U-Pb Dating, Lead Isotopes, and Trace Element Composition of Pyrite Hosted in Black Shale and Magmatic Rocks, Malaysia: Implications for Orogenic Gold Mineralization and Exploration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
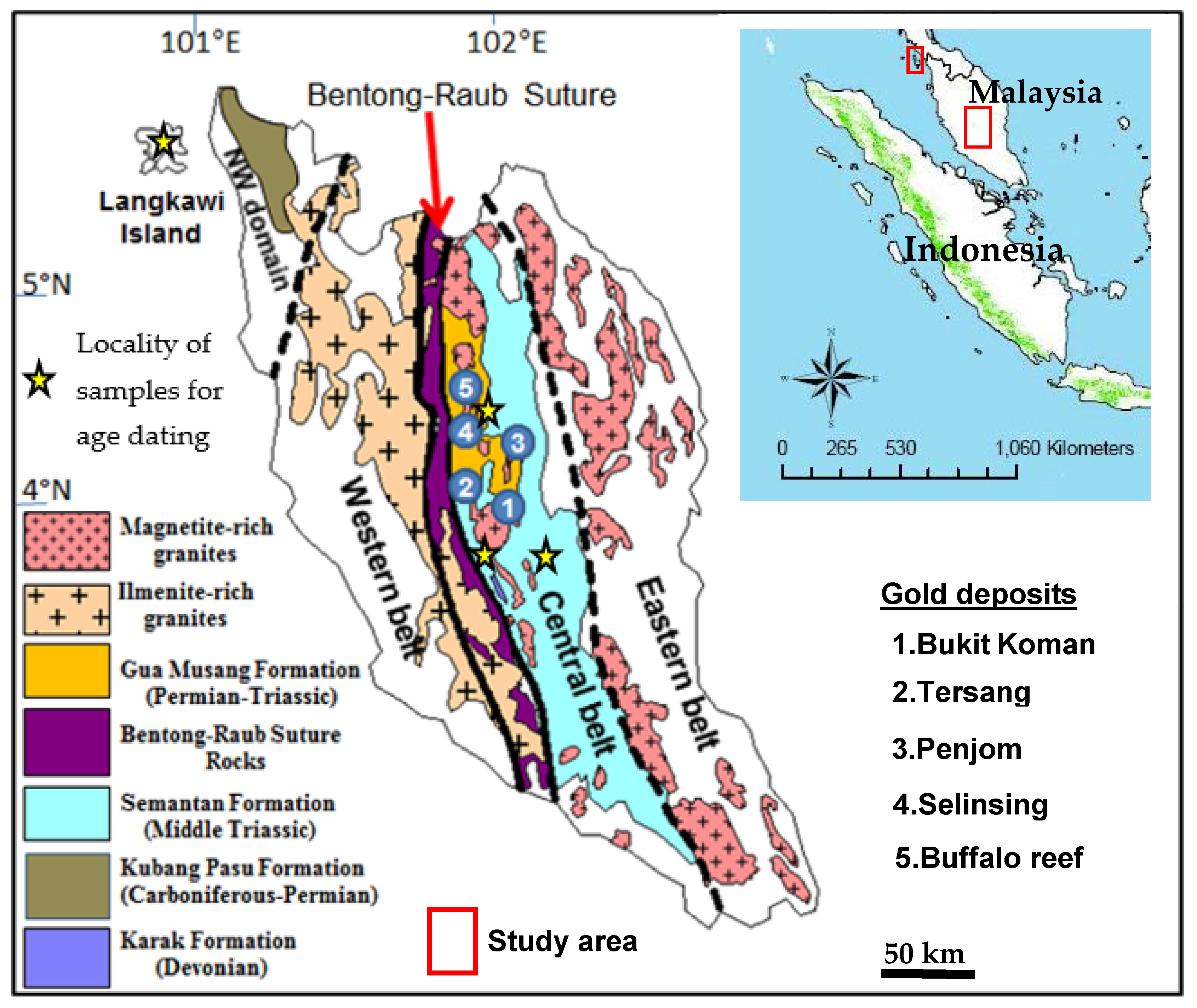
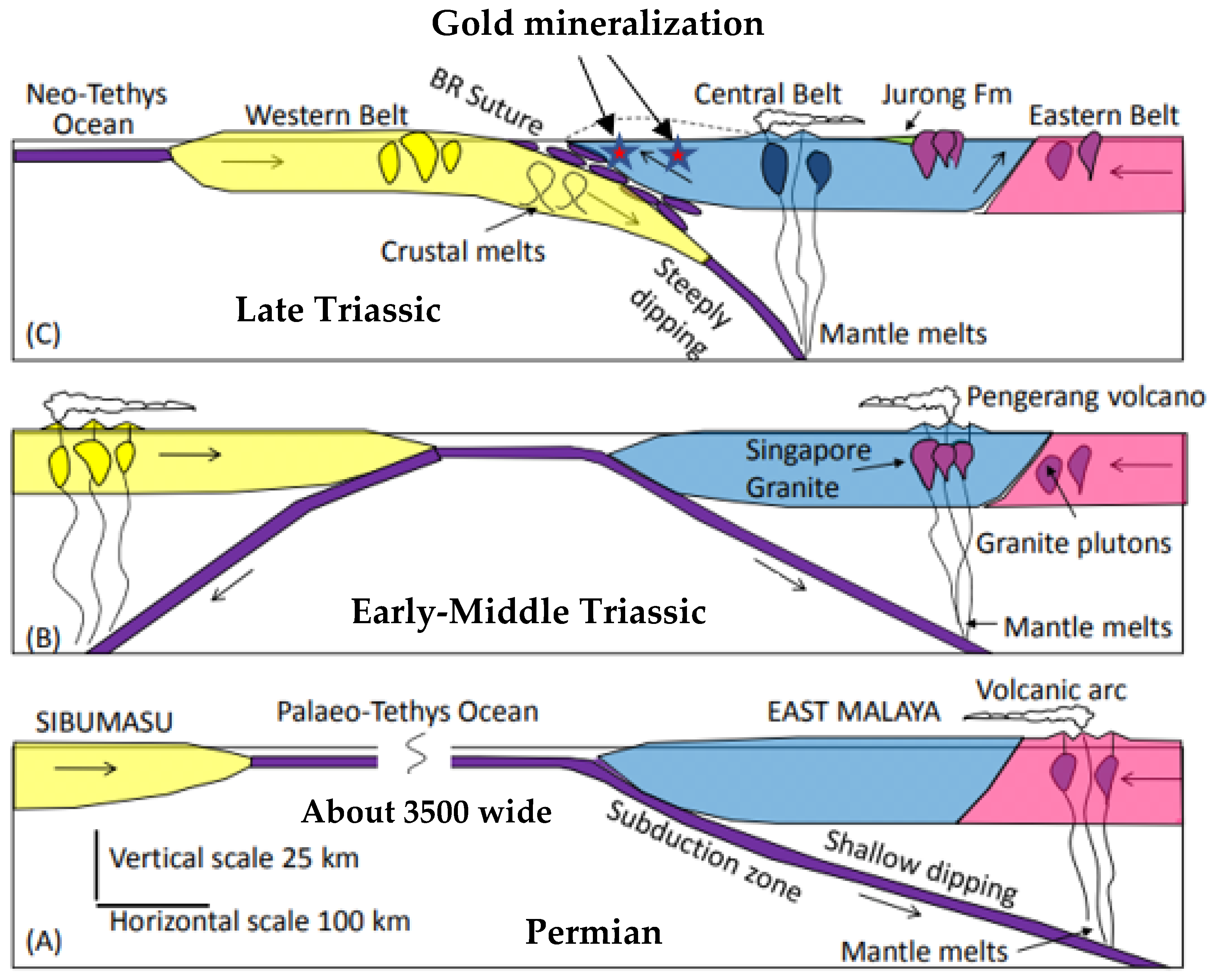
2. Regional and Tectonic Setting
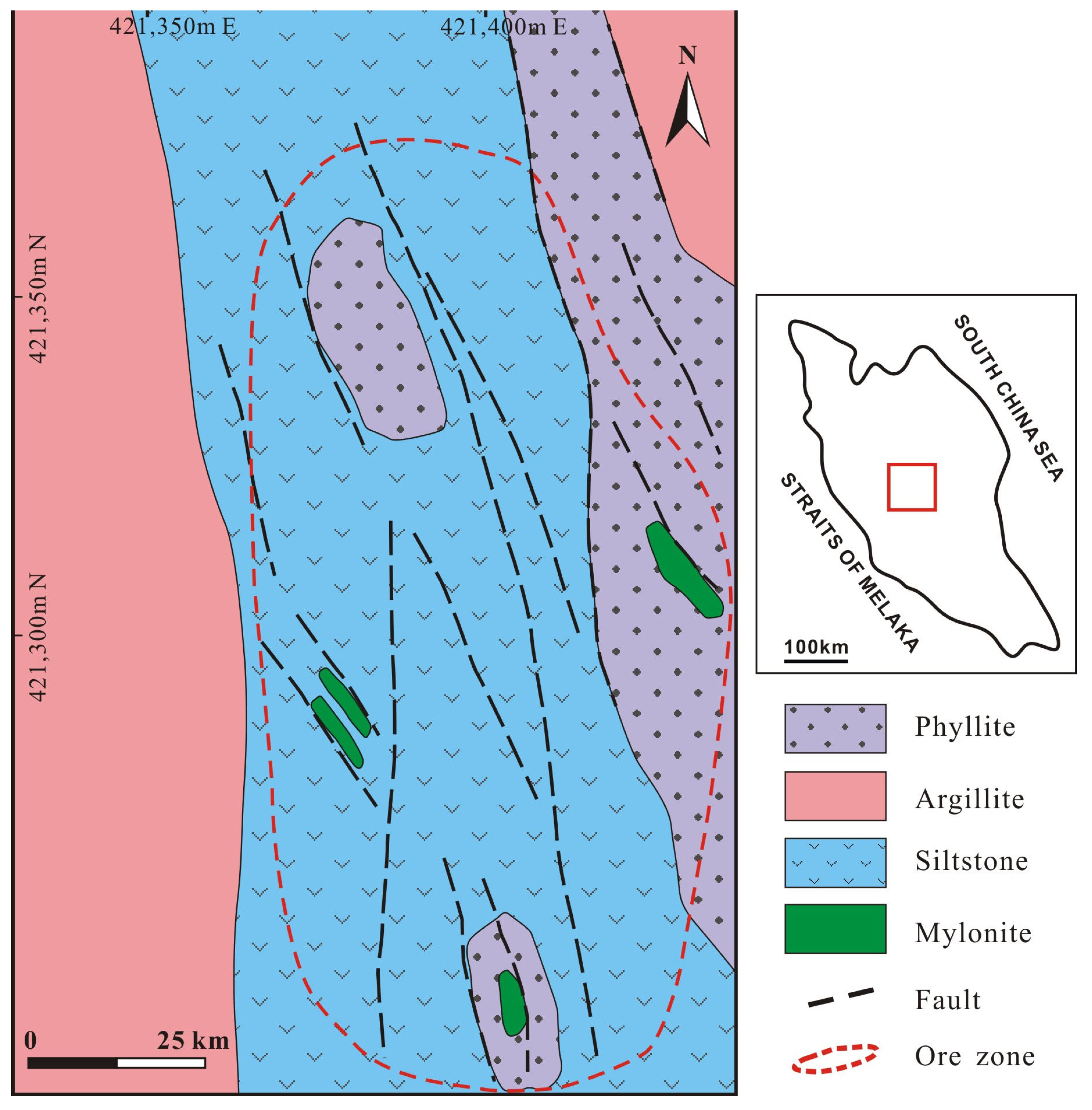
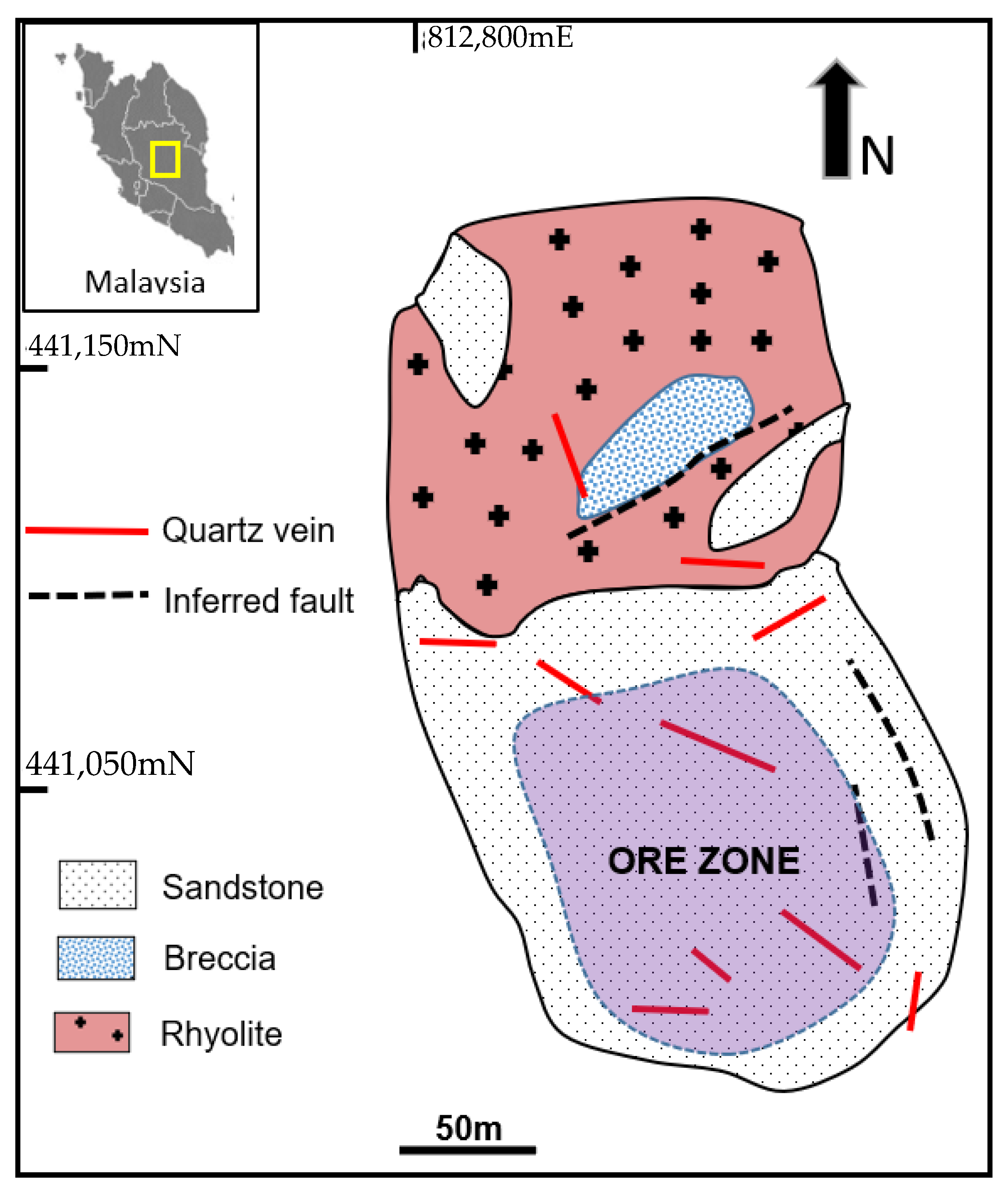
3. Ore Deposits
4. Materials and Methods
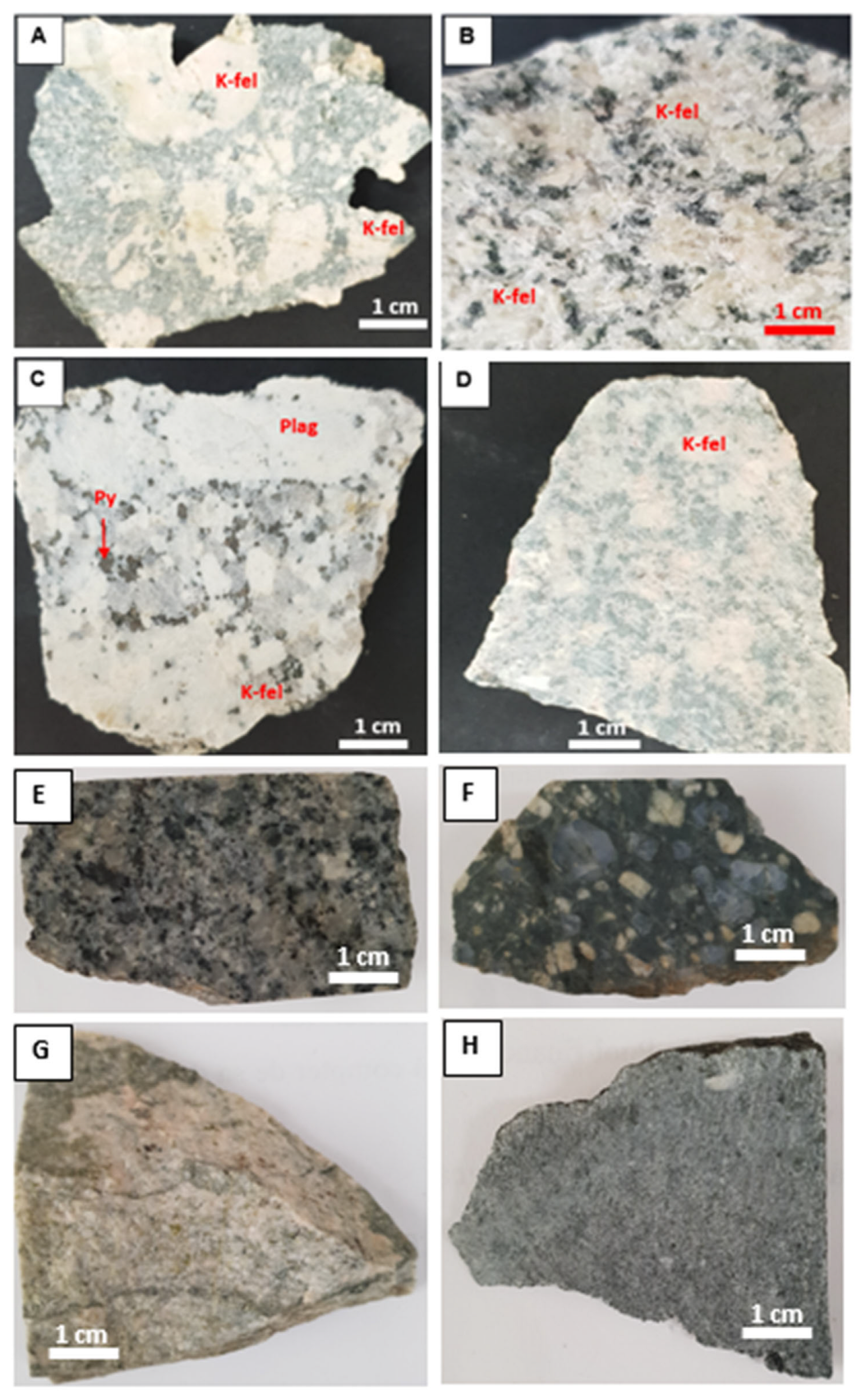
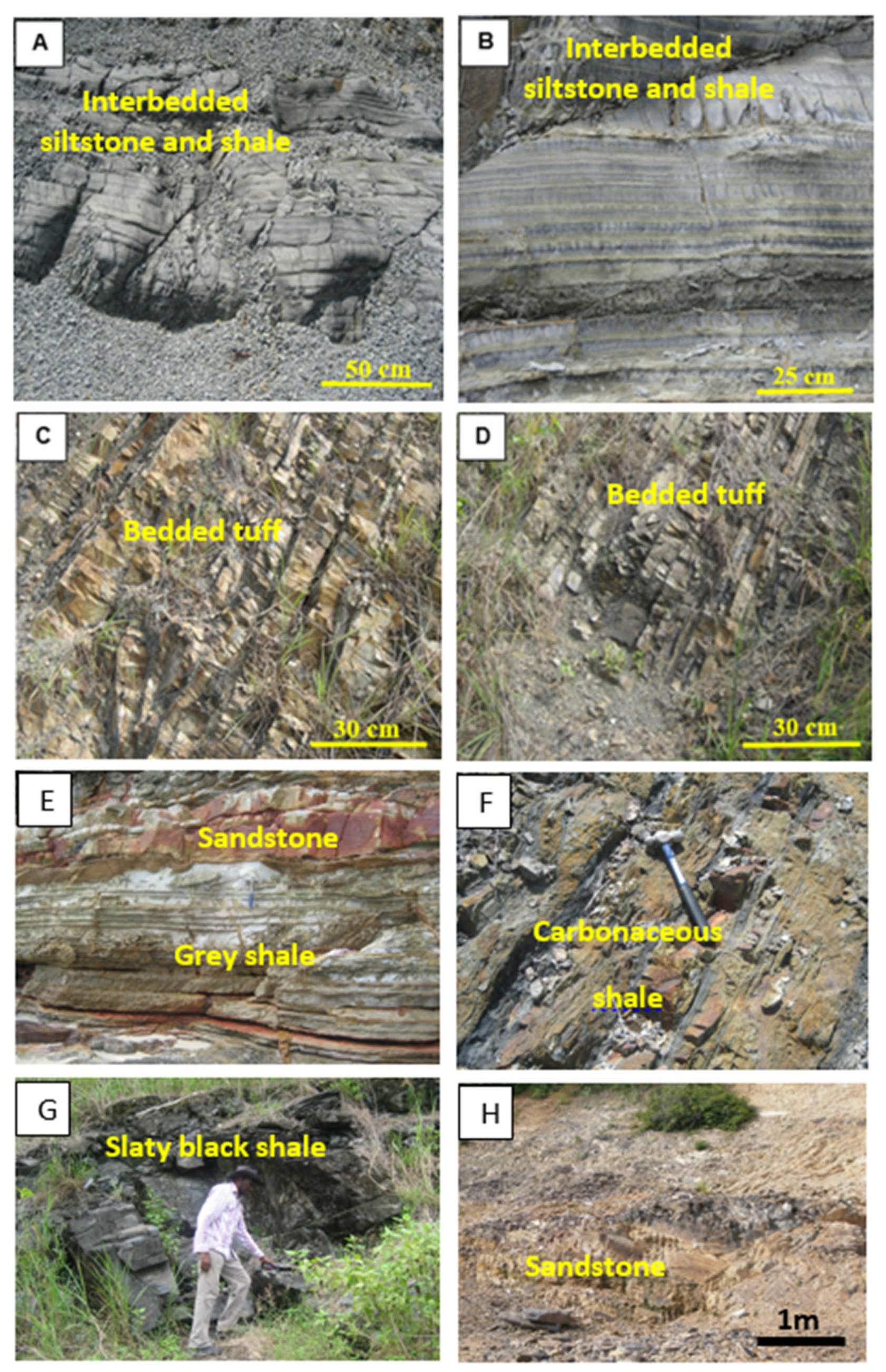
4.1. Pyrite Samples
4.2. U-Pb Zircon Dating
4.3. Pb Isotope Analysis
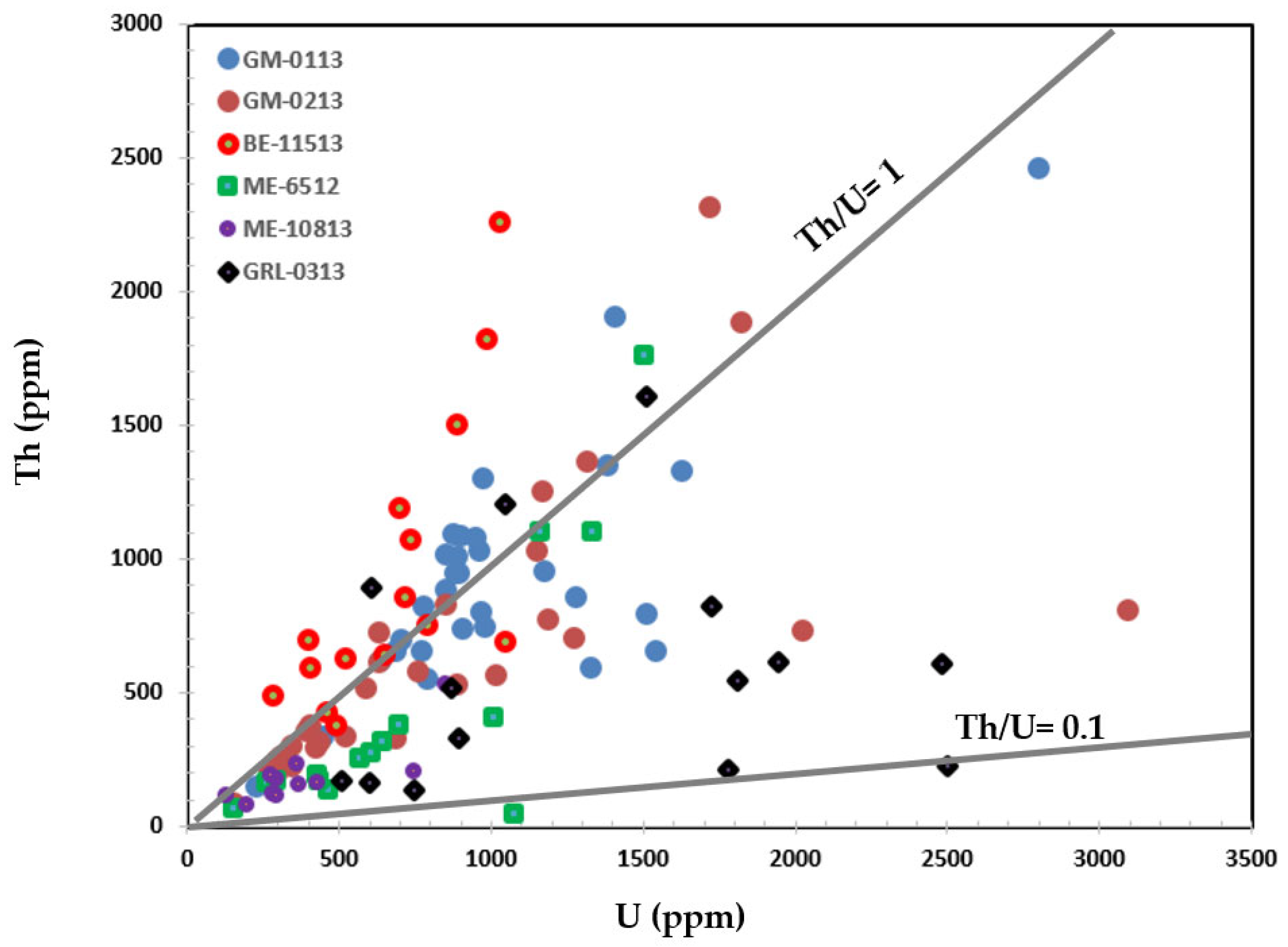
4.4. Pyrite Trace Element Geochemistry
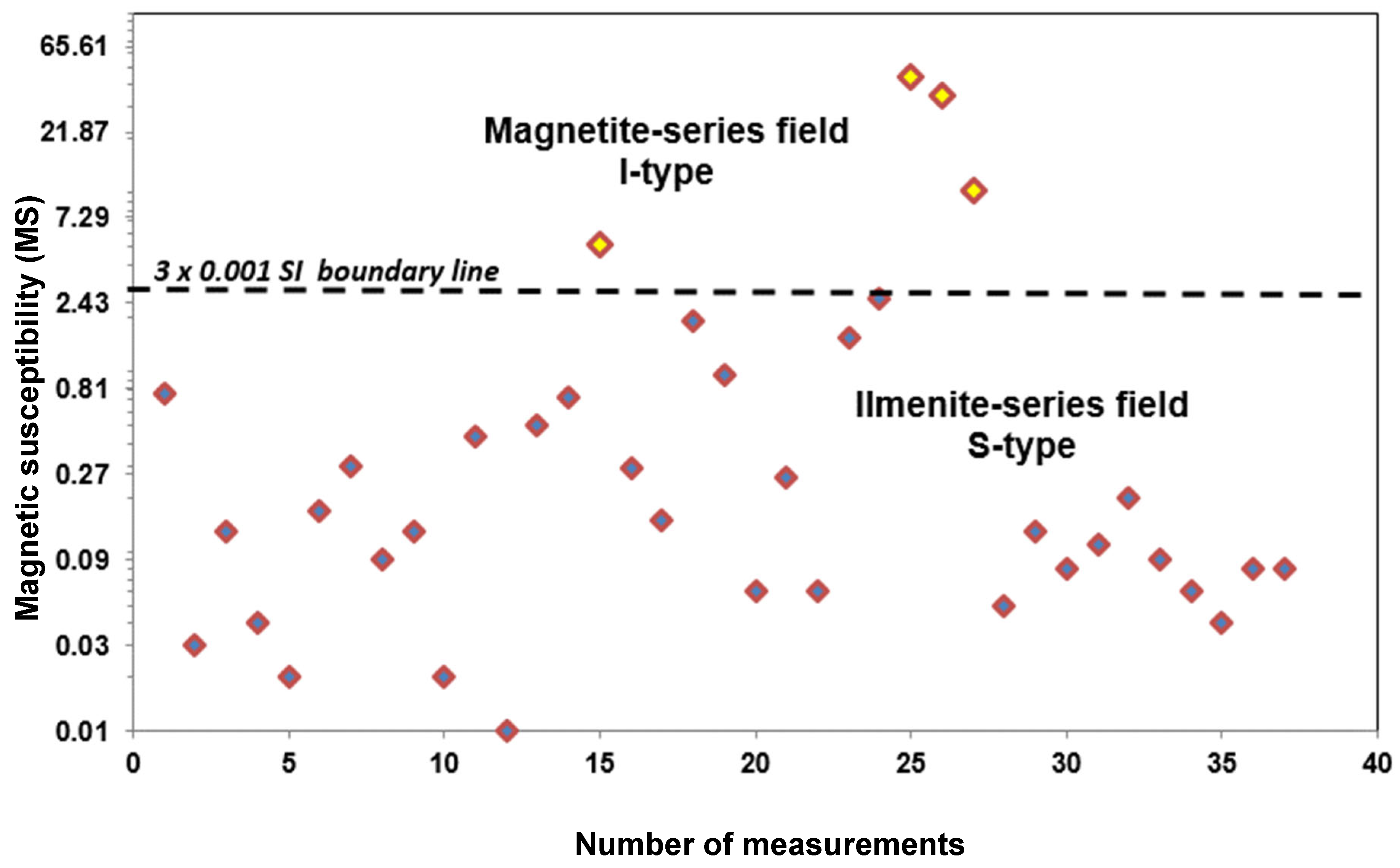
4.5. Magnetic Susceptibility
5. Results
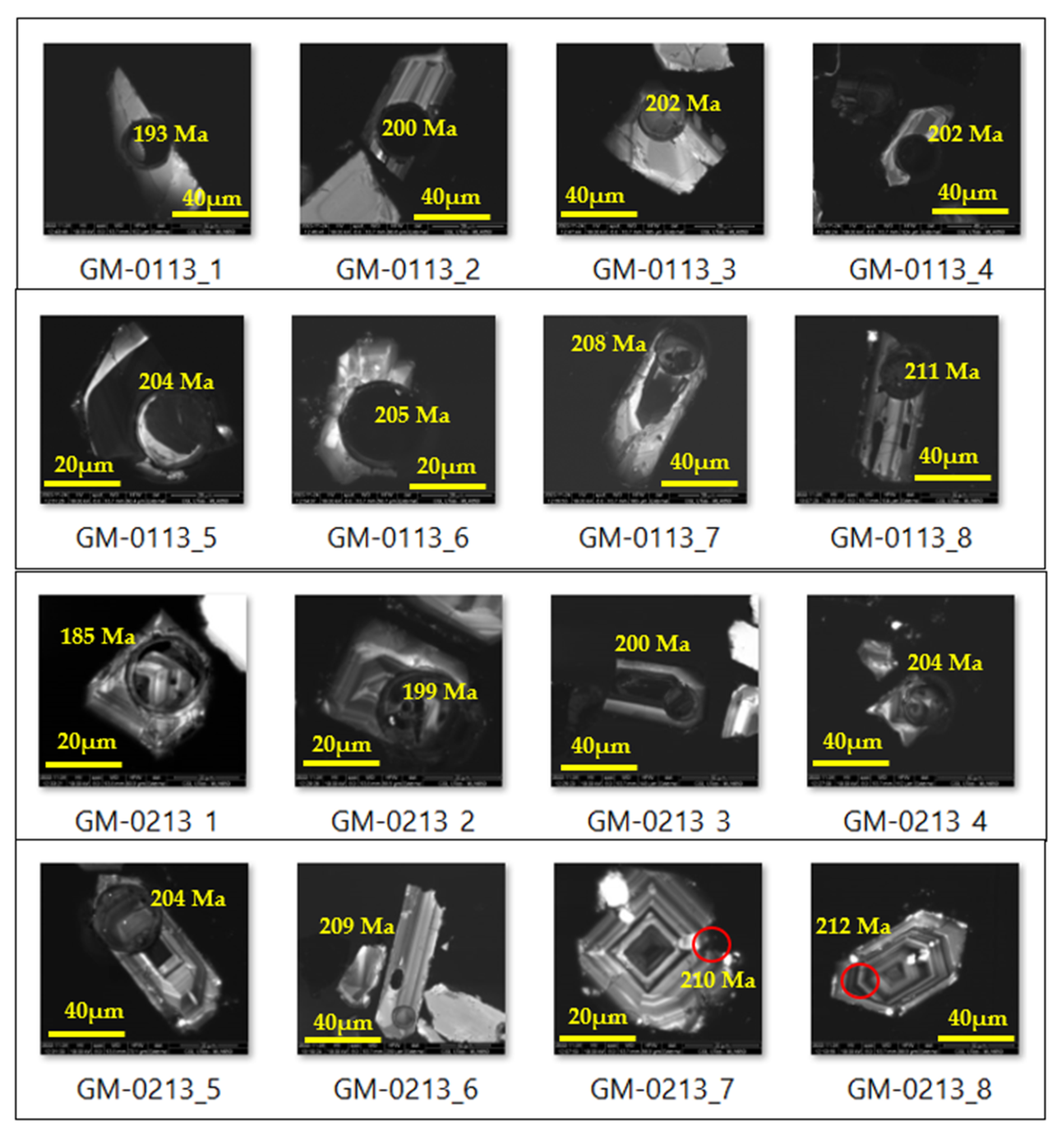
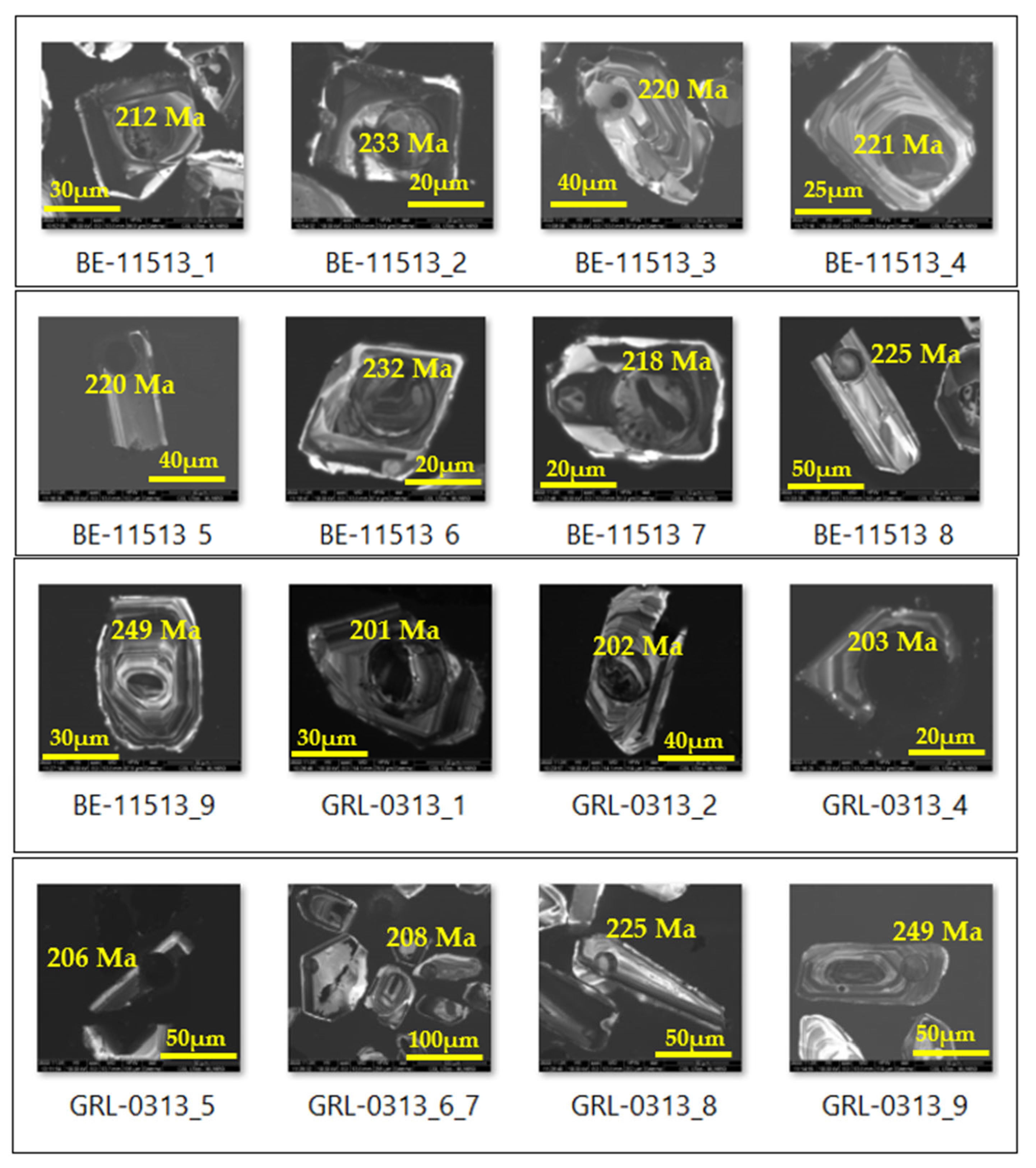
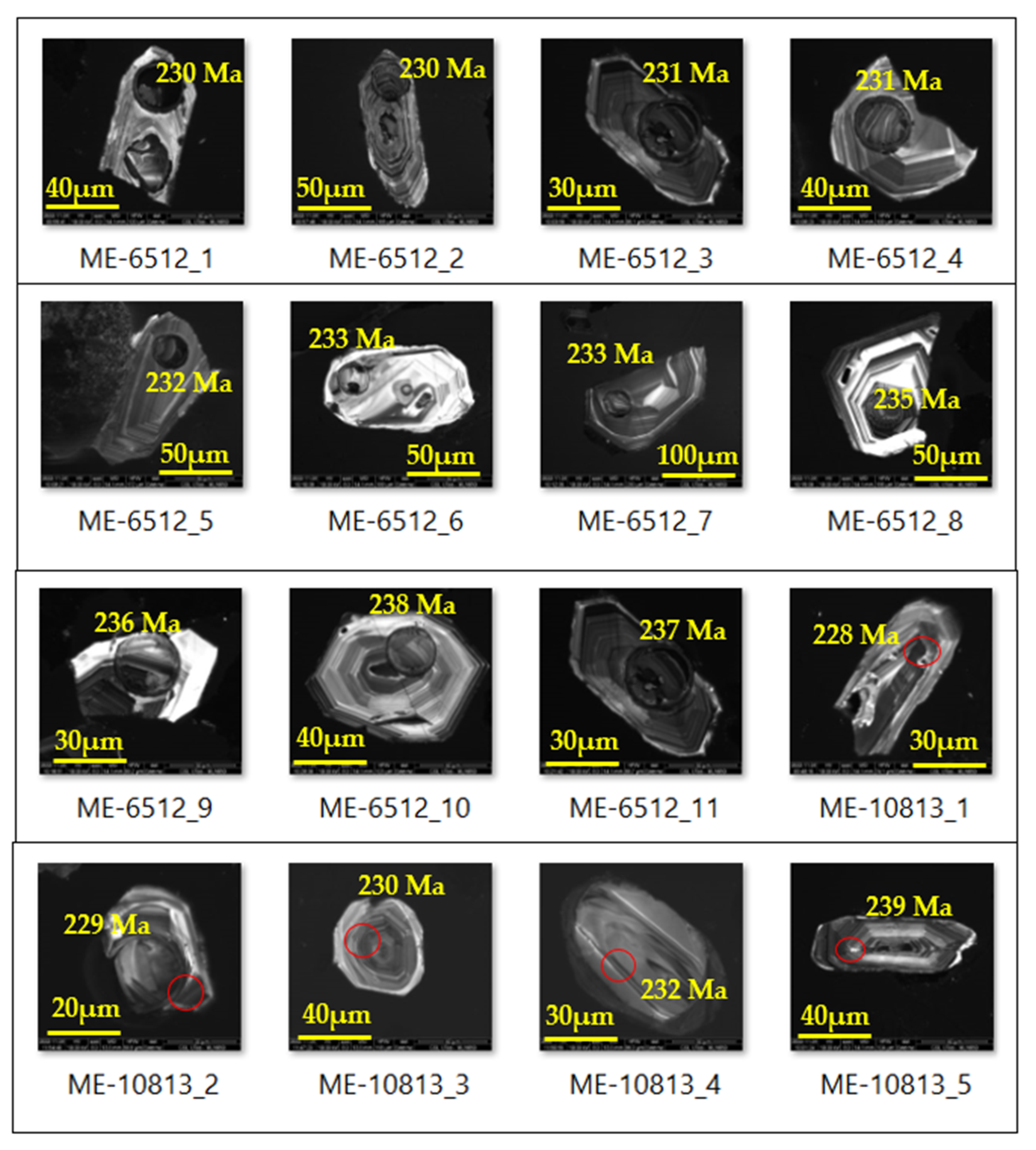
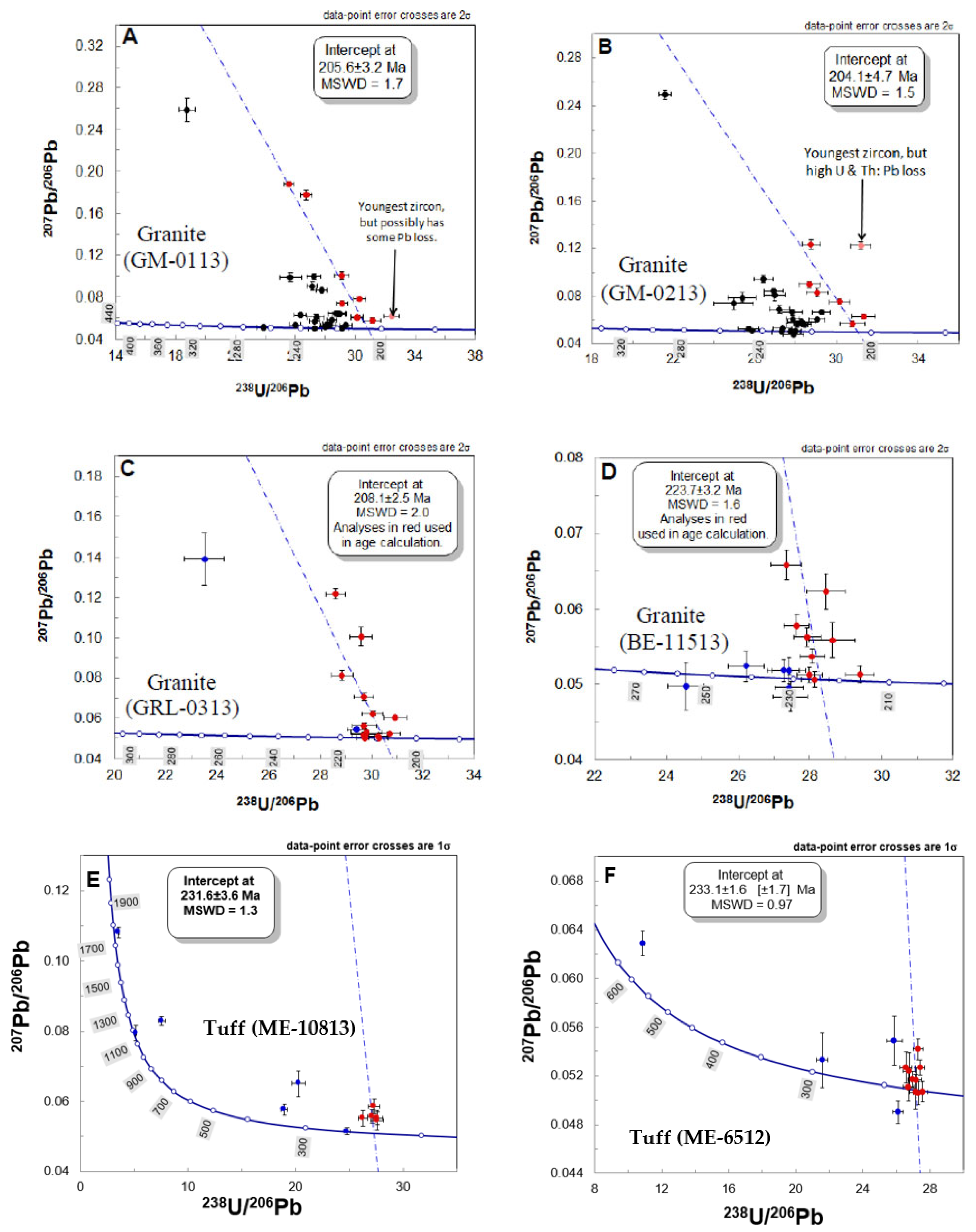
5.1. U-Pb Zircon Dating of Granite and Volcaniclastic Sediments
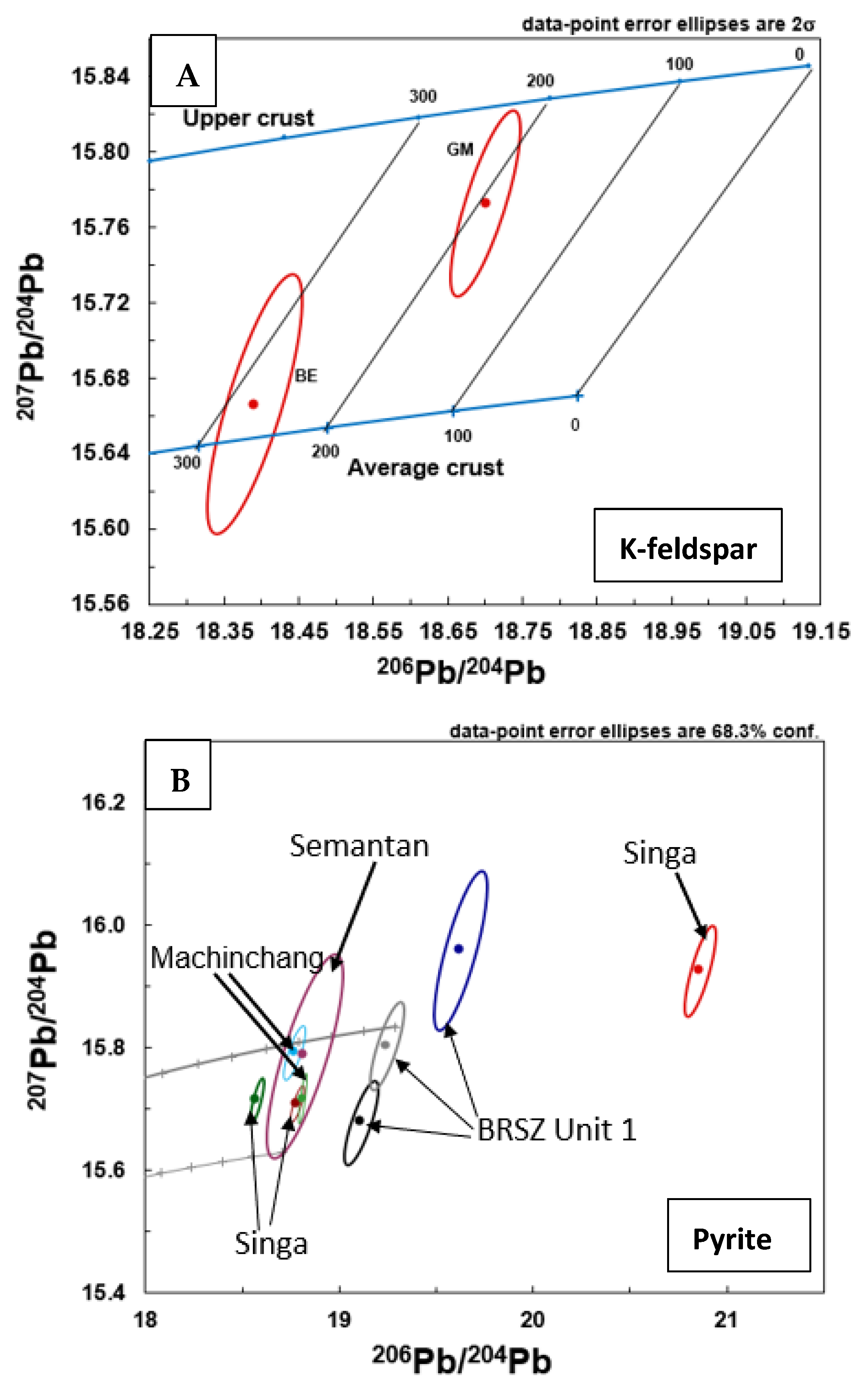
5.2. Lead Isotope from K-Feldspar
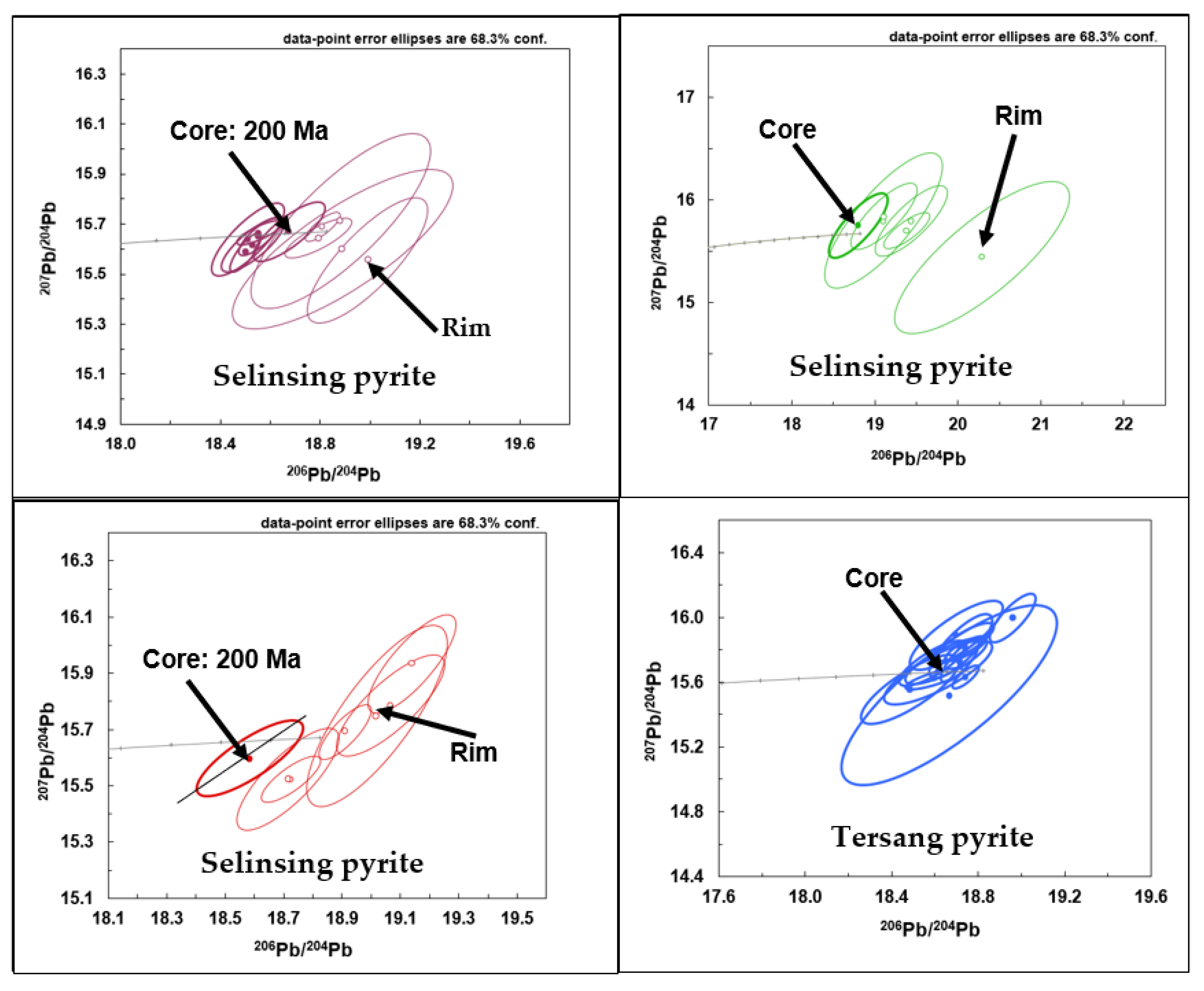
5.3. Pyrite Pb Isotope Composition
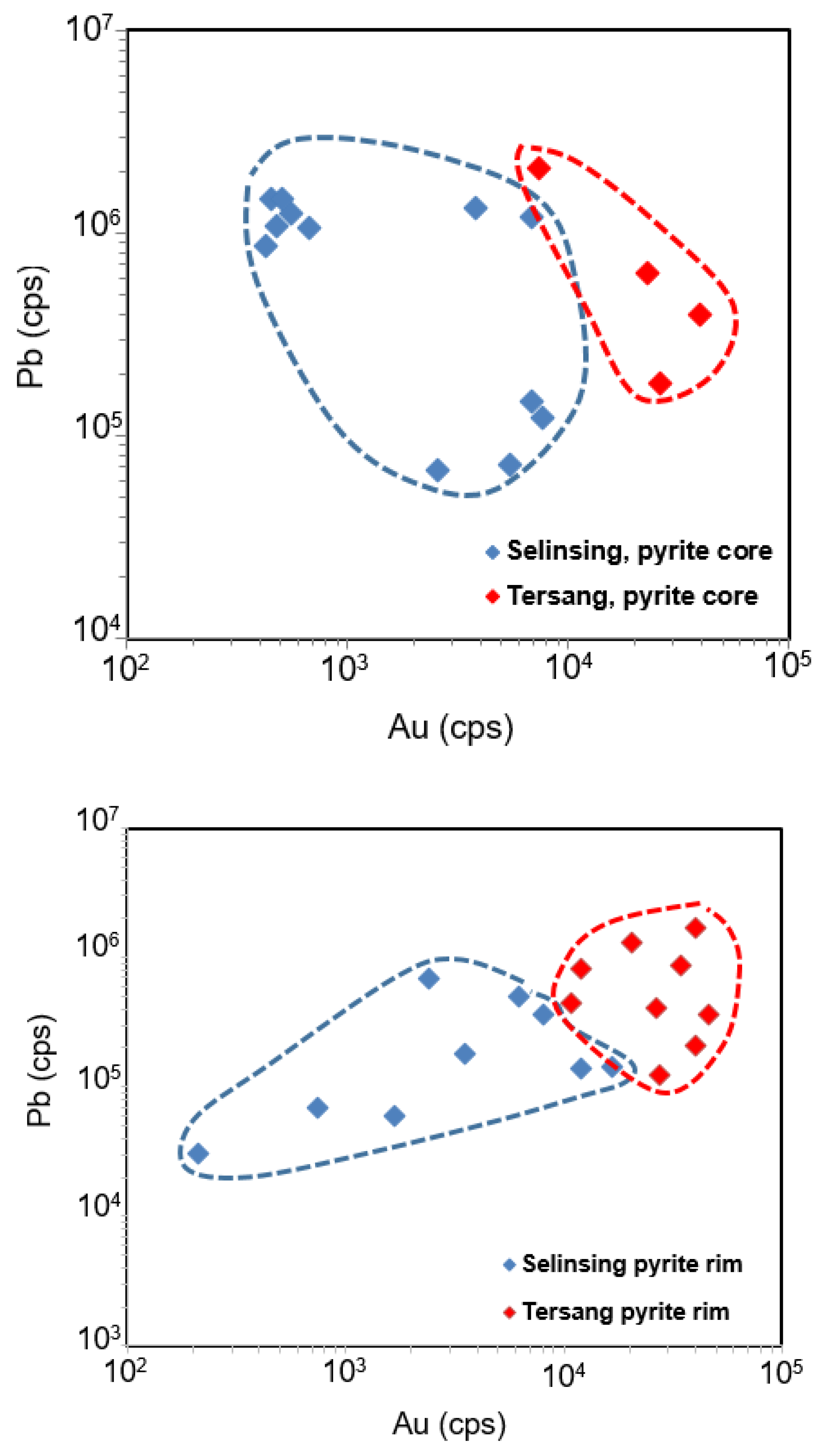
5.4. Trace Elements in Igneous Rock-Hosted Pyrite
5.5. Magnetic Susceptibility
6. Discussion
6.1. Zircon Age Dating
6.2. Pb Isotopes and Age of Gold Mineralization
6.3. Pyrite Trace Elements
6.4. Timing of Gold Mineralization Relative to Volcanism
6.5. Exploration Implications
- Au (Cu, Ag, Cd, Te, Pb)—for diorite-hosted pyrite
- Au (Cu, Zn, Cd, Te)—for granodiorite-hosted pyrite
- Au (Cu, Ni, Ag, Te, Pb)—for dolerite-hosted pyrite
- Au (Cu, Zn, As, Sn, Sb, Te, Pb)—for rhyolite-hosted pyrite
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, J.A. The Geology and mineral resources of the neighborhood of Raub, Pahang with an account of the Geology of the Raub Australian Gold Mine. Geol. Surv. Malays. Kuala Lumpur 1939, 3, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Yeap, E.B. Tin and gold mineralization in Peninsular Malaysia and their relationships to the tectonic development. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 1993, 8, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoundi, C. Geology, Geochemistry and Metallogenesis of Selected Sediment-hosted gold deposits in the Central Gold Belt, Peninsular Malaysia. Master’s Thesis, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zaw, K.; Meffre, S.; Lai, C.-K.; Burrett, C.; Santosh, M.; Graham, I.; Manaka, T.; Salam, A.; Kamvong, T.; Cromie, P. Tectonics and metallogeny of mainland Southeast Asia—A review and contribution. Gondwana Res. 2014, 26, 5–30. [Google Scholar]
