Genesis of the Sartohay Podiform Chromitite Based on Microinclusions in Chromite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Regional Geology
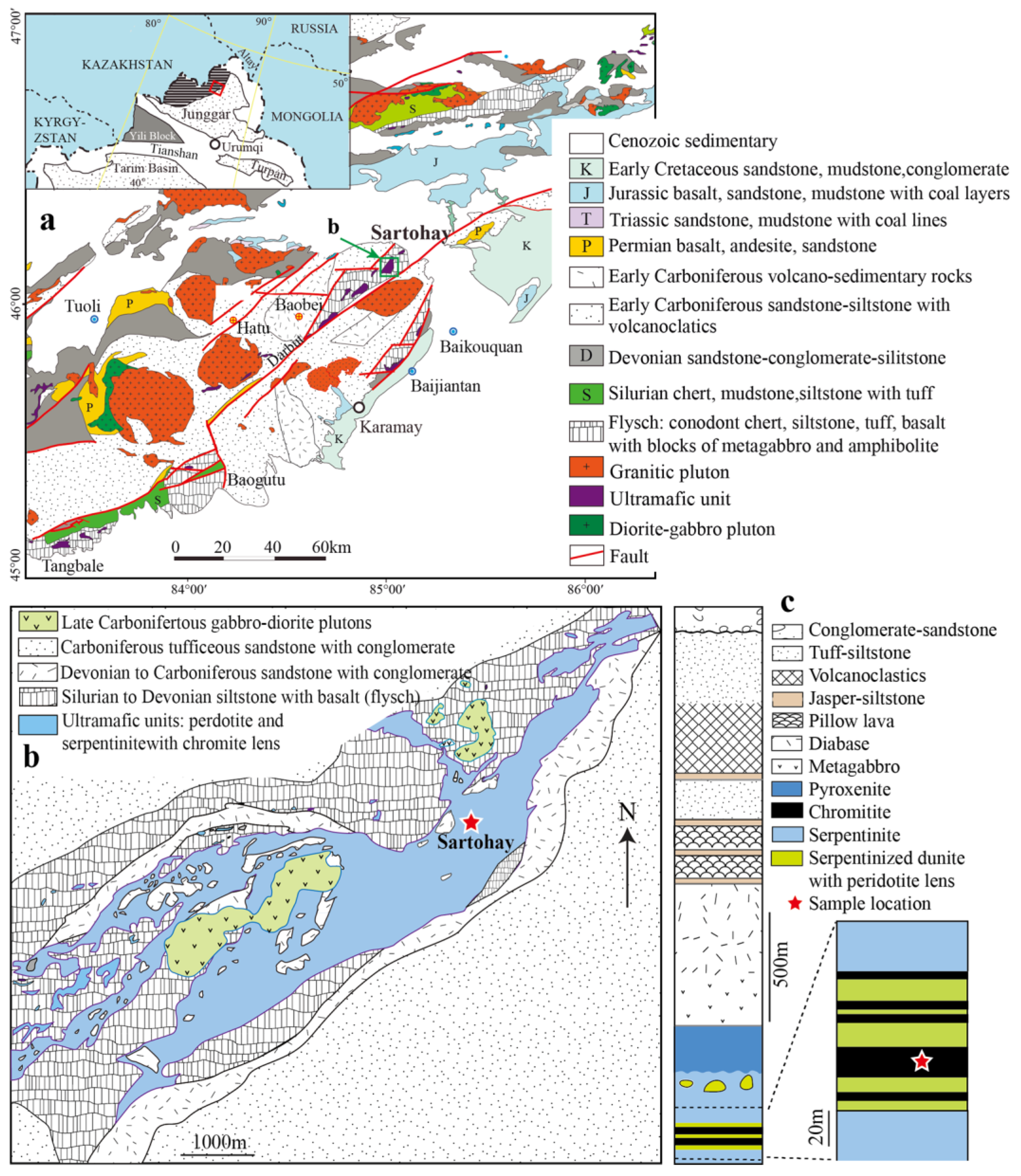
