Metal Exchangeability in the REE-Enriched Biogenic Mn Oxide Birnessite from Ytterby, Sweden
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
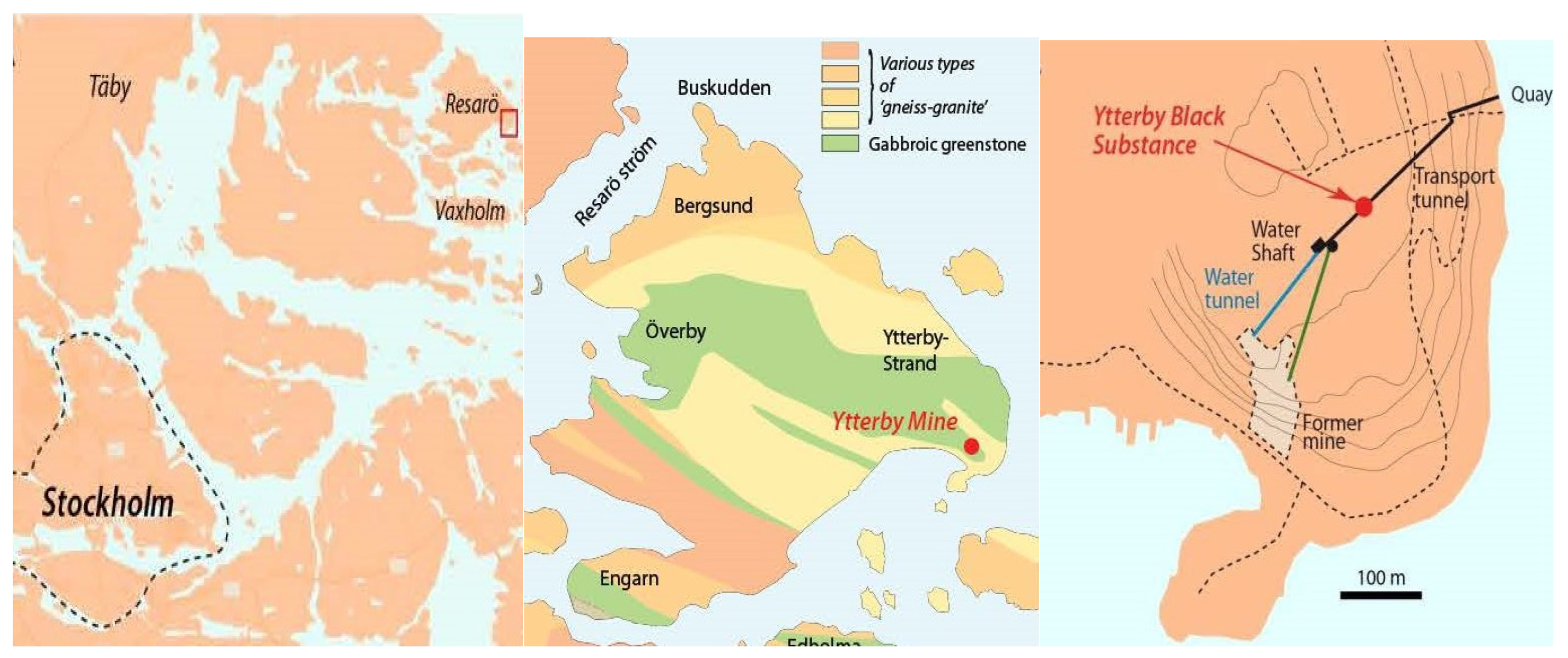
2.1. Sampling of YBS and Fracture Water
2.2. Characterization and Analysis of YBS
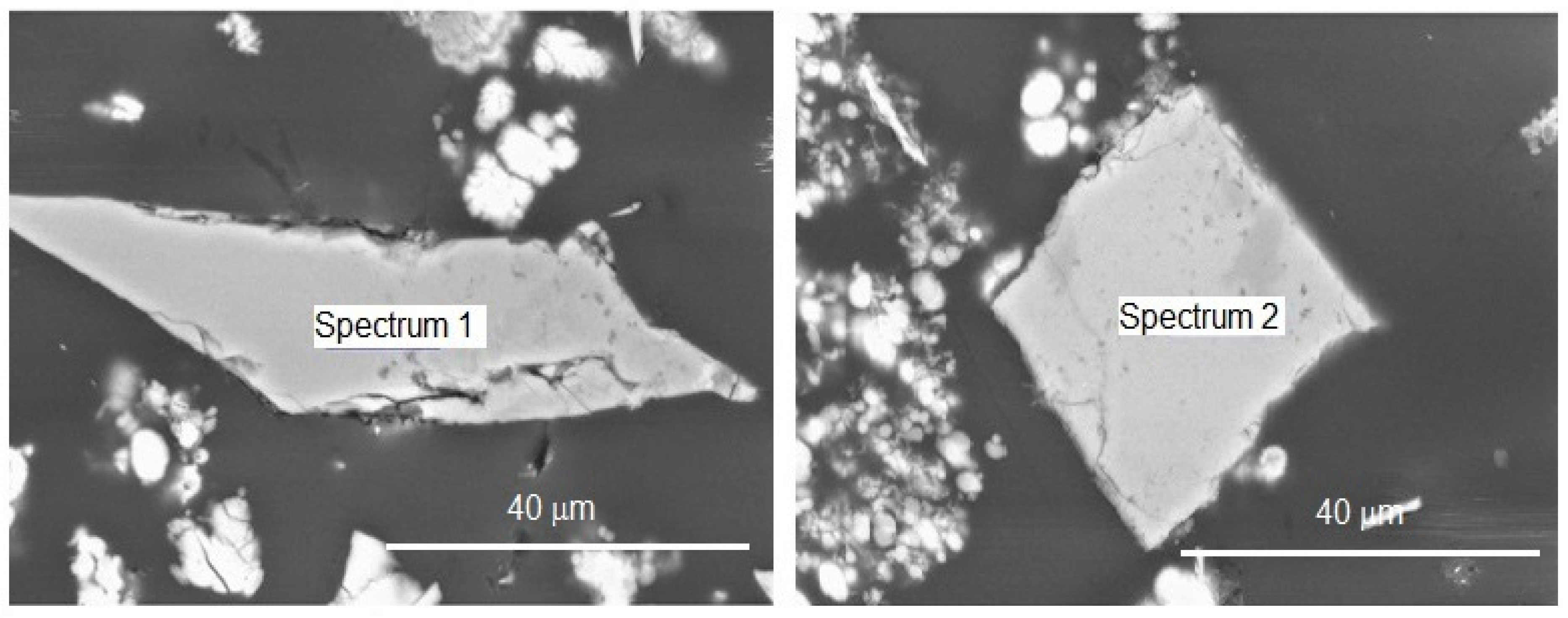
2.2.1. Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy (ESEM-EDS)
2.2.2. Sequential Washing
- C1 Organics, dichloromethane/methanol (CH2Cl2/CH3OH) 1:1; 2 times
- C2 Exchangeable ions, 0.11 M acetic acid (CH3COOH, HAc), pH 4.2
- C3 Suspended colloids, deionized water (18.2 MΩ); 3 times
2.2.3. Element Exchange
2.2.4. X-ray Diffractometry
2.2.5. IR Spectroscopy
2.2.6. Element Analysis
2.3. Analysis of Water
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy (ESEM-EDS)
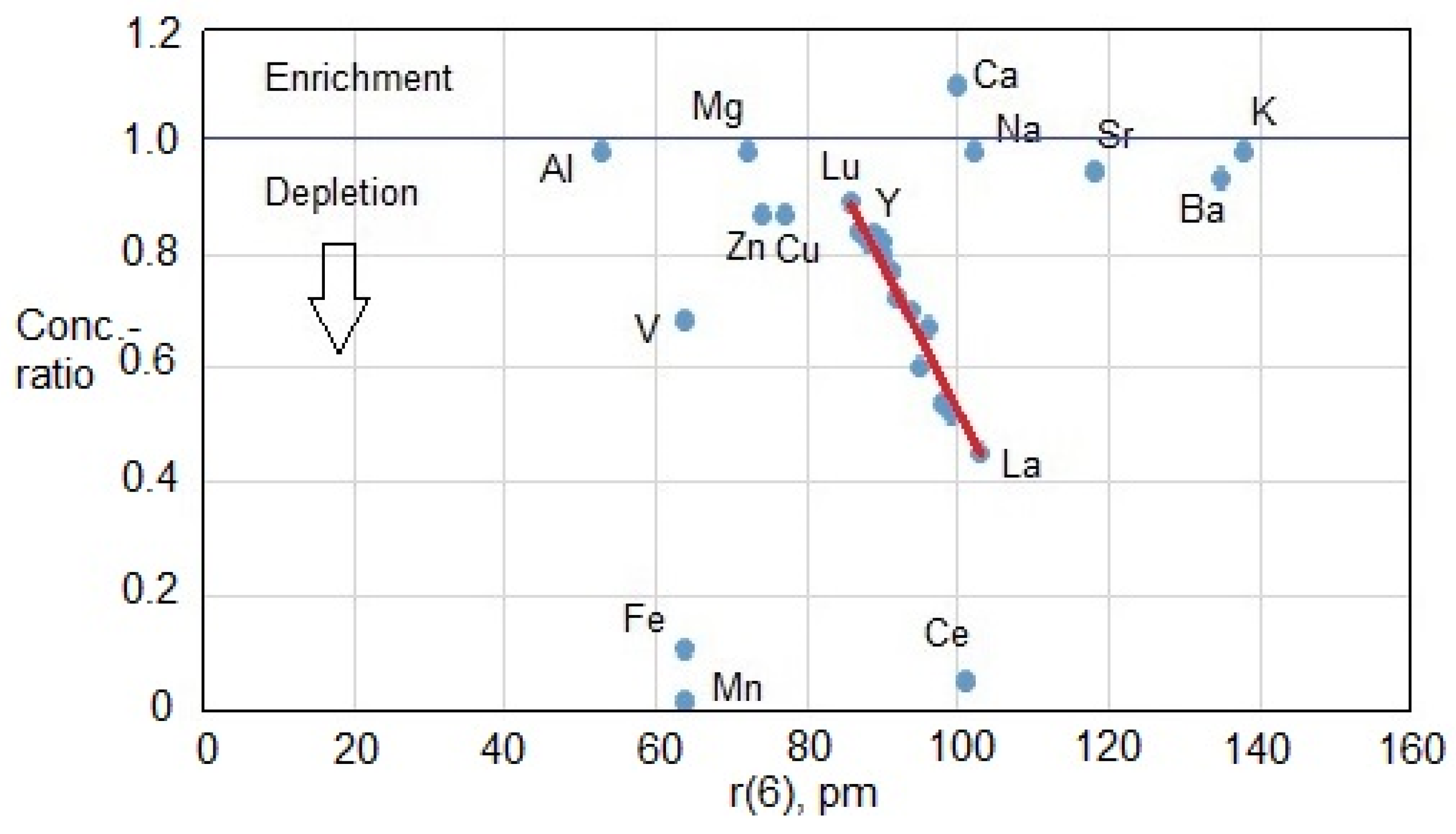
3.2. Fracture Water Chemistry and YBS Metal Enrichment
3.3. Phase Analysis
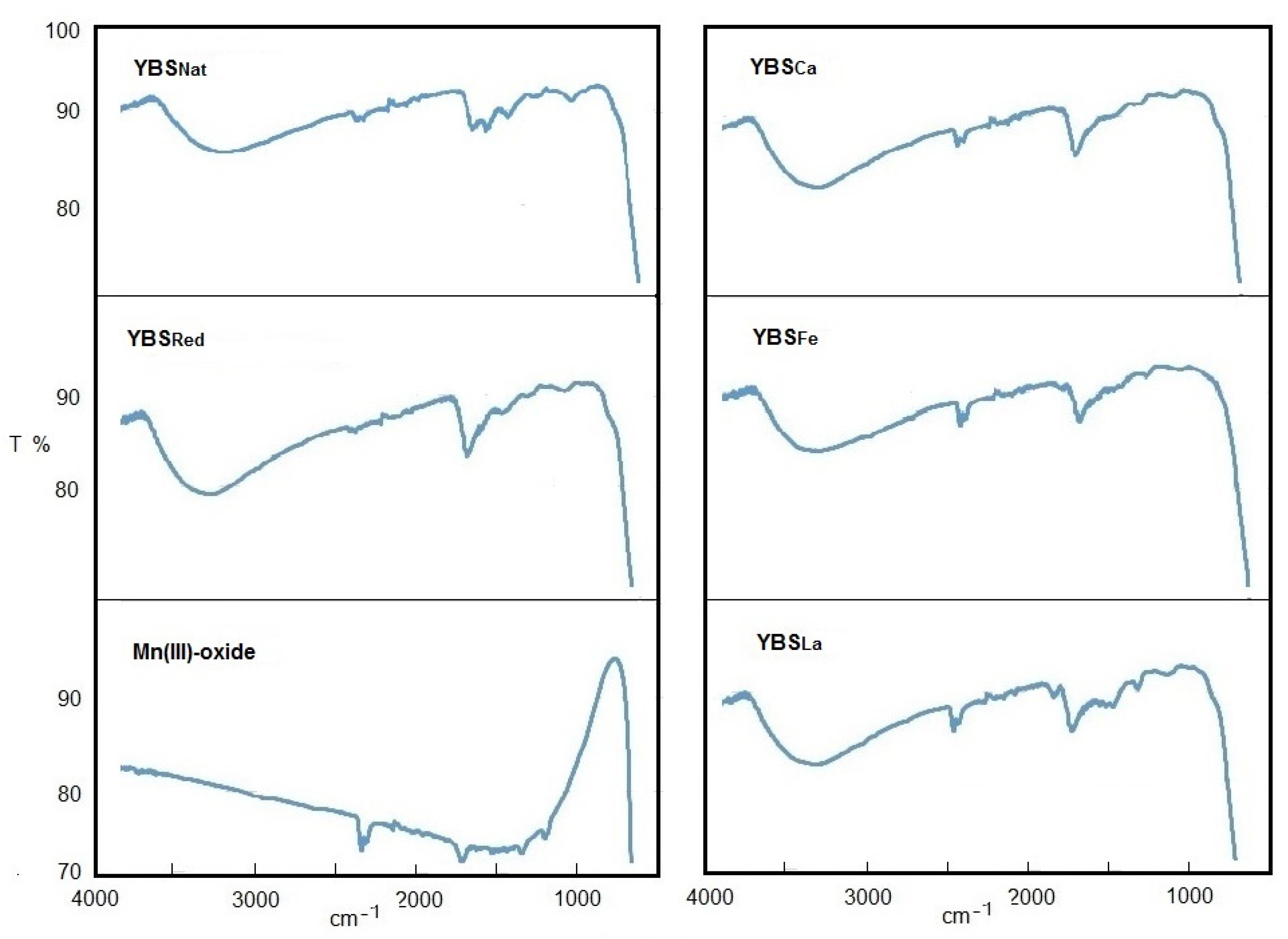
3.4. Infrared Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sjöberg, S.; Allard, B.; Rattray, J.E.; Callac, N.; Grawunder, A.; Ivarsson, M.; Sjöberg, V.; Karlsson, S.; Skelton, A.; Dupraz, C. Rare earth element enriched birnessite in water-bearing fractures, the Ytterby mine, Sweden. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 78, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordenskjöld, I. Der Pegmaitite von Ytterby. Bull. Geol. Inst. Univ. Uppsala 1910, IX, 1908–1909. [Google Scholar]
- Sundius, N. Description of the Bedrock Map of the Stockholm Region; Sveriges Geologiska Undersökning, Ser. Ba No: 13, Kungl. Boktryckeriet. P.A; Norstedt & Söner: Stockholm, Sweden, 1948. (In Swedish) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Ralph, J.; Zhang, J.; Que, X.; Prabhu, A.; Morrison, S.M.; Hazen, R.M.; Wyborn, L.; Lehnert, K. OpenMindat: Open and FAIR mineralogy data from the Mindat database. Geosci. Data J. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.H.P.; Milne, A.A. Birnessite, a new manganese oxide mineral from Aberdeenshire, Scotland. Miner. Mag. 1956, 31, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, E.D. Characterization of a marine birnessite. Am. Mineral. 1977, 62, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, R.M.; Rossman, G.R. The tetravalent manganese oxides: Identification, hydration, and structural relationships by infrared spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 1979, 64, 1199–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Drits, V.A.; Silvester, E.; Gorshkov, A.I.; Manceau, A. Structure of synthetic monoclinic Na-rich birnessite and hexagonal birnessite: I. Results from X-ray diffraction and selected-area electron diffraction. Am. Miner. 1997, 82, 946–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebo, B.M.; Bargar, J.R.; Clement, B.G.; Dick, G.J.; Murray, K.J.; Parker, D.; Verity, R.; Webb, S.M. Biogene manganese oxides: Properties and mechanisms of formation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet Sci. 2004, 32, 287–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, M.; Lanson, B.; Manceau, A.; Toner, B.; Sposito, G. Structural model for biogenic Mn oxide produced by Pseudomonas putida. Am. Mineral. 