Fe(III)–Chitosan Microbeads for Adsorptive Removal of Cr(VI) and Phosphate Ions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
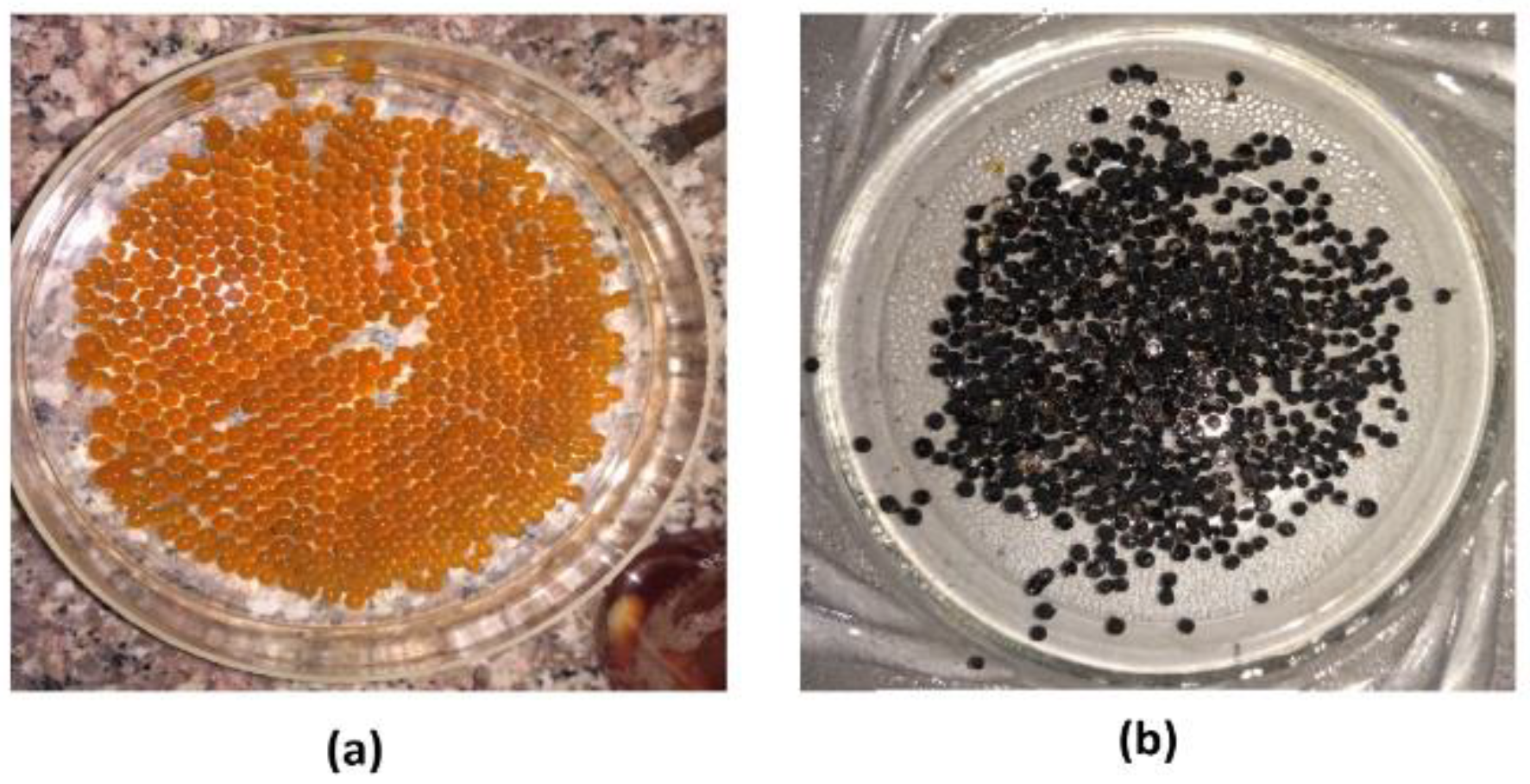
2.2. Synthesis of Fe–CTB Microbeads
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
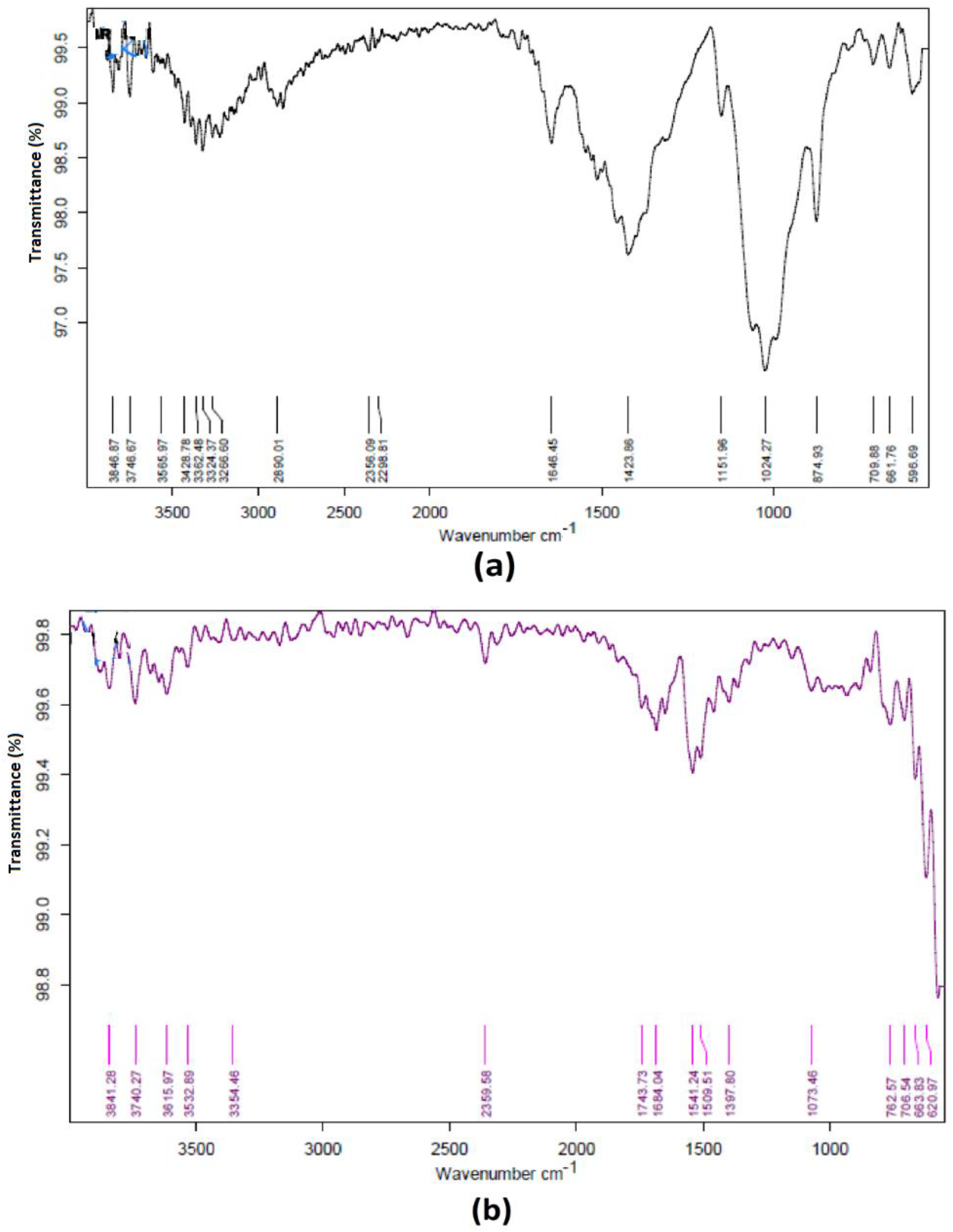
3.1. FTIR Spectral Analysis
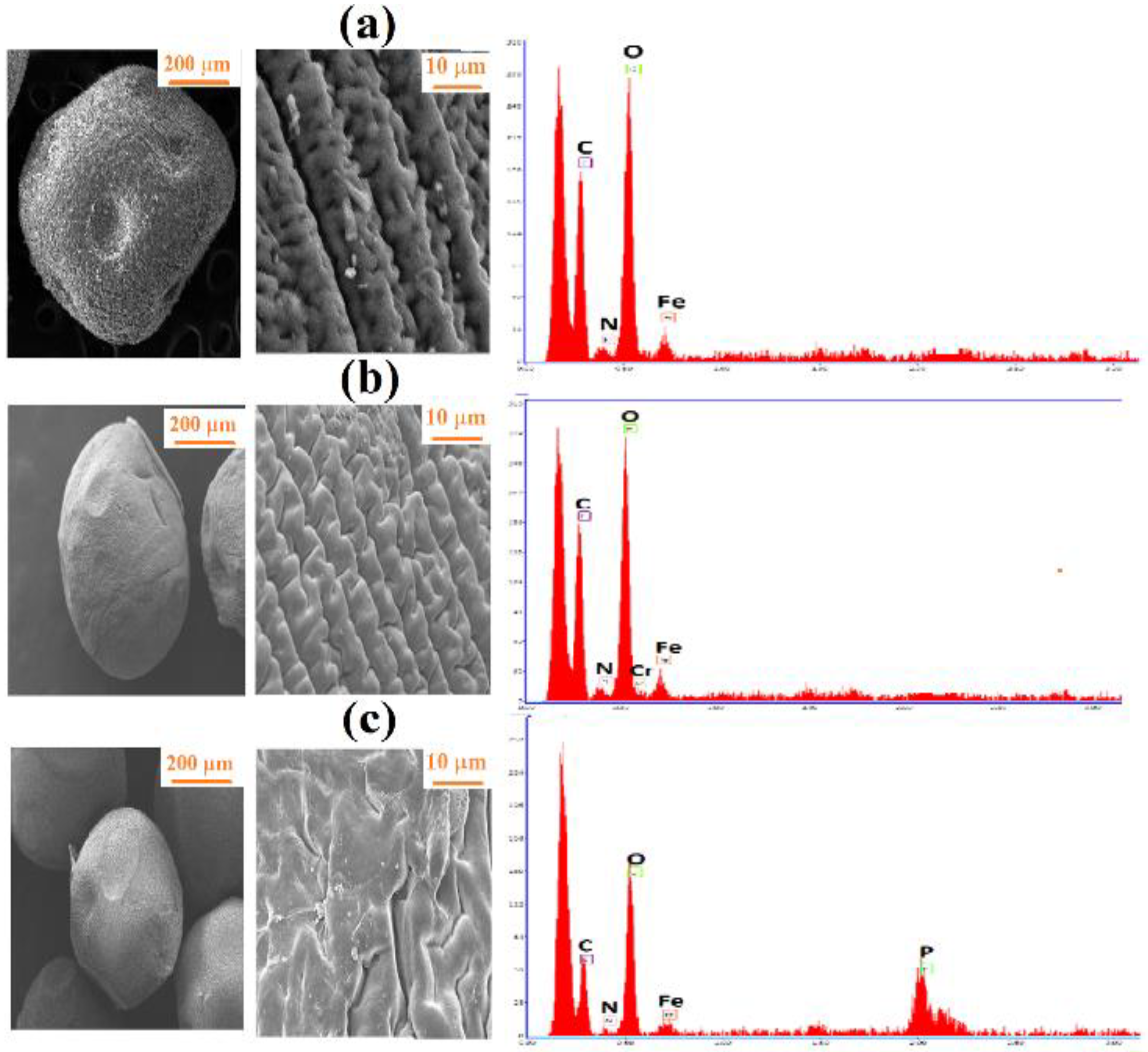
3.2. Surface Morphology and Elemental Composition
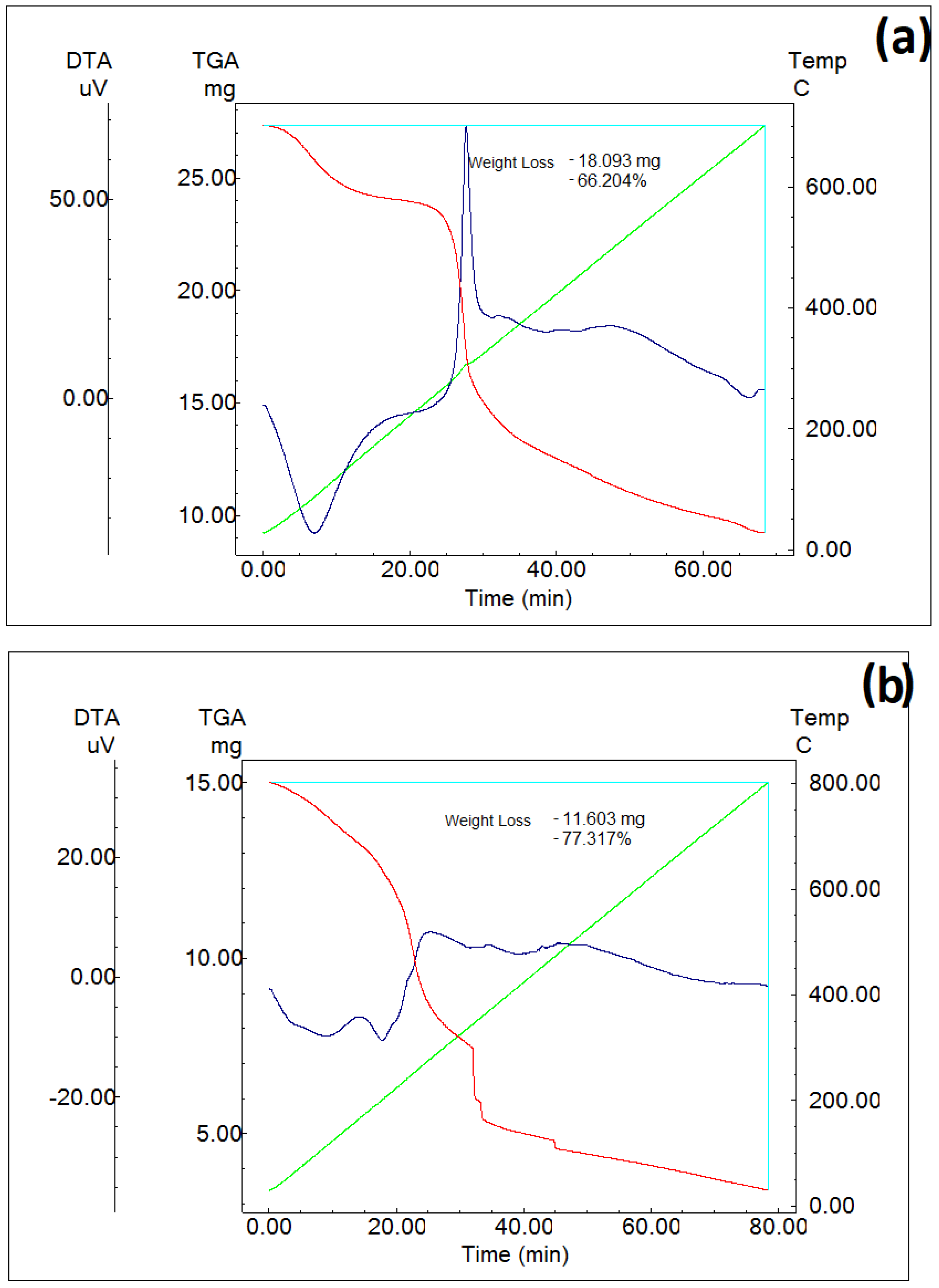
3.3. Thermal Studies
3.4. BET Surface Area
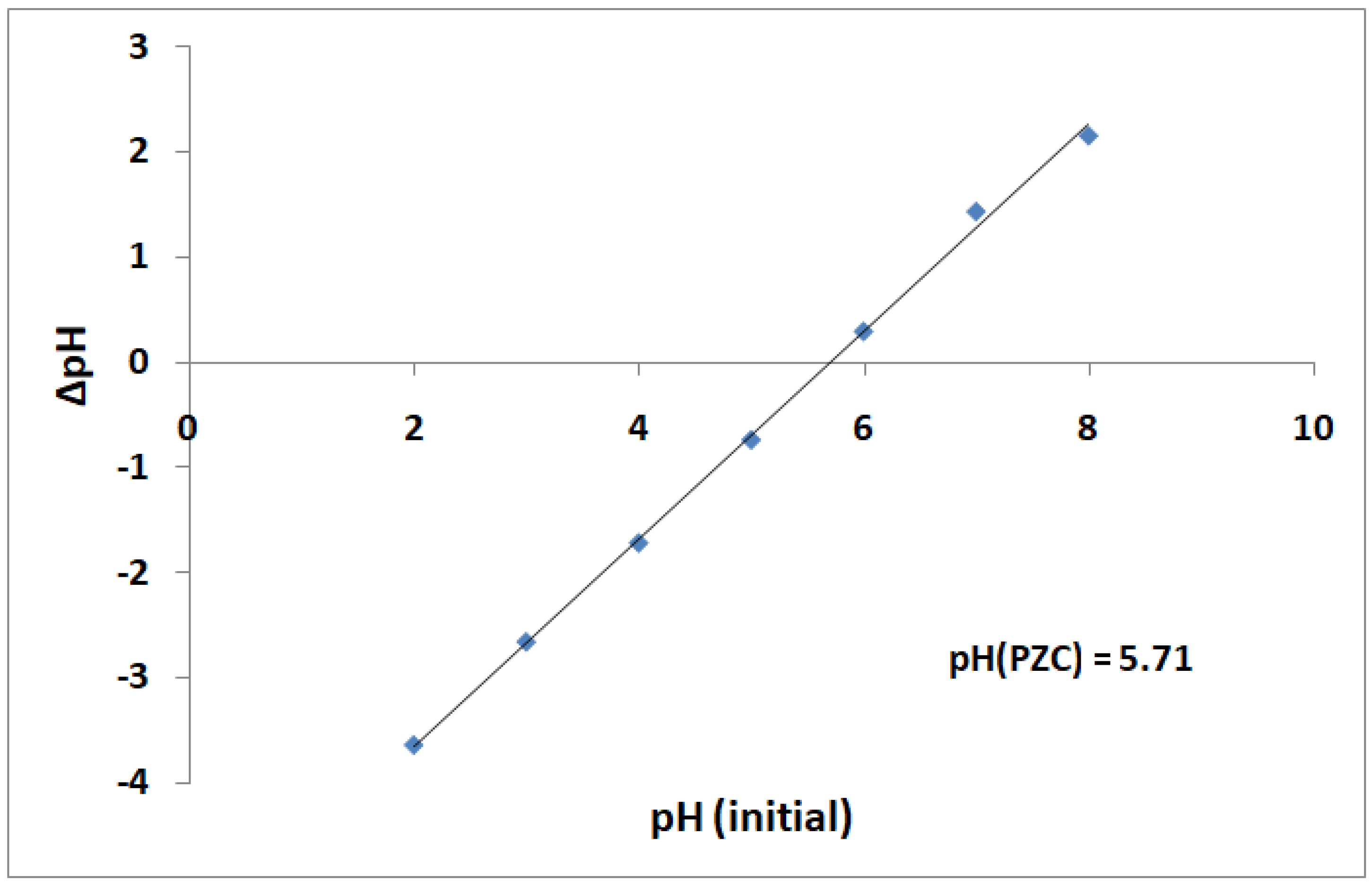
3.5. pH Point of Zero Charge (pHPZC)
3.6. Batch Adsorption Studies
3.6.1. Effect of Solution pH
3.6.2. Effect of Contact Time
3.6.3. Effect of Amount of Adsorbent
3.6.4. Effect of Initial Concentration
3.7. Adsorption Isotherms
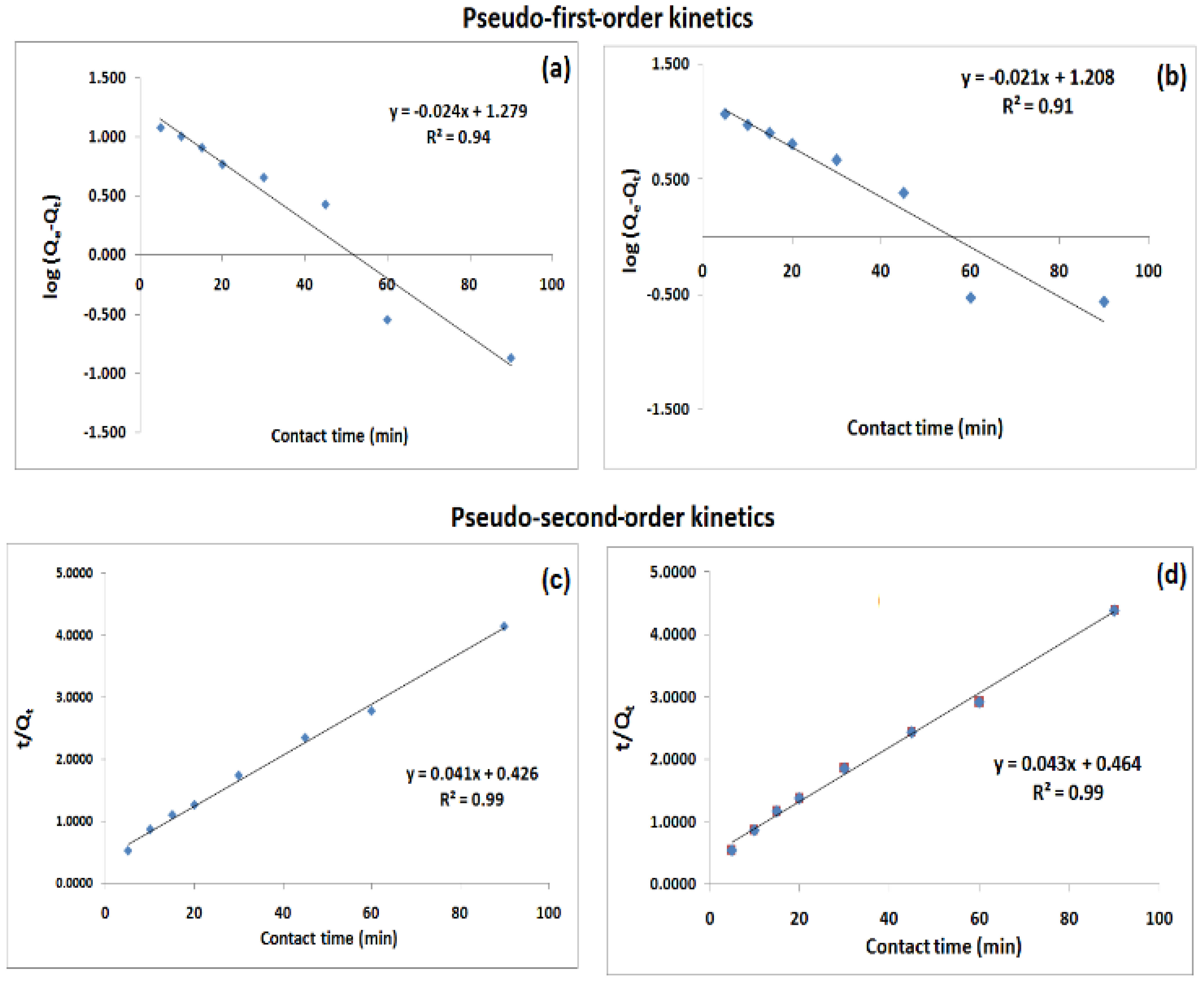
3.8. Adsorption Kinetics
3.9. Adsorption Thermodynamics
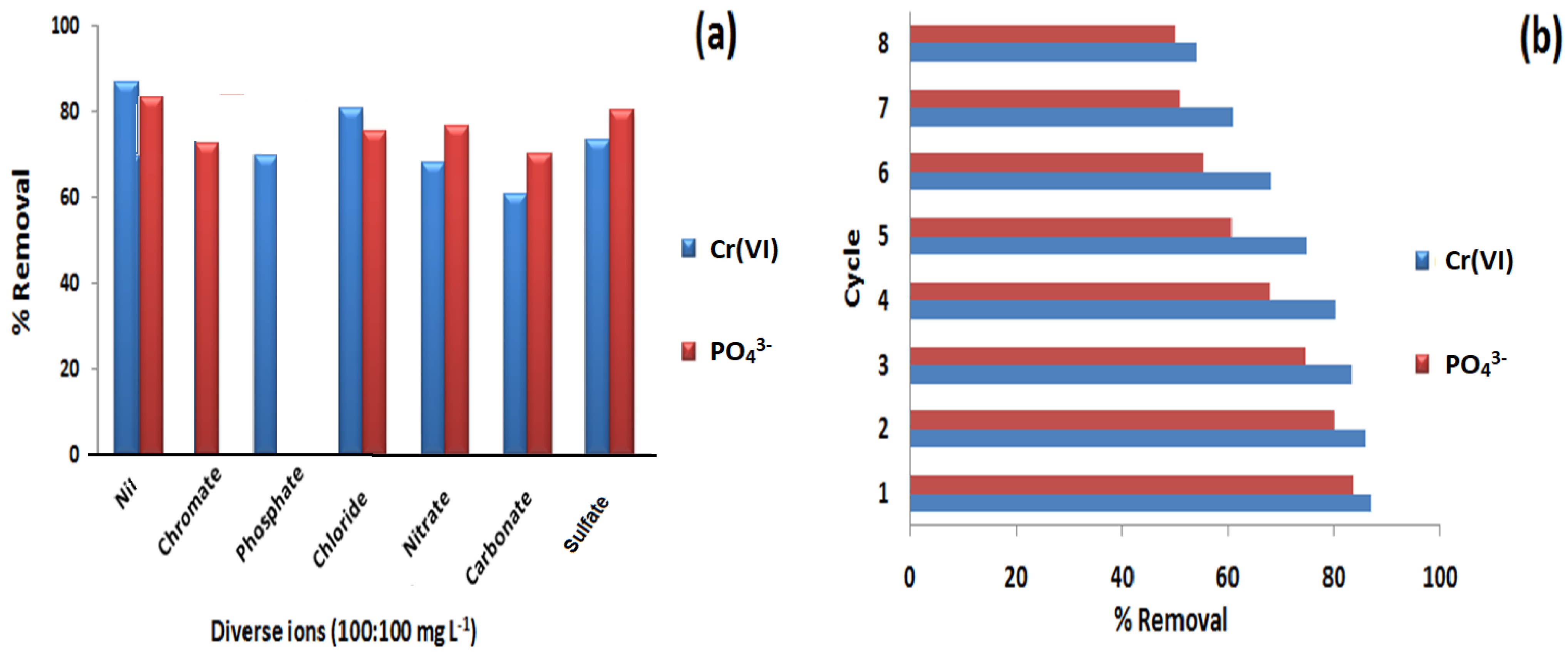
3.10. Diverse Ions Effect
3.11. Reusability Studies
3.12. Comparison of Fe–CTB with Reported Materials
3.13. Proposed Mechanism of Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, S.; Cao, Q.; Zheng, Y.M.; Huang, Y.Z.; Zhu, Y.G. Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing. China Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertz, W. Chromium and its Relation to Carbohydrate Metabolism. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1976, 60, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S.A.; Salem, H. The Biological and Environmental Chemistry of Chromium; VCH Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Shen, Y.; Shen, C.; Wen, Y.; Liu, W. Al-doping