Characterization of a Metamorphosed Volcanic Stratigraphy and VMS Alteration Halos Using Rock Chip Petrography and Lithogeochemistry: A Case Study from King North, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia
Abstract
1. Introduction
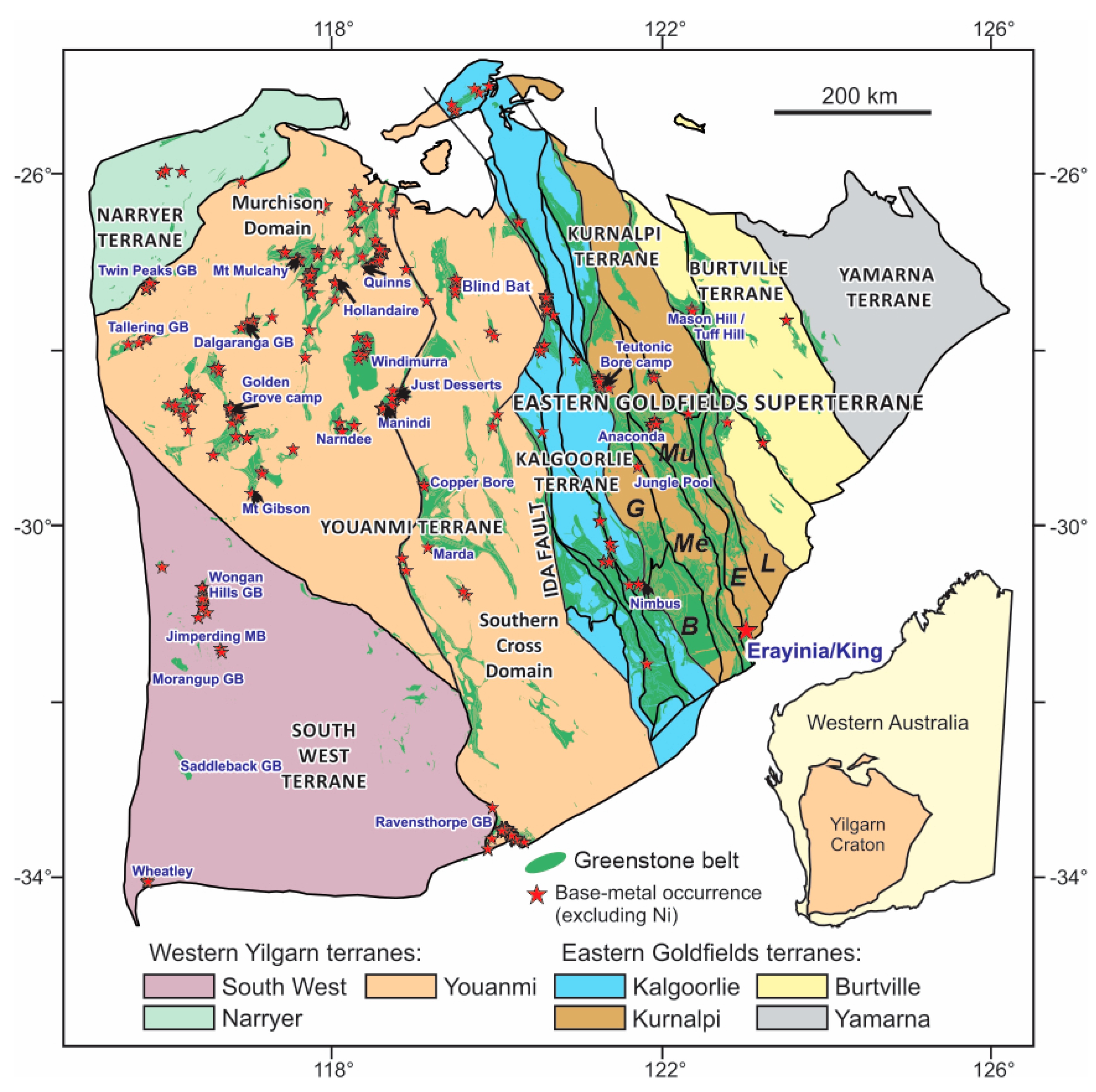
2. Regional Geology of the Southern Kurnalpi Terrane
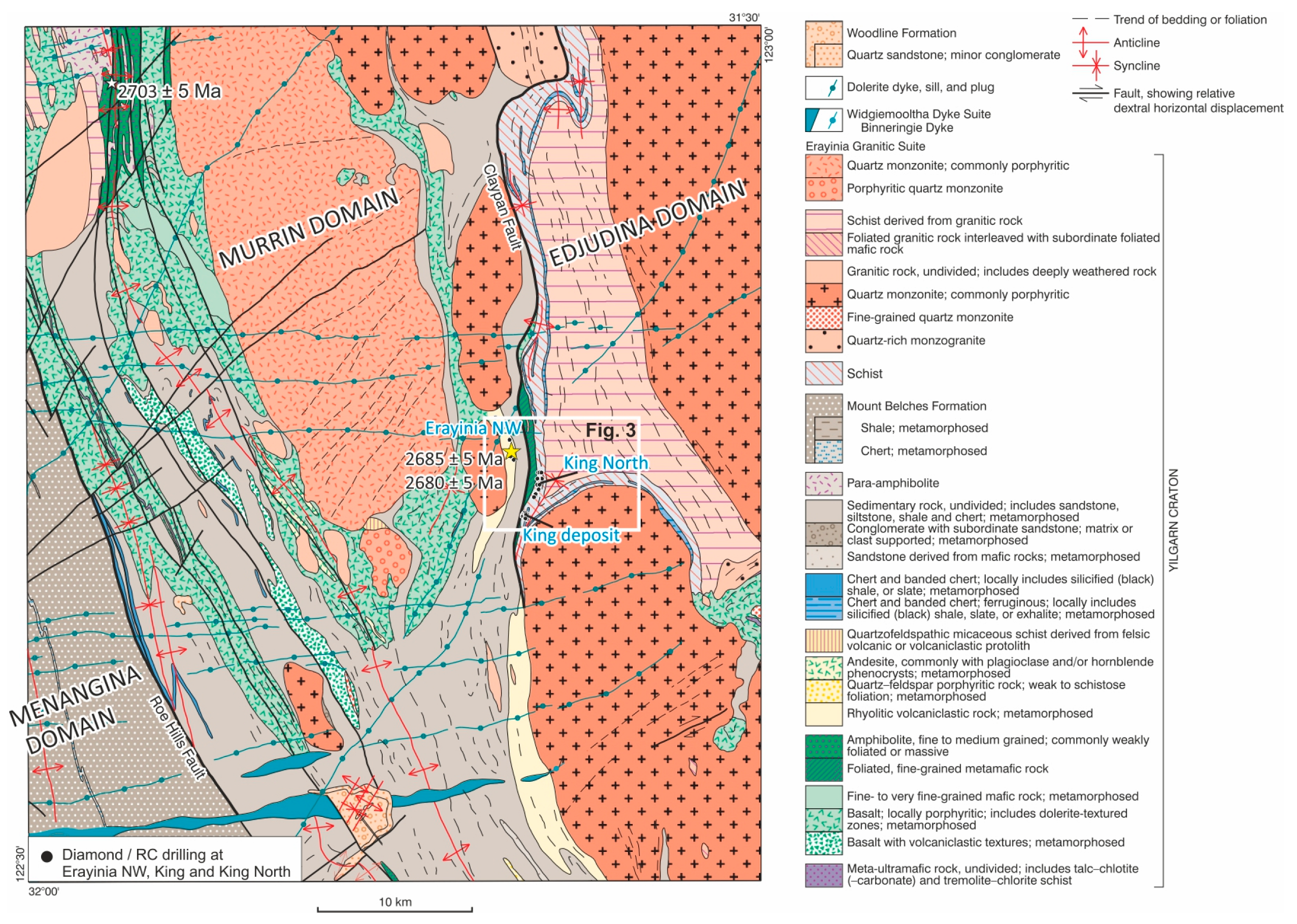
3. Stratigraphy of the King Deposit
4. Exploration History
- EC175: 24 m at 0.1% Zn and 16 m at 0.3% Cu,
- EC179: 18 m at 0.2% Cu, 0.16 g/t Au, 4.6 ppm Ag,
- EC164: 1 m at 4.7% Zn, 2.0% Pb, 0.69 g/t Au, 128 ppm Ag.
5. Methods
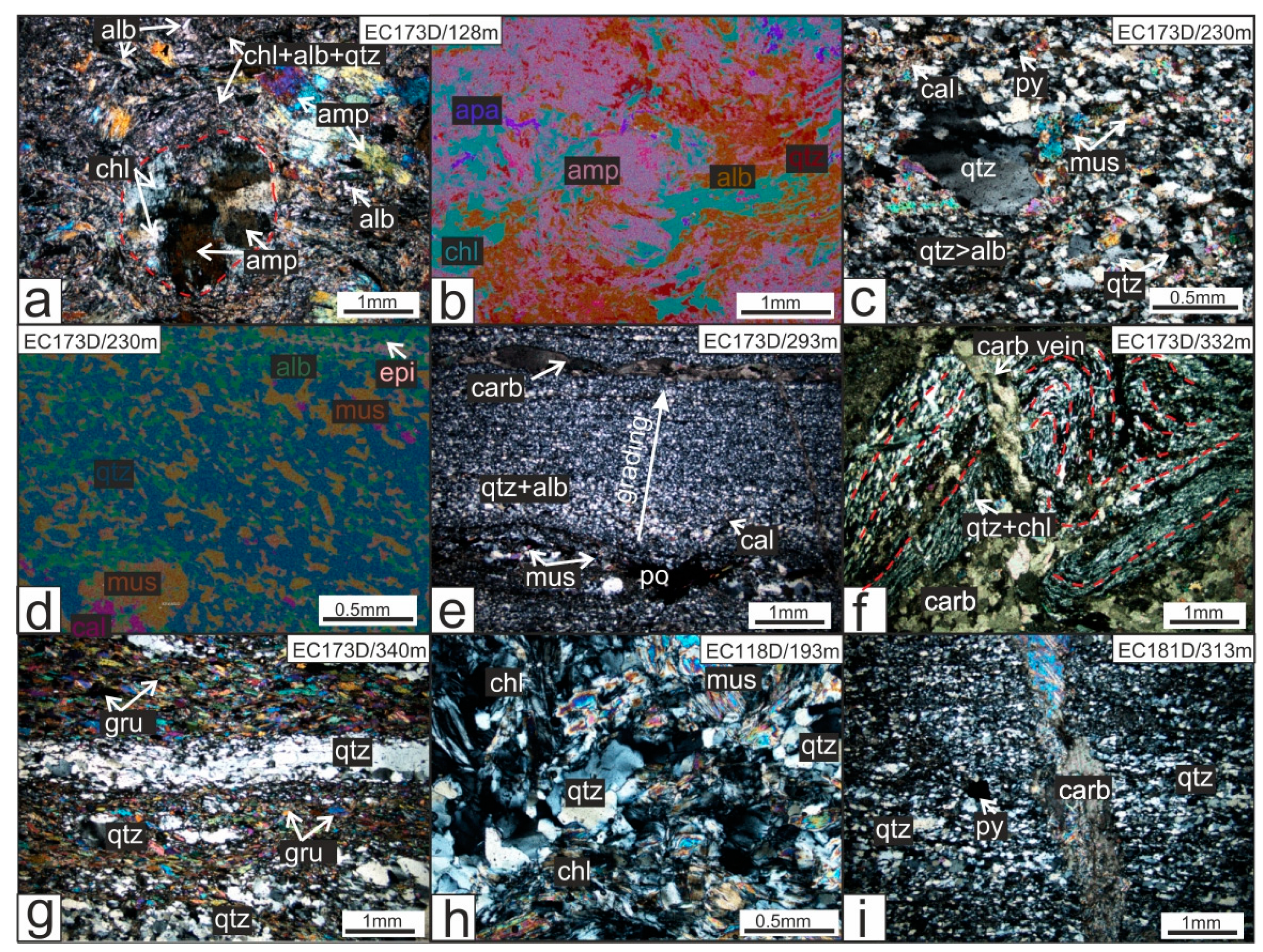
5.1. Petrography
5.2. Whole Rock Geochemistry
5.3. X-ray Diffraction
6. Results
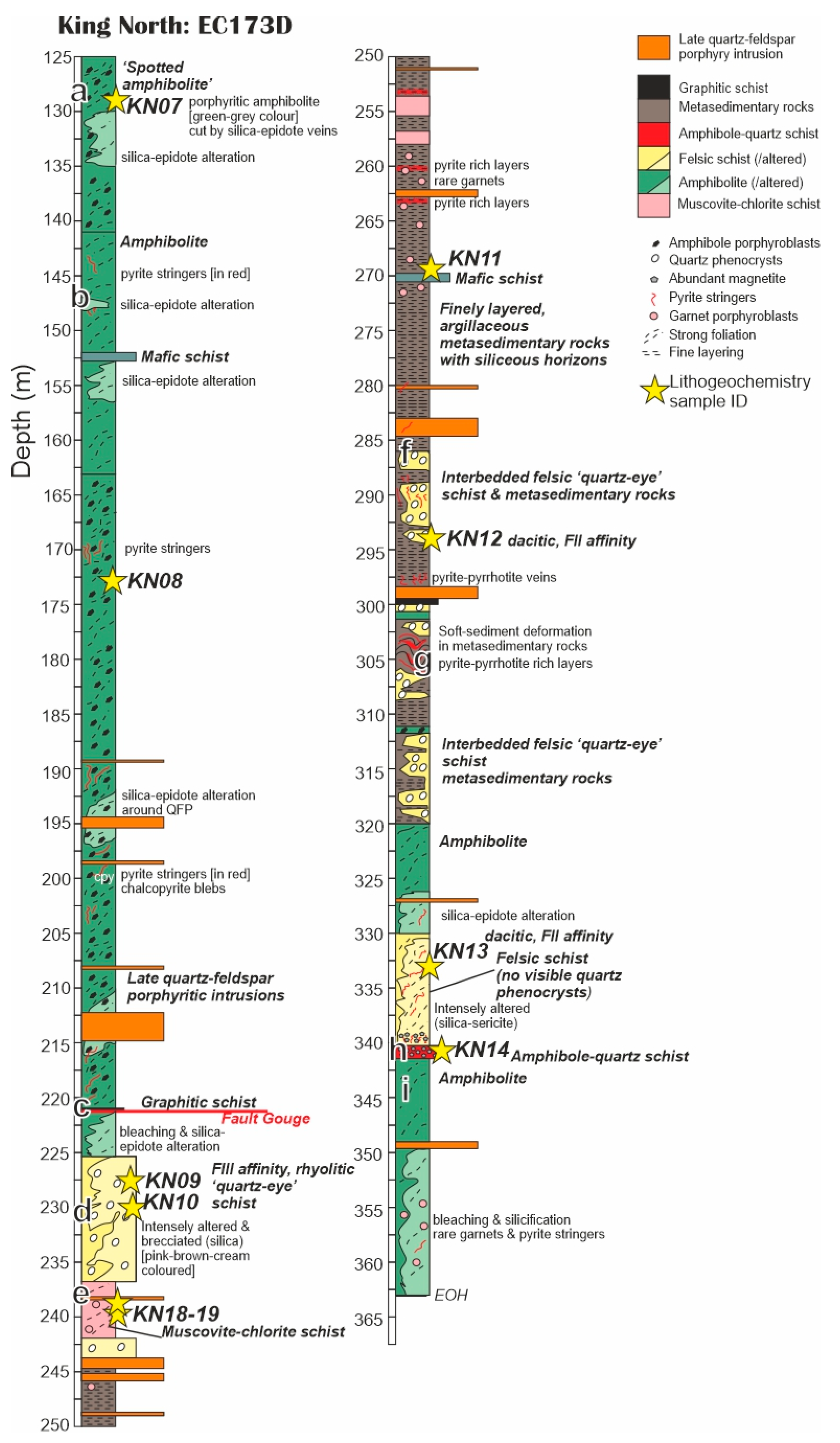
6.1. Shallow King North Stratigraphy
6.2. Deep King North Stratigraphy
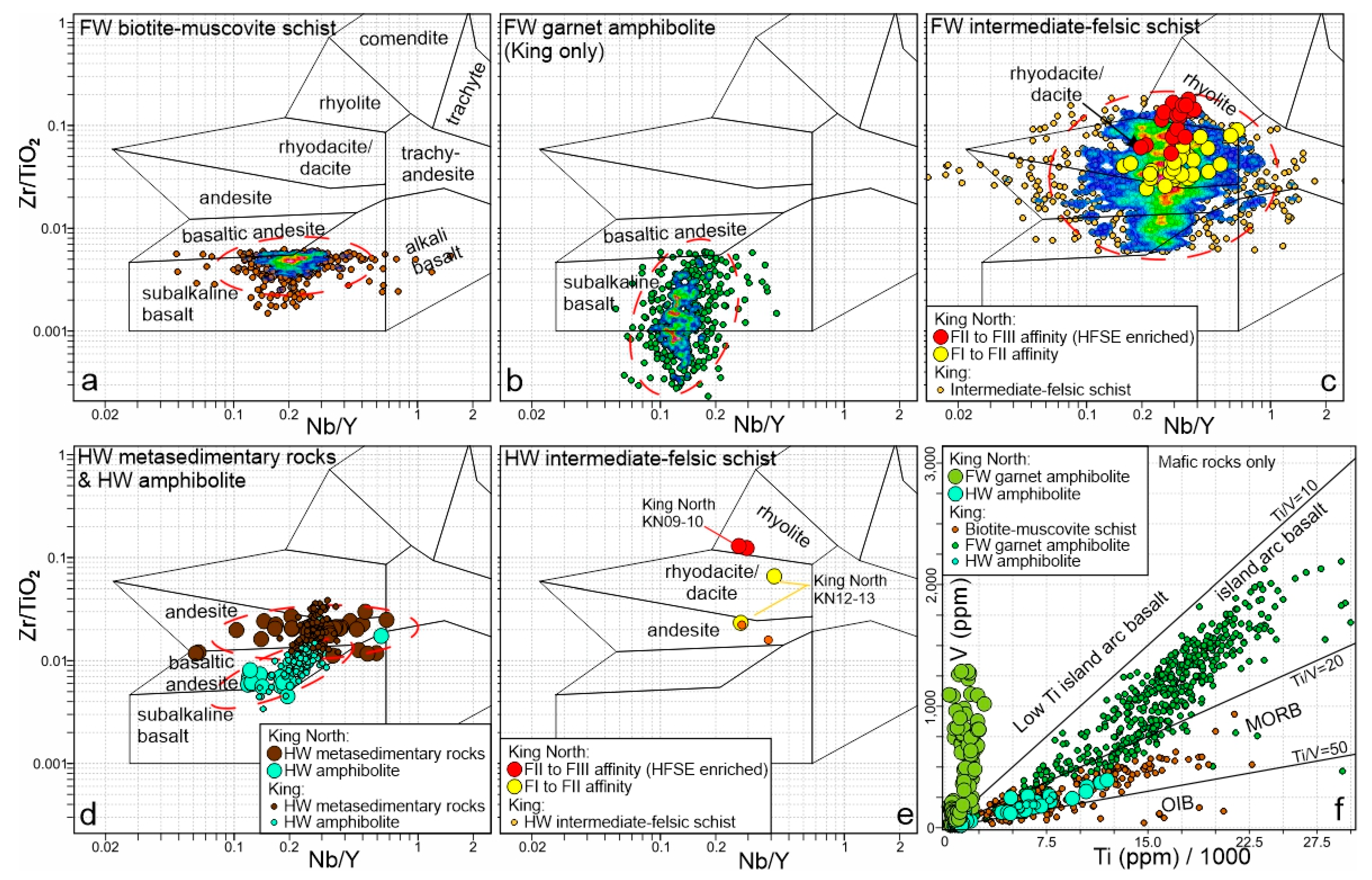
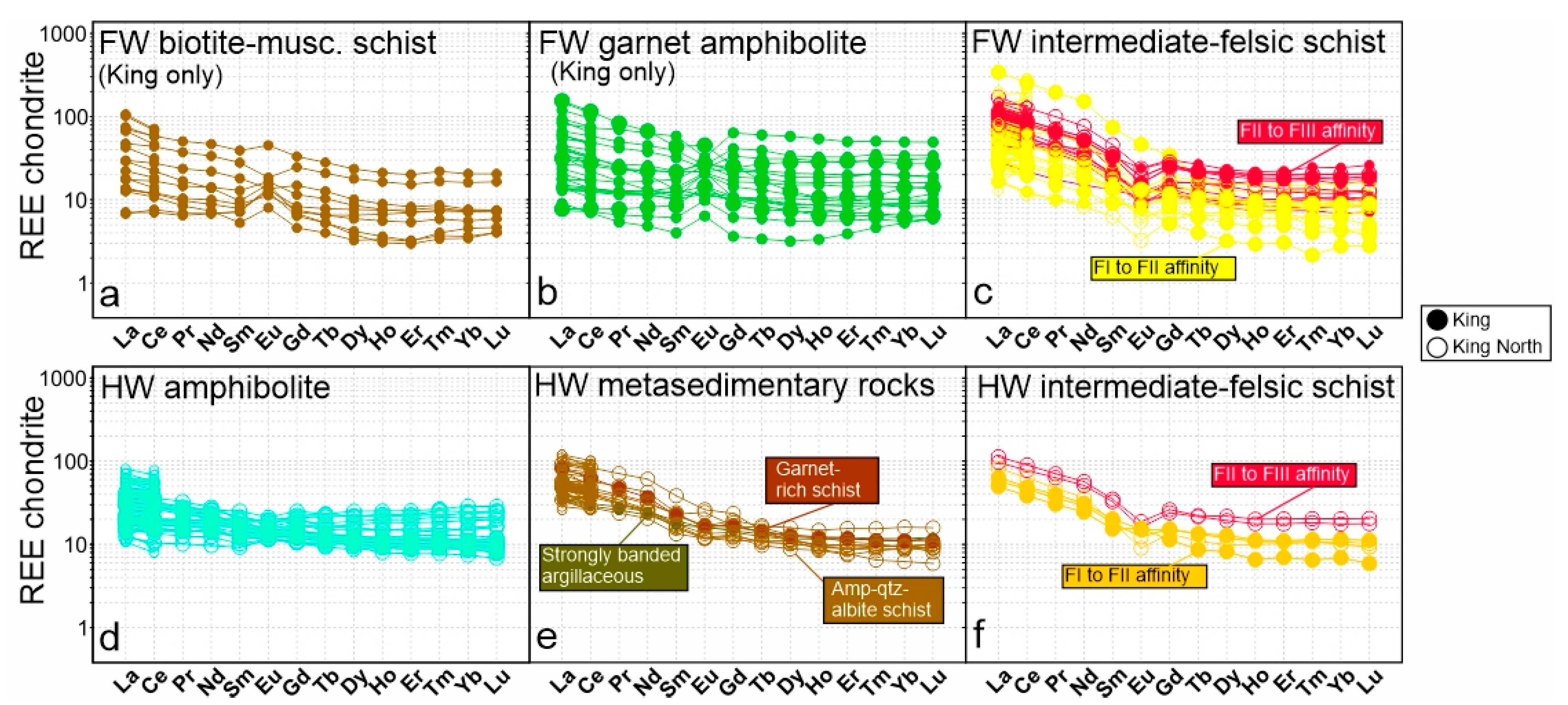
6.3. King North Lithogeochemistry
7. Discussion
7.1. Geology of the King North Prospect and Correlations with the King Area
7.2. An Overturned VMS System at King North
7.3. Implications for Exploration at King North
7.4. Stacked VMS Potential in the King Greenstone Belt?
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeats, C.J. VHMS mineral systems in the Yilgarn—Characteristics and exploration potential. In Proceedings of the Geoconferences (WA) Inc. Kalgoorlie 07 Conference, Kalgoorlie, Australia, 25–27 September 2007; Bierlein, F.P., Ed.; Geoconferences Inc.: Perth, WA, USA, 2007; pp. 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Hollis, S.P.; Yeats, C.J.; Wyche, S.; Barnes, S.J.; Ivanic, T.J.; Belford, S.M.; Davidson, G.J.; Roache, A.J.; Wingate, M.T.D. A review of volcanic-hosted massive sulfide (VHMS) mineralization in the Archaean Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia: Tectonic, stratigraphic and geochemical associations. Precambrian Res. 2015, 260, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayman, P.C.; Hull, S.E.; Cas, R.A.; Summerhayes, E.; Amelin, Y.; Ivanic, T.J.; Price, D. A new period of volcanogenic massive sulfide formation in the Yilgarn: A volcanological study of the ca 2.76 Ga Hollandaire VMS deposit, Yilgarn craton, Western Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 62, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duuring, P.; Hassan, L.; Zelic, M.; Gessner, K. Geochemical and spectral footprint of metamorphosed and deformed VMS-style mineralization in the Quinns district, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Econ. Geol. 2016, 111, 1411–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrote, V.R.; McNaughton, N.J.; Tessalina, S.G.; Evans, N.J.; Talavera, C.; Zi, J.