Spatial Heterogeneity of Rare Earth Elements: Implications for the Topsoil of Regional Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Deposit Areas in Southern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
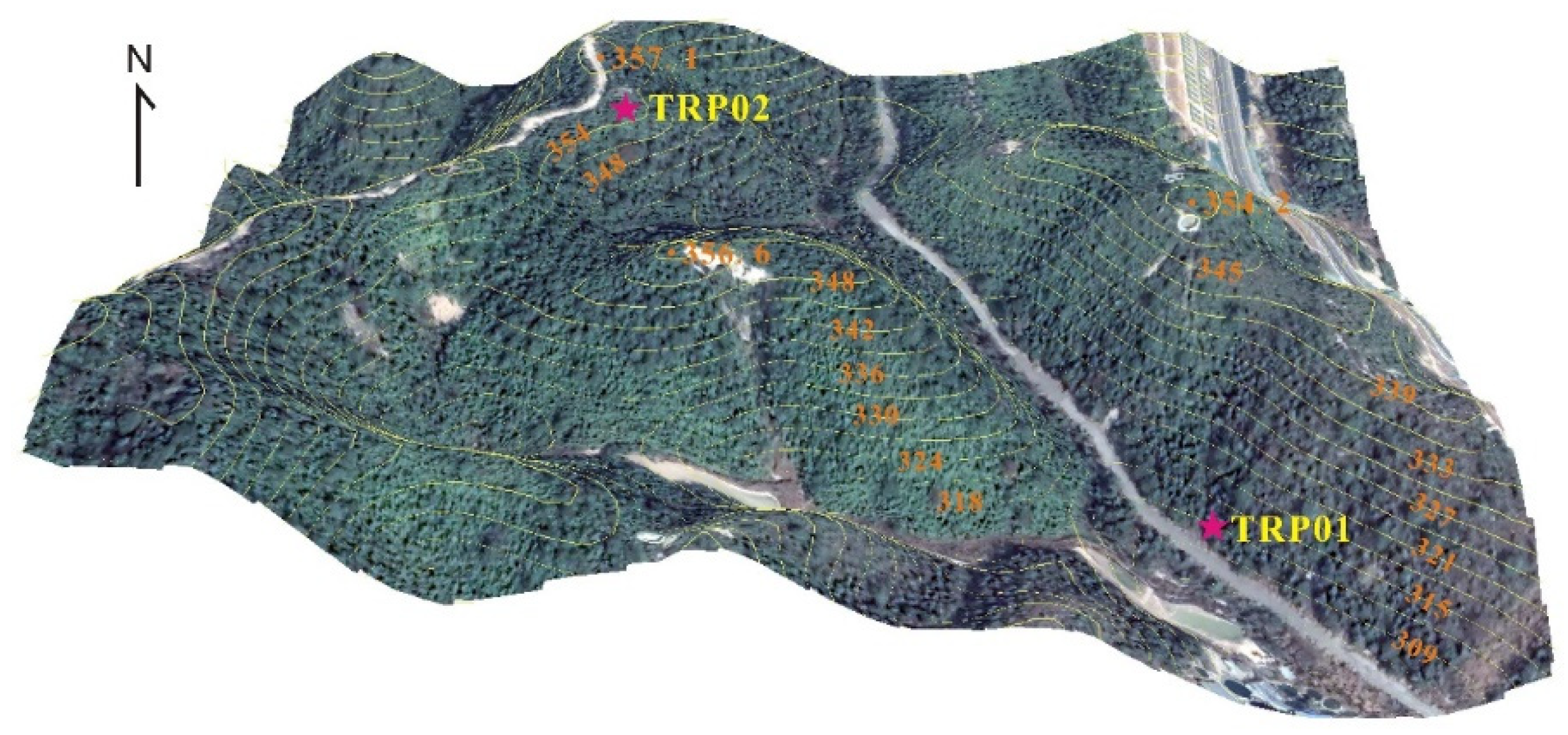
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling Methods
2.3. Analysis of REEs
2.4. Data Processing and Application Software
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rare Earth Element Concentrations in Topsoil
