Minor Elements and Color Causing Role in Spinel: Multi-Analytical Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Matrials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Physical Properties
3.2. Mineral Chemistry
3.3. Heat Treatment
3.4. UV-VIS-NIR-Spectroscopy
3.5. Raman Spectroscopy
3.6. Photoluminescence Spectroscopy
3.7. X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS)
4. Discussion
4.1. Color-Causing Elements
4.2. Indication of Heated Spinel
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sickafus, K.E.; Wills, J.M.; Grimes, N.W. Structure of Spinel. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 82, 3279–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretti, A.; Günther, D.; Haris, M.T.M. New Type of treatment of spinel involving heat-treatment and cobalt diffusion (Updated 22 May 2015). In World of Magnificent Spinels. Provenance and Identification: Contributions to Gemology; Gemresearch Swisslab: Lucerne, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Biagioni, C.; Pasero, M. The systematics of the spinel-type minerals: An overview. Am. Mineral. 2014, 99, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosi, F.; Biagioni, C.; Pasero, M. Nomenclature and classification of the spinel supergroup. Eur. J. Mineral. 2019, 31, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, H.; James, M.; Dollase, W.A.; Redfern, S. Temperature dependence of the cation distribution in CuAl2O4 spinel. Eur. J. Mineral. 2005, 17, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsova, V.; Mironova-Ulmane, N.; Riekstiņa, D. Structure and Phase Changes in Natural and Synthetic Magnesium Aluminum Spinel. In Environment, Technologies, Resources, Proceedings of the 8th International Scientific and Practical Conference, Rezekne, Latvia, 20–22 June 2011; RA Izdevniecība: Rezekne, Latvia, 2015; Volume 2, p. 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, G.B.; D’Ippolito, V.; Skogby, H.; Hålenius, U.; Bosi, F. Color mechanisms in spinel: A multi-analytical investigation of natural crystals with a wide range of coloration. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2018, 46, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, W.H. XXX. The structure of the spinel group of crystals. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1915, 30, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbonin, S.; Russo, U.; Della Giusta, A. Cation distribution in some natural spinels from X-ray diffraction and Mössbauer spectroscopy. Miner. Mag. 1996, 60, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, V.; Andreozzi, G.B.; Hålenius, U.; Skogby, H.; Hametner, K.; Günther, D. Color mechanisms in spinel: Cobalt and iron interplay for the blue color. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2015, 42, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, E.S. Spectra of Tetrahedral Fe2+ in MgAl2O4. Phys. Rev. B 1973, 8, 3484–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorghinian, A.; Mottana, A.; Rossi, A.; Oltean, F.M.; Esposito, A.; Marcelli, A. Investigating the colour of spinel: 1. Red gem-quality spinels (“balas”) from Ratnapura (Sri Lanka). Rend. Lincei 2013, 24, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhin, A.; Brouder, C.; Arrio, M.-A.; Cabaret, D.; Sainctavit, P.; Balan, E.; Bordage, A.; Seitsonen, A.P.; Calas, G.; Eeckhout, S.G.; et al. X-ray linear dichroism in cubic compounds: The case of Cr3+ in MgAl2O4. