Mantle-Derived Noble Gas Isotopes in the Ore-Forming Fluid of Xingluokeng W-Mo Deposit, Fujian Province
Abstract
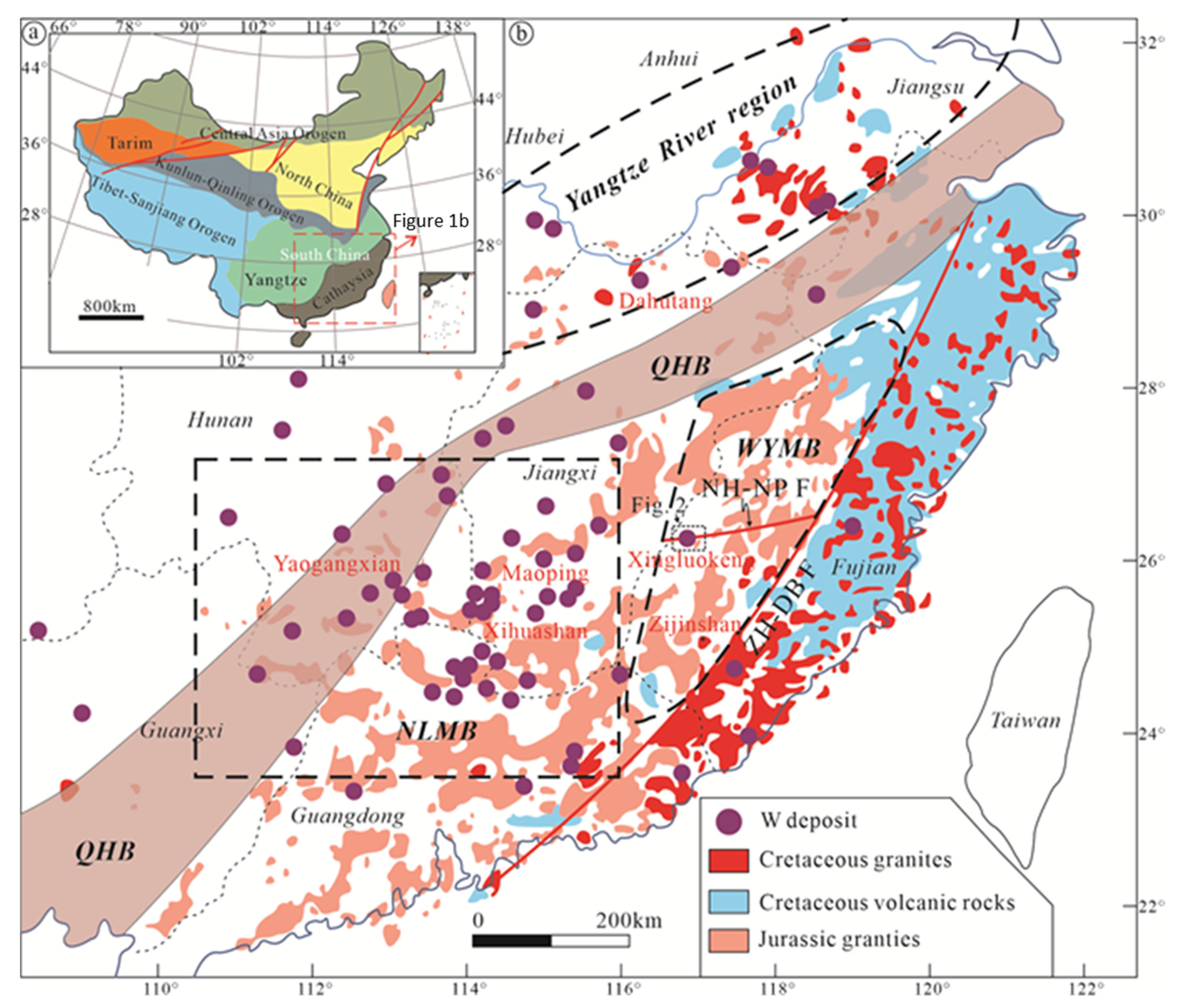
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Background
3. Deposit Geology
4. Sampling and Analytical Methods
5. Results
6. Discussion
6.1. The Effect of Post-Ore Processes on He-Ar Isotopes
6.2. Source of He and Ar
6.3. Role of Mantle Upwelling in Granite-Related W Mineralization in South China
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.X.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, D.H.; Chen, Z.H.; Liu, S.B.; Wang, C.H.; Ying, L.J. A new type of tungsten deposit in southern Jiangxi and the new model of “Five floors + Basement” for prospecting. Acta Geol. Sin. 2008, 82, 880–887, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.J.; Chen, Z.H.; Wang, D.H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, S.B.; Wang, C.H. Geological characteristics and metallogenic epoch of the Xingluokeng tungsten deposit, Fujian province. Geotecton. Metallog. 2008, 32, 92–97, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, J.F.; Chen, Z.H.; Liu, L.; Ying, L.J.; Huang, F.; Wang, D.H.; Wang, J.H.; Zeng, L. A preliminary review of metallogenic regularity of tungsten deposits in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 1359–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, W.W. Introduction to the special issue of mesozoic W-Sn deposits in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 101, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirajno, F. Hydrothermal Processes and Mineral Systems; Intrusion-Related Hydrothermal Mineral Systems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 226, pp. 205–354. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.W.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.H.M.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, J. Genetic types, mineralization styles, and geodynamic settings of Mesozoic tungsten deposits in South China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 137, 109–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H.; Huang, F.; Wang, Y.; He, H.H.; Li, X.M.; Liu, X.X.; Sheng, J.F.; Liang, T. Regional metallogeny of Tungsten-tin-polymetallic deposits in Nanling region, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 120, 103305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaw, K.; Peters, S.G.; Cromie, P.; Burrett, C.; Hou, Z. Nature, diversity of deposit types and metallogenic relations of South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2007, 31, 3–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Cheng, Y.B.; Chen, Y.C. Mineral deposit models of mesozoic ore deposits in South China. Geol. Rev. 2009, 55, 347–354, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ni, P.; Wang, G.G.; Li, W.S.; Chi, Z.; Li, S.N.; Gao, Y. A Review of the Yanshanian ore-related felsic magmatism and tectonic settings in the Nanling W-Sn and Wuyi Au-Cu metallogenic belts, Cathaysia Block, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 133, 104088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.Q.; Hu, S.X.; Sun, M.Z.; Ye, J. On the two genetic series of granites in southeastern China and their metallogenteic characteristics. Miner. Deposits. 1982, 2, 1–14, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Xiang, Y.X. Petrogenesis of Jurassic tungsten-bearing granites in the Nanling Range, South China: Evidence from whole-rock geochemistry and zircon U–Pb and Hf–O isotopes. Lithos 2017, 278–281, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yang, X.; Du, J.; Wu, Q.; Kong, H.; Li, H.; Wan, Q.; Xi, X.; Gong, Y.; Zhao, H. Formation and geodynamic implication of the Early Yanshanian granites associated with W–Sn mineralization in the Nanling range, South China: An overview. Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 1744–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Cheng, Y.B.; Chen, M.H.; Pirajno, F. Major types and time–space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings. Miner. Depos. 2012, 48, 267–294. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Jiang, S.Y.; Li, W.Q.; Zhao, K.D.; Peng, N.J. Highly fractionated jurassic I-type granites and related tungsten mineralization in the Shirenzhang deposit, Northern Guangdong, South China: Evidence from cassiterite and zircon U-Pb ages, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes. Lithos 2018, 312–313, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.Q.; Shao, Y.J.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, S.Y. Discrete jurassic and cretaceous mineralization events at the Xiangdong W(-Sn) deposit, Nanling Range, South China. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 385–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Y. Advances of noble gas isotope geochemistry application in the study of ore deposits. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 215–232, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.Z.; Bi, X.W.; Jiang, G.H.; Chen, H.W.; Peng, J.T.; Qi, Y.Q.; Wu, L.Y.; Wei, W.F. Mantle-derived noble gases in ore-forming fluids of the granite-related Yaogangxian tungsten deposit, Southeastern China. Miner. Depos. 2012, 47, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnard, P.G.; Hu, R.Z.; Turner, G.; Bi, X.W. Mantle, crustal and atmospheric noble gases in Ailaoshan gold deposits, Yunnan Province, China. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnard, P.G.; Polya, D.A. Importance of mantle derived fluids during granite associated hydrothermal circulation: He and Ar isotopes of ore minerals from Panasqueira. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.Y.; Hofstra, A.H.; Hunt, A.G.; Liu, J.Z.; Yang, W.; Li, J.W. Noble Gases Fingerprint the Source and Evolution of Ore-Forming Fluids of Carlin-Type Gold Deposits in the Golden Triangle, South China. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.; Dória, A.; Neiva, A.M.R.; Leal Gomes, C.; Creaser, R.A. Metallogenesis at the Carris W–Mo–Sn deposit (Gerês, Portugal): Constraints from fluid inclusions, mineral geochemistry, Re–Os and He–Ar isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, F.M.; Burnard, P.G.; Taylor, R.P.; Turner, G. Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluids: He-Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from Dae Hwa W-Mo mineralisation, South Korea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 4663–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Hu, R.; Bi, X.; Jiang, G.; Yan, B.; Yin, R.; Yang, J. Mantle-derived and crustal He and Ar in the ore-forming fluids of the Xihuashan granite-associated tungsten ore deposit, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 105, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Hu, R.; Peng, J.; Bi, X.; Jiang, G.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y. He and Ar isotopic compositions and genetic implications for the giant Shizhuyuan W–Sn–Bi–Mo deposit, Hunan Province, South China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2011, 53, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ni, P.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, K.; Wang, T. Origin of ore-forming fluid in the Piaotang tungsten deposit in Jiangxi Province: Evidence from helium and argon isotopes. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 55, 628–634, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.Q.; Pan, L.C.; Wei, W.F. He and Ar isotopes of ore-forming fluids in the Taoxikeng tungsten deposit, southern Jiangxi Province, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 243–251, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, W.