Abstract
In order to reveal the metallogenic potential of the Indosinian Ziyunshan granite in central Hunan, the temporal, spatial and genetic relationship between the mineralization and the granite is discussed, and the concentrations of ore-forming elements for different granites are measured. The geochemistry of the elements, isotope geochemistry and chronology, and the data derived from the analysis on Au-W deposit in the area are compared with the geologic features of the regional metallogenic rock. The results indicate that Ziyunshan granite is an irregular shaped complex of late Indosinian by multi-stage intrusion. Elements such as W, Sn, Cu, Pb, Ag, Sb, Be, Li and Ta are enriched in the granite. The sulfophilic elements including Au, Pb, Zn and Ag are relatively enriched in the main body of the Ziyunshan granite, while the lithophilic elements including W and Sn are relatively enriched in the late phase of the Ziyunshan granite. The zoning of the ore-forming elements could be observed in the granite: Nb and Ta (inside the granite); W, Sn, Mo and Bi (inner contact zone); Pb, Zn and Cu (contact zone); and Au and Sb (outer contact zone). All the deposits in the area are formed after the intrusion of the Ziyunshan granite except the Ni-Ta-Sn ore formed simultaneously with the Ziyunshan granite. The Ziyunshan granite provides necessary heat, active fluid and partial ore-forming materials sources, which may show good metallogenic potential.
1. Introduction
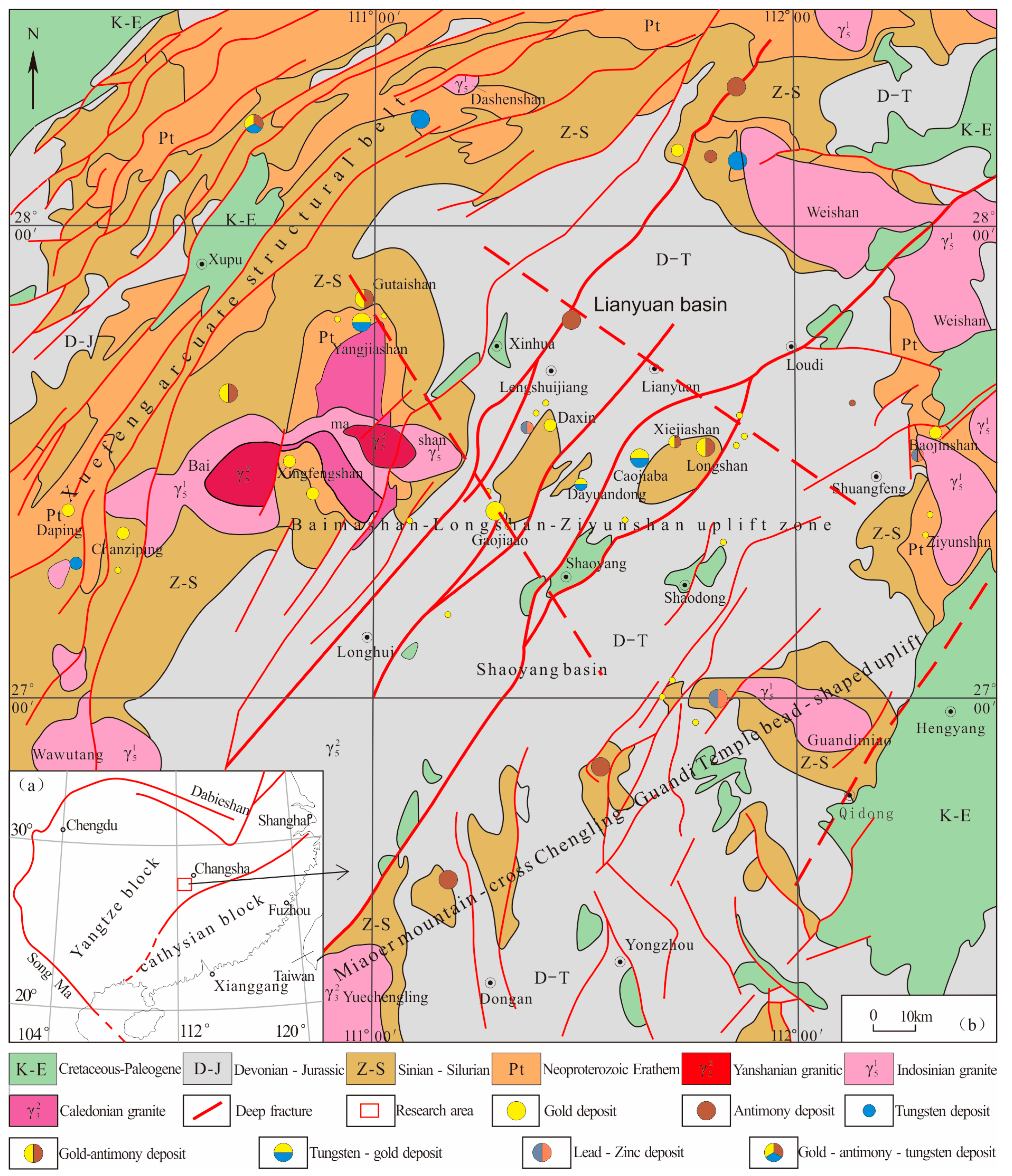
The central Hunan, which is situated in the middle junction zone of the Yangtze and the Cathaysia (Figure 1a), is the world’s important antimony and gold metallogenic province [1]. A large number of gold (antimony) deposits were developed in Precambrian shallow metamorphic rocks (Figure 1b). The geological features of gold (Au), antimony (Sb) and tungsten (W) deposits in this area are different obviously from those of orogenic-type Au deposits but are related closely to magmatism [1]. These deposits all occurred near the acid rock or vein of the late Indosinian, even as the adjacent rock of ore bodies. The ages of ore deposits during the late Indosinian were mainly in the range of 195~225 Ma, which are roughly approaching the rock-forming ages of granitic bodies or acidic dike near the deposits and belonging to the late Triassic [2,3,4]. The metallogenic age of Longshan Au-Sb deposit is 195 ± 36 Ma [4], and the formation age of granodiorite porphyry dikes in the area range from 217 to 220 Ma [5]. Additionally, the ages of the Chanziping Au deposit, the Daping Au deposit and the scheelite of the Xiejiashan deposit are 205.6 ± 9.4 Ma, 204.8 ± 6.3 Ma [2] and 210 ± 2 Ma [6], respectively, while the zircon crystallization age of the Baimashan–Longshan super-unit granite in the nearby area is 228.2 ± 1.3 Ma [7]. The formation age of molybdenite in the Dayongxi tungsten deposit is 223.3 ± 3.9 Ma [8], and the zircon crystallization age in nearby Dashenshan granite is 224 ± 1.0 Ma [9]. The scheelite in the Baojinshan Au deposit was formed in 207.8 ± 1.5 Ma [1], and the granodiorite porphyry dikes in the mining area and the adjacent at Ziyunshan granite were 223–225 Ma [10] and 220–225 Ma [11], respectively. With the accumulation of high-precision formed at data in chronology, the cognition to the scale and strength of Indosinian granites in Central Hunan is more widely compared to the traditional ones [1,7,11,12], and its mineralization has also attracted the attention of many scholars. Yet, there has been very little research on the metallogenic potential of Indosinian granites in this area, which is worth further study.
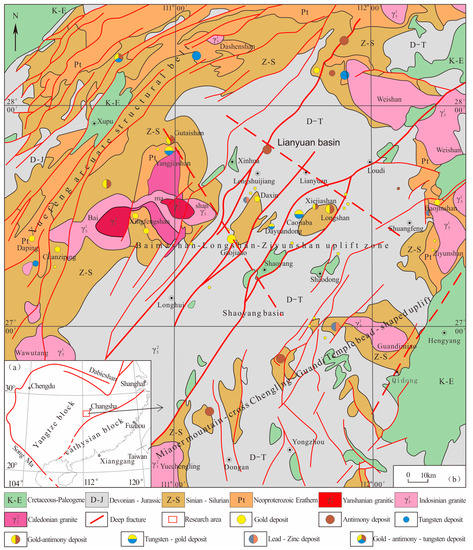
Figure 1.
Geological structure and mineral map of Central Hunan Province (Modified from [1]). (a) Geotectonic location map of South China; (b) Regional geological map of Hunan Province.
The Ziyunshan pluton is located in the east of the Baimashan–Longshan–Ziyunshan Au-Sb-W metallogenic belt in Central Hunan, where there occur many Au, Sb, W, Pb, Zn, Cu, Ni and Ta deposits. Research in this area has been extended with the breakthrough of prospecting technology. In recent years, researchers mainly focused on fluid inclusions [3], geochronology [1] and petrogenesis of biotite gneiss [10] and Ziyunshan rock [12] in this area, which indicated mineralization in this area is closely related to Ziyunshan granite. However, the metallogenic potential of rock mass has not been discussed yet. Based on the field investigation of the Ziyunshan pluton, this paper conducted some analyses about a series of elements, such as W, Sn, Cu, Pb, Zn and Au, which are genetically related to ore formation.. Combined with the previous research work on element geochemistry, isotope geochemistry and chronology of granite and Au-Sb-W deposits in the area, the metallogenic potential of rock was analyzed. This study provides some information to regional metallogenic research and mineral exploration to promote further study of the Indochinese mineralization in South China.
2. Regional Geological Background and Geological Characteristics of Ziyunshan Pluton
Quaternary are uninterruptedly exposed in Central Hunan, in which the Upper Paleozoic carbonate strata are widely distributed, and the old strata are only distributed on the margin and secondary uplifted region of the basin (Figure 1). The folded basement in this area is mainly composed of flysch formation from the pre-Sinian to the Lower Paleozoic. The whole area can be roughly divided into the Baimashan–Longshan–Ziyunshan EW-trending secondary uplifted belt, the Weishan–Nanyue NW-trending secondary uplift belt and the Miaoershan–Guandimiao NE-trending secondary uplift belt. The folded overlying strata contains the lower Devonian to upper Triassic strata and is trapped in the syncline basin. It is mainly composed of Lianyuan syncline basin and Shaoyang syncline basin under the influence of the Baimashan–Longshan–Ziyunshan EW-trending uplift belt. The faults in the study area are well developed with the characteristics of multiphase activities, which are mainly formed by three groups of fractures and arc-shaped structures in the NE, NNE and NW directions (Figure 1) [13].
