Abstract
Lacustrine sediments are good recorders of palaeoenvironment changes and have been widely studied in recent years. The study of lacustrine sediments in Southwest China will improve our understanding of the complex environmental evolution history of Southwest China. Therefore, this paper presents a high-resolution rock magnetism study from the Pengtun drilling hole (PT2) in the Heqing Basin, Southwest China. The results show that the dominant magnetic minerals in the PT2 drill core are magnetite, maghemite and haematite. The magnetic susceptibility (χ) of the upper part of the core (0–13.5 m) is lower than that of the lower part (13.5–33.5 m). There is no maghemite in the upper sections. The minerals with high χ values have the characteristics of pseudosingle-domain (PSD), single-domain (SD), superparamagnetic (SP) and multidomain (MD) grains. The magnetic domains are widely distributed, and the particles are coarser. When χ is low, the magnetic domains of the different samples vary greatly, and the particles are finer. Combined with the magnetic and nonmagnetic characteristics of the sediment, we infer that the change in χ in the PT2 drill core is related to clastic input, water erosion, and reductive dissolution.
1. Introduction
The Asian monsoon is an important part of the global climate system. It connects climate change across high, middle, and low latitudes and affects the local environment and humanity through events such as rainfall or weather disasters [1]. The mechanism driving the Asian monsoon is related to the seasonal migration of the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ). The Asian monsoon is also influenced by sea–land thermal differences and the regional topography [2,3]. The Asian monsoon brings abundant heat and moisture inland from low latitudes. People in monsoon areas are affected by monsoon floods [4]. The systematic study of the Asian monsoon can help us understand the processes involved in contemporary climate evolution and help humanity develop a more harmonious relationship with the land [5]. When studying the Asian monsoon, studies of the southwest monsoon (Indian monsoon) that encompass long-time scales and have high resolutions are essential. The Heqing basin, located on the southeast edge of the Tibetan Plateau uplift zone, consists of a structural fault within a subsidence basin. It is not only a transitional zone between the Tibetan Plateau and the subtropical lowlands but also a transitional area between the Indian monsoon region and the southeast monsoon region. The Heqing basin contains thick lacustrine sediment, which provides an excellent opportunity to explore the evolution of the Indian monsoon and the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau [6,7,8].
At present, high-resolution research on the Indian monsoon has achieved many results. Examples of this research include stalagmite records from the Indian subcontinent and southwestern China [9,10,11], marine sediments from the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal [12,13,14,15], and lacustrine sediments from southwestern China [16,17]. Additionally, the methods of researching lake sediments are constantly updated and improved [8,18,19,20]. Rock magnetism has been widely used in studies of paleoenvironmental changes and erosion history in recent years [21,22] because it requires only a small sample amount, offers high sensitivity, and is convenient. Rock magnetism is the basis of paleoenvironmental references for environmental magnetic parameters. Magnetic parameters are related to the concentration, mineralogy and grain size of magnetic components. Rock magnetism is often influenced by a series of processes related to physical, chemical and biological changes. Thus, the interpretation of magnetic parameters within paleoenvironmental and paleoclimatic studies (e.g., identifying the enhance mechanisms that the magnetic susceptibility of lacustrine sediments in SW China) remains controversial.
Peng [23] and Xu et al. [22] suggest that the increase in magnetic susceptibility may be related to the presence of maghemite. This is different from the view of Hu et al., who assert that “the presence of magnetite is the reason for the high susceptibility”. Therefore, rock magnetism and environmental magnetism analyses of the Pengtun (PT2) core recovered from the Heqing Basin are presented here. AMS 14C dating was accomplished at the Radiocarbon Laboratory of the Institute of Earth Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Table 1). The dating results were calibrated using the CALIB 7.0, and the INTCAL13 calibration curve [24]. The objectives of this paper are to further understand the characteristic variation in magnetic susceptibility in the Heqing Basin, to explore the internal mechanism driving magnetic parameter variability and to expand the understanding of paleoenvironmental changes in the Heqing Basin.

Table 1.
Radiocarbon dates from the PT2 drill core.
2. Study Area
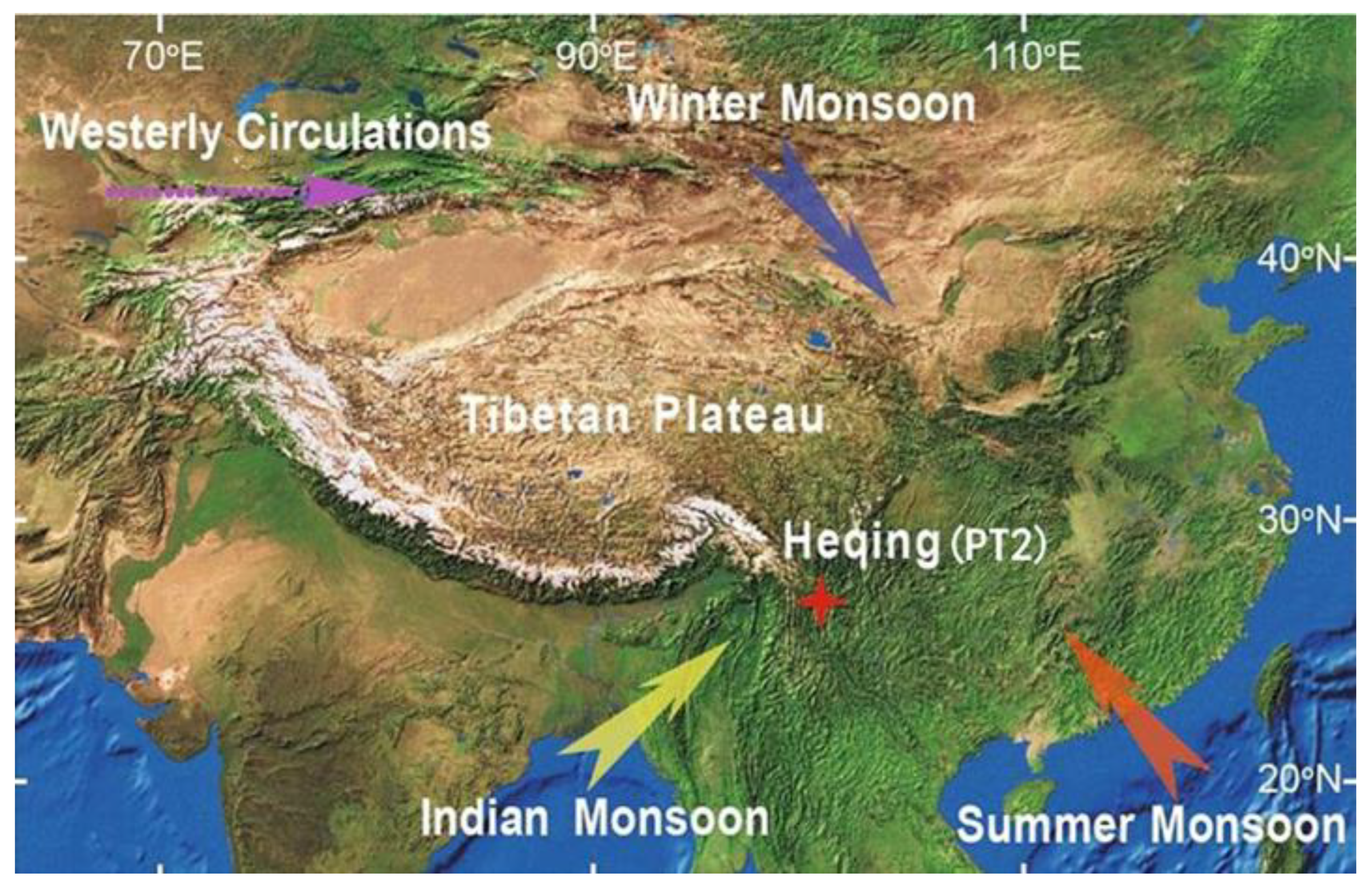
The Heqing Basin (26°27′~26°46′ N, 100°08′~100°17′ E) is located in Heqing County, northwest Yunnan Province, and consists of a long strip of land oriented from south to north, which is consistent with the strike of the structural belt [25] (Figure 1). The Heqing Basin covers an area of ~144 km2. It is bounded by continuous and high mountains to the east and west, lower mountains to the south, and Yulong Snow Mountain to the north. The average elevation of the Heqing Basin is approximately 2193 m above sea level. Furthermore, it is situated in the middle of the Honghe deep fault that extends northwards and the Jinsha River deep fault, which belongs to the Hengduanshan residual vein in northwest Yunnan [26]. The basin bedrock is mainly composed of limestone, calcareous conglomerate, sandstone, and silty shale [17]. The local climate is dominated by warm and humid air from the Bay of Bengal in summer and by the southwesterly jet in winter [25]. The local climate is also related to the local climate of the Tibetan Plateau, which means that it is warm and humid in summer and dry in winter. The Heqing Basin has a mean annual temperature of 13.5 °C. The annual average precipitation is between 900 and 1000 mm and is mainly concentrated in summer.
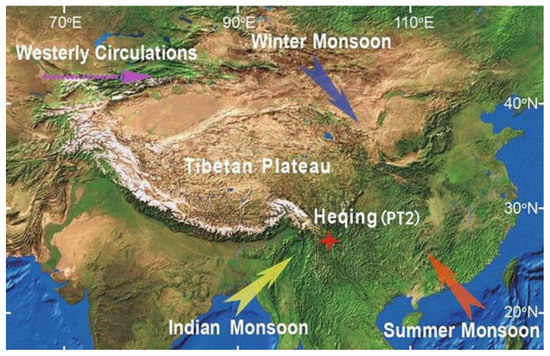
Figure 1.