chitosan–Fe (III) hydrogel for the removal of fluoride from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 248, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.A.; Ansari, A.A. Eutrophication: An Ecological Vision. Bot. Rev. 2005, 71, 449–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.; Pham, T.-L.; Dao, T.-S. Prediction of cyanobacterial blooms in the Dau Tieng Reservoir using an artificial neural network. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2017, 68, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Dong, J.; Yang, H.; Van Zwieten, L.; Lu, H.; Alshameri, A.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X.; et al. A critical review of methods for analyzing freshwater eutrophication. Water J. 2021, 13, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, N.; Tang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Feng, C. A study of the mechanism of fluoride adsorption from aqueous solutions onto Fe-impregnated chitosan. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 12041–12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirbagheri, S.A.; Hosseini, S.N. Pilot plant investigation on petrochemical wastewater treatment for the removal of copper and chromium with the objective of reuse. Desalination 2005, 171, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, M.; Guha, B.K. Effect of pH on rejection of hexavalent chromium by nanofiltration. Desalination 2008, 219, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ölmez, T. The optimization of Cr (VI) reduction and removal by electrocoagulation using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgin, J.; Franco, D.; Drumm, F.; Grassi, P.; Netto, M.; Allasia, D.; Dotto, G. Powdered biosorbent from the mandacaru cactus (cereus jamacaru) for discontinuous and continuous removal of Basic Fuchsin from aqueous solutions. Powder Technol. 2020, 364, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgin, J.; Dotto, G.; Mazutti, M.; Foletto, E. Preparation of activated carbon from peanut shell by conventional pyrolysis and microwave irradiation-pyrolysis to remove organic dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomón, Y.; Georgin, J.; Franco, D.; Netto, M.; Piccilli, D.; Foletto, E.; Oliveira, L.; Dotto, G. High-performance removal of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicide in water using activated carbon derived from Queen palm fruit endocarp (Syagrus romanzoffiana). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgin, J.; Franco, D.; Netto, M.; Allasia, D.; Foletto, E.; Oliveira, L.; Dotto, G. Transforming shrub waste into a high-efficiency adsorbent: Application of Physalis peruvian chalice treated with strong acid to remove the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicide. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.; Fagundes, J.; Georgin, J.; Salau, N.; Dotto, G. A mass transfer study considering intraparticle diffusion and axial dispersion for fixed-bed adsorption of crystal violet on pecan pericarp (Carya illinoensis). Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Xia, W.; Zhang, W. Preparation and characterization of chitosan-zirconium (IV) composite for adsorption of vanadium (V). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinha, I.; Freitas, F. Chemically modified chitin, chitosan, and chitinous polymers as biomaterials. In Handbook of Chitin and Chitosan; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 43–69. [Google Scholar]
- Kahu, S.; Shekhawat, A.; Saravanan, D.; Jugade, R. Ionic solid-impregnated sulphate-crosslinked chitosan for effective adsorption of hexavalent chromium from effluents. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 2269–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva Alves, D.C.; Healy, B.; Pinto, L.A.; Cadaval, T.R.; Breslin, C.B. Recent developments in chitosan-based adsorbents for the removal of pollutants from aqueous environments. Molecules 2021, 26, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandekar, S.; Jugade, R. Chitosan-zirconia microballs for proficient removal of chromate and phosphate ions from water bodies. J. Chem. Sci. 2021, 133, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendham, D.S.; Sankaran, K.V.; O’connell, A.M.; Grove, T.S. Eucalyptus globulus harvest residue management effects on soil carbon and microbial biomass at 1 and 5 years after plantation establishment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczenko, Z. Separation and Spectrophotometric Determination of Elements; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986; Volume 161. [Google Scholar]
- Thakre, D.; Jagtap, S.; Sakhare, N.; Labhsetwar, N.; Meshram, S.; Rayalu, S. Chitosan based mesoporous Ti–Al binary metal oxide supported beads for defluoridation of water. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 158, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Jimenez, L.H.; Hurt, R.H.; Matos, J.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Zirconium–carbon hybrid sorbent for removal of fluoride from water: Oxalic acid mediated Zr (IV) assembly and adsorption mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batistella, L.; Venquiaruto, L.D.; Di Luccio, M.; Oliveira, J.V.; Pergher, S.B.C.; Mazutti, M.A.; de Oliveira, D.; Mossi, A.J.; Treichel, H.; Dallago, R. Evaluation of Acid Activation under the Adsorption Capacity of Double Layered Hydroxides of Mg–Al–CO3 Type for Fluoride Removal from Aqueous Medium. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 6871–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhawat, A.; Kahu, S.S.; Saravanan, D.; Jugade, R.M. Assimilation of chitin with tin for defluoridation of water. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 18936–18945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayawei, N.; Ebelegi, A.N.; Wankasi, D. Modelling and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherms. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3039817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H. Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnaji, C.C.; Ebeagwu, C.J.; Ugwu, E.I. Physicochemical Conditions for Adsorption of Lead from Water by Rice Husk Ash. BioResources 2017, 12, 