Multistage magmatic activities occurred in Central Hunan during the period from the Caledonian to Yanshanian, and various magmas were formed on the margin of the Central Hunan basin and the center of secondary uplift. The most intense magmatic activity occurred during the Triassic period and became weaker in the late Paleozoic and late Mesozoic [1,14,15].
Mineral resources are rich in Central Hunan, where more than 20 kinds of minerals and 200 ore points (deposit) have been explored. The Baimashan–Longshan–Ziyunshan Au-Sb-W polymetallic metallogenic belt is the most typical [16]. Au-Sb deposits of the GaoYandong, Gutaishan, Qingjingzhai, Shooping, Jinshanli, Baizhuping, Tuping and Yunxi have been discovered in the Baimashan dome [17]; Au (Sb) deposits of the Daxin, Daheng, Xintianpu Linchang, San-langmiao, Hongshuiping, Baiyunpu, Gaojia ‘ao, Changfu, Hongmiao, Heqing and Shaishuidong have been discovered in the Dachengshan vault (Tianlongshan rock body) [16]; Au deposits of the Longshan, Maogongling, Houlithong and Lijiachong have been discovered in Longshan vault; and Au (Sb) deposits of the Baojinshan, Lingshan, Nanchong, Qingjiawan and Zhujiachong have been discovered in the Ziyunshan vault [10,18,19,20].
The Ziyunshan pluton is located in the east of the Baimashan–Longshan–Ziyunshan Au-Sb-W metallogenic belt in Central Hunan (Figure 1). The pluton’s main lithologies are porphyritic adamellite and minor granodiorite, which are distributed in the edge of the pluton, with a large exposed area in the north and south and a 3~5 km stretch of about 175 km2 area in the direction of east and west. The complement of Ziyunshan pluton is composed of two-mica granite, which intruded into the porphyritic quartz monzonite base with weak sericitization at the exo-contact zone and several to tens of centimeters of chilled border in the inner contact zone. It is similar to the main rock in shape and has an area of about 105 km2. In addition, there are various dikes in and around the pluton, mainly acidic dikes and with a few mafic dikes. The dikes are characterized by a NE direction, followed by the EW and SN directions. The granodiorite porphyry veins are mainly distributed in the north; granitic aplite veins and granitic pegmatite veins are near the contact belt between the main and complement of the pluton.
3. Materials and Methods
Systematic sampling method from different sections and lithology of the Ziyunshan pluton were conducted based on the 1/50,000 geological map and field geological investigation. Three sets of samples were collected: 9 samples of the first set are from porphyritic quartz monzonite in the north part of the pluton; 8 samples of the second set are from two-mica granite in the central part of the pluton; and 7 samples of the third set are from porphyritic quartz monzonite in the south part of the pluton.
XRF analyses of the bulk elements were conducted at the School of Geosciences and Info-physics at Central South University (Changsha, China), using a ZSX Primus IIX-ray fluorescence spectrometer where the test accuracy is better than 5%. Trace elements and rare earth elements were tested at the State Key Laboratory of Mineral Deposit Geochemistry, Institute of Geochemistry Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guiyang, China), using ELAN DRC-e inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The test accuracy was better than 5% for the elements content was higher than 10 × 10−6, while the test accuracy was 10% when the elements content was lower than 10 × 10−6. The data of the bulk elements, trace elements and rare earth elements analyses were published in reference [11]. The test of ore-forming element Au was conducted in ALS Minerals-ALS chemex (Guangzhou, China), using ICP-OES.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Geological Characteristics of Typical Mineral Deposits
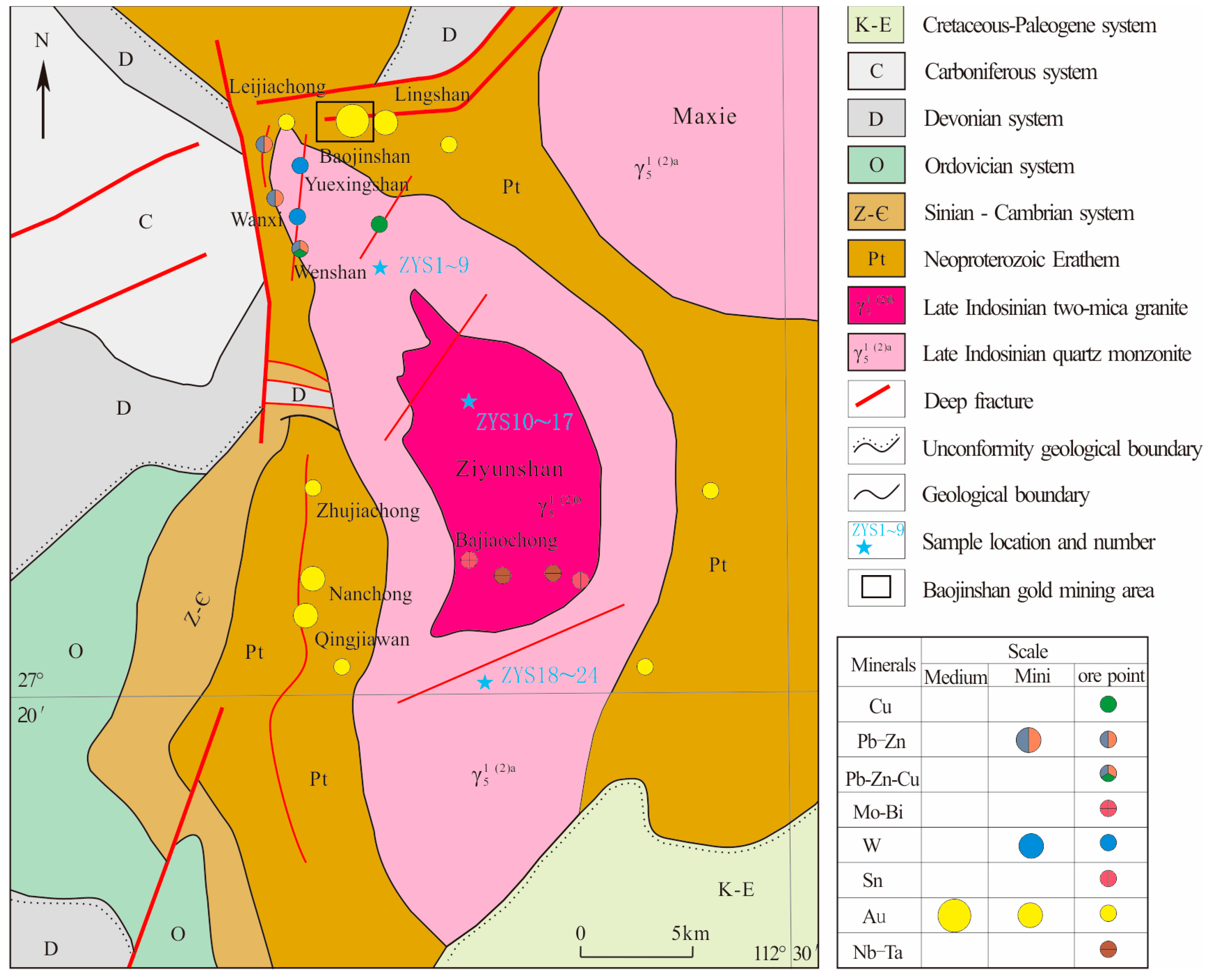
The Ziyunshan area is situated in the east of the Baimashan–Longshan–Ziyunshan east–west gold polymetallic belt (Figure 1). The main minerals in the area include Au, Sb, Ag, Pb, Zn, Cu, W, Sn, Mo, Bi, Ni and Ta, which are related to the magmatic activity. The distribution of deposits and Ziyunshan pluton is shown in Figure 2.
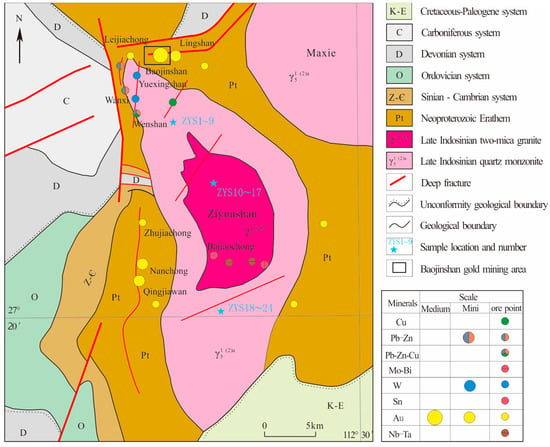
Figure 2.
Geological and mineral distribution map of the Ziyunshan pluton (Modified from [10]).