3. Analytical Methods
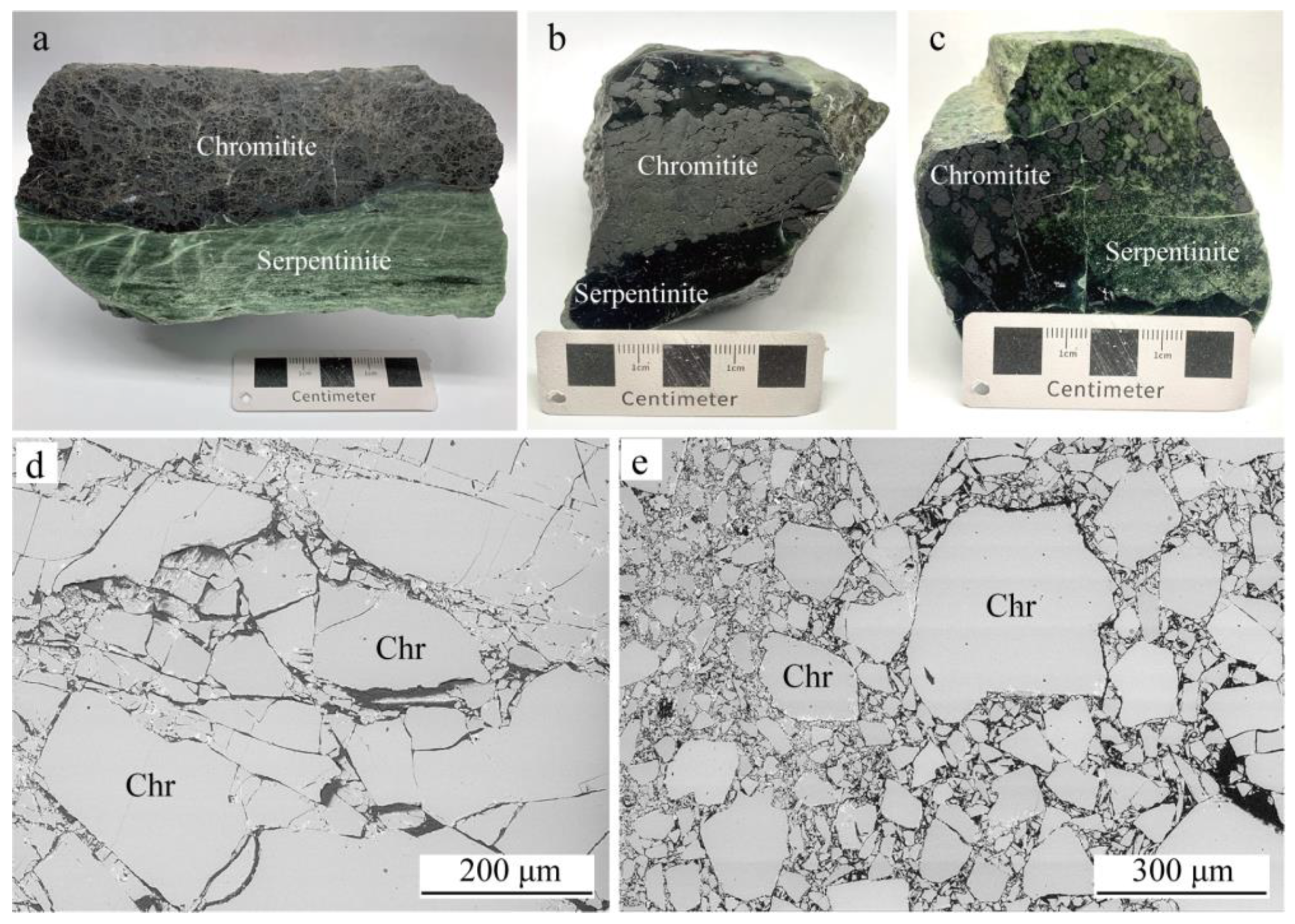
4. Results
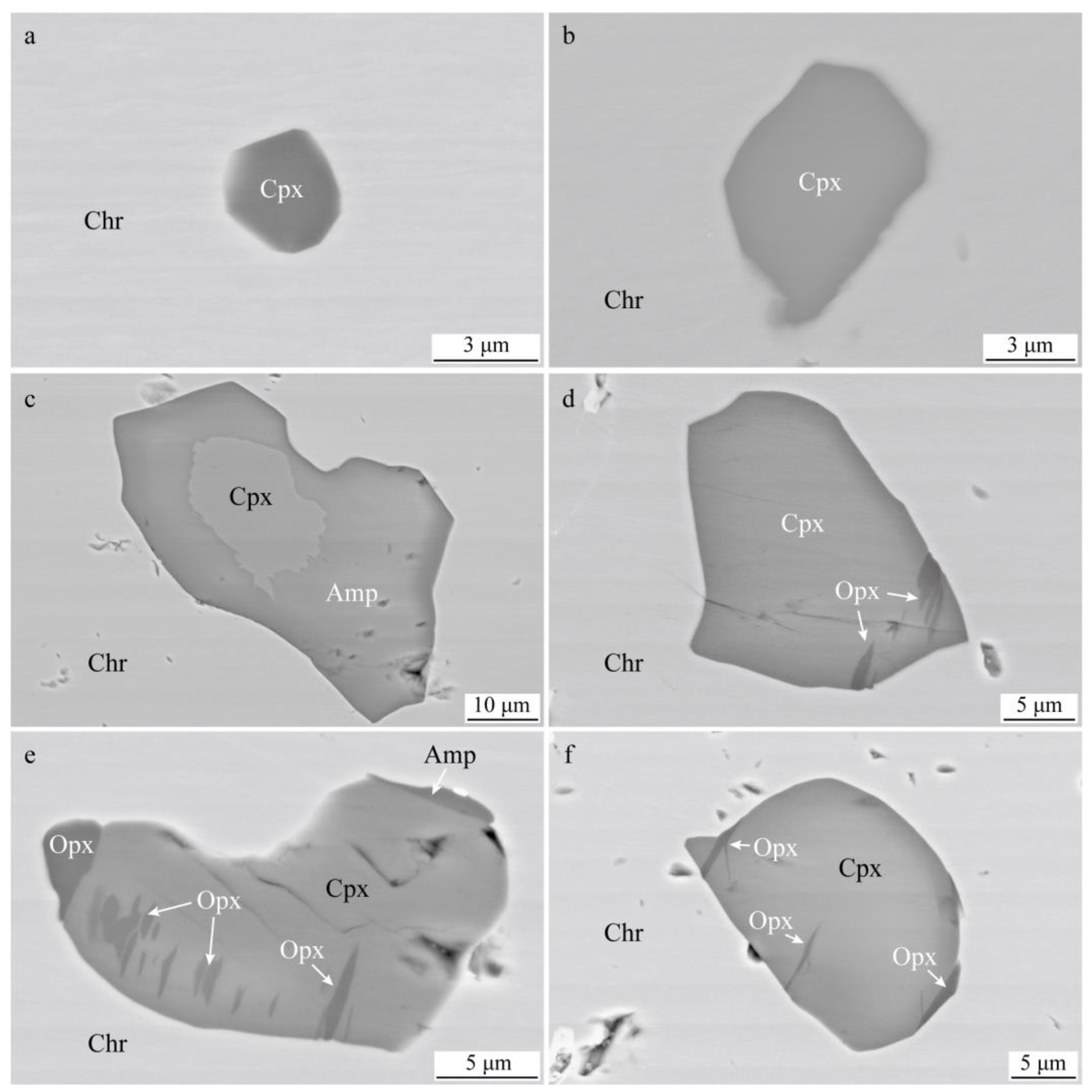
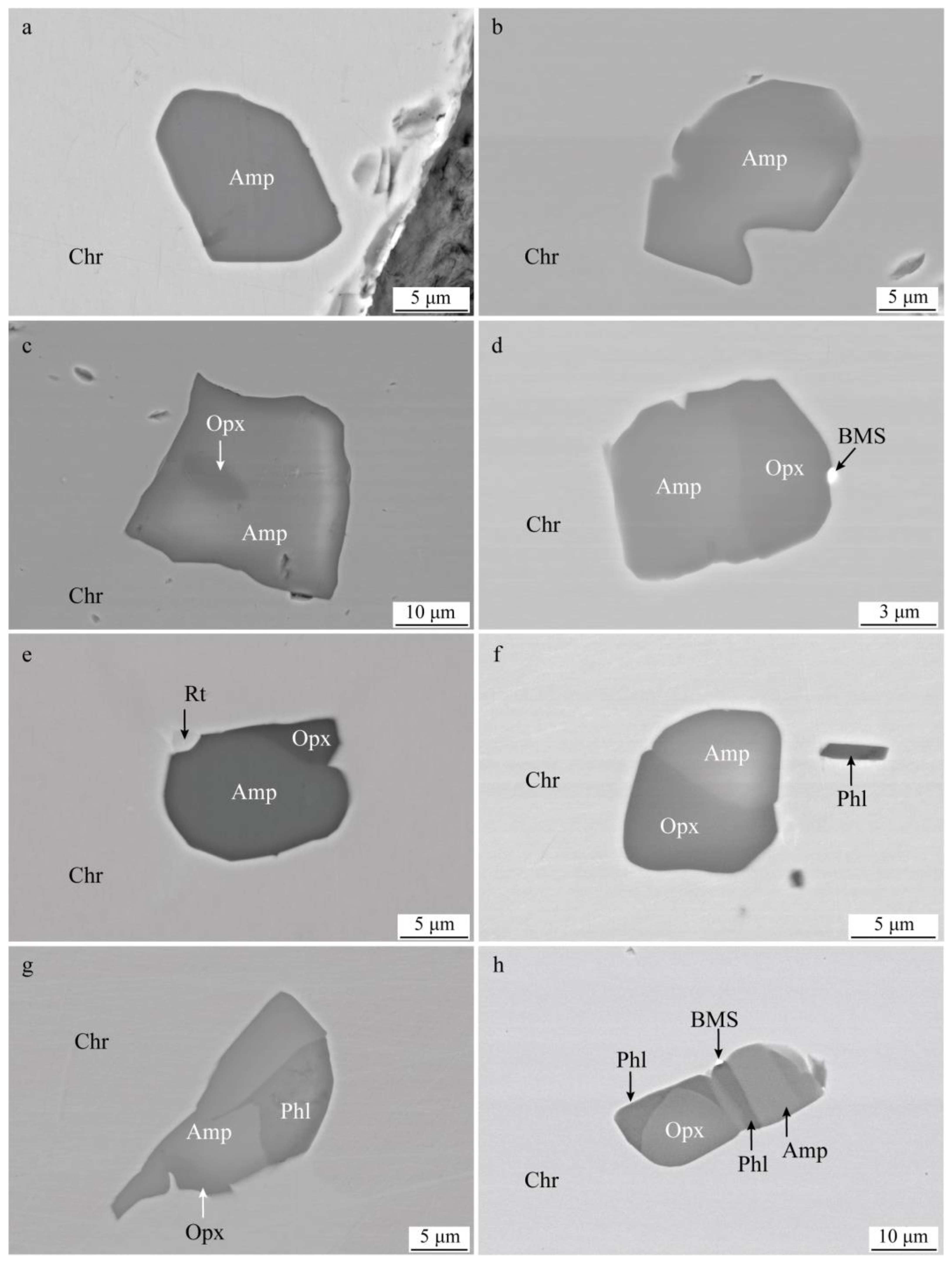
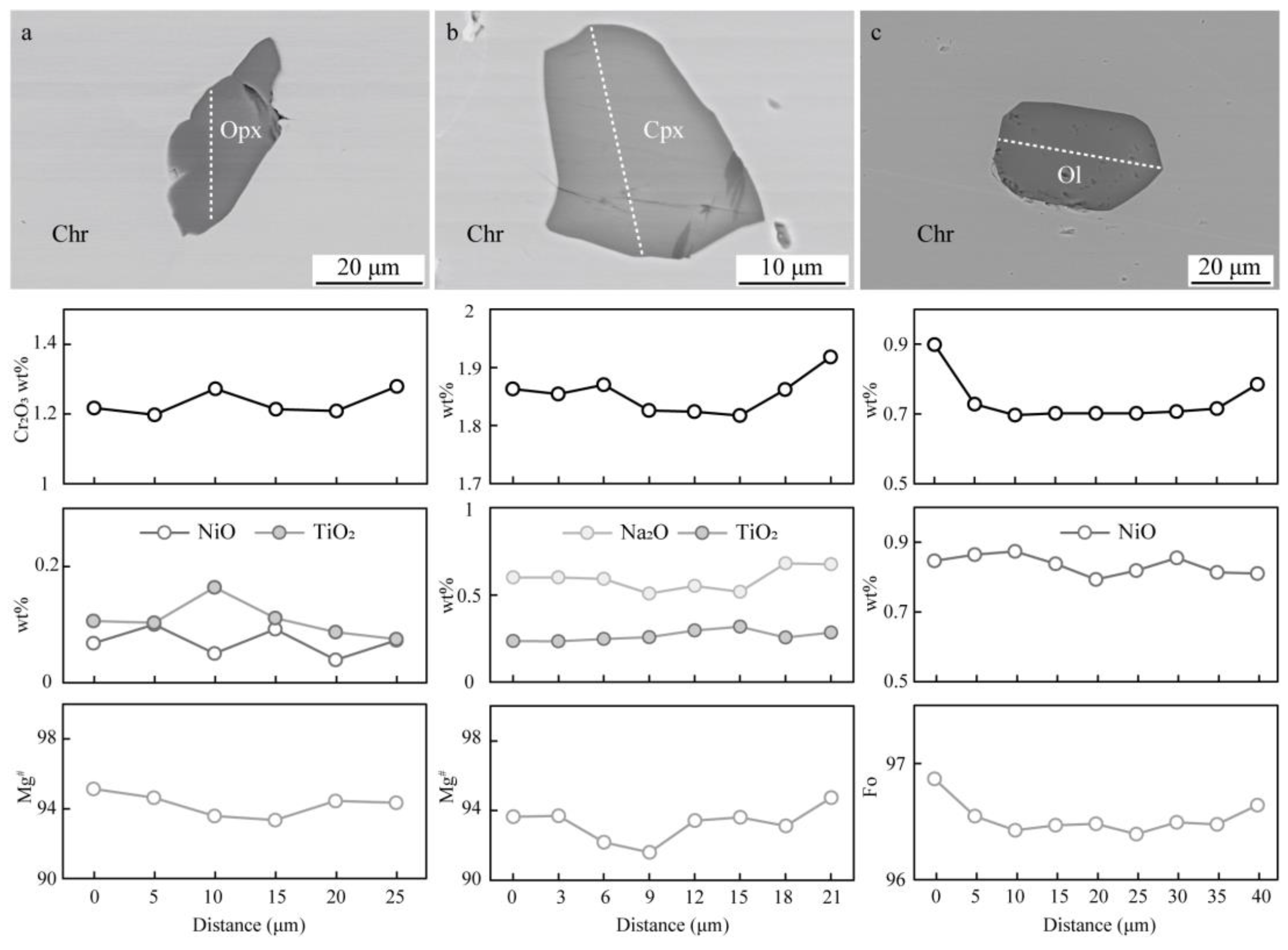
