Involvement of Evaporite Layers in the Formation of Iron Oxide-Apatite Ore Deposits: Examples from the Luohe Deposit in China and the El Laco Deposit in Chile
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Deposit Geology
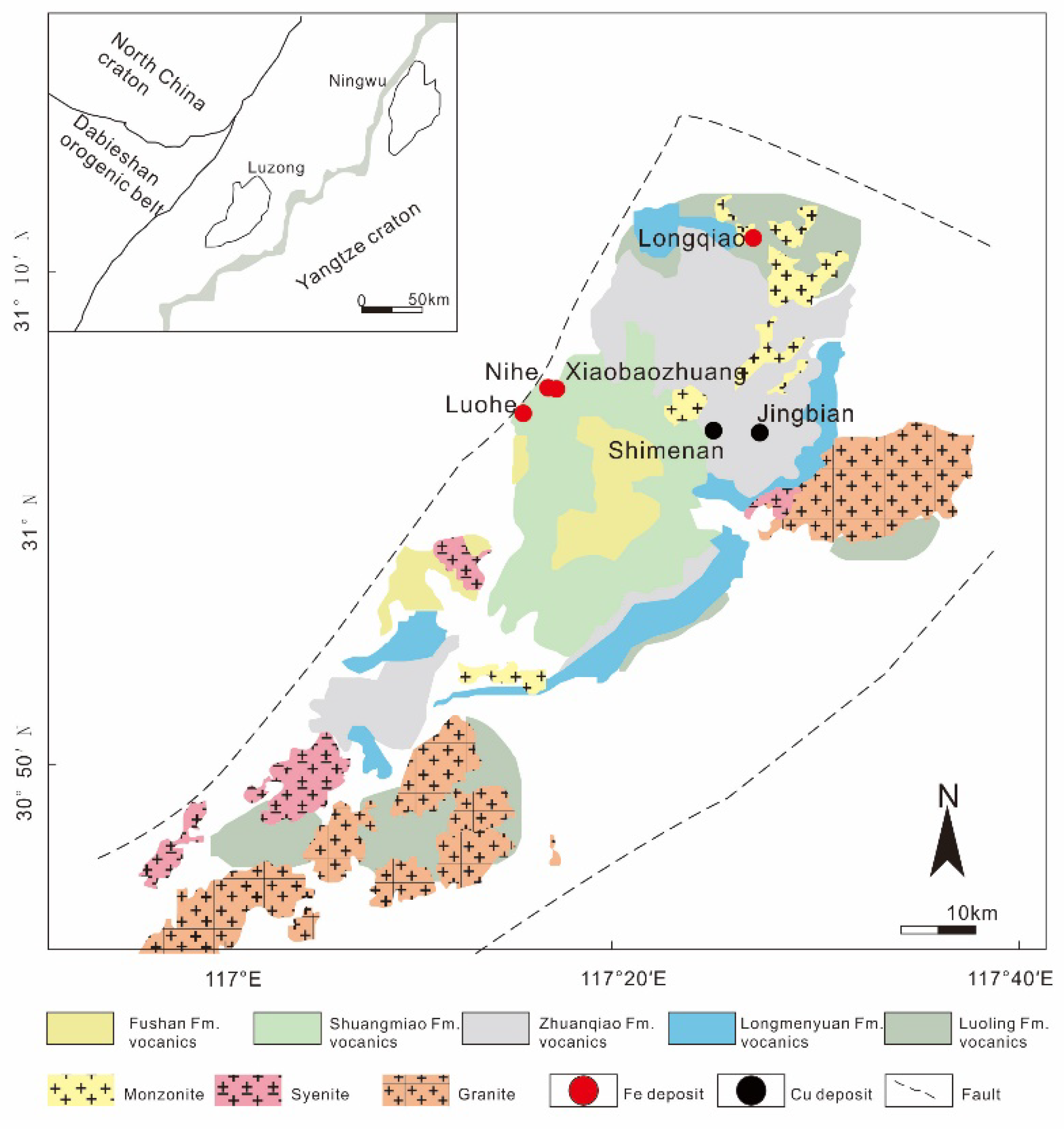
2.1. Luohe Deposit
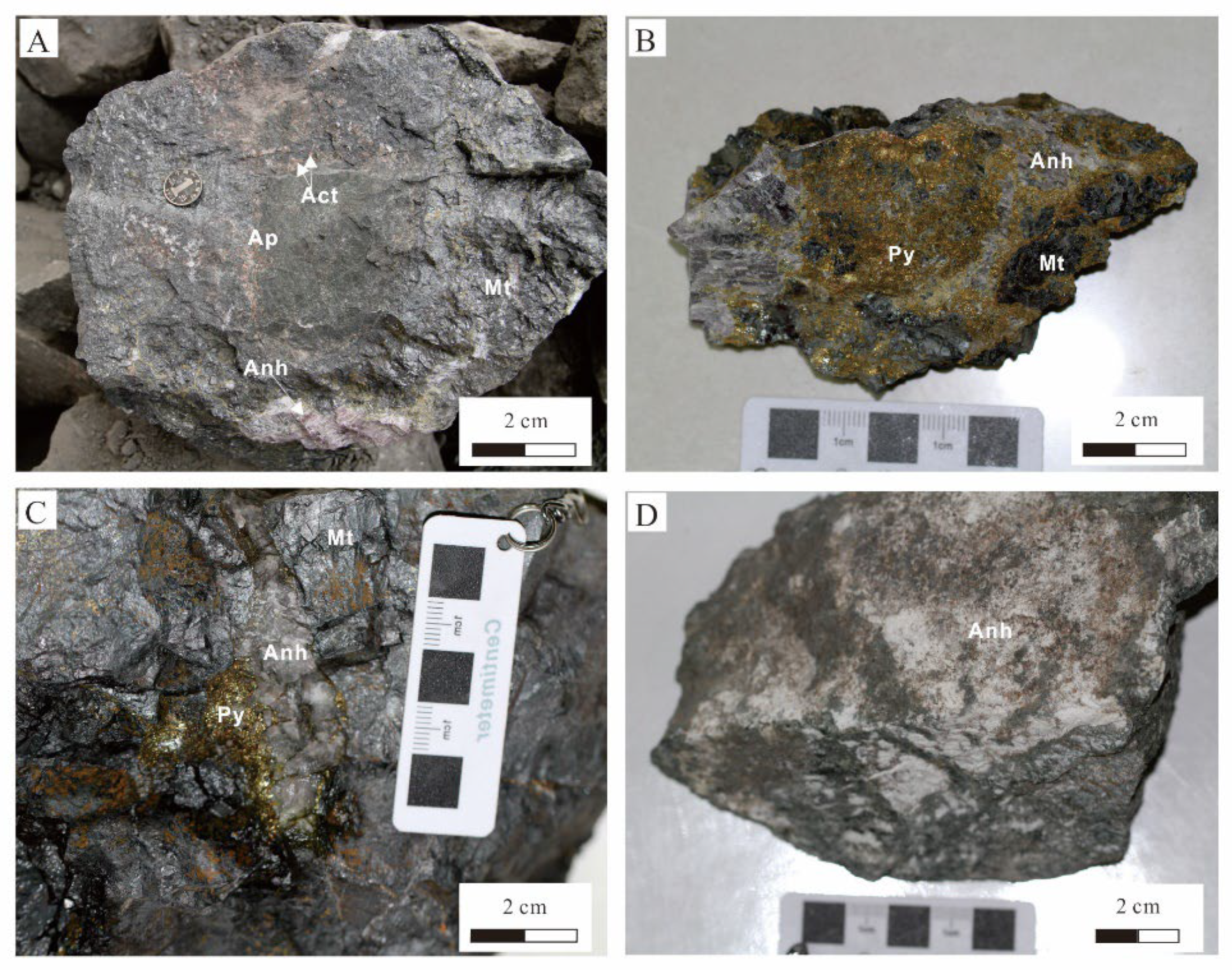


2.2. El Laco Deposit


3. Discussion
3.1. Sulfur Source
3.1.1. Luohe Deposit

3.1.2. El Laco Deposit


3.2. The Participation of Evaporite Layers in the Process of Mineralization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nabatian, G.; Ghaderi, M.; Corfu, F.; Neubauer, F.; Bernroider, M.; Prokofiev, V.; Honarmand, M. Geology, alteration, age, and origin of iron oxide–apatite deposits in upper eocene quartz monzonite, Zanjan district, NW Iran. Miner. Depos. 2013, 49, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Duan, C.; Han, D.; Chen, X.-W.; Wang, C.-L.; Yang, B.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F. Effect of sulfate evaporate salt layer for formation of porphyrite iron ores in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River area. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 1355–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, M.-A.; Zhao, W.-G.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, X.-D.; Wang, J. Geochemistry characteristics of Nihe iron deposit in Lujiang, Anhui Province and their constrains to ore genesis. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 1382–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.-T.; Audetat, A.; Zhang, J. The role of evaporites in the formation of magnetite–apatite deposits along the Middle and Lower Yangtze River, China: Evidence from LA-ICP-MS analysis of fluid inclusions. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 67, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neymark, L.A.; Holm-Denoma, C.S.; Pietruszka, J.; Aleinikoff, N.; Fanning, C.M.; Pillers, R.M.; Moscati, R.J. High spatial resolution U-Pb geochronology and Pb Isotope geochemistry of magnetite-apatite ore from the Pea Ridge Iron Oxide-apatite deposit, St. Francois Mountains, Southeast Missouri, USA. Econ. Geol. 2016, 111, 1915–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Charlier, B.; Namur, O.; Philip, S.; Ulrich, S.S.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Holtz, F. Experimental study of liquid immiscibility in the Kiruna-type Vergenoeg iron-fluorine deposit, South Africa. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 203, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ootes, L.; Snyder, D.; Davis, W.J.; Acosta-Gongora, P.; Corriveau, L.; Mumin, A.H.; Gleeson, S.A.; Samson, I.M.; Montreuil, J.F.; Potter, E.; et al. A paleoproterozoic Andean-type iron oxide copper-gold environment, the Great Bear magmatic zone, Northwest Canada. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 81, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, M.-A.; Lv, B.; Wang, K.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-M. Geological characteristics and 40Ar-39Ar geochronology of Xiaobaozhuang iron deposit in Luzong volcanic basin. Mineral Deposits. 2017, 36, 795–815. [Google Scholar]