Location of the study area, redrawn after An et al., 2011 [25].
The core collected from the Pengtun No. 2 hole (PT2), 2 km away from Heqing County, was obtained in Caohai Town, Heqing County, Pengtun Village. The geographic coordinates are 26°35′24.0″ N,100°11′08.2″ E, and the wellhead is 2188 m above sea level. According to the difference in lithology, the sedimentary sequence can be divided into an upper part (0–13.5 m) and a lower part (13.5–33.9 m).
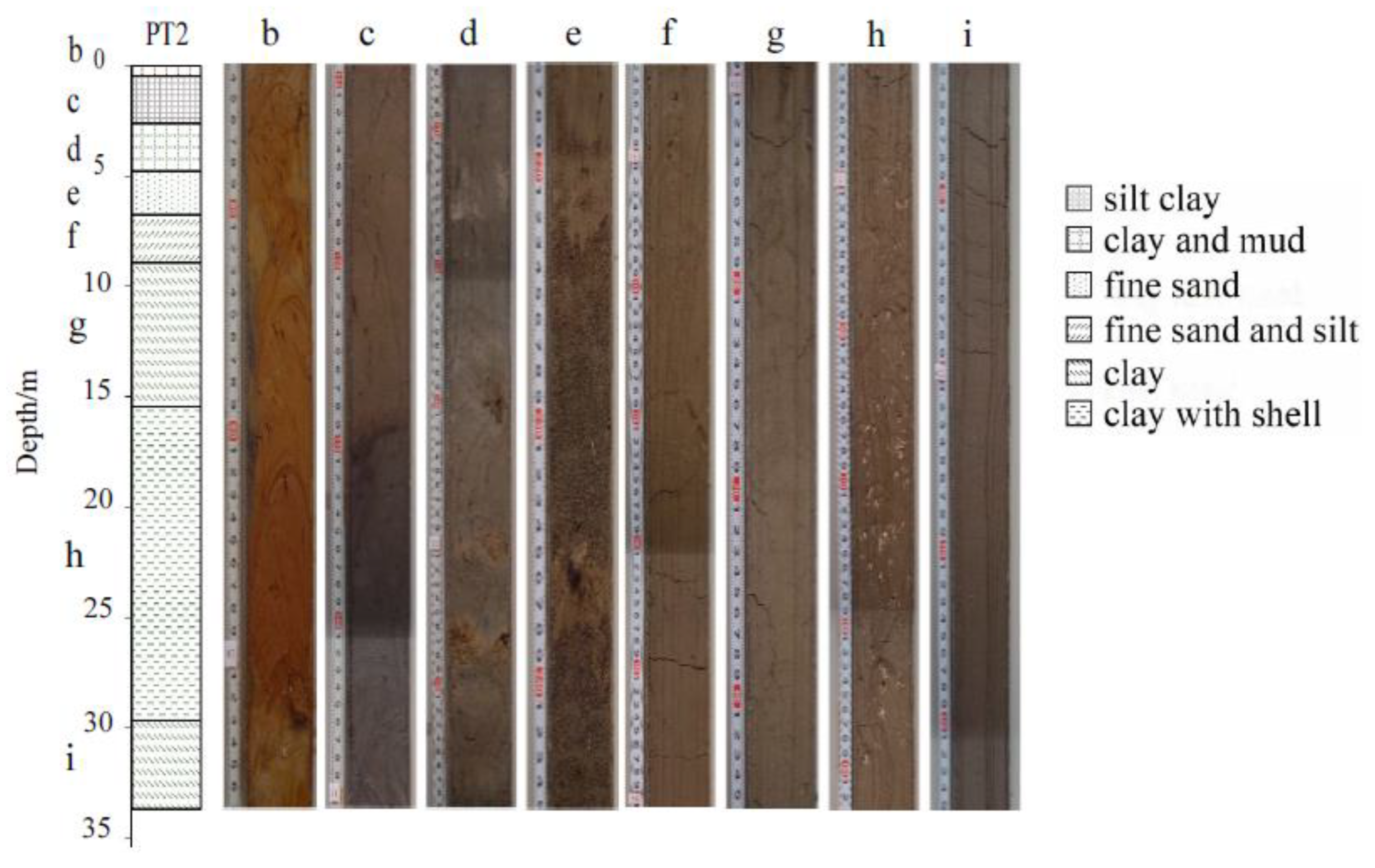
The sediments in PT2 drill core are mainly green-grey and brownish red clay, and the upper part has obvious colour variations and a more complex lithology. The lower lithology is relatively simple and is composed, mainly of green-grey clay and contains a shell (Figure 2). The deposition is described in detail as follows:
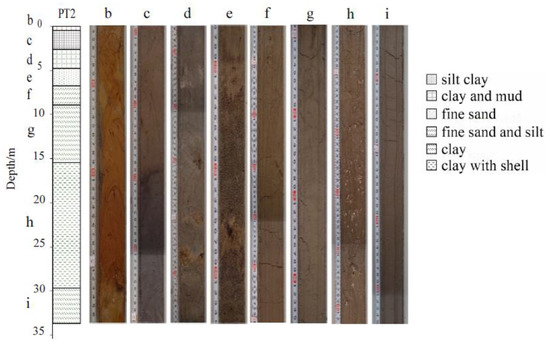
Figure 2.
Lithology of core PT2 and the typical photograph of various parts of the core sediment.
- 0–0.22 m, brownish red clay;
- 0.22–0.68 m, brownish red clay at the top, grey mud at the bottom;
- 0.68–2.85 m, grey mud at the top, green-grey silty clay at the bottom;
- 2.85–4.98 m, green-grey clay with brown peat visible in the middle;
- 4.98–6.96 m, green-grey fine sand with two layers of lignite in the middle;
- 6.96–9.14 m, green-grey fine sand at the top, green-grey clay at the bottom;
- 9.14–15.65 m, green-grey clay;
- 15.65–29.85 m, green-grey clay, contains shell debris;
- 29.85–33.87 m, green-grey clay.
In this study, a detailed rock magnetic analysis was carried out on the drill core from PT2. We discuss the mechanisms that impact the magnetic properties and the geographical environment changes of each depositional unit in this area.
3. Materials and Methods
We collected U-Channel samples from the PT2 drill core, performed alternating demagnetization experiments at intervals of 2 cm, and then measured the environmental magnetic parameters such as the anhysteretic remanent magnetization (ARM) and the isothermal remanent magnetization (IRM). The magnetic susceptibility was measured with a Bartington MS2 magnetic susceptibility instrument at frequencies of 4700 Hz (high) and 470 Hz (low) in turn, and normalized by mass. χ is often used to indicate low-frequency susceptibility. The ARM was obtained in a direct-current field of 0.05 mT and a superimposed alternating field with a peak of 80 mT. Then, the gradual alternating demagnetization of the ARM was performed according to 2 mT, 5 mT, 10 mT, 20 mT, 30 mT, 40 mT, 50 mT, 60 mT, and 80 mT. The saturation isothermal remanent magnetization (SIRM) was obtained using a pulse magnetometer with a 1 T pulse field and then demagnetized at magnetic fields of 2 mT, 5 mT, 10 mT, 20 mT, 30 mT, 40 mT, 50 mT, 60 mT, and 80 mT. ARM/SIRM were used to reflect the changes in size of magnetic minerals, especially ferromagnetic minerals. χfd (frequency characteristic of magnetic susceptibility) can be used to show the absolute concentration of superparamagnetic particles [27]. χfd = χlf − χhf (χlf is low-frequency susceptibility, and χhf is high-frequency susceptibility). Finally, collecting samples at 5 cm intervals, air-drying, grinding, and compacting were carried out, and the Ti value was measured with an Axios advanced wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer.
A total of 24 samples were selected at the crest and trough of the χ wave to conduct detailed rock magnetic testing. The χ-T curve was measured using an MFK1FA Kappabridge in an argon atmosphere. The heating system used was a CS-3 type high-temperature furnace; the heating range was 40–700 °C. Each sample had a mass of approximately 0.25 g. The IRM acquisition curves, hysteresis loops and first-order reversal curve (FORC) were obtained by a MicroMag3900 vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The saturation magnetization (Ms), saturation remanent magnetization (Mrs), coercivity (Bc) and coercivity of remanence (Bcr) were obtained at the same time. The FORC diagram was processed with FORCinelv.1.18 [28], and the smoothing factor was 3–5.
