Effect of Paleoenvironmental Conditions on the Distribution of Lower Carboniferous Shale in Yaziluo Rift Trough, South China: Insights from Major/Trace Elements and Shale Composition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- To analyze the paleoenvironmental conditions of Lower Carboniferous shales in the Yaziluo Rift Trough by examining variations in geochemical proxy data.
- (ii)
- To discuss the various controlling factors on organic matter accumulation in the Lower Carboniferous shale during the deposition process.
- (iii)
- To reconstruct the lithofacies distribution pattern of Lower Carboniferous shale and propose a relevant model for the Yaziluo Rift Trough.
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. Analytical Methods
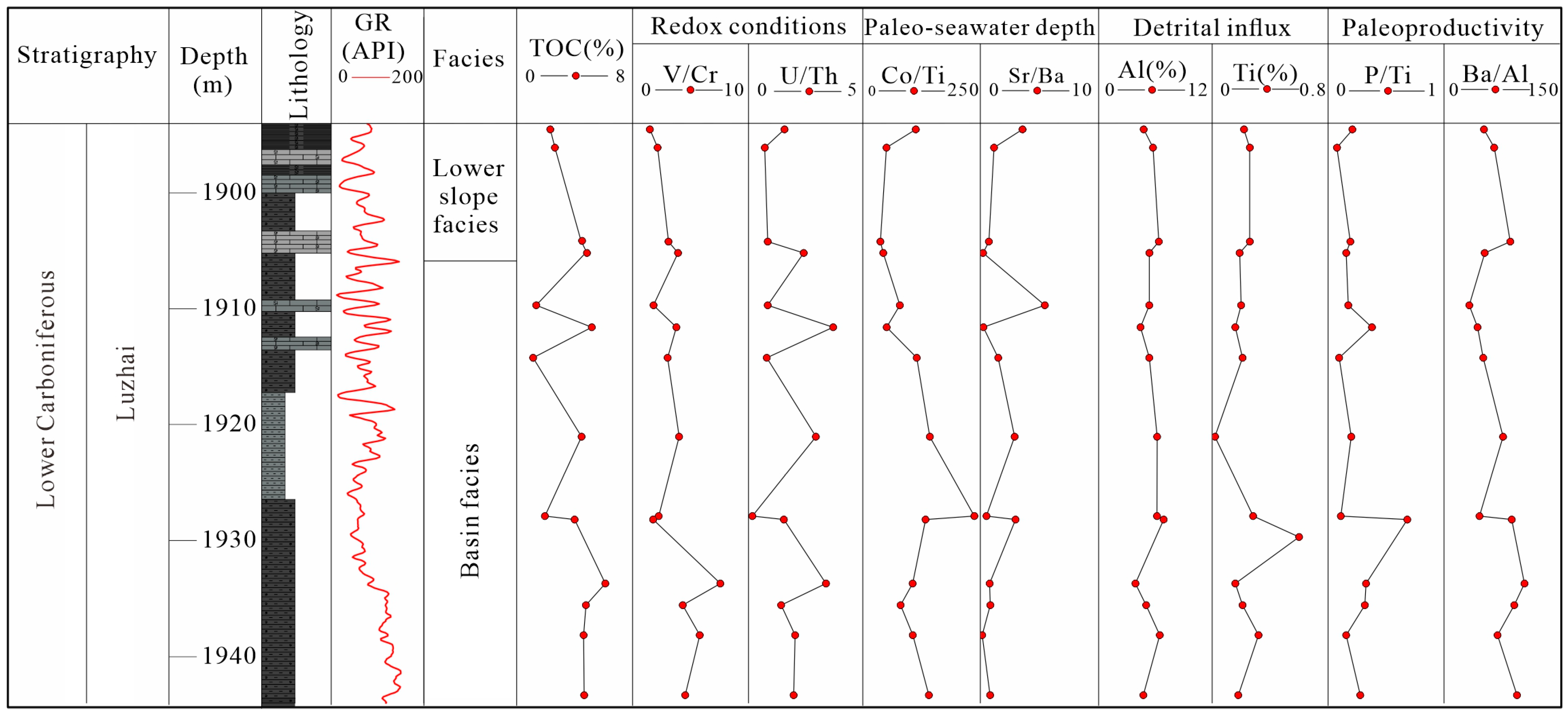
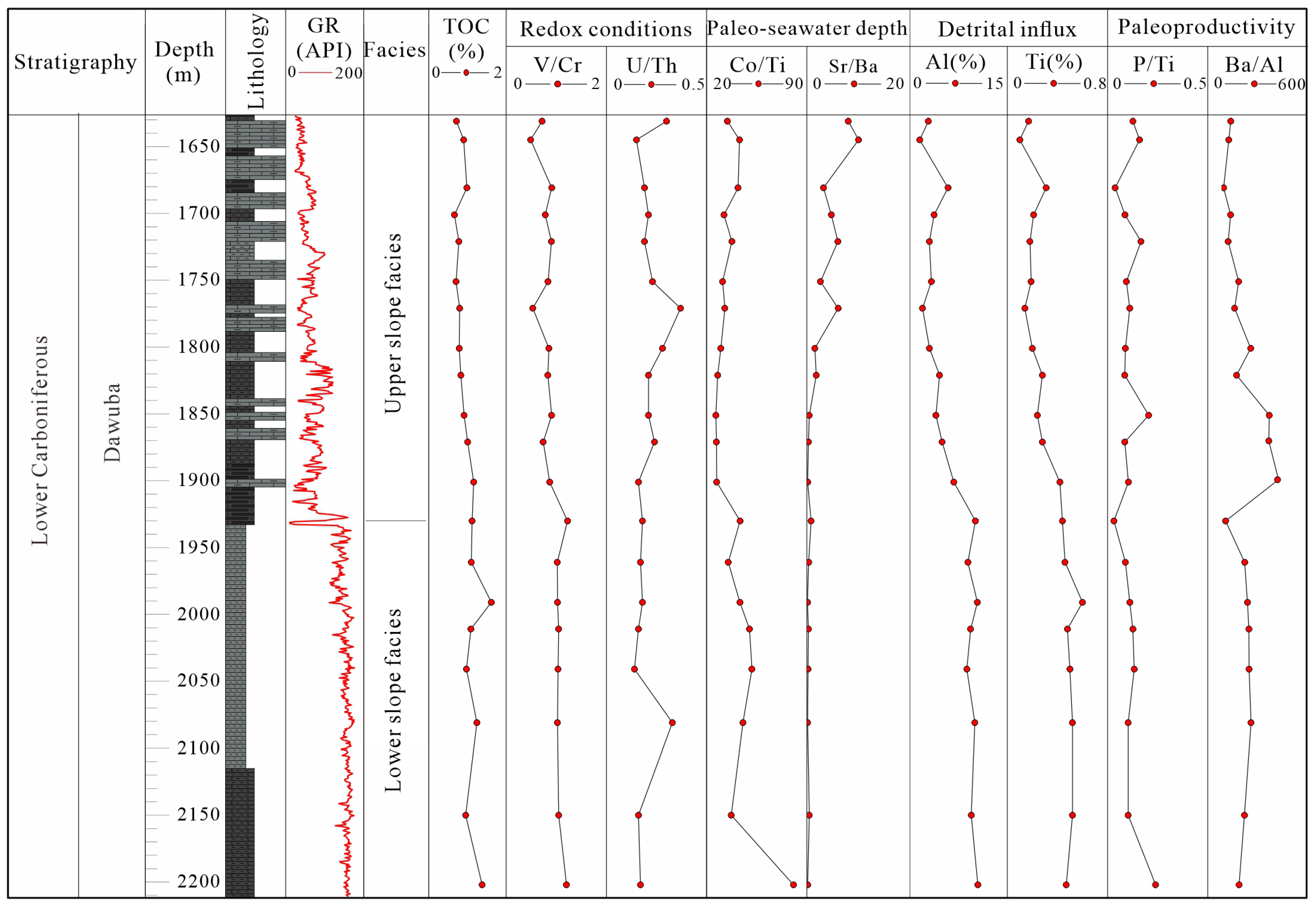
4. Results
4.1. Major and Trace Elements
4.2. Characteristics of Organic Geochemistry
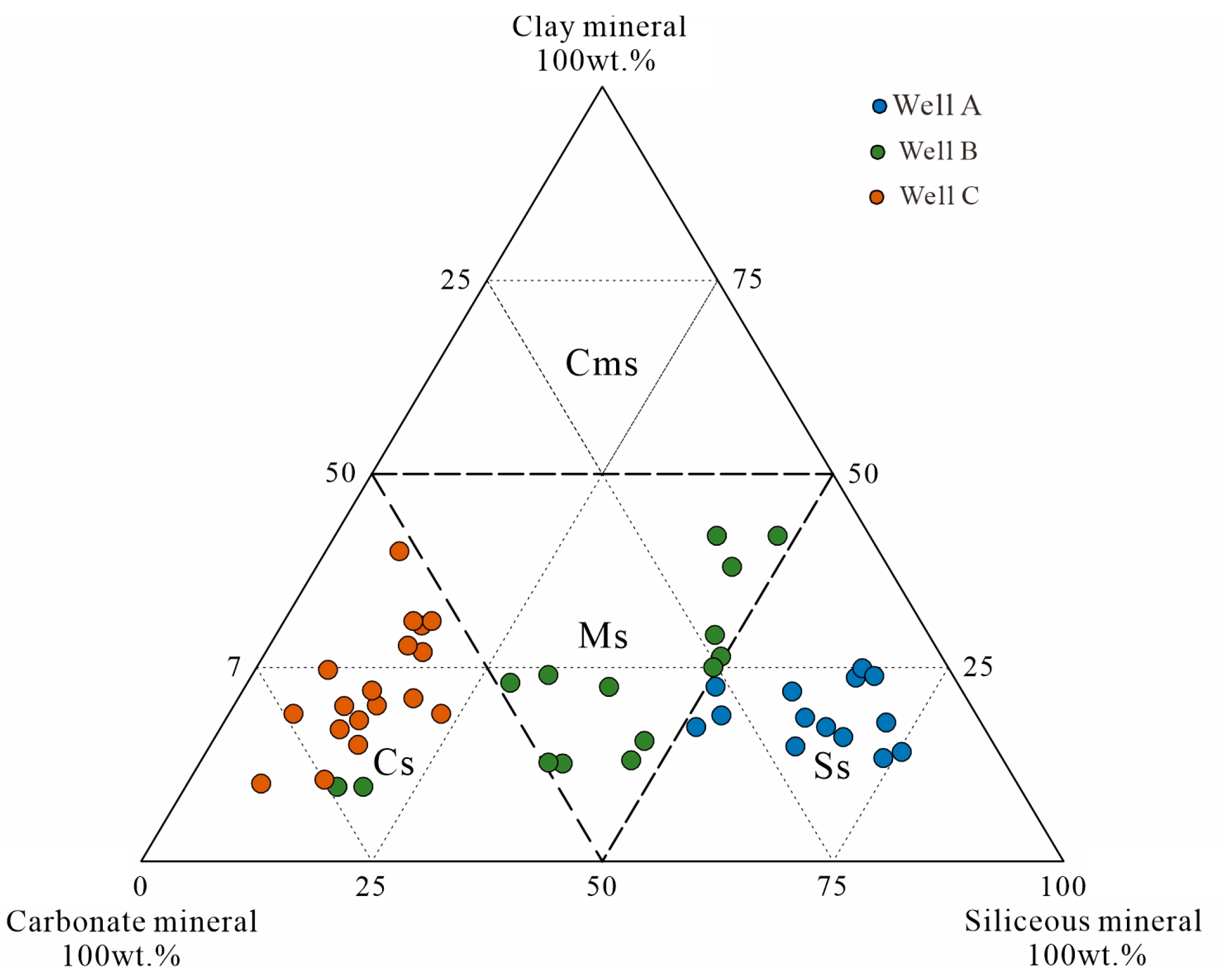
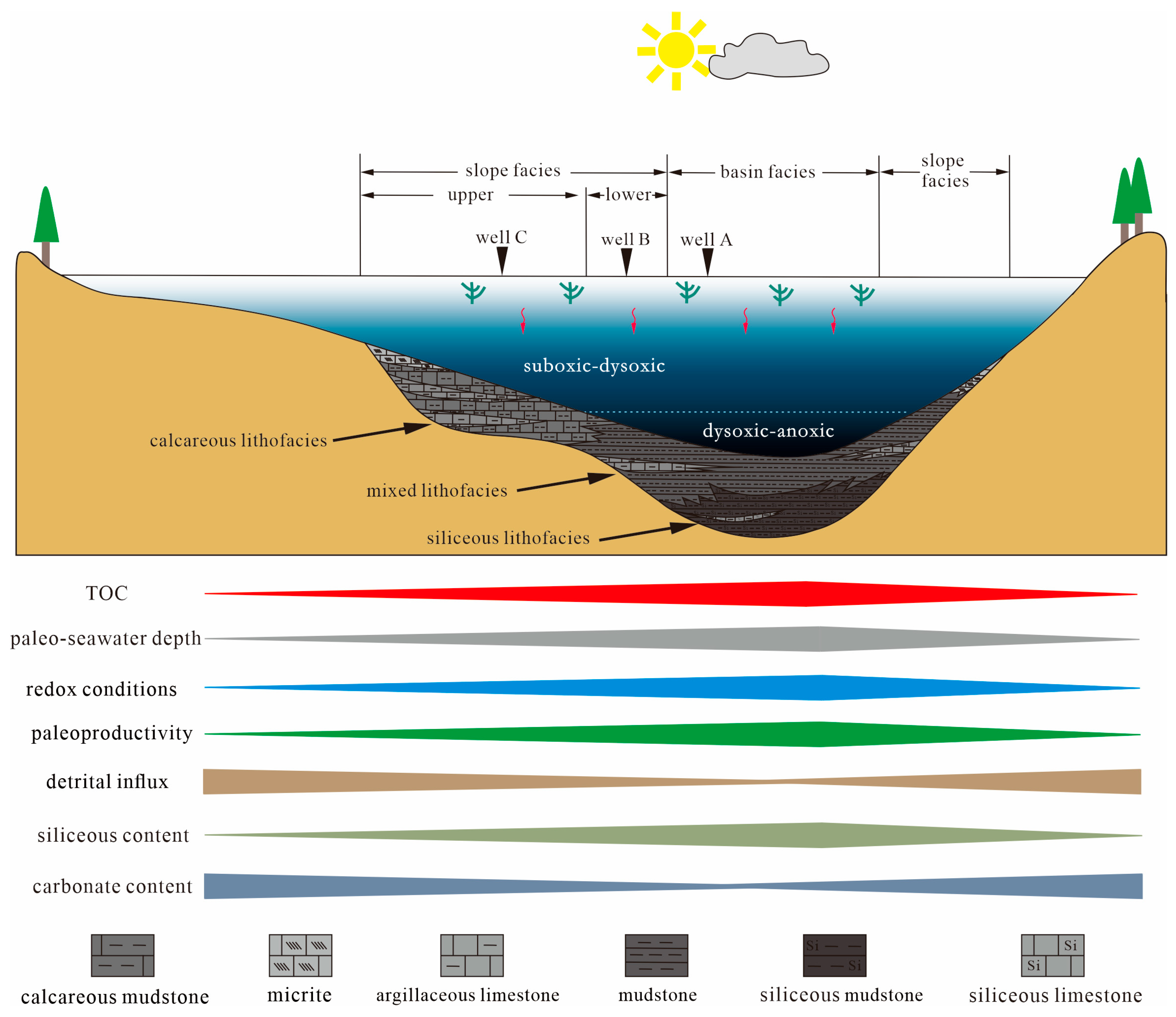
4.3. Mineralogical Characteristics and Lithofacies
5. Discussion
5.1. Reconstruction of Paleoenvironmental Conditions
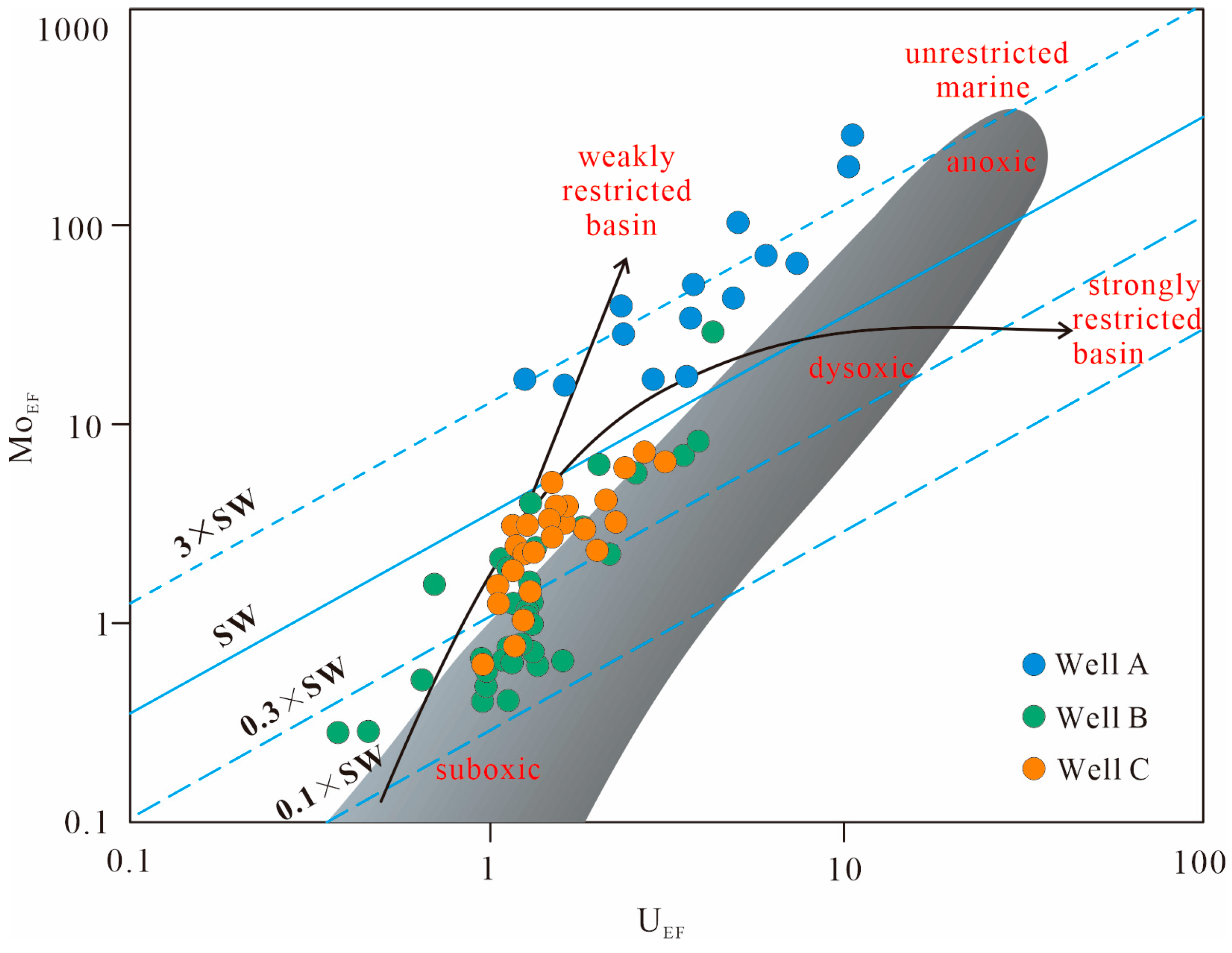
5.1.1. Redox Proxies
5.1.2. Paleoproductivity Proxies
5.1.3. Terrigenous Detrital Influx Proxies
5.1.4. Paleo-Seawater Depth
5.2. Influencing Factors of Organic Matter Enrichment
5.3. Shale Distribution Patterns
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, G.C.; Ju, Y.W.; Huang, C.; Long, S.X.; Peng, Y.M. Longmaxi-Wufeng shale lithofacies identification and 3-D modelling in the northern Fuling gas field, Sichuan basin. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 47, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Q.; Lu, Y.C.; Liu, X.F.; Zhai, G.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, C. Depositional environment and organic matter enrichment of the lower Cambrian Niutitang shale in western Hubei Province, South China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2019, 109, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, M.; Tian, X.; Hong, H.T.; Wen, L.; Wang, W.Z. Climate-ocean control on the depositional watermass conditions and organic matter enrichment in lower Cambrian black shale in the upper Yangtze Platform. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 120, 104570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.S.; Mou, C.L.; Tan, Q.; Yu, Q. A discussion on Kaijiang-Liangping ocean trough. Oil Gas Geol. 2006, 27, 326–331. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.H.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, X.Q.; Lang, Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Xu, L.F. Characteristics and controlling factors of organic matter enrichment of Lower Carboniferous black rock series deposited in inter-platform region, Southern Guizhou Depression. Lithol. Reserv. 2019, 31, 83–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Awan, R.S.; Liu, C.L.; Gong, H.W.; Chao, D.; Chao, T.; Lawali, G.C. Paleo-sedimentary environment in relation to enrichment of organic matter of Early Cambrian black rocks of Niutitang Formation from Xiangxi area China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 112, 104057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, T.W.; Tuo, J.C.; Song, D.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.F.; Xing, L.T. Reconstruction of paleoceanic redox conditions of the lower Cambrian Niutitang shales in northern Guizhou, Upper Yangtze region. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 538, 109457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Kang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.Y.; Xiao, H.F. Sedimentary geochemical investigation for paleoenvironment of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation shales in the Yangtze Platform. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2017, 159, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Chen, J. Occurrence characteristics and exploration potential of Carboniferous shale gas in western Guizhou. Pet. Reserv. Eval. Dev. 2022, 12, 82–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.M.; Yang, R.D.; Gao, J.B.; Xu, S.L.; Zhang, Z. REE Geochemical Signatures and Sedimentary Environments of the Early Carboniferous Dawuba Formation Black Rock Series in Huishui, Guizhou. J. Chin. Soc. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 620–631. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, W.F.; Liang, Y.P.; Deng, B. Analysis on black shale feature and depositional environment of first member of Luzhai Formation, Luzhai area of Guangxi. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2017, 31, 605–612. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.Y.; Hu, Z.Q.; Shen, B.J.; Pan, A.Y.; Li, C.X.; Wang, R.H.; Zhang, M.L. Sedimentary characteristics and model of platform-trough shale in the Lower Carboniferous, Guizhong Depression, Dianqiangui Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2022, 43, 365–377. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.W.; Guo, T.L.; Wo, Y.J.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, L.Z.; Zhang, R.Q.; Li, S.J. Characteristics of deep structure segmentation and transformation of Yaziluo fault zone. Oil Gas Geol. 2013, 34, 220–228. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Rui, Y.; Tang, Z. Elemental Geochemical Characterization of Sedimentary Conditions and Organic Matter Enrichment for Lower Cambrian Shale Formations in Northern Guizhou, South China. Minerals 2020, 10, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.H.; Wang, C.H.; Peng, C.L.; Hu, R.F.; Chen, M.H.; Shi, L. Filling and evolution the Late Paleozoic Shuicheng-Ziyun aulacogen in western Guizhou, China. Geol. Bull. China 2006, 25, 402–407. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.F.; Yang, R.D. Lithofacies and paleogeography evolution and characteristics of shale gas accumulation in Lower Carboniferous, Guizhou, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. (Sci. Technol. Ed.) 2016, 43, 291–299. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Geology and Mineral Resources Bureau of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Regional Geology of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1985; pp. 853–854. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 19145-2003[S]; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Determination of Total Organic Carbon in Sedimentary Rock. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Yang, W.; Zuo, R.S.; Jiang, Z.X. Effect of lithofacies on pore structure and new insights into pore-preserving mechanisms of the over-mature Qiongzhusi marine shales in Lower Cambrian of the southern Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 746–762. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Jiang, S.; Lu, Y.C.; Xu, S.; Shu, Y.; Wang, Y.X. Productivity or preservation? The factors controlling the organic matter accumulation in the late Katian through Hirnantian Wufeng organic-rich shale, South China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2019, 109, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algeo, T.J.; Tribovillard, N. Environmental analysis of paleoceanographic systems based on molybdenum-uranium covariation. Chem. Geol. 2009, 268, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.C.; Xiao, D.S.; Lu, S.F.; Jiang, S.; Lu, S.D. Effect of sedimentary environment on the formation of organic-rich marine shale: Insights from major/trace elements and shale composition. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2019, 204, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribovillard, N.; Algeo, T.J.; Baudin, F.; Riboulleau, A. Analysis of marine environmental conditions based on molybdenum-uranium covariation-Applications to Mesozoic paleoceanography. Chem. Geol. 2012, 324, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Wei, H.Y.; Liu, H.; Shao, N.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, Q. Accumulation of sediments with extraordinary high organic matter content: Insight gained through geochemical characterization of indicative elements. Oil Gas Geol. 2021, 42, 931–948. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jones, B.; Manning, D.A. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones. Chem. Geol. 1994, 111, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribovillard, N.; Algeo, T.J.; Lyons, T.; Riboulleau, A. