Abstract
Red mud (RM), a byproduct of aluminum production, is used as amendments to increase the pH and reduce the available Cd in soil, but the effects of RM treatments on rice and rhizosphere chemistry changes at different radial-oxygen-loss (ROL) rates and developmental stages remain unclear. To address this concern, a rhizobox trial was conducted to investigate the effect of 0%, 0.5%, and 1.0% RM, on Cd accumulation by rice cultivars differing in ROL rate (‘Zheyou12’ (ZY12), ‘Qianyou1’ (QY1), and ‘Chunjiangnuo2’ (CJN2)) at two growth stages (tillering and bolting). The results showed that mobility factors of Cd in the soil were decreased significantly at both stages. The Cd mobility factor (MF) of CJN2 was decreased by 33.01% under 1% RM treatment at bolting stage. The pH value was increased by 0.39–0.53 units at two stages. RM contains large amounts of metals, which can increase soil iron (Fe) and manganese (Mn) concentrations, reduce redox potential, and transform the available Cd into Fe/Mn oxide-bound Cd. In addition, the Fe plaque further increased to inhibit the transformation of Cd. These changes reduced the available Cd in the soil and further decreased Cd absorption by rice. With the increase in RM concentration, the shoot and root biomass increased, and Cd accumulation in the plant significantly decreased. Compared with that under 0% RM treatment, the shoot Cd concentrations of ZY12, QY1, and CJN2 under 1% RM treatment at the bolting stage decreased by 27.59%, 36.00%, and 46.03%, respectively. The relative Cd accumulation ability of the three rice cultivars was CJN2 < QY1 < ZY12. The ROL promotes Fe plaque formation on the root surface. The Fe plaque is an obstacle or buffer between Cd and rice, which can immobilize Cd in Fe plaque and further reduce Cd absorption by rice. The addition of RM, in combination with a high-ROL rice cultivar, is a potential strategy for the safe production of rice on Cd-contaminated soils.
1. Introduction
Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic substance and one of the most highly toxic pollutants in soil [1,2]. Cadmium in soil can be absorbed by crops and enter the human body through the food chain, thus posing a threat to human health [3]. According to the report of the National General Survey of Soil Contamination (2014), the proportion of pollutant Cd in contaminated farmland is the highest in inorganic pollution, at 7%, with mild to moderate pollution in China. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is a staple food in China, which can accumulate high quantities of Cd in the seeds and shoots grown in Cd-contaminated paddy soil and generally pose a higher health risk to humans compared with other crops [4,5,6]. The high demand for rice and pressure for foodstuff production mean that farmers cannot practice fallowing to remediate Cd-polluted paddy soils. Such paddy soils must be remediated properly to reduce Cd accumulation by rice and prevent its entry into the food chain [7].
In situ remediation techniques, including phytoremediation, immobilization, and chemical washing, are effective methods used to reduce the Cd concentration of plants grown in mildly Cd-polluted soil [8]. Among these techniques, immobilization is considered the most effective method for Cd-contaminated soil remediation [8]. The bioavailable Cd in soil can be immobilized by adding amendments or sorbents, thereby reducing Cd uptake by plants and exposure of living organisms to Cd [9]. Red mud (RM), a byproduct of aluminum (Al) production [10,11,12,13], contains high concentrations of iron (Fe) hydroxides, including hematite and goethite, which can transform the fraction of exchangeable Cd in soil to the iron/manganese (Fe/Mn) oxide-bound fraction, effectively reducing Cd accumulation by rice [8,14,15]. Moreover, hydroxide ions (OH−) are released into the soil after RM addition owing to its high alkalinity. The gradually alkalized soil may form complexes with Cd to induce precipitation, decreasing the soil content of bioavailable Cd and thereby reducing Cd absorption by plants [16]. Simultaneously, the released OH− ions may be neutralized by H+, resulting in Cd2+ adsorption by soil colloids, thus further reducing Cd uptake by rice [16,17]. Liu et al. [14] found that the absorption of Cd by rice was significantly decreased with red mud increasing under pot experiments. However, the changes in the soil rhizosphere environment and the absorption of Cd by rice in different periods are still yet to be studied.
Similar to other wetland species, rice plants form extensive aerenchyma in the stem and show high root porosity, which are essential for survival in flooded soils under anaerobic conditions. Radial oxygen loss (ROL) is an important pathway to detoxify plant toxins (e.g., hydrogen sulfide), which can affect Cd accumulation by rice [18,19,20]. Some researchers have reported that the higher root porosity tends to lead to higher ROL, resulting in higher biomass and lower arsenic (As) concentrations in paddy soils [18]. The rate of ROL and oxidization capacity of plant roots are important biological factors that control Fe plaque formation and the ROL of paddy rice oxygenates th e rhizosphere [21]. The main components of Fe plaques in wetland plants are ferric oxide/hydroxide, which show a strong adsorption capacity to bind with heavy metals to protect plants from heavy-metal toxicity, and are variously obstacles or buffers for heavy metals and plants [20,22].
