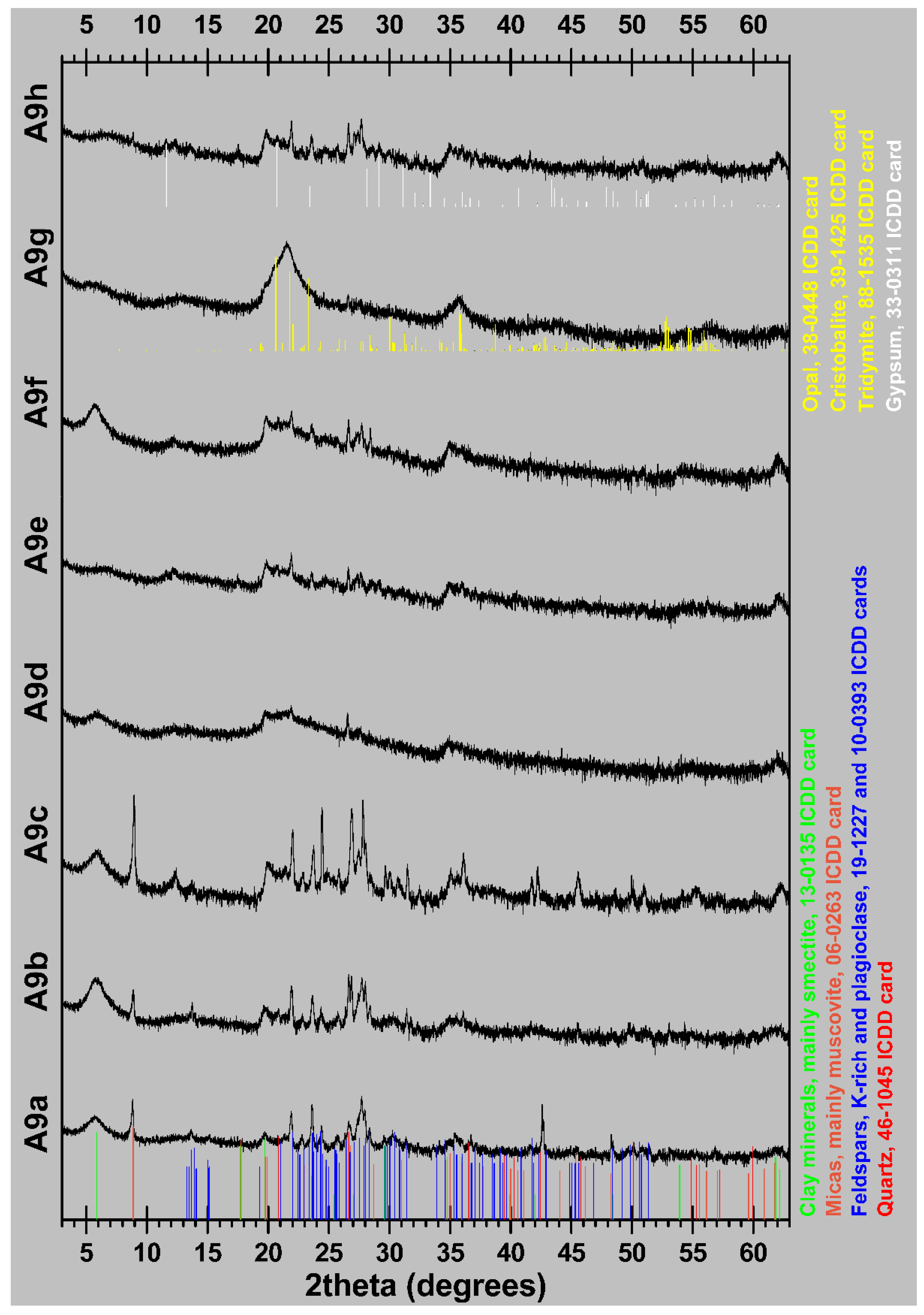
The mineralogical composition of the studied samples is presented in Table 1, while their XRD patterns are shown in Figure 2. Opal-A and opal-CT were found in five samples and its total percentage varied from 22 (sample A9h) to 85 wt% (sample A9g). According to glycolated samples, the only identified clay mineral is smectite and in particular montmorillonite (very good matching of the montmorillonte ICDD file 13-0135), with contents between 4 (sample A9g) and 45 wt% (sample A9f).