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update. Chem. Geol. 2006, 232, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M. Thermodynamic solubility relationships of inorganic vanadium in the marine environment. Mar. Chem. 1988, 23, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranston, R.E.; Murray, J.W. The determination of chromium species in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1978, 99, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, S.M. Geochemical paleoredox indicators in Devonian-Mississippian black shales, central Appalachian Basin (USA). Chem. Geol. 2004, 206, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.F.; Dong, D.Z.; Wang, Y.M.; Huang, J.L.; Pu, B.L. Geochemistry Evaluation Index of Redox-sensitive Elements for Depositional Environments of Silurian Longmaxi Organic-rich Shale in the South of Sichuan Basin. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2014, 19, 27–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ingall, E.D.; Bustin, R.M.; Van, C.P. Influence of water column anoxia on the burial and preservation of carbon and phosphorus in marine shales. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepfer, S.D.; Shen, J.; Wei, H.Y.; Tyson, R.V.; Ingall, E.; Algeo, T. Total organic carbon, organic phosphorus, and biogenic barium fluxes as proxies for paleomarine productivity. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 149, 23–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.G.; Lv, D.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Yu, C.; Zhao, K.H.; Liu, X.X.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, B.; Qiang, X.K.; et al. Evolution of sedimentary environment in the Eastern Henan Basin since the Late Pliocene. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2024, 633, 111896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, E.D.; Arrhenius, G.O.S. Chemistry of Pacific pelagic sediments. Geo-Chim. Cosmochim. Acta 1958, 13, 153–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Cheng, P.; Fan, C.W.; Song, P.; Huang, Q.T. Evolutions of sedimentary facies and palaeoenvironment and their controls on the development of source rocks in