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hua, R.; Ye, X. He-Ar isotope geochemistry of the Yaoling-Meiziwo tungsten deposit, North Guangdong Province: Constraints on Yanshanian crust-mantle interaction and metallogenesis in SE China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1150–1159, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Li, L.; Xu, M.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Jin, G.; Jiang, Y. Control of basement on Paleozoic mineralizations in the Wuyi metallogenic belt. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 131, 104037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, C.; Li, R.; Zhao, C.; Liu, P.; Wang, G.; Hao, Y. Petrogenesis of the Xingluokeng W-bearing granitic stock, Western Fujian Province, SE China and its genetic link to W mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 132, 103987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y. Geochemical features of granites at Xingluokeng. Fujian Geol. 1983, 3, 33–45, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.L. A study of the genetic type of Xingluokeng tungsten (molybdenum) deposit, Fujian Province. Miner. Deposits. 1984, 3, 27–36, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Feng, C.; Li, R.; Li, C.; Zhao, C.; Wang, G. Ore-forming mechanism and fluid evolution processes of the Xingluokeng tungsten deposit, Western Fujian Province: Constraints form in-situ trace elemental and Sr isotopic analyses of scheelite. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2021, 37, 698–716, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, Y. Geological-geochemical characteristics and origin of the Xingluokeng W deposit. Geochimica 1993, 2, 187–196, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Gao, J.F.; Tang, Y.W.; Min, K. In-situ LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and ttrace element analyses of wolframites from the Xingluokeng tungsten deposit in Fujian province, China. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2020, 39, 1–15, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.S.; Zhou, X.M.; Deng, P.; Wang, B.; Jiang, S.Y.; Yu, J.H.; Zhao, X.X. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Southeast China Block: New insights from basin analysis. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 34, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.S. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block. Geol. Bull. China 2012, 31, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Suo, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Santosh, M.; Wang, P.; Wang, G.; Guo, L.; Yu, S.; Lan, H.; et al. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic response in the East Asian ocean-continent connection zone to subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 192, 91–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Dong, S.W.; Li, J.H.; Cui, J.J.; Shi, W.; Su, J.B.; Li, Y. The new progress in the study of mesozoic tectonics of South China. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2012, 33, 257–279, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Li, H.L.; Shi, W.; Xue, H.M.; Li, J.H.; Huang, S.Q.; Wang, Y.C. The Yanshan orogeny and late Mesozoic multi-plate convergence in East Asia—Commemorating 90th years of the “Yanshan Orogeny”. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 49, 913–938, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Wang, D.H.; Xu, Z.G.; Huang, F. Outline of regional metallogeny of ore deposits associated with the mesozoic magmatism in South China. Geotecton. Metallog. 