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 195103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishikawa, S. Structure of Some Crystals of Spinel Group. Proc. Tokyo Math. Phys. Soc. 1915, 8, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.L.; Imbusch, G.F.; Macfarlane, R.M.; Kisliuk, P.; Larkin, D.M. Optical Spectrum of Cr3+ Ions in Spinels. J. Chem. Phys. 1968, 48, 5255–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.W. Magnesium-zinc-spinels from Ceylon. Miner. Mag. 1937, 24, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, V.; Andreozzi, G.B.; Bosi, F.; Hålenius, U. Blue spinel crystals in the MgAl2O4-CoAl2O4 series: Part I. Flux growth and chemical characterization. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 1828–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, W.A.; Howie, R.A.; Zussman, J. An Introduction to the Rock-Forming Minerals, 3rd ed.; Berforts Information Press: Hastings, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Atsawatanapirom, N.; Bupparenoo, P.; Nilhud, N.; Saeneekatima, K.; Leelawatanasuk, T. Identification and Stability of Cobalt Diffusion-Treated Spinel. In Proceedings of the 5th GIT International Gem and Jewelry Conference: Treatment and Synthetics Update and Disclosure, Pattaya, Thailand, 14–15 November 2016; pp. 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Chauvire, B.; Rondeau, B.; Fritsch, E.; Ressigeac, P.; Devidal, J.-L. Blue Spinel from the Luc Yen District of Vietnam. Gems Gemol. 2015, 51, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, L.T.T.; Haeger, T.; Phan, L. Study of impurity in blue spinel from the Luc Yen mining area, Yen Bai province, Vietnam. Vietnam J. Earth Sci. 2018, 40, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krzemnicki, M.; Wang, H.; Stephan, T.; Henn, U. Cobalt diffusion treated spinel. In Proceedings of the 35th IGC 2017, Windhoek, Namibia, 11–15 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Krzemnicki, M.S. Spinel, a Gemstone on the Rise; Swiss Gemmological Institute: Basel, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 18, pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Peretti, A.; Günther, D. Spinel from Namya. In Contributions to Gemology; Gemresearch Swisslab: Lucerne, Switzerland, 2003; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Shigley, J.E.; Stockton, C.M. Cobalt-blue gem spinels. Gems Gemol. 1984, 20, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.T. Mineral determination by absorption spectra II. Am. Mineral. 1929, 14, 323–328. [Google Scholar]
- Fregola, R.A.; Skogby, H.; Bosi, F.; D’Ippolito, V.; Andreozzi, G.B.; Hålenius, U. Optical absorption spectroscopy study of the causes for color variations in natural Fe-bearing gahnite: Insights from iron valency and site distribution data. Am. Mineral. 2014, 99, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palke, A.C.; Sun, Z. What is cobalt spinel? Unraveling the causes of color in blue spinels. Gems Gemol. 2018, 54, 262–263. [Google Scholar]
- Saeseaw, S.; Wang, W.; Scarratt, K.; Emmett, J.; Douthit, T. Distinguishing Heated Spinels from Unheated Natural Spinels and from Synthetic Spinels—A short review of on-going research. GIA Res. News 2009. 13p. Available online: https://www.gia.edu/doc/distinguishing-heated-spinels-from-unheated-natural-spinels.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2022).