2006, 91, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargar, J.R.; Fuller, C.C.; Marcus, M.A.; Brearley, A.J.; De la Rosa, M.P.; Webb, S.M.; Caldwell, W.A. Structural characterization of terrestrial microbial Mn oxides from Pinal Creek, AZ. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 889–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, G.J.; Clement, B.G.; Webb, S.M.; Fodrie, F.J.; Bargar, J.R.; Tebo, B.M. Enzymatic microbial Mn(II) oxidation and Mn biooxide production in the Guyamas Basin deep-sea hydrothermal plume. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 6517–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, J.; Kwon, K.D.; Refson, K.; Bargar, J.R.; Sposito, G. Mechanisms of nickel sorption by a bacteriogenic birnessite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 3076–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiro, T.G.; Bargar, J.R.; Sposito, G.; Tebo, B.M. Bacteriogenic manganese oxides. Accounts Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Santelli, C.M.; Webb, S.M.; Dohnalkova, A.C.; Hansel, C.M. Diversity of Mn oxides produces by Mn(II)-oxidizing fungi. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 2762–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, S.; Gutierrez, L.; Fontaine, C.; Croue, J.-P.; Gallard, H. Organic matter interactions with natural manganese oxide and synthetic birnessite. Sci. Totel Environ. 2017, 583, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, J.E.; Veblen, D.R. Crystal structure determinations of synthetic sodium, magnesium, and potassium birnessite using TEM and the Rietveld method. Am. Miner. 1990, 75, 477–489. [Google Scholar]
- Drits, V.A.; Lanson, B.; Gorshkov, A.I.; Manceau, A. Substructure and superstructure of four-layer Ca-exchanged birnessite. Am. Mineral. 1998, 83, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvester EManceau, A.; Drits, V.A. Structure of synthetic Na-rich birnessite and hexagonal birnessite: II. Results from chemical studies and EXAFS spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 1997, 82, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. A consistent model for surface complexation on birnessite (–MnO2) and its application to a column experiment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 3039–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanson, B.; Drits, V.A.; Feng, Q.; Manceau, A. Structure of triclinic Na-rich birnessite. Acta Cryst. 2000, A56, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanson, B.; Drits, V.A.; Gaillot, A.C.; Silvester, E.J.; Plancon, A.; Manceau, A. Structure of heavy-metal sorbed birnessite: Part 1. Results from X-ray diffraction. Am. Mineral. 2002, 87, 1631–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drits, V.A.; Lanson, B.; Bougerol-Chaillout, C.; Gorshkov, A.I.; Manceau, A. Structure of heavy-metal sorbed birnessite. Part 2: Results from electron diffraction. Am. Mineral. Soc. Am. 2002, 87, 1646–1661. [Google Scholar]