- (1)
- Baojinshan Au-W deposit
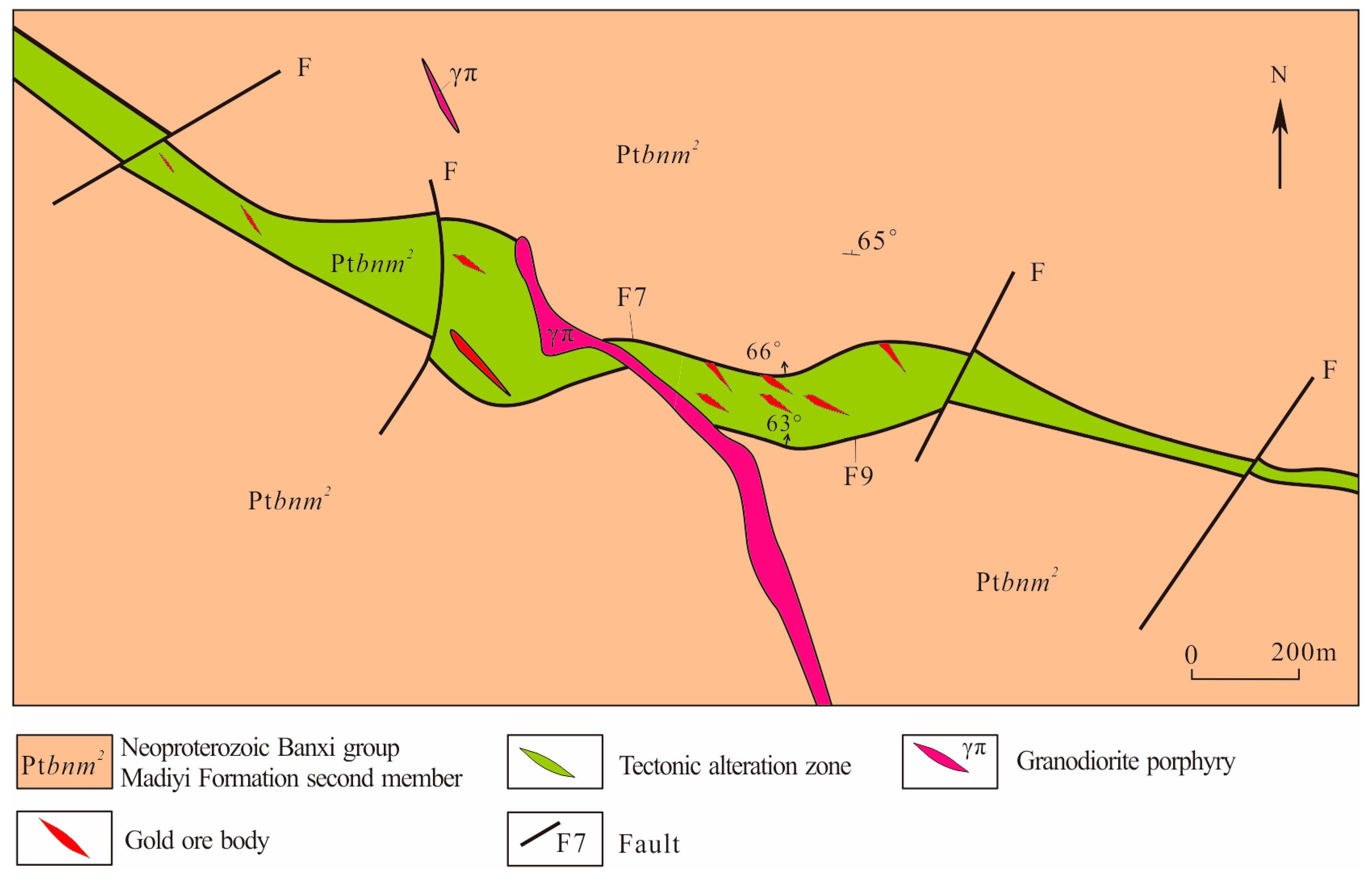
The Baojinshan Au-W deposit is about 3 km away at the north end of the Ziyunshan pluton (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Its stratum was a set of slightly metamorphosed argillaceous and silty clastic rock of Neoproterozoic Banxi Group Madiyi Formation (Figure 3). It is subdivided into three members based on the petrographic characteristics. The first lithological member (Ptbnm1) is metasandstone in southernmost mine. The second member (Ptbnm2) is calcic slate and the ore-bearing horizon, with lithologic features of dark gray medium-thick calcic silty banded slate and spotted slate and thick silty slate and sandy slate [21]. The third member (Ptbnm3) is sandy slate mainly to the northeast of the mine, with a lithology of dark gray sandy slate, sericite slate and silty slate with a thickness of about 530 m.
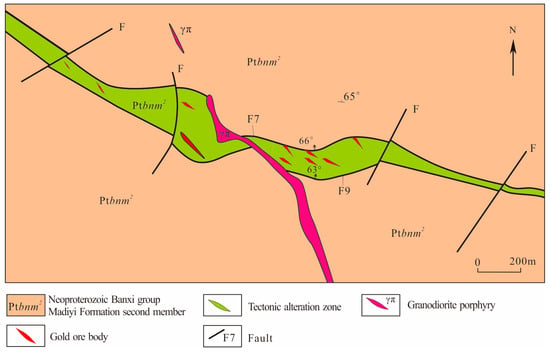
Figure 3.
The sketch geological map of the Baojinshan gold deposit, Central Hunan.
The structure of Baojinshan mine district is generally monocline dipping north with an angle of 20~30°. The fault tectonic system is mainly formed by four groups of fractures in east–west, north–east, south–north and east–west directions (Figure 3). Additionally, the distribution of the ore belt is controlled by the east–west tensional and torsional fractures, which are composed of the parallel F9 and F7 fractures dipping north of 46~77°. Between F9 and F7, a group of secondary extension fractures of NW direction on stretch and SE direction on trend was developed as the main ore-bearing structure, as well as a group of secondary shear fractures of NEE direction on strike and NNW direction on trend was developed as the local ore-bearing structure. They both jointly control the location of ore bodies. However, the NE, NW and NS fractures are ore intersecting structures.
The magmatic rock in the area are granodiorite porphyry dikes, and the surface rocks are mostly gray under the influence of weathering, whereas the deep rocks are dark gray. These dikes extend to the northwest and have a drop to the northeast, interspersing with the gold orebodies. Rich and thick gold orebodies often exist near the dikes, and the dikes are obviously affected by late hydrothermal activities, and their color is obviously green. The outlines of feldspar phenocrysts are dim because of sericitization and chloritization, whereas quartz phenocrysts are dissolved into rounded or semi-rounded shape [10].
The Baojinshan deposit is of the quartz vein type; large-grained gold is common visible in the quartz veins near the surrounding rock [1]. The orebody appears in short veins, with a NW strike and a SW dip angle of about 60°. Their thickness is usually several tens of centimeters, the strike extension is short (about 20 m), dip depth is relatively large and the veins are usually arranged in echelon. The tubular orebody is formed in the area of dense short vein orebodies in a similar occurrence. However, its scale is relatively larger than the vein orebody, with a thickness up to ten meters and a dip depth up to 100 m.
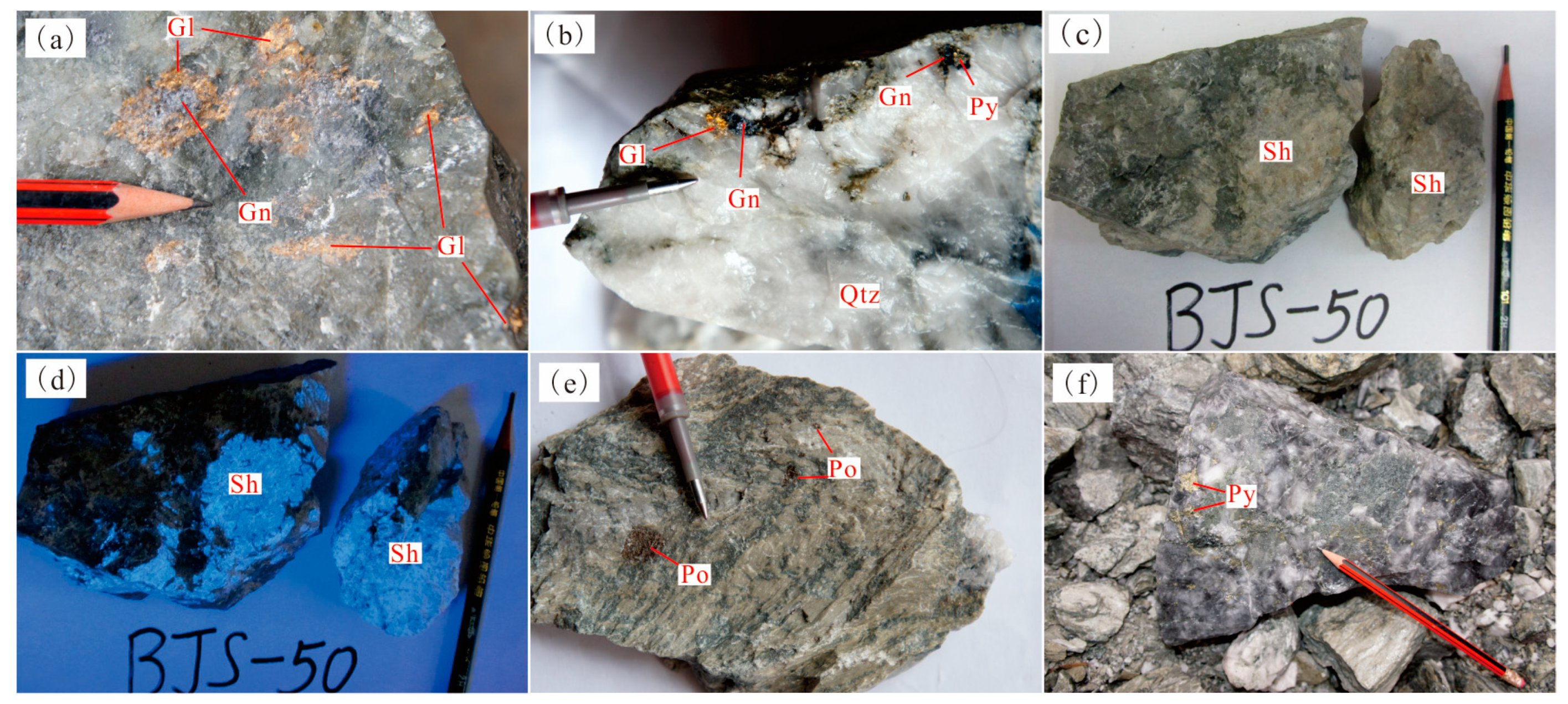
The ore minerals of the Baojinshan deposit include natural gold, stibnite, pyrrhotite, pyrite, scheelite, arsenopyrite, chalcopyrite, etc. (Figure 4). Gangue minerals are quartz, sericite, dolomite, calcite, chlorite, pyrophyllite and kaolinite. Scheelite is distributed in the gold-bearing quartz veins in crumbs or spots (Figure 4a,b). Its colors are beige, light yellow and partial light fresh red, as well as sky blue under fluorescent light (Figure 4c,d). An oily luster can be seen on the crystal surface [1]. The ore has the impregnation, breccia, net vein and allotriomorphic granular structure (Figure 5a–d) and metasomatic pseudomorph, allotriomorphic granular and cataclastic textures (Figure 5e–g), as well as dissolution, inclusion, euhedral and semi-euhedral granular textures (Figure 5h,i). Host-rock alteration is made up of discoloration, pyritization, silicification, sericitization and chloritization. Pyritization, pyritization and silicification are closely related to the mineralization [3].