3.2. Vertical Distribution of REEs in Soil Profiles
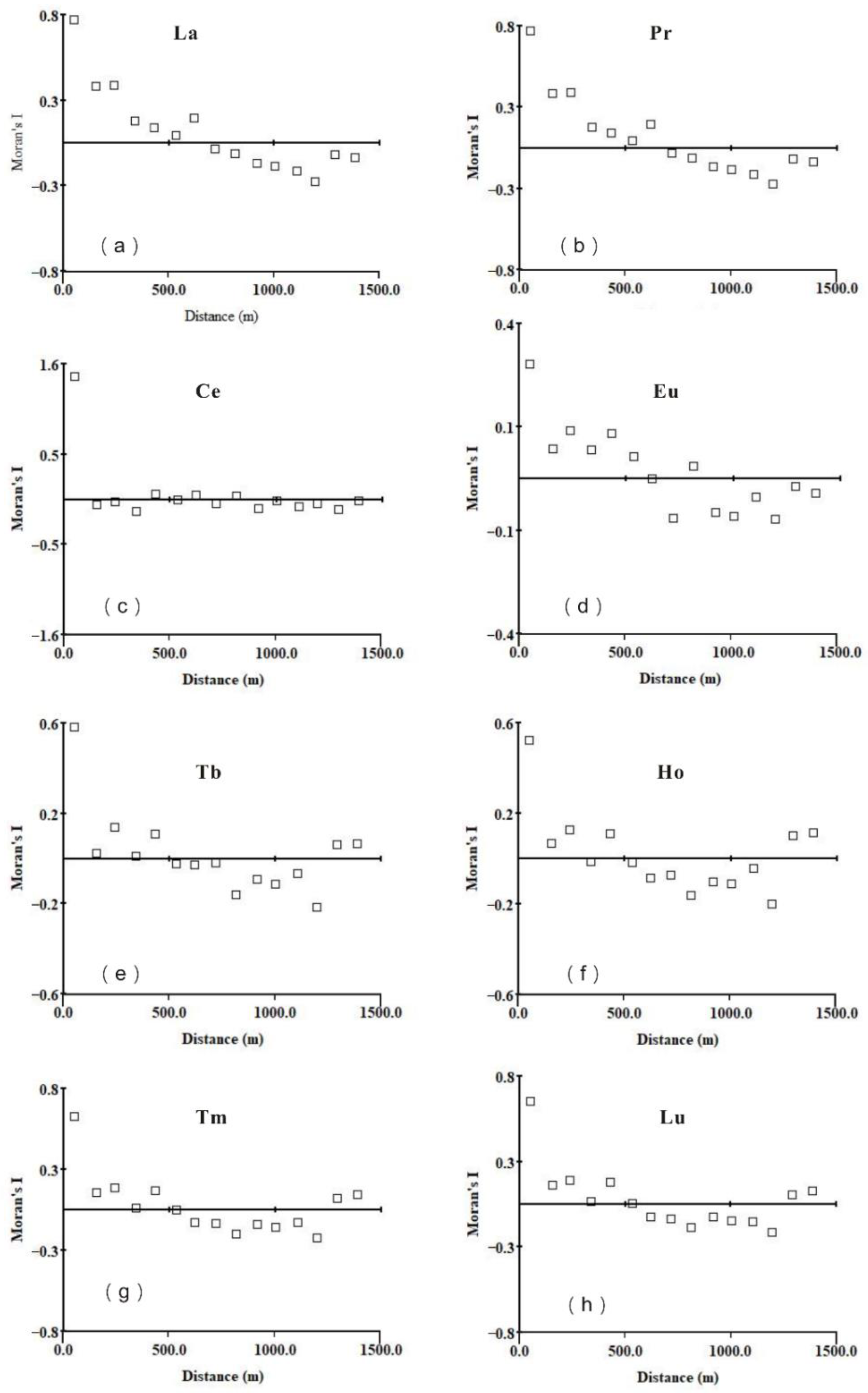
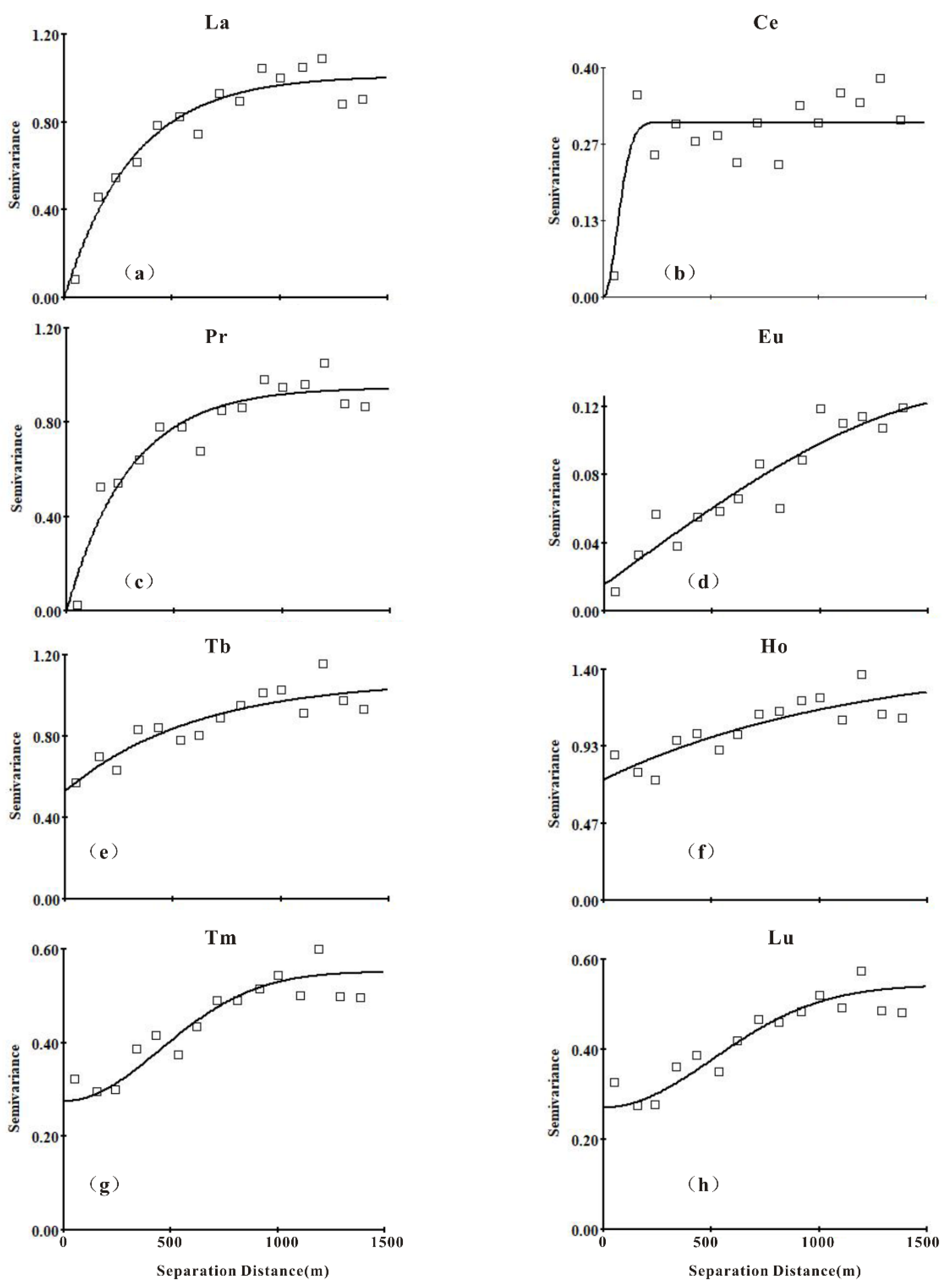
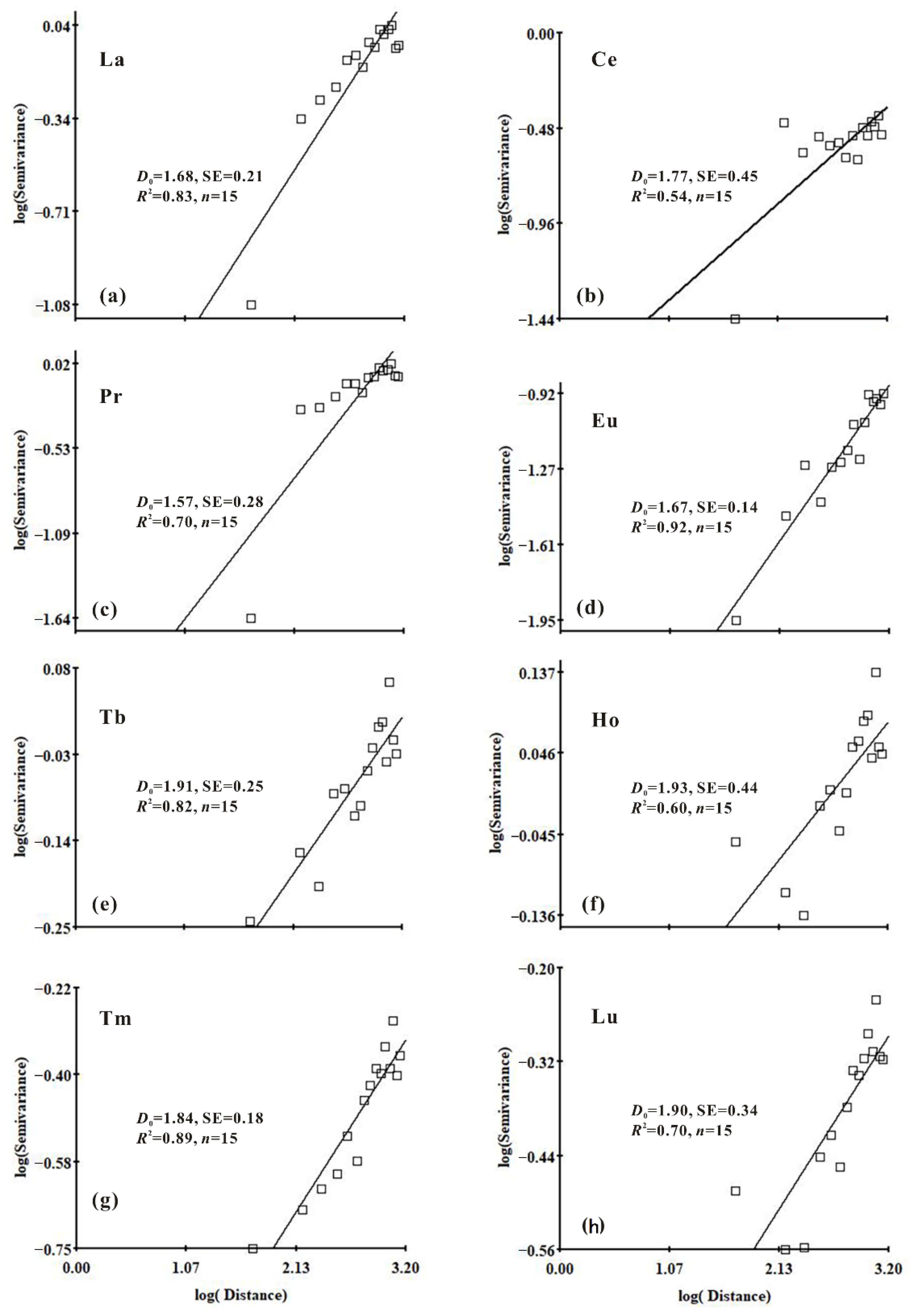
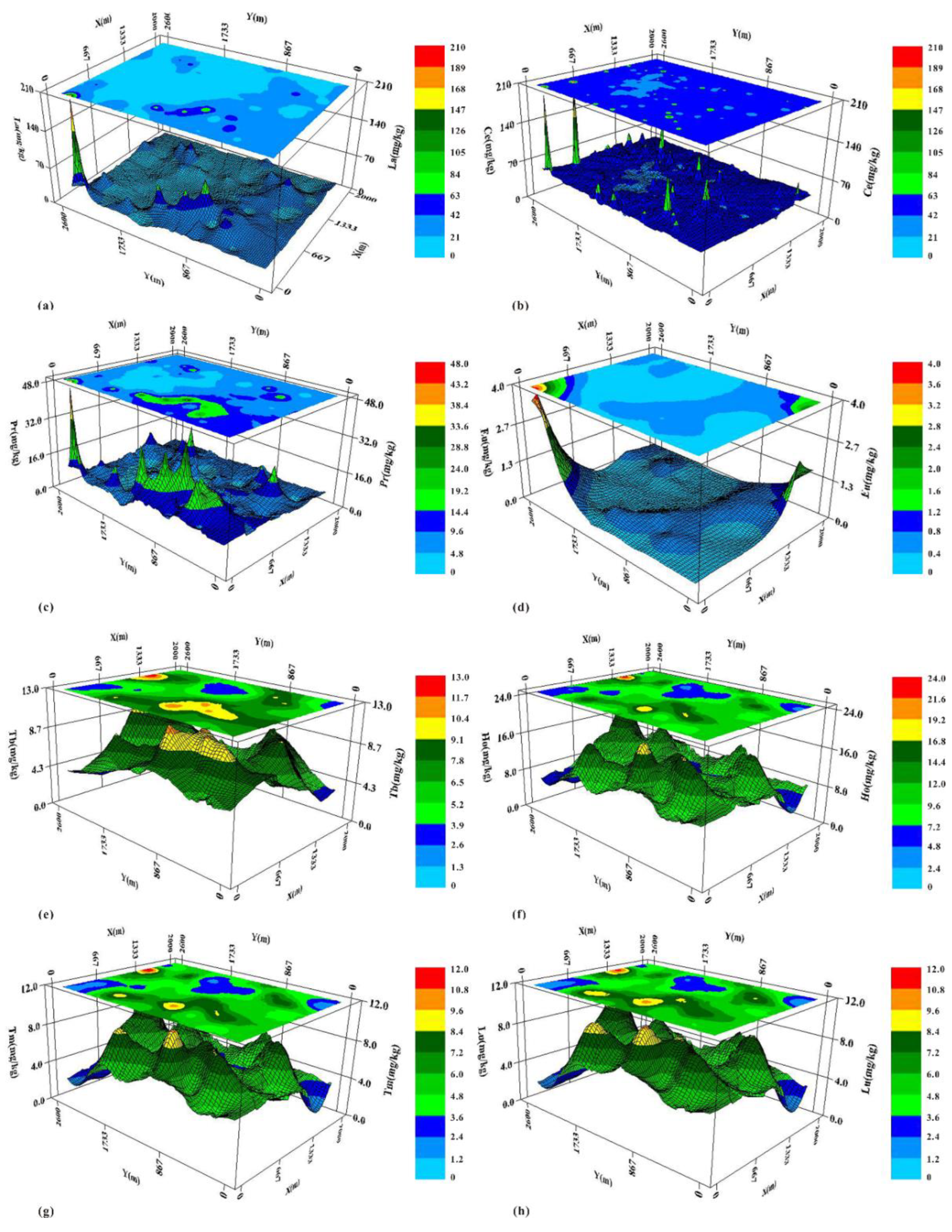
3.3. Spatial Heterogeneity of REEs
4. Implication
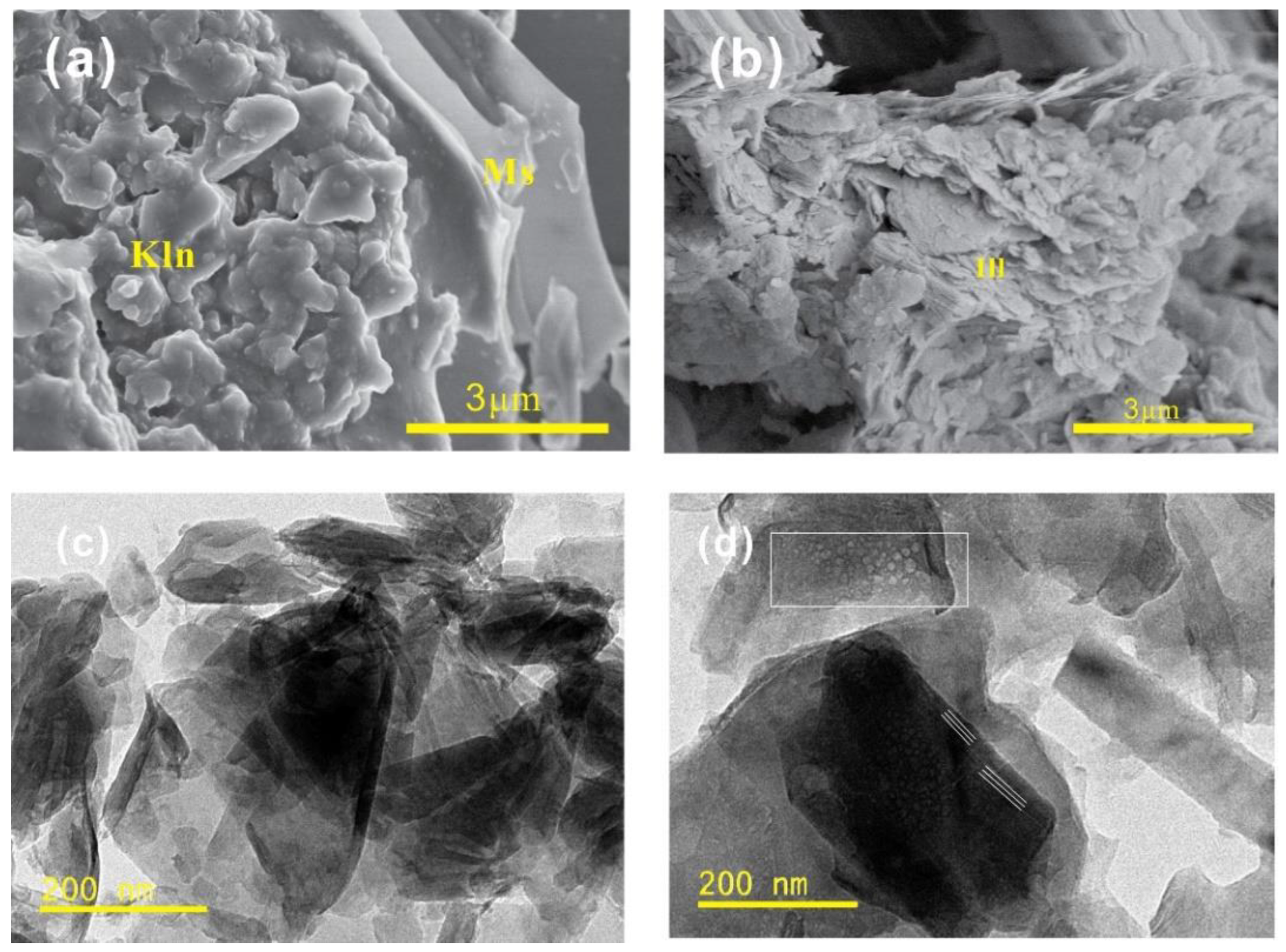
4.1. Rare Earth Element Differentiation Patterns in Topsoil
4.2. Enrichment Factors of REEs in Topsoil