Table 1.
Mineralogical composition (w/w%) of the studied samples as measured by XRD.
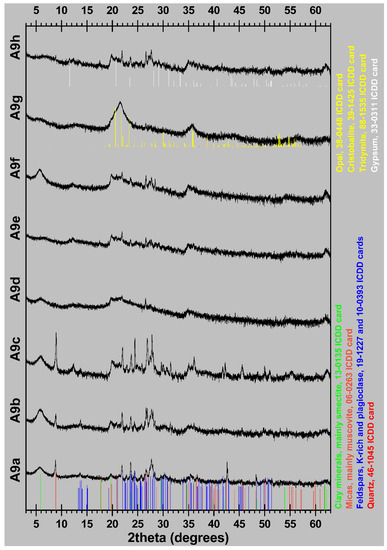
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of the studied samples.
The opal-A rich samples which contain significant amounts of clay minerals and micas can be classified as clayey and marly diatomites, while the diatomaceous samples with a predominance of opal-CT can be classified as porcelanites, or porcelaneous diatomites. According to Stamatakis et al. [35] and Minoura et al. [36], porcelanites are related to the diagenetic transformation of opal-A-rich diatomite beds. Specifically, the conversion of diatomite deposits into porcelanite formations is attributed to the dissolution of opal of the former (opal-A) and its conversion initially to cristobalite-tridymite and finally to quartz [37], with increasing depth, heat flow rates, age, or elevated salinity-alkalinity of the basin. Clayey diatomites or Mole-type diatomites, according to Harben [38] and Stamatakis et al. [35], refer to clay minerals-rich diatomite deposits. The most significant diatomite deposits of