- Makoundi, C.; Zaw, K.; Large, R.R.; Meffre, S.; Lai, C.K.; Hoe, T.G. Geology, geochemistry, and metallogenesis of the Selinsing gold deposit, Central Malaysia. Gondwana Res. 2014, 26, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endut, Z.; Tham Fatt, N.G.; Abdul Aziz, J.H.; Meffre, S.; Makoundi, C. Characterization of Galena and Vein Paragenesis in the Penjom Gold Mine, Malaysia: Trace Elements, Lead Isotope Study and Relationship to Gold Mineralization Episodes. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 1801–1840. [Google Scholar]
- Makoundi, C. Geochemistry of Black Shales, Sandstones; Chert in Malaysia: Insights into Gold Source Rocks. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Makoundi, C.; Zaw, K.; Large, R. Laser Ablation ICPMS Analysis of Pyrite and U-Pb Zircon Dating of Host Rocks from the Tersang Gold Deposit, Malaysia. AIMS Geosci. 2017, 3, 396–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatman, R.E.; Stacey, J.S. Lead isotope and mineralization ages in belt supergroup rocks, Northwestern Montana and Northern Idaho. Econ. Geol. 1971, 66, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatman, R.E.; Doe, B.R. Plumbotectonics—the model. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulson, B.L. Lead isotopes in mineral exploration. Dev. Econ. Geol. 1986, 23, 1–245. [Google Scholar]
- Rollinson, H.R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, R.S.; Pierce, A.P.; Antweiler, J.C.; Buck, K.L. The data of lead isotope geology related to problems of ore genesis. Econ. Geol. 1961, 56, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meffre, S.; Large, R.R.; Scott, R.; Woodhead, J.; Chang, Z.; Gilbert, S.E.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Maslennikov, V.; Hergt, J.M. Age and pyrite Pb-isotopic composition of the giant Sukhoi Log sediment-hosted gold deposit, Russia. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 2377–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, R.R.; Maslennikov, V.V.; Robert, F.