5. Conclusions
- (1)
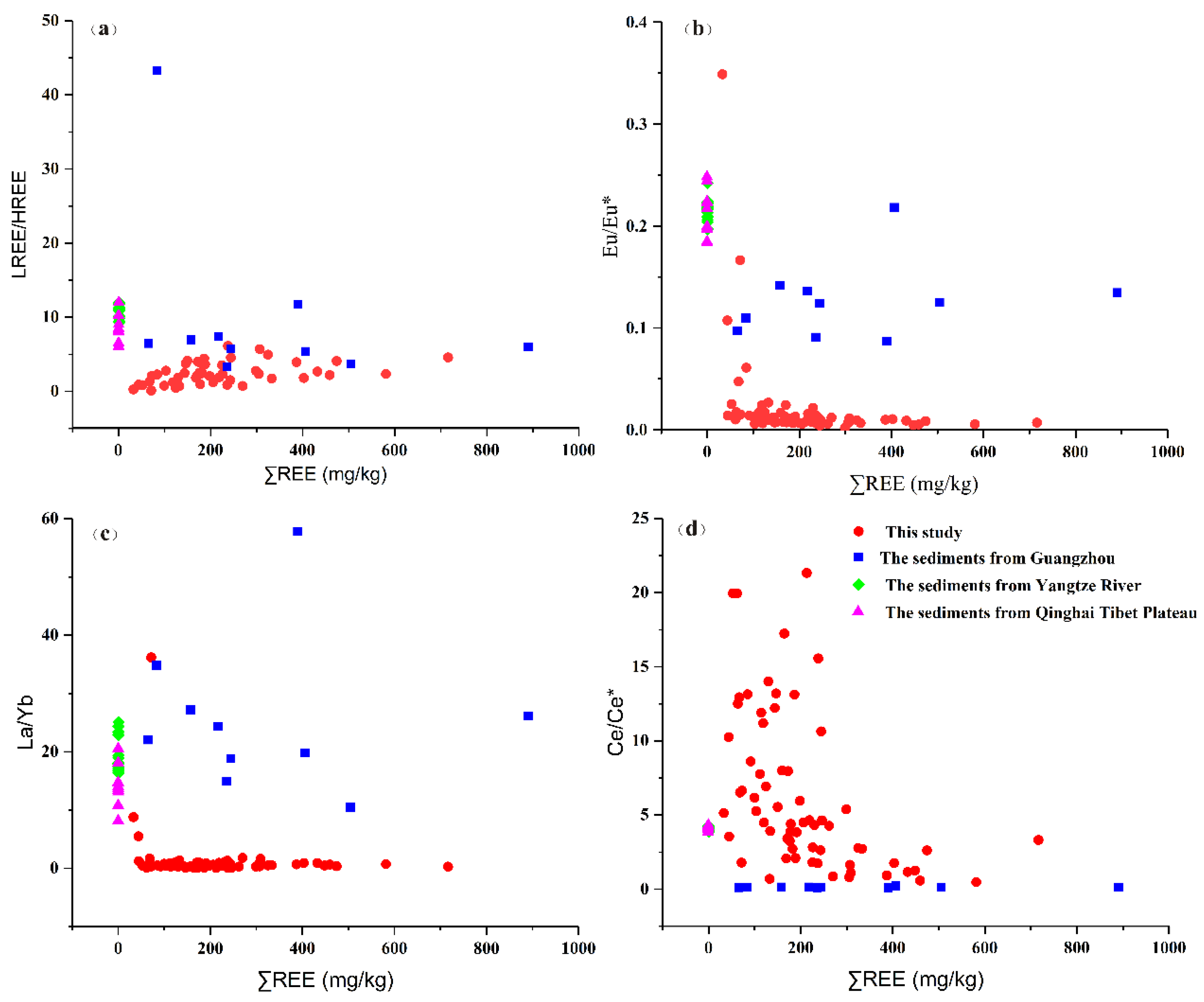
- The total REE content, average, and CV value in topsoil in the study area varied from 156.28–2397.74 mg/kg, 767.25 mg/kg, 55.49%–143.05%, respectively. The average ratio of LREE/HREE was 0.32. The Eu/Eu* value, Ce/Ce* value, and La/Yb value indicated that the uneven distribution of REEs in the topsoil; the HREEs were more evenly distributed in space than the LREEs.