this type are located in Denmark, mainly on the islands of Fur and Mors. They are one of the most important centers for the production of clay diatomaceous earth in the world. In volcanic terrains, detrital and/or volcanogenic minerals, such as feldspars, quartz and muscovite are commonly found intercalated within diatomaceous horizons, examples are from Samos and Milos islands, Greece [35,41]. In the studied area, similar mixing of biogenic and volcanic components are present, i.e. sample A9c. Evaporitic minerals such as gypsum were found in the deepest horizons (samples A9e and A9h) with percentages varying from 11 to 16 wt%. The presence of gypsum in the studied samples is particularly important as it indicates an evaporative deposition environment [39]. Carbonate minerals are absent, and this is beneficial for certain industrial applications [40].
3.2. Morphology of the Studied Diatomites
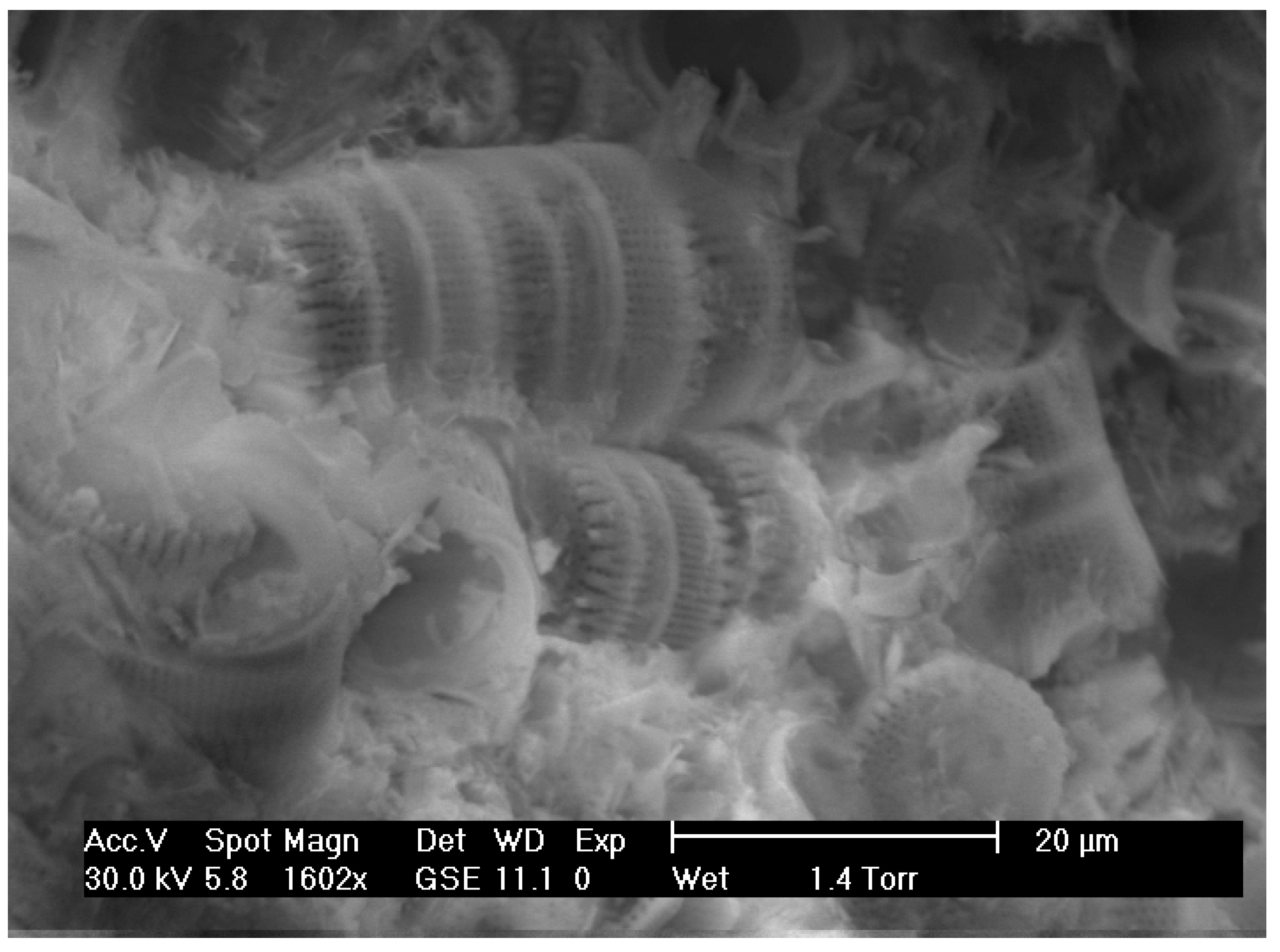
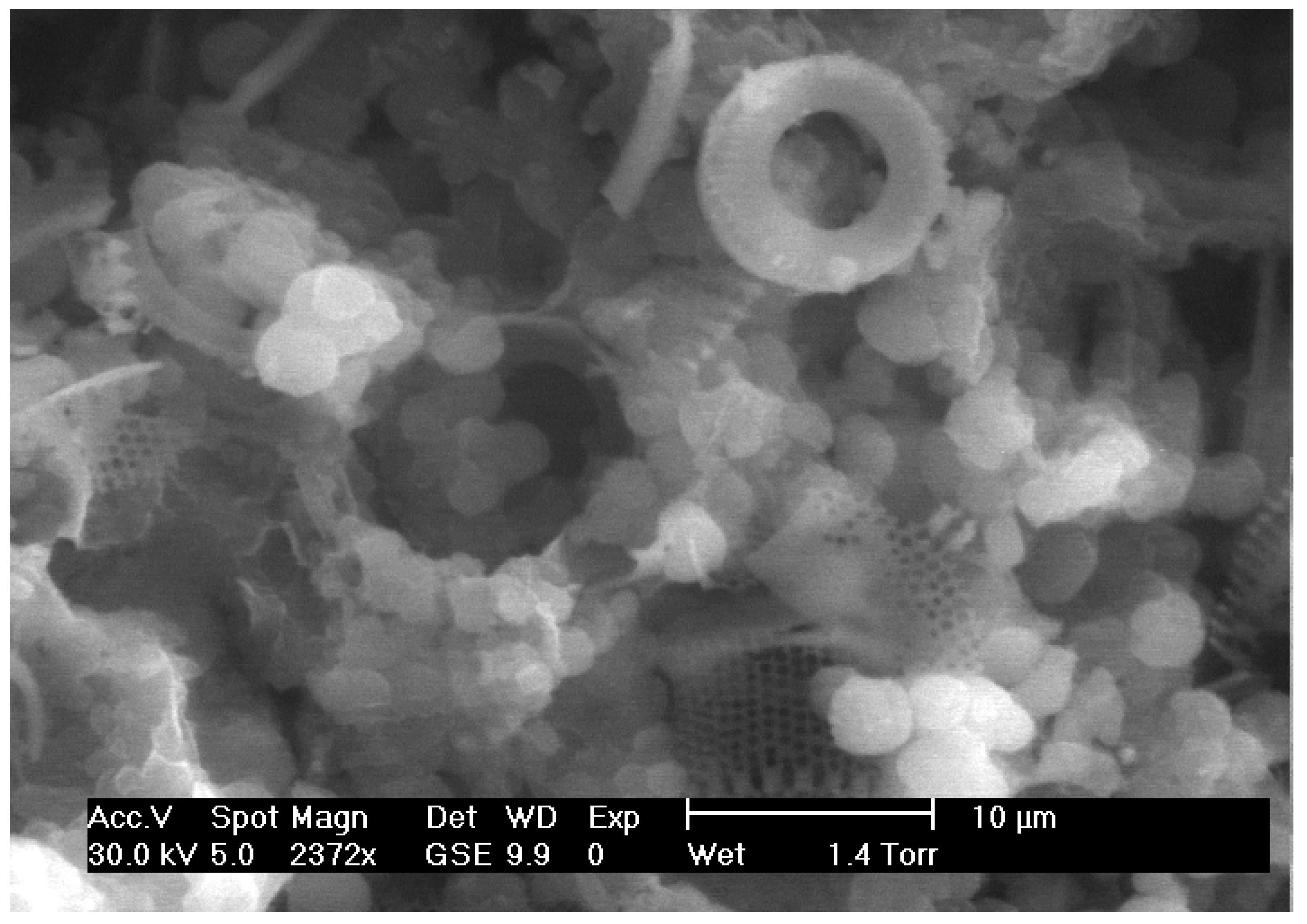