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Chang, Z. Multistage Sedimentary and Metamorphic Origin of Pyrite and Gold in the Giant Sukhoi Log Deposit, Lena Gold Province, Russia. Econ. Geol. 2007, 102, 1233–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, R.R.; Danyushevsky, L.; Hollit, C.; Maslennikov, V.; Meffre, S.; Gilbert, S.; Bull, S.; Scott, R.; Emsbo, P.; Thomas, H.; et al. Gold and Trace Element Zonation in Pyrite Using a Laser Imaging Technique: Implications for the Timing of Gold in Orogenic and Carlin-Style Sediment-Hosted Deposits. Econ. Geol. 2009, 104, 635–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhu, L.; Yuan, H.; Lu, R.; Xiong, X.; Yang, T. Geology, Pb Isotope Geochemistry and Ore Genesis of the Liziyuan Gold Deposit, West Qinling Orogen, Central China. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2018, 92, 1082–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, C.; Gao, L.; Xia, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Arkin, K. Ore Genesis of the Kuergasheng Pb–Zn Deposit, Xinjiang Province, Northwest China: Constraints from Geology, Fluid Inclusions, and H–O–C–S Isotopes. Minerals 2020, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S.; Sparks, N.H.C.; Frankel, R.B.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Jannasch, H.W. Biomineralization of ferromagnetic greigite (Fe3S4) and iron pyrite (FeS2) in a magnetotactic bacterium. Nature 1990, 343, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Deditius, A.; Chryssoulis, S.; Li, J.W.; Ma, C.Q.; Parada, M.A.; Barra, F.; Mittermayr, F. Pyrite as a record of hydrothermal fluid evolution in a porphyry copper system: A SIMS/EMPA trace element study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 104, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellón, C.I.; Toro, N.; Gálvez, E.; Robles, P.; Leiva, W.H.; Jeldres, R.I. Froth Flotation of Chalcopyrite/Pyrite Ore: A Critical Review. Materials 2022, 15, 6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, D.L.; Sie, S.H.; Suter, G.F.; Cooke, D.R.; Both, R.A. Trace-elements in sulfide minerals from eastern Australian volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits. 1. Proton microprobe analyses of pyrite, chalcopyrite; sphalerite; 2. Selenium levels in pyrite—comparison with delta-s-34 values and implications for the source of sulfur in volcanogenic hydrothermal systems. Econ. Geol. 1995, 90, 1167–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Deditius, A.P.; Utsunomiya, S.; Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Ewing, R.C.; Hough, R.; Walshe, J. Trace metal nanoparticles in pyrite. In Proceedings of the Goldschmidt Conference 2010, Knocville, TN, USA, 13–18 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wakita, K.; Metcalfe, I. Ocean Plate Stratigraphy in East and Southeast Asia. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2005, 24, 679–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppie, D.F. How the closure of paleo-Tethys and Tethys oceans controlled the early breakup of Pangaea. Geology 2015, 43, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zou, H.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. The Mesozoic Closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean: Constraints from Zircon U–Pb Ages, Hf and Nd Isotopes of the Granitic Plutons in the Hoh-Xil-Songpan-Ganzi. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 94, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, I. The Bentong-Raub Suture Zone. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2000, 18, 691–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.; Rajah, S.; Askury, A.; Putthapiban, P.; Djaswadi, S. The Southeast Asian tin belt. Earth Sci. Rev. 1995, 38, 95–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Tamura, M. Myophoria in Malaya with a note on the Triassic Trigoniacea. In Geology and Paleontology of Southeast Asia; Kobayashi, T., Toriyama, R., Eds.; the University of Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1968; pp. 88–137. [Google Scholar]
- Makoundi, C. Facies analysis of the Triassic Jelai Formation in the Central Basin of Peninsular Malaysia: Implications on paleogeography and tectonics. Master’s Thesis, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Proctor, W.D. Geology and Mineral Resources Benta area, Pahang. Geological Survey of Malaysia. Map Bull. 1972, 4, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Gobbett, D.J.; Hutchison, C.S. Geology of the Malay Peninsular: West Malaysia and Singapore; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1973; p. 438. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.K. The tectonic framework and evaluation of the Central Belt and its margin, Peninsular Malaysia. Geol. Soc. Malays. Bull. 1984, 17, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leman, M.S. The significance of Upper Permian Brachiopods from Merapoh area, northwest Pahang. Geol. Soc. Malays. Bull. 1994, 35, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, I. Permian tectonic framework and palaeogeography of SE Asia. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2002, 20, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustaffa, K.; Hadi, A.; Rahman, A. A fivefold stratigraphic and tectonic subdivision of Peninsular Malaysia. In Dynamic stratigraphy and tectonics of Peninsular Malaysia—Problems and Issues; Geological Society of Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1999; pp. 38–63. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, G.; Zaw, K.; Hoston, M. Dating rocks in Singapore: Plate tectonics between 280 and 200 million years ago. Singap. Mag. Res. 2011, 10, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bignell, J.D.; Snelling, N.J. K-Ar ages on some basic igneous rocks from Peninsular Malaysia and Thailand. Bull. Geol. Soc. Malays. 1977, 8, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, T.C.; McCulloch, M.T. Genesis of granitoid batholiths of Peninsular Malaysia and implications for models of crustal evolution: Evidence from Nd-Sr isotopic and U-Pb zircon study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, A.A. Geochemical characteristics of S- and I-Type Granites: Example from Peninsular Malaysia granites. Bull. Geol. Soc. Malays. 2005, 51, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoundi, C.; Zaw, K.; Endut, Z. Fluid Inclusion Study of the Penjom, Tersang, and Selinsing Orogenic Gold Deposits, Peninsular Malaysia. Minerals 2020, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, M.A.; Alle, P.; Corfu, F.; Griffin, W.L.; Meier, M.; Oberli, F.V.; von Quadt, A.; Roddick, J.C.; Spiegel, W. Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace element and REE analyses. Geostand. Newsl. 1995, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, L.P.; Kamo, S.L.; Allen, C.M.; Aleinikoff, J.N.; Davis, D.W.; Korsch, R.J.; Foudoulis, C. TEMORA 1: A new zircon standard for Phanerozoic U–Pb geochronology. Chem. Geol. 2003, 200, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.E.; Pearson, N.J.; Griffin, W.L.; Belousova, E.A. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U–Pb zircon geochronology. Chem. Geol. 2004, 211, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, L.P.; Gulson, B.L. The age of the Mud tank Carbonatite, Strangways Range, Northern Territory. BMR J. Aust. Geol. Geophys. 