Mineralogical and Geochemical Evolution During Limestone Weathering and Pedogenesis in Shimen, Hunan Province, South China
Abstract
1. Introduction
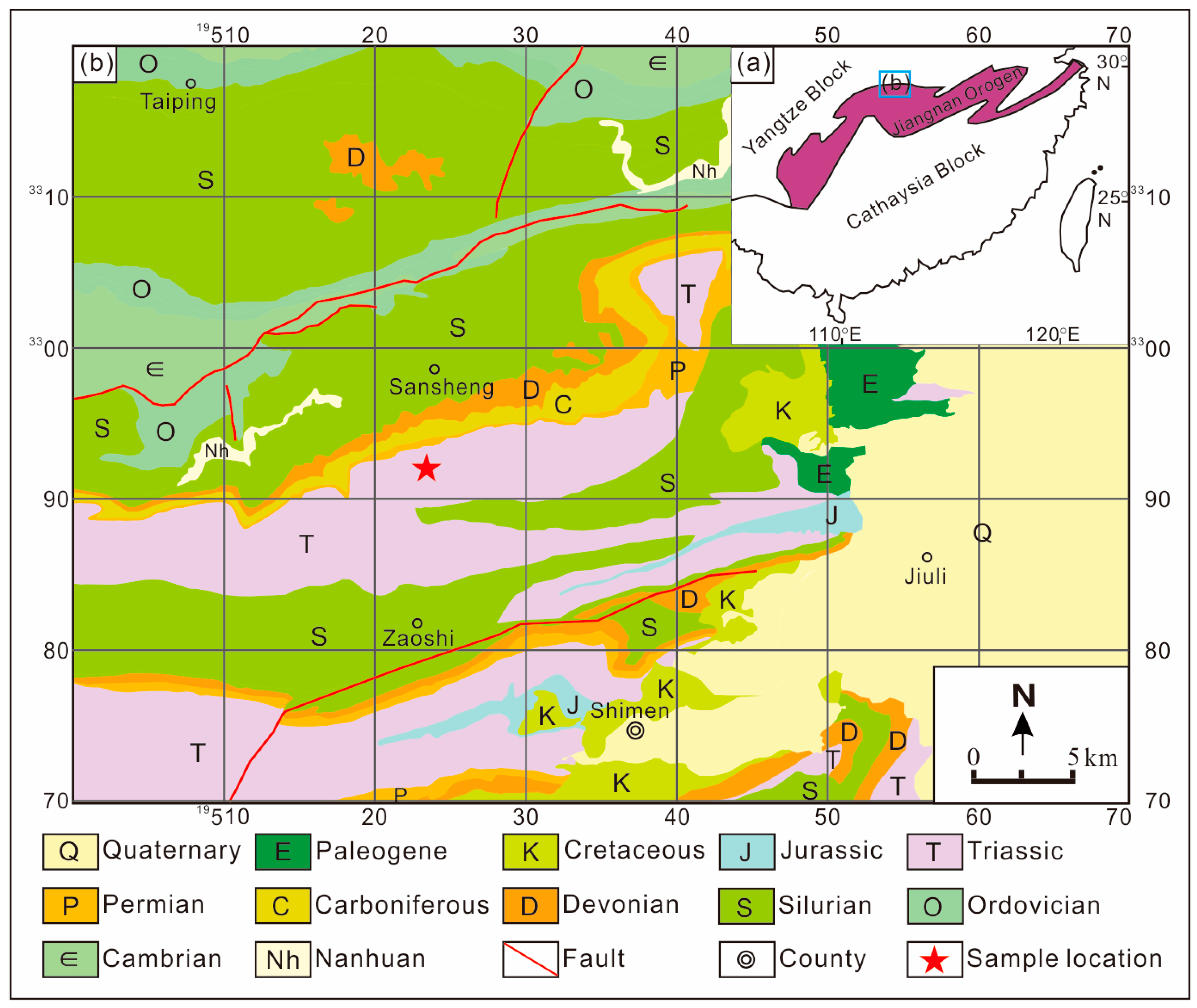
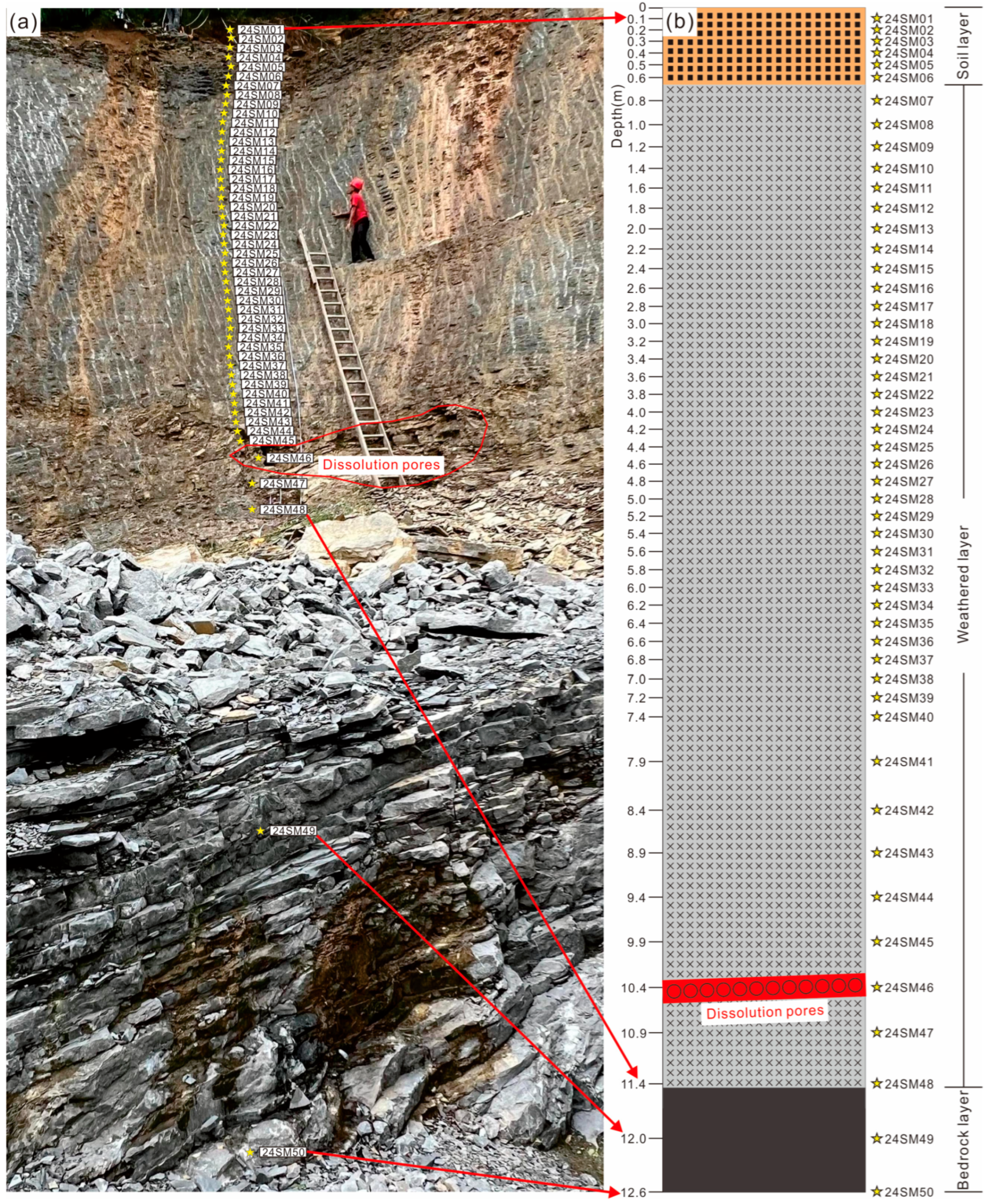