Cadmium concentrations in various tissues and Fe plaque formation in rice vary with growth stage. The rate of Fe plaque formation on the root surface at the tillering stage is quicker than that at other developmental stages [23]. Soil amendment with RM can significantly reduce Cd accumulation of plants in pot or field experiments. However, the changes in Cd accumulation by rice, the root ROL/oxidization capacity, and the changes in the soil rhizosphere in rice cultivars differing in ROL rate at different developmental stages under RM treatment remain unclear. We hypothesize that RM has different effects on the Cd uptake by rice and chemical changes in rhizospheres with different ROL and porosity rice cultivars in different growth stages. Therefore, a rhizobox trial was conducted with the following objectives: (1) to elucidate the physiological effects of RM addition on rice cultivars differing in ROL rates at different growth stages (such as on biomass and Cd accumulation capacity); (2) to study the effects of RM on Fe plaque formation on rice root surfaces and physicochemical properties in the soil; and (3) to clarify the mechanism of reduced Cd uptake in response to RM amendment in rice cultivars differing in ROL rate. The aim was to screen suitable rice cultivars and determine the optimal amount of RM addition, to provide a theoretical basis for the safe production of rice on mildly to moderately Cd-polluted soils.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
Three rice cultivars that differed in ROL rate were selected for the study according to Liu et al. [14]. ‘Zheyou12’ (ZY12), ‘Qianyou1’ (QY1), and ‘Chunjiangnuo2’ (CJN2) have a low, moderate, and high ROL rate, respectively. Seeds were sterilized in 10% H2O2 for 30 min and then washed with deionized water.
2.2. Soil and Red Mud Samples
Soil (0–20 cm depth) was collected from a paddy field at Qiyang City, Hunan Province, China. The soil samples were thoroughly mixed, air-dried, ground, and passed through a sieve (<2 mm mesh). The physicochemical properties of the soil were as follows: pH 5.31, total nitrogen content 1.72 g·kg−1, organic matter content 27.5 g·kg−1, and total Cd content 1.73 mg·kg−1. Different quantities of RM were mixed thoroughly with the soil and allowed to blend for 2 months, while maintaining the moisture content at 70% of the maximum water-holding capacity. The amended soil was then air-dried and sieved (2 mm mesh) to obtain the soils used in the trial.
The RM (pH 11.1) sampled was the residue from the Bayer process for extraction of alumina from bauxite and was collected from the Shandong Aluminum Company Ltd. (Zibo City, Shandong Province, China). The mineralogical composition of the RM sample (determined by X-ray diffraction analysis (X’Pert Pro X-ray, PANAnalytical, Almelo, Netherlands) and X-ray fluorescence (PHECDA-PRO, Anchor Wisom, Beijing, China)) was Fe2O3 (28%), Al2O3 (21%), SiO2 (20%), Na2O (11%), CaO (6.2%), TiO2 (3.3%), MgO (1.3%), and K2O (0.26%) (Yang et al. 2015; Luo et al. 2011). X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed using a PANAnalytical X’Pert Pro X-ray (Almelo, Netherlands) diffractometer equipped with a Cu source (Cu Kα). In addition, the As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn concentrations in RM were 0.43, <0.01, 133, 31, 0.10, 4.2, 119, and 94 mg·kg−1, respectively. The specific surface area was determined to be 12.2 m2·g−1 using the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller/N2-adsorption method with a Sorptomatic instrument (Carlo Erba, Milan, Italy). The RM samples were dried at 105 °C to constant weight, ground, and passed through a sieve (<1 mm).
2.3. Rhizobox Trial
The rhizobox trial was performed with three factors: (1) two rice growth stages (tillering and bolting stages, with samples collected at 60th days and 90th days after sowing of rice growth, respectively); (2) three rice cultivars that differed in ROL rate (ZY12, QY1, and CJN2, with low, moderate, and high ROL rates, respectively); and (3) three RM concentrations (0%, 0.5%, and 1% (w/w)). Given all combinations, a total of 18 treatments were applied with three replicates per treatment, thus comprising a total of 54 plexiglass boxes.
First, three kilograms dry soil was placed in a plexiglass box (15 cm × 15 cm × 12 cm, length × width × height). The plexiglass box was divided into four zones using nylon mesh, designated S1, S2, S3, and S4. The soil zones were identical in width and height but differed in length. S1 was located in the center of the plexiglass box, 4 mm left and right, 8 mm in total. S2 was adjacent to S1, a left and right near S1, 4 mm each, for a total of 8 mm. S3 was adjacent to S2, a left and right near S2, each 32 mm, a total of 64 mm. S4 was adjacent to S3, a left and right near S3, >40 mm. Two rice seedlings of uniform growth were transplanted in the center of each plexiglass box. For the trial, the plexiglass boxes were randomly arranged and rice seedlings were grown in a greenhouse under flooded conditions with the water level maintained at 2 cm above the soil surface. At harvest, the shoots and roots of rice plants and soil samples were collected.
2.4. Chemical Analysis of Plant and Soil Samples
The determination method for ROL rate and root porosity (percentage of gas volume/root volume) of rice seedlings followed the procedure of Kludze et al. [24]. The ROL rate was determined by the Ti3+-citrate method and root porosity was measured with a pycnometer.
The shoots and roots of rice plants were harvested separately. The samples were washed three times with tap water and then three times with ultrapure water. The samples were dried at 105 °C for 30 min, and then dried at 65 °C to constant weight, and the dry weight was recorded. The shoot and root samples were digested with 4 mL aqua regia (HNO3/HCl, 1:3, v/v). The cadmium (Cd), iron (Fe), and manganese (Mn) on the Fe plaque were extracted using the dithionite–citrate–bicarbonate method. The digested samples, as well as a blank control and standard reference material [GBW07603 (GSV-2)] for quality control, were analyzed using an inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometer (ICP-MS; Elan DRC-e, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) to determine the Cd content, and an inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometer (Optima 2000 DV, PerkinElmer) to determine the Fe and Mn contents of rice tissues. The recovery rate was 90% ± 10%.
The content total nitrogen was analyzed by Elemental analyzer (Costech ECS4010/4024, Santa Clarita, CA, USA) and the content of organic matter was measured by wet oxidation with H2SO4-K2Cr2O7. The total Cd concentration in soil was measured by X-Ray fluorescence (XRF, PHECDA-PRO, Anchor Wisom, Beijing, China) in soil that passed through a 100-mesh sieve.