All measurements were carried out in the Laboratory of Environmental Magnetism, Xi’an Institute of Earth Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
4. Results
4.1. χ, ARM, SIRM, and ARM/SIRM
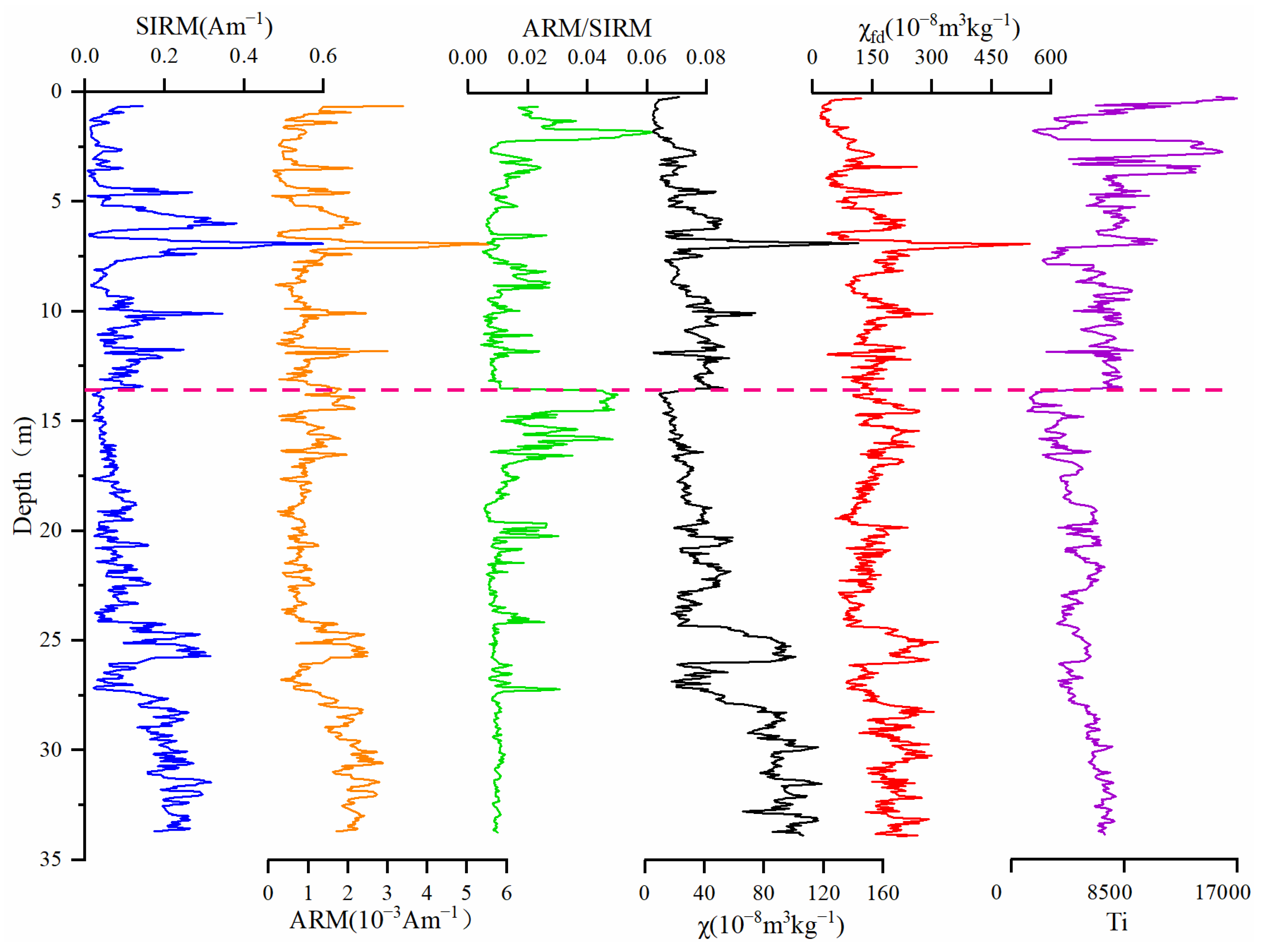
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) is commonly used to determine the concentration of ferrimagnetic minerals [19,27]. The maximum value of χ is 265.48 × 10−8 m3/kg. The minimum value is 5.19 × 10−8 m3/kg, and the average value is 46.41 × 10−8 m3/kg. χfd and χ change in the same way (Figure 3). χ decreases from bottom to top, indicating that the ferrimagnetic minerals contents decreases. χfd represents the decrease in superparamagnetic particles. SIRM also reflects the concentration of ferromagnetic minerals. This showed a similar change as χ (Figure 3). Compared with χ, SIRM had a weak overall decreasing trend, a larger change in the upper part (0–13.5 m) and a smaller change in the lower part (13.5–33.5 m). ARM is more susceptible to the influence of single-domain particles and was used to reflect the absolute content of single-domain particles [19]. Therefore, ARM/SIRM is often used to reflect the relative content of single-domain particles. Compared to the ARM/SIRM ratio, the ARM and SIRM values change in phase within the PT2 drill core (Figure 3). This suggests that the magnetic properties of the sediments are mainly affected by the changes in magnetic mineral content, which originate from terrigenous input [29,30].
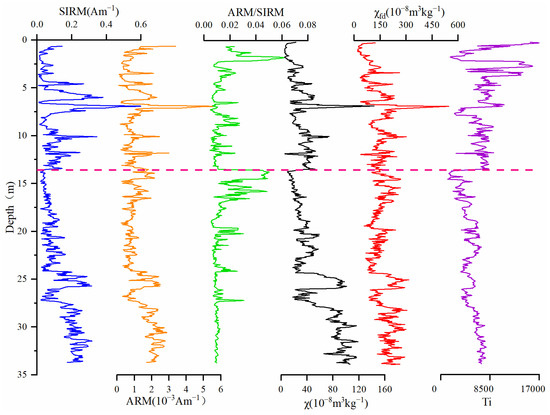
Figure 3.
SIRM, ARM, ARM/SIRM, χ, χfd, and Ti of the PT2 drill core. They are shown in blue, orange, green, black, red and purple. Additionally, there is a pink line at 13.5 m that divides the entire core into upper (0−13.5 m) and lower (13.5−33.5 m).
4.2. Temperature-Dependent Magnetic Susceptibility (χ-T)
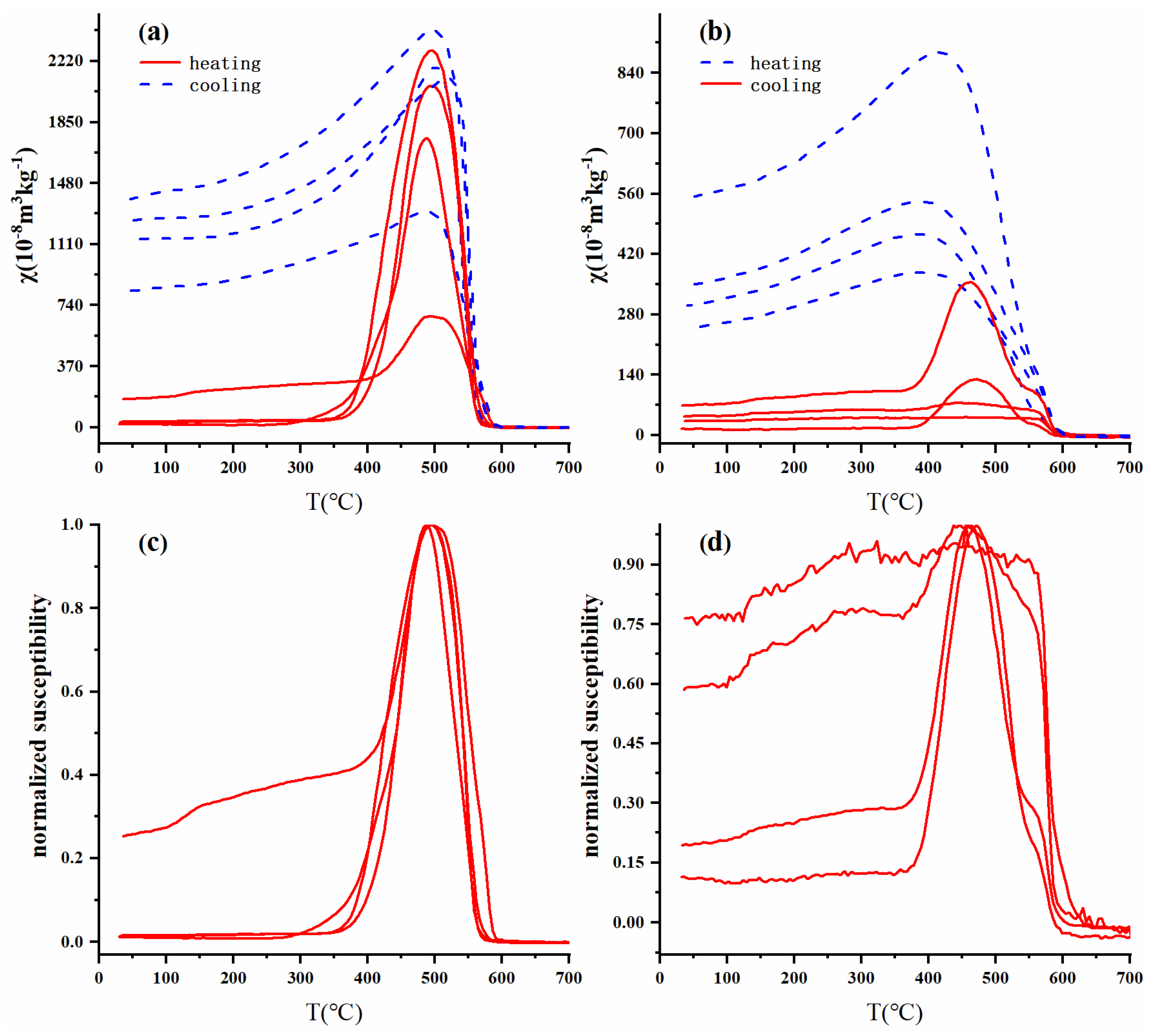
The magnetic components in representative samples can be identified according to the temperature dependence of magnetic susceptibility (χ-T curve) [30,31,32]. We normalized the curves obtained (Figure 4c,d). As shown in Figure 2, all the final values after cooling were higher than the initial values before heating. This indicates that new minerals may have been formed during heating.