Results from the SEM-EDS study showed that the diatom frustules were mostly cylindrical, resembling the diatom species that have been recorded previously in the lacustrine basins of central and northern Greece [3,41]. The frustules were either well preserved (clayey diatomite beds, Figure 3) or highly dissolved from diagenetic transformations (opaline beds, Figure 4). Lepispheres constitute the intermediate stage of the gradual diagenetic transformation of the amorphous silicon of diatom shells to more crystalline phases such as opal-CT.
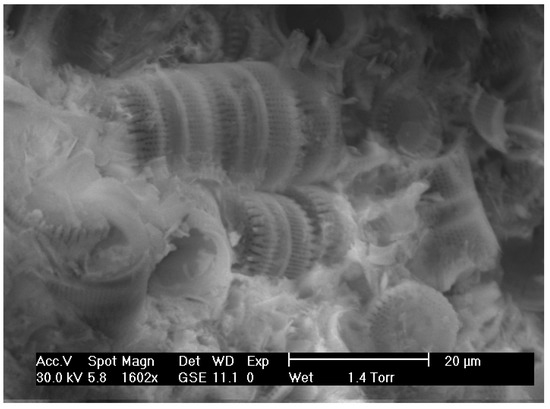

Figure 3.
Colonies of well-preserved cylindrical diatom frustules hosted in a clayey matrix.

Figure 4.
The association of opal-CT micro-plates and lepispheres (i) with diatom frustules.
Similar diagenetic changes have been recorded in the volcanic islands of Milos and Aegina, where the opal-A has been diagenetically altered due to the high heat flow rates, related to contemporary volcanism in those islands [35,41].
3.3. Chemical Analysis
XRF measurements (Table 2) showed that SiO2 and Al2O3 were the dominant major elements with percentages varying from 49.76 (sample A9h) to 81.60 wt% (sample A9g) and 4.50 (sample A9g) to 21.26 wt% (sample A9c), respectively.