4.1. Silicate Mineral Inclusions in Chromite
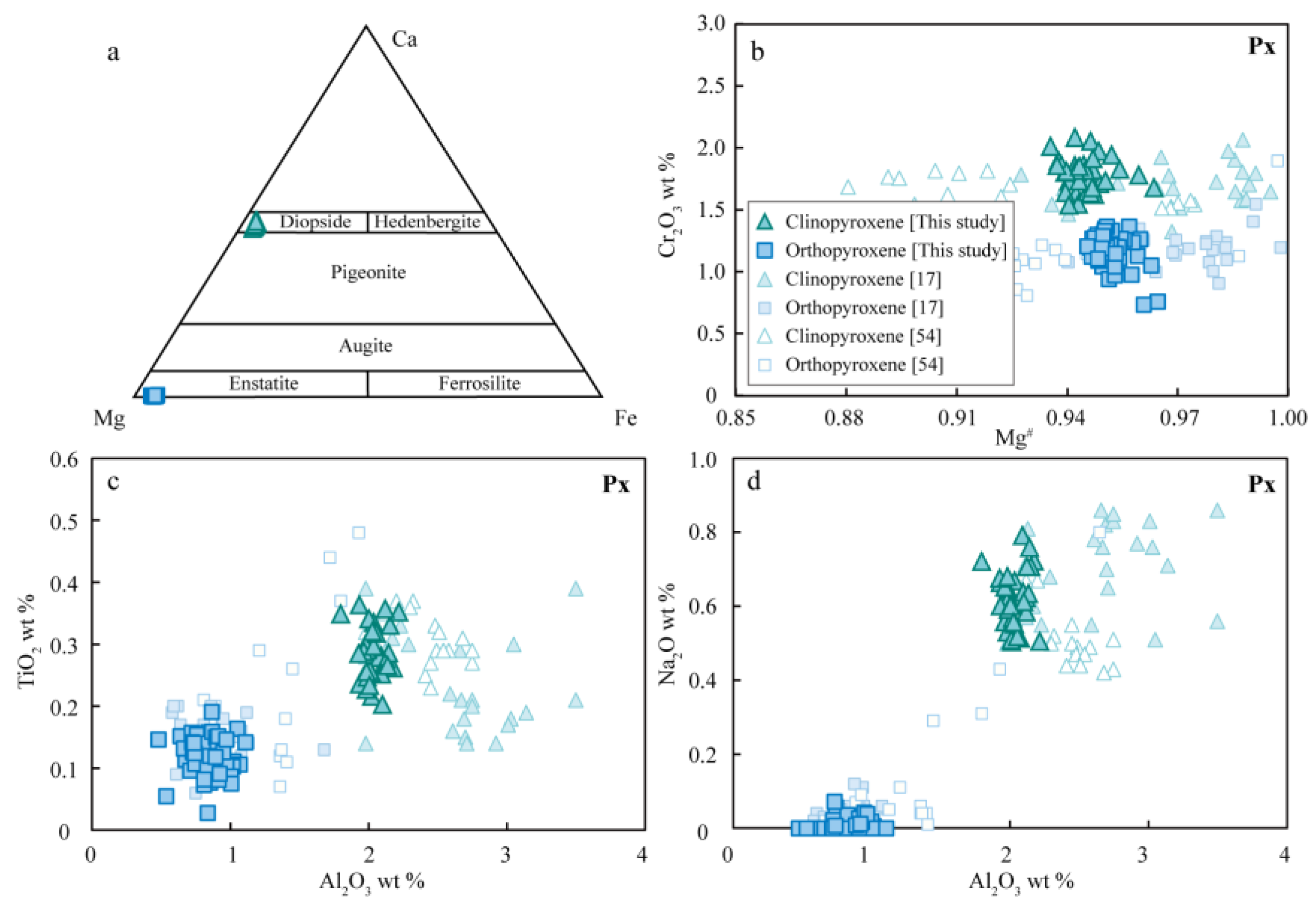
4.2. Mineral Composition
5. Discussion
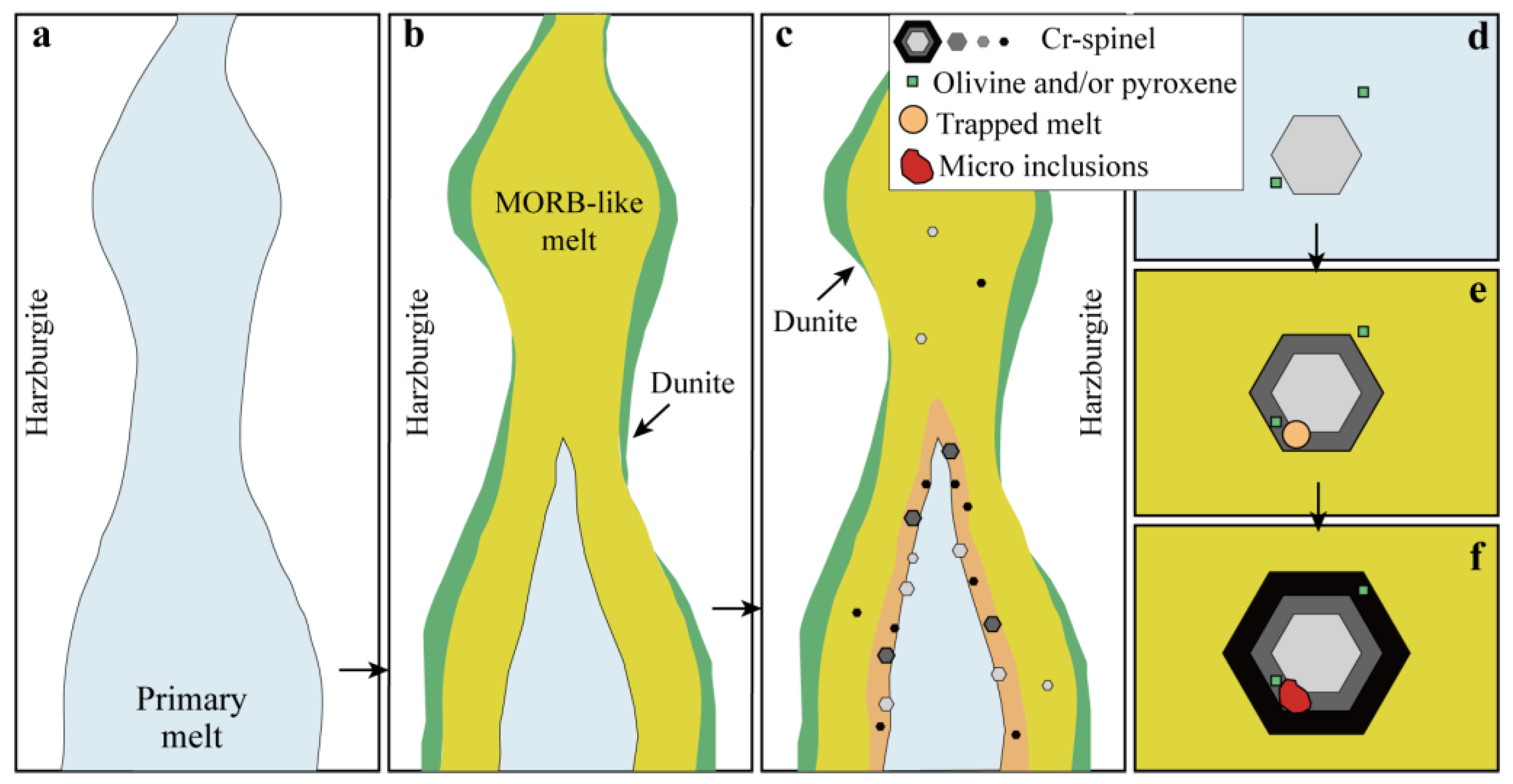
5.1. The Genesis of Silicate Inclusions