-W.; McDonald, B.J. The 4D evolution of the Teutonic Bore Camp VHMS deposits, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 120, 103448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kranendonk, M.J.; Ivanic, T.J.; Wingate, M.T.D.; Kirkland, C.L.; Wyche, S. Long-lived, autochthonous development of the Archean Murchison Domain, and implications for Yilgarn Craton tectonics. Precambrian Res. 2013, 229, 49–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanic, T.J.; Wingate, M.T.D.; Kirkland, C.L.; Van Kranendonk, M.J.; Wyche, S. Age and significance of voluminous mafic-ultramafic magmatic events in the Murchison Domain, Yilgarn Craton. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2010, 57, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollis, S.; Podmore, D.; James, M.; Menuge, J.F.; Doran, A.L.; Yeats, C.J.; Wyche, S. VHMS mineralisation at Erayinia in the Eastern Goldfields Superterrane: Geology and geochemistry of the metamorphosed King Zn deposit. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 66, 153–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, D.L.; Champion, D.C.; Cassidy, K.F. Tectonic controls on the endowment of Archean cratons in VHMS deposits: Evidence from Pb and Nd isotopes. In Mineral Deposit Research: Meeting the Global Challenge, Proceedings of the Eighth Biennial SGA Meeting, Beijing, China, 18–21 August 2005; Mao, J., Bierlein, F.P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Huston, D.L.; Champion, D.C.; Cassidy, K.F. Tectonic controls on the endowment of Neoarchean cratons in volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits: Evidence from lead and neodymium isotopes. Econ. Geol. 2014, 109, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, R.; Gemmell, J.B. Alteration characteristics of the Archean Golden Grove Formation at the Gossan Hill deposit, Western Australia: Induration as a focusing mechanism for mineralizing hydrothermal fluids. Econ. Geol. 2001, 96, 1239–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belford, S.M.; Davidson, G.J.; McPhie, J.; Large, R.R. Architecture of the Neoarchean Jaguar VHMS deposit, Western Australia: Implications for prospectivity and presence of depositional breaks. Precambrian Res. 2015, 260, 136–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, P.; Belford, S.M.; Maier, R.; Lynn, S.; Stewart, W. Teutonic Bore-Jaguar–Bentley volcanogenic massive sulfide field. In Australian Ore Deposits; Phillips, G.N., Ed.; The Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Melbourne, Australia, 2017; pp. 