Involvement of Soil Microorganisms in C, N and P Transformations and Phytotoxicity in Soil from Post-Industrial Areas Treated with Chemical Industry Waste
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
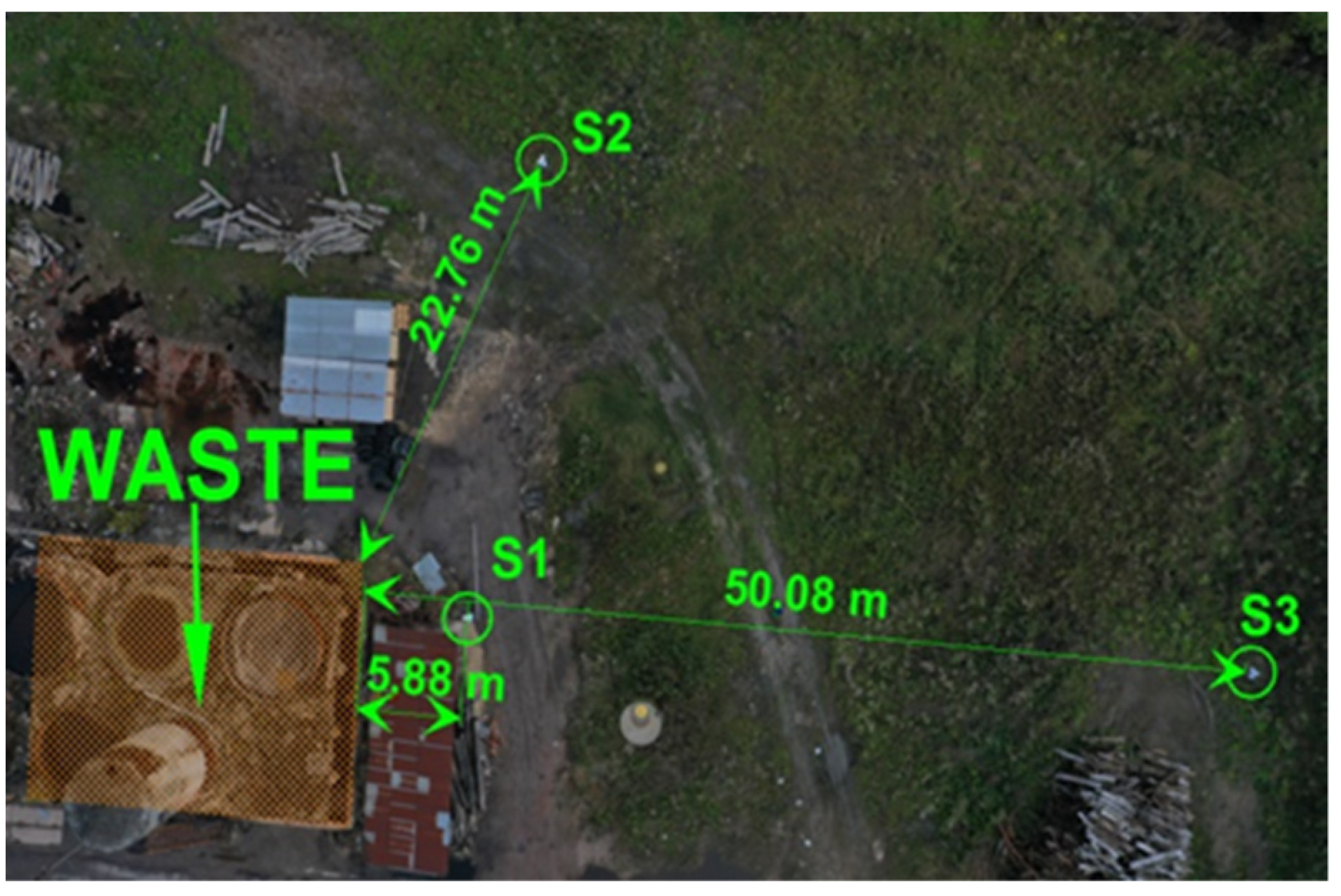
2.1. Description of the Research Area
2.2. Sampling Description
2.3. Characteristics of Soil Chemical Properties
2.4. Microbiological Analyses
2.5. Biochemical Analyses
2.6. Enzymatic Analyses
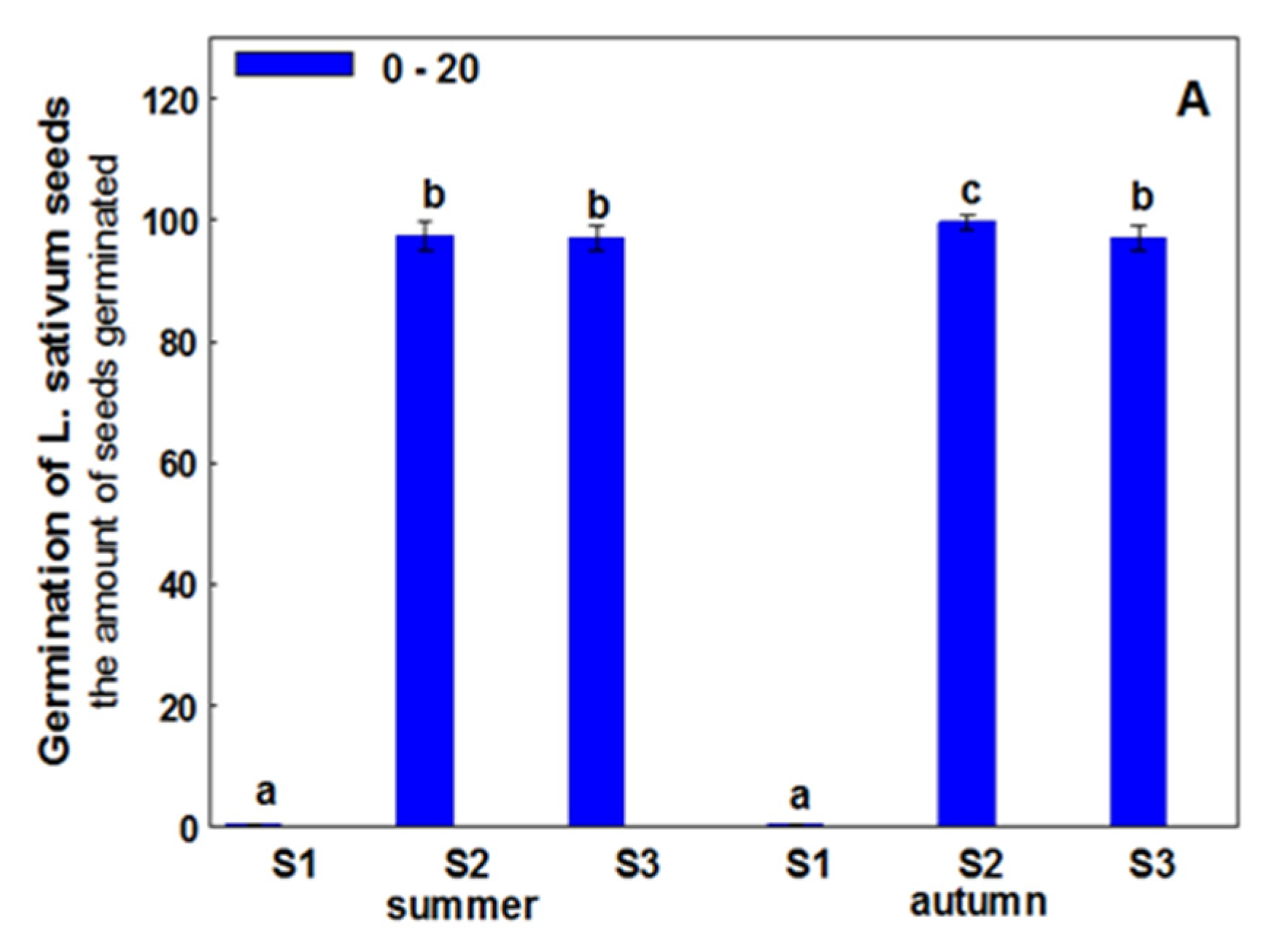
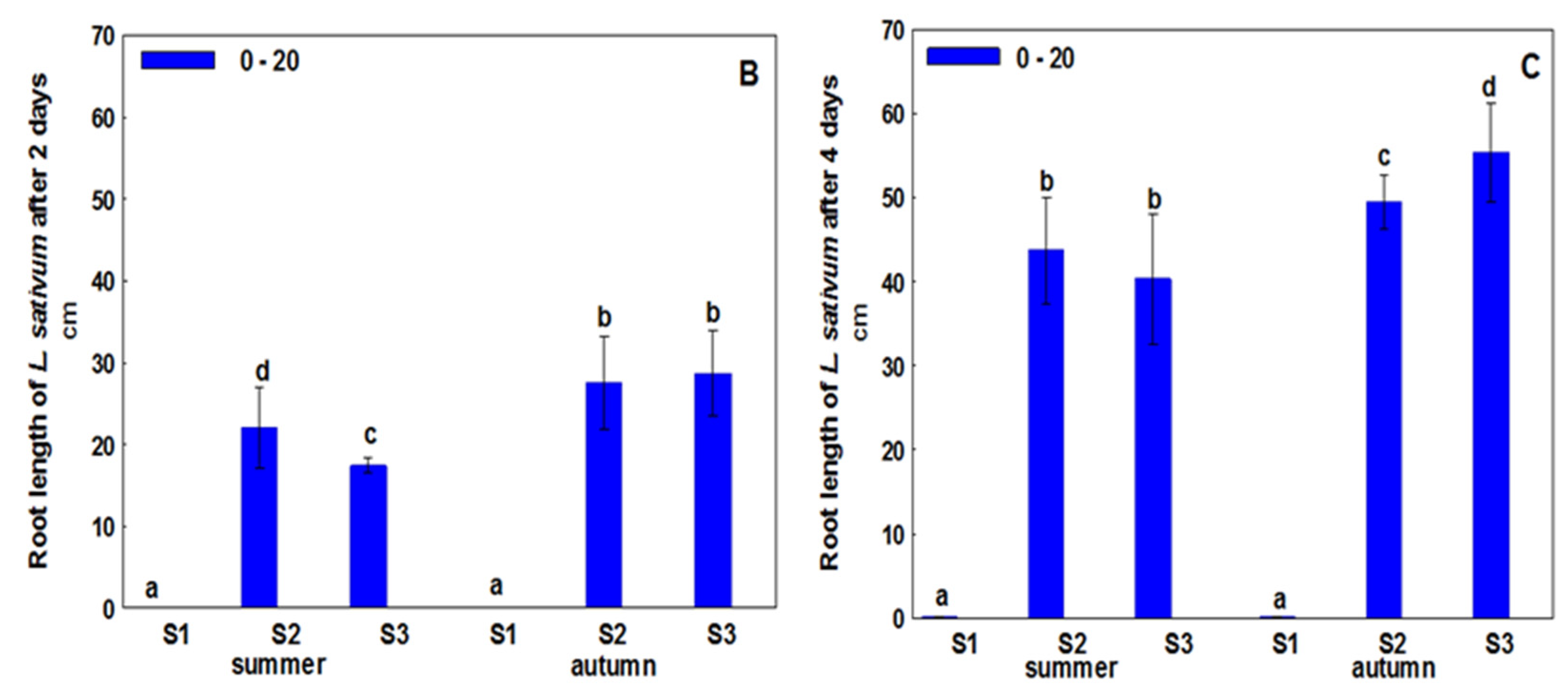
2.7. Soil Phytotoxicity
2.8. Statistical Analysis
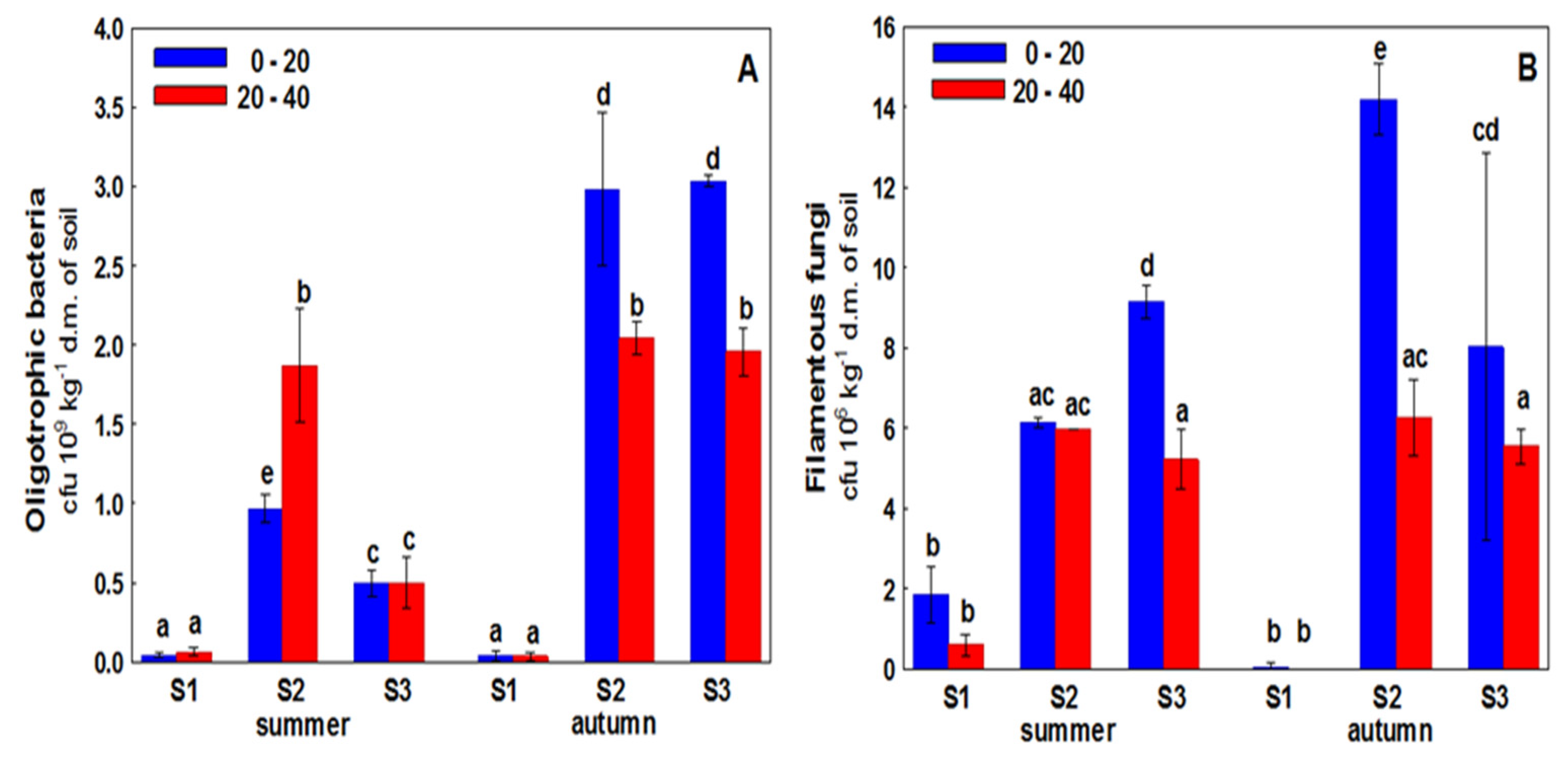
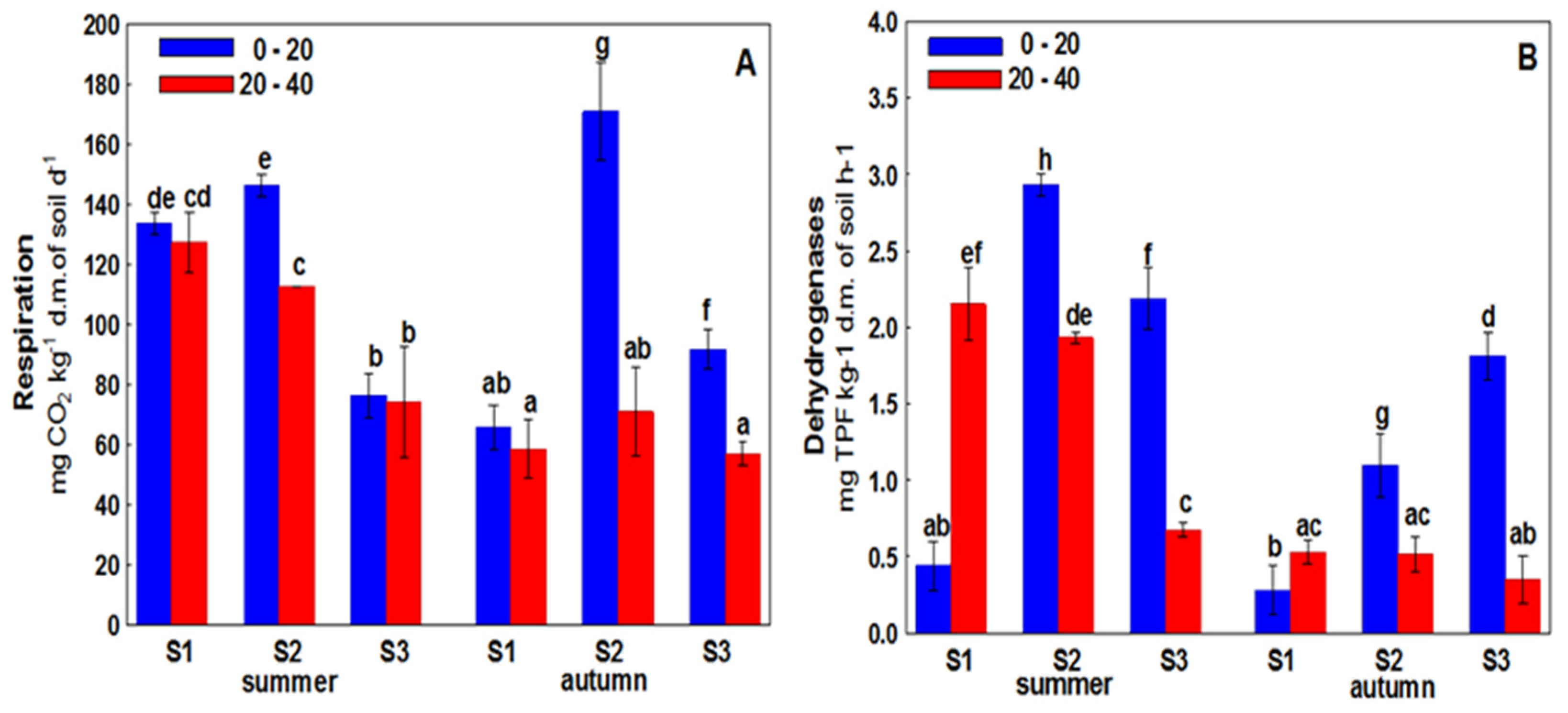
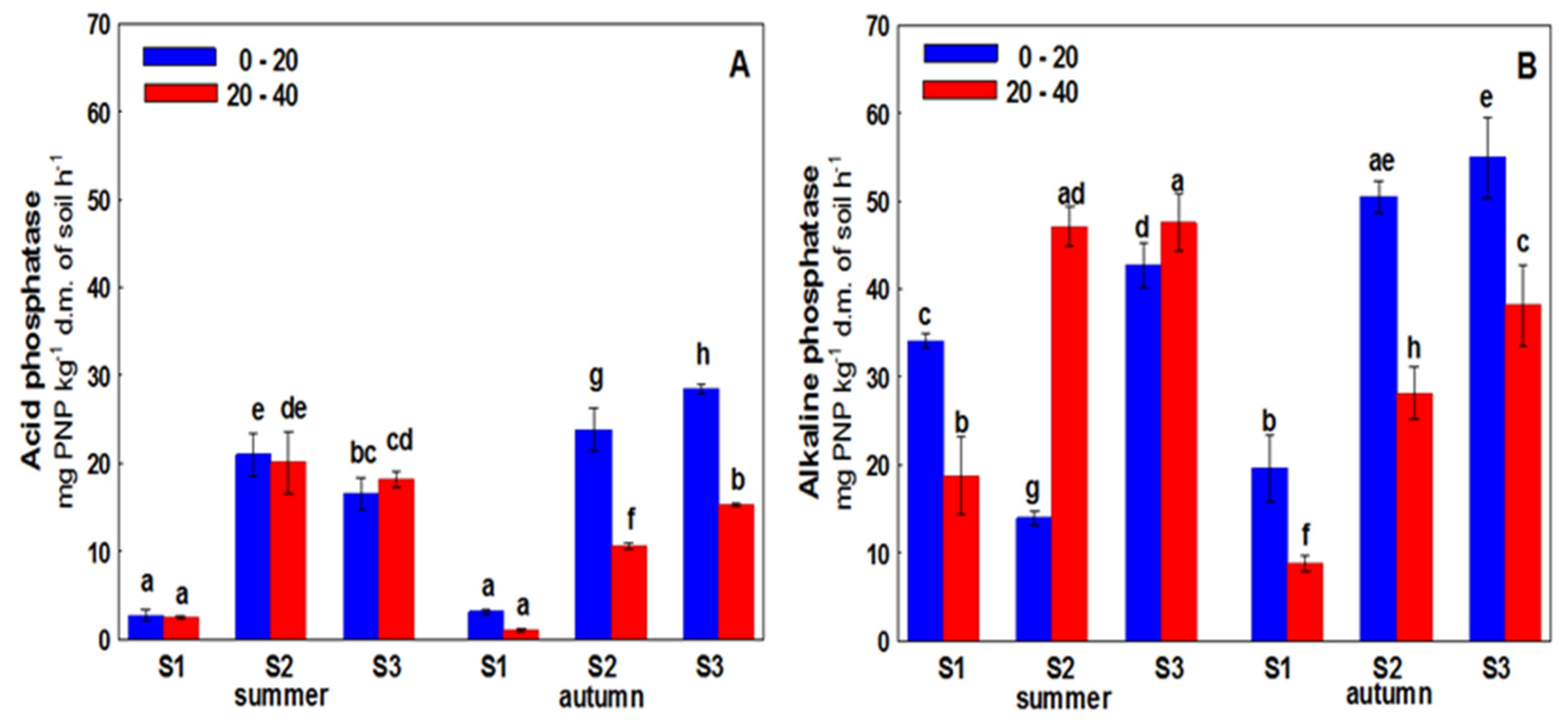
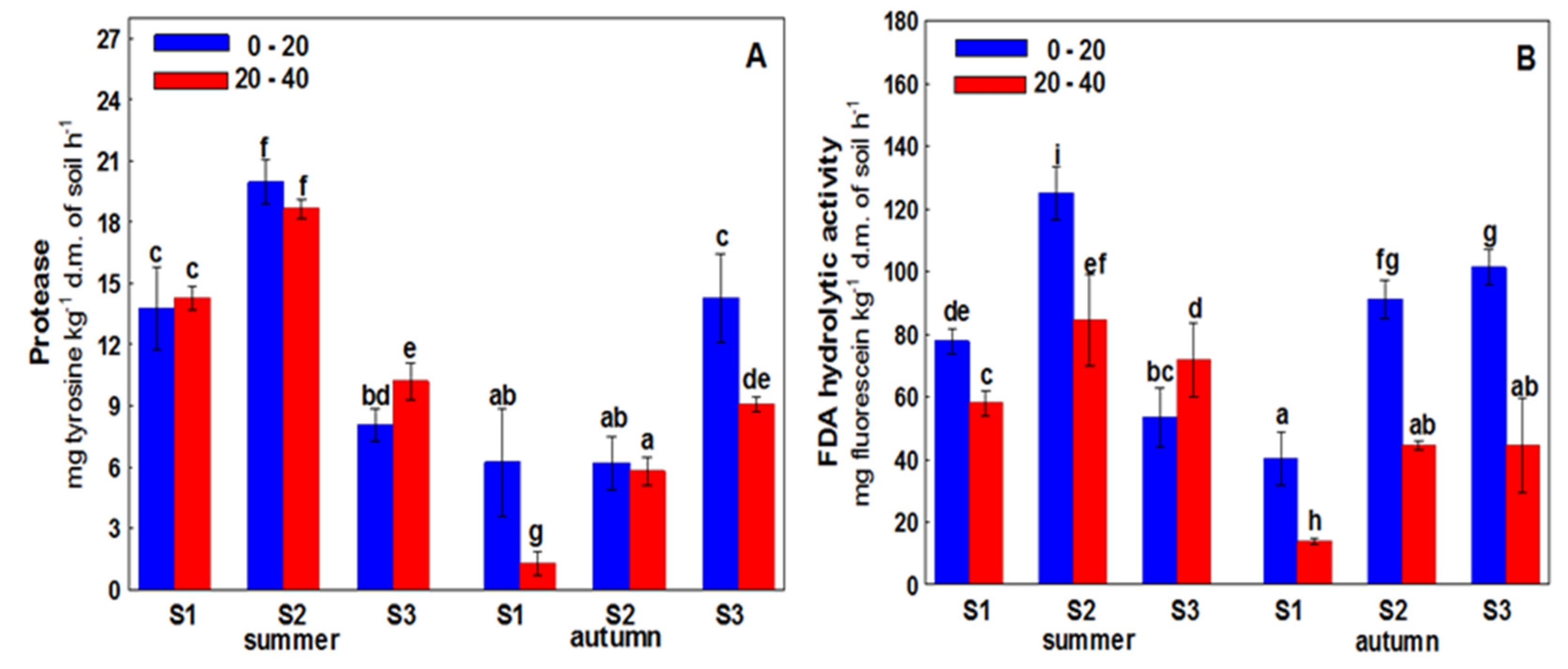
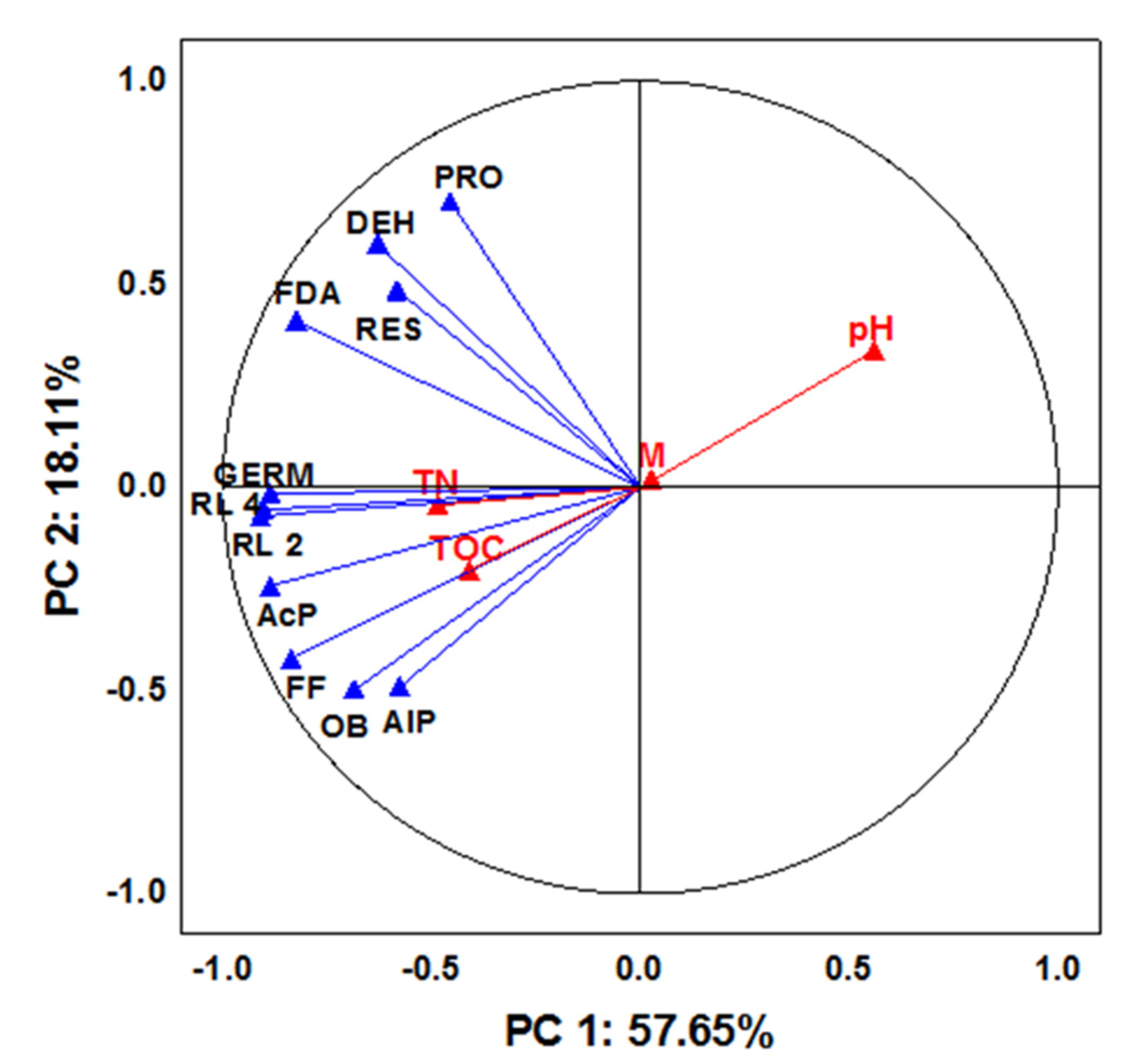
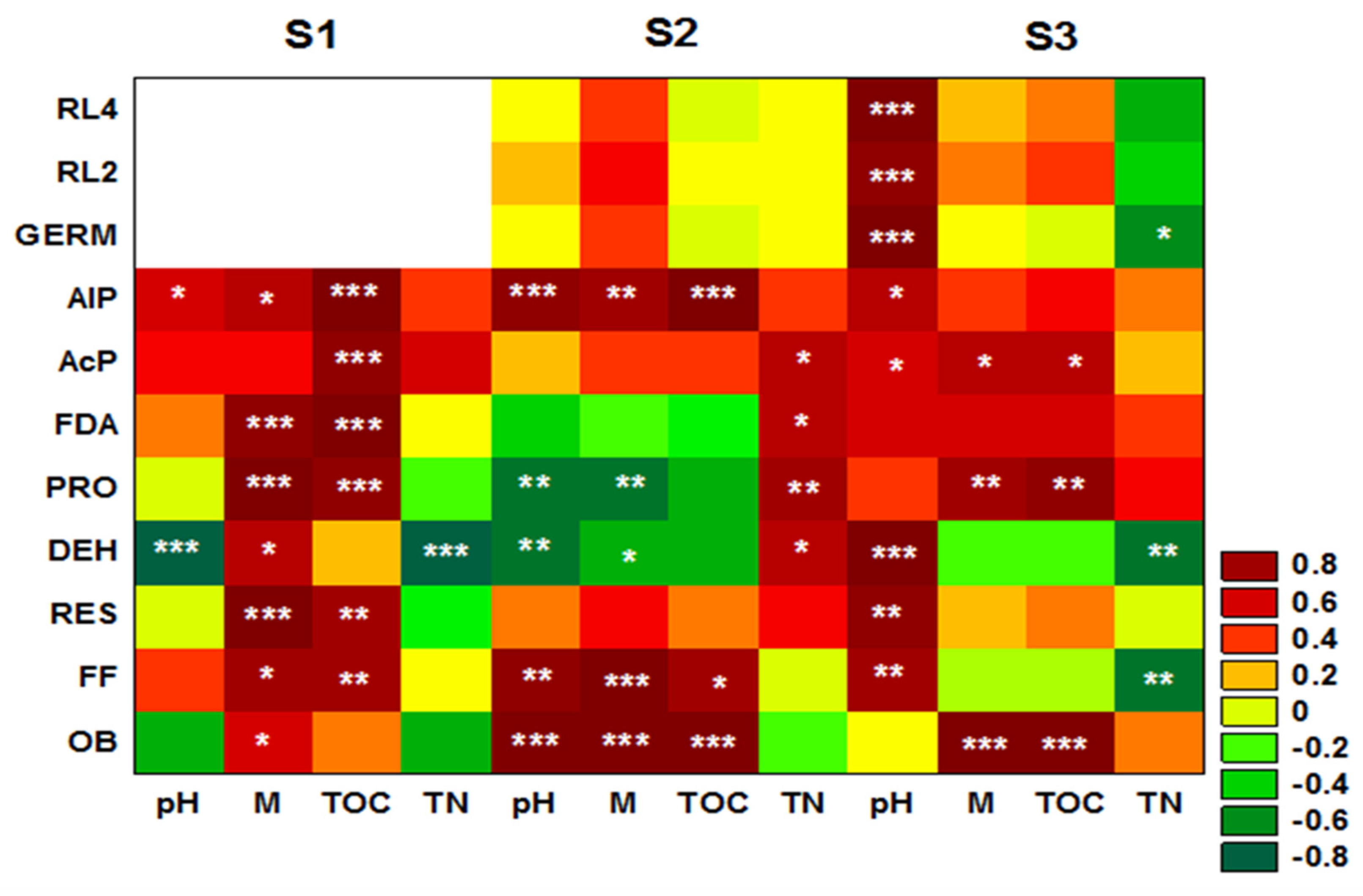
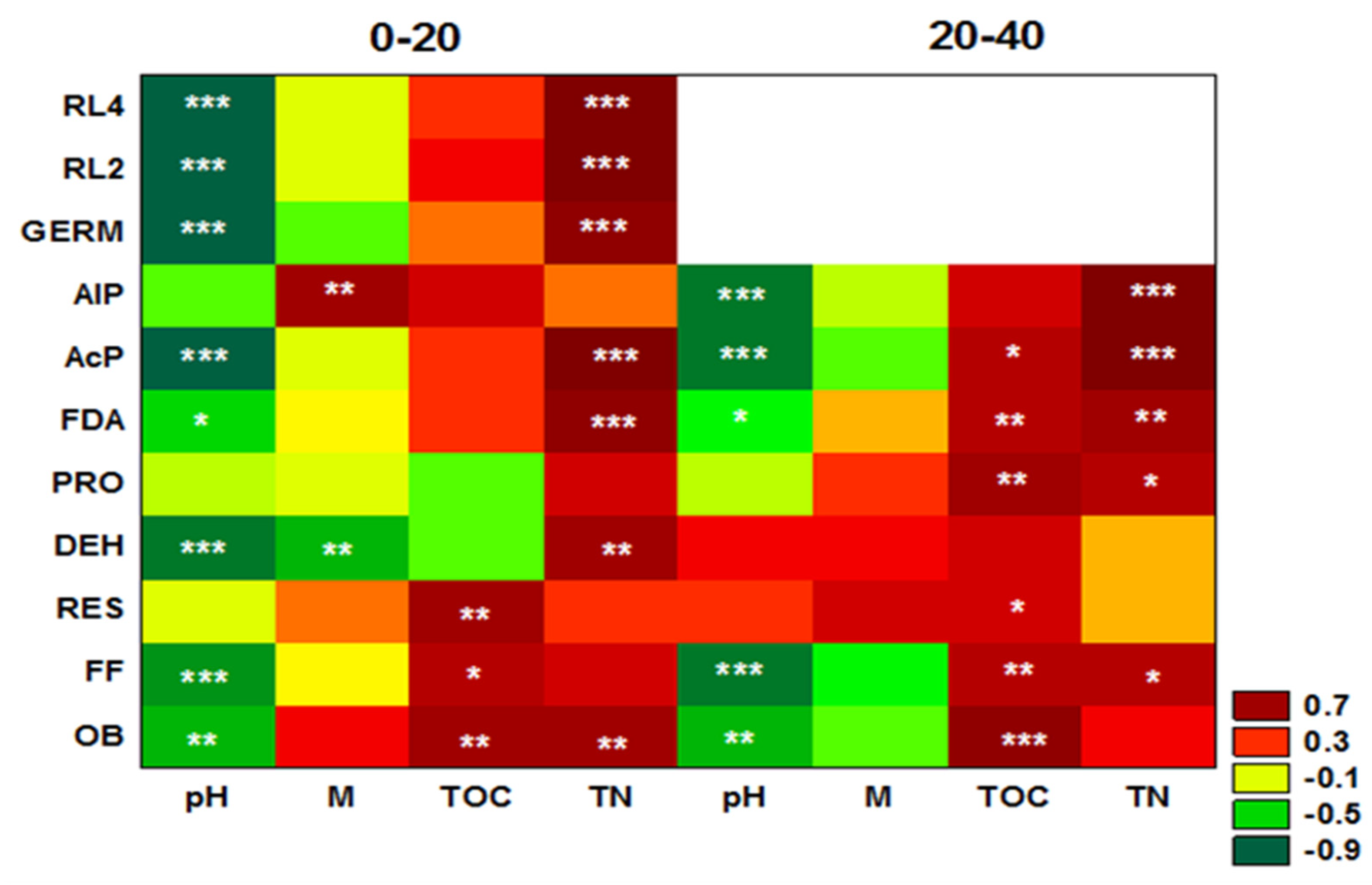
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.; Creamer, R.E.; De Deyn, G.; de Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mäder, P.; et al. Soil quality—A critical review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Lugato, E.; Yang, J.E.; Alewell, C.; Wuepper, D.; Montanarella, L.; Ballabio, C. Land use and climate change impacts on global soil erosion by water (2015–2070). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21994–22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Gunina, A.; Zamanian, K.; Tian, J.; Luo, Y.; Xu, X.; Yudina, A.; Aponte, H.; Alharbi, H.; Ovsepyan, L.; et al. New approaches for evaluation of soil health, sensitivity and resistance to degradation. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Zamanian, K. Reviews and syntheses: Agropedogenesis–humankind as the sixth soil-forming factor and attractors of agricultural soil degradation. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 4783–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunes, F.C.; de Jesus Alves, L.; de Carvalho, C.C.N.; Gross, E.; de Marchi Soares, T.; Prasad, M.N.V. Soil as a complex ecological system for meeting food and nutritional security. In Climate Change and Soil Interactions; Prasad, M.N.V., Pietrzykowski, M., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 229–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; ITPS. Status of the World’s Soil Resources (SWSR)—Main Report. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils, Rome, Italy. 2015. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i5199e.