Soil samples were collected from S1 at the tillering stage and all four zones (S1, S2, S3, and S4) at the bolting stage. During sampling, all plexiglass boxes were transferred to N2-filled boxes to ensure that no oxidation occurred. The soil samples in the same zone from the left and right were mixed thoroughly, and then placed in a vacuum tube for later use.
Soil pH was determined using a pH meter (TM-39, Germany) at a 1:5 soil: water ratio (w/v) with an ORION combined electrode. Additionally, redox potential (Eh) was determined using an Eh meter (TM-39, Germany). To determine the Fe2+ and Fe3+ contents and to ensure that they were not oxidized, 0.8–1.0 g soil samples were placed quickly into the test tube and immersed immediately with deoxygenated 5 mM CaCl2; the entire process took <20 s. Then, Fe2+ was measured by adding 10 cm3 CH3COONH4 (1 mol·L−1 with pH 2.8) to the suspension and shaking for 30 min, and then Fe3+ was measured by adding 10 cm3 H2SO4 (2 mol·L−1) to the centrifuged residue and shaking for 30 min, according to Begg [25].
The cadmium (Cd) fractions in the soil were determined using the five-step sequential-extraction method according to Tessier, which is briefly listed in Table 1 [26]. The soil Cd fractions were defined as exchangeable, carbonate-bound, Fe/Mn oxide-bound, organic-matter-bound, and residual forms, and were designated F1, F2, F3, F4, and F5, respectively. The fractions, together with a blank control and standard material (GBW-08303) for quality control, were analyzed using an ICP-MS (Elan DRC-E, PerkinElmer) to determine the Cd content in each fraction.

Table 1.
Procedure for the five-step sequential extraction of Cd from soil.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The cadmium (Cd) mobility factor (MF) was calculated as follows:
Analysis of variance (Waller–Duncan) was used to test for significance with IBM SPSS Statistics 26 software (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). Analysis of Pearson correlation coefficients was used to test for the correlations of Cd concentration in the shoots and soil physicochemical variables with IBM SPSS Statistics 26 software (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). Figures were prepared using OriginPro 2022 software (Origin Lab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Root Porosity and ROL Rate of Three Rice Cultivars
Root porosity and ROL rate at the bolting stage were higher (Figure 1). For CJN2, compared with those at the tillering stage, root porosity and ROL ratio at the bolting stage increased by 12.57% and 22.99%, respectively, which are beneficial for growth and improve the tolerance to heavy metals of rice [18], consistent with the findings of a previous study [23]. The highest root porosity and ROL rate were recorded for CJN2, whereas those of QY1 and ZY12 were lower at both growth stages. Compared with those of ZY12, the root porosity and ROL rate of CJN2 were increased by 37.23% and 60.90% at the bolting stage. Mei et al. [18] found that the correlation between ROL rate and porosity was positive. Generally, the higher the rate of ROL and porosity, the lower the accumulation of heavy metals by rice. ROL rate affects the Fe plaque formation, and root porosity affects the water-holding capacity of the soil. Generally, the water-holding capacity is greater with an increase in the soil porosity, which is more conducive to the growth of rice [25].
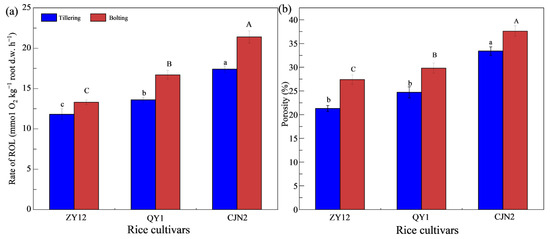
Figure 1.
Radial-oxygen-loss rates (ROL) (a), and root porosity (b) of rice. Data are the mean ± SE (n = 3). Different upper- and lowercase letters above bars indicate significant differences among the cultivars at the tillering and bolting stages, respectively.
3.2. Plant Growth of Rice Cultivars Differing in ROL Rate
The shoot and root biomass differed significantly among the three rice cultivars, which were ranked as CJN2 > QY1 > ZY12 (Figure 2.). In the 0% RM treatment, compared with that of ZY12, the shoot biomasses of QY1 and CJN2 at the tillering and bolting stages were increased by 10.22% and 13.73%, and 8.52% and 5.50%, respectively. CJN2 and QY1 had a higher root porosity and ROL rate, which can increase the water-holding capacity of the soil and nutrients, to promote biomass accumulation of rice [18,27]. The addition of RM positively affected rice growth at the tillering and bolting stages and biomass was obviously increased in response to RM addition. The shoot biomasses of ZY12, QY1, and CJN2 with 1% RM treatment were 3611, 3911, and 4259 mg·pot−1 at the bolting stage, respectively, which represented increases of 1.8%, 4.5%, and 5.58%, respectively, compared with those with the 0% RM treatment. This finding was consistent with previous results for rice and other plant species [3]. Yang et al. [3] found that the cucumber shoot biomass in response to RM addition was approximately two-times greater than that of plants without RM application. The addition of RM might relieve rice growth in Cd-contaminated soil from two aspects. First, RM provides additional nutrients for plant growth, such as calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and silicon (Si) [28,29], which may improve the soil fertility and increase plant biomass. Second, the application of RM as an amendment can immobilize the available Cd in the soil and reduce Cd accumulation by rice, thereby reducing Cd toxicity and enhancing the growth of rice [30].
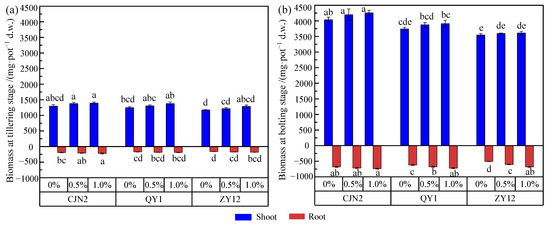
Figure 2.