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Hollis, S.P.; Podmore, D.; James, M.; Mole, D.R.; Turner, O.; Kneeshaw, A.; Beaton, R. Targeting VHMS mineralization at Erayinia in the Eastern Goldfields Superterrane using lithogeochemistry, soil chemistry and HyLogger data. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 207, 106379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Perdrix, R.L. Pisolithic laterite geochemistry in the Golden Grove massive sulfide district, Western Australia. J. Geochem. Explor. 1983, 18, 131–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Singh, B. Recognizing, in lateritic cover, detritus shed from the Archaean Gossan Hill Cu–Zn–Su volcanic-hosted massive sulphide deposit, Western Australia. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2007, 7, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.J.; Yeats, C.J.; Noble, R.R.P.; Reid, N. Hydrogeochemical exploration for volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits in semi-arid Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 65, 249–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeats, C.J.; Groves, D.I. The Archaean Mount Gibson gold deposits, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia: Products of combined synvolcanic and syntectonic alteration and mineralisation. Ore Geol. Rev. 1998, 13, 103–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, L.Y. The Yuinmery Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Prospects: Mineralization, Metasomatism and Geology; Geological Survey of Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 2014; Report 131; Volume 65. [Google Scholar]
- Hollis, S.P.; Mole, D.R.; Gillespie, P.; Barnes, S.J.; Tessalina, S.; Cas, R.A.F.; Hildrew, C.; Pumphrey, A.; Goodz, M.D.; Caruso, S.; et al. 2.7 Ga plume associated VHMS mineralization in the Eastern Goldfields Superterrane, Yilgarn Craton: Insights from the low temperature and shallow water, Ag-Zn-(Au) Nimbus deposit. Precambrian Res. 2017, 291, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, D.C.; Cassidy, K.F. An overview of the Yilgarn Craton and its crustal evolution. Geosci. Aust. Rec. 2007, 14, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mole, D.R.; Fiorentini, M.L.; Cassidy, K.F.; Kirkland, C.L.; Thebaud, N.; McCuaig, T.C.; Doublier, M.P.; Duuring, P.; Romano, S.S.; Maas, R.; et al. Crustal evolution, intra-cratonic architecture and the metallogeny of an Archaean craton. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2013, 393, SP393-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, K.F.; Champion, D.C.; Krapež, B.; Barley, M.E.; Brown, S.J.A.; Blewett, R.S.; Groenewald, P.B.; Tyler, I.M. A Revised Geological Framework for the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia; Western Australia Geological Survey: Perth, WA, Australia, 2006; Record 2006/8; 8p. [Google Scholar]