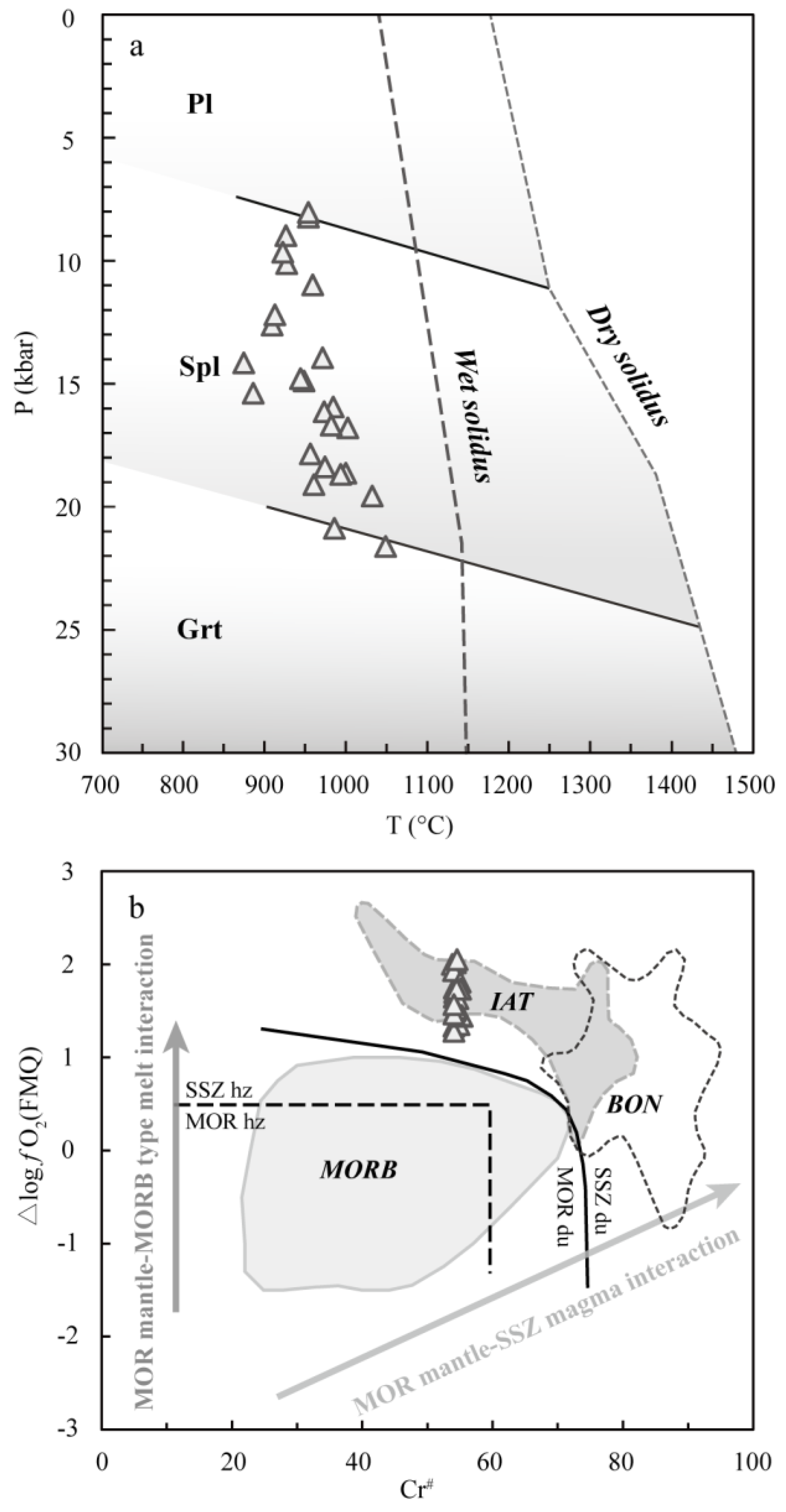
5.2. Estimates of the P-T-fO2 Conditions
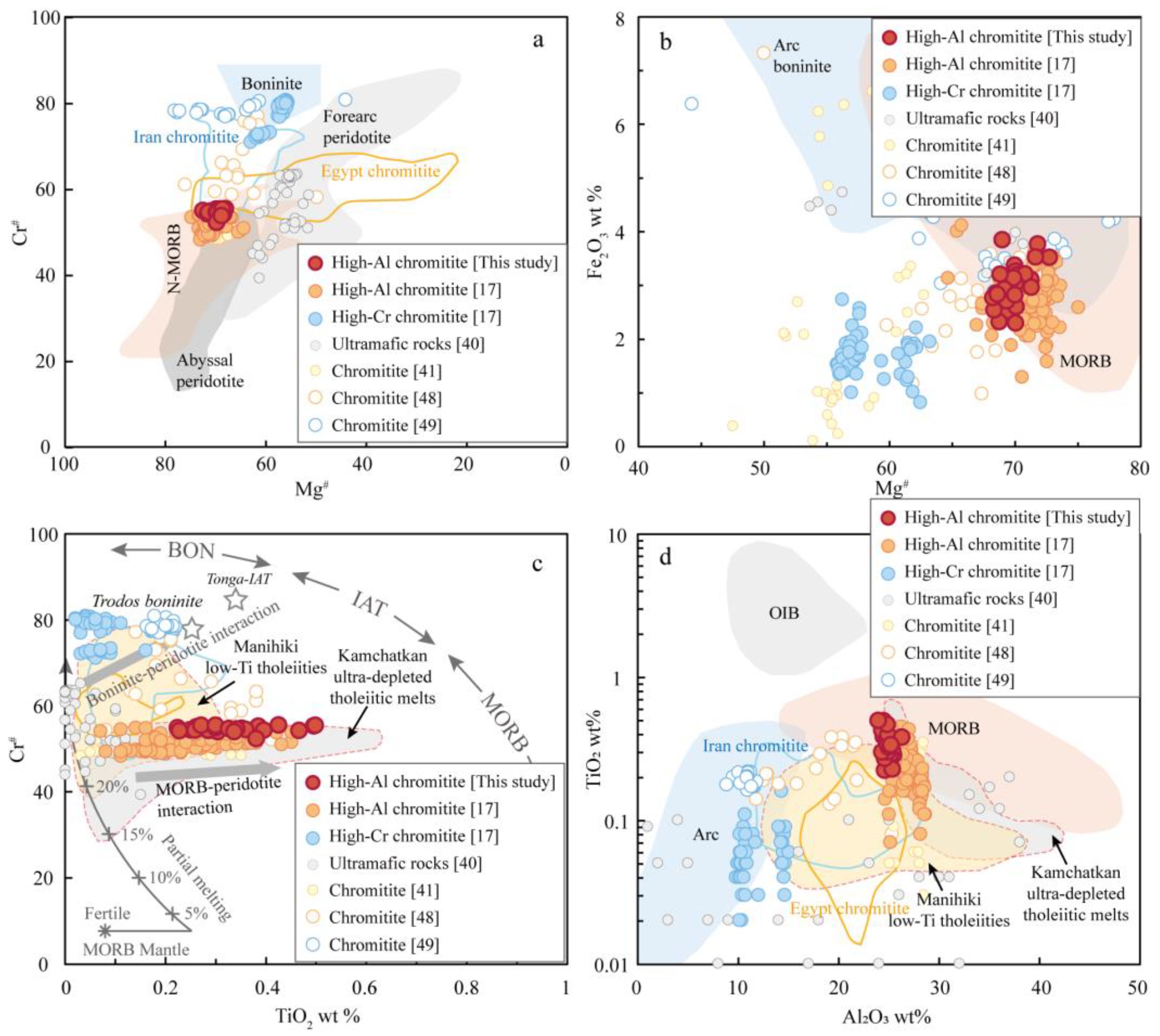
5.3. Constraints for Parental Melts of Chromitite
ln(FeO/MgO) (melt)