- (2)
- Standard chondrite rare earth analysis showed that a negative Eu anomaly was inherited from the distribution pattern of the parent rock. The ratio of rare earth in the topsoil to parent rock showed that Eu was obviously enriched, and Ce showed abnormally positive and negative expression patterns. This reflected the differences in rare earth element fractionation in the topsoil.
- (3)
- Moran index analysis showed that the positive correlation between sampling points was significant within the range of 0–500 m, the negative correlation increased with distance. The best fitting models of the semi variance variogram were the exponential model, Gaussian model, and spherical model. Spatial structure (C0 + C) revealed the order of spatial structure from strong to weak: Ho > Tb > La > Pr > Nd > Sm > Gd > Tm > Lu > Dy > Er > Yb > Ce > Eu. The largest fractal dimension of HREEs was Ho (1.93), followed by Tb (1.91) and Lu (1.90). This indicated that their spatial distribution pattern was relatively simple and their spatial dependence was strong.
- (4)
- Scatter plots of LREE/HREE, Eu/Eu*, Ce/Ce*, La/Yb, and Σ REE showed that the LREE/HREE ratio of topsoil in the study area was the lowest compared to other mining areas. This indicated that the enrichment of rare earth in the topsoil of the study area was controlled by macroscopic factors (parent rock, weathering degree, topography, and so on), and other factors including the particle size of the topsoil, the type and content of clay minerals, the organic matter content, and human activities that controlled the adsorption and spatial distribution of rare earth.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tyler, G. Rare earth elements in soil and plant systems—A review. Plant Soil 2004, 267, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Q.; Liang, T. Geochemical fractions of rare earth elements in soil around a mine tailing in Baotou, China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedepohl, H. The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.R.; Niu, H.C.; Li, X.C.; Yang, K.F.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, Q.W. The types, ore genesis and resource perspective of endogenic REE deposits in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 3778–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lei, Y.; Ge, J.; Wu, S. Production forecast of China’s rare earths based on the Generalized Weng model and policy recommendations. Resour. Policy 2015, 43, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J. Recovery of rare earth from ion-adsorption rare earth ores with a compound lixiviant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 142, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Qiao, J.Y.; Xue, Q.; Liu, F.; Chen, H.H.; Zhang, G.C. Leach of the weathering crust elution-deposited rare earth ore for low environmental pollution with a combination of (NH4)2SO4 and EDTA. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.P.; Zhang, B.; Ma, G.T.; Pan, Z.W.; Hu, Z.G.; Zhang, B.T. Mineralization of ion-adsorption type rare earth deposits in Western Yunnan, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 148, 104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–200. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, R.A.; Tian, J. Review of Weathered Crust Rare Earth Ore. J. Rare Earths 2007, 25, 641–650. [Google Scholar]
- Kynicky, J.; Smith, M.P.; Xu, C. Diversity of rare earth deposits: The key example of China. Elements 2012, 8, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.K.; Chen, H.X.; Jin, X.W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Xu, S.; Wu, K.X.; He, S.; Sun, T.; et al. Research and Prospect of Particle Size, Clay Minerals, Base Ion Migration and Heavy Metal Release of Ionic Rare Earth Ore. J. Rare Earths 2022, 40, 194–215. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Huang, D.H.; Guo, Z.X. REE geochemistry in the weathered crust of granites, Longnan area, Jiangxi Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 1990, 3, 193–209. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, R.A.; Zhu, G.C.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Y.H. Chemical behavior of cerium element in rock weathering system. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 1999, 9, 158–164. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.H.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.H.; Dai, J.J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, T.; Li, J.K.; Huang, F.; Chen, Z.Y.; et al. A Review of the Achievements in the Survey and Study of Ion-absorption Type REE Deposits in China. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2017, 38, 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Harlavan, Y.; Erel, Y. The release of Pb and REE from granitoids by the dissolution of accessory phases. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, E.; Fernandez-Caliani, J.C.; Miras, A.; Aparicio, P.; Marquez, M.G. Residence and fractionation of rare earth elements during kaolinization of alkaline peraluminous granites in NW Spain. Clay Miner. 