Figure 4.
The photographs of hand specimens of mineral in the Baojinshan ore district: (a,b) native gold occurred in quartz crack, often associated with metal sulfides such as galena; (c) scheelite occurred as block mass in quartz; (d) blue scheelite under ultraviolet ray; (e) pyrrhotite aggregates retained pyrite crystal shape; and (f) chalcopyrite ore. Gl—Gold; Gn—Galena; Po—Pyrrhotite; Py— Pyrite; Qtz—Quartz; Sh—Scheelite.

Figure 5.
Ore fabric characteristics of the Baojinshan gold–tungsten deposit: (a) disseminated structure; (b) breccia form structure; (c) small net vein structure; (d) stripped structure; (e) xenomorphic granular texture (-); (f) crash texture (-); (g) metasomatic pseudomorph texture (-); (h) poikilitic texture (-); and (i) solution texture (-). Cal—Calcite; Cp—Chalcopyrite; Gl—Gold; Po—Pyrrhotite; Qtz—Quartz; Sh—Scheelite.
- (2)
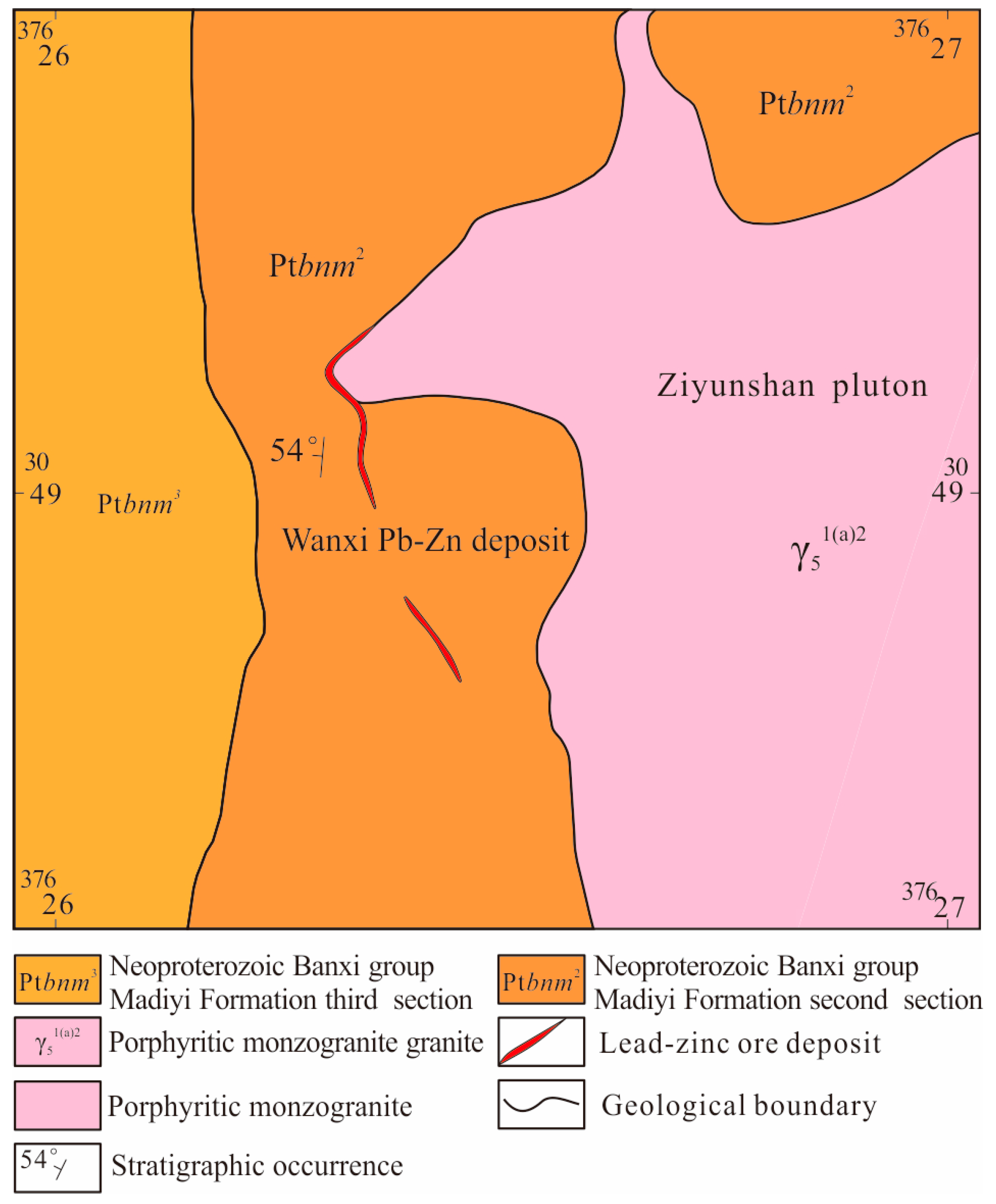
- Wanxi Pb-Zn deposit
The Wanxi Pb-Zn deposit is located in the northwest of the Ziyunshan pluton (Figure 6). The calcic slate of the Neoproterozoic Banxi Group Madiyi Formation (Ptbnm2) is the main exposed strata, whose lithology is dark-gray medium-thick calcareous silty banded slate and spotted slate, thick silty slate and sandy slate and some calcium limestone lens or calcium stripe with a thickness of 1300 m. The structure of the Wanxi mine district is generally monocline dipping west with an angle of 50°. The fault is mainly contact fault. As the only mineral transfer and ore-bearing fault in the area, its appearance is similar to the shape of Ziyunshan pluton from south to north and from near north–south to north–west with an elongation of about 1000 m and dipping 45~65° to the west. Quartz veins are filled along this fault; breccia and polymetallic mineralization of lead, zinc, copper and other metals are localized.
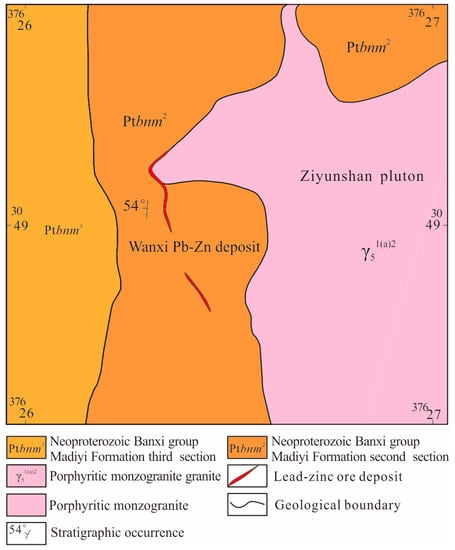
Figure 6.
The sketch geological map of the Wanxi lead and zinc deposit, Central Hunan.
The Pb-Zn orebodies occurred in the contact zone between pluton and stratum (Ptbnm2) and occurred in discontinuous veins or lenses with the characteristic of balk reappear. There are two main orebodies: The northern one is about 300 m in length and 0~2 m in thickness, and the occurrence is 230° ∠ 60~75°. The southern one is about 150 m long and 0.5–2.5 m thick with the proneness of 280~290° and dip of 50~70°. The orebody grades varies greatly; gelenite-dominated in the upper part and zinc blende in the lower part. From the surface to deep layers, there is a zonation of As→Pb→Zn→Cu enrichment. The ore structure is mainly a brecciated structure, followed by massive structure and veinlet structure. The ore texture mainly consists of allotriomorphic granular structure, filling metasomatic structure and cataclastic structure. The main ore minerals are galena, marmatite, chalcopyrite, pyrite, arsenopyrite, pyroxene, etc. Gangue minerals are quartz, calcite and fluorite. The stratigraphic rocks were eroded into hornstone or silicified slate under the influence of the contact metamorphism of Ziyunshan rock. Wall–rock alterations near the orebodies include silicification, sericitization, pyritization, chloritization and epidotization, with local fluoritization.
- (3)
- Yuexingshan tungsten (lead and zinc) deposit
Yuexingshan W-Pb-Zn deposit occurred in the northwestern part of the Ziyunshan pluton (Figure 2). It is a small deposit controlled by the north–south faulted fracture. The host rock of the mineral body was porphyritic adamellite of the Ziyunshan massif, which existed in the fracture with vein style and lenticular style. The mineral body is oriented from north to south, and it is dipped to west with an average inclination of 71°. The exposure length of the ore vein in surface is about 430 m, and the average thickness is 2.41 m. It is mainly composed by tungsten ore; lead–zinc mineralization is only found in the north. The grades of Pb, Zn and W is 6.72%, 0.81% and 0.13%, respectively. The mineralization of Pb and Zn gradually deteriorated to no lead–zinc mineralization and became only scheelite mineralization toward to the south along the strike and deep along the dip direction.
The main texture of ore is a lepido granoblastic structure that formed by magmatic gas–hydrothermal metasomatic granite, followed by granoblastic and euhedral–granular textures. The ore structures include a disseminated structure, massive structure, vein structure and brecciated structure. The main minerals are scheelite, galena, sphalerite, arsenopyrite, pyrite and chalcopyrite, followed by limonite and tetrahedrite. Gangue minerals are quartz, mica (sericite, Muscovite and lithium mica) and chlorite.
According to the mineral composition of the ore, it is divided into quartz–lead–zinc ore, quartz–sphalerite W ore, quartz–mica Pb-Zn-W ore, greisen Pb-Zn ore, Pb-Zn ore, Pb-Zn-W-bearing granite ore, Pb-Zn-W-bearing greisen ore and one Pb-Zn-W-bearing quartz ore.
The host–rock alteration in the mining area was extensively developed, mainly including silicification, chloritization, greisenization, vulcanization and fluoritization. The greisenization is closely related to tungsten mineralization and distributed in the middle of rift alteration zone type tungsten vein within the rock mass contact zone.
4.2. Relationship between Deposits and Ziyunshan Pluton
- (1)
- Spatial relationship between deposits and rock mass
The distribution relationship between the endogenetic metallic ore deposits and the Ziyunshan pluton is shown in Figure 2. The spatial distribution of deposits was related to the geological structure and closely related to the Ziyunshan pluton. The endogenous metallic ore deposits are concentrated in the northwest projection, west hollow and the central faults of the rock mass.