Table 2.
Chemical analysis of the studied samples as determined by XRF.
The measured values of chemical analyses are in agreement with the international literature, with SiO2 values for porcelaneous diatomites ranging from 65–80 wt% and Al2O3 for clayey diatomites ranging from 14 to 16 wt% [42,43,44,45,46].
All the other major oxides measured were present in minor amounts. Chemical analysis showed that the results from the XRF analysis are in good agreement with those of the mineralogical analysis. It is noteworthy that samples containing high percentages of SiO2 also have high percentages of silica minerals (opal A + CT).
3.4. Physical Properties
In Table 3, the physical properties measured for the studied samples are presented.

Table 3.
Insulation block density (g/cm3), porosity (% v/v) and specific surface area (m2/g) measurements for the clay-diatomite sample (A) and the silica polymorphs-rich sample (B).
3.4.1. Insulation Block Density and Specific Surface Area
In particular, blocks of sample A (moler type) and sample B (porcelanite type) dried at 105 °C, had densities of 0.831 g/cm3 (51.8 lb/ft3) and 0.819 g/cm3 (51.1 lb/ft3), respectively. After calcination at 1100 °C, block samples A and B showed similar insulation block densities, 0.753 g/cm3 (47.0 lb/ft3) and 0.757 g/cm3 (47.3 lb/ft3), respectively. It is well known that smectites dehydroxylate at about 600 °C [47], forming a stable phase retaining the initial clay structure up to about 850 °C. As temperature increases, cristobalite and probably mullite crystallize at temperatures up to 1250 °C, resulting to crystals with high length [47,48,49]. According to Yang et al. [50], the crystal length is dependent on the chemical composition of the initial material melting in high temperatures. Materials containing high amounts of K2O and Na2O favor the development of long mullite crystals and a more porous structure [49].
Moreover, dried at 105 °C, diatomite samples of porcelanite-type showed higher specific surface area (132 m2/g) compared to diatomite samples of molar-type (77 m2/g). This difference can be attributed to the higher participation of diatoms in the porcelanite-type sample as shown by the opal concentration (A + CT), due to the complex microporous structure that the diatoms present and also to the contribution of the microporosity of clay minerals present in significant amounts of the studied porcelanite-type samples. However, both samples had almost the same insulation block density at 1100 °C (Table 3). Chen [42] found that clayey diatomite (molar-type) showed lower specific surface area values (92.51 m2/g) compared to treated diatomite (111.53 m2/g).
3.4.2. Porosity
According to Kantiranis et al. [33,34], the measurement of the P waves velocity is a reliable method to determinate a rock sample’s porosity. Vogiatzis [51] has proved that the P wave velocity is dependent on the grain size and the porosity of the mortar materials. Porosity of the initial materials A and B, dried at 105 °C, measured 26.1 and 28.6% v/v, respectively (Table 3). Differences between the studied samples can be attributed to the complex microporous structure of the diatoms contained in higher amounts in sample B. After the samples were calcined, at 1100 °C porosity decreased to 15.7% v/v for sample A and 16.0% v/v for sample B. According to Pimraksa and Chindaprasit [52], the percentage of clay minerals in a sample decreased while the temperature rises, resulting in a decrease in the porosity. On the other hand, the decrease in the porosity of sample B (porcelanite-type material) is due to the progressive transformation of diatoms opal-A at elevated temperature (1100 °C) in a more crystalline and dense structure (opal-CT) losing a significant part of their microporous structure.
Considering mineralogical and chemical analyses and measurements of selected physical properties, both samples could be used as an absorbent or for the production of insulation bricks. In particular, the “moler type” diatomite is favorable as a potential insulation material due to its high percentages of aluminum oxide. Another potential use, based on the specific properties of diatomite, is as lightweight aggregates with various cements in mortar and concrete for insulating properties too. This insulation technique, among other advantages, leads to avoiding heavy construction elements, while respecting the requirements of thermal regulation standards [53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60].