1978, 3, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.; Peate, D.; Waight, T.; Meyzen, C. Pb isotopic analysis of standards and samples using a Pb207/Pb204 double spike and thallium to correct for mass bias with a double-focusing MC-ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2004, 211, 275–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, L.P.; Kamo, S.L.; Allen, C.M.; Davis, D.W.; Aleninikoff, J.N.; Valley, J.W.; Mundil, R.; Campbell, I.H.; Korsch, R.J.; Williams, I.S.; et al. Improved 206Pb/238U microprobe geochronology by the monitoring of a trace-element related matrix effect; SHRIMP, ID-TIMS, ELA-ICP-MS; oxygen isotope documentation for a series of zircon standards. Chem. Geol. 2004, 205, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.; Woodhead, J.D.; Hellstrom, J.C. Improved laser ablation U-Pb zircon geochronology through robust down-hole fractionation correction. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2010, 11, 1525–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosler, J. Laser-ablation ICPMS study of metamorphic minerals and processes. In Laser-Ablation-ICPMS in the Earth Sciences; Principles and Applications: Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Handbook; Sylvester, P.J., Ed.; Mineralogical Association of Canada: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2001; pp. 185–202. [Google Scholar]
- Danyushevsky, L.V.; Robinson, P.; Gilbert, S.; Norman, M.; Large, R.R.; McGoldrick, P.; Shelley, J.M.G. Routine quantitative multi-element analysis of sulfide minerals by laser ablation ICP-MS: Standard development and consideration of matrix effects. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2011, 11, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousov, I. New calibration standard for LA-ICPMS analysis of sulphides. AGU, 2014 Fall Meeting. Available online: https://agu.confex.com/agu/fm14/webprogram/Paper19453.html (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Belousov, I.A.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Olin, P.H.; Gilbert, S.E.; Thompson., J. STDGL3: A new calibration standard for sulphide analysis by LAICP-MS. In Proceedings of the 25th Goldschmidt Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, 16–21 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jochum, K.; Enzweiler, J. Reference Materials in Geochemical and Environmental Research. Analytical Geochemistry/Inorganic Instrumental Analysis, 2nd. ed; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 15, pp. 43–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, S.E.