- Newville, M. Fundamentals of XAFS. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2014, 78, 33–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurand, P.; Rose, J.; Briois, V.; Salome, M.; Proux, O.; Nassif, V.; Olivi, L.; Susini, J.; Hazemann, J.-L.; Bottero, J.-Y. New Methodological Approach for the Vanadium K-Edge X-ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure Interpretation: Application to the Speciation of Vanadium in Oxide Phases from Steel Slag. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 5101–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrail, J.; Farges, F. Not all chromates show the same pre-edge feature. Implications for the modelling of the speciation of Cr in environmental systems. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 190, 012176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farges, F. Chromium speciation in oxide-type compounds: Application to minerals, gems, aqueous solutions and silicate glasses. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2009, 36, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuli, G.; Paris, E.; Mungall, J.; Romano, C.; Dingwell, D. V oxidation state and coordination number in silicate glasses by XAS. Am. Mineral. 2004, 89, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, F.E.; Najih, M.; Huffman, G.P. Direct speciation of chromium in coal combustion by-products by X-ray absorption fine-structure spectroscopy. Fuel 1999, 78, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.L.; Brown, G.E.; Parks, G.A. Quantitative Determination of Chromium Valence in Environmental Samples Using Xafs Spectroscopy. MRS Proc. 1996, 432, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.L.; Brown, G.E.; Parks, G.A.; Stein, C.L. Differential redox and sorption of Cr (III/VI) on natural silicate and oxide minerals: EXAFS and XANES results. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 3399–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, M.; Farges, F.; Petit, P.-E.; Brown, G.E., Jr.; Martin, F. Oxidation state and coordination of Fe in minerals: An Fe K-XANES spectroscopic study. Am. Mineral. 2001, 86, 714–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, M.; Partzsch, G.M.; Bernhardt, R.; Lattard, D. Determination of the iron oxidation state in basaltic glasses using XANES at the K-edge. Chem. Geol. 2005, 220, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnag, N.; Kasri, B.; Setwong, W.; Sirisurawong, E.; Chotsawat, M.; Chirawatkul, P.; Saiyasombat, C. Study of Fe ions in aquamarine and the effect of dichroism as seen using UV–Vis, NIR and x-ray. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 177, 109107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newville, M. Larch: An Analysis Package for XAFS and Related Spectroscopies. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2013, 430, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farges, F.; Brown, G.E.; Rehr, J.J. Coordination chemistry of Ti(IV) in silicate glasses and melts: I. XAFS study of titanium coordination in oxide model compounds. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 3023–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Cheng, Y.; Gundakaram, R.; Jang, L. Crystal and electronic structures of inverse spinel-type LiNiVO4. Mater. Res. Bull. 2001, 36, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, P.V.; Papike, J.J.; Bell, A.S.; Shearer, C.K. Vanadium Valence in Spinel from a Y98 Composition Melt as Determined by X-Ray Absorption Near Edge Structure (XANES). In Proceedings of the 46th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 16–20 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Westre, T.E.; Kennepohl, P.; DeWitt, J.G.; Hedman, B.; Hodgson, K.O.; Solomon, E.I. A Multiplet Analysis of Fe K-Edge 1s → 3d Pre-Edge Features of Iron Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 6297–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balan, E.; De Villiers, J.P.; Eeckhout, S.G.; Glatzel, P.; Toplis, M.J.; Fritsch, E.; Allard, T.; Galoisy, L.; Calas, G. The oxidation state of vanadium in titanomagnetite from layered basic intrusions. Am. Mineral. 