- Heidarian, H.; Lentz, D.R.; Alirezaei, S.; McFarlane, C.R.M.; Peighambari, S. Multiple Stage Ore Formation in the Chadormalu Iron Deposit, Bafq Metallogenic Province, Central Iran: Evidence from BSE Imaging and Apatite EPMA and LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Geochronology. Minerals 2018, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, G.; Barra, F.; Reich, M.; Valencia, V.; Simon, A.C.; Vervoort, J.; Leisen, M.; Romero, R. Halogens, trace element concentrations, and Sr-Nd isotopes in apatite from iron oxide-apatite (IOA) deposits in the Chilean iron belt: Evidence for magmatic and hydrothermal stages of mineralization. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 246, 515–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.-H.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Hou, T.; Cheng, Z.-G.; Campos, E.; Wang, Z.-C.; Fei, X.-H. New insights for the formation of Kiruna-type iron deposits by immiscible hydrous Fe-P melt and high-temperature hydrothermal processes: Evidence from El Laco deposit. Econ. Geol. 2019, 114, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cruz, N.L.; Ovalle, J.T.; Simon, A.C.; Konecke, B.A.; Barra, F.; Reich, M.; Leisen, M.; Childress, T.M. The geochemistry of magnetite and apatite from the el laco iron oxide-apatite deposit, Chile; implications for ore genesis. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econo. Geol. 2020, 115, 1461–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-N.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, T.-F.; Fu, B.; Ireland, T.R.; Wang, J.-F.; Zhang, L.-J. Hydrothermal fluid characteristics and implications of the makou IOA deposit in Luzong basin, eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 127, 103867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.-W.; Zhou, T.-F.; Xie, G.-Q.; Yuan, F.; Duan, C. Metallogeny in Middle-Lower Yangtze River ore belt: Advances and problems remained. Min. Depos. 2020, 39, 547–558. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, M.; Nikolaos, A.; Anna, L. Geochemistry of Rare Earth Elements in Bedrock and Till, Applied in the Context of Mineral Potential in Sweden. Minerals 2020, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-J.; Chen, B.-Y.; Che, L.R.; Wang, T.Z.; Liu, S.-J.; Horvath, P. Genesis of the meishan iron oxide–apatite deposit in the ningwu basin, eastern China: Constraints from apatite chemistry. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 1450–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-F.; Zeng, L.P.; Liao, W.; Li, W.-T.; Hu, H.; Li, J.-W. An overview of recent advances in porphyrite iron (iron oxide-apatite, IOA) deposits in the middle-lower Yangtze river valley metallogenic belt and its implication for ore genesis. Di Xue Qian Yuan 2020, 27, 197–217. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, C.; Li, Y.-H.; Mao, J.-W.; Zhu, Q.-Q.; Xie, G.-Q.; Wan, Q.; Jian, W.; Hou, K.-J. The Role of Evaporite Layers in the Ore-Forming Processes of Iron Oxide-Apatite and Skarn Fe Deposits: Examples from the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt, East China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 138, 104352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-N.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, T.-F.; Yan, L.; Fu, B.; Wang, F.-Y.; Wang, J.