The gold deposit is located in the range of 0~3.5 km outside the Ziyunshan rock contact zone and was controlled by the ring fractures formed during the Ziyunshan pluton intrusion. In the north of the pluton, gold mineralization occurred in the EW faults, such as the Baojinshan, Lingshan and Leijiachong gold deposits. In the west, it is in the NS faults, such as the Nanchong, Qingjiawan, Zhujiachong gold deposits. Lead, zinc and copper deposits (points) are mainly distributed in the Ziyunshan rock contact zone. For example, the mineralization of Wanxi, Wenshan and other deposits in the northwest appea in the NW-trending contact faults and its secondary fractures. Tungsten, tin, molybdenum and bismuth ores are in the rock contact zone, such as Yuexingshan and Bajiaochong tungsten (lead–zinc) ores. Niobium and tantalum ores are in the center of the pluton as the accessory mineral of Muscovite alkali-feldspathic granite and enriched in ore-formation by surface weathering. Additionally, tin ore was deposited as the accessory mineral of granitic pegmatite.
Overall, the spatial distribution of endogenous metal deposits (points) in the Ziyunshan area has a close relationship with Ziyunshan rock. A zoning outward from the rock mass is shown as rare metals such as Nb and Ta (inner) → W, Sn, Mo and Bi (inner contact zone) → Pb, Zn and Cu (contact zone) → Au and Sb (outer contact zone), which is a typical characteristic of magmatic hydrothermal mineralization.
- (2)
- Temporal relationship between mineralization and diagenesis
The Baojinshan gold deposit is sin-magmatic to the post-magmatic hydrothermal deposit within the outer contact zone in the north of Ziyunshan. A gold-bearing quartz vein and a granodiorite porphyry vein with strong alteration were interspersed with each other, and the quartz was dissolved to roundness [10], which indicated that the mineralization of Baojinshan deposit and formation of granodiorite porphyry occurred almost simultaneously. The newest research reported that the Sm-Nd isochron age of scheelite in Baojinshan deposit is 207.8 ± 1.5 Ma (Table 1), and slightly later than that of granodiorite porphyry in the mine (223–225 Ma) and Ziyunshan granite (220–225 Ma) [10,11]. The Wanxi Pb-Zn deposit occurred in the Ziyunshan contact zone, while Yueshengshan W (Pb and Zn) deposit was in the inner contact zone of Ziyunshan rock. They both are typical magmatic hydrothermal filling deposits, and the main metallogenic ages were slightly later than that of the main body of Ziyunshan granite [3]. The elements Nb, Ta and Sn mainly occur in accessory minerals of granite, their metallogenic ages should be consistent with the time that Ziyunshan late granite intruded. Therefore, niobium, tantalum and tin ore were formed simultaneously with Ziyunshan granite, while other deposits (points) formed immediately after it.
- (3)
- Genetic relationship between ore deposit and rock mass
Pyrrhotite retain its original crystal form, which generally developed near the ore body of the Baojinshan gold mine (Figure 5g). The dissolution temperature of monoclinic pyrrhotite was about 254 ℃, indicating that the metamorphism temperature at the peak stage was relatively high [22]. The fluid-inclusion study showed that the metallogenic temperature of Baojinshan was 250–380 ℃, which is broadly consistent with that of the Longshan gold–antimony deposit, the Gaojiaao gold–antimony deposit and the Xingfengshan gold deposit in central Hunan (Table 2) but is significantly higher than that of the Woxi gold–antimony–tungsten deposit in western Hunan [23], the Herenping gold deposit [24] and the Xiaojia gold mine [25]. Aqueous inclusions were the main type in the Baojinshan mine, followed by the CO2-bearing aqueous inclusions and a small amount of pure CO2 inclusions [3]. Their characteristics are similar to those of the Xinfengshan gold mine, the Longshan gold–antimony mine and the Gaojia’ao gold-antimony mine in central Hunan [26], but different from those in the hot water depositional ore deposits and epithermal deposits are whose ore-forming fluids probably originated from magmatic hydrothermal. Studies about hydrogen and oxygen isotopes revealed that the hydrogen and oxygen isotope composition of the Baojinshan gold deposit is highly homogeneous, which is similar to the Longshan gold–antimony deposit and the Gutaishan gold deposit in central Hunan [3]. This indicates that the ore-forming fluid of the deposit was derived from primary magma.

Table 1.
The mineralization timing of gold deposits in Central Hunan [1,2,3,4,10,11,26].
Table 1.
The mineralization timing of gold deposits in Central Hunan [1,2,3,4,10,11,26].
| Deposit/pluton | Type | Material and method | Age (Ma) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baojinshan | Au-W | Scheelite, Sm-Nd | 204.7 ± 1.5 | [1] |
| Daping | Au | Quartz, Rb-Sr | 204.8 ± 6.3 | [2] |
| Chanziping | Au | 205.6 ± 9.4 | [2] | |
| Xingfengshan | Au-W | Saltpeter, LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | 215.2 ± 2.7 | [26] |
| Gutaishan | Au-Sb | Muscovite, Ar-Ar | 223.6 ± 5.3 | [3] |
| Longshan | Au-Sb | Pyrite, Re-Os | 195 ± 36 | [4] |
| Xiejiashan | Au-Sb-W | Scheelite, Sm-Nd | 210 ± 2 | [2] |
| Ziyunshan | Granite | Zircon, SIMS U-Pb | 227.0 ± 2.2, 225.2 ± 1.7 | [11] |
| Baojinshan | Granodiorite porphyry | Zircon, SIMS U-Pb | 225.1±1.5, 223.3±1.4 | [10] |

Table 2.
Statistical table of micro-thermometry of inclusions in gold deposits in Central Hunan [3,24,26,27,28,29,30].
Table 2.
Statistical table of micro-thermometry of inclusions in gold deposits in Central Hunan [3,24,26,27,28,29,30].
| Deposit | Mineral | Method | Result (℃) | Mean (℃) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baojinshan | quartz | homogenization | 250~380 | [3] | |
| Longshan | quartz | decrepitation | 262~340 | 302 | [27] |
| stibnite | 205~290 | 241 | |||
| Xingfengshan | quartz | homogenization | 187~410 | 289 | [26] |
| Gaojia’ao | quartz | decrepitation | 204~351 | 348 | [28] |
| Woxi | quartz | homogenization | 170~220 | 195 | [29] |
| Herenping | quartz | homogenization | 140~230 | 175 | [24] |
| Xiaojia | quartz | homogenization | 135~313 | 236 | [30] |
The δ34S values of sulfur isotopes in the Baojinshan gold deposits and Jinkengchong gold deposit are −7.7;~−1.9‰ and −5.4~−1.54‰, respectively. It is inferred that the sulfur isotopic composition is enriched in δ34S, with the maximum value closing to 0 [21]. This differs from Central Hunan (Table 3) as well as the Woxi gold–antimony–tungsten and Zhazixi gold–antimony deposit in western Hunan but is similar to the Shuikoushan lead–zinc polymetallic deposit and the Tongshanling copper polymetallic deposit related to the magmatic rocks in southern Hunan, indicating that sulfur of the gold deposit in Ziyunshan region may come from magmatic rocks in the area. The δ34S values of Wanxi lead–zinc deposit ranged from −17.1‰ to −13.5 and are enriched in δ34S, suggesting that the sulfur in the mine mainly comes from wall rock (calcareous slate) [3]. The 87 Sr/86 Sr values of scheelite in the Baotjinshan area is 0.73164–0.73974, which are roughly equivalent to the values of the late granite (0.735888~0.745734, unpublished data) in Ziyunshan. It suggested that the mineralization was probably related to the late magmatic activity of Ziyunshan rock [1].

Table 3.
Statistical table of sulfur isotopic composition of deposits in Hunan Province.
Studies show that the hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions of the Baojinshan gold deposit are highly homogenized, and all of them fall into the magmatic water region in the δ18D–δ18O diagram (Figure 7). This is similar to that of the Longshan gold–antimonite deposit in Central Hunan, indicating that the ore-forming fluids of the deposit mainly derived from the primary magmatic water.
In conclusion, the mineralization in this area is closely related to the late Indochinese acidic magmatism in Ziyunshan area, suggesting that Ziyunshan pluton provided heating source, necessary ore-forming hydrothermal fluid and provenance for mineralization in this area.
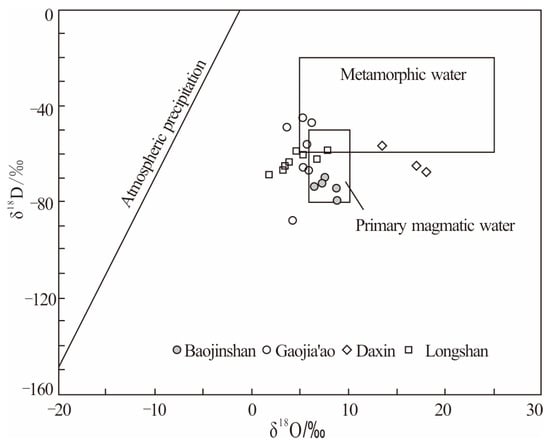
Figure 7.
Diagram of δ18D-δ18O relationship of gold deposits in Central Hunan (Data from reference [3,16,17,27]).
Figure 7.
Diagram of δ18D-δ18O relationship of gold deposits in Central Hunan (Data from reference [3,16,17,27]).
4.3. Potential Mineralization of Ziyunshan Pluton
- (1)
- Regional metallogenic conditions
The EW-trending Baimashan–Longshan–Ziyunshan gold polymetallic metallogenic belt in Central Hunan (Figure 1) was the product of magmatism mainly caused by large-scale crustal melting [11,12]. From the discovered deposits in the west part of the metallogenic belt, the ore-forming elements consist of Au, Sb, W, Pb, Zn and various metals. For example, Au, Sb and W are the main ore-forming elements in the Baimashan area.