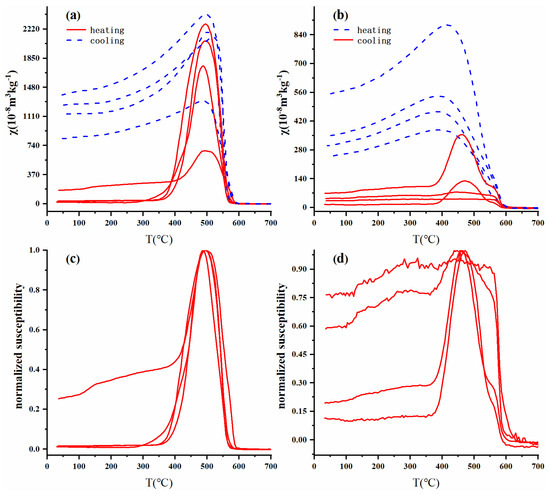
Figure 4.
High-temperature magnetic susceptibility (χ-T curves) of typical samples from core PT2. (a,c) and (b,d) represent samples with high χ values and low χ values, respectively, and (c,d) represent the heating curve after normalization.
There were some differences between the upper and lower parts of the χ-T curve. In the upper part of the sediment (0–13.5 m) (Figure 4c), the χ-T curve increased slowly as the temperature increased from 0 to 400 °C and began to significantly increase at approximately 400 °C. The increase is mainly due to the formation of a large number of magnetic minerals, which may be caused by the decomposition of iron-containing clay minerals and/or silicates [33,34]. χ reached a peak at approximately 500 °C and then decreased rapidly, which may indicate the Hopkinson effect of magnetite or the formation of ferrimagnetic minerals [22,35,36]. Finally, the curve decreased rapidly at 580 °C and did not fall to the lowest value near 600 °C, implying the presence of magnetite and haematite in the sample [33,37,38]. In the lower part of the sediment (13.5–33.5 m) (Figure 4d), some samples showed a decline at 300–400 °C in the χ-T curve, which may be attributed to the conversion of thermally unstable maghemite to haematite [32,39,40].
4.3. IRM Acquisition Curve and Hysteresis Loops
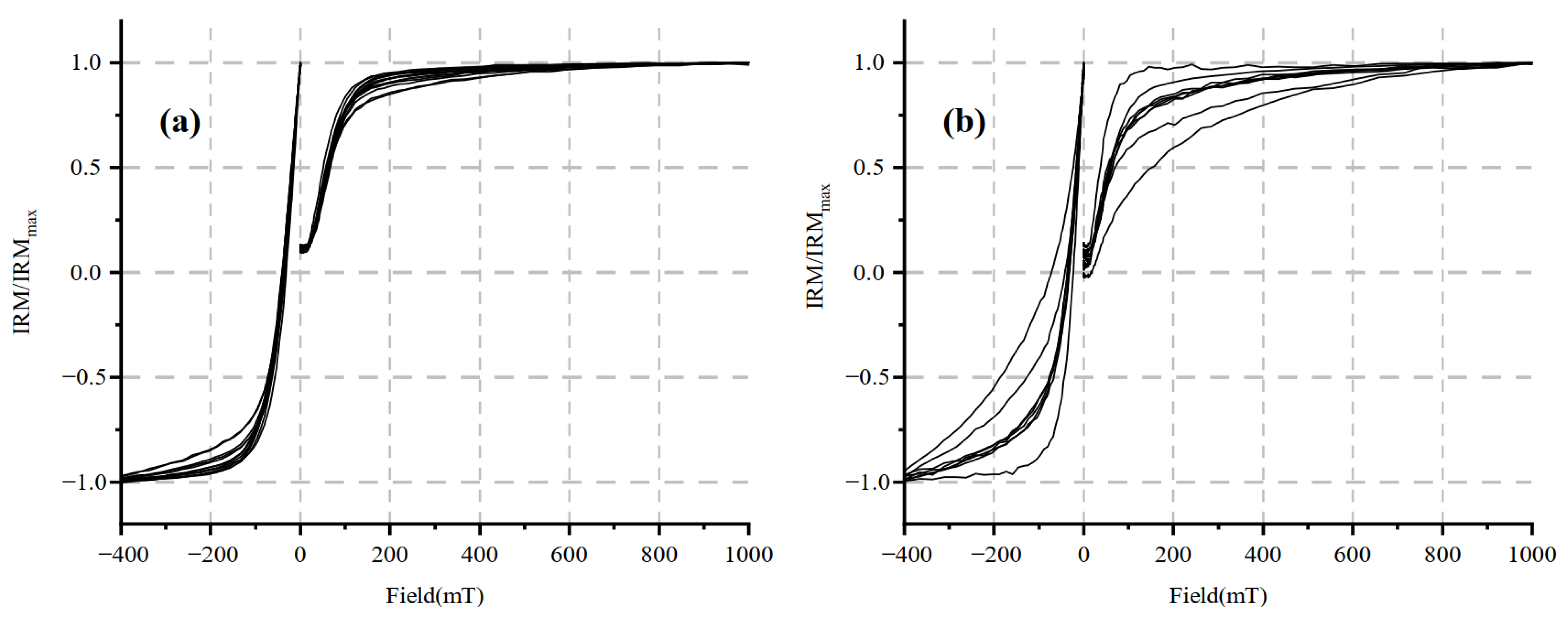
The IRM acquisition curves in the upper part of the sediment are more dispersed, while those in the lower part are more concentrated. The IRM acquisition curves for the high χ sample rise rapidly below 100 mT, reach 90% of the SIRM values at 200 mT and are close to the highest value but are not saturated in the range of 600–800 mT (Figure 5a). Most of the IRM acquisition curves for the low χ samples reached 80% of the SIRM values at 200 mT but were not saturated at 1000 mT (Figure 5b). These results indicate that the sediment is mainly composed of low-coercivity magnetite and maghemite. There are a few hard magnetic minerals that exist [38]. The maximum value of Bcr is 72.35 mT, the minimum value is 23.30 mT and the average value is 38.05 mT. The hysteresis loops of the samples also show similar characteristics.
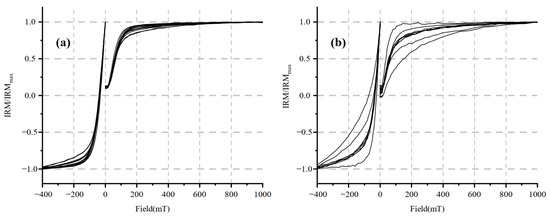
Figure 5.
Isothermal remanent magnetization (IRM) acquisition curves for core PT2, (a) high χ value samples, (b) low χ value samples.
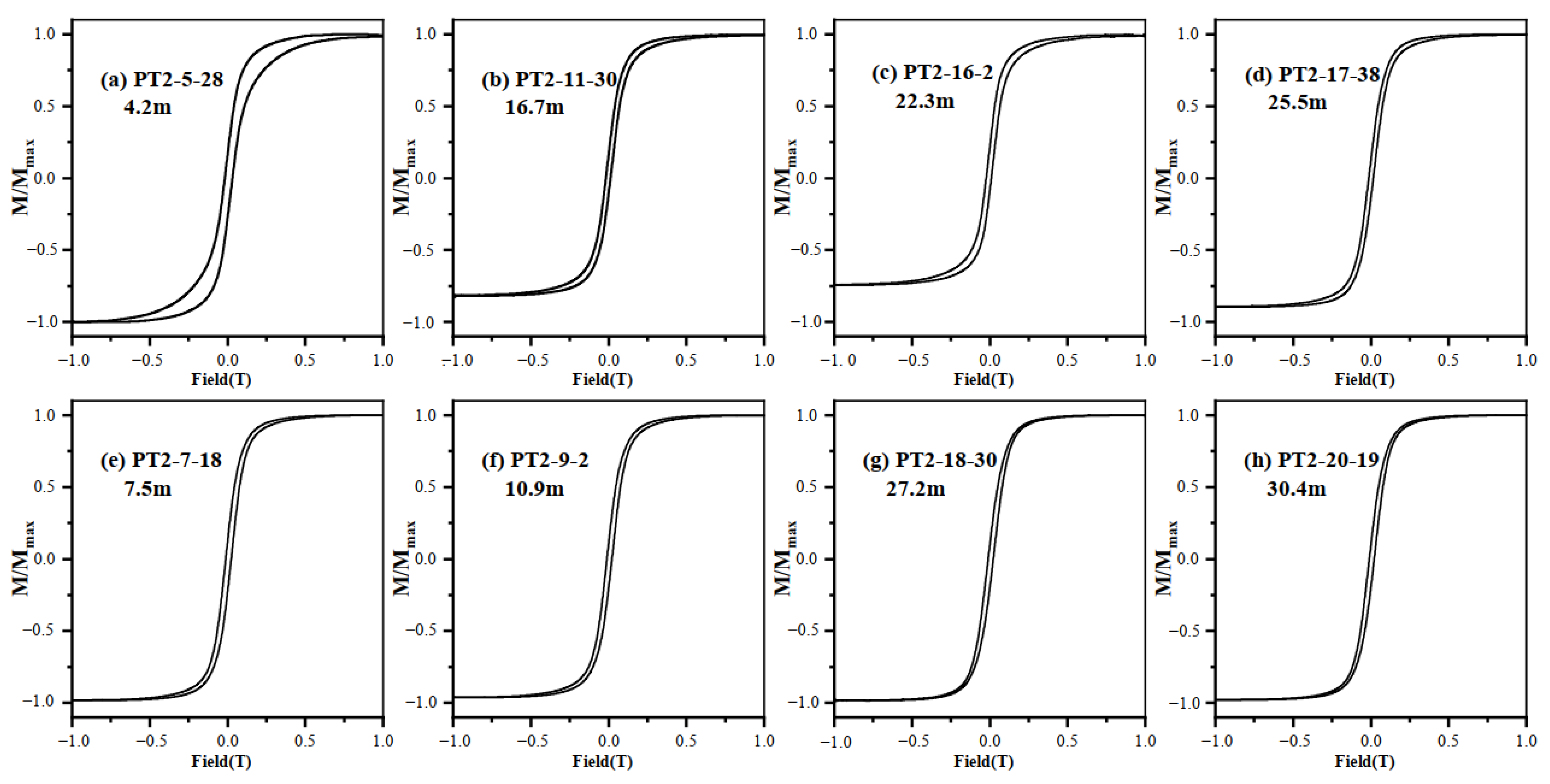
The hysteresis loops for high χ values are close at approximately 300 mT (Figure 6e–h), and those for low χ values are close at approximately 500 mT (Figure 6a–d). The small fluctuation after the curve closure shows that the sample is less affected by paramagnetic minerals. The appearance of wasp-waist hysteresis loops at low χ values may be related to the mixing of magnetic minerals with different coercivities or the contribution of hard magnetic minerals due to the low magnetic mineral contents (Figure 6a–d). The maximum value of Bc is 17.28 mT, the minimum value is 8.36 mT and the average value is 13.11 mT.
