The Role of Particle Size and Shape on the Recovery of Copper from Different Electrical and Electronic Equipment Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.1.1. End-of-Life Printed Circuit Boards (EOL PCBs)
2.1.2. Waste Electric Wires (WEWs)
2.2. Beneficiation Methods
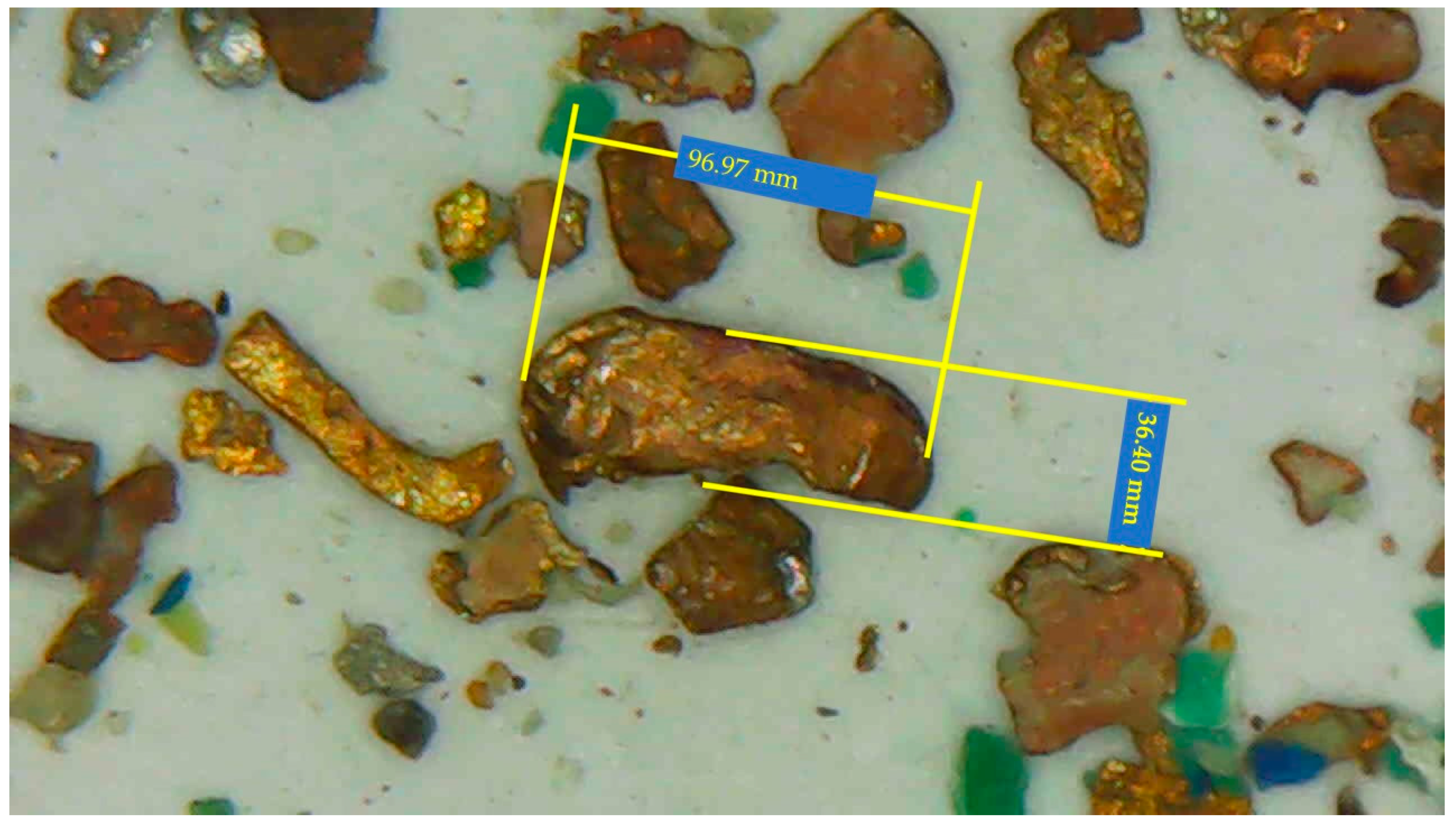
2.3. Particle Shape Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
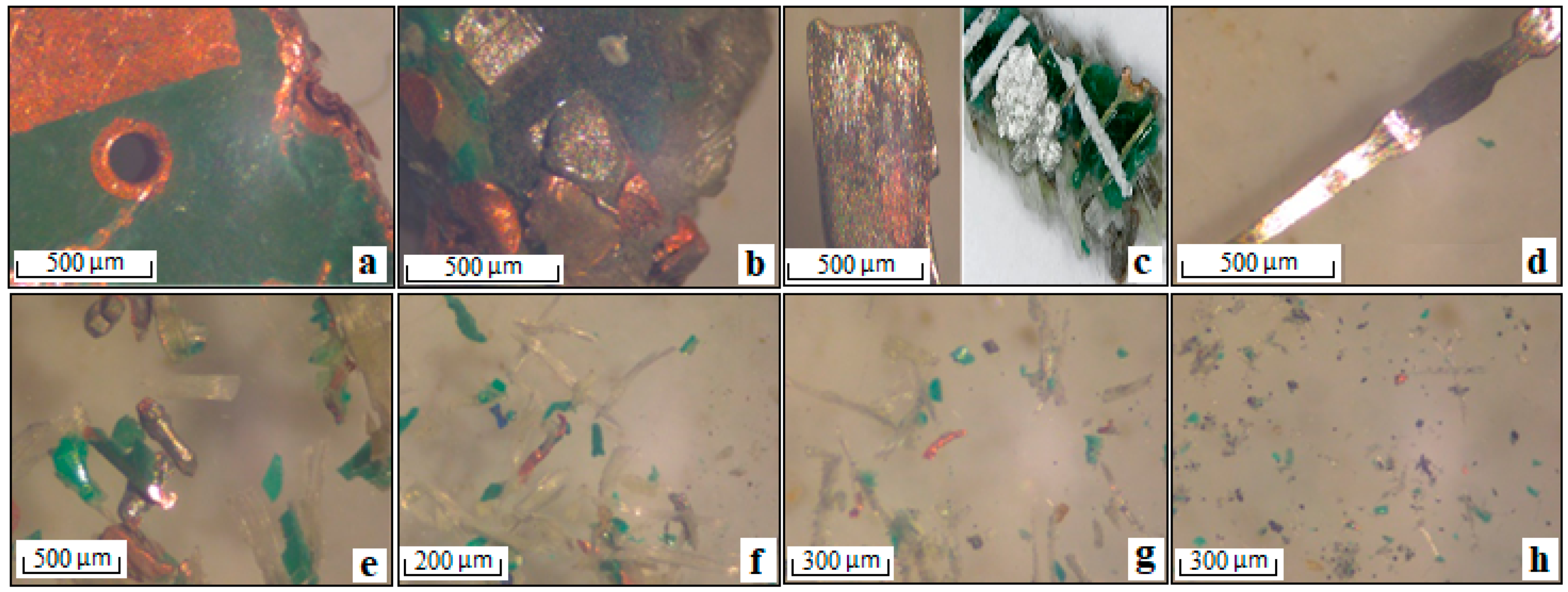
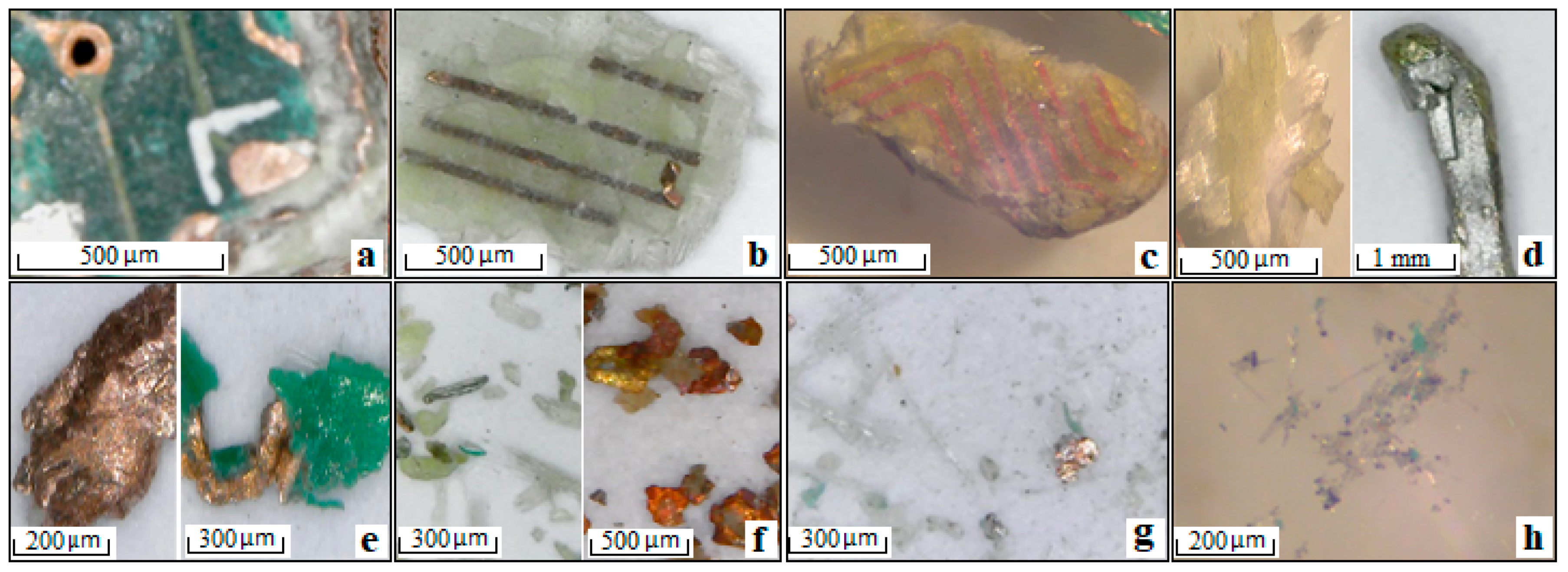
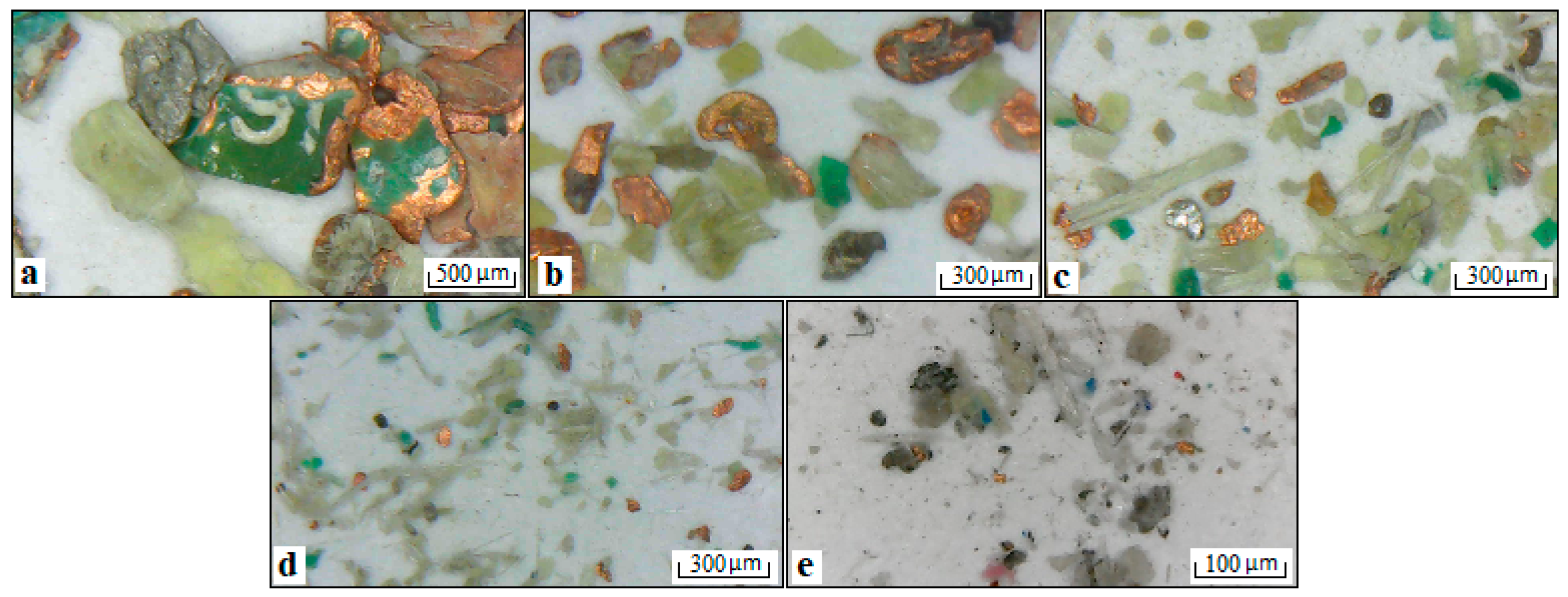
3.1. End-of-life Printed Circuit Boards (EOL PCBs)
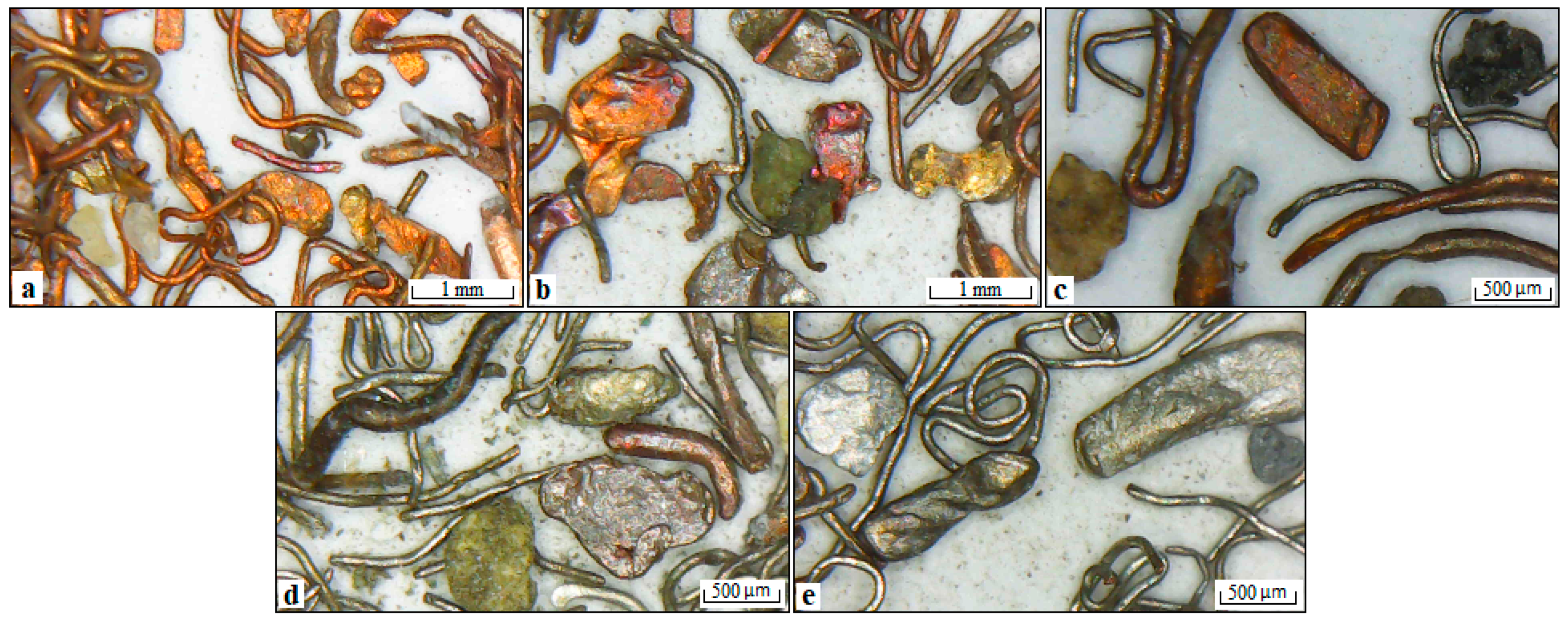
3.2. Waste Electric Wires (WEWs)
3.3. Shape Characterization of Copper Particles in Gravity and Flotation Separation Stages
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forti, V.; Baldé, C.P.; Kuehr, R.; Bel, G. The Global E-Waste Monitor 2020: Quantities, Flows and the Circular Economy Potential. Available online: https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-D/Environment/Documents/Toolbox/GEM_2020_def.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Nithya, R.; Sivasankari, C.; Thirunavukkarasu, A. Electronic waste generation, regulation and metal recovery: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1347–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, R.; Salem, F.Z.; Allam, N.K. E-waste recycled materials as efficient catalysts for renewable energy technologies and better environmental sustainability. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M. Recovery of metals and nonmetals from electronic waste by physical and chemical recycling processes. Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 64–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, M. Current WEEE recycling solutions. In Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Recycling: Aqueous Recovery Methods; Veglio, F., Birloaga, I., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Delhi, India, 2018; pp. 33–39. ISBN 978-0-08-102058-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ulusoy, U. Review of the recovery of cobalt from secondary resources. In Critical and Rare Earth Elements: From Secondary Resources, 1st ed.; Pillai, A., Akcil, A., Eds.; CRS Press/Taylor and Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 115–153. ISBN 978-0-367-08647-3. [Google Scholar]