2. Geological Setting and Sampling Description
3. Analytical Methods
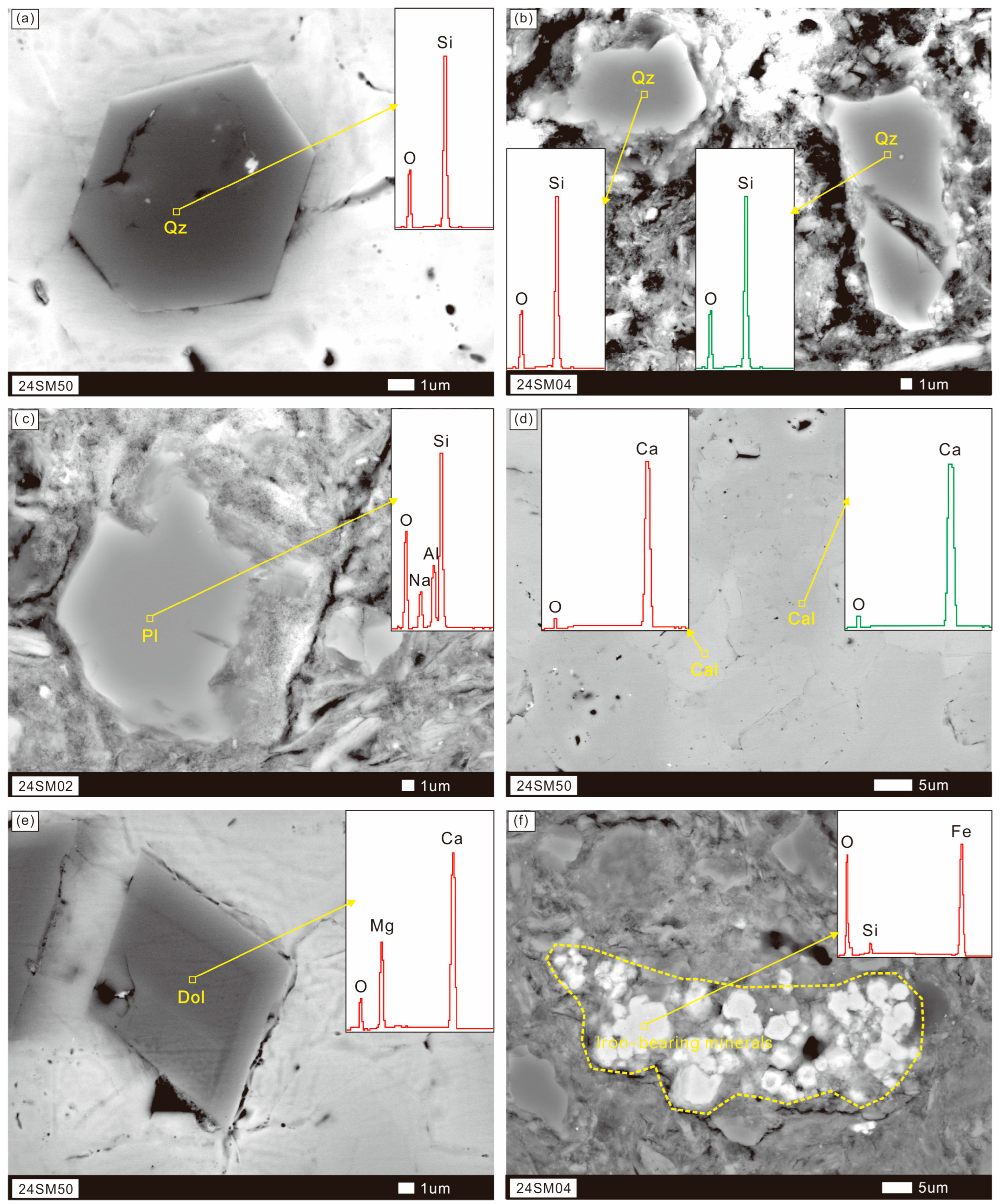
3.1. Mineralogical Composition