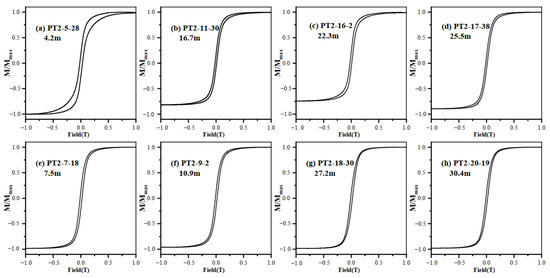
Figure 6.
Typical magnetic hysteresis loops (after slope correction) for core PT2, with (a–d) low χ value samples and (e–h) high value samples.
4.4. Hysteresis Parameters and First-Order Reversal Curve (FORC) Diagrams
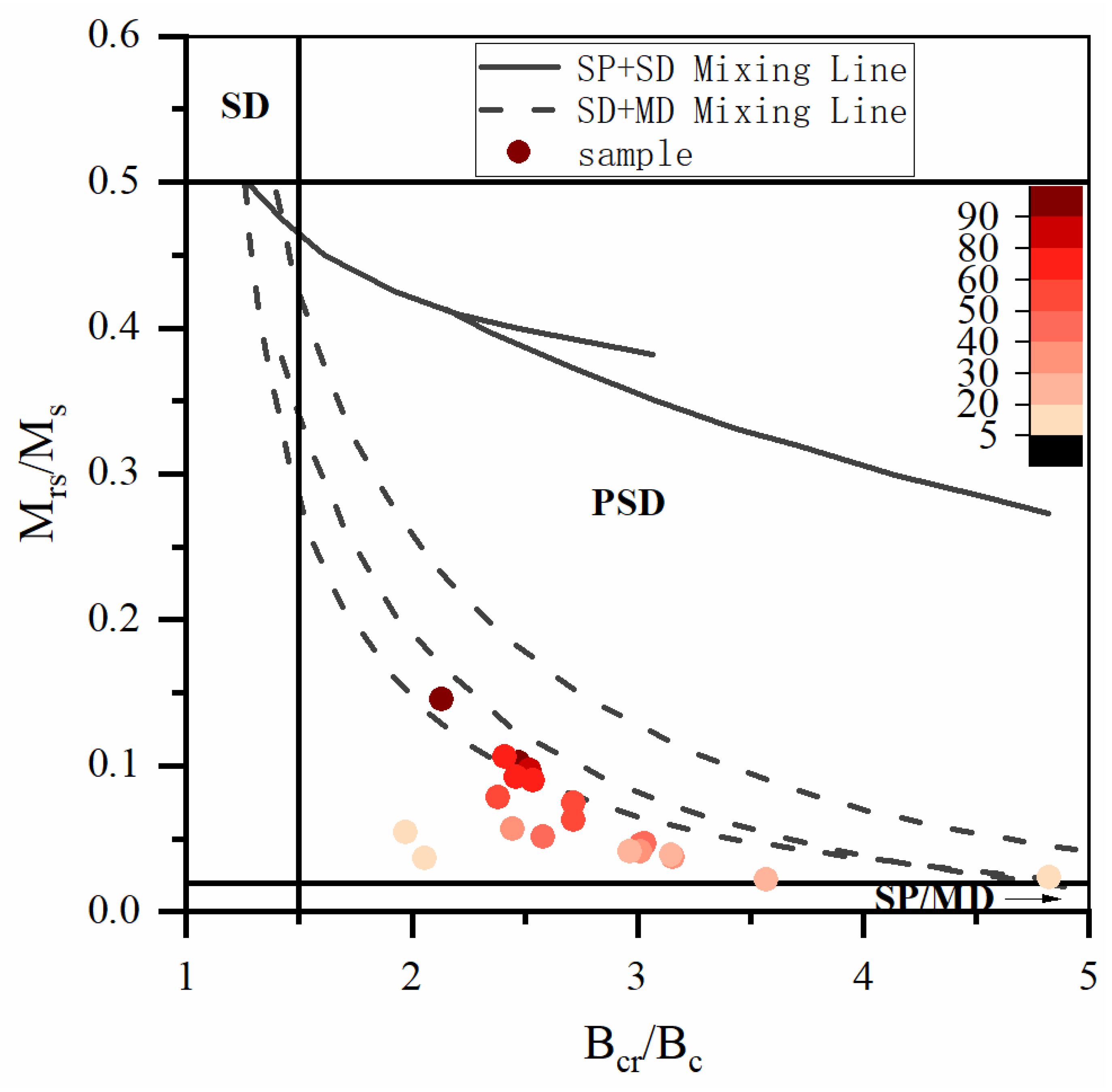
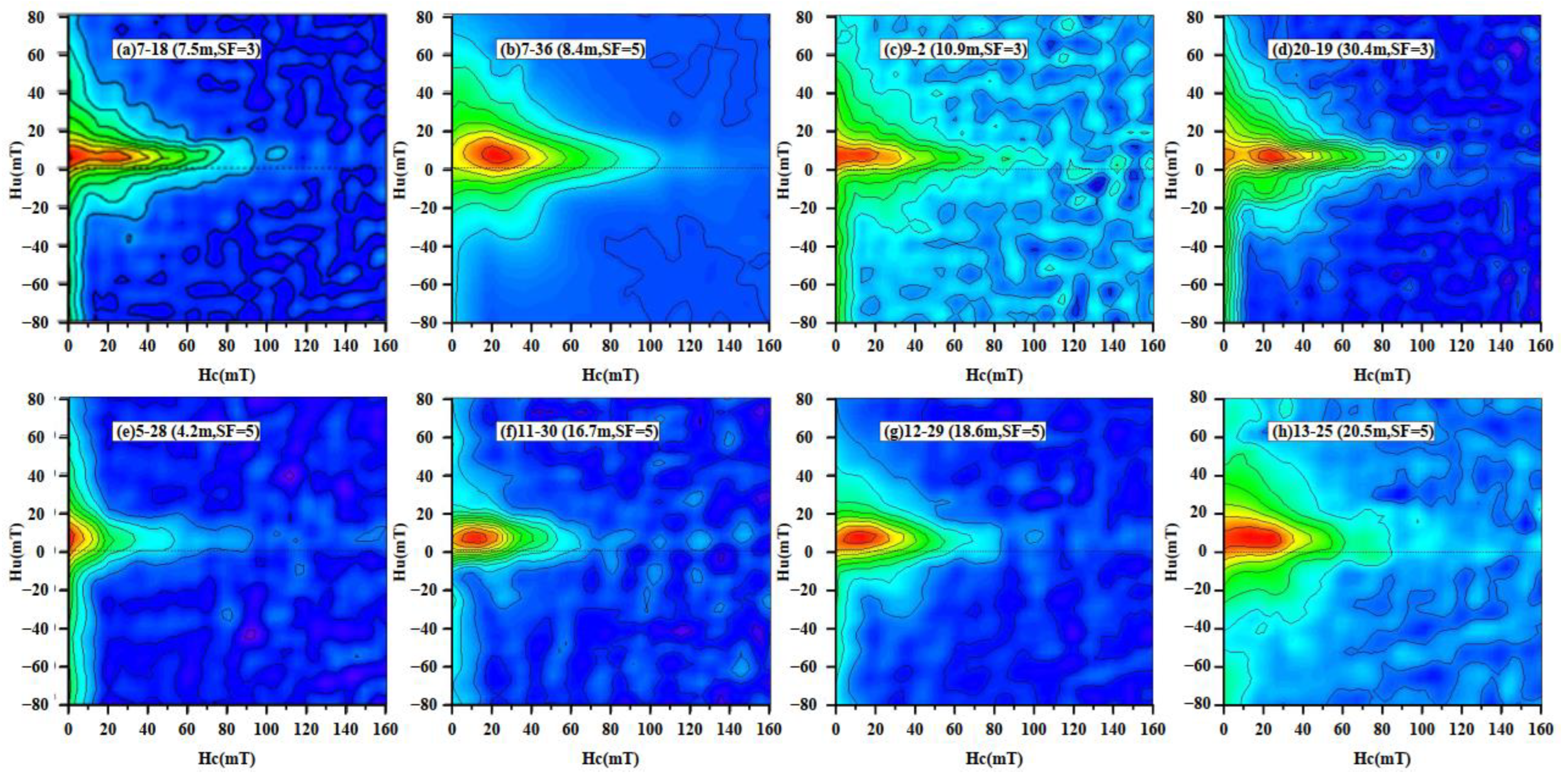
The Day plot diagram is plotted with Bcr/Bc and Mrs/Ms as horizontal and vertical coordinates [27]. It is used to reflect the particle size of ferrimagnetic minerals contained in the sample [18,41]. The Day plot diagram shows that the state of the magnetic domain of the selected samples is mostly the vortex state (the PSD range) [41,42]. The projection points of typical samples are approximately along the SD + MD mixing curve, and with decreasing χ, they extend to the direction of MD grains (Figure 7). However, determining the field state of the Day plot diagram is often fuzzy [43]. To better distinguish the magnetic domain state of ferrimagnetic minerals and understand the interaction between particles, the first-order reversal curve (FORC) is proposed [44,45,46]. The sample with high χ values has a Hu peak at approximately Hc = 20 mT, indicating the presence of SD particles (Figure 8a–d). The vertical distribution at less than 10 mT shows the information for the SP particles. In addition, the FORC diagram as a whole is more divergent, demonstrating strong PSD grain characteristics [44]. The distribution of the unclosed peripheral curve on the Hu axis shows the characteristics of the MD grains. However, in the samples with lower susceptibility (Figure 8e–h), there is a larger domain change. The difference is that the curves for low χ samples have a weak distribution along the Hu axis. Some samples show obvious SD and/or SP grain information, and some samples are similar to the curves for high χ value samples.