- Goosey, M.; Kellner, R. Recycling technologies for the treatment of end of life printed circuit boards (PCBs). Circuit World 2003, 29, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive, E.U. 96/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 January 2003 on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE), L 37/24. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2003, 37, 24–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Holuszko, M.; Espinosa, D.C.R. E-waste: An overview on generation, collection, legislation and recycling practices. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 122, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.; Richard, G.; Medles, K.; Zeghloul, T.; Dascalescu, L. Distinct recovery of copper and aluminum from waste electric wires using a roll-type electrostatic separator. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, F.R.; Weng, H.; Qi, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, F.S.; Chen, M. A novel recovery method of copper from waste printed circuit boards by supercritical methanol process: Preparation of ultrafine copper materials. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Copper Association (ICA). Copper—The Pathway to Net Zero, March 2023. Available online: copperalliance.org (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Martinho, G.; Pires, A.; Saraiva, L.; Ribeiro, R. Composition of plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) by Direct Sampling. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Qiu, K. A New Technology for recycling materials from waste printed circuit boards. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanısalı, E.; Özer, M.; Burat, F. Precious metals recovery from waste printed circuit boards by gravity separation and leaching. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2020, 42, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilone, D.; Kelsall, G.H. Metal recovery from electronic scrap by leaching and electrowinning IV. In Proceedings of the TMS Fall Extraction and Processing Conference; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1565–1575. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Shrivastava, P.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.C. Printed circuit board recycling: A state-of-the-art survey. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2004, 27, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Hou, K.; Li, J.; Zhu, X. Examining the technology acceptance for dismantling of waste printed circuit boards in light of recycling and environmental concerns. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wire and Cable Recycling Market Is Estimated to Gain a Valuation of US$ 30.5 Bn by 2031, TMR Report. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2022/06/27/2469853/0/en/Wire-and-Cable-Recycling-Market-is-Estimated-to-Gain-a-Valuation-of-US-30-5-Bn-by-2031-TMR-Report.html (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Li, L.; Liu, G.; Pan, D.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zuo, T. Overview of the recycling technology for copper-containing cables. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 126, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kumagai, S.; Kameda, T.; Saito, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Hayashi, H.; Yoshioka, T. Separation of copper and polyvinyl chloride from thin waste electric cables: A combined pvc-swelling and centrifugal approach. Waste Manag. 2019, 89, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinová, L.; Godovčin, P. Importance of recycling the waste-cables containing copper and PVC. Res. Pap. Fac. Mater. Sci. Technol. Slovak Univ. Technol. 