799–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonin, J.P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyah, Y.; Lahrichi, A.; Kachkoul, R.; El Mouhri, G.; Idrissi, M.; Iaich, S.; Zerrouq, F. Multi-parametric filtration effect of the dyes mixture removal with the low cost materials. Arab. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2020, 27, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, Y.; David, V.E.; Mmereki, D. A comparative study on removal of hazardous anions from water by adsorption: A review. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3975948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, C.; Puls, R.W. Arsenate and arsenite removal by zerovalent iron: Effects of phosphate, silicate, carbonate, borate, sulfate, chromate, molybdate, and nitrate, relative to chloride. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4562–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanesh, S.; Anjali, S. Chitosan for the removal of chromium from waste water. Int. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 1, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Szymczyk, P.; Filipkowska, U.; Jóźwiak, T.; Kuczajowska-Zadrożna, M. Phosphate removal from aqueous solutions by chitin and chitosan in flakes. Chem. Appl. Chitin. Deriv. 2016, 21, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nthumbi, R.M.; Ngila, J.C.; Moodley, B.; Kindness, A.; Petrik, L. Application of chitosan/polyacrylamide nanofibres for removal of chromate and phosphate in water. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2012, 50, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, P.; Luo, S.; Tu, X.; Cao, Q.; Shu, M. Synthesis of novel nanocomposite Fe3O4/ZrO2/chitosan and its application for removal of nitrate and phosphate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 284, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, T.; Ecevit, H. Cr (VI) removal using Fe2O3-chitosan-cherry kernel shell pyrolytic charcoal composite beads. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Isotherm | Parameters | Cr(VI) Ion | PO43− Ion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich | kf (mg1−1/nL1/n/g) | 10.15 | 6.06 |
| n | 4.138 | 2.99 | |
| R2 | 0.981 | 0.941 | |
| Langmuir | qo (mg g−1) | 34.15 | 32.27 |
| b (L mg−1) | 0.0045 | 0.0025 | |
| RL | 0.69 | 0.80 | |
| R2 | 0.992 | 0.984 |
| Rate Model | Parameters | Cr(VI) Ion | PO43− Ion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | K1 (min−1) | 0.0568 | 0.0497 |
| R2 | 0.944 | 0.915 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | K2 (L mol−1 min−1) | 0.0040 | 0.0040 |
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.995 |
| Temp. (K) | Cr(VI) | PO43− | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆G⁰ (kJ mol−1) | ∆H⁰ (kJ mol−1) | ∆S⁰ (kJ mol−1 K−1) | ∆G⁰ (kJ mol−1) | ∆H⁰ (kJ mol−1) | ∆S⁰ (kJ mol−1 K−1) | |
| 298 | −4.37 | −33.69 | −0.098 | −3.57 | −29.6 | −0.087 |
| 313 | −3.00 | −2.36 | ||||
| 323 | −2.02 | −1.49 | ||||
| 333 | −1.04 | −0.62 |
| Adsorbent | pH | Temp | Time | Adsorption Capacity (mg g−1) for | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr(VI) | PO43− | |||||
| Chitosan | 2.0 | 40 °C | 140 min | 2.48 | - | [37] |