- Pawley, M.J.; Wingate, M.T.D.; Kirkland, C.L.; Wyche, S.; Hall, C.E.; Romano, S.S.; Doublier, M.P. Adding pieces to the puzzle: Episodic crustal growth and a new terrane in the northeast Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2012, 59, 603–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barley, M.E.; Brown, S.J.A.; Krapež, B.; Kositcin, N. Physical volcanology and geochemistry of a Late Archaean volcanic arc: Kurnalpi and Gindalbie Terranes, Eastern Goldfields Superterrane, Western Australia. Precambrian Res. 2008, 161, 53–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyche, S.; Pawley, M.; Chen, S.; Ivanic, T.; Zibra, I.; Van Kranendonk, M.; Spaggiari, C.; Wingate, M. Geology of the northern Yilgarn Craton. In Youanmi and Southern Carnarvon Seismic and Magnetotelluric (MT) Workshop; Wyche, S., Ivanic, T.J., Zibra, I., Eds.; Geological Survey of Western Australia: East Perth, WA, Australia, 2013; Volume 6, pp. 33–65. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.A. Geology of the Erayinia 1: 100 000 Sheet; Geological Survey of Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wingate, M.T.D.; Bodorkos, S. 177919: Felsic metavolcanic rock, Urania Prospect; Geochronology dataset 666. In Compilation of Geochronology Data; Western Australia Geological Survey: Perth, WA, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Swager, C. Geology of the Greenstone Terranes in the Kurnalpi-Edjudina Region, Southeastern Yilgarn Craton; Geological Survey of Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 1995; Volume 47. [Google Scholar]
- Swager, C.P. Tectono-stratigraphy of late Archaean greenstone terranes in the southern Eastern Goldfields, Western Australia. Precambrian Res. 1997, 83, 11–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.R. 104973: Metadacite porphyry, east of Liberty Bore. In Compilation of SHRIMP U–Pb Zircon Geochronology Data, 1994 (158–161); Western Australia Geological Survey: Perth, WA, USA, 1995; Record 1995/3. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.R. 104971: Metatonalite, Round Hill. In Compilation of SHRIMP U–Pb Zircon Geochronology Data, 1995 (43–46); Western Australia Geological Survey: Perth, WA, USA, 1996; Record 1996/5. [Google Scholar]