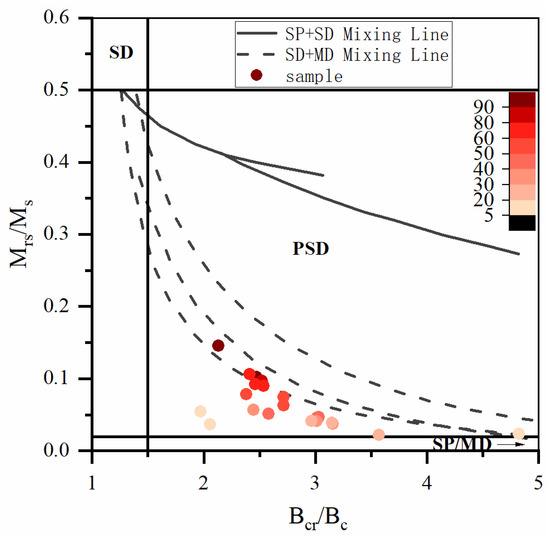
Figure 7.
Hysteresis ratios plotted on a Day plot [41] for representative samples from the PT2 drill core. SD—single domain; PSD—pseudosingle domain; MD—multidomain; SP—superparamagnetic. The colour change in the colour bar corresponds to the magnetic susceptibility. The higher the magnetic susceptibility value is, the darker the sample point.
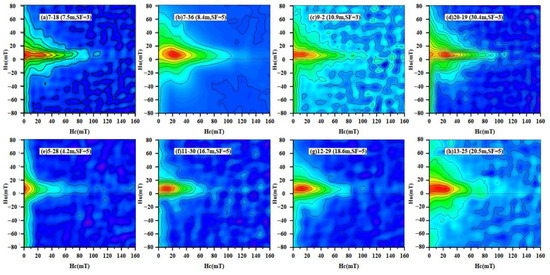
Figure 8.
FORC diagrams for representative samples from the PT2 drill core. (a–d) are samples with high χ values, and (e–h) are samples with low χ values. Red means strong signal, blue means weak signal.
5. Discussion
5.1. Characteristics of Magnetic Susceptibility
Detailed rock magnetic studies show that the major magnetic minerals in the PT2 drill core are mostly magnetite and some haematite. There is maghemite in the lower part of the core. In terms of the domain state, the hysteresis loops and Day plot diagrams of the samples with high χ values show typical PSD particle characteristics. The FORC diagram implies that the magnetic particles are widely distributed, mainly the SD, MD and SP grains. The magnetic domains of samples with lower χ values vary greatly between different samples. Some of the FORC diagrams show SD and/or SP grain characteristics, and others show PSD particle characteristics, which is consistent with the results of the hysteresis loops and Day plot diagram. In terms of ferrimagnetic mineral content, SIRM, ARM and the χfd of samples with high χ values are higher, and ARM/SIRM is lower. These layers have higher ferrimagnetic mineral contents. The absolute content of single-domain particles and superparamagnetic particles is higher. The ARM, SIRM and the χfd in parts of the core where χ is low are lower, and ARM/SIRM is higher, demonstrating that the ferrimagnetic mineral content is low. Single-domain particles and superparamagnetic particles have a low absolute content.
5.2. Mechanism of Magnetic Susceptibility Variability
Numerous studies have focused on the factors influencing the magnetic properties of lake sediments [47,48]. The mechanisms that drive changes in χ can be explained in the following ways: (1) the change in material source [49,50]; (2) low-temperature oxidation of primary magnetite [51,52]; (3) pedogenesis [53,54]; (4) reductive dissolution under anaerobic conditions [22,48,55]; and (5) precipitation status in catchment areas [47].
The sources of magnetic minerals in sediments can be divided into two categories: endogenous and exogenous. Endogenic refers to the authigenic minerals generated by sediments in the secondary environment. Greigite is a typical mineral in lake environments. The external sources are divided into detrital input and aeolian input, which are brought into the lake by transport via water or wind, respectively. The FORC figure shows that the coercivity of minerals is low, indicating that secondary minerals such as greigite are not formed [22]. The aeolian input of sand in Southwest China is very limited [56,57]. Therefore, the main terrestrial source of Heqing Lake is detrital material transported by flowing water. Furthermore, differences in the composition of the underlying bedrock may result in changes in material provenance [47]. The bedrock around the Heqing Basin is mainly composed of Triassic limestone and Palaeogene calcareous conglomerate. The material source is relatively simple and stable. Therefore, there is no obvious change in the source area of the PT2 drill core.
Zhang et al. [52] argued that the low χ value is caused by low-temperature oxidation of the primary magnetite (the process of magnetite transforming into maghemite and finally forming haematite) [19,48]. After undergoing the low-temperature oxidation, more haematite is often formed; thus, the χ value is reduced. However, our data do not support this view. The χ-T curve shows that haematite is present in all parts of the core, but it is more obvious in the lower part of high χ. Therefore, the low-temperature oxidation process may not be a dominant factor in the sediment of the PT2 drill core.
A large amount of maghemite and SP particles are often formed during pedogenesis [40,54]. However, maghemite exists only in the lower part of the PT2 drill core, and there is no maghemite in the upper part of the core with high χ. The overall change of χfd in the lower core is not significant, and there is no obvious increasing or decreasing trend. These features indicate that the influence pedogenesis has on the magnetic change in the PT2 drill core is small [47].
Post-depositional diagenesis of detrital magnetic minerals is common in lacustrine sediments [48,52,55]. The reductive dissolution process often takes place under anaerobic and waterlogged conditions [48,52,58]. Fine-grained magnetite and maghemite were preferentially dissolved [4,22,59]. The χ is generally low in the upper part of the PT2 drill core, and there is no maghemite, which may be due to strong dissolution. The χ is generally higher in the lower part of the core; in addition, part of the maghemite is not completely decomposed, and the dissolution process may have been weak. In addition, the dissolution process may result in a wider range of grain sizes [54]. Both the Day plot diagram and the FORC diagram show a wide distribution of magnetic domains. The colour of the sediments in the core is mostly green-grey, which also shows the existence of the reduction environment from another point of view [60].
As an insoluble substance, Ti is not easily lost during the transport of terrestrial debris. Therefore, it is often used to reflect the input of terrestrial sources [61,62]. Although there was no significant positive correlation between Ti and χ values in the sediment of PT2, the pattern of variability was basically the same (Figure 3). This indicates that the input of foreign debris is the main source of sediment in PT2 [22,63]. In the lower part of the PT2 drill core, the lithology is basically composed of green-grey clay with uniform texture, and the overall climate conditions were relatively stable. This may be the reason why the Ti content in the lower layer does not change significantly. Moreover, the change in lithology may also lead to a change in the range of Ti.