2021, 29, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinned Copper Wire. Available online: https://www.remingtonindustries.com/uninsulated-wire/tinned-copper-wire/ (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Copper, Brass & Bronze Wire. Available online: https://www.metalassociates.net/copper-brass-bronze-wire/ (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Scrap Copper Prices. Available online: https://www.hurmetsan.com/hurda-kablo-fiyatlari/ (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Pita, F.; Castilho, A. Separation of copper from electric cable waste based on mineral processing methods: A case study. Minerals 2018, 8, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xu, J.; Kumagai, S.; Kameda, T.; Saito, Y.; Yoshioka, T. Separation mechanism of polyvinyl chloride and copper components from swollen electric cables by mechanical agitation. Waste Manag. 2019, 93, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, B.A. Wills’ Mineral Processing Technology: An Introduction to the Practical Aspects of Ore Treatment and Mineral Recovery, 7th ed.; Elsevier/BH: Oxford, UK, 2006; ISBN 0750644508. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Forssberg, E. Intelligent liberation and classification of electronic scrap. Powder Technol. 1999, 105, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Duan, H.; Yu, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, S. Characteristic of low-temperature pyrolysis of printed circuit boards subjected to various atmosphere. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvar, M.; Salarirad, M.M.; Shabani, M.A. Characterization and mechanical separation of metals from computer printed circuit boards (PCBs) based on mineral processing methods. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, K.A.; Dahmen, K.A.; Jaeger, H.M. Transforming mesoscale granular plasticity through particle shape. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 011014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, U.; Yekeler, M.; Hiçyilmaz, C. Determination of the shape, morphological and wettability properties of quartz and their correlations. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burat, F.; Özer, M. Physical separation route for printed circuit boards. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2018, 54, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, U. A Review of particle shape effects on material properties for various engineering applications: From macro to nanoscale. Minerals 2023, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, U.; Hiçylmaz, C.; Yekeler, M. Role of shape properties of calcite and barite particles on apparent hydrophobicity. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2004, 43, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kademli, M.; Gulsoy, O.Y. The role of particle size and solid contents of feed on mica-feldspar separation in gravity concentration. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2012, 48, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Forssberg, E. Mechanical recycling of waste electric and electronic equipment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 99, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunniyi, I.O.; Vermaak, M.K.G. Froth flotation for beneficiation of printed circuit boards comminution fines: An overview. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2009, 30, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori-Sarpong, G.; Amankwah, R.K. Comminution environment and gold particle morphology: Effects on gravity concentration. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenial, Ü.; Burat, F.; Yüce, A.E.; Güney, A.; Kangal, M.O. Separation of PET and PVC by flotation technique without using alkaline treatment. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2013, 34, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güney, A.; Özdilek, C.; Kangal, M.O.; Burat, F. Flotation Characterization of PET and PVC in the presence of different plasticizers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burat, F.; Baştürkcü, H.; Özer, M. Gold&silver recovery from jewelry waste with combination of physical and physicochemical methods. Waste Manag. 2019, 89, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennik, F.; Dinç, N.İ.; Burat, F. Selective recovery of metals from spent mobile phone lithium-ıon batteries through froth flotation followed by magnetic separation procedure. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinç, N.