(a,b) Effect of red mud (RM) on root and shoot biomass of rice grown in rhizoboxes. Different lowercase letters within shoot or root biomass indicate a significant difference among treatments (p < 0.05). 0%, 0.5%, and 1% indicated the RM concentrations in soil (w/w), the same as below.
3.3. Cadmium (Cd), Fe, and Mn Concentrations of Rice Cultivars Differing in ROL Rate
The cadmium (Cd), Fe, and Mn concentrations in the shoots, roots, and root surface (Fe plaque) were consistently higher at the bolting stage (Figure 3). However, the three rice cultivars differed in Cd-accumulation abilities. The roots and shoots of CJN2 (high ROL rate, high porosity) and ZY12 (low ROL rate, low porosity) had the lowest and highest Cd concentrations at both growth stages with an increase in RM (p < 0.05) (Figure 3a). The cadmium (Cd) concentration in shoots of ZY12 was 1.42 times higher than that of QY1 and 2.43 times higher than that of CJN2 under 1% RM treatment at the bolting stage. These results further indicated that the cultivar with a high ROL rate and porosity accumulated the lowest Cd concentrations in the shoot among the three cultivars, which is consistent with previous studies [18]. The ROL rate is considered to be a critical biological factor to control Fe plaque formation [31,32]. It is well known that a higher ROL rate can promote Fe plaque formation under the same Fe2+ concentration in the growth environment [20]. The Fe plaque decreases the absorption of heavy metals by rice roots owing to adsorption or coprecipitation. This may explain the lower Cd accumulation by the rice cultivar with a high ROL rate and porosity. The cadmium (Cd) concentration in shoots and roots of the three rice cultivars decreased, whereas the Fe and Mn concentrations increased, at both growth stages, in response to RM addition (Figure 3b,c). Compared with those under the 0% RM treatment, the Cd concentrations in the shoots of ZY12, QY1, and CJN2 under the 1% RM treatment decreased by 42.37%, 35.14%, and 50.00% at the tillering stage, and decreased by 27.59%, 36.00%, and 46.03% at the bolting stage, respectively. The present and previous studies confirm that RM can significantly reduce Cd accumulation by plants [14,33]. The Fe and Mn concentrations in the shoots of ZY12, QY1, and CJN2 under 1% RM treatment were increased by 28.26% and 4.46%, 39.43% and 5.75%, and 47.11% and 15.25%, respectively, compared with those under the 0% RM treatment. RM is a byproduct of aluminum production and contains quantities of Fe and Mn [28]. The Fe and Mn concentrations in the soil would be increased after RM addition; thus, higher Fe and Mn quantities would be absorbed by rice plants.
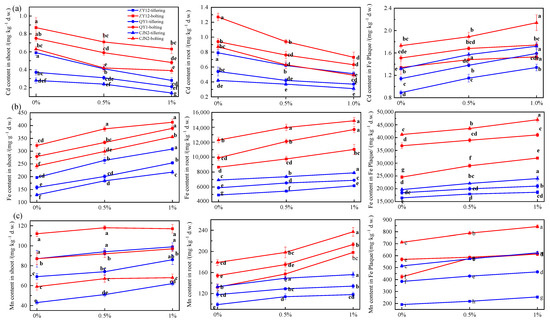
Figure 3.
Effect of red mud (RM) on metals’ concentrations in the shoots, roots, and Fe plaque. (a) cadmium (Cd) concentration in rice tissues; (b) iron (Fe) concentration in rice tissues; (c) manganese (Mn) concentration in rice tissues. Different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference among treatments (p < 0.05).
The cadmium (Cd), Fe, and Mn concentrations in the Fe plaque significantly increased at both growth stages with the increase in RM concentration (p < 0.05). Notably, RM contains certain amounts of Fe and Mn, which could react with the available Cd in the soil to form Fe/Mn oxides [8]. This interaction reduces the Cd extractability in the soil and Cd accumulation by rice, but increases the Cd, Fe, and Mn concentrations in the Fe plaque.
3.4. Effects of RM on Transportability of Rice Cultivars Differing in ROL Rate
The cadmium (Cd) transportability of the three rice cultivars was influenced by the growth stage and ROL rate (Figure 4). For example, the Cd transportability of ZY12 decreased with the increase in RM concentration at the tillering stage, but did not have significant changes at the bolting stage. At the same growth stage, the Cd transportability differed among the rice cultivars. For example, at the bolting stage, ZY12 showed an increase in Cd transportability in response to RM addition, whereas CJN2 showed a decrease. The addition of RM had a strong impact on the Cd transportability of rice. Compared with the Cd transportability of QY1 under the 0% RM treatment, that of QY1 increased by 8.06% under 0.5% RM treatment, but decreased by 5.96% under 1% RM treatment at the tillering stage. Overall, 1% RM addition with high ROL rate in rice cultivar CJN2 is the best strategy to inhibit the Cd transport from the roots to the shoots in rice, which indicated that the high-ROL trait conferred the ability to limit Cd transport from the roots to the shoots.
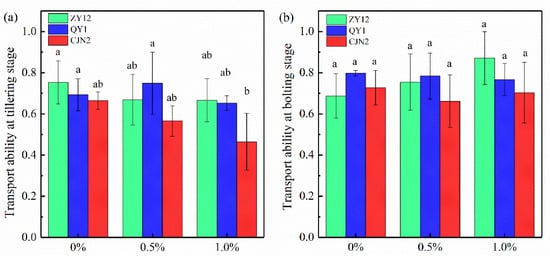
Figure 4.
Effect of red mud (RM) on cadmium (Cd) transportability in three rice cultivars. (a) the Cd transportability in rice at tillering stage, (b) the Cd transportability in rice at bolting stage.