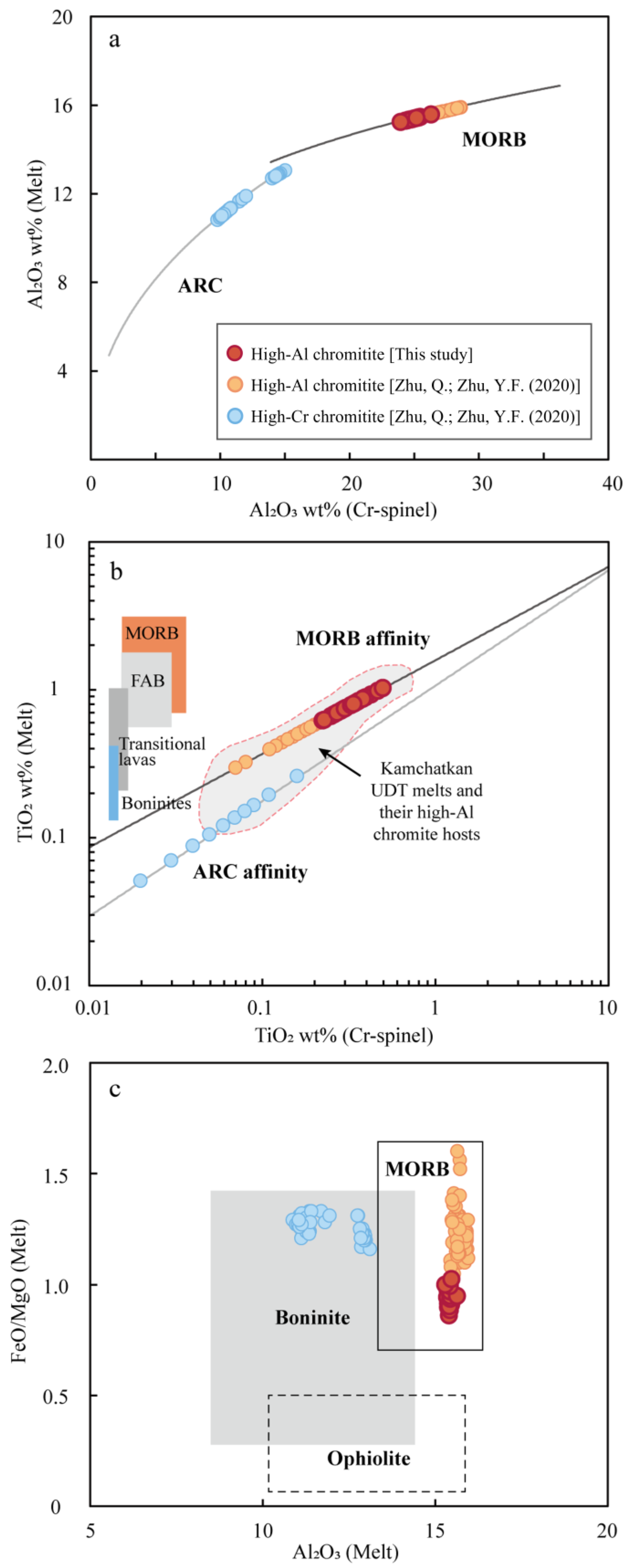
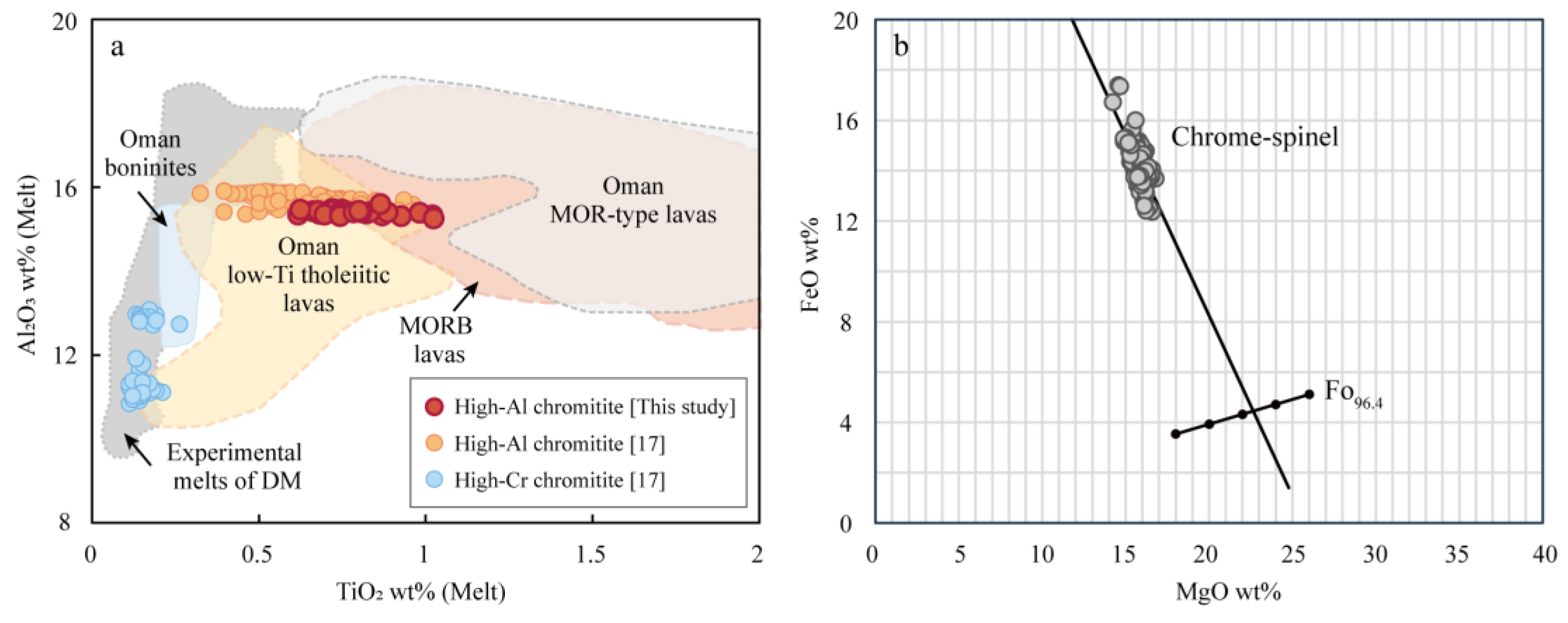
5.4. Genesis of Chromitites in Sartohay
Spl in podiform chromitite + low-MgO MORB-like tholeiite melt.