- Post, J.E.; Heaney, P.J.; Hanson, J. Rietveld refinement of a triclinic structure for synthetic Na-birnessite using synchrotron powder diffraction data. Powder Diffract. 2002, 17, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillot, A.-C.; Flot, D.; Drits, V.A.; Manceau, A.; Burghammer, M.; Lanson, B. Structure of synthetic K-rich birnessite obtained by high-temperature decomposition of KMnO4. I. Two-layer polytype from 800C experiment. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 4666–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, M.; Toner, B.; Bargar, J.; Sposito, G. Characterization of the manganese oxide produced by Pseudomonas putida strain MnB1. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 2649–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davranche, M.; Pourret, O.; Gruau, G.; Dia, A.; Le Coz-Bouhnik Caren, M. Adsorption of REE(III)-humate complexes onto MnO2: Experimental evidence for cerium anomaly and lanthanide tetrad effect suppression. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 4825–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.H.; Tan, W.F.; Liu, F.; Huang, Q.; Liu, X. Pathways of birnessite formation in alkali medium. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2005, 48, 1438–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davranche, M.; Pourret, O.; Gruau, G.; Dia, A.; Jin, D.; Gaertner, D. Competitive binding of REE to humic acid and manganese oxide: Impact of reaction kinetics on development of cerium anomaly and REE adsorption. Chem. Geol. 2008, 247, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.A.; Post, J.E. Water in the interlayer region of birnessite: Importance in cation exchange and structural stability. Am. Mineral. 2006, 91, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopano, C.L.; Heaney, P.J.; Post, J.E.; Hanson, J.; Komarneni, S. Time-resolved structural analysis of K- and Ba-exchange reactions with synthetic Na-birnessite using synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Am. Miner. 2007, 97, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopano, C.L.; Heaney, P.J.; Post, J. Cs-exchange in birnessite: Reaction mechanisms inferred from time-resolved X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy. Am. Mineral. 2009, 94, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.C.; Ju, J.H.; Kiim, S.S.; Baik, M.H.; Rhee, S.W. Sorption of aqueous Pb2+ ion on synthetic manganese oxides-intercalated with exchangeable cations. J. Industr. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cygan, R.T.; Post, J.E.; Heaney, P.J.; Kubick, J.D. Molecular models of birnessite and related hydrated layered minerals. Amer. Mineral. 2012, 97, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, X.; Villalobos, M.; Tan, W.; Liu, F. Sorption behaviour of heavy metals on birnessite: Relationship with its Mn average oxidation state and implications for types of sorption sites. Chem. Geol. 2012, 292–293, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Tan, W.; Zheng, L.; Cui, H.; Qiu, G.; Liu, F.; Feng, X. Characterization of Ni-rich hexagonal birnessite and its geochemical effects on aqueous Pb2+/Zn2+ and As(III). Geochim. Cosmichim. Acta 2012, 93, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Liu, F.; Feng, X.; Hu, T.; Zheng, L.; Qui, G.; Koopal, L.K.; Tan, W. Effects of Fe doping on the structures and properties of hexagonal birnessites—Comparison with Co and Ni doping. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 117, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumaiza, H.; Coustel, R.; Medjahdi, G.; Ruby, C.; Bergaoui, L. Conditions for the formation of pure birnessite during the oxidation of Mn(II) cations in aqueous alkaline medium. J. Solid State Chem. 2017, 248, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Vito, C.; Scheetz, E. The mineralogy and trace element chemistry of black manganese oxide deposits from caves. J. Cave Karst Studies 2009, 71, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Frierdich, A.J.; Hasenmueller, E.A.; Catalano, J.G. Composition and structure of nanocrystalline Fe and Mn oxide cave deposits: Implications for trace element mobility in karst systems. Chem. Geol. 2011, 284, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.Z.; Dionisio, A.; Sequeira Braga, M.A.; Hernandez-Mariné, M.; Afonso, M.J.; Muralha, V.S.F.; Herrera, L.K.; Raabe, J.; Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Cuezva, S.; et al. Biogenic Mn oxide minerals coating in a subsurface granite environment. Chem. Geol. 2012, 322–323, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöberg, S. Microbially Mediated Manganese Oxides Enriched in Yttrium and Rare Earth Elements in the Ytterby Mine. Ph.D. Thesis, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg, S.; Callac, N.; Allard, B.; Smittenberg, R.H.; Dupraz, C. Microbial communities inhabiting a rare earth element enriched birnessite-type manganese deposit in the Ytterby mine, Sweden. Geomicrobiol. J. 2018, 35, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöberg, S.; Stairs, C.; Allard, B.; Hallberg, R.; Homa, F.; Martin, T.; Ettema, T.J.G.; Dupraz, C. Bubble biofilm: Bacterial colonization of air-air interface. Biofilm 2020, 2, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöberg, S.; Stairs, C.; Allard, B.; Homa, F.; Martin, T.; Sjöberg, V.; Ettema, T.J.G.; Dupraz, C. Microbiomes in a manganese oxide producing ecosystem in the Ytterby mine, Sweden: Impact on metal mobility. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöberg, S.; Yu, C.; Stairs, C.W.; Allard, B.; Hallberg, R.; Henriksson, S.; Åström, M.; Dupraz, C. Microbe-Mediated Mn Oxidation—A Proposed Model of Mineral Formation. Minerals 2021, 11, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylward, G.; Findlay, T. SI Chemical Data, 5th ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Melbourne, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bau, M.; Koschinsky, A. Oxdative scavenging of cerium on hydrous Fe oxide: Evidence from the distribution of rare earth elements and yttrium between Fe oxides and Mn oxides in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts. Chem. Geol. 2009, 43, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- De Carlo, E.H.; Wen, X. The influence of redox reactions on the uptake of dissolved Ce by suspended Fe and Mn oxide particles. Aquat. Geochem. 