2006, 91, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordage, A.; Balan, E.; de Villiers, J.P.R.; Cromarty, R.; Juhin, A.; Carvallo, C.; Calas, G.; Raju, P.V.S.; Glatzel, P. V oxidation state in Fe–Ti oxides by high-energy resolution fluorescence-detected X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2011, 38, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, J.A.; Wandzilak, A.; Maganas, D.; Wurster, N.I.C.; Hugenbruch, S.; Kowalska, J.K.; Pollock, C.J.; Lima, F.A.; Finkelstein, K.D.; Debeer, S. Experimental and theoretical correlations between vanadium K-edge X-ray absorption and Kβ emission spectra. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 21, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutton, S.; Karner, J.; Papike, J.; Delaney, J.; Shearer, C.; Newville, M.; Eng, P.; Rivers, M.; Dyar, M. Vanadium K edge XANES of synthetic and natural basaltic glasses and application to microscale oxygen barometry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waychunas, G.A.; Apted, M.J.; Brown, G.E. X-ray K-edge absorption spectra of Fe minerals and model compounds: Near-edge structure. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1983, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Lytle, F.W.; Messmer, R.P.; Maylotte, D.H. K-edge absorption spectra of selected vanadium compounds. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 30, 5596–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeckhout, S.G.; Bolfan-Casanova, N.; McCammon, C.; Klemme, S.; Amiguet, E. XANES study of the oxidation state of Cr in lower mantle phases: Periclase and magnesium silicate perovskite. Am. Mineral. 2007, 92, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandeur, D.; Juillot, F.; Morin, G.; Olivi, L.; Cognigni, A.; Webb, S.M.; Ambrosi, J.-P.; Fritsch, E.; Guyot, F.; Brown, G.E., Jr. XANES Evidence for Oxidation of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) by Mn-Oxides in a Lateritic Regolith Developed on Serpentinized Ultramafic Rocks of New Caledonia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7384–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhin, A.; Calas, G.; Cabaret, D.; Galoisy, L.; Hazemann, J.-L. Structural relaxation around substitutional Cr3+ in MgAl2O4. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 054105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odake, S.; Fukura, S.; Arakawa, M.; Ohta, A.; Harte, B.; Kagi, H. Divalent chromium in ferropericlase inclusions in lower-mantle diamonds revealed by micro-XANES measurements. J. Miner. Pet. Sci. 2008, 103, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villain, O.; Calas, G.; Gaioisy, L.; Cormier, L.; Hazemann, J.-L. XANES Determination of Chromium Oxidation States in Glasses: Comparison with Optical Absorption Spectroscopy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 3578–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkokua, W.; Pongkrapan, S.; Dararutana, P.; T-Thienprasert, J.; Wathanakul, P. X-ray absorption near-edge structure of chromium ions in α-Al2O3. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 185, 012054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlmeister, S.; Koivula, J.I.; Kammerling, R.C.; Smith, C.P.; Fritsch, E.; Shigley, J.E. Flux-Grown Synthetic Red and Blue Spinels from Russia. Gems Gemol. 1993, 29, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, G.B.; Hålenius, U.; Skogby, H. Spectroscopic active IVFe3+-VIFe3+ clusters in spinel-magnesioferrite solid solution crystals: A potential monitor for ordering in oxide spinels. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2001, 28, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmetzer, K.; Haxel, C.; Amthauer, G. Colour of natural spinels, gahnospinels and gahnites. J. Mineral. Geochem. 1989, 159–180. [Google Scholar]