and Microscale Morphology
3.2. Whole-Rock Geochemistry
3.3. Calculation of the Chemical Index of Alteration and Mass Transfer Coefficients
4. Results
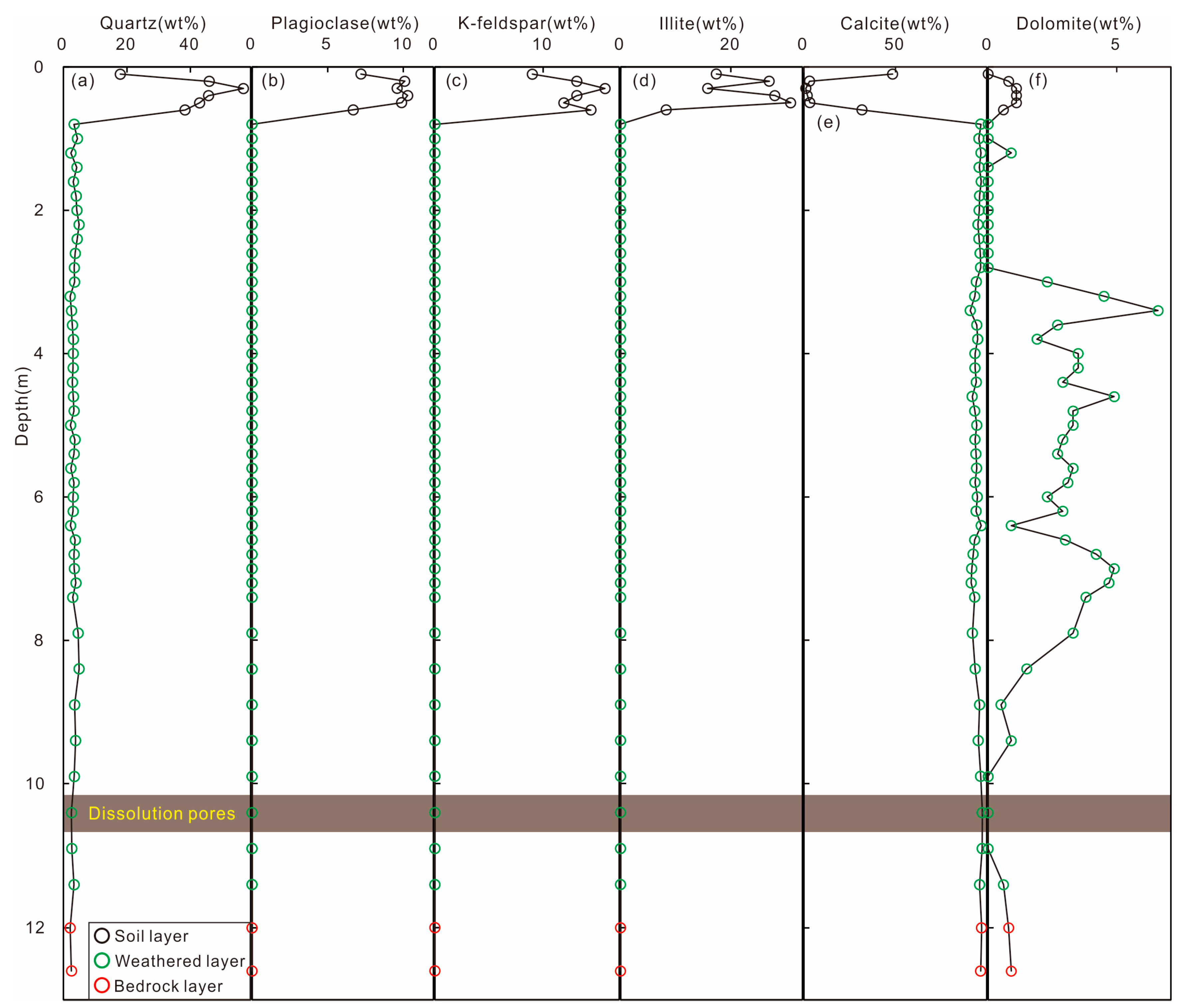
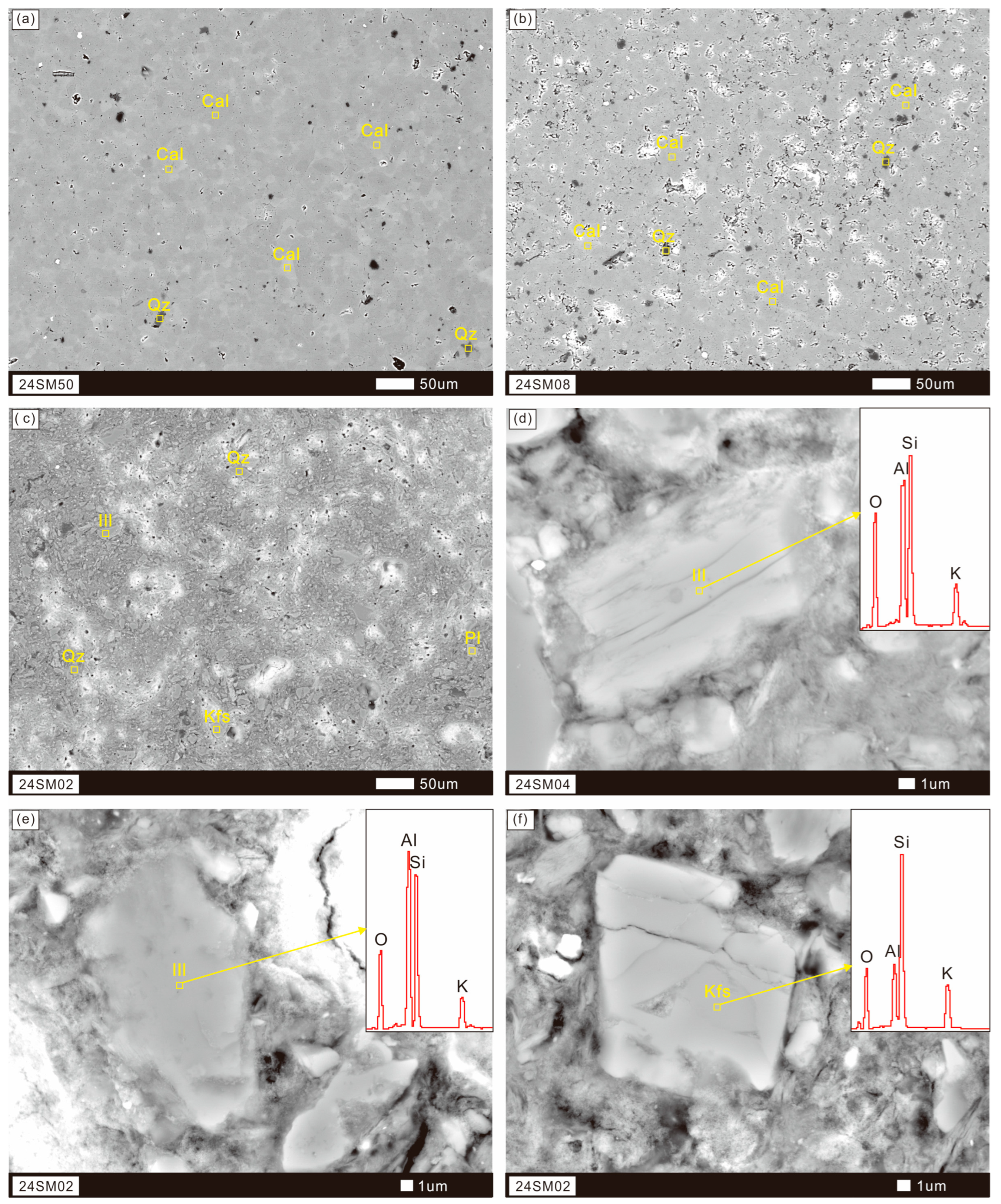