At present, the minerals found in the Ziyunshan area include gold, tungsten, lead, zinc, copper and rare metals. It is worth noting that the known reserves in the Baojinshan gold deposit have reached medium scale, and the tungsten orebodies in different scales have been found in the deep areas. Overall, the metallogenic elements in the Ziyunshan area and the Baimashan area are roughly the same. Compared with the ore-forming conditions of the Baimashan area, the core outcropping strata in the Ziyunshan area are also Neoproterozoic Banxi Group shallow metamorphic rocks with high Au content, providing rich provenance for gold mineralization in this area. There were multi-stage active basement faults in this area, which provided a good channels for the activities of magma and metallogenic hydrothermal fluid. Radial and ring fractures with similar structural properties were also developed in the core of this area and provided a good structural space for the deposit in place. The granites in the core of the uplift and the Indochinese granites of Baimashan were the simultaneous products of magmatism that provided a heating source, a partial provenance and necessary ore-forming hydrothermal fluid for mineralization. In addition, the 1:50,000 heavy sand and dispersed flow in the area circled geochemical anomalies dominated by gold and stacked by various elements, which were in good agreement with known deposits [3]. Therefore, Ziyunshan and Baimashan have similar conditions in the regional stratigraphy, structure and magmatic rock, as well as metallogenic elements, suggesting better regional metallogenic conditions in this area.
- (2)
- Shape, occurrence and scale of intrusive bodies
It has been found that only the scale of rare earth element mineralization is large; the scale of other ore-forming rocks is small, such as Wangxianling, Qianlishan, Yaogangxian and other ore-forming rocks. If large rock mass was a complex massif and composed of (small) rocks of different periods (stages) and experienced thorough evolution and fractionation, it was made for mineralization [36]. The complex massifs such as Baimashan, Xitian and Qitianling were all related to the formation of large deposits. Moreover, the rock mass in a regular shape was not conducive to mineralization. Additionally, the irregular shape of the intrusive bodies such as the convex and depressed parts were good for mineralization. When the occurrence of intrusive bodies is flat or overlapped, it is better for mineralization [36].
Ziyunshan rock is an irregular and multi-stage intrusive complex with a high degree of evolution and fractionation [11], which is favorable for mineralization in general, especially the small-scale intrusive bodies (veins) formed in the late stage. Additionally, the intrusive bodies in the northwest protruded in a tongue shape with a flat occurrence, contacting unevenly with the wall rock. This became the best place for mineralization, such as in the Baojinshan gold mine, the Wanxi lead–zinc mine and other mineral points (Figure 2). The inward depressions in the west of intrusive bodies were also conducive to mineralization, such as the Nanchong gold deposit and the Qingjiawan gold deposit (Figure 2).
- (3)
- Petrogeochemical conditions
The uneven distribution of chemical elements in magma made the formed rock either enriched with or relatively deficient in a certain element or a group of elements. The contents of ore-forming elements in granite represented the mineral concentrations in magma and hydrothermal fluid and the scale of deposit during diagenesis and mineralization, which directly constrained the mineralization potential of the rock mass [37]. The ore-forming element contents in the Ziyunshan pluton are shown in Table 4. Elements such as Sn, Cu, Pb, Ag, Sb, Be, Li and Ta are relatively enriched in Ziyunshan rocks, and the main rock is more enriched in Cu and Ag, while the late-phase rocks are enriched in Sn and Li. It suggests that it provided the provenance for the mineralization of Sn, Cu, Pb, Ag, Sb, Be, Li and Ta. According to the data of 1:50,000 regional survey, the W element was obviously enriched in the late-phase granite of the Ziyunshan pluton, with the contents of 34.07 × 10−6 and 250 × 10−6, respectively, [38] which is far greater than that of acid rock in China [39] and Clark value [40], demonstrating that ore-forming materials for tungsten mineralization in this area came from the pluton to a certain degree.

Table 4.
Analysis results of metallogenic elements of the Ziyunshan granite.
The content of Au in Ziyunshan, Longshan and Baimashan rocks in Central Hunan is generally low (Table 5), and significantly lower than that in the southern Hunan granite (100~1300 × 10−9) which is directly provided ore-forming elements [41], indicating that these rock masses were probably not the source of gold mineralization. However, the Au content in the Precambrian strata of Central Hunan is generally high, and the enrichment coefficient was more than ten times higher [42], suggesting that the Au in the gold deposits in the Ziyunshan area could originate from the Precambrian strata. This is consistent with the geological fact that the gold deposits occurred in the outer contact zone of the Ziyunshan pluton.

Table 5.
Statistics of ore-bearing properties for strata and granites in Central Hunan and adjacent areas.
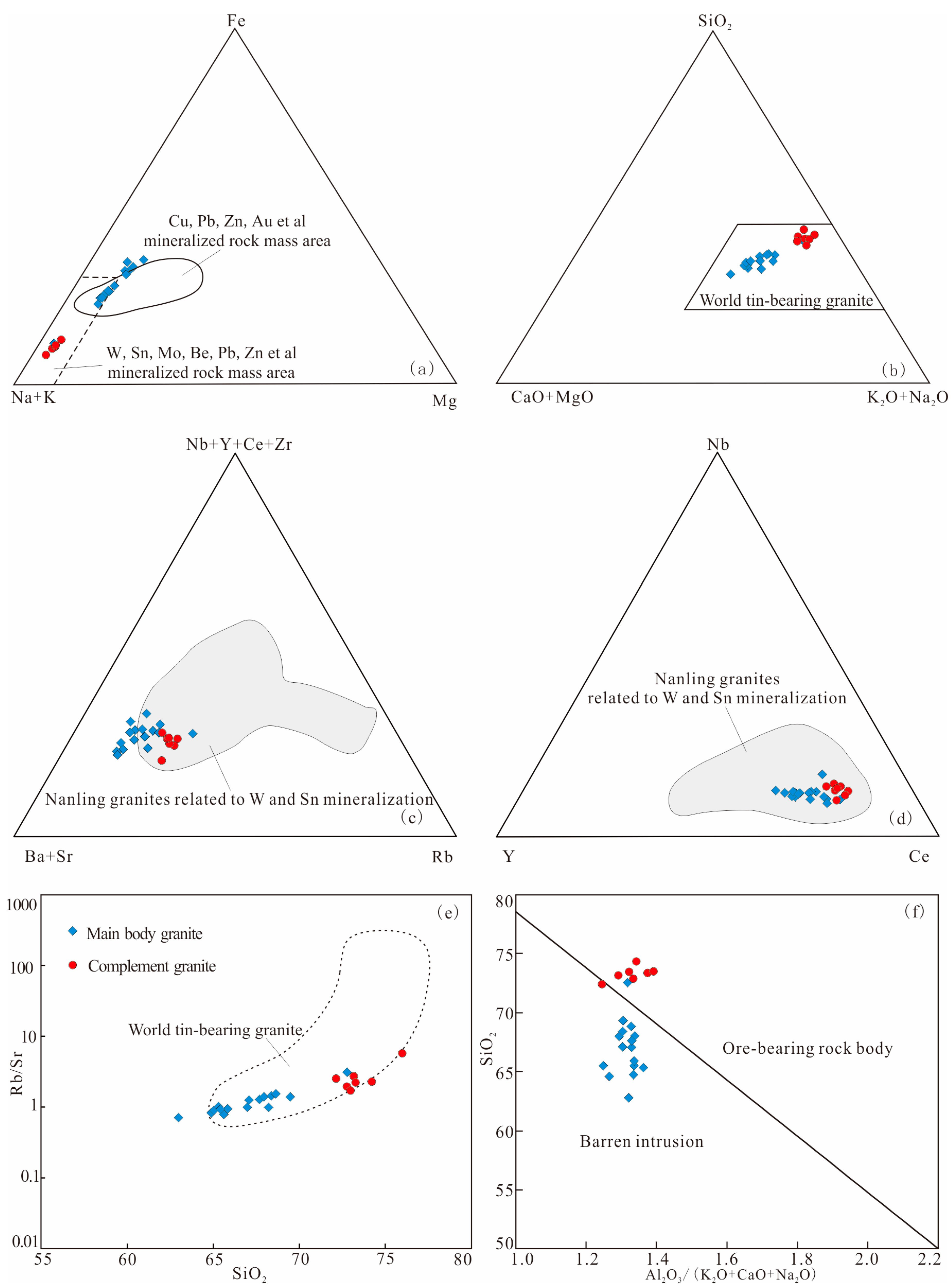
Previous studies have shown that the major, trace and rare earth elements of granites related to gold, lead, zinc, tungsten, tin and rare earth minerals in the Nanling area have different characteristics (Table 6). In comparison, the elemental geochemical characteristics of the granite in Ziyunshan rocks are similar to those of the granites related to Au and Pb-Zn deposits in the Nanling area, and the Ziyunshan late-phase rocks are similar to the related Nanling tungsten–tin deposit in the geochemical features. In the Fe-(Na+K)-Mg correlation diagram (Figure 8a), the test data of the main phase mostly fell into the range of Cu, Pb, Zn and Au mineralized rocks, while the late-phase rocks are all in the range of W, Sn, Mo, Be, Pb and Z. In the SiO2/10-(CaO+MgO)-(Na2O+K2O) diagram (Figure 8b) and SiO2-(Rb/Sr) diagram (Figure 8f), the data of samples all fell into the range of granite of the world-famous Sn deposit [42]. In the NB-Y-CE diagram (Figure 8c) and (Nb+Y+Ce+Zr)-(Ba+Sr)-Rb diagram (Figure 8d), most of the points fell into the area of granite related to W and Sn mineralization in Nanling. In the discrimination diagram of the ore-bearing property of the rock mass (Figure 8d), the results of the main rock in Ziyunshan are almost within the region of barren rock, while the late-phase rock is within the ore-bearing region. These results show a strong connection between the subject of study Ziyunshan rocks and Au, Pb and Zn mineralization and between the late-phase rocks and W and Sn mineralization. Therefore, the Ziyunshan pluton has the potential for Au, Pb, Zn, W and Sn mineralization; the main rock has the greater potential for Au, Pb and Zn mineralization, while the late-phase rock has a higher potential for W and Sn.

Table 6.
Comparison of geochemical characteristics with metallogenic granites in Nanling area.
Table 6.