İ.; Tosun, A.U.; Baştürkcü, E.; Özer, M.; Burat, F. Recovery of valuable metals from WPCB fines by centrifugal gravity separation and froth flotation. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2022, 24, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, U.; Atagun, O.N. Particle shape characterization of shaking table streams in a turkish chromite concentration plant by using dynamic ımaging and microscopical techniques. Part. Sci. Technol. 2023, 41, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forssberg, E.; Zhai, H. Shape and surface properties of particles liberated by autogenous grinding. Scand. J. Metall. 1985, 1, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Beyer, W.H. Handbook of Mathematical Sciences, 6th ed.; Beyer, W.H., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1978; pp. 7–30. [Google Scholar]
- Heywood, H. The scope of particle size analysis and standardization. In Proceedings of the Institution of Chemical Engineers, Symposium on Particle Size Analysis, London, UK, 4 February 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Hausner, H.H. Characterization of the powder particle shape. Planseeber. Pulvermetall. 1966, 14, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman, T.H.; Black, K.; Lilliesköld. Shape and Surface of Mineral Grains Tested for Mortar and Concrete Purposes through Image Analysis; Swedish Council for Building Research: Stockholm, Swedish, 1980; Volume 26, pp. 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Koyanaka, S.; Ohya, H.; Lee, J.C.; Iwata, H.; Endoh, S. Impact milling of printed circuit board wastes for resources recycling and evaluation of the liberation using heavy medium separation. J. Soc. Powder Technol. Jpn. 1999, 36, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burat, F.; Demirağ, A.; Şafak, M.C. Recovery of noble metals from floor sweeping jewelry waste by flotation-cyanide leaching. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Duan, C.; Li, G.; Huang, L.; Chai, X.; Wang, D. The influence of waste printed circuit boards characteristics and nonmetal surface energy regulation on flotation. Waste Manag 2018, 80, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Duan, C. Recovery of metallic concentrations from waste printed circuit boards via reverse floatation. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 6018–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, G.C.; Woodcock, J.T. A review of the flotation of native gold and electrum. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 931–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suponik, T.; Franke, D.M.; Nuckowski, P.M.; Matusiak, P.; Kowol, D.; Tora, B. Impact of Grinding of Printed Circuit Boards on the Efficiency of Metal Recovery by Means of Electrostatic Separation. Minerals 2021, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

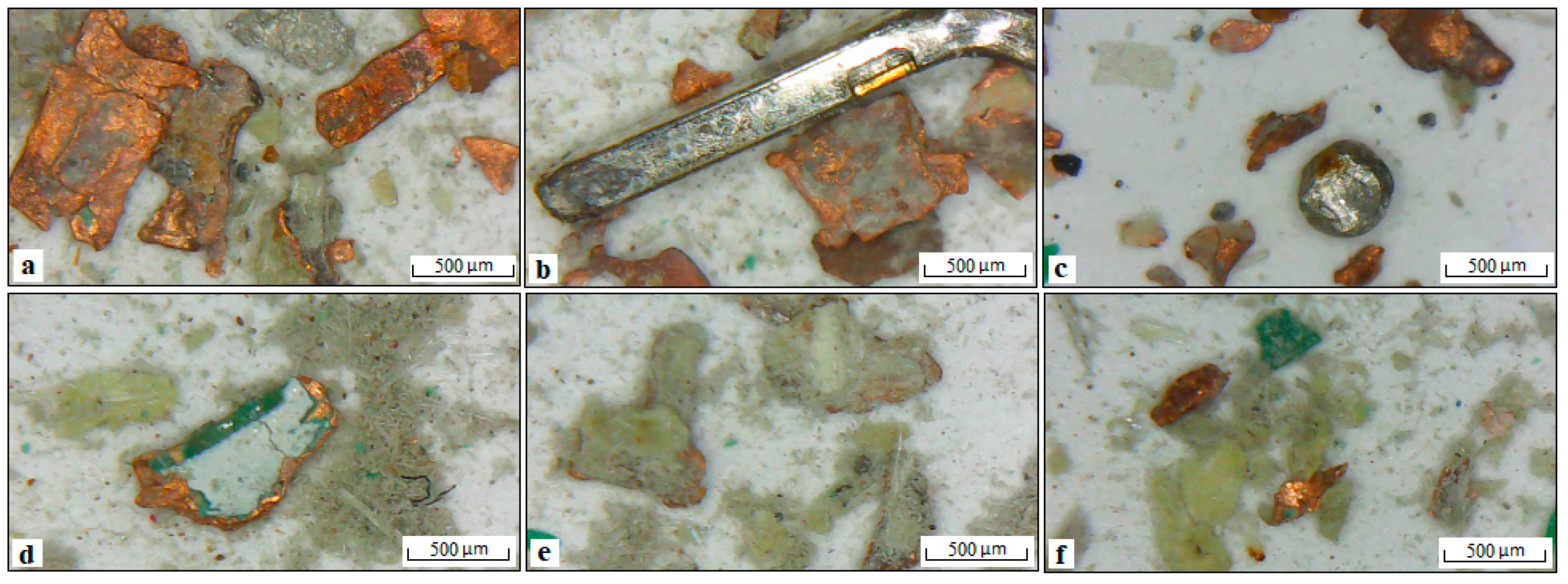
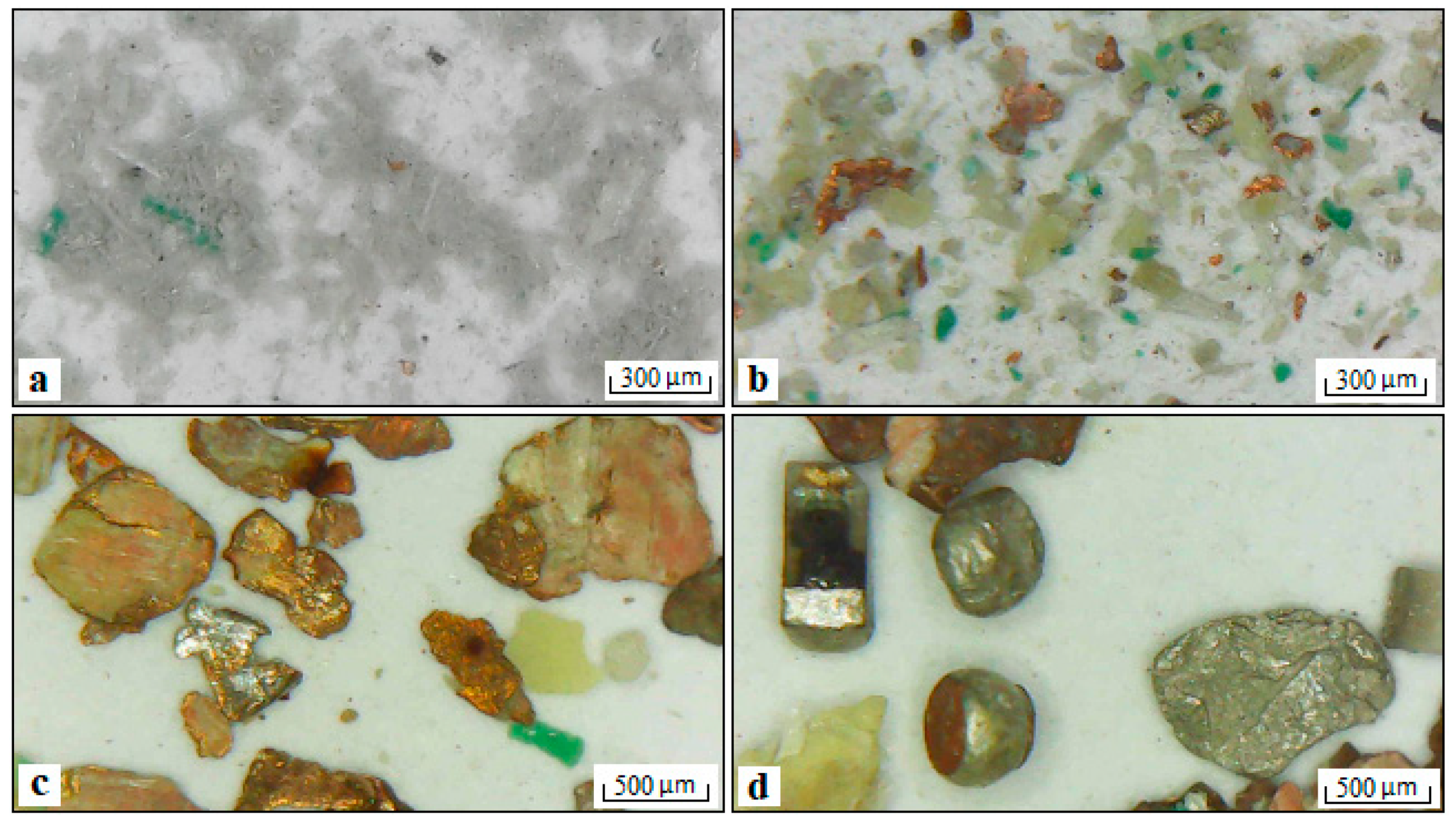





| Products | Amount, % | Cu | Au | Ag | Sn | Al | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C, % | R, % | C, g/t | R, % | C, g/t | R, % | C, % | R, % | C, % | R, % | ||
| Heavy | 28.4 | 62.46 | 52.1 | 53 | 58.4 | 1884 | 51.0 | 5.46 | 58.92 | 0.7 | 9.3 |
| Light | 71.6 | 22.74 | 47.9 | 15 | 41.6 | 719 | 49.0 | 1.51 | 41.08 | 2.72 | 90.7 |
| Total | 100.0 | 34.02 | 100.0 | 26 | 100.0 | 1050 | 100.0 | 2.63 | 100.0 | 2.15 | 100.0 |
| Products | Amount, % | Cu | Au | Ag | Sn | Al | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C, % | R, % | C, g/t | R, % | C, g/t | R, % | C, % | R, % | C, % | R, % | ||
| Float 1 | 26.4 | 1.58 | 1.2 | 47 | 49.6 | 381 | 9.6 | 0.7 | 7.3 | 4.15 | 48.0 |
| Float 2 | 29.5 | 12.32 | 10.6 | 16 | 18.7 | 426 | 12.0 | 0.87 | 10.1 | 2.68 | 34.6 |
| Float 3 | 21.4 | 82.11 | 51.4 | 14 | 11.9 | 1025 | 21.0 | 1.5 | 12.6 | 0.75 | 7.0 |
| Sink | 22.7 | 55.4 | 36.8 | 22 | 19.8 | 2642 | 57.4 | 7.85 | 70.0 | 1.05 | 10.4 |
| Total | 100.0 | 34.17 | 100.0 | 25 | 100.0 | 1045 | 100.0 | 2.54 | 100.0 | 2.29 | 100.0 |
| Products | Amount, % | Cu | Al | Fe | Sn | Zn | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C, % | R, % | C, % | R, % | C, % | R, % | C, % | R, % | C, % | R, % | ||