2007, 42, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanematsu, K.; Murakami, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Duangsurigna, S.; Vilayhack, S. Enrichment of rare earth elements (REE) in granitic rocksand their weathered crusts in central and southern Laos. Bull. Geolog. Sur. Jap. 2009, 60, 527–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W. Mobility and fractionation of rare earth elements during weathering of a granodiorite. Nature 1979, 279, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.K.; Krishnamurthy, N. Extractive metallurgy of rare earths. Int. Mater. Rev. 1992, 37, 197–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.Q.; Zhou, X.J.; Li, A.C.; Li, T.G. Quantitatively distinguishing sediments from the Yangtze River and the Yellow River using δEuN-ΣREEs plot. Sci. China 2009, 52, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.Y.; Liu, S.L.; Wu, M.; Zhong, M.Y.; Shahid, M.Z.; Liu, Y.L. Effects of topography and soil properties on the distribution and fractionation of REEs in topsoil: A case study in Sichuan Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, G.F.; Sun, M.Q.; Liang, X.L.; He, H.P.; Zhu, J.X.; Takahashi, Y. Environmental risk assessment of the potential “Chemical Time Bomb” of ion-adsorption type rare earth elements in urban areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.J. Study on Characteristics of Soil Environment and Geochemical Behavior of Rare Earth Metals in Rare Earth Mining Area of Southern Jiangxi Province; Yunnan University: Kunming, China, 2012; pp. 1–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.S.; Liu, T.L.; Teng, E.J.; Rui, K.S. Background values of rare earth elements in Chinese soil. Environ. Sci. 1991, 12, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, X.L.; Chen, Z.B.; Chen, X.L.; Li, X.F.; Wang, J.; Ren, T.J.; Chen, H.B.; Feng, L.J.; Wang, Y.K.; Chen, Z.Q.; et al. Redistribution and chemical speciation of rare earth elements in an ion-adsorption rare earth tailing, Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows (Version 26.0.0.0) [Computer Software]. IBM Corp. 2019. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/products/spss-statisticsIn-textreferencing (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Gamma Design Software, LLC. GS+Geostatistics for the Environmental Sciences (Version 9.0) [Computer Software]. Gamma Design Software, LLC. 2008. Available online: https://geostatistics.com (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Ersi Inc. Arcgis 10.2 for Desktop (Version 10.2.0.3384) [Computer Software]. Ersi Inc. 2013. Available online: https://www.esri.com (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Chen, L.K.; Jin, X.W.; Chen, H.X.; He, Z.W.; Qiu, L.R.; Duan, H.R. Grain size distribution and clay mineral distinction of rare earth ore through different methods. Minerals 2020, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.; Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 3, 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.C.; Dong, Y.S.; Jin, Z.; Peng, Q.; Xiao, S.; He, Y.T. Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Nutrients and Respiration in the Desertified Grasslands of Inner Mongolia, China. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanlik, S.; Aqca, N.; Yalcin, M. Spatial distribution of heavy metals content in soils of Amik plain (Hatay, Turkey). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.H.; Zhou, M.F.; Williams-Jones, A.E. The Genesis of Regolith-Hosted Heavy Rare Earth Element Deposits: Insights from the World-Class Zudong Deposit in Jiangxi Province, South China. Econ. Geol. 2019, 114, 541–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogova, O.B.; Fedotov, P.S.; Dzhenloda, R.K.; Karandashev, V.K. Fractionation and fixation of rare earths elements in soils: Effect of spiking with lanthanum, cerium, and neodymium chlorides. J. Rare Earths 2022, 40, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.H.; Zhou, M.F. The role of clay minerals in formation of the regolith-hosted heavy rare earth element deposits. Am. Mineral. 2020, 105, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.J.; Riotte, J.; Battacharya, S.; Violette, A.; Oliva, P.; Prunier, J.; Maréchal, J.C.; Ruiz, L.; Audry, S.; Subramanian, S. REY-Th-U dynamics in the critical zone: Combined influence of reactive bedrock accessory minerals, authigenic phases, and hydrological sorting (Mule HoleWatershed, South India). Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2018, 19, 1611–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Terakado, Y. Rare earth elements in stream waters from the Rokko granite area, Japan: Effect of weathering degree of watershed rocks. Geochem. J. 2003, 37, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.A.P. Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lark, R.M. Geostatistics for Environmental Scientists. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2001, 52, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangxi Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Drawing Instructions of Digital Geological Map of Jiangxi Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1984; pp. 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, M.H.; Wu, J.H.; Guan, T.Y. Bimodal volcanic geochemistry characteristics and structural setting of Yutian Group, south Jiangxi. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2006, 26, 320–327. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Hou, M.C.; Liu, X.C.; Huang, S.G.; Chao, H.; Zhang, R.; Deng, X. Geological and geochemical characteristics of marine-continental transitional shale from the Upper Permian Longtan formation, Northwestern Guizhou, China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2018, 89, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, C.; Liu, D.J.; Maes, N. Influence of Boom Clay organic matter on the adsorption of Eu3+ by illite-geochemical modelling using the component additivity approach. Radiochim. Acta 2010, 98, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidman, F.; Laudon, H.; Taberman, I.; Köhler, S. Eu anomalies in soils and soil water from a boreal hillslope transect-a tracer for Holocene lanthanide transport? Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 267, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.L.; Chang, H.; Zhou, X.H.; Zhu, J.Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, T.F.; Long, K.; Song, Y.X. Geochemical Characteristics and Factors of Transfer and Accumulation of Rare Earth Elements in Rock-Soil-Tea of the Mengku Tea Region in Yunnan Province, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Radionuclide Table: Radionuclide Carcinogenicity Slope Factors; United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA Office of Radiation and Indoor Air (ORIA). Radiation Protection Division. Radionuclide Carcinogenicity Slope Factors: Heast; US EPA Office of Radiation and Indoor Air (ORIA): Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.L.; Wu, G.J.; Gao, S.P. A Preliminary Study of the Rare Earth Elements in Surface Soil on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Glac. Geo. 2008, 30, 259–265. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Y.; Jung, H.S.; Choi, M.S.; Li, C.X. The rare earth element compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze) and Huanghe (Yellow) river sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 201, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.S.; Wang, L.J.; Zhang, S. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in the mainstream of the Yangtze River, China. Appl. Geochem. 1998, 13, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Kang, S.C.; Wang, X.P.; Marsan, F.A.; Zhang, Q.G. Heavy metals and rare earth elements (REEs) in soil from the Nam Co Basin, Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry; Elsevier Science Publishing Company Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Semhi, K.; Chaudhuri, S.; Clauer, N. Fractionation of rare-earth elements in plants during experimental growth in varied clay substrates. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, J.S. REE and fractionation and Ce anomalies in weathering Karoo dolerite. Chem. Geol. 1991, 90, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.B.; Wang, S.J.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, C.X.; Liu, X.M.; Zhou, D.Q. Geochemistry of red residua underlying dolomites in karst terrains of Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau: II. The mobility of rare earth elements during weathering. Chem. Geol. 2004, 203, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugeng, S.P.; Godang, S.; Priadi, B.; Basuki, N.I.; Himawan, B. Geochemical study of Al–Fe–Ti enrichment in rock weathering: Implications for the recognizing of igneous protolith and the enrichment of REE in soil profile. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 140, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.W.; Chen, L.K.; Chen, H.X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.J.; Ji, H.; Deng, S.F.; Jiang, L. XRD and TEM analyses of a simulated leached rare earth ore deposit: Implications for clay mineral contents and structural evolution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, H.; Stattegger, K.; Garbe-Schönberg, C.D. Composition and trace-element geochemistry of detrital clay and heavy-mineral suites of the lowermost Amazon River: A provenance study. J. Sediment. Res. 1999, 69, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Haneklaus, S.; Sparovek, G.; Schnug, E. Rare Earth Elements in Soils. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plan. 2006, 37, 1381–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution. J. Geol. 1985, 94, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, H.; Kon, Y.; Sanematsu, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Ito, M. Microscopic analyses of weathered granite in ion-adsorption rare earth deposit of Jiangxi Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Elderfield, H. The cycling of dissolved rare-earth elements in Chesapeake Bay. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1988, 2, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmez, I.; Sholkovitz, E.R.; Hermann, D.; Eganhouse, R.P. Rare earth elements in sediments off Southern California: A new anthropogenic indicator. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, T.O.P.D.; Pedreira, R.M.A.; Hatje, V. Distribution and fractionation of rare earth elements in sediments and mangrove soil profiles across an estuarine gradient. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadi, R.; Saeedi, M.; Karbassi, A. Redox-induced mobilization of rare earth elements in sediments of the northwestern part of the Persian Gulf. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 11037–11050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukovskii, Z.I.; Guzeva, A.V.; Dauvalter, V.A. Rare earth elements in surface lake sediments of Russian arctic: Natural and potential anthropogenic impact to their accumulation. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 142, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Wu, T.; Feng, X. Rare earth elements in street dust and associated health risk in a municipal industrial base of Central China. Environ. Environ. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 1469–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Lin, A.J.; Li, X.L.; Wu, Y.D.; Zhou, W.B.; Chen, Z.H. China’s ion-adsorption rare earth resources, mining consequences and preservation. Environ. Dev. 2013, 8, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.F.; Feng, Z.Y.; Huang, X.W.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, L.S.; Long, Z.Q. Recovery of rare earths from weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore without ammonia-nitrogen pollution: I. Leaching with magnesium sulfate. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 153, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
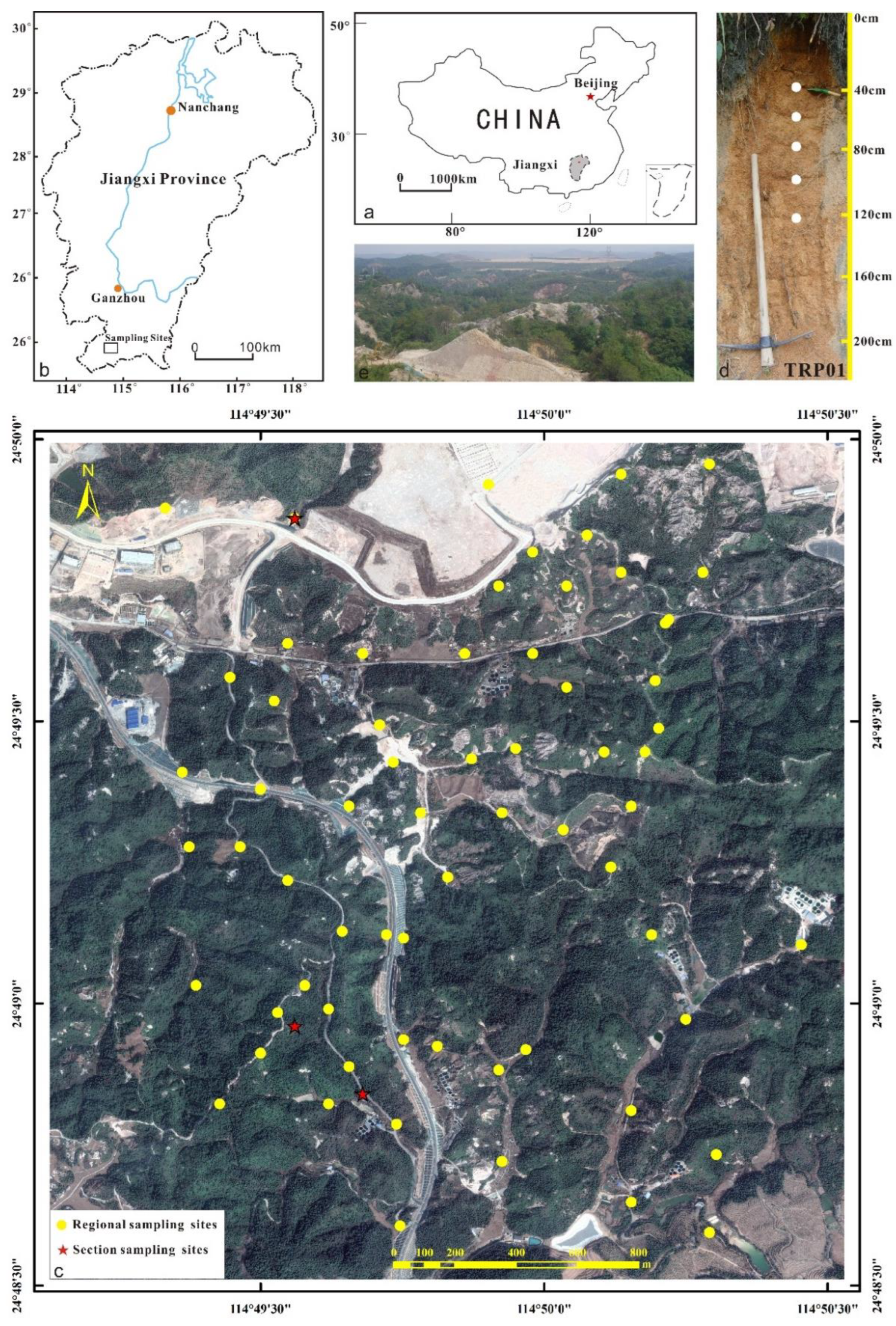
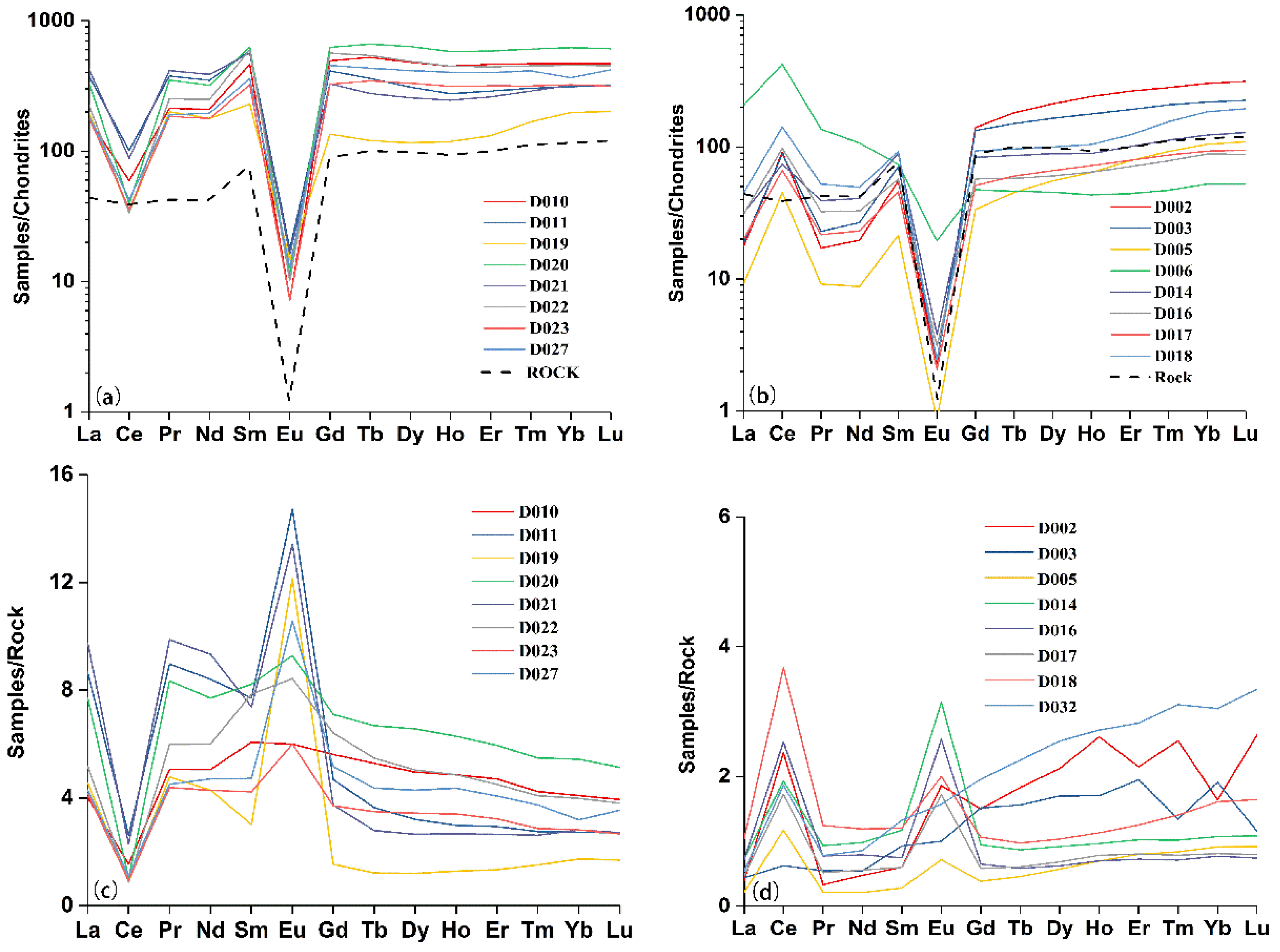
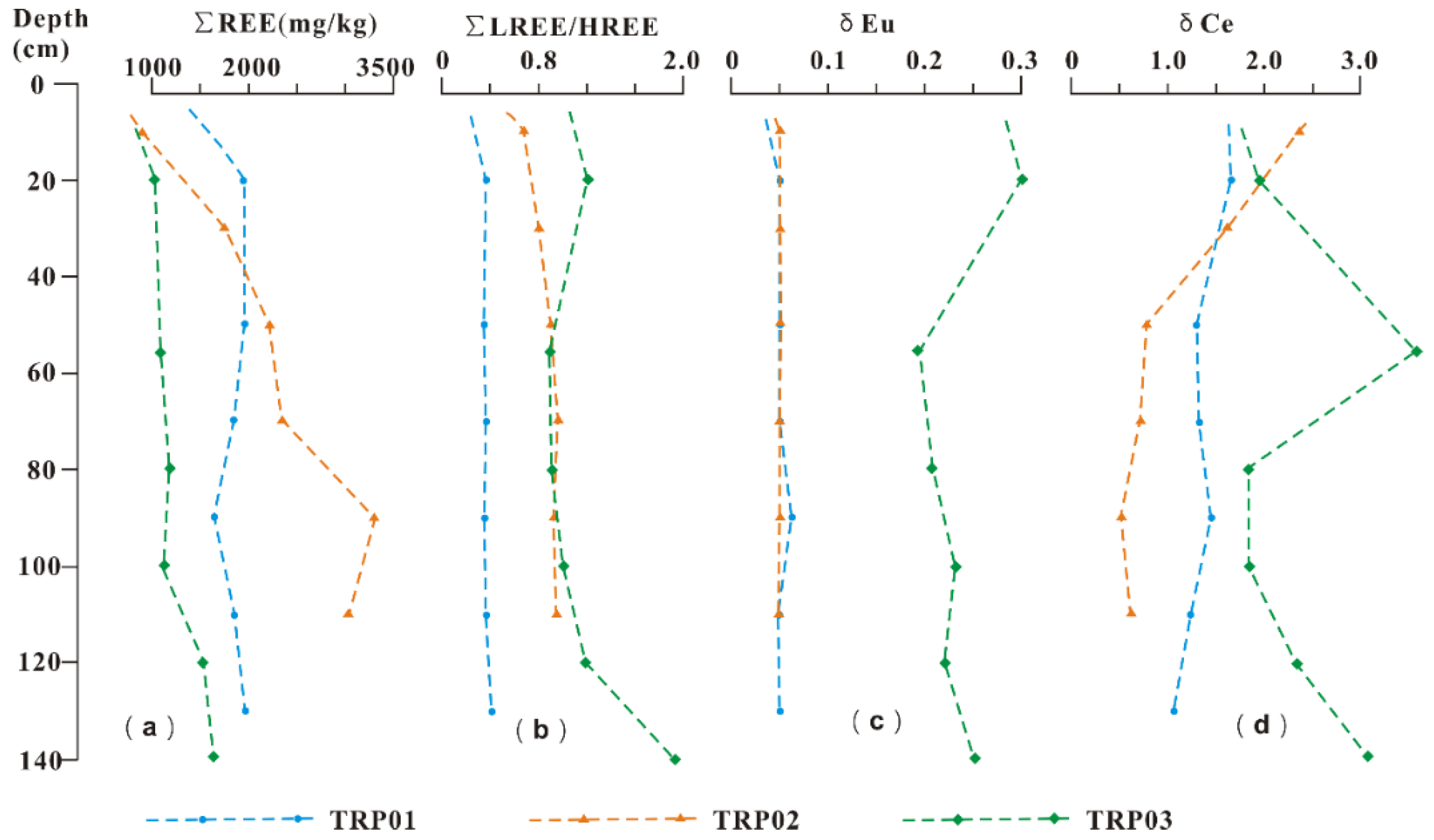
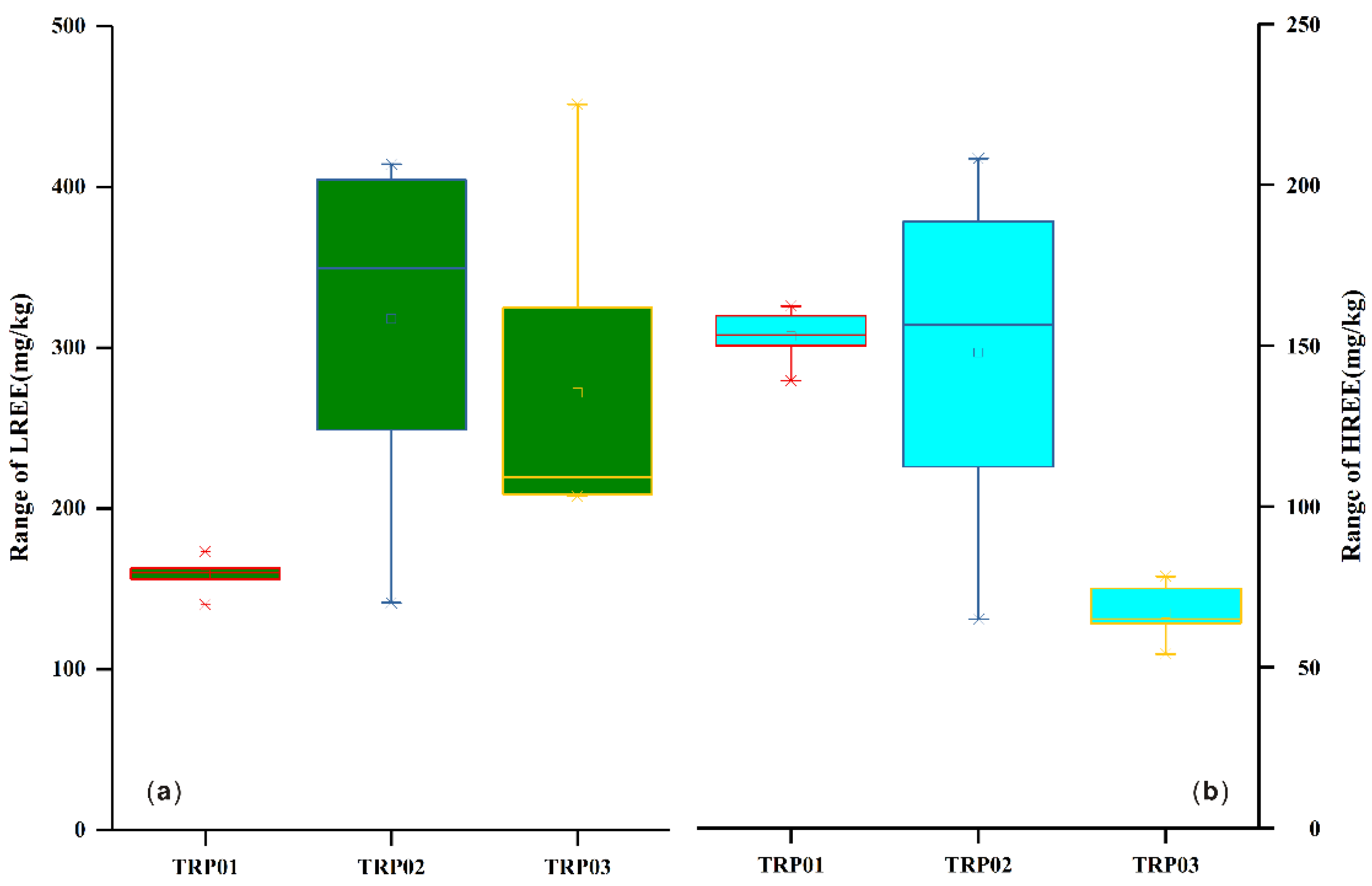
| Section Name | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Elevation (m) | Sample Number | Sampling Depth (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRP01 | 114.828 | 24.814 | 308 | TRP01-1 | 20 |
| TRP01-2 | 50 | ||||
| TRP01-3 | 70 | ||||
| TRP01-4 | 90 | ||||
| TRP01-5 | 110 | ||||
| TRP01-6 | 130 | ||||
| TRP02 | 114.826 | 24.816 | 368 | TRP02-1 | 10 |
| TRP02-2 | 30 | ||||
| TRP02-3 | 50 | ||||
| TRP02-4 | 70 | ||||
| TRP02-5 | 90 | ||||
| TRP02-6 | 110 | ||||
| TRP03 | 114.826 | 24.831 | 282 | TRP03-1 | 20 |
| TRP03-2 | 55 | ||||
| TRP03-3 | 80 | ||||
| TRP03-4 | 100 | ||||
| TRP03-5 | 120 | ||||
| TRP03-6 | 140 |
| No. | Element | Detection Range | No. | Element | Detection Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | La | 0.5–9000 | 8 | Tb | 0.01–990 |
| 2 | Ce | 0.5–9000 | 9 | Dy | 0.05–990 |
| 3 | Pr | 0.03–990 | 10 | Ho | 0.01–990 |
| 4 | Nd | 0.1–990 | 11 | Er | 0.03–990 |
| 5 | Se | 1–900 | 12 | Tm | 0.01–990 |
| 6 | Eu | 0.03–990 | 13 | Yb | 0.03–990 |
| 7 | Gd | 0.05–990 | 14 | Lu | 0.01–990 |
| Elements | Mean | SD | CV | Min | Max | K-S | GM | BV | UCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | 29.3 | 35.3 | 120 | 2.20 | 253 | <0.001 | 19.1 | 42.4 | 31.0 |
| Ce | 60.6 | 41.7 | 68.7 | 20.3 | 259 | <0.001 | 51.2 | 75.0 | 63.0 |
| Pr | 11.1 | 10.5 | 94.5 | 0.87 | 57.1 | <0.001 | 7.51 | 7.89 | 7.10 |
| Nd | 52.1 | 44.6 | 85.7 | 4.10 | 199 | <0.001 | 36.6 | 28.9 | 27.0 |
| Sm | 30.3 | 24.5 | 81.1 | 3.27 | 96.2 | <0.001 | 22.2 | 5.59 | 4.70 |
| Eu | 0.53 | 0.75 | 143.1 | 0.05 | 5.08 | <0.001 | 0.34 | 0.89 | 1.00 |
| Gd | 44.3 | 32.9 | 74.2 | 6.91 | 154 | <0.001 | 34.2 | 5.03 | 4.00 |
| Tb | 8.39 | 6.00 | 71.5 | 1.55 | 31.4 | <0.001 | 6.61 | 0.74 | 0.70 |
| Dy | 55.6 | 37.9 | 68.2 | 9.62 | 207 | 0.001 | 44.7 | 5.48 | 3.90 |
| Ho | 12.1 | 7.85 | 65.0 | 1.88 | 44.0 | 0.007 | 9.87 | 1.07 | 0.83 |
| Er | 36.6 | 22.3 | 61.1 | 4.70 | 124 | 0.018 | 30.3 | 3.44 | 2.30 |
| Tm | 6.04 | 3.58 | 59.3 | 0.57 | 20.2 | 0.020 | 5.04 | 0.44 | 0.30 |
| Yb | 39.5 | 21.9 | 55.5 | 3.58 | 117 | 0.041 | 33.4 | 3.05 | 2.00 |
| Lu | 6.28 | 3.48 | 55.5 | 0.55 | 19.1 | 0.027 | 5.29 | 0.46 | 0.31 |
| LREE | 184 | 125 | 68.2 | 38.1 | 764.7 | 0.005 | 11.2 | 160.7 | 133.8 |
| HREE | 583 | 385 | 66.0 | 84.2 | 2096.7 | 0.005 | 21.0 | 49.9 | 35.3 |
| LREE/HREE | 0.32 | 0.33 | 1.03 | 0.45 | 0.36 | 1.00 | 0.53 | 3.22 | 3.79 |
| Eu/Eu* | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.84 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.23 | |
| Ce/Ce* | 12.0 | 0.93 | 0.64 | 4.99 | 5.80 | 4.28 | 4.10 | 4.25 | |
| La/Yb | 0.74 | 1.61 | 2.17 | 0.61 | 2.16 | 0.57 | 13.9 | 15.5 | |