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dickey, J.S. A Hypothesis of Origin for Podiform Chromite Deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1975, 39, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, A. A Melt Extraction Model Based on Structural Studies in Mantle Peridotites. J. Petrol. 1986, 27, 999–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Robinson, P.T.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Bai, Y.; Uysal, I.; Zhang, P. A New Model for Chromitite Formation in Ophiolites: Fluid Immiscibility. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveliev, D.E.; Fedoseev, V.B. Solid-State Redistribution of Mineral Particles in the Upwelling Mantle Flow as a Mechanism of Chromite Concentration in the Ophiolite Ultramafic Rocks (on the Example of Kraka Ophiolite, the Southern Urals). Georesursy 2019, 21, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveliev, D.E. Chromitites of the Kraka Ophiolite (South Urals, Russia): Geological, Mineralogical and Structural Features. Min. Depos. 2021, 56, 1111–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveliev, D.E.; Shilovskikh, V.V.; Sergeev, S.N.; Kutyrev, A.V. Chromian Spinel Neomineralisations and the Microstructure of Plastically Deformed Ophiolitic Peridotites (Kraka Massifs, Southern Urals, Russia). Min. Pet. 2021, 115, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.T.; Trumbull, R.B.; Schmitt, A.; Yang, J.-S.; Li, J.-W.; Zhou, M.-F.; Erzinger, J.; Dare, S.; Xiong, F. The Origin and Significance of Crustal Minerals in Ophiolitic Chromitites and Peridotites. Gondwana Res. 2015, 27, 486–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Wirth, R.; Zheng, J.; Lian, D.; Qiu, T.; Milushi, I. Carbon and Nitrogen Isotopes and Mineral Inclusions in Diamonds from Chromitites of the Mirdita Ophiolite (Albania) Demonstrate Recycling of Oceanic Crust into the Mantle. Am. Mineral. 2019, 104, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, W.; Lian, D.; Rui, H. Peridotites, Chromitites and Diamonds in Ophiolites. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, A.; Grieco, G.; Bussolesi, M.; Ichiyama, Y.; Lenaz, D.; Skogby, H.; Kutyrev, A.V.; Cavallo, A.; Khedr, M.Z. Co-Occurrence of Compositionally Variable Chromitites in the Sabzevar Ophiolite, NE Iran. Lithos 2023, 446–447, 107133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.; Adetunji, J. Comment on ‘Podiform Chromitites Do Form beneath Mid-Ocean Ridges’ by Arai, S. and Miura, M. Lithos 2016, 254–255, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.-F.; Robinson, P.T.; Malpas, J.; Li, Z. Podiform Chromitites in the Luobusa Ophiolite (Southern Tibet): Implications for Melt-Rock Interaction and Chromite Segregation in the Upper Mantle. J. Petrol. 1996, 37, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Miura, M. Formation and Modification of Chromitites in the Mantle. Lithos 2016, 264, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveev, S.; Ballhaus, C. Role of Water in the Origin of Podiform Chromitite Deposits. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 203, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Tamura, A.; Miura, M.; Morishita, T. Origin of Spinel-Hosted Mineral Inclusions in Mantle Peridotite from Setogawa in the Circum-Izu Massif Serpentine Belt, Central Japan: Implications for the Chromitite Genesis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 140, 104422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusky, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Robinson, P.T.; Wirth, R.; Polat, A.; Wei, H. Vestiges of Early Earth’s Deep Subduction and CHONSP Cycle Recorded in Archean Ophiolitic Podiform Chromitites. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 227, 103968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhu, Y.F. Chromitite Genesis Based on Chrome-Spinels and Their Inclusions in the Sartohay Podiform Chromitites in West Junggar of Northwest China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 119, 103401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsiotis, A.; Economou-Eliopoulos, M.; Zheng, H.; Su, B.-X.; Lenaz, D.; Jing, J.-J.; Antonelou, A.; Velicogna, M.; Xia, B. Refractory Chromitites Recovered from the Eretria Mine, East Othris Massif (Greece): Implications for Metallogeny and Deformation of Chromitites within the Lithospheric Mantle Portion of a Forearc-Type Ophiolite. Geochemistry 2019, 79, 130–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballhaus, C.; Berry, R.F.; Green, D.H. High Pressure Experimental Calibration of the Olivine-Orthopyroxene-Spinel Oxygen Geobarometer: Implications for the Oxidation State of the Upper Mantle. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1991, 107, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dare, S.A.S.; Pearce, J.A.; McDonald, I.; Styles, M.T. Tectonic Discrimination of Peridotites Using fO2–Cr# and Ga–Ti–FeIII Systematics in Chrome–Spinel. Chem. Geol. 2009, 261, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K.D. Thermometers and Barometers for Volcanic Systems. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2008, 69, 61–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Su, B.-X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, C.; Uysal, I.; Jing, J.-J.; Zhang, P.-F.; Chu, Y.; Lin, W.; Asamoah Sakyi, P. Initial Subduction of Neo-Tethyan Ocean: Geochemical Records in Chromite and Mineral Inclusions in the Pozantı-Karsantı Ophiolite, Southern Turkey. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 110, 102926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Q.; Malpas, J.; Yumul, G.P.; Wang, C.Y. Sluggish Slab Rollback at the Early Stage of Flux Melting During Subduction Initiation: Li Isotopic Evidence from the Coto High-Al Chromite Deposit, Zambales Ophiolite, Philippines. JGR Solid Earth 2023, 128, e2022JB025562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, M.Z.; Arai, S. Chemical Variations of Mineral Inclusions in Neoproterozoic High-Cr Chromitites from Egypt: Evidence of Fluids during Chromitite Genesis. Lithos 2016, 240–243, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisova, A.Y.; Ceuleneer, G.; Kamenetsky, V.S.; Arai, S.; Béjina, F.; Abily, B.; Bindeman, I.N.; Polvé, M.; De Parseval, P.; Aigouy, T.; et al. A New View on the Petrogenesis of the Oman Ophiolite Chromitites from Microanalyses of Chromite-Hosted Inclusions. J. Petrol. 2012, 53, 2411–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.; Mameri, L.; Barry, T. Polymineralic Inclusions in Mantle Chromitites from the Oman Ophiolite Indicate a Highly Magnesian Parental Melt. Lithos 2018, 310–311, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.-F.; Robinson, P.T.; Malpas, J.; Aitchison, J.; Sun, M.; Bai, W.-J.; Hu, X.-F.; Yang, J.-S. Melt/Mantle Interaction and Melt Evolution in the Sartohay High-Al Chromite Deposits of the Dalabute Ophiolite (NW China). J. Asian Earth Sci. 2001, 19, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; He, G. Tectonic Entities Connection between West Junggar (NW China) and East Kazakhstan. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 72, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Chen, B.; Qiu, T. Geology and Geochemistry of the Baijiantan–Baikouquan Ophiolitic Mélanges: Implications for Geological Evolution of West Junggar, Xinjiang, NW China. Geol. Mag. 2015, 152, 41–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Karamay ophioliic mélange formed during Early Paleozoic in western Junggar basin. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 1573–1576, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Yang, Z.; Gong, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; He, P.; Zhang, Z. Construction of an Early Cambrian Intra-Oceanic Arc within the West Junggar, NW China: Magmatic Records from Proto- to Mature-Arc. Lithos 2023, 458–459, 107343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Cao, P. An Ordovician Ophiolitic Complex in West Junggar, NW China: Implications for Subduction Initiation and Oceanic Arc Evolution of the Paleo-Asian Ocean. Gondwana Res. 2022, 111, 122–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Chen, B.; Xu, X.; Qiu, T.; An, F. A New Geological Map of the Western Junggar, North Xinjiang (NW China): Implications for Paleoenvironmental Reconstruction. Episodes 2013, 36, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Song, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Zhou, J.; Song, M.; Yuan, X. Geochronological and Geochemical Study of the Late Carboniferous Volcanic Drilling Cores from the Piedmont of the Hala’alate Mountain in West Junggar: Implications for Stratigraphic Division and Tectonic Evolution. Lithos 2023, 456–457, 107305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Xu, X.; Luo, Z.; Shen, P.; Ma, H.D.; Chen, X.H.; An, F.; Wei, S.N. Geological Evolution and Ore-Formation in the Core Part of Central Asian Metallogenic Region; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, R.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, T.; Gong, Y. Late Devonian Radiolarian-Bearing Siliceous Rocks from the Karamay Ophiolitic Mélange in Western Junggar: Implications for the Evolution of the Paleo-Asian Ocean. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2016, 448, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Guo, Z. Time constraints, tectonic setting of Darabut ophiolitic complex and its significance for late Paleozoic tectonic evolution in West Junggar. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 2336–2344, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Ma, X.; Liu, J.; Gong, E.; Shi, W.; Han, B. Timing of the Final Closure of the Irtysh–Zaysan Ocean: New Insights from the Earliest Stitching Pluton in the Northern West Junggar, NW China. Geol. J. 2018, 53, 2810–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhu, Y.F. Characterization of Anhydrous to Hydrous Paragenetic Sequence from Pyroxene-Bearing and Pyroxene-Absent Variants of the Late Carboniferous Baobei Pluton in West Junggar of China. Gondwana Res. 2018, 63, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Zhu, Y. Chromian Spinels in Highly Altered Ultramafic Rocks from the Sartohay Ophiolitic Mélange, Xinjiang, NW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 159, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Tan, J.; Qiu, T. Platinum Group Mineral (PGM) and Fe–Ni–As–S Minerals in the Sartohay Chromitite, Xinjiang (NW China): Implications for the Mobility of Os, Ir, Sb, and As during Hydrothermal Processes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Wang, X.; Peng, G.; Hao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Yang, T. Study on mineralization constraints and assessment of ore potential of main chrome-bearing rock bodies in Western Junggar. In Proceedings of the Bulletin of the Institute of Geology Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 1992; pp. 1–177, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bao, P.; Wang, X.; Hao, Z.; Peng, G.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Q.; Yang, T. A new idea about the genesis of the aluminium-rich podiform chromite deposit—With the Sartuohai chromite deposit of Xinjiang as an example. Miner. Depos. 1990, 9, 3–17, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Philemon, L.; Wan, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, P. Prospecting for Ophiolite-Type Chromite Deposit in Sartohay, West Junggar (NW China): Constraints from Geological and Geophysical Data. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 156, 105379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Parkinson, I.J. Geochemistry and Tectonic Signi®cance of Peridotites from the South Sandwich Arc ± basin System, South Atlantic. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2000, 139, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.-F.; Robinson, P.T.; Su, B.-X.; Gao, J.-F.; Li, J.-W.; Yang, J.-S.; Malpas, J. Compositions of Chromite, Associated Minerals, and Parental Magmas of Podiform Chromite Deposits: The Role of Slab Contamination of Asthenospheric Melts in Suprasubduction Zone Environments. Gondwana Res. 2014, 26, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H. The Geochemistry of Mantle Chromitites from the Northern Part of the Oman Ophiolite: Inferred Parental Melt Compositions. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2008, 156, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.; Adetunji, J. The Geochemistry and Oxidation State of Podiform Chromitites from the Mantle Section of the Oman Ophiolite: A Review. Gondwana Res. 2015, 27, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.-F.; Zhou, M.-F.; Malpas, J.; Robinson, P.T. Origin of High-Cr Chromite Deposits in Nascent Mantle Wedges: Petrological and Geochemical Constraints from the Neo-Tethyan Luobusa Ophiolite, Tibet. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 123, 103581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois-Côté, V.; Hébert, R.; Dupuis, C.; Wang, C.S.; Li, Y.L.; Dostal, J. Petrological and Geochemical Evidence for the Origin of the Yarlung Zangbo Ophiolites, Southern Tibet. Chem. Geol. 2005, 214, 265–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenetsky, V.S. Factors Controlling Chemistry of Magmatic Spinel: An Empirical Study of Associated Olivine, Cr-Spinel and Melt Inclusions from Primitive Rocks. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portnyagin, M.; Hoernle, K.; Savelyev, D. Ultra-Depleted Melts from Kamchatkan Ophiolites: Evidence for the Interaction of the Hawaiian Plume with an Oceanic Spreading Center in the Cretaceous? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 287, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golowin, R.; Portnyagin, M.; Hoernle, K.; Sobolev, A.; Kuzmin, D.; Werner, R. The Role and Conditions of Second-Stage Mantle Melting in the Generation of Low-Ti Tholeiites and Boninites: The Case of the Manihiki Plateau and the Troodos Ophiolite. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 2017, 172, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yang, J. Study on the mineral inclusions in Sartohay chromitites. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 3114–3128, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne, F.C.; Oberti, R.; Harlow, G.E.; Maresch, W.V.; Martin, R.F.; Schumacher, J.C.; Welch, M.D. Nomenclature of the Amphibole Supergroup. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 2031–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rospabé, M.; Ceuleneer, G.; Le Guluche, V.; Benoit, M.; Kaczmarek, M.-A. The Chicken and Egg Dilemma Linking Dunites and Chromitites in the Mantle–Crust Transition Zone beneath Oceanic Spreading Centres: A Case Study of Chromite-Hosted Silicate Inclusions in Dunites Formed at the Top of a Mantle Diapir (Oman Ophiolite). J. Petrol. 2021, 62, egab026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Yang, J.; Robinson, P.T.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, S. Origin of Podiform Chromitite, a New Model Based on the Luobusa Ophiolite, Tibet. Gondwana Res. 2015, 27, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Mao, W.L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Liou, J.G.; Ernst, W.G.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, B. Characteristics and Implications of Podiform-Chromite Hosted Silicate Inclusions in the Zedang Ophiolite, Southern Tibet. Lithos 2021, 396–397, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelieva, G.N.; Batanova, V.G.; Sobolev, A.V. Pyroxene–Cr-Spinel Exsolution in Mantle Lherzolites of the Syum-Keu Ophiolite Massif (Arctic Urals). Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2016, 57, 1419–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveliev, D.E.; Puchkov, V.N.; Sergeev, S.N.; Misabirov, I.I. Deformation-Induced Decomposition of Enstatite in Mantle Peridotite and Its Role in Partial Melting and Chromite Ore Formation. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2017, 476, 1058–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveliev, D.E.; Makatov, D.K.; Rakhimov, I.R.; Gataullin, R.A.; Shilovskikh, V.V. Silicates from Lherzolites in the South-Eastern Part of the Kempirsay Massif as the Source for Giant Chromitite Deposits (the Southern Urals, Kazakhstan). Minerals 2022, 12, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S. Origin of Podiform Chromitites. J. Asian Earth Sci. 1997, 15, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Zoheir, B.; Robinson, P.T.; Wirth, R.; Xu, X.; Qiu, T.; Sun, Y. Microchemistry and Magnesium Isotope Composition of the Purang Ophiolitic Chromitites (SW Tibet): New Genetic Inferences. Am. Mineral. 