Methodology for the Identification of Moisture Content in Tailings Dam Walls Based on Electrical Resistivity Tomography Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
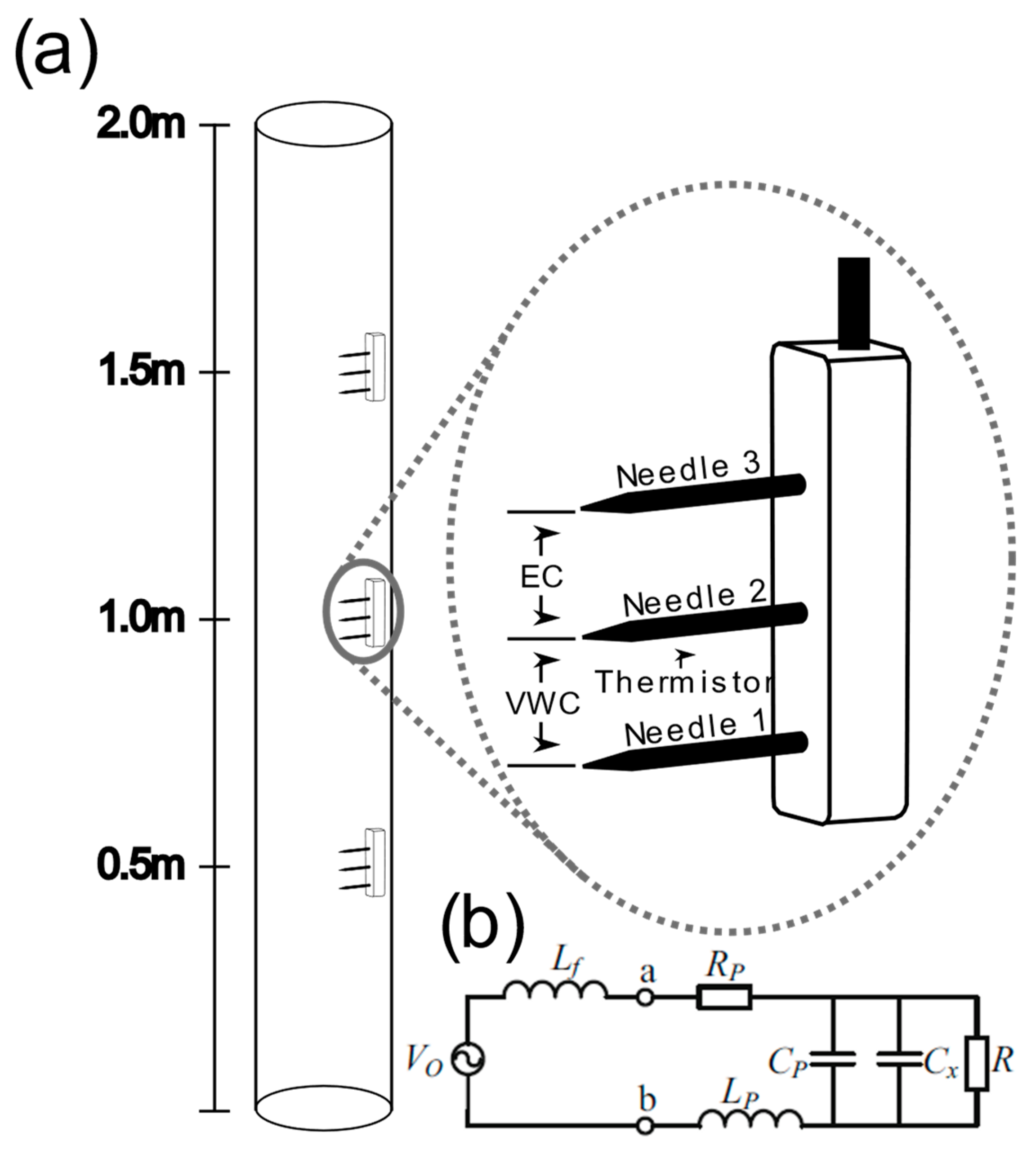
2. Data Acquisition and Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
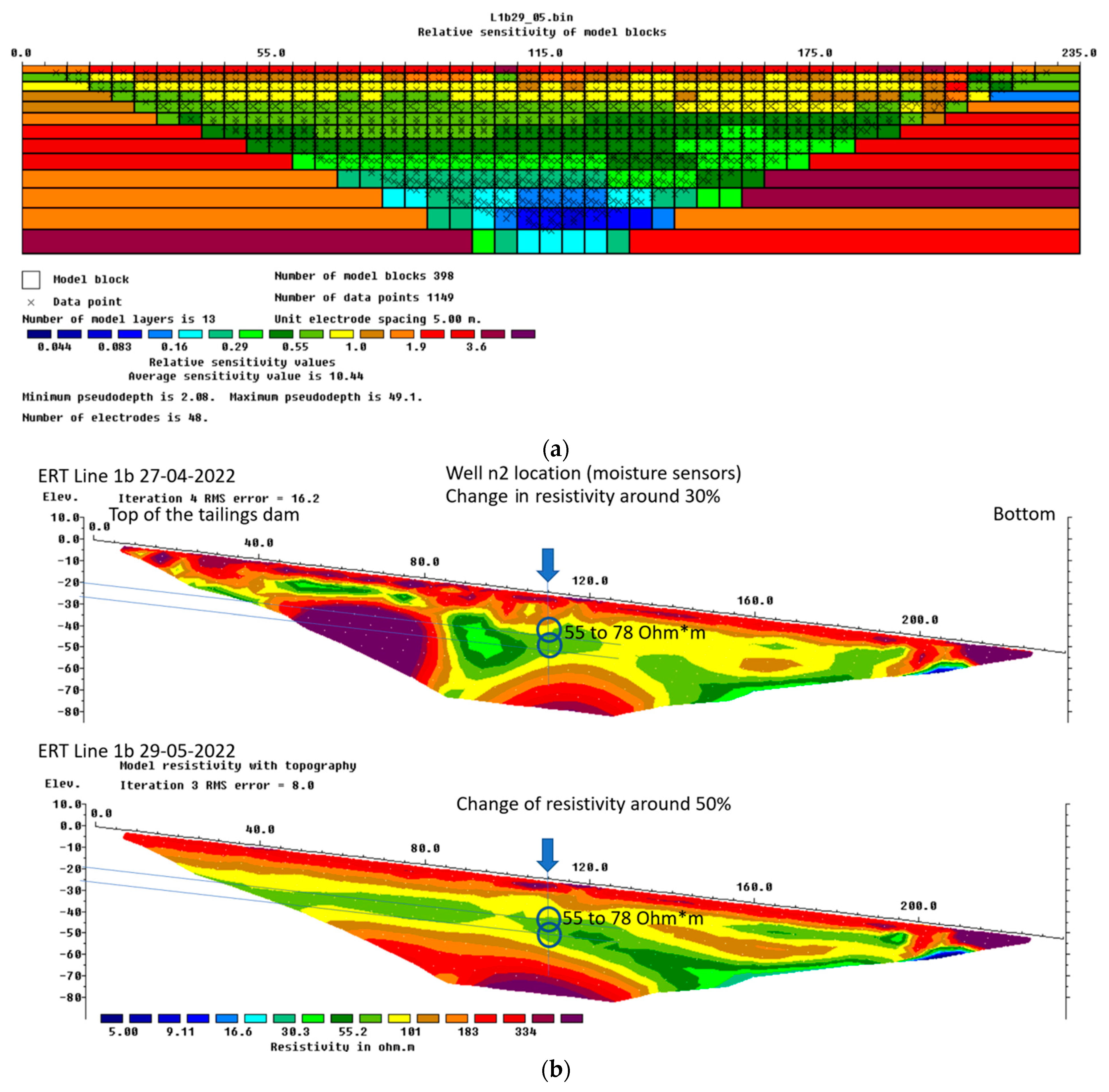
3.1. Electrical Resistivity Values
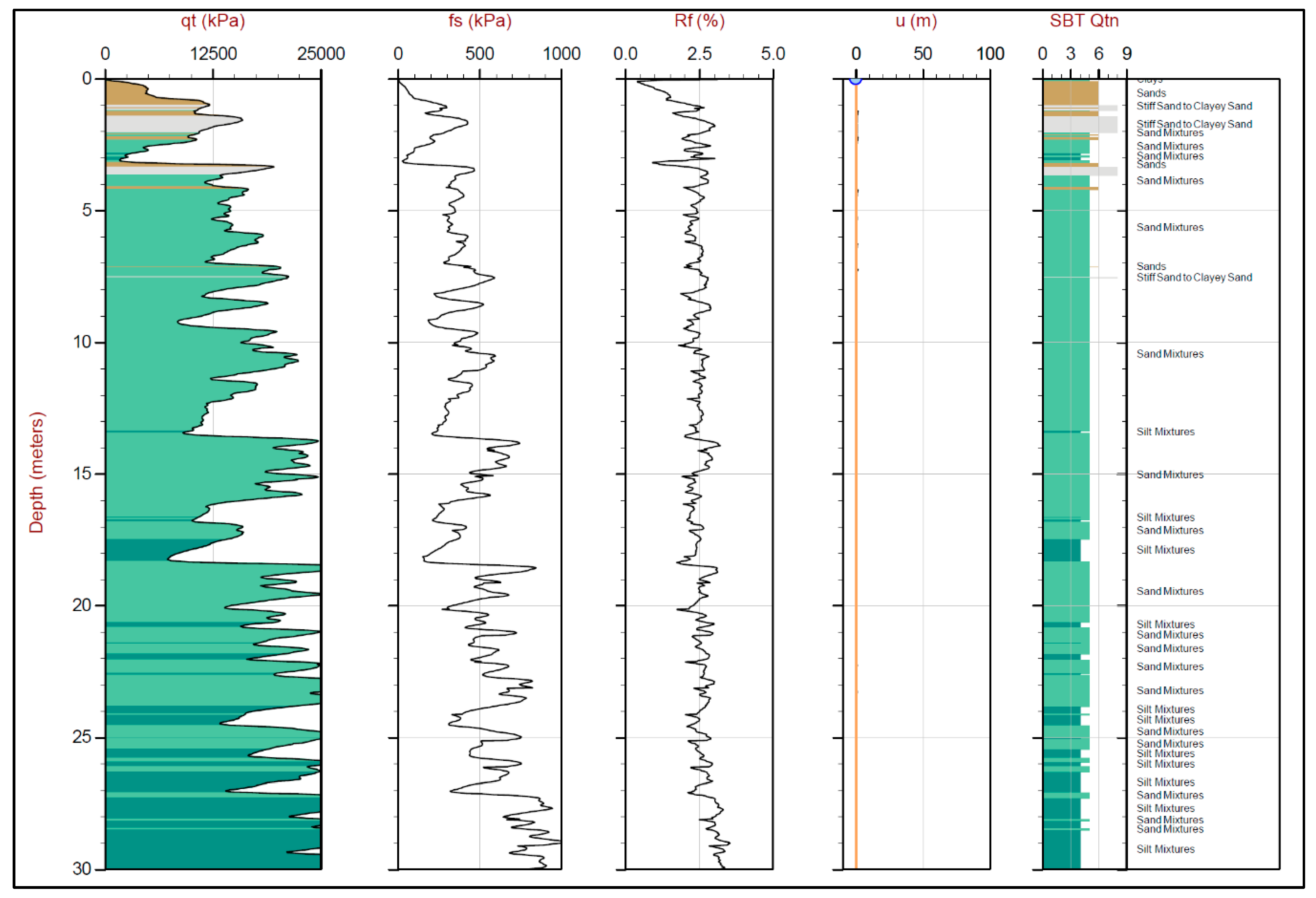
3.2. Laboratory Tests
3.3. Field-Deployed High-Frequency Humidity Sensors
3.4. Comparative Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dimech, A.; Cheng, L.; Chouteau, M.; Chambers, J.; Uhlemann, S.; Wilkinson, P.; Meldrum, P.; Mary, B.; Fabien-Ouellet, G.; Isabelle, A. A Review on Applications of Time-Lapse Electrical Resistivity Tomography Over the Last 30 Years: Perspectives for Mining Waste Monitoring. Surv. Geophys. 2022, 43, 1699–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aracil Ávila, E.; Maruri Brouard, U.; Vallés Iriso, J.; Martínez Pagán, P.; Porres Benito, J.