- Wingate, M.T.D.; Lu, Y.; Kirkland, C.L.; Spaggiari, C.V. 182419: Granite Gneiss, Coonana Hill, Geochronology Record 1300; Geological Survey of Western Australia: Perth, WA, Australia, 2016; 4p. [Google Scholar]
- Fettes, D.; Desmons, J. Metamorphic rocks: A classification and glossary of terms. In Recommendations of the International Union of Geological Sciences; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Black Raven Mining. Annual Report. For the Period 12 December 2017 to 11 December 2018; Black Raven Mining: Canning Vale, Australia, 2019; 50p. [Google Scholar]
- Black Raven Mining. Annual Report. For the Period 19 December 2015 to 18 December 2016; Black Raven Mining: Canning Vale, Australia, 2017; Erayinia Project C229/2007; 39p. [Google Scholar]
- Grunsky, E.C. Predicting Archaean volcanogenic massive sulphide deposit potential from lithogeochemistry: Application to the Abitibi Greenstone Belt. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2013, 13, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.M.; Lydon, J.W.; Sangster, D.F. Volcanic-associated massive sulfide deposits. In Economic Geology 75th Anniversary Volume; Skinner, B.J., Ed.; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 1981; pp. 485–627. [Google Scholar]
- Large, R.R. Australian volcanic-hosted massive sulphide deposits: Features, styles and genetic models. Econ. Geol. 1992, 87, 471–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, A.G.; Hannington, M.D.; Jonasson, I.R. Volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits. In Mineral Deposits of Canada: A Synthesis of Major Deposit-Types, District Metallogeny, the Evolution of Geological Provinces, and Exploration Methods; Geological Association of Canada, Mineral Deposits Division: St. John’s, NL, Canada, 2007; Special Publication; Volume 5, pp. 141–161. [Google Scholar]
- Lobanov, K.; Yakubchuk, A.; Creaser, R. A Besshi-type VMS deposits of the Rudny Altai (Central Asia). Econ. Geol. 2014, 109, 1403–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, W.H.; Barrett, T.J. Lithogeochemical techniques using immobile elements. J. Geochem. Explor. 1993, 48, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, G.A. Trace element geochemistry of igneous rocks: Geochemical nomenclature and analytical geochemistry. In Trace Element Geochemistry of Volcanic Rocks: Applications for Massive Sulfide Exploration; Wyman, D.A., Ed.; Geological Association of Canada: St. John’s, NL, Canada, 1996; Short Course Notes; Volume 12, pp. 51–77. [Google Scholar]