4. Conclusions
In this study, analysis of the diatomaceous samples obtained from the area of Paranisia in Limnos Island showed that they can be classified as porcelaneous diatomite (with a predominance of opal-A and opal-CT) and clayey diatomite (moler-type, with a predominance of clay minerals, micas and opal-A). Opal-CT forms micro-plates disseminated in the groundmass and is diagenetically formed in expense of opal-A dissolution. The purest diatomaceous beds have been transformed into opaline beds (opal-CT-rich rocks), whereas the clayey beds were not influenced by diagenetic transformations. The presence of gypsum in the studied samples is particularly important as it indicates an evaporative deposition environment, while the absence of carbonate minerals is beneficial for certain industrial applications.
Analysis of two samples, one rich in clay, volcanic and detrital minerals (molar-type), and the other rich in silica polymorphs (opal-A and opal-CT), showed that the latest polcelanite-type sample has a higher specific surface area after drying at 105 °C. Both samples have almost the same insulation block density and significant porosity at 1100 °C, thus indicating that the diatomite could be used as an absorbent or for the production of insulation bricks. The “moler type” diatomite is favorable as potential insulation material due to its high percentages of aluminum oxide, while both diatomitic materials can be used as lightweight aggregates to prepare mortars and concretes with thermal insulating properties and avoid heavy constructions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.K., E.S.; methodology and experiments, E.S. and N.K.; writing—original draft preparation, N.K., E.S. and C.M.; writing—review and editing, K.C., M.S. and G.G.; supervision, N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Breese, O.Y.R. Diatomite. In Industrial Minerals and Rocks; Carr, D.D., Ed.; Society of Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration Inc.: Englewood, CO, USA, 1994; pp. 397–411. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Dai, H. Mg3Si4O10(OH)2 and MgFe2O4 in situ grown on diatomite: Highly efficient adsorbents for the removal of Cr(VI). Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 271, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilia, K.I.; Stamatakis, G.M.; Perraki, S.T. Mineralogy and technical properties of clayey diatomites from north and central Greece. Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 2009, 1, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.A.; Selim, A.Q.; Zayed, A.M.; Komarneni, S.; Mobarak, M.; Seliem, M.K. Enhancing adsorption capacity of Egyptian diatomaceous earth by thermo-chemical purification: Methylene bule uptake. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 534, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taoukil, D.; El Meski, Y.; Lahlaouti, M.I.; Djedjig, R.; El Bouardi, A. Effect of the use of diatomite as partial replacement of sand on thermal and mechanical properties of mortars. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 42, 103038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, M.; Tsipoura-Vlachou, M. Diatomaceous rocks in Greece. In Proceedings of the 14th International Congress of IMM on Minerals Materials and Industry (Ed IMM), Edinburgh, UK, 2–6 July 1990; pp. 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Koukouzas, N. Komnina diatomaceous clay deposit overburden lignite and its suitability (W. Macedonia, Northern Greece). Miner. Wealth 1992, 81, 39–52. [Google Scholar]
- Dermitzakis, M.; Triantafyllou, M.; Stamatakis, M.; Tsaparas, N. Diatomaceous sediments of Gavdos Island, Southern Greece, Stratigraphical and Petrological analysis. In Proceedings of the Interim Colloquium/RCMNS Meditarrenean Geogene Cyclostratigraphy in Marine-Continental Paleo-Environments, Patras, Greece, 27–29 May 1998; Books of Abstracts. p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, M.; Calvo, J.; Regueiro, M.; Neri, R. Alternating diatomaceous and volcaniclastic deposits in northern Milos Island, Aegean Sea, Greece. In Proceedings of the 15th International Sedimentological Congress, Alicante, Spain, 12–17 April 1998; pp. 738–739. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, H.Q.; Dong, B.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhou, X.F.; Yu, Z.X. Pollutant removal mechanisms in a bio-diatomite dynamic membrane reactor for micro-polluted surface water purification. Desalination 2012, 293, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.L.; Zhu, M.F.; Li, Y.G.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, H.Z. Synthesis of dental resins using diatomite and nano sized SiO2 and TiO2. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2012, 22, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skubiszewska-Zieba, J.; Charmas, B.; Leboda, R.; Gunko, V.M. Carbon-mineral adsorbents with a diatomaceous earth/perlite matrix modified by carbon deposits. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 156, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.L.; Chen, S.F.; Chen, H.X. Effects of diatomite on the properties of asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergun, A. Effects of the usage of diatomite and waste marble powder as partial replacement of cement on the mechanical properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Sun, D.; Liu, G. Surface complexation modeling calculation of Pb(II) adsorption onto the calcined diatomite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 359, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, J.; Gao, W.; Yan, S.; Liu, G.; Hao, H. Preparation of porous brick from diatomite and sugar filter mud at lower temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San, O.; İmaretli, A. Preparation and filtration testing of diatomite filtering layer by acid leaching. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyngsie, G.; Katika, K.; Fabricius, I.L.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Borggaard, O.K. Phosphate removal by iron oxide-coated diatomite: Laboratory test of a new method for cleaning drainage water. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.A. Phase change materials integrated in building walls a state-of-the-art review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 31, 870–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, C.; Jin, Q. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of La and N co-doped TiO2/diatomite composite. Powder Technol. 2017, 322, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losic, D.; Mitchell, J.G.; Voelcker, N.H. Diatomaceous lessons in nanotechnology and advanced materials. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2947–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraishen, M.A.M.; Alg-Houti, M.S. Enhanced dye adsorption by microemulsion-modified calcined diatomite (le-cd). Adsorpt. J. Int. Adsorpt. Soc. 2005, 11, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.M.; Tian, X.K.; Yu, C.Y. Capturing and storage of CO2 by micron-nano minerals: Evidence from the nature. Chin. J. Geochem. 2011, 30, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediz, N.; Bentli, İ.; Tatar, İ. Improvement in filtration characteristics of diatomite by calcination. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 94, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Pan, J.; Cai, J. Separation of diatom valves and girdle bands from coscinodiscus, diatomite by settlin method. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5736–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenti, F.; Manetti, P.; Mazzuoli, R.; Pertusati, P.; Fytical, M.; Kolios, N. Geological map of the Limnos Island (Northern Aegean Sea—Greece); Lithografia Artistica Cartografica: Firenze, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kantiranis, N.; Stergiou, A.; Filippidis, A.; Drakoulis, A. Calculation of the percentage of amorphous material using PXRD patterns. Bull. Geol. Soc. of Greece 2004, 36, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantiranis, N.; Sikalidis, K.; Godelitsas, A.; Squires, C.; Papastergios, G.; Filippidis, A. Extra-framework cation release from heulandite-type rich tuffs on exchange with NH4+. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haul, R.; Dümbgen, G. Vereinfachte méthode zur messung von oberflächengrößen durch gasadsorption. Chem. Ing. Tech. 1963, 35, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyllie, M.R.J.; Gregory, A.R.; Gardner, G.H.F. An experimental investigation of factors affecting elastic wave velocities in porous media. Geophysics 1958, 23, 421–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasnis, S.D. Principles of Applied Geophysics; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1997; p. 429. [Google Scholar]
- Kantiranis, N.; Christaras, B.; Filippidis, A.; Tsirambides, A. The usage of ultrasonic techniques at calcination studies. In Proceedings of the International Meeting “Aggregate 2001—Environment and Economy”, Helsinki, Finland, 6–10 August 2001; pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Kantiranis, N.; Filippidis, A.; Tsirambides, A.; Christaras, B. Thermal decomposition study of crystalline limestone using P-wave velocity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, M.G.; Hein, J.R.; Magganas, A.C. Geochemistry and diagenesis of Miocene lacustrine siliceous sedimentary and pyroclastic rocks, Mitilinii basin, Samos Island, Greece. Sediment. Geol. 1989, 64, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoura, K.; Susaki, T.; Horiuchi, K. Lithification of biogenic siliceous sediments: Evidence from Neogene diatomaceous sequences of northeast Japan. Sediment. Geol. 1996, 107, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.; Mc Intyre, J.L. Monterey Formation porcelanite reservoirs of the Elk Hills field, Kern County, California. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 2001, 85, 169–189. [Google Scholar]