Transportability = Cdshoot/Cdroot. Different lowercase letters within shoot or root biomass indicate a significant difference among treatments (p < 0.05).
3.5. Effects of RM on the Rhizosphere of Rice Cultivars Differing in ROL Rate
Wetland plants, including rice, can actively change the rhizosphere O2 concentration, Eh, and pH, which are crucial physicochemical properties for biogeochemical processes [34,35] (Figure 5). In the present study, the Eh values in S1 (154–279 mv) were distinctly higher than those in S4 (72–107 mv) (Figure 5a). In contrast, the pH in S1 was obviously lower than that in S4; for each cultivar at the tillering and bolting stages under the RM treatments, the differences ranged from 0.02 to 0.22 pH units (Figure 5b). These results reflected that the water management strategies in paddy fields are either continuous flooding or intermittent flooding. The flooding of paddy fields leads to anaerobic conditions [36], which may decrease the pH and increase Eh in the rhizosphere soil, leading to higher Eh and lower pH in S1. The pH in the soil zones of soil amended with RM at both developmental stages was distinctly higher than that of the 0% RM treatment, and increased with the elevation in RM concentration. The pH value was significantly increased by 0.39–0.53 units at two stages under RM treatments. Such an increase in soil pH is consistent with many previous reports in which RM was used as an amendment [15,37]. This response reflects the alkaline nature of RM, for which the pH is usually >10 [13]. In contrast to the pH, the Eh value decreased with RM addition. Positively charged ions (such as Ca2+ and Mg2+) are the main reason for the reduction in Eh [38].
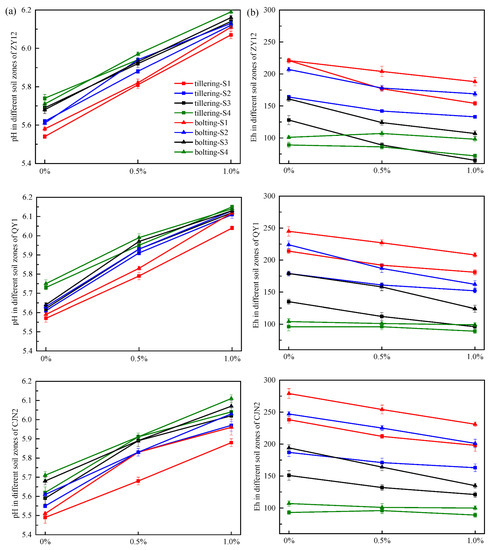
Figure 5.
Effect of red mud (RM) on pH and redox potential (Eh) in different soil zones. (a) the pH value in soil; (b) Eh (Redox potential) in soil.
The Fe3+ and Fe2+ concentrations differed significantly between soil zones S1 and S4, and the Fe3+ concentration in S1 was higher, whereas the Fe2+ concentration in S1 was lower than those in S4 for three rice cultivars at both stages under the RM treatments (Figure 6). The rhizosphere Fe3+ and Fe2+ concentrations significantly increased for each cultivar at the tillering and bolting stages under the RM treatments. The rice roots appeared reddish under treatment with 0.5% and 1% RM. These results indicated that RM addition leads to an increment in Fe2+ concentration, which facilitates Fe plaque formation on the root by oxidization of Fe2+ to Fe3+ [39]. The degree of Fe plaque formation on the roots of the rice cultivars was ranked as follows: CJN2 > QY1 > ZY12 under RM amendment. In addition, the increase in RM concentration was indicated to enhance Fe plaque formation of the cultivar with high ROL and root porosity.
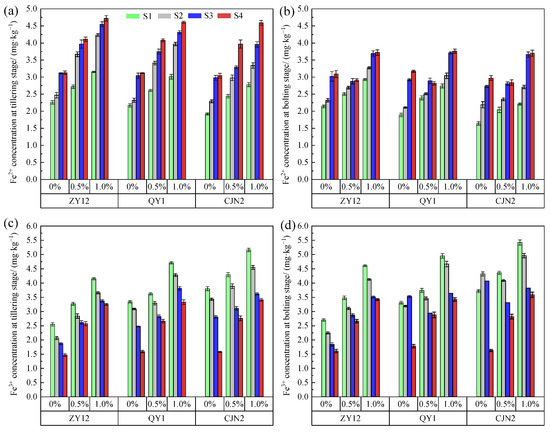
Figure 6.
Effect of red mud (RM) on Fe3+ and Fe2+ concentrations in different soil zones. (a) Fe2+ concentration in different zones at tillering stage; (b) Fe2+ concentration in different zones at bolting stage; (c) Fe3+ concentration in different zones at tillering stage; (d) Fe3+ concentration in different zones at bolting stage. S1, S2, S3, and S4 indicate different soil zones in rhizoboxes.
3.6. Fractions of Cd in Soil Zones
The concentrations of the five fractions of Cd in paddy soil in the present study are given in Figure 7. In general, plants tend to absorb F1 in soil, whereas Cd of the F3, F4, and F5 fractions are not easily absorbed.
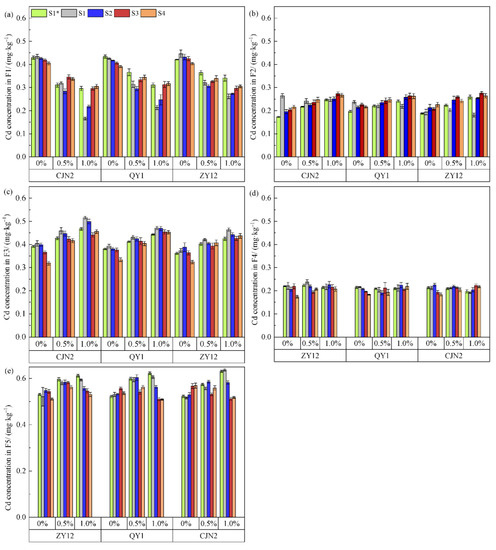
Figure 7.