- Taran, M.N.; Koch-Müller, M.; Langer, K. Electronic absorption spectroscopy of natural (Fe2+, Fe3+)-bearing spinels of spinel s.s.-hercynite and gahnite-hercynite solid solutions at different temperatures and high-pressures. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2005, 32, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootkul, D.; Tengchaisri, T.; Tippawan, U.; Intarasiri, S. Analysis and modification of natural red spinel by ion beam techniques for jewelry applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 306, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hålenius, U.; Skogby, H.; Andreozzi, G.B. Influence of cation distribution on the optical absorption spectra of Fe3+ -bearing spinel s.s.–hercynite crystals: Evidence for electron transitions in VIFe2+-VIFe3+ clusters. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2002, 29, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeseaw, S. Cobalt diffusion of natural spinel: A report describing a new treatment on the gem market. GIA Res. News 2015. 22p. Available online: https://www.gia.edu/doc/Cobalt-Diffusion-in-Spinel-v2.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2022).
- Cynn, H.; Sharma, S.K.; Cooney, T.F.; Nicol, M. High-temperature Raman investigation of order-disorder behavior in the MgAl2O4 spinel. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 45, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotznick, S.P.; Shim, S.-H. In situ Raman spectroscopy measurements of MgAl2O4 spinel up to 1400 °C. Am. Mineral. 2008, 93, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, R.; Malsy, A.-K.; Armbruster, T. Effects of heat treatment on red gemstone spinel: Single-crystal X-ray, Raman, and photoluminescence study. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2015, 42, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phyo, M.M.; Bieler, E.; Franz, L.; Balmer, W.; Krzemnicki, M.S. Spinel from Mogok, Myanmar—A Detailed Inclusion Study by Raman Microspectroscopy and Scanning Electron Microscopy. J. Gemmol. 2019, 36, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraas, L.M.; Moore, J.E.; Salzberg, J.B. Raman characterization studies of synthetic and natural MgAl2O4 crystals. J. Chem. Phys. 1973, 58, 3585–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, A.H.; Breeding, C.M.; DeGhionno, D. Lab Notes: Natural spinel identified with Photoluminescence. Gems Gemol. 2004, 40, 168–169. [Google Scholar]
- Mikenda, W. N-lines in the luminescence spectra of Cr3+-doped spinels (III) partial spectra. J. Lumin. 1981, 26, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.-L.; Yu, S.-C.; Phan, M.-H.; Han, T. Photoluminescence properties of Cr3+-doped MgAl2O4 natural spinel. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2004, 45, 63–66. [Google Scholar]






| Parameters | Iron | Chromium | Vanadium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edge energy (E0) | 7112 eV | 5989 eV | 5465 eV |
| Number of scans | 3–5 | 3–5 | 3–5 |
| Energy (eV) | −80, −15, 30, 60, 90, 200 | −80, −15, 30, 60, 90, 200 | −80, −15, 30, 60, 90, 200 |
| Energy step (eV) | 5, 0.2, 0.4, 2,4 | 5, 0.2, 0.4, 2, 4 | 5, 0.2, 0.4, 2, 4 |
| Time step (s) | 1–4 | 1–4 | 1–4 |
| Beam size | 2 × 3/4 × 3/4 × 4 mm | 2 × 3/4 × 3/4 × 4 mm | 2 × 3/4 × 3/4 × 4 mm |
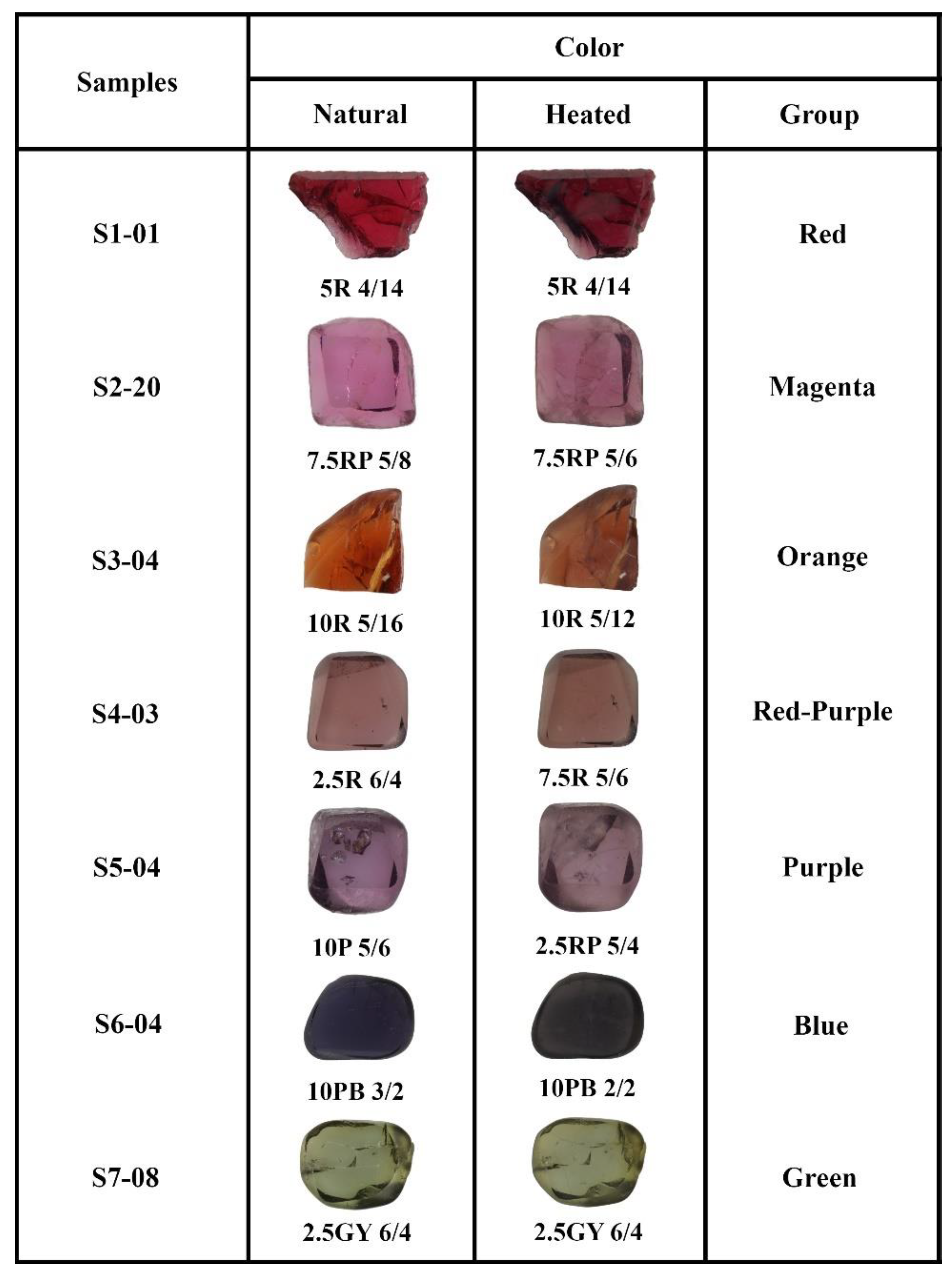
| Sample/ Properties | Color Group | Refractive Index | Specific Gravity | UV Fluorescence | Color Code | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short Wave | Long Wave | Natural | Heated | ||||
| S1-01 | S1 Red | 1.722 | 3.52 | inert | inert | 5R 4/14 | 5R 3/10 |