Á. Evaluación de Problemas Medioambientales Mediante Tomografía Eléctrica. 2003. Available online: https://repositorio.upct.es/handle/10317/1993 (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Jefferies, M.; Morgenstern, N.R.; Van Zyl, D.; Wates, J. Report on NTSF Embankment Failure. Cadia Valley Operations for Ashurst Australia; H356804-00000-22A-230–0001; Newcrest: Subiaco, Australia, 2019; p. 119. [Google Scholar]
- Segura, F.R.; Nunes, E.A.; Paniz, F.P.; Paulelli, A.C.C.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Braga, G.Ú.L.; dos Reis Pedreira Filho, W.; Barbosa, F., Jr.; Cerchiaro, G.; Silva, F.F. Potential risks of the residue from Samarco’s mine dam burst (Bento Rodrigues, Brazil). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarero, P.L.; Moreira, C.A.; Pereira, H.G. Analysis of the Physical Integrity of Earth Dams from Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) in Brazil. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 5363–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, M.T.; Boaga, J.; Bersan, S.; Cassiani, G.; Cola, S.; Deiana, R.; Simonini, P.; Patti, S. River embankment characterization: The joint use of geophysical and geotechnical techniques. J. Appl. Geophys. 2014, 110, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjödahl, P.; Dahlin, T.; Johansson, S. Detection of internal erosion and seepage evaluation using resistivity monitoring. WasserWirtschaft 2007, 97, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Loke, M.H. Electrical imaging surveys for environmental and engineering studies. Pract. Guide 1999, 2, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Telford, W.M.; Geldart, L.P.; Sheriff, R.E. Applied Geophysics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Archie, G.E. The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics. Trans. AIME 1942, 146, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Han, W.; Li, T.; Wang, H.; Du, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L. Experimental Study on the Electrical Resistivity Characteristics of Uniformly Graded Calcareous Sand. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descloitres, M.; Ribolzi, O.; Le Troquer, Y.; Thiébaux, J.P. Study of water tension differences in heterogeneous sandy soils using surface ERT. J. Appl. Geophys. 2008, 64, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova, L.; Comte, D.; Diaz, D.; Bravo, I. ERT Methodology for Identifying Humidity Content in Tailings Dams. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; 2022; Volume 2022, p. NS41A–01. Available online: https://agu.confex.com/agu/fm22/meetingapp.cgi/Paper/1094870 (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Díaz, E.E.; Díaz, D.; Montes, G.; Vera, E. Estimación del grado de saturación a partir de resistividades eléctricas, aplicados al caso de una pila de lixiviación: Minera Amalia, Región de Valparaíso. Master’s Thesis, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, Y. Resolution of resistivity tomography inferred from numerical simulation 1. Geophys. Prospect. 1992, 40, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H.; Barker, R.D. Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by a quasi-Newton method1. Geophys. Prospect. 1996, 44, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, A.; Ferré, T.P.; Warrick, A.W. A sensitivity analysis of electrical resistivity tomography array types using analytical element modeling. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binley, A.; Kemna, A. DC resistivity and induced polarization methods. In Hydrogeophysics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Mendoza, R.; Rey, J.; Sandoval, S.; Hidalgo, M.C. Characterization of Tailings Dams by Electrical Geophysical Methods (ERT, IP): Federico Mine (La Carolina, Southeastern Spain). Minerals 2021, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto AS, P.; Pregnolato, M.C.; Silva, A.; Yamasaki, M.T.; Conte Junior, F. Development of an electrical resistivity measure for geotechnical and geoenvironmental characterization. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Cone Penetration Testing, Huntington Beach, CA, USA, 9–11 May 2010; pp. 63–70. Available online: https://www.geoengineer.org/storage/publication/18335/publication_file/2574/1-09Peieoa.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Zimmerman, R.W. Pore Volume and Porosity Changes under Uniaxial Strain Conditions. Transp. Porous Media 2017, 119, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

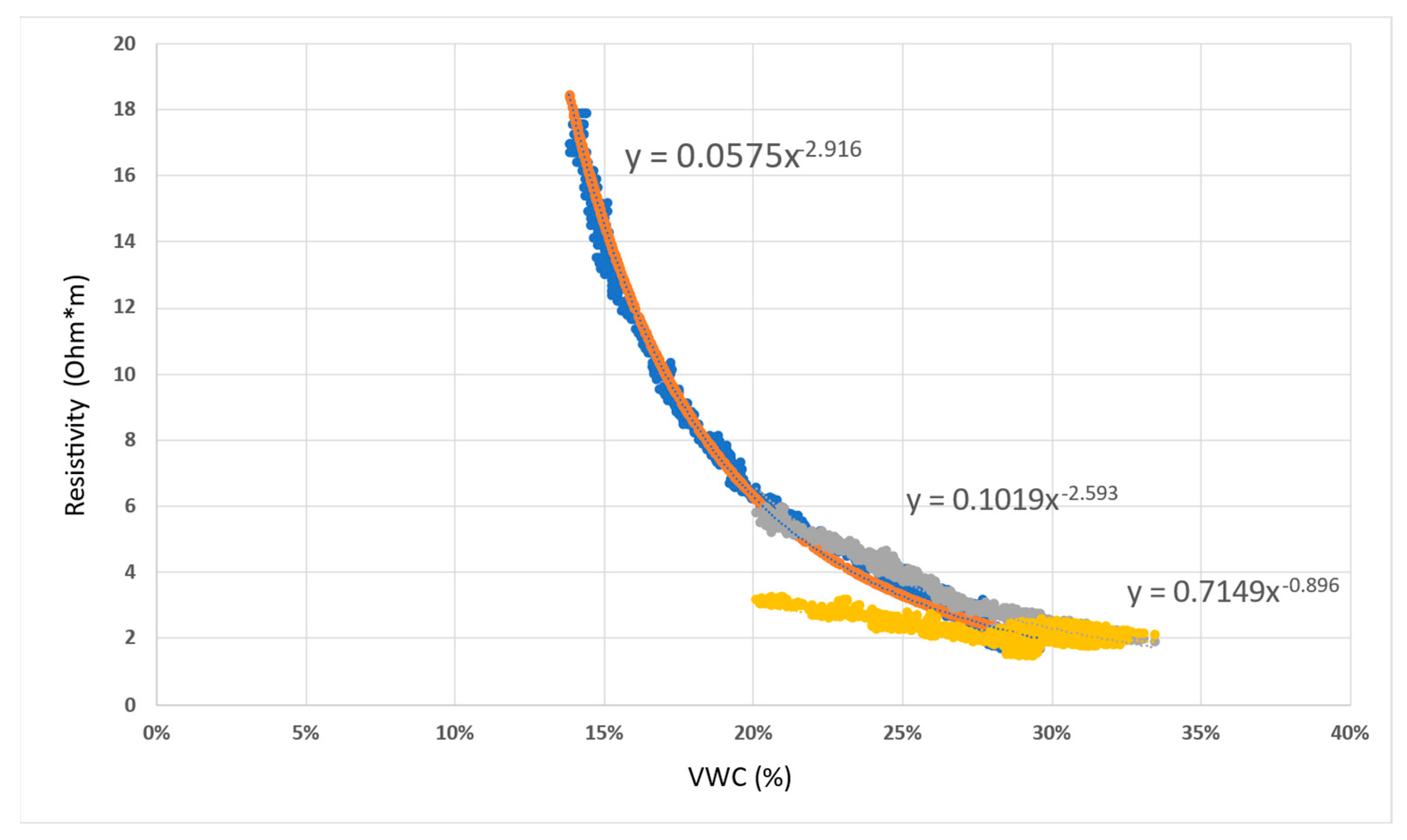
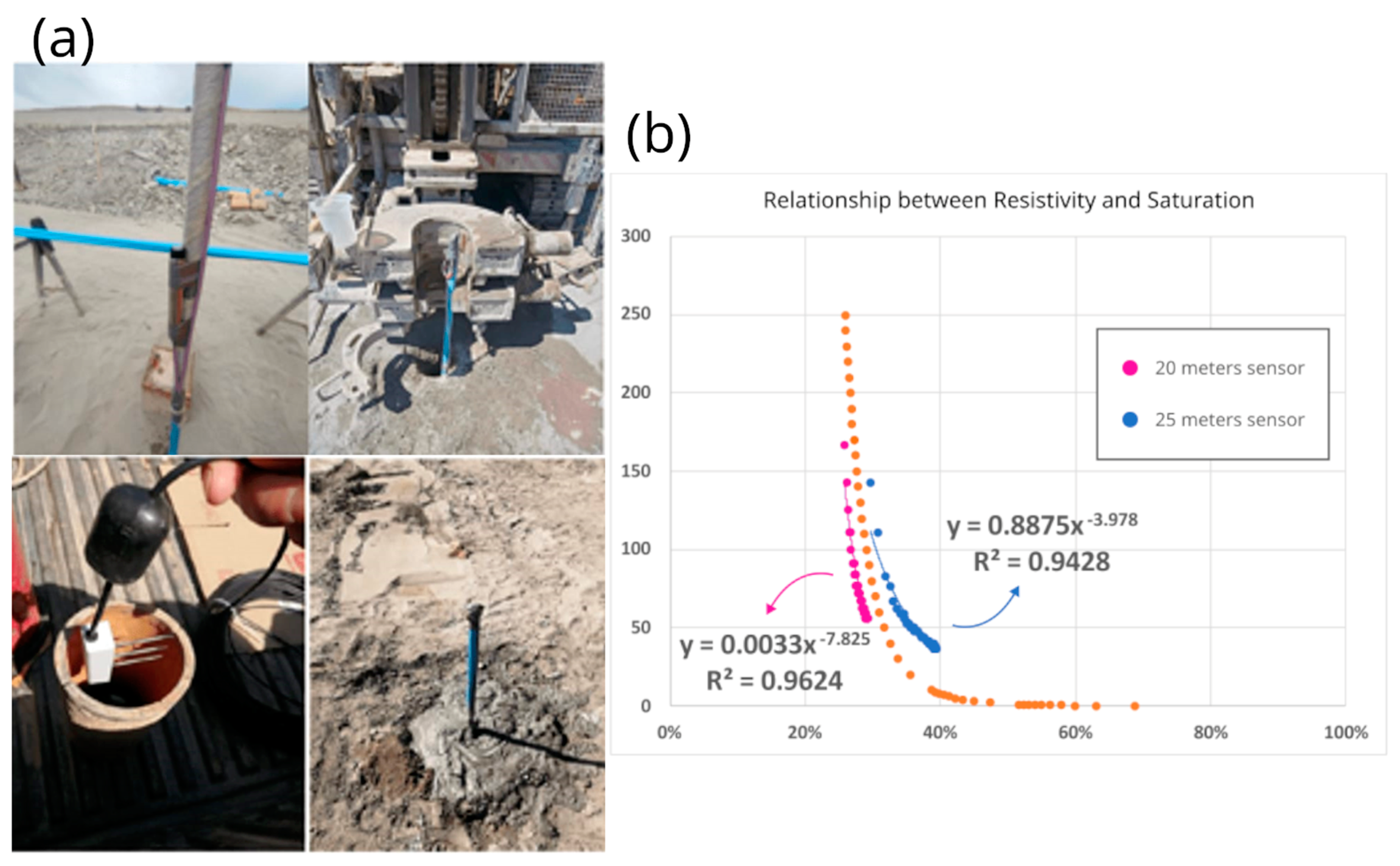
| Sensor at 1.5 m height | 0.7149 | 0.896 |
| Sensor at 1 m height | 0.1019 | 2.593 |
| Sensor at 0.5 m height | 0.0575 | 2.916 |
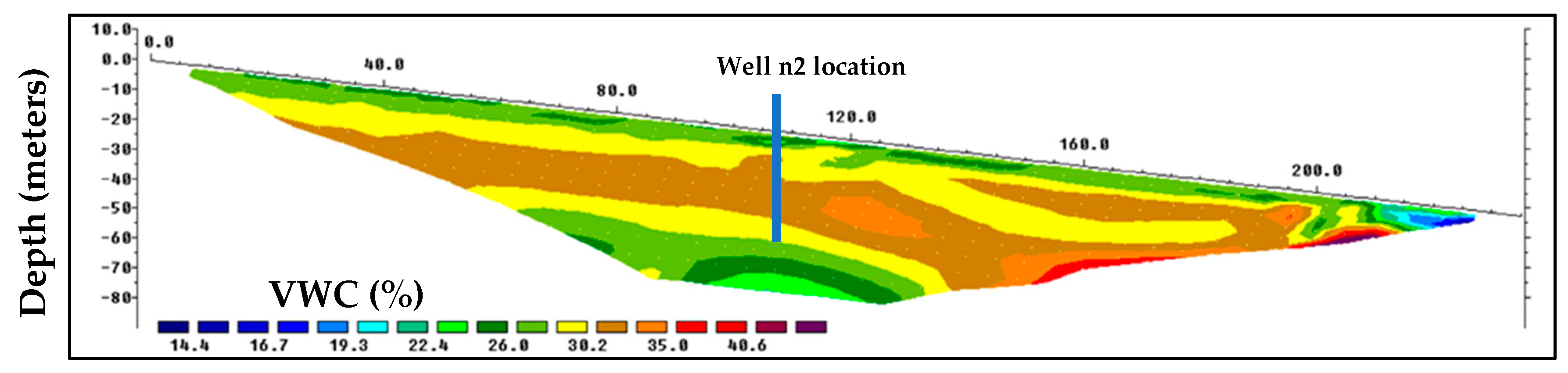
| Field-deployed TEROS12 Sensors in Well n2 | 0.005 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Córdova, L.; Moya, A.; Comte, D.; Bravo, I. Methodology for the Identification of Moisture Content in Tailings Dam Walls Based on Electrical Resistivity Tomography Technique. Minerals 2024, 14, 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080760
Córdova L, Moya A, Comte D, Bravo I. Methodology for the Identification of Moisture Content in Tailings Dam Walls Based on Electrical Resistivity Tomography Technique. Minerals. 2024; 14(8):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080760
Chicago/Turabian StyleCórdova, Leopoldo, Aaron Moya, Diana Comte, and Igor Bravo. 2024. "Methodology for the Identification of Moisture Content in Tailings Dam Walls Based on Electrical Resistivity Tomography Technique" Minerals 14, no. 8: 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080760
APA StyleCórdova, L., Moya, A., Comte, D., & Bravo, I. (2024). Methodology for the Identification of Moisture Content in Tailings Dam Walls Based on Electrical Resistivity Tomography Technique. Minerals, 14(8), 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14080760