1998, 3, 357–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, A.; Kawabe, I. REE(III) adsorption onto Mn dioxide (δ-MnO2) and Fe oxyhydroxide: Ce(III) oxidation by δ-MnO2. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Tani, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Tanimizu, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Kozai, N.; Ohnuki, T. A specific Ce oxidation process during sorption of rare earth elements on biogenic Mn oxide produced by Acremonium sp. Strain KR21-2. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 5463–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loges, A.; Wagner, T.; Barth, M.; Bau, M.; Göb, S.; MArkl, G. Negative Ce anomaliesin Mn oxides: The role of Ce4+ mobility during water-mineral nteraction. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 86, 296–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuki, T.; Jiang, M.; Sakamoto, F.; Kozai, N.; Yamasaki, S.; Yu, Q.; Tanaka, K.; Utsumomiya, S.; Xia, X.; Yang, K.; et al. Sorption of trivalent cerium by a mixture of microbial cells and manganese oxides: Effect of microbial cells on the oxidation of trivalent cerium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 163, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, D.; Tepe, N.; Pourret, O.; Bau, M. Negative cerium anomalies in manganese (hydr)oxide precipitates due to cerium oxidation in the presence of dissolved siderophores. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 196, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, B.; Karlsson, M.; Tullborg, E.-L.; Larson, S.Å. Ion Exchange Capacities and Surface Areas of Some Major Components and Common Fracture Filling Materials of Igneous Rocks; SKBF Technical Report 83-64; Swedish Nuclear Fuel Supply Co/Division KBS: Stockholm, Sweden, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, C.W.; Grigal, D.F. A rapid and simple procedure using Sr85 for determining cation exchange capacities of soils and clays. Soil. Sci. 1971, 112, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Liao, Q.; Linghu, W.; Huang, Y.; Shen, R.; Alsaedi, A.; Wang, J.; Hayar, Y.T.; Sheng, G. Application of EXAFS with a bent crystal analyzer to study the pH-dependent microstructure of Eu(III) onto birnessite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.D.; Refson, K.; Sposito, G. Understanding the trends in transition in transition metal sorption by vacancy sites in birnessite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 101, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratovsky, I.; Wightman, P.G.; Pasten, P.A.; Gaillard, J.-F.; Poeppelmeier, K.R. Manganese oxides: Parallells between abiotic and biotic structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11188–11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saratovsky, I.; Gurr, S.J.; Hayward, M.A. The structure of manganese oxide formed by the fungus Acremonium sp. Strain KR21-2. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 3291–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Sasaki, K.; Tanaka, K.; Ohnuki, T.; Hirajima, T. Structural factors of biogenic birnessite produced by fungus Paraconiothyrium sp. WL-2 strain affecting sorption of Co2+. Chem. Geol. 2012, 310–311, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Sasaki, K.; Tanaka, K.; Ohnuki, T.; Hirajima, T. Zinc sorption during bio-oxidation and precipitation of manganese modifies the layer stacking of biogenic birnessite. Geomicrobiol. J. 2013, 30, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayanna, S.; Peacock, C.L.; Schaffner, F.; Grawunder, A.; Merten, D.; Kothe, E.; Buchel, G. Biogenic precipitation of manganese oxides and enrichment of heavy metals at acidic soil pH. Chem. Geol. 2015, 402, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, D.C.; Chen, C.C.; Dixon, J.B. Transformation of birnessite to buserite, todorokite, and manganite under mild hydrothermal treatment. Clays Clay Minerals 1987, 35, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Huang, A.; Park, S.H.; Suib, S.L.; O’Young, C.-L. Crystallization of sodium-birnessite and accompanied phase transformation. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.S.; Wang, M.K. Synthesis and characterization of well-crystallized birnessite. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 2589–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, G.V.; Kulikova, L.N.; Bogdanova, O.Y.; Sychkova, G.I. Layered hydrous manganese dioxide saturated with alkaline-earth cations: Synthesis and sorption properties. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 51, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.-H.; Ooi, K. IR spectra of manganese oxides with either layered or tunnel structures. Spectrochim. Acta 2007, A67, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, E.; Gumus, H.; Sarihan, A. Synthesis, structural characterization and Pb(II) adsorption behaviour of K- and H-birnessite samples. Desalination 2011, 279, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Liu, F.; Feng, X.; Liu, M.; Tan, W.; Qiu, G. Co2+-exchange mechanism of birnessite and its application for the removal of Pb2+ and As(III). J. Hazardous Mater. 2011, 196, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, A.L.; Shaw, S.; Peacock, C.L. Nucleation and growth of todorokite from birnessite: Implications for trace metal cycling in marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 144, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kwon, K.D.; Lee, J.-Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Feng, X. Distinct effects of Al3+ doping on the structure and properties of hexagonal turbostratic birnessite: A comparison with Fe3+ doping. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 208, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
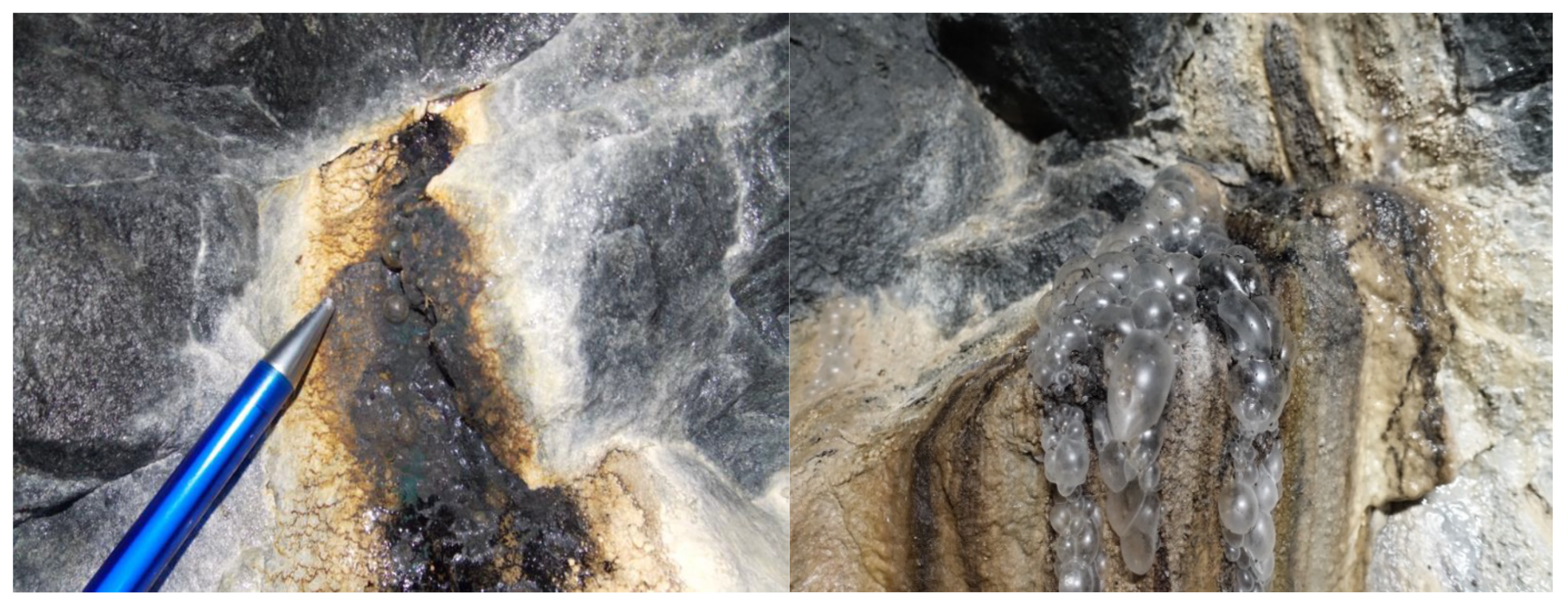


| Element | YBSNat mg/kg | AqA μg/L | AqB μg/L | [AqB]/[AqA] | log ke L/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.31 | 8.33 | |||
| Cl− | 20,900 | 20,700 | 0.99 | ||