| ∑REE | 767 | 437 | 57.0 | 156 | 2397.7 | 0.007 | 16.4 | 211.6 | 169.1 |
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Ce | 0.46 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Pr | 0.96 ** | 0.36 * | 1 | |||||||||||
| Nd | 0.87 ** | 0.24 | 0.98 ** | 1 | ||||||||||
| Sm | 0.54 ** | −0.07 | 0.79 ** | 0.88 ** | 1 | |||||||||
| Eu | 0.82 ** | 0.53 ** | 0.67 ** | 0.58 ** | 0.22 | 1 | ||||||||
| Gd | 0.34 ** | −0.18 | 0.56 ** | 0.66 ** | 0.89 ** | 0.08 | 1 | |||||||
| Tb | 0.26 * | −0.21 | 0.47 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.82 ** | 0.02 | 0.99 ** | 1 | ||||||
| Dy | 0.21 | −0.23 | 0.42 ** | 0.52 ** | 0.78 ** | −0.02 | 0.97 ** | 0.99 ** | 1 | |||||
| Ho | 0.18 | −0.24 | 0.38 ** | 0.48 ** | 0.75 ** | −0.04 | 0.95 ** | 0.99 ** | 0.99 ** | 1 | ||||
| Er | 0.16 | −0.26 * | 0.36 ** | 0.46 ** | 0.74 ** | −0.08 | 0.94 ** | 0.98 ** | 0.99 ** | 0.99 ** | 1 | |||
| Tm | 0.15 | −0.25 * | 0.36 ** | 0.47 ** | 0.74 ** | −0.09 | 0.94 ** | 0.97 ** | 0.99 ** | 0.99 ** | 0.99 ** | 1 | ||
| Yb | 0.15 | −0.27 * | 0.37 ** | 0.48 ** | 0.75 ** | −0.12 | 0.92 ** | 0.97 ** | 0.97 ** | 0.97 ** | 0.98 ** | 0.99 ** | 1 | |
| Lu | 0.13 | −0.27 * | 0.35 ** | 0.46 ** | 0.74 ** | −0.12 | 0.92 ** | 0.95 ** | 0.97 ** | 0.97 ** | 0.98 ** | 0.99 ** | 0.99 ** | 1 |
| Element | Model | C0 | C0 + C | C/(C0 + C) | A | RSS | R2 | D0 | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | Exponential | <0.01 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 951. | 0.08 | 0.93 | 1.68 | 0.21 |
| Ce | Gaussian | <0.01 | 0.30 | 1.00 | 159.1 | 0.03 | 0.68 | 1.77 | 0.45 |
| Pr | Exponential | <0.01 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 846. | 0.09 | 0.90 | 1.57 | 0.28 |
| Nd | Exponential | <0.01 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 810. | 0.09 | 0.89 | 1.55 | 0.30 |
| Sm | Exponential | <0.01 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 753. | 0.10 | 0.82 | 1.61 | 0.31 |
| Eu | Spherical | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.88 | 1810 | <0.01 | 0.89 | 1.67 | 0.14 |
| Gd | Exponential | 0.13 | 0.61 | 0.78 | 963 | 0.05 | 0.81 | 1.83 | 0.22 |
| Tb | Exponential | 0.53 | 1.07 | 0.51 | 1809 | 0.07 | 0.80 | 1.91 | 0.25 |
| Dy | Spherical | 0.21 | 0.51 | 0.58 | 1081 | 0.02 | 0.85 | 1.87 | 0.20 |
| Ho | Exponential | 0.73 | 1.47 | 0.50 | 3480 | 0.13 | 0.70 | 1.93 | 0.44 |
| Er | Gaussian | 0.22 | 0.45 | 0.51 | 1053.1 | 0.01 | 0.88 | 1.87 | 0.23 |
| Tm | Gaussian | 0.28 | 0.55 | 0.50 | 1089.5 | 0.02 | 0.88 | 1.84 | 0.18 |
| Yb | Gaussian | 0.18 | 0.44 | 0.58 | 1274.8 | 0.01 | 0.92 | 1.84 | 0.21 |
| Lu | Gaussian | 0.27 | 0.54 | 0.50 | 1228. | 0.02 | 0.88 | 1.90 | 0.34 |
| REE | SF (kg·day−1·μg−1) [48] | Mean of CI Chondrite Standardization (μg·kg−1) | Riski | Concentrations of Ion-Exchangeable REEs (μg·kg−1) [23] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | 1.10 × 10−8 | 1.24 × 10−4 | 6.09 × 10−7 | 2.44 × 10−5 |
| Ce | 3.52 × 10−8 | 9.90 × 10−5 | 1.95 × 10−6 | 3.58 × 10−5 |
| Pr | 7.92 × 10−9 | 1.16 × 10−4 | 4.39 × 10−7 | 6.65 × 10−6 |
| Nd | 5.44 × 10−10 | 1.11 × 10−4 | 3.01 × 10−8 | 2.61 × 10−5 |
| Sm | 3.74 × 10−8 | 1.98 × 10−4 | 2.07 × 10−6 | 4.69 × 10−6 |
| Eu | 1.03 × 10−8 | 9.07 × 10−6 | 5.71 × 10−7 | 6.82 × 10−7 |
| Gd | 1.52 × 10−9 | 2.15 × 10−4 | 8.42 × 10−8 | 3.92 × 10−6 |
| Tb | 4.88 × 10−9 | 2.24 × 10−4 | 2.70 × 10−7 | 5.65 × 10−7 |
| Dy | 4.14 × 10−10 | 2.18 × 10−4 | 2.29 × 10−8 | 2.88 × 10−6 |
| Ho | 9.21 × 10−9 | 2.13 × 10−4 | 5.10 × 10−7 | 5.27 × 10−7 |
| Er | 2.53 × 10−9 | 2.20 × 10−4 | 1.40 × 10−7 | 1.43 × 10−6 |
| Tm | 6.99 × 10−10 | 2.37 × 10−4 | 3.87 × 10−8 | 1.89 × 10−7 |
| Yb | 4.00 × 10−9 | 2.32 × 10−4 | 2.21 × 10−7 | 1.07 × 10−6 |
| Lu | 3.53 × 10−9 | 2.47 × 10−4 | 1.96 × 10−7 | 1.53 × 10−7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Guo, M. Spatial Heterogeneity of Rare Earth Elements: Implications for the Topsoil of Regional Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Deposit Areas in Southern China. Minerals 2023, 13, 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13060784
Chen H, Chen L, Zhang L, Guo M. Spatial Heterogeneity of Rare Earth Elements: Implications for the Topsoil of Regional Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Deposit Areas in Southern China. Minerals. 2023; 13(6):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13060784
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Haixia, Lingkang Chen, Lian Zhang, and Min Guo. 2023. "Spatial Heterogeneity of Rare Earth Elements: Implications for the Topsoil of Regional Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Deposit Areas in Southern China" Minerals 13, no. 6: 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13060784
APA StyleChen, H., Chen, L., Zhang, L., & Guo, M. (2023). Spatial Heterogeneity of Rare Earth Elements: Implications for the Topsoil of Regional Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Deposit Areas in Southern China. Minerals, 13(6), 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13060784