Comparison of geochemical characteristics with metallogenic granites in Nanling area.
| Category of Granite | Major Element | Ratio | REE | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main body | SiO2: 62.98%~72.80%; (K2O+Na2O):8.46%~9.65%; A/CNK < 1.1, belong to high potassium Ca-alkaline series. | Rb/Sr: 0.76~3.35 (average of 1.25); Ba/Sr: 2.69~5.27 (average of 3.50). | ΣREE: 125 × 10−6~257 × 10−6, enriched in LREE, (La/Yb)N: 15.49~22.66, pattern of right tendency, δEu: 0.59. | [10,11] |
| Complement | SiO2: 72.14%~74.23%, K2O+Na2O: 7.79%~9.10%, A/CNK < 1.1, belong to high potassium Ca-alkaline series. | Rb/Sr: 1.72~2.70 (average of 2021); Ba/Sr: 3.50~4.25. | ΣREE: 76 × 10−6~446 × 10−6, enriched in LREE, (La/Yb)N: 6.06~17.37, pattern of right tendency, δEu: 0.39. | [10,11] |
| Related to the rare earth | SiO2: about 72%; K2O + Na2O: 7%~13%; A/CNK > 1.1, belong to high potassium Ca-alkaline series. | Rb/Sr: < 10; Ba/Sr > 3. | High ΣREE, almost enriched in LREE, pattern of right tendency, obvious negative Eu anomaly. | [44] |
| Related to the gold deposit | SiO2 < 73%, high contents of Al2O3, CaO, MgO, FeO+Fe2O3 and TiO2, (K2O+ Na2O) < 7%, A/CNK < 1.1, belong to shoshonitic and high potassium Ca-alkaline series. | Depleted in Ba, Sr, Nb, Ta; Rb/Sr:1~10; Ba/Sr < 3. | ΣREE: 76 × 10−6~250 × 10−6, high LREE/HREE, slight Eu loss, enriched in LREE with pattern of right tendency. | [45] |
| Related to the Pb-Zn deposit | SiO2: 57%~74%; (K2O+ Na2O): 3.6%~8%; A/CNK: 0.9~2%; belong to shoshonitic and high potassium Ca-alkaline series. | Rb/Sr < 10, Ba/Sr > 3. | ΣREE: 130 × 10−6~300 × 10−6, (La/Yb)N: 1.6~21, obvious fractionation of LREE and HREE, moderate Eu deficit. | [46] |
| Related to the W-Ti deposit | SiO2 > 73%, (K2O+Na2O) > 8%, A/CNK > 1.1, belong to high potassium Ca-alkaline series. | Rb/Sr > 10, Ba/Sr < 3. | Various ΣREE, lower LREE/HREE, patterns in seagull and slope forms, Eu loss in the former one stronger than the later. | [47] |
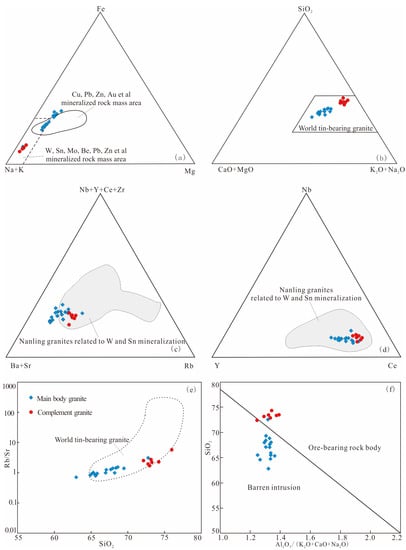
Figure 8.
Discrimination diagram of ore bearing property of the Ziyunshan granite. (a) Plot of Fe–(Na + K)–Mg for the Ziyunshan granite; (b) Plot of SiO2–(CaO + MgO)–(K2O + Na2O) for the Ziyunshan granite; (c) Plot of (Nb + Y + Ce + Zr)–(Ba + Sr)–Rb for the Ziyunshan granite; (d) Plot of Nb–Y–Ce for the Ziyunshan granite; (e) Plot of SiO2–Rb/Sr for the Ziyunshan granite; (f) Plot of Al2O3/(K2O + CaO + Na2O)–SiO2 for the Ziyunshan granite. (based on map from [48]. Data from reference [11]).
Figure 8.
Discrimination diagram of ore bearing property of the Ziyunshan granite. (a) Plot of Fe–(Na + K)–Mg for the Ziyunshan granite; (b) Plot of SiO2–(CaO + MgO)–(K2O + Na2O) for the Ziyunshan granite; (c) Plot of (Nb + Y + Ce + Zr)–(Ba + Sr)–Rb for the Ziyunshan granite; (d) Plot of Nb–Y–Ce for the Ziyunshan granite; (e) Plot of SiO2–Rb/Sr for the Ziyunshan granite; (f) Plot of Al2O3/(K2O + CaO + Na2O)–SiO2 for the Ziyunshan granite. (based on map from [48]. Data from reference [11]).
- (4)
- Magmatic evolution
Generally speaking, different sources of magma vary in their metallogenic element types and capacities, and the plutons are more complex due to the various mixing proportions and degrees with crust–mantle components [49]. With an increasing degree of fraction, the magma tends to be K-rich and alkali-rich, and the increase in Na+ concentration is more conducive to the release of W and Sn from the lattice of petrogenic minerals, so that biotite and other minerals reduced and led to the decrease in REE content, which was adverse impact on the mineralization of REEs [47]. Compared with metallogenic granites of Nanling and Ziyunshan, the main granite of Ziyunshan has similar characteristics to the gold-forming granite source region in Nanling, and the late-phase rock is similar to W-Ti-forming granite source region (Table 7). This is calculated using the calculation formula of the zircon saturation thermometer: (T = 12,900/[2.95 + 0.85 M + lnD]), where T is the absolute temperature, and M=[(Na+K+2Ca)/(Al×Si)], where D is the concentration ratio of Zr element in zircon calculated and in melt. Without Zr and Hf correction of zircon minerals in total rock, the Zr content in pure zircon (496 × 10−2) and in the total rock is used as the contents in zircon and melt, respectively. The results of the calculation of crystallization temperature of Ziyunshan rock showed that the equilibrium temperature of zircon in the main rock is 767–842 ℃ with an average of 806 ℃ and that of the late-phase rock is 747–778 ℃ with an average of about 764 ℃, approaching to the temperature of W and Sn ore-forming granite in Nanling area. In addition, the characteristics of major, trace and rare earth elements of Ziyunshan rocks reveal that the rocks in Ziyunshan experienced high differentiation, and the higher differentiation of late-phase rocks showed more benefit to W, Sn and other polymetallic mineralization. Therefore, in terms of the features of magma evolution, the main body of the Ziyunshan pluton is characterized in enrichment of Pb, Zn, Au, Ag, Cu and other chalcophile elements, while the late-phase rocks are enriched in W, Sn and other lithophilic elements.
Above all, the emplacement of Ziyunshan pluton possibly provided the necessary heating source, active fluid and partial provenance for mineralization in this area, which implied a good metallogenic potential.

Table 7.
Comparison of magmatic evolution characteristics of ore-forming granite in Nanling area.
Table 7.
Comparison of magmatic evolution characteristics of ore-forming granite in Nanling area.
| Types of Granite | Characteristics of Magmatic Evolution | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Ziyunshan granite | The acid magma derived from the crust. The mixed magma source was formed by some mantle-derived components. The mantle-derived components of the main granite are higher. There is magmatic mixing. The degree of differentiation is higher, and the degree of differentiation of complement granite is higher; the whole is I type. | [10,11] |
| Granite related to gold mine | It is mainly neutral (basic) or intermediate-acid rocks. Its origin has the characteristics of multiple sources. The crust–mantle interaction is obvious, and multi-source and multi-evolution is its biggest feature. The granite is mostly I-type, and the degree of differentiation is low. | [45] |
| Granite related to lead–zinc ore | The magma source area is complex, but the general characteristics are as follows: the granites related to Pb-Zn-W-Sn polymetallic ore are from metamorphic sandstone melting source area. The origin of the granites associated with Pb, Zn, Ag and Cu polymetallic ore is deep, mostly in the crust–mantle mixed source area. The degree of differentiation of granites is relatively low, most of them are I-type granites. | [46] |
| Granite related to tungsten–tin ore | It is mainly acidic or ultra-acid rocks. The magma source area is crust source, mainly variable mudstone melting source area. The granites have a high degree of differentiation and are mostly A-type and S-type granites. | [47] |
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Au, W, Pb, Zn, Cu, Sb and rare metal deposits (points) are widely distributed in the Ziyunshan complex and its surrounding area, and an obvious zonation of ore-forming elements could be observed outwards from the rock mass. Rare metal elements such as Nb and Ta appear within the rock mass; W, Sn, Mo and Bi occur in the inner contact zone; Pb, Zn and Cu occur in the contact zone; and Au and Sb occur in the outer contact zone.
- (2)
- The ore-forming elements, such as W, Sn, Cu, Pb, Ag, Sb, Be, Li and Ta, are relatively enriched in the Ziyunshan pluton, where the main rock is more enriched with Pb, Zn, Ag, Cu and other chalcophile elements and the late-phase rock is enriched with W, Sn, Li and other lithophilic elements.