- MacLean, W.H. Mass change calculations in altered rock series. Miner. Depos. 1990, 25, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynton, W.V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. In Developments in Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 63–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Sawaguchi, T.; Iwaya, S.; Horiuchi, M. Delineation of prospecting targets for Kuroko deposits based on modes of volcanism of underlying dacite and alteration halos. Min. Geol. 1976, 26, 105–117, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Schardt, C.; Cooke, D.R.; Gemmell, J.B.; Large, R.R. Geochemical modeling of the zoned footwall alteration pipe, Hellyer volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposit, Western Tasmania, Australia. Econ. Geol. 2001, 96, 1037–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Large, R.R.; Gemmell, J.B.; Paulick, H. The Alteration Box Plot: A simple approach to understanding the relationship between alteration mineralogy and lithogeochemistry associated with volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits. Econ. Geol. 2001, 96, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winchester, J.A.; Floyd, P.A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements. Chem. Geol. 1977, 20, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shervais, J.W. Ti-V plots and the petrogenesis of modern and ophiolitic lavas. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1982, 59, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, A.R.; Kerr, A.C.; Pearce, J.A.; Mitchell, S.F. Classification of altered volcanic island arc rocks using immobile trace elements: Development of the Th–Co discrimination diagram. J. Petrol. 2007, 48, 2341–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesher, C.M.; Goodwin, A.M.; Campbell, I.H.; Gorton, M.P. Trace-element geochemistry of ore-associated and barren, felsic metavolcanic rocks in the Superior Province, Canada. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1986, 23, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piercey, S.J. The setting, style, and role of magmatism in the formation of volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. Miner. Depos. 2011, 46, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeats, C.J.; Hollis, S.P.; Halfpenny, A.; Coronoa, J.-C.; LaFlamme, C.; Southam, G.; Fiorentini, M.; Herrington, R.J.; Spratt, J. Actively forming Kuroko-type volcanic-hosted massive sulfide (VHMS) mineralization at Iheya North, Okinawa Trough, Japan. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 84, 20–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusel-Bacon, C. Petrology of metamorphic rocks associated with volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. In Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence Model; U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010-5070-C; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; Chapter 17; 10p. [Google Scholar]