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Rodemann, T.; Shimizu, N.; Gurenko, A.; Meffre, S.; Thomas, H.; Large, R.R.; Death, D. Optimisation of laser parameters for the analysis of sulphur isotopes in sulphide minerals by laser ablation ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2014, 29, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulana, A.; Watanabe, K.; Imai, A.; Yonezu, K. Origin of Magnetite- and Ilmenite-series Granitic Rocks in Sulawesi, Indonesia: Magma Genesis and Regional Metallogenic Constraint. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2013, 6, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaseca, C.; Ruiz-Martinez, V.C.; Perez-Soba, C. Magnetic susceptibility of Variscan granite-types of the Spanish Central System and the redox state of magma. Geol. Acta Int. Earth Sci. J. 2017, 15, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, J.S.; Kramer, J.D. Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two-stage model. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1975, 26, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P.W.O.; Schaltegger, U. The Composition of Zircon and Igneous and Metamorphic Petrogenesis. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2003, 53, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Lu, Y.; Chen, L.-M.; Song, X.-Y.; Deng, Y.-F.; Zhao, Y. Zircon Th/U ratios suggest a post-collision extensional setting for the Permian Ni-Cu sulfide deposits in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 144, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 1554–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, M.A.; Aleinikoff, J.N.; Marcos, A.; Martínez, F.J.; Llana-Fúnez, S. An example of low-Th/U zircon overgrowths of magmatic origin in a late orogenic Variscan intrusion: The San Ciprián massif (NW Spain). J. Geol. Soc. 2015, 173, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castineiras, P.; Barneiro, J.G.; Fernandez, F.J.; Aguilar, C.; Perez, J.M.B. Reso;ving uncertainties in the application of zircon Th/U and CL gauges to interpret U-Pb ages: A case study of eclogites in polymetamorphic terranes of NW Iberia. Solid Earth Discuss. 2020, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbyshire, D.P.F. South-East Asia Granite Project: Geochronology of Malaysian Granites. Nat. Environ. Res. Counc. Isot. Geol. 1988, 88, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Ghani, A.A.; Searle, M.P.; Robb, L.J.; Chung, S.-L. Transitional I-S type characteristic in the Main Range Granite, Peninsular Malaysia. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 76, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, I. Tectonic evolution of the Malay Peninsula. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 76, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.W.-P.; Whitehouse, M.; Searle, M.P.; Robb, L.J.; Ghani, A.A.; Chung, S.-L.; Oliver, G.J.; Sone, M.; Gardiner, N.; Roselee, M.H. Petrogenesis of Malaysian granitoids in the Southeast Asian tin belt: Part 2. U-Pb zircon geochronology and tectonic model. GSA Bull. 2015, 127, 1238–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivenor, J.B. The Geology of Malayan Ore Deposits; Macmillan: London, UK, 1928; 216p. [Google Scholar]
- Ingham, F.T. The geology of the neighborhood of Tapah and Telok Anson, Perak, F.M.S with accounts of mineral deposits. Geol. Surv. Dep. Fed. Malaya Mem. 1938, 2, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Bogie, I. Petrology Report on 15 Samples from the Penjom Gold Mine, Malaysia; Internal Report for Specific Resources; Sdn. Bhd: Malaysia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagi, H.M.; Fan, H.-R. An oxidized intrusion-related origin in the controversial Jiaodong gold province (China) for the Shicheng Au-Cu deposit. All Earth 2021, 33, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makoundi, C.; Zaw, K.; Endut, Z. U-Pb Dating, Lead Isotopes, and Trace Element Composition of Pyrite Hosted in Black Shale and Magmatic Rocks, Malaysia: Implications for Orogenic Gold Mineralization and Exploration. Minerals 2023, 13, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13020221
Makoundi C, Zaw K, Endut Z. U-Pb Dating, Lead Isotopes, and Trace Element Composition of Pyrite Hosted in Black Shale and Magmatic Rocks, Malaysia: Implications for Orogenic Gold Mineralization and Exploration. Minerals. 2023; 13(2):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13020221
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakoundi, Charles, Khin Zaw, and Zakaria Endut. 2023. "U-Pb Dating, Lead Isotopes, and Trace Element Composition of Pyrite Hosted in Black Shale and Magmatic Rocks, Malaysia: Implications for Orogenic Gold Mineralization and Exploration" Minerals 13, no. 2: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13020221
APA StyleMakoundi, C., Zaw, K., & Endut, Z. (2023). U-Pb Dating, Lead Isotopes, and Trace Element Composition of Pyrite Hosted in Black Shale and Magmatic Rocks, Malaysia: Implications for Orogenic Gold Mineralization and Exploration. Minerals, 13(2), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13020221