| Chitosan | 4.0 | 30 °C | 40 min | - | 6.65 | [38] |
| Chitosan–zirconia microballs | 5.0 | 30 °C | 60 min | 73.81 | 65.51 | [22] |
| Chitosan–polyacrylamide nanofibers | 6.0 | 45 °C | 60 min | 0.26 | 392 | [39] |
| Chitosan/Fe3O4/ZrO2 | 3.0 | 25 °C | 240 min | - | 26.5 | [40] |
| Cherry kernel charcoal chitosan composite | 2.0 | 25 °C | 120 min | 14.455 | - | [41] |
| Fe–CTB | 3.0 | 25 °C | 60 min | 34.15 | 32.27 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tandekar, S.A.; Pande, M.A.; Shekhawat, A.; Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Pandey, S.; Jugade, R.M. Fe(III)–Chitosan Microbeads for Adsorptive Removal of Cr(VI) and Phosphate Ions. Minerals 2022, 12, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12070874
Tandekar SA, Pande MA, Shekhawat A, Fosso-Kankeu E, Pandey S, Jugade RM. Fe(III)–Chitosan Microbeads for Adsorptive Removal of Cr(VI) and Phosphate Ions. Minerals. 2022; 12(7):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12070874
Chicago/Turabian StyleTandekar, Swati A., Manoj A. Pande, Anita Shekhawat, Elvis Fosso-Kankeu, Sadanand Pandey, and Ravin M. Jugade. 2022. "Fe(III)–Chitosan Microbeads for Adsorptive Removal of Cr(VI) and Phosphate Ions" Minerals 12, no. 7: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12070874
APA StyleTandekar, S. A., Pande, M. A., Shekhawat, A., Fosso-Kankeu, E., Pandey, S., & Jugade, R. M. (2022). Fe(III)–Chitosan Microbeads for Adsorptive Removal of Cr(VI) and Phosphate Ions. Minerals, 12(7), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12070874