Effect of red mud (RM) on concentrations of Cd fractions in soil zones of rhizoboxes. (a) Cd concentration in F1; (b) Cd concentration in F2; (c) Cd concentration in F3; (d) Cd concentration in F4; (e) Cd concentration in F5. S1* indicates different soil zones in rhizoboxes at tillering stage; S1, S2, S3, S4 indicates different soil zones in rhizoboxes at bolting stage.
The cadmium (Cd) fractions in paddy soil hosting rice cultivars with different ROL rates at the tillering and bolting stages were mainly of the forms F5, F3, and F1. However, addition of RM resulted in different changes in the Cd fractions in different soil zones. The concentration of F1 in S1 (0.426–0.446 mg·kg−1) at the bolting stage was significantly higher than that of S4 (0.391–0.404 mg·kg−1) under the 0% RM treatment. With RM addition, the concentration of F1 in the soil decreased significantly, and that of S4 (0.305–0.317 mg·kg−1) was significantly higher than that in S1 (0.166–0.262 mg·kg−1) under 1% RM treatment. In contrast to F1, the concentration of F5 at the bolting stage was highest in S4 (0.511–0.569 mg·kg−1) under 0% RM treatment, but was highest in S1 (0.594–0.637 mg·kg−1) under 1% RM treatment. In addition, compared with those under the 0% RM control, the concentrations of the different Cd fractions showed different trends with the increase in RM concentration. The F1 concentration under 0.5% and 1.0% RM of ZY12, QY1, and CJN2 at the tillering stage decreased by 13.54% and 19.02%, 15.67% and 28.34%, and 27.51% and 31.00%, respectively. The concentrations of F2, F3, and F5 all showed an upward trend at the tillering and bolting stages in response to 0.5% and 1.0% RM treatment. Under the 1% RM treatment, the concentration of F3 in the S1 zone in CJN2 paddy soil at the tillering and bolting stages was increased by 24.06% and 27.72%, respectively.
In response to RM application, a significant decrease in F1 concentration, but a significant increase in F3 and F5 concentrations, in the rhizosphere soils of the three rice cultivars was observed. These results suggested that F1 was transformed to a non-extractable form in the soil after RM addition. The present and previous studies indicate that RM addition effectively immobilizes the available Cd in soils [3]. Treatment with RM may affect Cd speciation/fractions and mobility through the specific sorption of metals by Fe and Al oxides [40]. Yao et al. [35] observed that Cd bioavailability was positively correlated with Eh, but negatively correlated with pH in paddy soil. After the addition of RM to paddy soil, OH− ions were released to the soil surface from the RM, which gradually alkalized the soil and reduced the availability of Cd [17]. In addition, RM contains large amounts of Al, Fe, and Mn, which can coprecipitate with Cd, further reducing the availability of soil Cd and converting exchangeable Cd to a stable form [41].
3.7. Mobility Factors of Cd in the Soil Zones
The MFs of Cd in the rhizosphere soil at the tillering stage and in different soil zones at the bolting stage were analyzed (Figure 8). The MFs of Cd in the rhizosphere soil were affected by RM addition and the ROL of the rice cultivars. For example, at both stages, the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils showed the lowest Cd MFs under 1% RM treatment, and the highest Cd MFs under 0% RM treatment. The MF of Cd in S1 under CJN2 with 1% RM treatment at the bolting stage was decreased by 33.01%. After the addition of RM, the soil pH and Fe, Mn, Fe2+, Fe3+, and Fe plaque contents increased, and Eh decreased, thereby reducing the amount of available Cd that could be directly absorbed by plants, leading to the reduction in soil Cd MFs. The rice cultivar with a high ROL exhibited a lower Cd MF. Previous studies have reported that ROL promotes Fe plaque formation [19], and a greater amount of available Cd is immobilized on Fe plaque, which further reduces the soil Cd MFs. In addition, the MFs were associated with the rice growth stage and soil zones. The MFs in S1 at the bolting stage were obviously lower, which indicated that higher ROL rates may release greater quantities of O2 and more strongly influence the rice rhizosphere zone, thereby causing a higher level of oxidation in rhizosphere soil amended with RM, which may decrease the bioavailability of Cd. The MFs of Cd in the rhizosphere zone were the lowest among the four soil zones for each rice cultivar, which revealed that rice changed the Cd MFs in the rhizosphere.
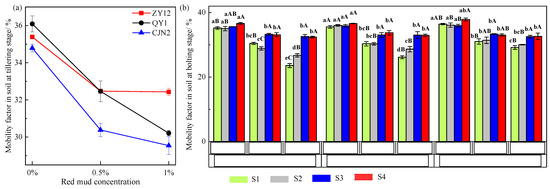
Figure 8.
Effect of red mud (RM) on the cadmium (Cd) mobility factor of rhizoboxes. (a) the mobility factor of Cd in soil at tillering stage; (b) the mobility factor of Cd in soil at bolting stage. Different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference between rice cultivars under the different RM treatments (p < 0.05). Different uppercase letters indicate a significant difference between soil zones (p < 0.05).