- Hollis, S.P.; Foury, S.; Caruso, S.; Johnson, S.; Barrote, V.; Pumphrey, A. Lithogeochemical and hyperspectral halos to Ag-Zn-Au mineralization at Nimbus in the Eastern Goldfields Superterrane, Western Australia. Minerals 2021, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, T.R.; Gibson, H.L.; Lesher, C.M. Trace element geochemistry and petrogenesis of felsic volcanic rocks associated with volcanogenic massive Cu-Zn-Pb sulfide deposits. Econ. Geol. 2004, 99, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrie, C.T. Zircon thermometry of high-temperature rhyolites near volcanic-associated massive sulfide deposits. Abitibi subprovince, Canada. Geology 1995, 23, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrie, C.T.; Ludden, J.N.; Green, T.H. Geochemistry of volcanic rocks associated with Cu–Zn and Ni–Cu deposits in the Abitibi Subprovince. Econ. Geol. 1993, 88, 1341–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, H.; Galley, A. Volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits of the Archean, Noranda District, Quebec. In Mineral Deposits of Canada: A Synthesis of Major Deposit-Types, District Metallogeny, the Evolution of Geological Provinces, and Exploration Methods; Special Publication; Goodfellow, W.D., Ed.; Mineral Deposits Division, Geological Association of Canada: St. John’s, NL, Canada, 2007; Volume 5, pp. 533–552. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, J.M.; Goodfellow, W.D. Mineralogy, bulk and rare earth element geochemistry of massive sulphide-associated hydrothermal sediments of the Brunswick Horizon, Bathurst Mining Camp, New Brunswick. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1996, 33, 252–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, J.M.; Goodfellow, W.D. Hydrothermal sedimentary rocks of the Heath Steele Belt, Bathurst Mining Camp, New Brunswick. Part 3. Application of mineralogy and mineral and bulk compositions to massive sulfide exploration. Econ. Geol. Monogr. 2003, 11, 317–433. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, G.J.; Stolz, A.J.; Eggins, S.M. Geochemical anatomy of silica iron exhalites: Evidence for hydrothermal oxyanion cycling in response to vent fluid redox and thermal evolution (Mt. Windsor Subprovince, Australia). Econ. Geol. 2001, 96, 1201–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, R.A. Data report: Petrography and geochemistry of jasperoids from site 1189, ocean drilling program Leg 193. In Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program Scientific Results; Barriga, F.J.A.S., Binns, R.A., Miller, D.J., Herzig, P.M., Eds.; Ocean Drilling Program: College Station, TX, USA, 2006; Volume 193, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollis, S.P.; Cooper, M.R.; Herrington, R.J.; Roberts, S.; Earls, G.; Verbeeten, A.; Piercey, S.J.; Archibald, S.M. Distribution, mineralogy and geochemistry of silica-iron exhalites and related rocks from the Tyrone Igneous Complex: Implications for VMS mineralization in Northern Ireland. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 159, 148–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kelly, J.; Hollis, S.P.; Dana, C.D.P.; Kneeshaw, A.; Podmore, D.; James, M.; Azri, R.; Rodgers, C.; Roberts, S. Characterization of a Metamorphosed Volcanic Stratigraphy and VMS Alteration Halos Using Rock Chip Petrography and Lithogeochemistry: A Case Study from King North, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Minerals 2024, 14, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050481
Kelly J, Hollis SP, Dana CDP, Kneeshaw A, Podmore D, James M, Azri R, Rodgers C, Roberts S. Characterization of a Metamorphosed Volcanic Stratigraphy and VMS Alteration Halos Using Rock Chip Petrography and Lithogeochemistry: A Case Study from King North, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Minerals. 2024; 14(5):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050481
Chicago/Turabian StyleKelly, Jamie, Steven P. Hollis, Cendi D. P. Dana, Allan Kneeshaw, Darryl Podmore, Megan James, Riquan Azri, Conal Rodgers, and Stephen Roberts. 2024. "Characterization of a Metamorphosed Volcanic Stratigraphy and VMS Alteration Halos Using Rock Chip Petrography and Lithogeochemistry: A Case Study from King North, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia" Minerals 14, no. 5: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050481
APA StyleKelly, J., Hollis, S. P., Dana, C. D. P., Kneeshaw, A., Podmore, D., James, M., Azri, R., Rodgers, C., & Roberts, S. (2024). Characterization of a Metamorphosed Volcanic Stratigraphy and VMS Alteration Halos Using Rock Chip Petrography and Lithogeochemistry: A Case Study from King North, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Minerals, 14(5), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050481