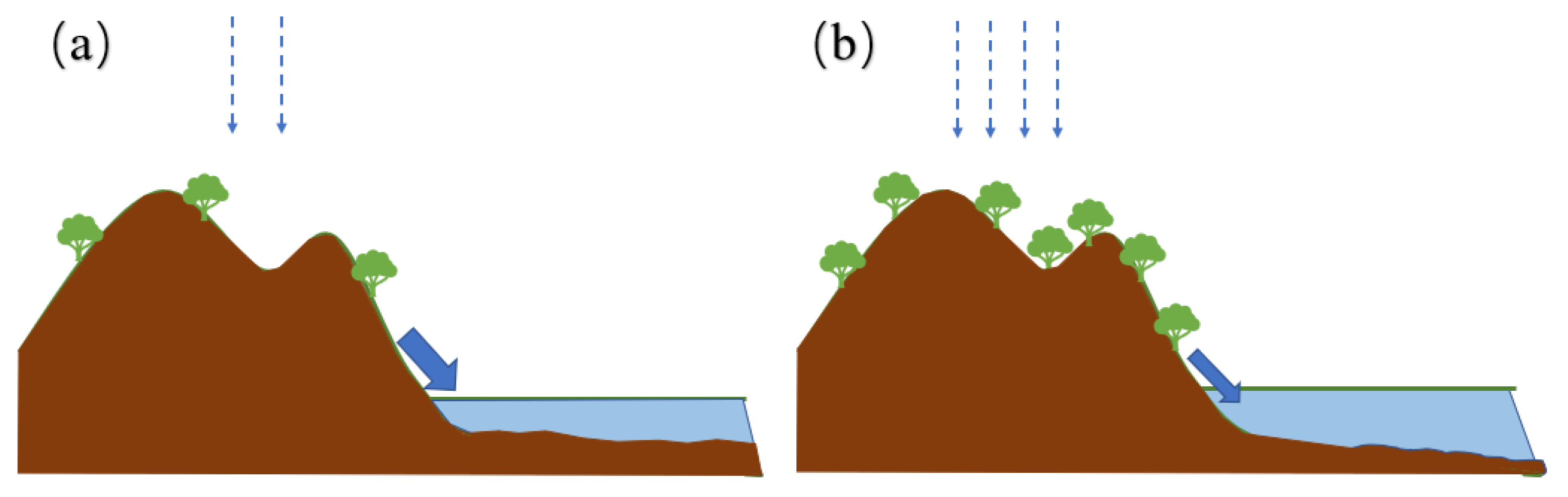
Additionally, regional precipitation will affect the amount of debris input. When precipitation decreases in catchment areas, a drier climate will inhibit the growth of vegetation. Therefore, there is little to resist debris during transport, and the erosion of the catchment increased, resulting in a substantial increase in debris being transported to the lake [47,63] (Figure 9a). Therefore, the χ, ARM, SIRM, and Ti values are relatively high, and ARM/SIRM is relatively low. The magnetic domains are widely distributed, with obvious PSD characteristics. The humid climate in the catchment area resulting from precipitation increases is conducive to the growth of vegetation, which increases the resistance encountered by debris during transport. In addition, the erosion caused by flowing water is weakened, and the debris entering the lake is reduced [47,51] (Figure 9b). Therefore, the χ, ARM, SIRM, and Ti values are relatively low, and the ARM/SIRM is relatively high. Wang et al. [64] included the influence of flowing water and land use/land cover change (human activities) when studying the Guizhou Plateau in Southwest China, and Liu et al. [65] demonstrated that the southern part of China would be affected by the input of aeolian sand through their research on the red soil in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Therefore, combined with the results presented in this paper, we believe that the southwest region is less affected by aeolian sand transport, and more consideration should be given to the influence of oxidation and reduction processes. The southeast region should consider aeolian sand transport, combined with the local topography for detailed analysis. The magnetic minerals in both places mainly enter the lake in the form of debris and are affected by the vegetation changes at that time.
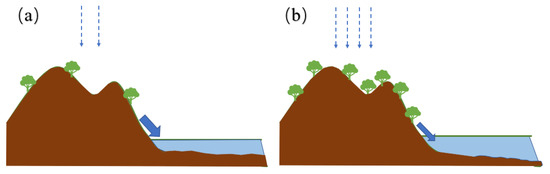
Figure 9.
The process of magnetic mineral input in dry and humid climates, where (a) is dry and (b) is humid. The blue dotted arrows represent rainfall. The solid blue arrows represent the direction of water flow.
In summary, the change in material source, the low-temperature oxidation of primary magnetite and pedogenesis are not the main factors causing the magnetic differences in the PT2 drill core; however, the process of reductive dissolution after lake deposition and precipitation in the catchment area have a substantial influence on the changes in χ. Therefore, the weak reductive dissolution process and the input of exogenous debris in this paper may be a better explanation for the magnetic enhancement mechanism.
6. Conclusions
In this work, the rock magnetism of the PT2 drilling core was studied in detail, and it was determined that the change in χ in the PT2 core was greatly affected by reductive dissolution and regional precipitation. The primary magnetic minerals in the PT2 core were magnetite, maghemite, and haematite. The χ values in the upper part (0–13.5 m) were lower than those in the lower part (13.5–33.5 m). There was no maghemite in the upper part. It can be concluded that the reductive dissolution was a stronger factor in the upper part of the core, which resulted in the complete decomposition of the magnetite in the upper part and the retention of magnetite in the lower part. The magnetic domains of minerals are distributed more widely through reductive dissolution. The particles were coarser in the parts of the core where χ was high, and the magnetic domains show obvious PSD information, as well as SD, SP, and MD characteristics. The magnetic domains in regions where χ was low vary greatly among the different samples, and the particle size was finer. When precipitation rates are low, the vegetation is poorly developed, which results in more debris flowing into the lake and strong magnetic properties. In the case of abundant precipitation, vegetation is abundant, the debris entering the lake is reduced, and the magnetism is weak.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Y., X.Q. and X.X.; methodology, Z.Y., X.X., F.Y. and X.Q.; software, Z.Y. and X.X.; validation, Z.Y., X.X., F.Y., Q.W. and X.Q.; formal analysis, Z.Y. and X.X.; investigation, Z.Y. and X.X.; resources, Z.Y., F.Y., Q.W. and X.Q.; data curation, Z.Y., X.X. and Q.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Y.; writing—review and editing, Z.Y., X.X., F.Y. and Q.W.; supervision, Z.Y.; project administration, X.X.; funding acquisition, Z.Y., X.X., F.Y. and Q.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant numbers 42172203, 41402151, 41572164, and the Open Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology, grant number SKLLQG2009.
Data Availability Statement
The data in this paper can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author (xuxinwen@nwu.edu.cn).
Acknowledgments
We thank the editors and reviewers for their advice on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- An, Z.S.; Sun, Y.B.; Cai, Y.J.; Zhou, W.J.; Shen, J. Asian monsoon change and its links to global climate. J. Earth Environ. 2017, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Geen, R.; Bordoni, S.; Battisti, D.S.; Hui, K. Monsoons, ITCZs and the Concept of the Global Monsoon. Rev. Geophys. 2020, 58, e2020RG000700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.X. Global monsoon in a geological perspective. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Wang, L.S.; Hu, S.Y.; Ma, M.M.; Wang, Q.; Cui, B.L.; Zhan, C.; Zeng, L.; Liu, X.B.; Shen, J. Indian summer monsoon variability over last 2000 years inferred from sediment magnetic characteristics in Lugu Lake, southwest China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 578, 110581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.Q.; Qiu, H.J.; Yang, D.D.; Liu, Z.J.; Ma, S.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Cao, M.M.; Wufuer, W. Increasing landslide activity in the Taxkorgan River Basin (eastern Pamirs Plateau, China) driven by climate change. Catena 2023, 223, 106911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.G.; Sha, Y.Y.; Liu, X.D. Effect of Yunnan–Guizhou Topography at the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau on the Indian Monsoon. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Y.; Goddu, S.R.; Appel, E.; Verosub, K.; Dong, Y.X.; Wang, S.M. Palaeoclimatic changes over the past 1 million years derived from lacustrine sediments of Heqing basin (Yunnan, China). Quat. Int. 2005, 136, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Zhang, Z.K. New progress of lake sediments and environmental changes research in China. Sci. Bull. 1999, 44, 1744–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Kong, X.G.; Cheng, H. High resolution stalagmite δ18O records over the past 1000 years from Dongge Cave in Guizhou. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2005, 50, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M. Climatic differences and similarities between Indian and East Asian Monsoon regions of China over the last millennium: A perspective based mainly on stalagmite records. Int. J. Speleol. 2007, 36, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.M.; Cheng, X.; Cai, Y.J.; Luo, Q.Z.; Zhang, J.L.; Tang, L.; Hu, Y.; Ren, J.G.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Asian Summer Monsoon Changes Inferred From a Stalagmite δ18O Record in Central China During the Last Glacial Period. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 863829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prell, L.W. Monsoonal climate of the Arabian sea during the Late Quaternary: A response to changing solar radiation. In Milankovitch and Climate; Understanding the Response to Astronomical Forcing: NATO Advanced Research; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, P.K.; Narayana, A.C.; Kumar, P.K.; Bhavani, P.G.; Yadava, M.G.; Jull, A.J.T. Indian monsoon variability during the last 46 kyr: Isotopic records of planktic foraminifera from southwestern Bay of Bengal. J. Quat. Sci. 2021, 36, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, Y.; Kawahata, H.; Kuroda, J.; Yamaguchi, A.; Suzuki, A.; Araoka, D.; Abe-Ouchi, A.; Yamada, Y.; Ijiri, A.; Kanamatsu, T.; et al. Indian Monsoonal Variations During the Past 80 Kyr Recorded in NGHP-02 Hole 19B, Western Bay of Bengal: Implications From Chemical and Mineral Properties. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2019, 20, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzi, C.; Goni, M.F.S.; Anupama, K.; Prasad, S.; Hanquiez, V.; Johnson, J.; Giosan, L. Indian monsoon variations during three contrasting climatic periods: The Holocene, Heinrich Stadial 2 and the last interglacial-glacial transition. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 125, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Deng, Y.K.; Peng, H.J.; Wen, Z.M.; Shang, G.C.; Guan, H.C.; Ma, C.M. Hydroclimatic changes since the Last Glacial Maximum recorded in mountain peat deposit on the southwestern margin of the Sichuan Basin, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 1050429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Y.; Goddu, S.R.; Herb, C.; Appel, E.; Gleixner, G.; Wang, S.M.; Yang, X.D.; Zhu, X.H. Climate variability and its magnetic response recorded in a lacustrine sequence in Heqing basin at the SE Tibetan Plateau since 900 ka. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 201, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, R.; Fuller, M.; Schmidt, V.A. Hysteresis properties of titanomagnetites: Grain-size and compositional dependence. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1977, 13, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.; Oldfield, F. Environmental Magnetism; Springer: London, UK, 1986; pp. 101–123. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop, D.J.; Özdemir, Ö. Magnetism of sediments and sedimentary rocks. In Rock Magnetism: Fundamentals and Frontiers; Cambridge Studies in Magnetism; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; pp. 425–460. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Qiu, S.F.; Rao, Z.G. A rock magnetic record of Asian cooling and aridification processes during 1.95-0.40 Ma in the Southeastern Chinese Loess Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 3636–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W.; Qiang, X.K.; Zhao, H.; Fu, C.F. Magnetic mineral dissolution recorded in a lacustrine sequence from the Heqing Basin, SW China, and its relationship with changes in the Indian monsoon. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 188, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, X.Q.; Toney, J.L.; Ruan, J.Y.; Li, G.H.; Zhou, Q.X.; Gao, H.H.; Xie, Y.X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, T.W. Indian Summer Monsoon variations and competing influences between hemispheres since ~35 ka recorded in Tengchongqinghai Lake, southwestern China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2019, 516, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, P.J.