3.8. Correlations of Cd Concentration in the Shoots and Soil Physicochemical Variables
A significant negative correlation was observed between Feroot, Mnroot, CdFe plaque, FeFe plaque, MnFe plaque, pH, Fe3+, F2, F3, F5, and F1, whereas a significant positive correlation with Cdroot and F1 in the S1 zone was observed (Figure 9). These results for the selected samples indicated that the Cd concentration in the roots and F1 should be reduced to decrease the accumulation of Cd in the shoots. Significant negative correlations were observed between F1 and pH, Fe2+, and Fe3+, which accounted for the significant decrease in Cd content in F1 after RM addition. The pH of the soil was increased because RM is alkaline and contains large amounts of Fe and Al, which can prevent the conversion of other forms of Cd to exchangeable Cd and reduce Cd accumulation by rice. The concentration of Cdroot was significantly negatively correlated with Fe and Mn content in the roots and Fe plaque on the root surface. The Cd2+ may be separated out owing to the increase in Fe and Mn contents of Fe plaque on the root surface, preventing the transport of Cd in rice roots and reducing the accumulation of Cd by rice. The present and previous studies have demonstrated that RM is an effective amendment to reduce the exchangeable Cd content in paddy soil and Cd accumulation by rice [13,17]. These results indicate the potential of in situ remediation by RM addition, which can improve the soil’s physicochemical properties by increasing the pH and reduce the risk to human health of rice consumption.
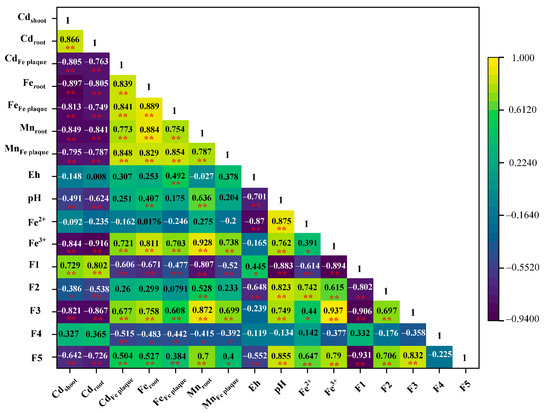
Figure 9.
Correlations of Cd concentration in the shoot of rice and soil physicochemical variables. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
4. Conclusions
The aim of this study was to explore the Cd fractions and mobility in the rhizosphere soil amended by RM addition (0%, 0.5%, and 1.0%) at two growth stages of three rice cultivars that differed in ROL rate. The results showed that RM addition significantly increased the growth of rice and Cd mobilization in the rhizosphere. In addition, RM reduced Cd transportability through promoting Fe plaque formation on the root surface and increasing the soil pH, especially for the cultivar with high ROL. Further studies are needed to optimize the combination of RM addition and rice cultivars with low Cd translocation and high ROL rates to evaluate the environmental risks of RM application.
Author Contributions
Methodology, J.Y.; formal analysis, X.M. and J.Y.; resources, J.Y.; data curation, J.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, X.M. and J.Y.; writing—review and editing, J.Y., G.Z. and T.X.; visualization, X.M.; supervision, J.Y.; funding acquisition, J.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Key R&D Program of China, grant number 2018YFC1802604; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number NSFC no. 41201312.
Acknowledgments
We thank Robert McKenzie for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Rinklebe, J.F.; Tack, M.G.; Ok, Y.S. A critical review on effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of cadmium in vegetables. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Yi, L.T.; Mao, X.Y.; Song, Q.; Korpelainen, H.; Liu, M. Nitrogen addition alleviated sexual differences in responses to cadmium toxicity by regulating the antioxidant system and root characteristics, and inhibiting Cd translocation in mulberry seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.X.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, J.M.; Wei, D.P.; Chen, S.B.; Guo, Q.J.; Ma, Y.B. Effects of rape straw and red mud on extractability and bioavailability of cadmium in a calcareous soil. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2015, 9, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.F.; Yang, T.; Chen, Y.H.; Hou, H.Q.; Liu, X.M.; Li, J.G.; Wei, L.G.; Li, J.H. Biochar-based fertilizer enhanced Cd immobilization and soil quality in soil-rice system. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 171, 106396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.M.; Gong, M.J.; Li, Y.S.; Chen, W.Z.; Yang, Y.A.; Qin, J.H.; Li, H.S. Low Cd-accumulating rice intercropping with Sesbania cannabina L. reduces grain Cd while promoting phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, R.G.; Tang, W.B.; Chen, Y.C.; Zhou, J.Q.; Ma, H.; Li, S.; Deng, H.B.; Han, L.; Chen, Y.B.; et al. Robust identification of low-Cd rice varieties by boosting the genotypic effect of grain Cd accumulation in combination with marker-assisted selection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Y.; Zhu, R.L.; Li, Z.H.; Han, C.L.; Li, W.Y.; Deng, Y.R. A combined remediation strategy of arsenic and cadmium in the paddy soil of polymetallic mining areas. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Mao, Q.M.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Peng, Q.H.; Luo, L. Effects of red mud based passivator on the transformation of Cd fraction in acidic Cd-polluted paddy soil and Cd absorption in rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Abbas, T.; Cai, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Di, H.; Tahir, M. Cd bioavailability and nitrogen cycling microbes interaction affected by mixed amendments under paddy-pak choi continued planting. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.C.; Tan, Y.Y.; Chen, D.; Song, W.; Cao, S. Optimization and stability of the bottom structure parameters of the deep sublevel stope with delayed backfilling. Minerals 2022, 12, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Guo, W. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Plastic Failure and Grouting Diffusion within Deep Roadway Surrounding Rock under Three-Dimensional Unequal Ground Stress and its Application. Minerals 2022, 12, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, J.; Gong, W.; Sun, Z. Model Test and Numerical Study on Surrounding Rock Deformation and Overburden Strata Movement Law of Gob-Side Entry Retaining via Roof Cutting. Minerals 2020, 10, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.G.; Li, M.; Jiang, J.; Millar, G.J.; Li, C.X.; Kong, X.F. Phosphogypsum stabilization of bauxite residue: Conversion of its alkaline characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 77, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Yang, J.X.; Wan, X.M.; Peng, Y.S.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.D.; Zeng, M. How red mud-induced enhancement of iron plaque formation reduces cadmium accumulation in rice with different radial oxygen loss. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.G.; Ke, W.S.; Zhu, F.; Ye, Y.Z.; Liu, Z.; Fan, J.R.; Hartley, W. Effect of phosphogypsum and poultry manure on aggregate-associated alkaline characteristics in bauxite residue. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 256, 109981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.M.; Lu, Z.Y.; Zhang, L.S.; Fan, H.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Li, J.W.; Lin, Y.L.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.H.; et al. Red mud based passivator reduced Cd accumulation in edible amaranth by influencing root organic matter metabolism and soil aggregate distribution. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.G.; Sun, W.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Long, S.X.; He, X.T.; Lin, Z.; Liang, J.L.; et al. Rhizobacteria communities reshaped by red mud based passivators is vital for reducing soil Cd accumulation in edible amaranth. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.Q.; Ye, Z.H.; Wong, M.H. The relationship of root porosity and radial oxygen loss on arsenic tolerance and uptake in rice grains and straw. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2550–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.Q.; Wong, M.H.; Yang, Y.; Dong, H.Y.; Qiu, R.L.; Ye, Z.H. The effects of radial oxygen loss on arsenic tolerance and uptake in rice and on its rhizosphere. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 165, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.X.; Ding, C.F.; Li, Y.S.; Zhang, T.L.; Wang, X.X. Selenium enhances iron plaque formation by elevating the radial oxygen loss of roots to reduce cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, B.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Naidu, R. Varietal variation and formation of iron plaques on cadmium accumulation in rice seedling. Sci. Adv. 2021, 5, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Leng, X.M.; Wang, M.X.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Dai, Q.H. Iron plaque formation on roots of different rice cultivars and the relation with lead uptake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanzyo, M.; Yaginuma, H.; Sasaki, K.; Ito, K.; Aikawa, Y.; Kanno, H.; Takahashi, T. Identification of vivianite formed on the roots of paddy rice frown in pots. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 56, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kludze, H.K.; DeLaune, R.D.; Patrick, W.H. Aerenchyma formation and methane and oxygen exchange in rice. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 1993, 51, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.M.; Kirk, G.J.D.; Mackenzie, A.F.; Neue, H.U. Root-induced iron oxidation and pH changes in the low land rice rhizosphere. New Phytol. 1994, 128, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.B.; Zhang, B.; Wang, G.J.; Jiang, W.C.; Jia, Y. Effects of different cultivation ways on soil physical capability in western semiarid area of Liaoning Province. J. Arid Land 2006, 20, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.; Zhu, F.; Kong, X.; Wu, C.; Huang, L.; Huang, N.; Hartley, W. A review of the characterization and revegetation of bauxite residues (red mud). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.F.; Liu, X.M. Applications of red mud as an environmental remediation material: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.Z.U.; Batool, Z.; Ayub, M.A.; Hussainia, K.M.; Murtaza, G.; Usmana, M.; Naeem, A.; Khalid, H.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S. Effect of acidified biochar on bioaccumulation of cadmium (Cd) and rice growth in contaminated soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.F.; Tian, L.Y.; Han, X.K. Red mud (RM)-Induced enhancement of iron plaque formation reduces arsenic and metal accumulation in two wetland plant species. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2016, 18, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Zou, Q.; Xue, S.G.; Pan, W.S.; Huang, L.; Hartley, W.; Mo, J.Y.; Wong, M.H. The effect of silicon on iron plaque formation and arsenic accumulation in rice genotypes with different radial oxygen loss (ROL). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.M.; Heal, K.V.; Friesl-Hanl, W. The use of red mud as an immobiliser for metal/metalloid-contaminated soil: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.X.; Guo, Q.J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.Y.; Ren, H.Y.; Zhang, H.Z.; Xu, R.X.; Wang, X.D.; Peters, M.; Zhu, G.X.; et al. Root-induced changes (pH, Eh, Fe2+ and speciation of Pb and Zn) in rhizosphere soils of four wetland plants with different ROL. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.B.; Lu, J.Q.; Li, X.H.; Qiu, Q.F.; Chen, J.; Yan, C.Q. Effect of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotype on yield: Evidence from recruiting spatially consistent rhizosphere microbiome. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 108395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.M.; Wang, S.Q.; Xie, S.T.; Li, G.; Sun, G.X. Optimal soil Eh, pH for simultaneous decrease of bioavailable Cd, As in co-contaminated paddy soil under water management strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.L.; Jia, Z.X.; Guo, J.J.; Li, T.L.; Sun, D.S.; Meng, H.S.; Yu, G.H.; He, X.H.; Ran, W.; Zhang, S.S.; et al. Ten-year long-term organic fertilization enhances carbon sequestration and calcium-mediated stabilization of aggregate-associated organic carbon in a reclaimed Cambisol. Geoderma 2019, 355, 113880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husson, O.; Brunet, A.; Babre, D.; Charpentier, H.; Durand, M.; Sarthou, J.P. Conservation Agriculture systems alter the electrical characteristics (Eh, pH and EC) of four soil types in France. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 176, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.Q.; Yang, X.J.; Shen, H. Root iron plaque alleviates cadmium toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombi, E.; Hamon, R.E.; McGrath, S.P.; McLaughlin, M.J. Lability of Cd, Cu, and Zn in polluted soils treated with lime, beringite, and red mud and identification of a non-labile colloidal fraction of metals using isotopic techniques. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lei, C.; Khan, E.; Chen, S.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Lin, D.; Feng, Y.; Li, X. Nanoscale zero-valent iron for metal/metalloid removal from model hydraulic fracturing wastewater. Chemosphere 2017, 176, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).