-F. Trace element evolution of magnetite in iron oxide-apatite deposits: Case study of Daling deposit, eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 144, 104842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvaresh, D.M.; Malekzadeh, S.A.; Azimzadeh, A.M.; Karimpour, M.H.; Klötzli, U. Textures and Chemical Compositions of the Narm Iron Oxide-Apatite Deposit in Kuh-e-Sarhangi District (Central Iran): Insights into the Magmatic-Hydrothermal Mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 141, 104631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.-C.; Liu, W. Rare earth elements in the iron-oxide apatite (IOA) deposit: Insights from apatite. Int. Geol. Rev. 2022, 140, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.-P.; Zhao, X.-F.; Spandler, C.; Hu, H.; Hu, B.; Li, J.-W.; Hu, Y. Origin of high-Ti magnetite in magmatic-hydrothermal systems; evidence from iron oxide-apatite (IOA) deposits of eastern China. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econo. Geol. 2022, 117, 923–942. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, B.-J. The relationship of gypsum salt beds with endogenic copper and iron. Geochimica 1980, 9, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.-Y.; Li, W.-D.; Wang, W. –B. On the relationship between the marine Triassic evaporate horizons and Cu(Au), Fe deposits in the Middle-Lower Yangtze area. Volcanol. Miner. Resour. 1995, 16, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.-Q.; Yang, Z.-S.; Li, Y.-Q.; Zeng, P.-S.; Meng, Y.-F.; Xu, W.-Y.; Tian, S.-H. Large-scale migration of fluids towards foreland basins during collisional orogeny: Evidence from Triassic anhydrock sequences and regional alteration in Middle-Lower Yangtze area. Miner. Depos. 2004, 23, 310–326. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.-F.; Fan, Y.; Yuan, F.; Wu, M.-A.; Zhao, W.-G.; Qian, B.; Ma, L.; Wang, W.-C.; Liu, Y.-N.; White, N. The metallogenic model of Nihe iron deposit in Lu-Zong basin and genetic relationship between gypsum-salt layer and deposit. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 562–573. [Google Scholar]
- Martinsson, O.; BillstrÖm, K.; Broman, C.; Weihed, P.; Wanhainen, C. Metallogeny of the Northern Norrbotten Ore Province, northern Fennoscandian Shield with emphasis on IOCG and apatite-iron ore deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 78, 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Li, Y.-H.; Mao, J.-W.; Wang, C.-L.; Yang, B.-Y.; Hou, K.-J.; Wang, Q.; Li, W. Study on the ore-forming process of the Heshangqiao IOA deposit in the Ningwu ore district: Insight from magnetite LA-ICP-MS in-situ analysis data. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2017, 33, 3471–3483. [Google Scholar]
- Bain, W.M.; Steele-MacInnis, M.; Tornos, F.; Hanchar, J.M.; Creaser, E.C.; Pietruszka, D.K. Evidence for iron-rich sulfate melt during magnetite (-apatite) mineralization at El Laco. Chile. J. Geology. 2021, 49, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.K. Evaporites, brines and base metals: What is an evaporite? Defining the rock matrix. Aust. J. Earth Sci. Int. Geosci. J. Geol. Soc. Aust. 1996, 43, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Duan, C.; Han, D.; Liu, F.; Wan, D.-F.; Wang, C.-Y. Oxygen isotopic discriminant marker of magmatic iron deposits: Ningwu porphyrite iron ore as an example. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 33, 3411–3421. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.-H.; Xie, G.