| Heavy | 87.5 | 92.84 | 94.9 | 2.98 | 30.1 | 0.04 | 63.6 | 0.39 | 97.5 | 0.56 | 95.6 |
| Light | 12.5 | 35.27 | 5.1 | 48.55 | 69.9 | 0.16 | 36.4 | 0.07 | 2.5 | 0.18 | 4.4 |
| Total | 100.0 | 85.64 | 100.0 | 8.68 | 100.0 | 0.06 | 100.0 | 0.35 | 100.0 | 0.51 | 100.0 |
| Products | Amount, % | Cu | Al | Fe | Sn | Zn | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C, % | R, % | C, % | R, % | C, % | R, % | C, % | R, % | C, % | R, % | ||
| Float 1 | 28.9 | 93.54 | 31.5 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 5.0 | 0.03 | 2.4 | 0.32 | 18.1 |
| Float 2 | 18.1 | 87.05 | 18.3 | 8.14 | 17.3 | 0.02 | 6.3 | 0.08 | 4.1 | 1.25 | 44.2 |
| Float 3 | 23.7 | 85.12 | 23.5 | 9.25 | 25.8 | 0.05 | 20.7 | 0.24 | 16.0 | 0.65 | 30.2 |
| Float 4 | 11.4 | 81.51 | 10.8 | 14.14 | 19.0 | 0.06 | 11.9 | 0.64 | 20.4 | 0.18 | 4.0 |
| Sink | 17.9 | 76.54 | 15.9 | 18.08 | 37.8 | 0.18 | 56.1 | 1.14 | 57.1 | 0.1 | 3.5 |
| Total | 100.0 | 85.95 | 100.0 | 8.52 | 100.0 | 0.06 | 100.0 | 0.36 | 100.0 | 0.51 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burat, F.; Dinç, N.İ.; Dursun, H.N.; Ulusoy, U. The Role of Particle Size and Shape on the Recovery of Copper from Different Electrical and Electronic Equipment Waste. Minerals 2023, 13, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070847
Burat F, Dinç Nİ, Dursun HN, Ulusoy U. The Role of Particle Size and Shape on the Recovery of Copper from Different Electrical and Electronic Equipment Waste. Minerals. 2023; 13(7):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070847
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurat, Fırat, Nazlım İlkyaz Dinç, Halide Nur Dursun, and Ugur Ulusoy. 2023. "The Role of Particle Size and Shape on the Recovery of Copper from Different Electrical and Electronic Equipment Waste" Minerals 13, no. 7: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070847
APA StyleBurat, F., Dinç, N. İ., Dursun, H. N., & Ulusoy, U. (2023). The Role of Particle Size and Shape on the Recovery of Copper from Different Electrical and Electronic Equipment Waste. Minerals, 13(7), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070847