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Beck, J.W.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, C.B.; Buck, C.E.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. IntCal13 and Marine13 Radiocarbon Age Calibration Curves 0–50,000 Years cal BP. Radiocarbon 2013, 55, 1869–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.S.; Clemens, S.C.; Shen, J.; Qiang, X.K.; Jin, Z.D.; Sun, Y.B.; Prell, W.L.; Luo, J.J.; Wang, S.M.; Xu, H.; et al. Glacial-Interglacial Indian Summer Monsoon Dynamics. Science 2011, 333, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Xiao, H.F.; Wang, S.M.; An, Z.S.; Qiang, X.K.; Xiao, X.Y. The orbital scale evolution of regional climate recorded in a long sediment core from Heqing, China. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.S.; Roberts, A.P.; Larrasoaña, J.C.; Banerjee, S.K.; Guyodo, Y.; Tauxe, L.; Oldfield, F. Environmental magnetism: Principles and applications. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.J.; Feinberg, J.M. FORCinel: An improved algorithm for calculating first-order reversal curve distributions using locally weighted regression smoothing. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2008, 9, Q05016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.W.; Channell, J.E.T. Sedimentary magnetism, environmental magnetism, and magnetostratigraphy. Rev. Geophys. 1991, 29, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.E.; Heller, F.; Bloemendal, J.; Thouveny, N. Natural Magnetic Archives of Past Global Change. Surv. Geophys. 1997, 18, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Liu, Q.S. Effects of the grain size distribution on the temperature-dependent magnetic susceptibility of magnetite nanoparticles. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.S.; Deng, C.L.; Yu, Y.; Torrent, J.; Jackson, M.J.; Banerjee, S.K.; Zhu, R.X. Temperature dependence of magnetic susceptibility in an argon environment: Implications for pedogenesis of Chinese loess/palaeosols. Geophys. J. Int. 2005, 161, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.L.; Zhu, R.X.; Jackson, M.J.; Verosub, K.L.; Singer, M.J. Variability of the temperature-dependent susceptibility of the Holocene eolian deposits in the Chinese loess plateau: A pedogenesis indicator. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A-Solid Earth Geod. 2001, 26, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Y.; Deng, C.L.; Appel, E.; Verosub, K.L. Environmental magnetic studies of lacustrine sediments. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2002, 47, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Zhang, W.G.; Dong, C.Y.; Dong, Y.; Bai, X.X.; Liu, J.Y.; Hien, N.T.T.; Feng, H.; Yu, L.Z. Magnetic mineral diagenesis in the river-dominated inner shelf of the East China Sea, China. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 4720–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P. Magnetic properties of sedimentary greigite (Fe3S4). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1995, 134, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.X.; Matasova, G.; Kazansky, A.; Zykina, V.; Sun, J.M. Rock magnetic record of the last glacial-interglacial cycle from the Kurtak loess section, southern Siberia. Geophys. J. Int. 2003, 152, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.M.; Zan, J.B.; Yan, M.D.; Zhang, W.L.; Fang, X.M.; Zhang, D.W.; Zhang, T. Comparative Rock Magnetic Study of Eocene Volcanogenic and Sedimentary Rocks From Yunnan, Southeastern Tibetan Plateau, and Its Geological Implications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB017946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, J.B.; Fang, X.M.; Yan, M.D.; Zhang, Z.G.; Zhang, D.W. Regional variations in magnetic properties of surface sediments in the Qaidam Basin and their paleoenvironmental implications. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 122, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.L.; Zhu, R.X.; Verosub, K.L.; Singer, M.J.; Yuan, B.Y. Paleoclimatic significance of the temperature-dependent susceptibility of Holocene loess along a NW-SE transect in the Chinese loess plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3715–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, D.J. Theory and application of the Day plot (Mrs/Ms versus Hcr/Hc) 1. Theoretical curves and tests using titanomagnetite data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2002, 107, B3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P.; Almeida, T.P.; Church, N.S.; Harrison, R.J.; Heslop, D.; Li, Y.L.; Li, J.H.; Muxworthy, A.R.; Williams, W.; Zhao, X. Resolving the Origin of Pseudo-Single Domain Magnetic Behavior. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 9534–9558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P.; Hu, P.X.; Harrison, R.J.; Heslop, D.; Muxworthy, A.R.; Oda, H.; Sato, T.; Tauxe, L.; Zhao, X. Domain State Diagnosis in Rock Magnetism: Evaluation of Potential Alternatives to the Day Diagram. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 5286–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P.; Pike, C.R.; Verosub, K.L. First-order reversal curve diagrams: A new tool for characterizing the magnetic properties of natural samples. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 28461–28475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muxworthy, A.R.; King, J.G.; Heslop, D. Assessing the ability of first-order reversal curve (FORC) diagrams to unravel complex magnetic signals. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2005, 110, B01105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.F.; Liu, Q.S.; Pan, Y.X. The first-order reversal curve (FORC) diagram: Theory and case study. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 2008, 51, 743–751. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.Q.; Zhang, W.L.; Fang, X.M.; Yan, M.D.; Zan, J.B.; Zhang, T. Rock magnetic record of core SG-3 since 1 Ma in the western Qaidam Basin and its paleoclimate implications for the NE Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 560, 109949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, J.B.; Kang, J.; Yan, M.D.; Fang, X.M.; Li, X.J.; Guan, C.; Zhang, W.L.; Fang, Y.H. A Pedogenic Model for the Magnetic Enhancement of Late Miocene Fluvial-Lacustrine Sediments From the Xining Basin, NE Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 6176–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.H.; Ji, S.; Yun, X.X. Paleoenvironmental evolution of Heqing basin in Yunnan Province since 2.78 Ma. Sci. Limnol. Sin. 2006, 18, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.W.; Qiang, X.K.; An, Z.S.; Li, X.B.; Li, P.; Sun, Y.F. Magnetic susceptibility of Heqing drill core and its paleoenvironmental implications. J. Geomech. 2010, 16, 372–382. [Google Scholar]
- Demory, F.; Oberhansli, H.; Nowaczyk, N.R.; Gottschalk, M.; Wirth, R.; Naumann, R. Detrital input and early diagenesis in sediments from Lake Baikal revealed by rock magnetism. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2005, 46, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Appel, E.; Fang, X.M.; Song, C.H.; Cirpka, O. Magnetostratigraphy of deep drilling core SG-1 in the western Qaidam Basin (NE Tibetan Plateau) and its tectonic implications. Quat. Res. 2012, 78, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W.; Qiang, X.K.; Fu, C.F.; Zhao, H.; Chen, T.; Sun, Y.F. Rock magnetic evidence for early diagenesis in the pleistocene lacustrine sediments from Heqing basin. Quat. Sci. 2012, 32, 812–819. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, H. Mineral-magnetic signal of long-term climatic variation in Pleistocene fluvio-lacustrine sediments, Nihewan Basin (North China). J. Asian Earth Sci. 2010, 39, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowball, I.F. Geochemical control of magnetite dissolution in subarctic lake sediments and the implications for environmental magnetism. J. Quat. Sci. 1993, 8, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.M.; Zhang, M.Y.; Liu, T.S. Spatial and temporal characteristics of dust storms in China and its surrounding regions, 1960-1999: Relations to source area and climate. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 10325–10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Lei, J.Q.; Wu, S.X.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Huang, S.Y.; Guo, Y.H.; Wang, Y.D.; Tang, X.; et al. Spatiotemporal evolution of aeolian dust in China: An insight into the synoptic records of 1984-2020 and nationwide practices to combat desertification. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2005–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.; Jelinowska, A.; Kissel, C.; Tucholka, P.; Gibert, E.; Gasse, F.; Massault, M.; Taieb, M.; Van Campo, E.; Wieckowski, K. Mineral-magnetic proxies of erosion/oxidation cycles in tropical maar-lake sediments (Lake Tritrivakely, Madagascar): Paleoenvironmental implications. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1998, 155, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.S.; Hu, S.Y.; Yu, G.; Ma, M.M.; Liao, M.N. Paleoenvironmental reconstruction of the radial sand ridge field in the South Yellow Sea (East China) since 45ka using the sediment magnetic properties and granulometry. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 122, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.P. Magnetic mineral diagenesis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 151, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.H.; Shao, L.; Liang, X.R. Climatic impact on Al, K, Sc and Ti in marine sediments: Evidence from ODP Site 1144, South China Sea. Geochem. J. 2003, 37, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.J.; Liu, Y.; Shao, L.; Li, X.H.; Liang, X.R. Climatic records in the major elements of the terrestrial detritus from the south china sea. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2003, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, T.P.; Tian, C.J.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Qiu, Y.; Appel, E.; Fu, S.Q. Magnetic characteristics and its environmental implications of core YSJD-86GC sediments from the southern South China Sea. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 3176–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Huo, Y.Y.; Zeng, L.Y.; Wu, X.Q.; Cai, Y.L. A 42-yr soil erosion record inferred from mineral magnetism of reservoir sediments in a small carbonate-rock catchment, Guizhou Plateau, Southwest China. J. Paleolimnol. 2008, 40, 897–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Deng, C.L. The effect of weathering on the grain-size distribution of red soils in South-Eastern China and its climatic implications. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 94, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).