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- IPBES. The IPBES assessment report on land degradation and restoration. In Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services; Montanarella, L., Scholes, R., Brainich, A., Eds.; Zenodo: Bonn, Germany, 2018; p. 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, T. Soil Degradation, Land Scarcity and Food Security: Reviewing a Complex Challenge. Sustainability 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keesstra, S.; Mol, G.; De Leeuw, J.; Okx, J.; Molenaar, C.; De Cleen, M.; Visser, S. Soil-Related Sustainable Development Goals: Four Concepts to Make Land Degradation Neutrality and Restoration Work. Land 2018, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saljnikov, E.; Lavrishchev, A.; Römbke, J.; Rinklebe, J.; Scherber, C.; Wilke, B.-M.; Tóth, T.; Blum, W.E.H.; Behrendt, U.; Eulenstein, F.; et al. Understanding and Monitoring Chemical and Biological Soil Degradation. In Advances in Understanding Soil Degradation. Innovations in Landscape Research; Saljnikov, E., Mueller, L., Lavrishchev, A., Eulenstein, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 75–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, N.T. Chemical soil degradation as a result of contamination: A review. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2015, 6, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neina, D. The role of soil pH in plant nutrition and soil remediation. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2019, 2019, 5794869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Wei, J.; Yu, H. The effect of soil pH on plant growth, leaf chlorophyll fluorescence and mineral element content of two blueberries. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1180, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.S.; Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S.; Destouni, G.; Ghajarnia, N.; Kalantari, Z. Soil degradation in the European Mediterranean region: Processes, status and consequences. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, P.; Rodrigues, D.; Mourinha, C.; Palma, P.; de Varennes, A.; Cruz, N.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Rodrigues, S. Use of wastes from the pulp and paper industry for the remediation of soils degraded by mining activities: Chemical, biochemical and ecotoxicological effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gałązka, A.; Marzec-Grządziel, A.; Grządziel, J.; Varsadiya, M.; Pawlik, Ł. Fungal genetic biodiversity and metabolic activity as an indicator of potential biological weathering and soil formation—Case study of towards a better understanding of Earth system dynamics. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joniec, J.; Oleszczuk, P.; Jezierska-Tys, S.; Kwiatkowska, E. Effect of reclamation treatments on microbial activity and phytotoxicity of soil degraded by the sulphur mining industry. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joniec, J.; Żukowska, G.; Bik-Małodzińska, M.; Kwiatkowska, E.; Rojek, K. Reaction of Microorganisms to Long-Term Waste Reclamation of Soil Degraded by the Sulfur Mining Industry. Minerals 2021, 11, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Zaborowska, M.; Kucharski, J. Evaluation of the Usefulness of Sorbents in the Remediation of Soil Exposed to the Pressure of Cadmium and Cobalt. Materials 2022, 15, 5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananyeva, N.D.; Ivashchenko, K.V.; Sushko, S.V. Microbial Indicators of Urban Soils and Their Role in the Assessment of Ecosystem Services: A Review. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2021, 54, 1517–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencel, J.; Mocek-Płóciniak, A.; Kryszak, A. Soil Microbial Community and Enzymatic Activity of Grasslands under Different Use Practices: A Review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, D.; McClure, R.; Jansson, J. Trends in Microbial Community Composition and Function by Soil Depth. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, S.M.; Buckley, H.L.; Case, B.S.; Curran-Cournane, F.; Taylor, M.; Lear, G. Using soil bacterial communities to predict physico-chemical variables and soil quality. Microbiome 2020, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, T.; Chu, H. Threshold effects of soil pH on microbial co-occurrence structure in acidic and alkaline arable lands. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Guo, D.; Zhao, J.; Yan, L.; Feng, G.; Gao, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhao, L. Soil pH is the primary factor driving the distribution and function of microorganisms in farmland soils in northeastern China. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majewska, M.; Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J. Mobilization of cadmium from Festuca ovina roots and its simultaneous immobilization by soil in a root-soil-extractant system (in vitro test). Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2017, 19, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joniec, J.; Furczak, J.; Kwiatkowska, E. Application of biological indicators for estimation of remediation of soil degraded by sulphur industry. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2015, 22, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gyawali, A.J.; Lester, B.J.; Stewart, R.D. Talking SMAAC: A New Tool to Measure Soil Respiration and Microbial Activity. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y. Sources of CO2 efflux from soil and review of partitioning methods. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 425–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joniec, J. Enzymatic activity as an indicator of regeneration processes in degraded soil reclaimed with various types of waste. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.-G.; Kim, S.-O. Use of Soil Enzymes as Indicators for Contaminated Soil Monitoring and Sustainable Management. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtak, K.; Gałązka, A. Enzymatic activity as a popular parameter used to determine the quality of the soil environment. Pol. J. Agron. 2019, 37, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patle, P.N.; Navnage, N.P.; Barange, P.K. Fluorescein diacetate (FDA): Measure of total microbial activity and as indicator of soil quality. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 2103–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.M.; Beetz, N.; Günther, P.M.; Möller, F.; Cao, J. Extremophiles in Soil Communities of Former Copper Mining Sites of the East Harz Region (Germany) Reflected by Re-Analyzed 16S rRNA Data. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-W.; Choi, Y.J. Extremophilic Microorganisms for the Treatment of Toxic Pollutants in the Environment. Molecules 2020, 25, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochhar, N.; Kavya, I.K.; Shrivastava, S.; Ghosh, A.; Rawat, V.S.; Sodhi, K.K.; Kumar, M. Perspectives on the microorganism of extreme environments and their applications. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foght, J.; Aislabie, J. Enumeration of Soil Microorganisms. In Monitoring and Assessing Soil Bioremediation. Soil Biology Part 5; Margesin, R., Schinner, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 261–280. ISBN 978-3-540-25346-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.P. Use of acid rose bengal and streptomycin in the plate method for estimating soil fungi. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühling, A.; Tyler, G. Heavy metal pollutions and decomposition of Spruce Needle litter. Oikos 1973, 24, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalmann, A. Zur Methodik der Bestimmung der dehydrogenaseactivität im boden mittels triphenyltetrazoliumchlorid (TTC). Landwirtsch Forsch. 1968, 21, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Ladd, J.N.; Butler, J.A.H. Short-term assays of soil proteolytic enzyme activities using proteins and dipeptide derivatives as substrates. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnurer, J.; Rosswall, T. Fluorescein Diacetate Hydrolysis as a measure of total microbial acticity in soil and litter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, A.M.; Khan, I.M.; Shah, T.I.; Bangroo, S.A.; Kirmani, N.A.; Nazir, S.; Malik, A.R.; Aezum, A.M.; Mir, Y.H.; Hilal, A.; et al. Soil Microbiome: A Treasure Trove for Soil Health Sustainability under Changing Climate. Land 2022, 11, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Reich, P.B.; Banerjee, S.; van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Ishii, S.; Jia, X.; Shao, M.; et al. Erosion reduces soil microbial diversity, network complexity and multifunctionality. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2474–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosrati, K.; Collins, A.L. A soil quality index for evaluation of degradation under land use and soil erosion categories in a small mountainous catchment, Iran. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 2577–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, I.; Lv, J.Z.; Wang, J.; Ahmad, S.; Farooq, S.; Ali, S.; Zhou, X.B. Regulation of Soil Microbial Community Structure and Biomass to Mitigate Soil Greenhouse Gas Emission. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 868862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Wang, S.; Du, L.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Effects of organic fertilization on functional microbial communities associated with greenhouse gas emissions in paddy soils. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Tarin, M.W.K.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Rong, J.; Cai, X.; Chen, L.; Shi, C.; Zheng, Y. Patterns of soil microorganisms and enzymatic activities of various forest types in coastal sandy land. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 28, e01625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kim, S.; Han, S.H.; Chang, H.; Du, D.; Son, Y. Precipitation affects soil microbial and extracellular enzymatic responses to warming. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanaszek-Tomal, E. Environmental Factors Causing the Development of Microorganisms on the Surfaces of National Cultural Monuments Made of Mineral Building Materials—Review. Coatings 2020, 10, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond-Lamberty, B.; Thomson, A. Temperature-associated increases in the global soil respiration record. Nature 2010, 464, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Quéré, C.; Andrew, R.M.; Friedlingstein, P.; Sitch, S.; Hauck, J.; Pongratz, J.; Pickers, P.A.; Korsbakken, J.I.; Peters, G.P.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. Global carbon budget 2013. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2013, 6, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grzyb, A.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Niewiadomska, A. Environmental Factors Affecting the Mineralization of Crop Residues. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowska, E.; Joniec, J. Effects of Agricultural Management of Spent Mushroom Waste on Phytotoxicity and Microbiological Transformations of C, P, and S in Soil and Their Consequences for the Greenhouse Effect. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zhu, X.; Chang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, B.; Luo, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Rui, Y.; Cui, X. Effects of soil temperature and moisture on soil respiration on the Tibetan plateau. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, F.; Jia, Q.; Wu, X.; Wang, E.; Hong, J. Soil Respiration Characteristics and Influencing Factors for Apple Orchards in Different Regions on the Loess Plateau of Shaanxi Province. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quemada, M.; Menacho, E. Soil respiration 1 year after sewage sludge application. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 33, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.B.; Liebig, M.A.; Hanson, J.D. Soil carbon dioxide fluxes in northern semiarid grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.N.; Dalal, R.C.; Greene, R.S. Salinity and sodicity effects on respiration and microbial biomass of soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2008, 44, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Quinones, V.; Stockdale, E.A.; Banning, N.C.; Hoyle, F.C.; Sawada, Y.; Wherrett, A.D.; Jones, D.L.; Murphy, D.V. Soil microbial biomass—Interpretation and consideration for soil monitoring. Soil Res. 2011, 49, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil Erosion and Gaseous Emissions. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M. Response of soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activities to long-term reclamation of coastal saline soil, Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueis, T.; Turrión, M.B.; Bravo, F.; Pando, V.; Muscolo, A. Factors determining enzyme activities in soils under Pinus halepensis and Pinus sylvestris plantations in Spain: A basis for establishing sustainable forest management strategies. Ann. For. Sci. 2018, 75, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wojewódzki, P.; Lemanowicz, J.; Debska, B.; Haddad, S.A. Soil Enzyme Activity Response under the Amendment of Different Types of Biochar. Agronomy 2022, 12, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, W.A.; Cheng, L.; Wang, P. Soil acid and alkaline phosphatase activity as pH adjustment indicators. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavi, M.S.; Marschnera, P. Impact of Salinity on Respiration and Organic Matter Dynamics in Soils is More Closely Related to Osmotic Potential than to Electrical Conductivity. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Berg, B.; Gu, W.; Wang, Z.; Sun, T. Effects of different forms of nitrogen addition on microbial extracellular enzyme activity in temperate grassland soil. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gan, B.; Li, Q.; Xiao, W.; Song, X. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Addition on Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activity and Stoichiometry in Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) Forests. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 834184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasen, B.; de Moura Lisbôa, R. Ecotoxicological Tests as a Tool to Assess the Quality of the Soil. In Soil Contamination and Alternatives for Sustainable Development; Vázquez-Luna, D., Cuevas-Díaz, M.D.C., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godlewska, P.; Jośko, I.; Oleszczuk, P. Ecotoxicity of sewage sludge- or sewage sludge/willow-derived biochar-amended soil. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, M.; Rajakaruna, N.; Rizwan, M.; Madawala, H.M.S.P.; Sik Ok, Y.; Vithanage, M. Heavy metal-induced oxidative stress on seed germination and seedling development: A critical review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1813–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joniec, J.; Kwiatkowska, E.; Kwiatkowski, C.A. Assessment of the Effects of Soil Fertilization with Spent Mushroom Substrate in the Context of Microbial Nitrogen Transformations and the Potential Risk of Exacerbating the Greenhouse Effect. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| pH 1 mol KCl | Ca mg kg−1 | K mg kg−1 | Na mg kg−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| waste | 14 | 37.6 | 328 | 87,000 |
| Sampling Location | Depth cm | pH 1 mol KCl | M % | TOC g kg−1 | TN g kg−1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s | a | s | a | s | a | s | a | ||
| S1 | 0–20 | 9.6 | 9.5 | 10.98 | 6.59 | 13.03 | 11.60 | 0.30 | 0.40 |
| 20–40 | 8.9 | 9.2 | 11.96 | 5.36 | 11.90 | 9.00 | 0.10 | 0.20 | |
| S2 | 0–20 | 7.9 | 8.1 | 3.39 | 8.96 | 10.69 | 21.00 | 0.60 | 0.50 |
| 20–40 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 4.73 | 5.16 | 18.21 | 15.10 | 0.90 | 0.10 | |
| S3 | 0–20 | 7.9 | 7.9 | 5.25 | 9.77 | 8.69 | 13.00 | 0.40 | 0.60 |
| 20–40 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 6.44 | 8.55 | 10.11 | 11.60 | 0.70 | 0.60 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwiatkowska, E.; Joniec, J.; Kwiatkowski, C.A. Involvement of Soil Microorganisms in C, N and P Transformations and Phytotoxicity in Soil from Post-Industrial Areas Treated with Chemical Industry Waste. Minerals 2023, 13, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010012
Kwiatkowska E, Joniec J, Kwiatkowski CA. Involvement of Soil Microorganisms in C, N and P Transformations and Phytotoxicity in Soil from Post-Industrial Areas Treated with Chemical Industry Waste. Minerals. 2023; 13(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwiatkowska, Edyta, Jolanta Joniec, and Cezary A. Kwiatkowski. 2023. "Involvement of Soil Microorganisms in C, N and P Transformations and Phytotoxicity in Soil from Post-Industrial Areas Treated with Chemical Industry Waste" Minerals 13, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010012
APA StyleKwiatkowska, E., Joniec, J., & Kwiatkowski, C. A. (2023). Involvement of Soil Microorganisms in C, N and P Transformations and Phytotoxicity in Soil from Post-Industrial Areas Treated with Chemical Industry Waste. Minerals, 13(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13010012