2014, 38, 219–229, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.Z.; Bi, X.W.; Zhou, M.F.; Peng, J.T.; Su, W.C.; Liu, S.; Qi, H.W. Uranium metallogenesis in South China and its relationship to crustal extension during the cretaceous to tertiary. Econ. Geol. 2008, 103, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.Z.; Zhou, M.F. Multiple Mesozoic mineralization events in South China—An introduction to the thematic issue. Miner. Depos. 2012, 47, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ni, P.; Wang, X. Mesozoic magmatism and mineralization in Southeastern China: An introduction. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 219, 104921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Liu, P.; Goldfarb, R.J.; Goryachev, N.A.; Pirajno, F.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, C.; Xie, G.; Yuan, S.; et al. Cretaceous large–scale metal accumulation triggered by post–subductional large–scale extension, East Asia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 136, 104270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.Y. Geological characteristics and prospecting marks of Guomuyang wolframite deposit in Qingliu county, Fujian province. Geol. Fujian 2016, 35, 146–152, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Wu, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Di, Y.; Qiu, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, C. New geochronological data from the paleozoic and mesozoic nappe structures, igneous rocks, and molybdenite in the North Wuyi area, Southeast China. Gondwana Res. 2012, 22, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, G.; Di, Y.; Lv, L.; Yao, J.M. Evolution of tectonic stress field in southwestern Wuyishan Mountain area and relationship with mineralization. Geol. Bull. China 2011, 30, 505–513, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Ma, M.; Chen, G.; Zhou, T.; Zhu, X.; Qiu, J.; Mao, J. Taoxi uplift of Wuyi metallogenic belt, its tectonics, magmatism and metallogeny. Earth Sci. J. China Univer Sity Geosci. 2010, 35, 966–984, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.J.; Huang, A.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wei, Y. Temporal-spatial distribution and mineralization sub-belt of Cu-polymetallic deposits in northern Wuyi area. J. Geol. 2014, 38, 387–391, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Ma, X.; Bagas, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, D.; Mou, Z. Late jurassic intracontinental extension and related mineralisation in Southwestern Fujian Province of SE China: Insights from deformation and Syn-tectonic granites. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 32, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piquer, J.; Cooke, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L. Synextensional emplacement of Porphyry Cu-Mo and epithermal mineralization: The Zijinshan district, Southeastern China. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 1055–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Ni, P.; Pan, J.Y.; Li, S.N.; Wang, G.G.; Yang, Y.L.; Xue, K.; Liao, J.F. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Cretaceous volcanic-intrusive complex in the Zijinshan ore district, Southeast China Implications for different stages of mineralization. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 192, 104265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Jin, G.; Zhang, J.; Han, J. Helium isotope composition of inclusions in mineral grains using Helix SFT gas mass spectrometer. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 1826–1831, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Dong, S.; Qing, C.; Li, Y. Genesis of the Jienagepu gold deposit in Zhaxikang ore concentration area, eastern Tethys Himalayas: Constraints from He-Ar and In-situ S isotope of pyrite. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 4291–4315, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Norman, D.I.; AMusgrave, J. N2-Ar-He compositions in fluid inclusions Indicators of fluid source. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, F.; Turner, G.; Taylor, R. He-Ar isotope systematics of fluid inclusions: Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to hydrothermal fluids, in Noble Gas Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry. J. Matsuda Editor. 1994, 261–277. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, S.F.; Sawkins, F.J.; Schlutter, D.J. Mantle-derived helium in two Peruvian hydrothermal ore deposits. Nature 1987, 329, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.Z.; Zhong, H.; Ye, Z.J.; Bi, X.W. Helium and argon isotope geochemistry of Jinding super large lead zinc deposit. Sci. China Ser. D 1998, 28, 208–213. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Turner, G.; Burnard, P.; Ford, J.L.; Gilmour, J.D.; Lyon, I.C.; Stuart, F.M.; Gruszczynski, M.; Halliday, A. Tracing fluid sources and interactions. Philos. Trans.R. Soc. Lond. Phys. Sci. Eng. 1993, 344, 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Bi, X. He and Ar isotopic geochemistry of ore forming fluids in Ailaoshan gold belt. Sci. China Ser. D 1999, 29, 321–330. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.Z.; Burnard, P.G.; Bi, X.W. Mantle-derived gaseous components in ore-forming fluids of the Xiangshan uranium deposit, Jiangxi province, China: Evidence from He, Ar and C isotopes. Chem. Geol. 2009, 266, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.E.; Evensen, N.M.; York, D.; Szatmari, P.; Oliveira, D.D. Single-crystal 40Ar-39Ar dating of pyrite: No fool’s clock. Geology 2001, 29, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, D.; Masliwec, A.; Kuybida, P.; Hanes, J.A.; Hall, C.M.; Kenyon, W.J.; Spooner, E.; Scott, S.D. 40Ar/39Ar dating of pyrite. Nature 1982, 300, 52–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Fan, H.R.; Liang, G.Z.; Zhu, R.X.; Yang, K.F.; Steele-MacInnis, M.; Hu, H.L. Texture, trace elements, sulfur and He-Ar isotopes in pyrite: Implication for ore-forming processes and fluid source of the Guoluolongwa gold deposit, East Kunlun metallogenic belt. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 136, 104260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballentine, C.J.; Burnard, P.G. Production, release and transport of noble gases in the continental crust. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 47, 481–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Geological characteristics and fluid inclusion research of Hongling tungsten deposit in Guangdong province. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2017, 31, 1022–1034, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Peng, N.H.; Huang, D.Z.; Xin, Y.J.; Liu, Z.F.; Liu, Y.K. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and genesis of Woxi Au-Sb-W deposit in Western Hunan, China. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2013, 23, 2605–2611, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.J. Study on Fluid Inclusions of the Zhangdou Tungsten Deposit in Southern Jiangxi. Master’s Thesis, East China University of Technology, Fuzhou, China, 2017. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Graham, W.D. Noble gas Isotope geochemistry of Mid-ocean ridge and ocean island basalts: Characterization of mantle source reservoirs. Noble Gases Geochem. Cosmochem. 2002, 47, 247–317. [Google Scholar]