continental margin basins: A case study from the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Petrol. Sci. 2023, 20, 2648–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.L.; Liu, B.; Song, X.M.; Wang, Q.P.; Chen, X.D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Hydrocarbon generation and organic matter enrichment of limestone in a lacustrine mixed sedimentary environment: A case study of the Jurassic Da’anzhai member in the central Sichuan Basin, SW China. Petrol. Sci. 2023, 20, 670–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Zhang, T.; Ye, J. Anoxic environment and formation of superlarge ore deposits. Sci. China Ser. D Ear. Sci. 1998, 41 (Suppl. S1), 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Q.; Chen, Z.H.; Liu, L.L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Shen, W.L. How to distinguish between marine and lacustrine sedimentary environments?—A case study of Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 228, 212032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J. Organic carbon, sulphur, and iron in recent semi-euxinic sediments of Kau Bay, Indonesia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.X.; Lu, G.; Deng, B.; Wang, C.C.; Li, Z.W.; Yu, Y.; Yang, R.J.; Jin, X. Tectonic–paleogeographic evolution of the Late Triassic in the Sichuan basin, SW China: Constraints from sedimentary facies and provenance nalysis of the Xujiahe Formation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 160, 106649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, X.M.; Gao, P.; Wang, E.Z.; Hu, D.F.; Liu, R.B.; Li, G.; Lu, C.G. Restoration of sedimentary environment and geochemical features of deep marine Longmaxi shale and its significance for shale gas: A case study of the Dingshan area in the Sichuan Basin, South China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 151, 106186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; He, S.; Yang, Z. The Marine Source Rock Formation Conditions and Control Factors. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2008, 27, 63–70. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, D.S.; Fang, H.; Zhang, P.H.; Pei, F.G.; Ming, C.D.; He, M.X.; Zhang, X.B. Geochemical characteristics of the Middle–Late Permian sedimentary rocks in the southern Great Xing’an Range, NE China, and their constraints on the closure time of the Paleo Asian Ocean (Eastern Segment). Sediment. Geol. 2023, 450, 106375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontakiotis, G.; Karakitsios, V.; Maravelis, A.G.; Zarkogiannis, S.D.; Agiadi, K.; Antonarakou, A.; Pasadakis, N.; Zelilidis, A. Integrated isotopic and organic geochemical constraints on the depositional controls and source rock quality of the Neogene Kalamaki sedimentary successions (Zakynthos Island, Ionian Sea). Med. Geosci. Rev. 2021, 3, 193–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontakiotis, G.; Karakitsios, V.; Cornée, J.; Moissette, P.; Zarkogiannis, S.D.; Pasadakis, N.; Koskeridou, E.; Manoutsoglou, E.; Drinia, H.; Antonarakou, A. Preliminary results based on geochemical sedimentary constraints on the hydrocarbon potential and depositional environment of a Messinian sub-salt mixed siliciclastic-carbonate succession onshore Crete (Plouti section, eastern Mediterranean). Med. Geosc. Rev. 2020, 2, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Tian, J.C.; Wang, F.; Liang, Q.S.; Yang, T.; Kneller, B.; Liang, X.W. Sedimentary environment and organic matter enrichment of black mudstones from the upper Triassic Chang-7 member in the Ordos Basin, Northern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 224, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


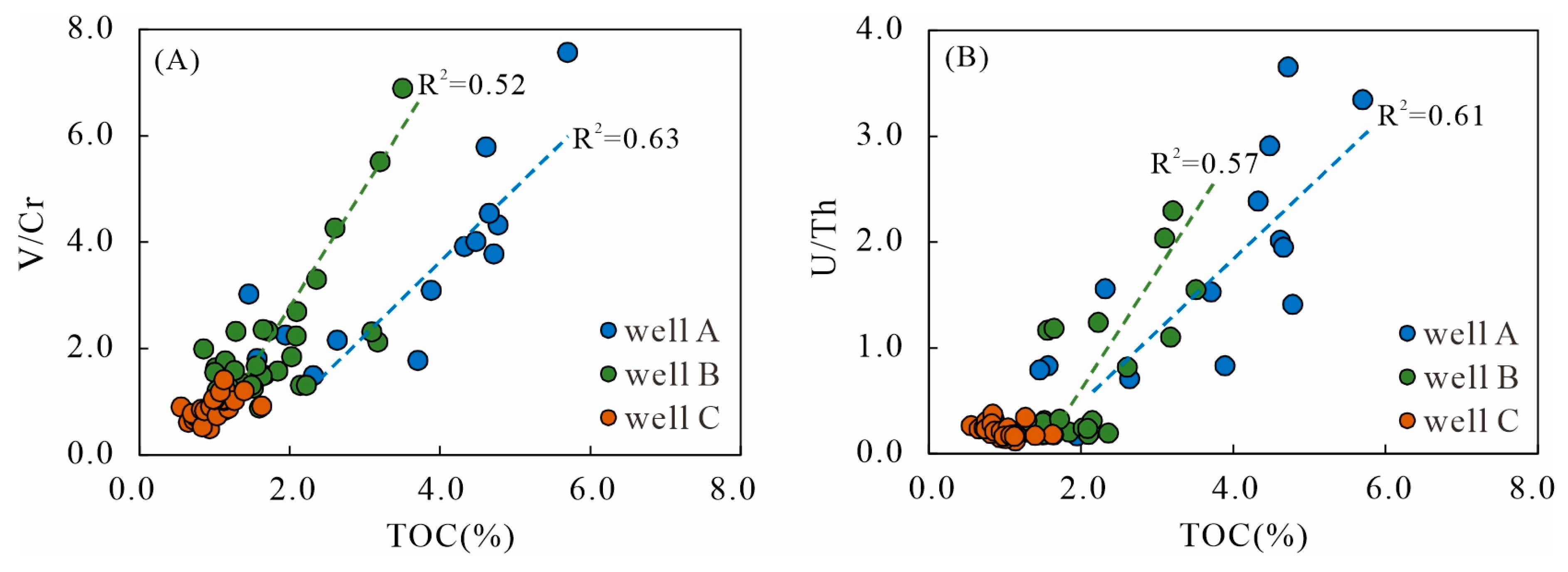
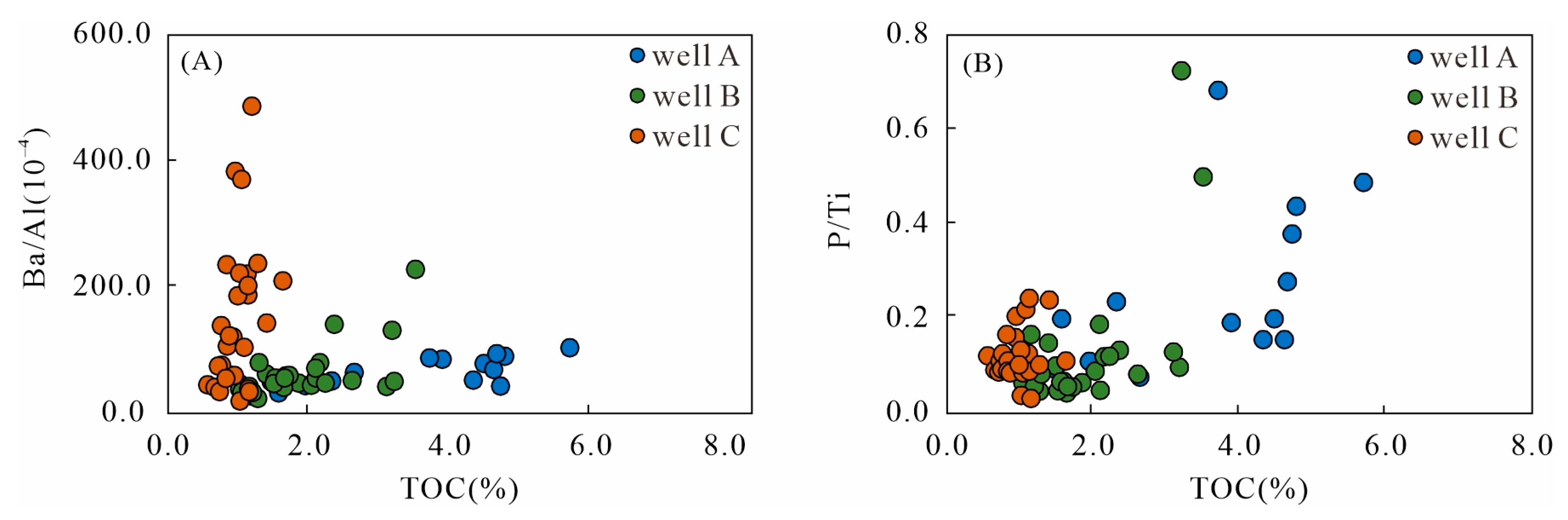
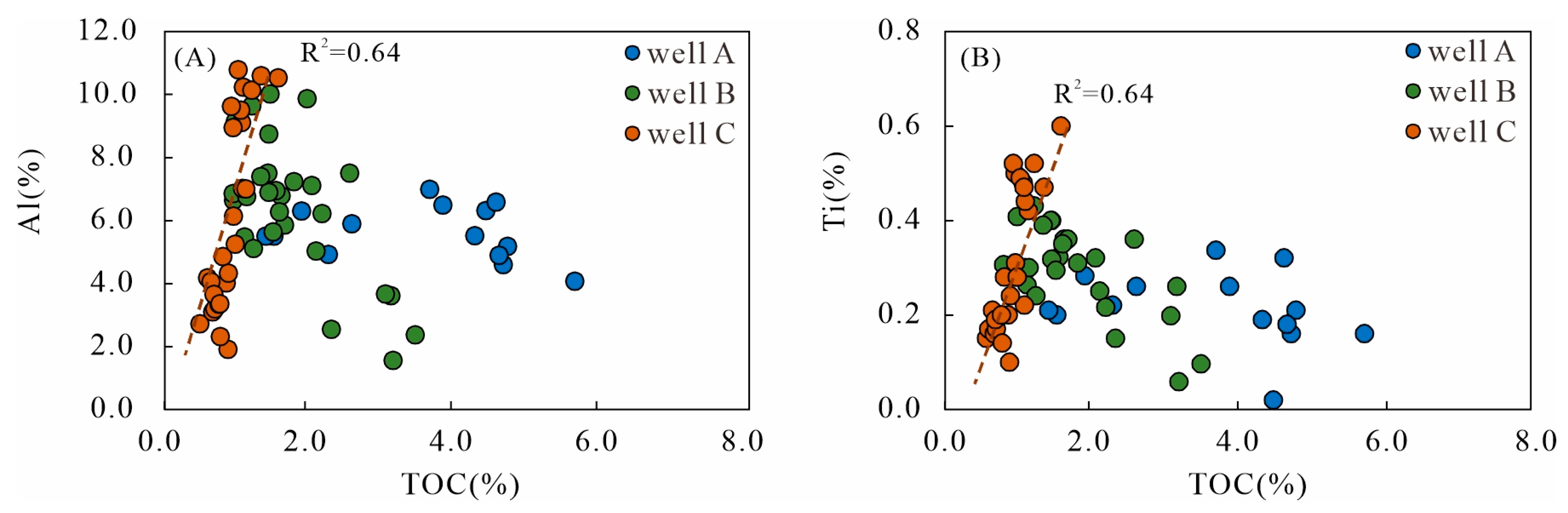
| Well | Geochemical Proxies | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redox Conditions | Paleo-Seawater Depth | Detrital Influx | Paleoproductivity | |||||
| V/Cr | U/Th | Co/Ti | Sr/Ba | Al (wt.%) | Ti (wt.%) | P/Ti | Ba/Al (10−4) | |
| Well A | 3.54 | 1.72 | 100.49 | 1.60 | 5.62 | 0.22 | 0.27 | 67.99 |
| Well B | 2.18 | 0.60 | 37.60 | 3.15 | 5.95 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 65.13 |