| SO42− | 29,100 | 35,000 | 1.20 | ||
| HCO3− | 205,000 | 228,000 | 1.11 | ||
| Mn(III,IV) | 452,710 | 172 | 2.72 | 0.016 | 6.42 |
| M(I) | |||||
| Na | 399 | 24,510 | 24,080 | 0.98 | 1.21 |
| K | 666 | 1720 | 1690 | 0.98 | 2.59 |
| M(II) | |||||
| Ca | 64,170 | 56,360 | 61,740 | 1.09 | 3.06 |
| Mg | 4075 | 8340 | 8140 | 0.98 | 2.69 |
| Ba | 1765 | 4.50 | 4.17 | 0.93 | 5.59 |
| Cu | 1555 | 3.89 | 3.40 | 0.87 | 5.60 |
| Sr | 639 | 250 | 237 | 0.95 | 3.41 |
| Zn | 276 | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.87 | 5.57 |
| M(III) | |||||
| Y | 1357 | 5.00 | 4.08 | 0.82 | 5.43 |
| Al | 841 | 5.26 | 5.14 | 0.98 | 5.20 |
| V | 683 | 2.68 | 1.82 | 0.68 | 5.41 |
| Fe | 583 | 0.40 | 0.044 | 0.11 | 6.16 |
| REE | |||||
| Ce | 3180 | 1.15 | 0.059 | 0.051 | 6.44 |
| La | 1825 | 1.04 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 6.24 |
| Nd | 1785 | 1.27 | 0.69 | 0.54 | 6.14 |
| Gd | 419 | 0.44 | 0.31 | 0.70 | 5.98 |
| Pr | 418 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.52 | 6.22 |
| Sm | 375 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 0.67 | 6.14 |
| Dy | 308 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.77 | 5.85 |
| Er | 150 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.83 | 5.63 |
| Yb | 99 | 0.31 | 0.26 | 0.84 | 5.50 |
| Ho | 60 | 0.11 | 0.088 | 0.80 | 5.74 |
| Tb | 56 | 0.061 | 0.044 | 0.72 | 5.96 |
| Eu | 31 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.60 | 6.09 |
| Tm | 18 | 0.049 | 0.040 | 0.82 | 5.57 |
| Lu | 15 | 0.055 | 0.049 | 0.89 | 5.46 |
| Element | YBSNat mg/kg | YBSRed mg/kg | YBSNa mg/kg | YBSCa mg/kg | YBSLa mg/kg | YBSFe mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn(III,IV) | 452,710 | 528,230 | 507,030 | 486,120 | 537,290 | 483,340 |
| M(I) | ||||||
| Na | 399 | 1823 | 19,265 | 73 | 69 | 84 |
| K | 666 | 1310 | 1109 | 1255 | 437 | 372 |
| M(II) | ||||||
| Ca | 64,170 | 57,930 | 68,067 | 104,270 | 10,723 | 8640 |
| Mg | 4075 | 2442 | 1826 | 1405 | 1250 | 700 |
| Ba | 1765 | 1959 | 1856 | 1817 | 2199 | 1250 |
| Cu | 1555 | 1838 | 1716 | 1652 | 1727 | 1035 |
| Sr | 639 | 707 | 627 | 504 | 178 | 45 |
| Zn | 276 | 237 | 224 | 204 | 232 | 81 |
| M(III) | ||||||
| Y | 1357 | 1515 | 1430 | 1350 | 909 | 372 |
| Al | 841 | 850 | 1208 | 925 | 693 | 532 |
| V | 683 | 664 | 627 | 591 | 630 | 605 |
| Fe | 583 | 666 | 1424 | 707 | 533 | 95,931 |
| REE | ||||||
| Ce | 3180 | 3121 | 2946 | 2785 | 2928 | 2203 |
| La | 1825 | 1634 | 1549 | 1474 | 124,315 | 497 |
| Nd | 1785 | 1685 | 1592 | 1499 | 984 | 516 |
| Gd | 419 | 419 | 394 | 377 | 291 | 137 |
| Pr | 418 | 403 | 383 | 363 | 220 | 122 |
| Sm | 375 | 369 | 347 | 329 | 239 | 121 |
| Dy | 308 | 335 | 329 | 303 | 230 | 103 |
| Er | 150 | 171 | 162 | 155 | 118 | 51 |
| Yb | 99 | 116 | 110 | 106 | 90 | 38 |
| Ho | 60 | 65 | 61 | 58 | 45 | 20 |
| Tb | 56 | 65 | 60 | 60 | 42 | 19 |
| Eu | 31 | 31 | 30 | 28 | 20 | 10 |
| Tm | 18 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 16 | 7 |
| Lu | 15 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 13 | 6 |