- Gautheron, C.; Moreira, M. Helium signature of the subcontinental lithospheric mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 199, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.N.; Lee, D.J. Inert gases in groundwater from the Bunter Sandstone of England as indicators of age and palaeoclimatic trends. J. Hydrol. 1979, 41, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, M.A.; Burgess, R.; Pattrick, R.; Turner, G. Fluid inclusion noble gas and halogen evidence on the origin of Cu-Porphyry mineralizing fluids. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2651–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.F.; Hu, R.Z.; Bi, X.W.; Jiang, G.H.; Yan, B.; Song, S.Q.; Shi, S. Study on rare gas isotopes of Xihuashan Tungsten Deposit, Jiangxi Province. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2015, 35, 731. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, M.; Peng, Z.; Nagao, K.; Wang, X.; Guo, T.; Liu, H. Isotopic characteristics of noble gases of the Fuchuan-Hezhou-Zhongshan W-Sn-polymetallic ore concentration area in Northeastern Guangxi and their geological significance. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2013, 34, 287–294, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Oxburgh, E.R.; O’Nions, R.K.; Hill, R.I. Helium isotopes in sedimentary basins. Nature 1986, 324, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballentine, C.J.; Burgess, R.; Marty, B. Tracing Fluid Origin, Transport and Interaction in the Crust. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 47, 539–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Mao, J.; Santosh, M.; Bao, Z.; Zeng, X.; Jia, L. Geochronology and petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous A-type granite from the Feie’shan W-Sn deposit in the eastern Guangdong Province, SE China: Implications for W-Sn mineralization and geodynamic setting. Lithos 2018, 300–301, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Duan, X.; Sun, H. Origin of highly fractionated peraluminous granites in South China: Implications for crustal anatexis and evolution. Lithos 2021, 341, 106145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.M.; Mao, J.W. A preliminary discussion on the mesozoic metallogenic explosion in east China. Miner. Depos. 1999, 18, 300–307, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, C.Q.; Mei, Y.X. Mesozoic large scale mineralization and multiple lithospheric extension in South China. Earth Sci. Front. (China Univ. Geosci. Beijing) 2004, 11, 45–55, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Zheng, W.; Xie, G.; Lehmann, B.; Goldfarb, R. Recognition of a Middle–Late Jurassic arc-related porphyry copper belt along the southeast China coast: Geological characteristics and metallogenic implications. Geology 2021, 49, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Guo, C.L.; Chen, Y.C. Large-scale tungsten-tin mineralization in the Nanling region, South China: Metallogenic ages and corresponding geodynamic processes. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2329–2338, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Guo, C.L.; Yuan, S.D.; Cheng, Y.B.; Chen, Y.C. Spatial-Temporal distribution of mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their metallogenic settings. Geol. J. China Univ. 2008, 14, 510–526, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Wu, S.H.; Song, S.W.; Dai, P.; Xie, G.Q.; Su, Q.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.G.; Yu, Z.Z.; Chen, X.Y.; et al. The world-class Jiangnan tungsten belt: Geological characteristics, metallogeny, and ore deposit model. Chin Sci Bull. 2020, 65, 3746–3762. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Li, Z.; Ye, H. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic activities in South China: Retrospect and prospect. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2853–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Li, Z.X.; Li, W.X.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wei, G.J.; Qi, C.S. U–Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of jurassic I- and A-type granites from central Guangdong, SE China: A major igneous event in response to foundering of a subducted flat-slab? Lithos 2007, 96, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample No. | Location | Mineral | Association |