4.1. Weathering Profile Mineral Composition
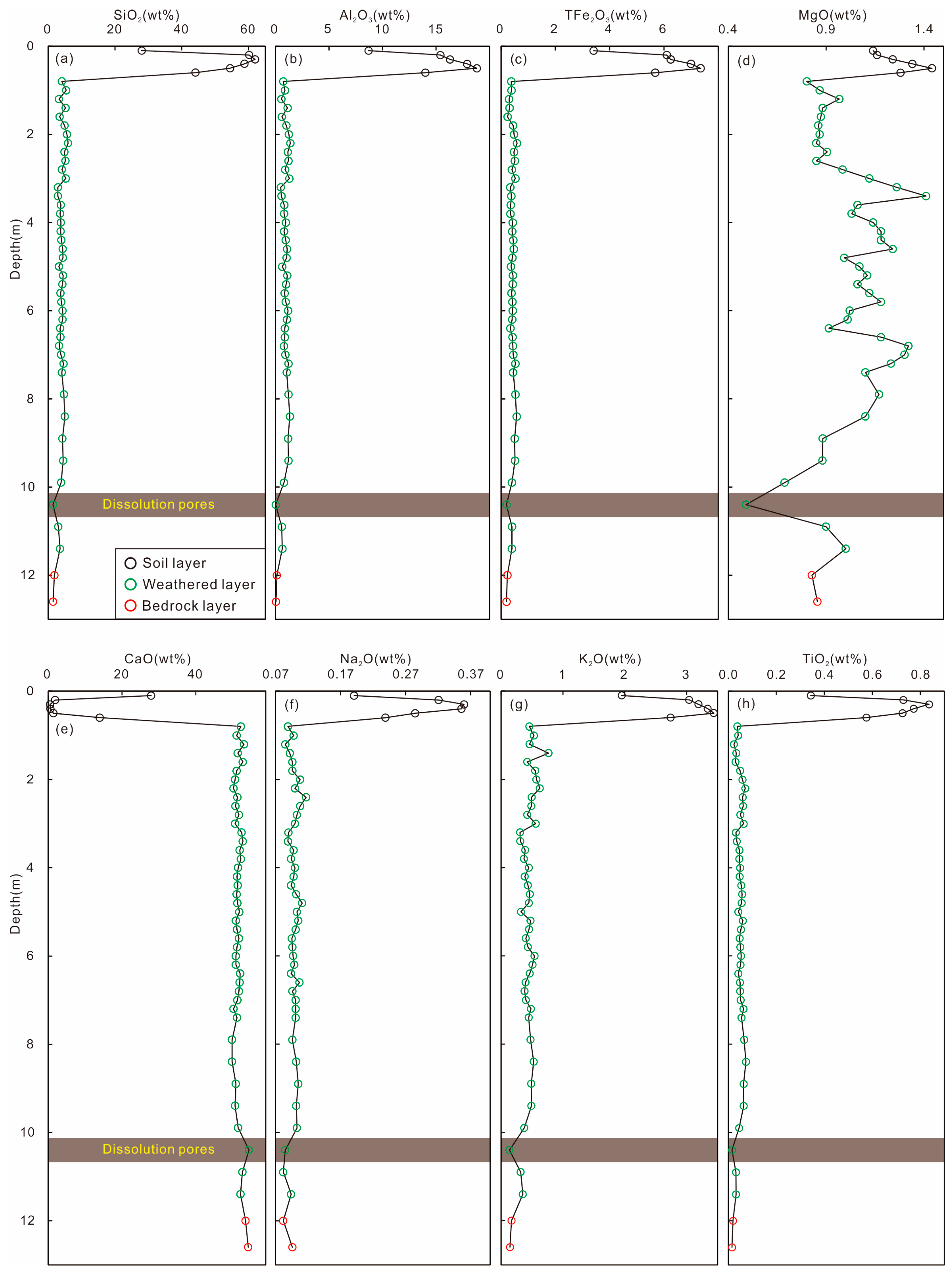
4.2. Whole-Rock Major Elements in Weathering Profile