| Well C | 0.89 | 0.21 | 38.87 | 2.45 | 6.40 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 178.77 |
| Lithofacies | Kerogen Types | TOC (wt.%) | Average Mineral Content (wt.%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Feldspar | Calcite | Dolomite | Pyrite | Clay | |||
| Siliceous lithofacies | I | 3.63 | 57.56 | 7.20 | 8.18 | 5.15 | 5.77 | 19.14 |
| Mixed lithofacies | II1 | 1.85 | 41.85 | 0.15 | 26.21 | 4.20 | 2.65 | 24.62 |
| Calcareous lithofacies | II2 | 1.02 | 13.60 | 0.30 | 40.20 | 21.20 | 2.30 | 22.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Xu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Shi, D.; Bai, J.; Yuan, K.; Cen, W.; Li, F.; et al. Effect of Paleoenvironmental Conditions on the Distribution of Lower Carboniferous Shale in Yaziluo Rift Trough, South China: Insights from Major/Trace Elements and Shale Composition. Minerals 2024, 14, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070659
Chen X, Xu Q, Qin Y, Chen R, Wang Y, Shi D, Bai J, Yuan K, Cen W, Li F, et al. Effect of Paleoenvironmental Conditions on the Distribution of Lower Carboniferous Shale in Yaziluo Rift Trough, South China: Insights from Major/Trace Elements and Shale Composition. Minerals. 2024; 14(7):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070659
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xianglin, Qiuchen Xu, Yinglun Qin, Rong Chen, Yufang Wang, Dishi Shi, Jing Bai, Kun Yuan, Wenpan Cen, Fei Li, and et al. 2024. "Effect of Paleoenvironmental Conditions on the Distribution of Lower Carboniferous Shale in Yaziluo Rift Trough, South China: Insights from Major/Trace Elements and Shale Composition" Minerals 14, no. 7: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070659
APA StyleChen, X., Xu, Q., Qin, Y., Chen, R., Wang, Y., Shi, D., Bai, J., Yuan, K., Cen, W., Li, F., & Lin, T. (2024). Effect of Paleoenvironmental Conditions on the Distribution of Lower Carboniferous Shale in Yaziluo Rift Trough, South China: Insights from Major/Trace Elements and Shale Composition. Minerals, 14(7), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070659