| S1-03 | 1.720 | 3.55 | inert | red | 10R 3//10 | 10R 3/8 | |
| S1-07 | 1.721 | 3.62 | inert | red | 10R 2/8 | 10R 1/8 | |
| S1-10 | 1.715 | 3.47 | inert | inert | 10R 2/12 | 10R 3/8 | |
| S2-20 | S2 Magenta | 1.718 | 3.42 | inert | red | 7.5RP 5/8 | 7.5RP 5/6 |
| S2-22 | 1.718 | 3.66 | inert | inert | 10RP 5/8 | 2.5R 5/6 | |
| S2-25 | 1.718 | 3.55 | inert | red | 5R 5/8 | 7.5R 4/6 | |
| S3-04 | S3 Orange | 1.718 | 3.68 | inert | inert | 10R 5/16 | 10R 5/12 |
| S3-11 | 1.718 | 3.50 | inert | inert | 2.5YR 5/12 | 2.5YR 6/6 | |
| S3-18 | 1.716 | 3.59 | inert | red | 2.5YR 4/10 | 2.5YR 5/6 | |
| S3-23 | 1.718 | 3.56 | inert | inert | 2.5YR 4/8 | 2.5YR 3/6 | |
| S3-27 | 1.718 | 3.56 | inert | red | 2.5YR 4/12 | 2.5YR 3/6 | |
| S4-02 | S4 Red-purple | 1.715 | 3.62 | inert | inert | 2.5R 4/6 | 7.5R 3/6 |
| S4-03 | 1.718 | 3.21 | inert | inert | 2.5R 6/4 | 7.5R 5/6 | |
| S4-06 | 1.719 | 3.61 | inert | inert | 2.5YR 3/8 | 2.5YR 3/6 | |
| S4-14 | 1.718 | 3.60 | inert | red | 10R 3/8 | 5R 3/8 | |
| S5-04 | S5 Purple | 1.716 | 3.52 | inert | inert | 10P 5/6 | 2.5RP 5/4 |
| S5-09 | 1.718 | 3.62 | inert | inert | 10RP 2/8 | 10RP 3/4 | |
| S5-13 | 1.720 | 3.50 | inert | inert | 2.5RP 5/6 | 2.5RP 6/4 | |
| S5-22 | 1.716 | 3.57 | inert | red | 7.5RP 7/4 | 10RP 7/4 | |
| S6-04 | S6 Blue | 1.720 | 3.68 | inert | inert | 10PB 3/2 | 10PB 2/2 |
| S7-08 | S7 Green | 1.720 | 3.63 | inert | inert | 2.5GY 6/4 | 2.5GY 6/4 |
| Oxide (wt%)/ Samples | S1 Red | S2 Magenta | S3 Orange | S4 Red-Purple | S5 Purple | S6 Blue | S7 Green | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1-01 | S1-03 | S1-07 | S1-10 | S2-20 | S2-22 | S2-25 | S3-04 | S3-11 | S3-18 | S3-23 | S3-27 | S4-02 | S4-03 | S4-06 | S4-14 | S5-04 | S5-09 | S5-13 | S5-22 | S6-04 | S7-08 | |
| SiO2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TiO2 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Al2O3 | 69.51 | 69.52 | 68.90 | 69.73 | 69.82 | 70.92 | 70.97 | 70.03 | 70.43 | 70.90 | 70.61 | 70.41 | 70.18 | 70.93 | 70.36 | 70.52 | 69.60 | 70.58 | 70.71 | 70.57 | 69.93 | 70.74 |
| V2O3 | 0.47 | 1.07 | 1.06 | 1.60 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.75 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.72 | 0.77 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.37 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| Cr2O3 | 1.84 | 0.25 | 1.02 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| Ga2O3 | 1.53 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.63 | 0.95 | 2.28 | 0.51 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 1.47 | 0.79 | 0.00 | 2.57 | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| FeO | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 1.00 | 1.14 | 0.98 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 1.13 | 1.30 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.15 | 0.74 | 2.66 | 1.14 |
| MnO | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.19 |
| MgO | 26.38 | 27.20 | 27.39 | 28.17 | 27.49 | 26.71 | 26.74 | 28.54 | 28.74 | 28.39 | 26.75 | 27.22 | 27.90 | 27.40 | 27.10 | 27.02 | 27.35 | 26.34 | 27.33 | 26.50 | 25.92 | 26.96 |
| CoO | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| ZnO | 0.09 | 1.02 | 0.96 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.72 | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.59 | 0.13 |
| CaO | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Total | 100.03 | 99.22 | 99.60 | 99.82 | 98.75 | 99.12 | 99.24 | 99.61 | 100.14 | 100.79 | 99.36 | 100.94 | 99.84 | 99.79 | 99.30 | 98.94 | 99.86 | 99.29 | 99.42 | 100.70 | 99.27 | 99.17 |