-Q.; Duan, C.; Han, D. Effect of sulfate evaporate salt layer over the formation of skarn-type iron ores. Acta Geol. Sin. 2013, 87, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Yaremchuk, Y.; Hryniv, S.; Peryt, T.; Vovnyuk, S.; Meng, F.-W. Controls on Associations of Clay Minerals in Phanerozoic Evaporite Formations: An Overview. Minerals 2020, 10, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.-T. A brief discussion on geological characteristics of the Luohe iron deposit in Anhui province. Miner. Depos. 1984, 4, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.-A.; Wang, Q.-S.; Zheng, G.-W.; Cai, X.-M.; Yang, S.-X.; Di, Q.S. Discovery of the Nihe Iron Deposit in Lujiang, Anhui, and its Exploration Significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2011, 85, 802–809. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.-F.; Gao, C.-S.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.-M. Zoning features of wall rock alteration of the Xiaobaozhuang iron deposit in Lujiang County, Anhui Province. Geol. Anhui 2014, 24, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.-N.; Fan, Y.; Gao, C.-S.; Zhang, Q.-M.; Zhang, L.-J. Geological characteristics of Xiaobaozhuang iron deposit in the Lu-Zong volcanic basin, the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley Metallogenic Belt. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 319–333. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, B.-B.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Xie, Q.-H.; Cheng, Z.-G.; Fei, X.-H.; Li, Z.X. Geological Characteristics and Metallogenic Mechanism of the Xiaobaozhuang Iron Deposit and Their Genetic Relationship with the Luohe Iron Deposit in the Lujian-Zongyang Basin, Anhui Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 2018, 92, 1474–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.-F.; Fan, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.-J.; Qian, B.; Ma, L.; Yang, X.-F.; Cooke, D. Geochronology and significance of volcanic rocks in the Ning-Wu basin of China. Sci. China 2011, 54, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, H.S.; David, R.B. New field evidence bearing on the origin of the El Laco magnetite deposit, northern Chile-a reply. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 2003, 98, 1501–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Nyström, J.O.; Billstrom, K.; Henriquez, F.; Fallick, A.E.; Naslund, H.R. Oxygen Isotope Composition of Magnetite in Iron Ores of the Kiruna Type in Chile and Sweden. GFF 2008, 130, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornos, F.; Velasco, F.; Hanchar, J. Iron oxide melts, magmatic magnetite, and superheated magmatic-hydrothermal systems: The El Laco Deposit, Chile. Geology 2016, 44, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungall, J.E.; Long, K.; Brenan, J.; Smythe, D.; Naslund, H.R. Immiscible shoshonitic and Fe-P-oxide melts preserved in unconsolidated tephra at El Laco volcano, Chile. Geology 2018, 46, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.J.; Marquillas, R.A.; Kemp, A.J.; Grange, F.K.; Gardeweg, M.C. Active skarn formation beneath Lascar Volcano, northern Chile: A petrographic and geochemical study of xenoliths in eruption products. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1996, 14, 509–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquillas, R.A.; del Papa, C.; Sabino, I.F. Sedimentary Aspects and Paleoenvironmental Evolution of a Rift Basin: Salta Group (Cretaceous-Paleogene), Northwestern Argentina. Int. J. Earth Sci. Geol. Rundsch. 2005, 94, 94–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuber, E.; Mertmann, D.; Ege, H.; Silva-González, P.; Heubeck, C.; Reutter, K.-J.; Jacobshagen, V. Exhumation and basin development related to formation of the Central Andean Plateau, 21 °S. In The Andes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 285–301. [Google Scholar]
- Rye, R.O.; Ohmoto, H. Sulfur and Carbon Isotopes and Ore Genesis: A Review. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 1974, 69, 826–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H. Stable Isotope Geochemistry of Ore Deposits. Rev. Mineral. 1986, 16, 491–559. [Google Scholar]
- Seal, R.R. Sulfur isotope geochemistry of sulfide minerals (Review). Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2006, 61, 633–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefs, J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry, 7th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–389. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Fan, Y.; Wu, M.-A.; Wang, K.-Y.; Zhao, W.-G.; Wei, G.-H. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids in Nihe iron deposit in Luzong volcanic basin, Anhui Province, China: Evidences from He-Ar-H-O isotopes. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, T.-F.; Wu, M.-A.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Xue, H.-M.; Li, X.-D. Geochronolgy and petrological geochemistry of intrusions in the Lujiang-Zongyang basin in the mineralization belt of the Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River by scientific drilling. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 91, 1483–1505. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.-F.; Fan, Y.; Yuan, F. Advances on petrogensis and metallogeny study of the mineralization belt of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River area. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2008, 24, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.-F.; Fan, Y.; Yuan, F.; Lu, S.-M.; Shang, S.-G.; Cooke, D.; Meffre, S.; Zhao, G.-C. Geochronology of the volcanic rocks in the Lu-Zong (Lujiang-Zongyang) basin and its significance. Sci. China 2008, 51, 1470–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.-F.; Fan, Y.; Yuan, F.; Song, C.-Z.; Zhang, L.-J.; Qian, C.-C.; Lu, S.-M.; Cooke, D.R. Temporal-spatial framework of magmatic intrusions in Luzong volcanic basin in East China and their constrain to mineralization. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 2694–2714. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.-N.; Zhou, T.-F.; Zhang, L.-J.; Yuan, F.; Wang, W.-C. Geochronology of the Nihe deposit and in the Lu-Zong basin and its metallogenic significances. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.-N.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, T.-F.; Zhang, L.-J.; White, N.; Hong, H.-L.; Zhang, W. LA-ICP-MS titanite U-Pb dating and mineral chemistry of the Luohe magnetite-apatite (MA)-type deposit in the Lu-Zong volcanic basin, Eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 92, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-J. Polymetallic Mineralization and Associated Magmatic and Volcanic Activity in the Luzong Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.