|---|---|---|---|
| X19-10-1 | level 828 m | Pyrite | Pyrite associated with wolframite and quartz |
| X19-21-2 | level 744 m | Pyrite | Pyrite associated with wolframite, quartz, and muscovite |
| X19-28-2 | level 672 m | Pyrite | Pyrite associated with wolframite, molybdenite, and quartz |
| X19-32-1 | level 690 m | Pyrite | Pyrite associated with wolframite, quartz, and muscovite |
| X19-33-4 | level 690 m | Pyrite | Pyrite associated with wolframite, chalcopyrite, and quartz |
| X19-24-1 | level 720 m | Pyrite | Pyrite associated with quartz and chalcopyrite |
| X21-1-1 | level 672 m | Wolframite | Wolframite associated with quartz and feldspar |
| X21-1-2 | level 792 m | Wolframite | Wolframite associated with quartz and feldspar |
| X19-26-4 | level 708 m | Wolframite | Wolframite associated with quartz |
| Sample No. | X19-10-1 | X19-21-2 | X19-28-2 | X19-32-1 | X19-33-4 | X19-24-1 | X21-1-1 | X21-1-2 | X19-26-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral | Pyrite | Pyrite | Pyrite | Pyrite | Pyrite | Pyrite | Wolframite | Wolframite | Wolframite |
| 3He (10−14 cm3STP/g) | 144 | 270 | 551 | 43 | 397 | 303 | 164 | 226 | 94 |
| 4He (10−8 cm3STP/g) | 156 | 212 | 390 | 218 | 278 | 267 | 558 | 646 | 292 |
| 3He/4He (10−7) | 9.24 | 12.74 | 14.14 | 1.96 | 14.28 | 11.34 | 2.94 | 3.50 | 3.22 |
| R/Ra (± 1σ) | 0.66 ± 0.01 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 1.01 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 1.02 ± 0.01 | 0.81 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.01 |
| Mantle He (%) | 9.88 | 13.73 | 15.28 | 1.85 | 15.43 | 12.19 | 2.93 | 3.55 | 3.24 |
| 40Ar (10−8 cm3STP/g) | 53.7 | 27.4 | 46.1 | 31.6 | 47.9 | 32.7 | 58.0 | 40.8 | 15.0 |
| 40Ar/36Ar (± 1σ) | 491 ± 0.4 | 683 ± 0.3 | 626 ± 0.4 | 361 ± 0.2 | 523 ± 0.3 | 582 ± 0.9 | 574 ± 0.8 | 816 ± 1.0 | 539 ± 0.7 |
| 38Ar/36Ar (± 1σ) | 0.191 ± 0.003 | 0.19 ± 0.002 | 0.187 ± 0.003 | 0.191 ± 0.002 | 0.189 ± 0.003 | 0.193 ± 0.003 | 0.193 ± 0.002 | 0.188 ± 0.002 | 0.189 ± 0.002 |
| 40Ar* (10−7) | 2.1 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 0.6 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 0.7 |
| 40Ar* (%) | 39.8 | 56.7 | 52.8 | 18.2 | 43.6 | 49.3 | 48.5 | 63.8 | 45.2 |
| 3He/36Ar (10−3) | 1.32 | 6.73 | 7.50 | 0.49 | 4.34 | 5.39 | 1.62 | 4.53 | 3.38 |
| F4He | 8648 | 32,036 | 32,132 | 15,106 | 18,427 | 28,815 | 33,474 | 78,370 | 63,661 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Chen, B.; Wu, L.; Gao, J.; Zeng, G.; Shen, J. Mantle-Derived Noble Gas Isotopes in the Ore-Forming Fluid of Xingluokeng W-Mo Deposit, Fujian Province. Minerals 2022, 12, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12050595
Gao Y, Chen B, Wu L, Gao J, Zeng G, Shen J. Mantle-Derived Noble Gas Isotopes in the Ore-Forming Fluid of Xingluokeng W-Mo Deposit, Fujian Province. Minerals. 2022; 12(5):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12050595
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yun, Bailin Chen, Liyan Wu, Jianfeng Gao, Guangqian Zeng, and Jinghui Shen. 2022. "Mantle-Derived Noble Gas Isotopes in the Ore-Forming Fluid of Xingluokeng W-Mo Deposit, Fujian Province" Minerals 12, no. 5: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12050595
APA StyleGao, Y., Chen, B., Wu, L., Gao, J., Zeng, G., & Shen, J. (2022). Mantle-Derived Noble Gas Isotopes in the Ore-Forming Fluid of Xingluokeng W-Mo Deposit, Fujian Province. Minerals, 12(5), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12050595