| Based on 32 oxygens | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Si | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Ti | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.015 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.015 | 0.011 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.000 |
| Al | 15.728 | 15.799 | 15.642 | 15.692 | 15.886 | 16.058 | 16.048 | 15.764 | 15.772 | 15.795 | 15.970 | 15.767 | 15.822 | 15.964 | 15.939 | 15.987 | 15.767 | 16.012 | 15.971 | 15.872 | 15.972 | 16.025 |
| V | 0.072 | 0.166 | 0.163 | 0.245 | 0.010 | 0.018 | 0.023 | 0.115 | 0.096 | 0.092 | 0.110 | 0.117 | 0.031 | 0.029 | 0.057 | 0.074 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.007 | 0.019 | 0.008 | 0.002 |
| Cr | 0.279 | 0.039 | 0.155 | 0.029 | 0.034 | 0.034 | 0.038 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.017 | 0.009 | 0.004 | 0.000 |
| Ga | 0.188 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.076 | 0.117 | 0.278 | 0.063 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.047 | 0.181 | 0.097 | 0.000 | 0.314 | 0.006 | 0.000 |
| Fe | 0.028 | 0.010 | 0.027 | 0.003 | 0.161 | 0.182 | 0.157 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.007 | 0.026 | 0.017 | 0.159 | 0.181 | 0.209 | 0.040 | 0.081 | 0.161 | 0.184 | 0.117 | 0.432 | 0.183 |
| Mn | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.030 |
| Mg | 7.551 | 7.820 | 7.865 | 8.021 | 7.913 | 7.650 | 7.649 | 8.128 | 8.143 | 8.000 | 7.654 | 7.712 | 7.956 | 7.801 | 7.767 | 7.749 | 7.839 | 7.558 | 7.809 | 7.540 | 7.490 | 7.727 |
| Co | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Zn | 0.013 | 0.145 | 0.137 | 0.004 | 0.011 | 0.000 | 0.009 | 0.016 | 0.026 | 0.009 | 0.019 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.027 | 0.102 | 0.044 | 0.007 | 0.018 | 0.085 | 0.019 |
| Ca | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 |
| Total | 23.864 | 23.991 | 24.005 | 24.007 | 24.029 | 23.945 | 23.939 | 24.051 | 24.060 | 24.004 | 23.900 | 23.913 | 24.039 | 23.996 | 23.996 | 23.940 | 24.004 | 23.915 | 24.001 | 23.891 | 24.004 | 23.986 |
| Absorption (nm)/Color | Cause | Red (S1) | Magenta (S2) | Orange (S3) | Red-Purple (S4) | Purple (S5) | Blue (S6) | Green (S7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 372 | Fe2+ and Fe3+ * | x | x | x | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| 387–396 | Fe2+, Cr3+, V3+ * | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ |
| 456–459 | Fe2+ and/or Fe3+ | x | x | x | x | x | ☑ | ☑ |
| 487 | Fe2+ | x | x | x | x | ☑ | x | x |
| 534–546 | Fe2+, Cr3+, V3+ * | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | x | x |
| 558 | Fe2+ | x | x | x | x | x | ☑ | x |
| 630 | Co2+ | x | x | x | x | x | ☑ | x |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pluthametwisute, T.; Wanthanachaisaeng, B.; Saiyasombat, C.; Sutthirat, C. Minor Elements and Color Causing Role in Spinel: Multi-Analytical Approaches. Minerals 2022, 12, 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12080928
Pluthametwisute T, Wanthanachaisaeng B, Saiyasombat C, Sutthirat C. Minor Elements and Color Causing Role in Spinel: Multi-Analytical Approaches. Minerals. 2022; 12(8):928. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12080928
Chicago/Turabian StylePluthametwisute, Teerarat, Bhuwadol Wanthanachaisaeng, Chatree Saiyasombat, and Chakkaphan Sutthirat. 2022. "Minor Elements and Color Causing Role in Spinel: Multi-Analytical Approaches" Minerals 12, no. 8: 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12080928
APA StylePluthametwisute, T., Wanthanachaisaeng, B., Saiyasombat, C., & Sutthirat, C. (2022). Minor Elements and Color Causing Role in Spinel: Multi-Analytical Approaches. Minerals, 12(8), 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12080928