- (3)
- The placement of the Ziyunshan pluton possibly provided the necessary heating source, active fluid and partial provenance for mineralization in this area, which implied a good metallogenic potential.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; Supervision, Y.L. (Yulong Lu); Software X.L. and X.Z.; Writing—review and editing, Y.L. (Yang Liu); All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Grant No. 2021JJ40197) and the Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Deposit Geochemistry (Grant No. 202203).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Peng, J.T.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.K.; Hu, A.X.; Lu, Y.L.; Chen, X.J. Geochemical characteristics and Sm-Nd geochronology of scheelite in the Baojinshan ore district, central Hunan. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2021, 37, 665–682. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Q.; Wang, D.H.; Chen, F.W.; Mei, Y.P.; Cai, H. Study on chronology of the Chanziping and Daping gold deposit in Xuefeng Mountains, Hunan Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 2008, 82, 900–905. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, P.J.; Lai, J.Q.; Mo, Q.Y.; Shi, J.; Tan, H.Y.; Tao, S.L. Ore-forming fluid characteristics and genesis of Baojinshan gold deposit in Shuangfeng County, Hunan Province, China. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2016, 26, 2625–2639. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.L.; Hu, R.Z.; Chen, Y.W.; Luo, J.C. Chronology of the Longshan Au-Sb deposit in central Hunan Province: Constraints from pyrite Re-Os and zircon U-Th/He isotopic dating. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 3507–3517. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.W.; Bi, X.W.; Fu, S.L.; Dong, S.H. Zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotope of the felsic dykes in the Longshan Au-Sb deposit in Central Hunan Province and their geological significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2016, 32, 3468–3469. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Xie, G.Q.; Mao, J.W.; Liu, W.G.; Olin, P.; Li, W. Sm-Nd dating and in-situ LA-ICP-MS trace element analyses of scheelite from the Longshan Sb-Au deposit, Xiangzhong metallogenic province, South China. Minerals 2019, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Peng, J.T.; Xu, J.B.; Yang, J.H.; Hu, A.X.; Chen, X.J. Petrogenesis and metallogenic effect of the Baimashan granitic complex in central Hunan, South China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2021, 37, 805–829. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.S.; Peng, J.T.; Hu, A.X.; Lin, F.M.; Zhang, T. Re-Os dating of molybdenite from Darongxi tungsten deposit in western Hunan and its geological implications. Miner. Depos. 2014, 33, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.S.; Peng, J.T.; Zhang, D.L.; Hu, A.X.; Yang, J.H. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Indosinian Dashenshan granite, western Hunan, South China. Geotecton. Metallog. 2012, 36, 137–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.L.; Peng, J.T.; Yang, J.H.; Li, Y.K.; Chen, X.J.; Zhou, X.; Li, G.L. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf-O isotopes of granodiorite-porphyry in Baojinshan mining area and their geological significance. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2017, 27, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.L.; Peng, J.T.; Yang, J.H.; Hu, A.X.; Li, Y.K.; Tan, H.Y.; Xiao, Q.Y. Petrogenesis of the Ziyunshan pluton in central Hunan, South China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb dating, element geochemistry and Hf-O isotopes. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2017, 33, 1705–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.J.; Ma, C.Q.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhang, J.F. Petrogenesis of Dashenshan I-type granodiorite: Implications for Triassic crust–mantle interaction, South China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.L.; Li, X.Q.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J.H. The Establishment of Ore-Controlling Fracture System of Baoginshan Gold Mine Based on Fracture-Tectonic Analysis. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 5887680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, D.P.; Shen, L.W.; Algeo, T.J.; Elatikpo, S.M. A general ore formation model for metasediment-hosted Sb-(Au-W) mineralization of the Woxi and Banxi deposits in South China. Chem. Geol. 2022, 607, 121020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kong, H.; Zhou, Z.K.; Tindell, T.; Xi, X.S. Genesis of the Banxi Sb deposit, South China: Constraints from wall-rock geochemistry, fluid inclusion microthermometry, Rb–Sr geochronology, and H–O–S isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115, 103162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.L.; Chen, G.H.; Dai, J.B.; Chen, X.; Li, W.Y. Tectono-controlling characteristics and genesis of Daxin gold deposit in Hunan Province. Geotecton. Metallog. 2007, 31, 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.S.; Kang, R.H.; Chen, Y.W. The metallogenic geological condition of Gaojia’ao. Hunan Prov. Its Ore-Prospect. Orientatioa Gold 2002, 22, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Z.K.; Evans, N.J.; Kong, H.; Xi, X.S. Fluid-zircon interaction during low-temperature hydrothermal processes: Implications for the genesis of the Banxi antimony deposit, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 114, 103137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Z.K.; Algeo, T.J.; Wu, J.H.; Jiang, W.C. Geochronology and geochemistry of tuffaceous rocks from the Banxi Group: Implications for Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the southeastern Yangtze Block, South China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 177, 152–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, Q.H.; Evans, N.J.; Zhou, Z.K.; Kong, H.; Lin, Z.W. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Banxi Sb deposit: Implications for fluid origin and the evolution of Sb mineralization in central-western Hunan, South China. Gondwana Res. 2018, 55, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Shao, Y.J.; Lai, J.Q.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z.B. Analysis on ore-controlling alteration rocks and structures in the Baojinshan-Jinkengchong gold deposit. Hunan. Miner. Explor. 2015, 5, 245–253. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, L.Q.; Liu, J.T.; Meng, J.Y.; Lu, L.; Sun, N.; Zhang, G.N.; Long, F. Mineralogy typomorphic characteristics of pyrrhotite and mineralization significance of Yangla copper deposit, Yunnan, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 2669–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.N.; Peng, J.T. Infrared microthermometric and noble gas isotope study of fluid inclusions in ore minerals at the Woxi orogenic Au–Sb–W deposit, western Hunan, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Q.; Peng, J.T.; Deng, M.K.; Li, Y.K. Characteristics of ore-forming fluid in the Herenping albite-quartz lode gold deposit, western Hunan China. Acta Miner. Sinica 2017, 37, 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.T.; Dai, T.G. Geochemical studies of ore-forming fluids in gold deposits, Southwestern Hunan. Miner. Depos. 1999, 18, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.Y.; Peng, J.T.; Hu, A.X.; Mu, L. Characteristics of fluid inclusions of the Xingfengshan gold deposit, central Hunan, and its genetic implications. Geol. Rev. 2020, 66, 1376–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.Y. Geochemistry of ore fluids and genesis of Longshan Au-Sb deposit, west Hunan, China. Geochimica 1991, 20, 342–350. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.C.; Wang, J.R.; Jian, O.U.; Wang, S.S.; Yang, S.F.; Li, Y.H. Inclusion-isotope geochemistry of the Baimashan-Longshan gold metallogenic belt in Hunan and its ore-forming fluids’ characteristics. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2007, 21, 673–678. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.T.; Huang, D.Z.; Xin, Y.J.; Liu, Z.F.; Liu, Y.K. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and genesis of Woxi Au-Sb-W deposit in western Hunan, China. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2013, 23, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S. Research on Mineralizing Fluid Geochemistry Characteristics of Xiaojiashan Gold Deposit. South. Met. 2020, 237, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Xu, Z.W.; Lu, J.J.; Wang, R.C.; Zuo, C.H.; Zhao, Z.X.; Miao, B.H. Genesis of the Shuikoushan lead-zinc deposit, Changning City, Hunan Province. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2013, 6, 732–746. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.X.; Tan, J.J.; Yang, H.M.; Lu, S.S.; Duan, R.C.; Qiu, X.F.; Cheng, S.B.; Yang, X.L. The origin of ore-forming material in the Tongshanling Cu-polymetallic ore field in Hunan Province: Constrains from S–Pb–C isotopes. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.Z.; Peng, E.S.; Sun, Z.J. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Qibaoshan Cu-polymetal deposit. Geotecton. Metallog. 2000, 24, 365–370. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Z.X.; Bao, Y.M.; Wan, R.J. The geological feature and ore-control factor of stibnite ore belt of Zhazixi and its geological prospection. Beijing Geol. 1998, 01, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.X.; Liu, J.M.; Schulz, O.; Franz, V.; Zheng, M.H. Syngenetic origin of the Woxi W-Sb-Au deposit in Hunan: Evidence from trace elements and sulfur isotopes. Chin. J. Geol. 2004, 39, 415, 424–439. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Hu, R.Z.; Bi, X.W.; Peng, J.T. Geochemistry and tin metallogenic potential for Qitianling granite mass in Southern Hunan. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2010, 40, 80–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.H.; Bi, X.W.; Hu, R.Z.; Chen, Y.W. Petrogenesis of the Yaogangxian granites and implications for W mineralization, Hunan Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Q. 1/5 Regional Geological Survey Report of Shuiche Part G-49-6-D and Luguan Part G-49-7-C: Geology Section; Regional Geological Survey Team, Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources: Changsha, China, 1992. (In Chinese)
- Yan, M.C.; Chi, Q.H.; Gu, T.X.; Wang, C.S. The Chemical Compositions of the Continental Crust and Rocks in the Eastern Part of China. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 1997, 0, 451–459. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.R. Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: A new table. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1964, 28, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Relations with gold and genetic types of the granites in Hunan Province. Geol. Resour. 1995, 4, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.M.; Lou, Y.L.; Gao, L.J.; Bao, Z.X. Geology and metallogenesis of Precambrian gold deposits in central Hunan Province. Geol. Resour. 2007, 16, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.H.; Hsieh, P.S.; Lee, C.Y.; Zhou, H.W. Two episodes of the Indosinian thermal event on the South China Block: Constraints from LA-ICPMS U–Pb zircon and electron microprobe monazite ages of the Darongshan S-type granitic suite. Gondwana Res. 2011, 19, 1008–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.W.; Dai, P.Y.; Mei, Y.P.; Li, H.Q.; Wang, D.H.; Cai, H. Metallogenetic and isotopic chronological study on the shenjiaya gold deposit in xuefeng mountains, hunan province. Acta Geol. Sin. 2008, 82, 906–911. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, D.H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Guo, N.X.; Liu, X.X.; He, H.H. Metallogenic specialization of rare earth mineralized igneous rocks in the Eastern Nanling Region. Geotecton. Metallog. 2014, 38, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Guo, C. Metallogenic specialization of the magmatic rocks associated with gold deposits in the Nanling Region. Geotecton. Metallog. 2014, 38, 276–288. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, D.H.; Zhang, C.Q.; He, Y.F. Metallogenic specialization of the magmatic rocks associated with the lead-zinc deposits in the Nanling region. Geotecton. Metallog. 2014, 38, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lu, J.J.; Chen, W.F.; Wang, R.C.; Ma, D.S.; Zhu, J.C.; Zhang, W.L.; Ji, J.F. W-Sn-Nb-Ta-bearing granites in the Nanling Range and their relationship to metallogengesis. Geol. J. China Univ. 2008, 14, 459. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.L.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lou, F.S.; Xu, Y.M. Geochemical characteristics and genetic types of the W-Sn bearing Late Jurassic granites in the Nanling Region. Geotec. Met. 2014, 38, 301–311. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).