| Element | YBSNat x | YBSRed x | YBSNa x | YBSCa x | YBSLa x | YBSFe x | r(6) pm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn(III,IV) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 64, 46 |
| M(I) | |||||||
| Na | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.182 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 102 |
| K | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 138 |
| M(II) | |||||||
| Ca | 0.388 | 0.301 | 0.368 | 0.588 | 0.179 | 0.049 | 100 |
| Mg | 0.040 | 0.021 | 0.016 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.007 | 72 |
| Ba | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 135 |
| Cu | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 73 |
| Sr | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 118 |
| Zn | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 74 |
| M(III) | |||||||
| Y | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 90 |
| Al | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.010 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 53 |
| V | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 64, 59 a |
| Fe | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.391 | 64, 78 b |
| REE | |||||||
| Ce | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 101, 87 c |
| La | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.183 | 0.001 | 103 |
| Nd | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 98 |
| Gd | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 94 |
| Pr | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 99 |
| Sm | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 96 |
| Element M | YBSNat x | YBSRed x | YBSNa x | YBSCa x | YBSLa x | YBSFe x |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na | 0.02 | 0.18 | ||||
| Ca | 0.39 | 0.30 | 0.37 | 0.59 | 0.18 | 0.05 |
| Mg | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Fe | 0.01 | 0.39 | ||||
| REE + Y | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.01 |
| ΣOthers, x < 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Σx | 0.48 | 0.39 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.41 | 0.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Allard, B.; Sjöberg, S.; Sjöberg, V.; Skogby, H.; Karlsson, S. Metal Exchangeability in the REE-Enriched Biogenic Mn Oxide Birnessite from Ytterby, Sweden. Minerals 2023, 13, 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13081023
Allard B, Sjöberg S, Sjöberg V, Skogby H, Karlsson S. Metal Exchangeability in the REE-Enriched Biogenic Mn Oxide Birnessite from Ytterby, Sweden. Minerals. 2023; 13(8):1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13081023
Chicago/Turabian StyleAllard, Bert, Susanne Sjöberg, Viktor Sjöberg, Henrik Skogby, and Stefan Karlsson. 2023. "Metal Exchangeability in the REE-Enriched Biogenic Mn Oxide Birnessite from Ytterby, Sweden" Minerals 13, no. 8: 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13081023
APA StyleAllard, B., Sjöberg, S., Sjöberg, V., Skogby, H., & Karlsson, S. (2023). Metal Exchangeability in the REE-Enriched Biogenic Mn Oxide Birnessite from Ytterby, Sweden. Minerals, 13(8), 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13081023