- Harben, P.W. Diatomite. In The Industrial Minerals Handybook IV; Industrial Minerals Informations: Surrey, UK, 1992; pp. 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanou, E.; Kantiranis, N.; Chatzicharalambous, K.; Stamatakis, M.; Georgiadis, G. Diatomaceous silica in environmental applications. A case study from the lacustrine deposit of Limnos Island, Aegean Sea Greece. In Proceedings of the Coastal Landscapes, Mining Activities & Preservation of Cultural Heritage, Milos Island, Greece, 17–20 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, K.K. Uses of Industrial Minerals, Rocks and Freshwater; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 584. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, M.G.; Fragoulis, D.; Antonopoulou, S.; Stamatakis, G. The opaline silica rich sedimentary rocks of Milos Island, Greece and their behavior as pozzolanas in the manufacture of cement. Adv. Cem. Res. 2010, 22, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Miao, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhan, F.; Wang, W.; Chen, N.; Xie, Q. Optimization of pore structure of a clayey diatomite. Part. Sci. Technol. 2019, 38, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, M.G.; Fragoulis, D.; Csirik, G.; Bedelean, I.; Pedersen, S. The influence of biogenic micro-silica-rich rocks on the properties of blended cements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Ediz, N. The use of raw and calcined diatomite in cement production. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouzas, N. Mineralogy and geochemistry of diatomite associated with lignite seams in the Komnina Lignite Basin, Ptolemais, Northern Greece. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2007, 71, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoulis, D.; Stamatakis, M.G.; Chaniotakis, E.; Columbus, G. Characterization of lightweight aggregates produced with clayey diatomite rocks originating from Greece. Mater. Charact. 2004, 53, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.E.; Souza, G.P.; McConville, C.J.; Tarvornpanich, T.; Iqbal, Y. Mullite formation in clays and clay-derived vitreous ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Y.; Lee, W.E. Microstructural evolution in triaxial porcelain. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 83, 3121–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, L.N.L.; Gomes, J.; Neves, G.A.; Lira, H.L.; Menezes, R.R.; Segadaes, A.M. Mullite formation from bentonites containing kaolinite: Effect of composition and synthesis parameters. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 87, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.H.; Wu, J.H.; His, C.S.; Lu, H.Y. Morphologically textured mullite in sintered tape-cast kaolin. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzis, D. Usage of Fly Ash and Natural Zeolite in Making Lightweight Mortar. Master’s Thesis, Aristotle University, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pimraksa, K.; Chindaprasirt, P. Lightweight bricks made of diatomaceous eart, lime and gypsum. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirmenci, N.; Yilmaz, A. Use of diatomite as partial replacement for Portland cement in cement mortars. Construct. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, Z. Performance of novel thermal energy storage engineered cementitious composites incorporating a paraffin/diatomite composite phase change material. Appl. Energy 2014, 121, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.A.C.; Martinelli, A.E.; Donascimento, R.M.; Mendes, A.M. Microstructural design and thermal characterization of composite diatomite-vermiculite paraffin-based form-stable PCM for cementitious mortars. Construct. Build. Mater. 2010, 232, 117–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Monteiro, P.J. Green concrete containing diatomaceous earth and limestone: Workability, mechanical properties, and life-cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 662–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, X. Effect of diatomite on thermal insulation properties of straw fiber cement-based composites. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 295, 032047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saridemir, M.; Çelikten, S.; Yıldırım, A. Mechanical and microstructural properties of calcined diatomite powder modified high strength mortars at ambient and high temperatures. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 3004–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, B.; Hamdi, S. Thermal properties of Algerian diatomite, study of the possibility to its use in the thermal insulation. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Energy Efficiency and Energy Related Materials, (ENEFM2013), Antalya, Turkey, 9–12 October 2013; Springer Proceedings in Physics. Volume 155, pp. 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Fragoulis, D.; Stamatakis, M.G.; Chaniotakis, E.; Columbus, G. The Utilization of Clayey Diatomite in the Production of Lightweight Aggregates and Concrete. Tile Brick Int. 2003, 19, 392–397. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).