2023, 108, 1117–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorand, J.P.; Ceuleneer, G. Silicate and Base-Metal Sulfide Inclusions in Chromites from the Maqsad Area (Oman Ophiolite, Gulf of Oman): A Model for Entrapment. Lithos 1989, 22, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElduff, B.; Stumpfl, E.F. The Chromite Deposits of the Troodos Complex, Cyprus? Evidence for the Role of a Fluid Phase Accompanying Chromite Formation. Miner. Depos. 1991, 26, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlini, A.; Grieco, G.; Ottolini, L.; Diella, V. Probe and SIMS Investigation of Clinopyroxene Inclusions in Chromites from the Troodos Chromitites (Cyprus): Implications for Dunite–Chromitite Genesis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 41, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Chen, J.; Xue, Y.; Feng, W.; Jiang, J. Spinel and Orthopyroxene Exsolved from Clinopyroxene in the Haladala Pluton in the Middle Tianshan (Xinjiang, China). Min. Pet. 2018, 112, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faryad, S.W.; Dolejš, D.; Machek, M. Garnet Exsolution in Pyroxene from Clinopyroxenites in the Moldanubian Zone: Constraining the Early Pre-convergence History of Ultramafic Rocks in the Variscan Orogen. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2009, 27, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satsukawa, T.; Piazolo, S.; González-Jiménez, J.M.; Colás, V.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Gervilla, F.; Fanlo, I.; Kerestedjian, T.N. Fluid-Present Deformation Aids Chemical Modification of Chromite: Insights from Chromites from Golyamo Kamenyane, SE Bulgaria. Lithos 2015, 228–229, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, T.B.; Milke, R.; Wunder, B. Experimental Reactions between Olivine and Orthopyroxene with Phonolite Melt: Implications for the Origins of Hydrous Amphibole + Phlogopite + Diopside Bearing Metasomatic Veins. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2014, 168, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, K.G.; Green, D.H. The Nature of the Upper-Most Mantle Beneath Victoria, Australia as Deduced from UL Tramafic Xenoliths. In Developments in Petrology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; Volume 11, pp. 161–178. ISBN 978-0-444-42274-3. [Google Scholar]
- Saveliev, D.E.; Shilovskikh, V.V.; Makatov, D.K.; Gataullin, R.A. Accessory Cr-Spinel from Peridotite Massifs of the South Urals: Morphology, Composition and Origin. Min. Pet. 2022, 116, 401–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, P.R.A. Pyroxene Thermometry in Simple and Complex Systems. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1977, 62, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, Y. Silicate mineral inclusions in spinel from the Hegenshan podiform chromitites: Implication for chromitite genesis. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 1805–1821, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Niida, K.; Green, D.H. Stability and Chemical Composition of Pargasitic Amphibole in MORB Pyrolite under Upper Mantle Conditions. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1999, 135, 18–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Jiménez, J.M.; Proenza, J.A.; Gervilla, F.; Melgarejo, J.C.; Blanco-Moreno, J.A.; Ruiz-Sánchez, R.; Griffin, W.L. High-Cr and High-Al Chromitites from the Sagua de Tánamo District, Mayarí-Cristal Ophiolitic Massif (Eastern Cuba): Constraints on Their Origin from Mineralogy and Geochemistry of Chromian Spinel and Platinum-Group Elements. Lithos 2011, 125, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurel, C.; Maurel, P. Étude expérimentale de la distribution de l’aluminium entre bain silicaté basique et spinelle chromifère. Implications pétrogénétiques: Teneur en chrome des spinelles. Bull. Minéralogie 1982, 105, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godard, M.; Bosch, D.; Einaudi, F. A MORB Source for Low-Ti Magmatism in the Semail Ophiolite. Chem. Geol. 2006, 234, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasylenki, L.E. Near-Solidus Melting of the Shallow Upper Mantle: Partial Melting Experiments on Depleted Peridotite. J. Petrol. 2003, 44, 1163–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzen, A.K.; Baker, M.B.; Beckett, J.R.; Stolper, E.M. Fe–Mg Partitioning between Olivine and High-Magnesian Melts and the Nature of Hawaiian Parental Liquids. J. Petrol. 2011, 52, 1243–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, A.J.; O’Neill, H.S.C.; Scott, D.R.; Foran, G.J.; Shelley, J.M.G. The Effect of Composition on Cr2+/Cr3+ in Silicate Melts. Am. Mineral. 2006, 91, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.J.; Roeder, P.L. The Range of Spinel Compositions in Terrestrial Mafic and Ultramafic Rocks. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 2279–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballhaus, C. Origin of Podiform Chromite Deposits by Magma Mingling. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1998, 156, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, V.J.; Arai, S.; Satish-kumar, M.; Santosh, M.; Tamura, A. High-Mg Low-Ni Olivine Cumulates from a Pan-African Accretionary Belt in Southern India: Implications for the Genesis of Volatile-Rich High-Mg Melts in Suprasubduction Setting. Precambrian Res. 2013, 227, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Jing, W. Imprints of fluid process of shell dunite in ophiolitic chromite deposits: Evidences from geology, petrology and crystal chemistry of olivine found in Luobusa and Zedang ophiolites in the Yarlung Zangbo suture zone,Tibet. Earth Sci. Front. 2019, 26, 272–285, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, T.; Sen, C. Mineral/Matrix Partition Coefficients for Orthopyroxene, Plagioclase, and Olivine in Basaltic to Andesitic Systems: A Combined Analytical and Experimental Study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.-J.; Zhou, M.-F.; Yudovskaya, M.A.; Vikentyev, I.V.; Malpas, J.; Zhang, P.-F. Trace Elements in Chromite as Indicators of the Origin of the Giant Podiform Chromite Deposit at Kempirsai, Kazakhstan. Econ. Geol. 2022, 117, 1629–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, T.N. Origin of Chromitite Layers in the Muskox Intrusion and Other Stratiform Intrusions: A New Interpretation. Geology 1977, 5, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Harbi, H.M.; Habtoor, A.M. Compositional Variations and Tectonic Settings of Podiform Chromitites and Associated Ultramafic Rocks of the Neoproterozoic Ophiolite at Wadi Al Hwanet, Northwestern Saudi Arabia. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 56, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveliev, D.E.; Makatov, D.K.; Vishnevskiy, A.V.; Gataullin, R.A. Accessory Minerals in the Chromitite Ores of Dzharlybutak Ore Group of Kempirsai Massif (Southern Urals, Kazakhstan): Clues for Ore Genesis. Minerals 2023, 13, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, X.; Zhu, Y. Genesis of the Sartohay Podiform Chromitite Based on Microinclusions in Chromite. Minerals 2024, 14, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14060530
Wen X, Zhu Y. Genesis of the Sartohay Podiform Chromitite Based on Microinclusions in Chromite. Minerals. 2024; 14(6):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14060530
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Xingying, and Yongfeng Zhu. 2024. "Genesis of the Sartohay Podiform Chromitite Based on Microinclusions in Chromite" Minerals 14, no. 6: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14060530
APA StyleWen, X., & Zhu, Y. (2024). Genesis of the Sartohay Podiform Chromitite Based on Microinclusions in Chromite. Minerals, 14(6), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14060530