-N.; Zhou, T.-F.; Zhang, L.-J.; Chen, X.-F.; Hong, H.-L. Geochemical Characteristics of Chlorite in the Luohe Iron Deposit in the Middle-Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt, Eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 133, 104062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-F.; Liu, X.-P.; Wu, Y.-C. The Copper-Iron Belt of the Lower and Middle Reaches of the Changjiang River; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1991; pp. 1–234. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.-T.; Yin, G.-P. The Luohe Iron Deposit in Lujiang County, Anhui Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1989; pp. 1–191. [Google Scholar]
- Naranjo, J.A.; Henríquez, F.; Nyström, J.O. Subvolcanic contact metasomatism at El Laco Volcanic Complex, Central Andes. Andean Geol. 2010, 37, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naslund, H.R.; Henríquez, F.; Nyström, J.O.; Vivallo, W.; Dobbs, F.M. Magmatic iron ores and associated mineralisation: Examples from the Chilean High Andes and Coastal Cordillera. Aust. Miner. Found. 2002, 2, 207–226. [Google Scholar]
- Tornos, F.; Velasco, F.; Hanchar, J.M. The magmatic to magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of the El Laco deposit (Chile) and its implications for the genesis of magnetite-apatite deposits. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 1595–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boso, M.-A.; Monaldi, C.R. Oolitic stratabound iron ores in the Silurian of Argentina and Bolivia. Spec. Publ. Soc. Geol. Appl. Miner. Depos. 1990, 8, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, F.C.; Salfity, J.A. Consideraciones sobre la estratigrafía del Cretá cico (Subgrupo Pirgua) del noroeste argentino. Actas De Las Jorn. Geol. Argent. 1973, 3, 355–385. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, S.M.; Coira, B.L. Shallowing and steepening subduction zones, continental lithospheric loss, magmatism and crustal flow under the Central Alpiplano-Puna plateau. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2009, 204, 229–259. [Google Scholar]
- Childress, T.; Simon, A.C.; Reich, M.; Barra, F.; Bilenker, L.D.; Cruz, N.L.L.; Bindeman, I.N.; Ovalle., J.T. Triple Oxygen (δ18O, Δ17O), Hydrogen (δ2H), and Iron (δ56Fe) Stable Isotope Signatures Indicate a Silicate Magma Source and Magmatic-Hydrothermal Genesis for Magnetite Orebodies at El Laco, Chile. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 1519–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyström, J.O.; Henriquez, F.; Naranjo, J.A.; Naslun, H.R. Magnetite Spherules in Pyroclastic Iron Ore at El Laco, Chile. Am. Mineral. 2016, 101, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyström, J.O.; Henriquez, F. Magmatic features of iron ores of the Kiruna type in Chile and Sweden: Ore textures and magnetite geochemistry. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 1994, 89, 820–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broman, C.; Nyström, J.O.; Henríquez, F.; Elfman, M. Fluid inclusions in magnetite-apatite ore from a cooling magmatic system at El Laco, Chile. GFF 1999, 121, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H. Systematics of Sulfur and Carbon Isotopes in Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-N. Mineralization of Luohe-Xiaobaozhuang Iron Deposit in the Lu-Zong Volcanic Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ohmoto, H.; Rye, R.O. Isotopes of sulfur and carbon. In Geochemistry of hydrothermal Ore Deposits, 2nd ed.; Barnes, H.L., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 10, pp. 509–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.-H.; Wang, H.-T.; LeMessurier, M.J. Sulfur isotope of the Dabaozhuang and Luohe iron deposits with an approach to their genesis. Miner. Depos. 1983, 4, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rouchy, J.M.; Camoin, G.; Casanova, J.; Deconinck, J.F. The Central Palaeo-Andean Basin of Bolivia (Potosi Area) during the Late Cretaceous and Early Tertiary: Reconstruction of Ancient Saline Lakes using Sedimentological, Paleoecological and Stable Isotope Records. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1993, 105, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.-L.; Chen, J.-S.; Wang, S.-X. Sulfur isotopic temperatures and their significance of Luohe iron deposit in Anhui Province. Geochemical 1984, 13, 350–356. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.-Z.; Fan, H.-R.; Ni, P. Fluid Inclusion; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bain, W.M.; Steele-MacInnis, M.; Li, K.; Li, L.; Mazdab, F.K.; Marsh, E.E. A fundamental role of carbonate–sulfate melts in the formation of iron oxide–apatite deposits. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B. Two-liquid partition coefficients: Experimental data and geochemical implications. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 1976, 56, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-Z. Iron ore types and genesis of Meishan iron ore deposit-the study of high temperature experiments. Geoscience 1990, 4, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hemley, J.J.; Cygan, G.L.; Fein, J.B.; Robinson, G.R.; d’Angelo, W.M. Hydrothermal Ore-Forming Processes in the Light of Studies in Rock-Buffered Systems; I, Iron-Copper-Zinc-Lead Sulfide Solubility Relations. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 1992, 87, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Charlier, B.; Holtz, F.; Veksler, I.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Thomas, R.; Namur, O. Immiscible hydrous Fe–Ca–P melt and the origin of iron oxide-apatite ore deposits. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philpotts, A.R. Silicate liquid immiscibility in tholeiitic basalts. J. Petrol. 1979, 20, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.-H.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Campos, E.; Deng, J.; Cheng, Z.G.; Fei, X.H.; Ke, S. Constraints of Fe-O isotopes on the origin of magnetite in the El Laco Kiruna-type iron deposit, Chile. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 130, 103967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, F.; Tornos, F.; Hanchar, J.M. Immiscible iron- and silica-rich melts and magnetite geochemistry at the El Laco volcano (northern Chile): Evidence for a magmatic origin for the magnetite deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 79, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naslund, H.R. The Effect of Oxygen Fugacity on Liquid Immiscibility in Iron-Bearing Silicate Melts. Am. J. Sci. 1983, 283, 1034–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.; Carmichael, I.S.E.; Wiebe, R.A. Experimental Study of Liquid Evolution in an Fe-Rich, Layered Mafic Intrusion: Constraints of Fe-Ti Oxide Precipitation on the T-fO2 and T-ϱ Paths of Tholeiitic Magmas. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1993, 113, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Deposits | Luohe | El Laco | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geological Characteristics | |||
| Host rock | Trachyandesite and diorite porphyrite | Andesite and rhyolite | |
| Evaporite layers | Marine evaporite layers of the Dongma’anshan Formation | Terrestrial evaporite layers of the Salta Group | |
| Ore-controlling structure | Rock fissures and fractures near contact zone | Diatreme | |
| Ore body | Nearly bedded and lenticular shapes | Stratified upper part and lower part with vertical veins and domes | |
| Ore structures | Veined, net-veined, disseminated, breccia and massive structures | Massive, vesicular, lava flows, skeleton and columnar structures | |
| Essential minerals | Mag, (Hem), Py, Ccp, Ab, Kfs, Di, Grt, Ap, Wo, Anh, Chl, Cal, Qz | Mag, (Hem), Di, Scp, Ap, Kfs, Anh, Act | |
| Alteration | Deep dark zone with skarn and anhydrite pyroxene alteration and shallow light zone with silicate and kaolinite alteration | Seep alkali-calcic alteration and shallow acid-sulfate alteration | |
| Main metallogenic age | 131.0–129.1 Ma | (5.3 ± 1.9)–(1.6 ± 0.5) Ma (host volcanic rock) | |
| Fluid temperature and salinity in early mineralization | >830 °C, ~90% NaCl eq | >900 °C (Magnetite–diopside oxygen isotope temperature); 40%–60% NaCl eq | |
| References | [4,58] | [42,64,70,71] | |
| Deposits/ Evaporite Layers | δ34SV-CDT (‰) of Pyrite | δ34SV-CDT (‰) of Gypsum | Δ34SSO4-S2- (‰) | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variation Range | Average | Variation Range | Average | ||||
| Luohe | deposit | −14.0–11.1 | 4.2 (174) | 13.6–24.4 | 18.1 (126) | 13.9 | [61,73,75]; this study |
| Xiaobaozhuang | deposit | 6.9–14.2 | 10.8 (17) | 16.4–32.2 | 23.3 (17) | 12.5 | [38] |
| El Laco | deposit | −2.3–0.9 | −1.8 (4) | 6.8–10.5 | 8.45 (8) | 10.25 | [64,76] |
| Dongma’anshan Formation | evaporite layers | 29.4–29.9 | 29.7 (3) | [18] | |||
| Salta Group | evaporite layers | 4.9–14.1 | 9.5 (12) | [76] | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, D.; Li, Y.; Duan, C.; Fan, C. Involvement of Evaporite Layers in the Formation of Iron Oxide-Apatite Ore Deposits: Examples from the Luohe Deposit in China and the El Laco Deposit in Chile. Minerals 2022, 12, 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12081043
Guo D, Li Y, Duan C, Fan C. Involvement of Evaporite Layers in the Formation of Iron Oxide-Apatite Ore Deposits: Examples from the Luohe Deposit in China and the El Laco Deposit in Chile. Minerals. 2022; 12(8):1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12081043
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Dongwei, Yanhe Li, Chao Duan, and Changfu Fan. 2022. "Involvement of Evaporite Layers in the Formation of Iron Oxide-Apatite Ore Deposits: Examples from the Luohe Deposit in China and the El Laco Deposit in Chile" Minerals 12, no. 8: 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12081043