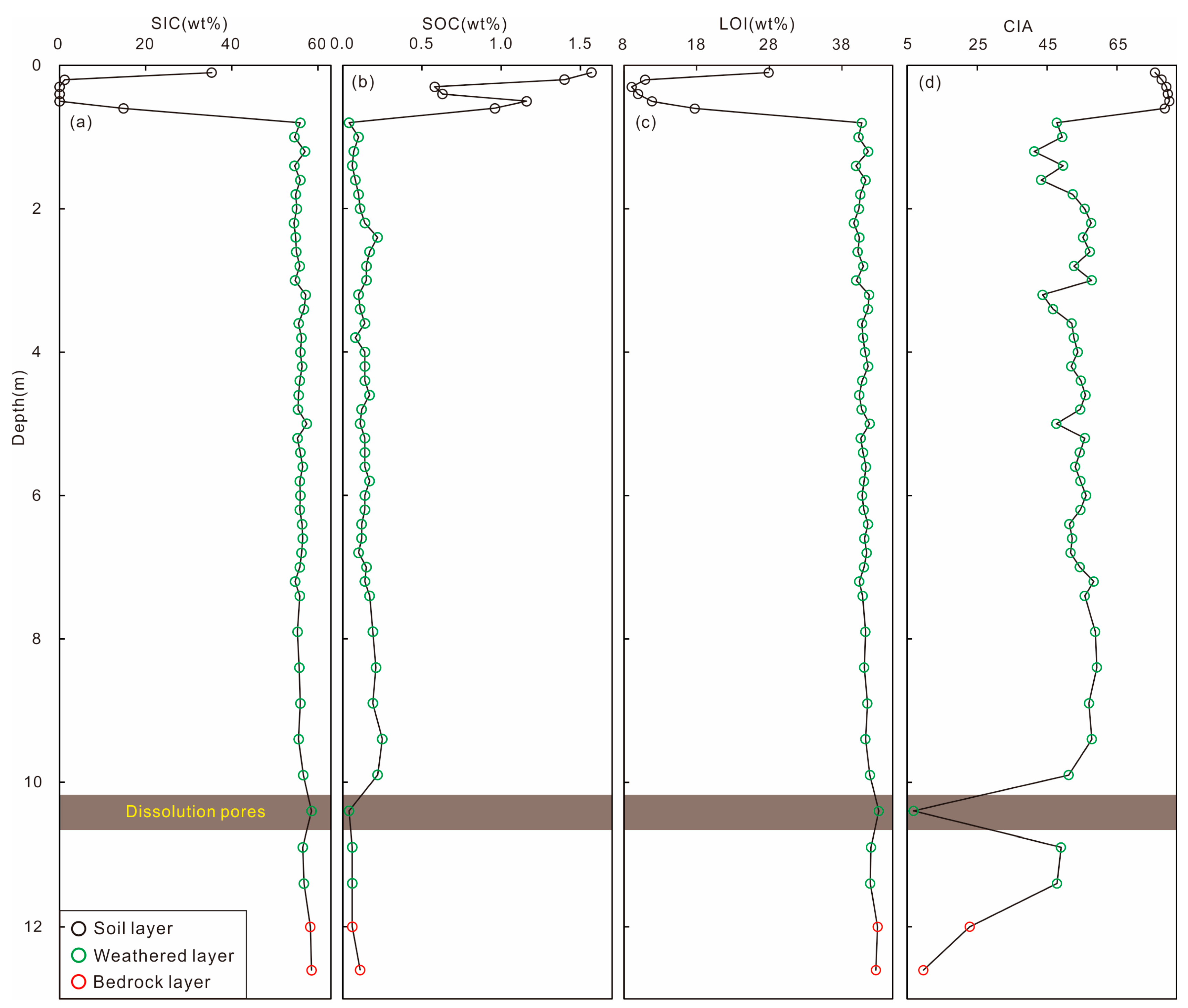
4.3. Whole-Rock Carbon and Weathering Indicators in Weathering Profile
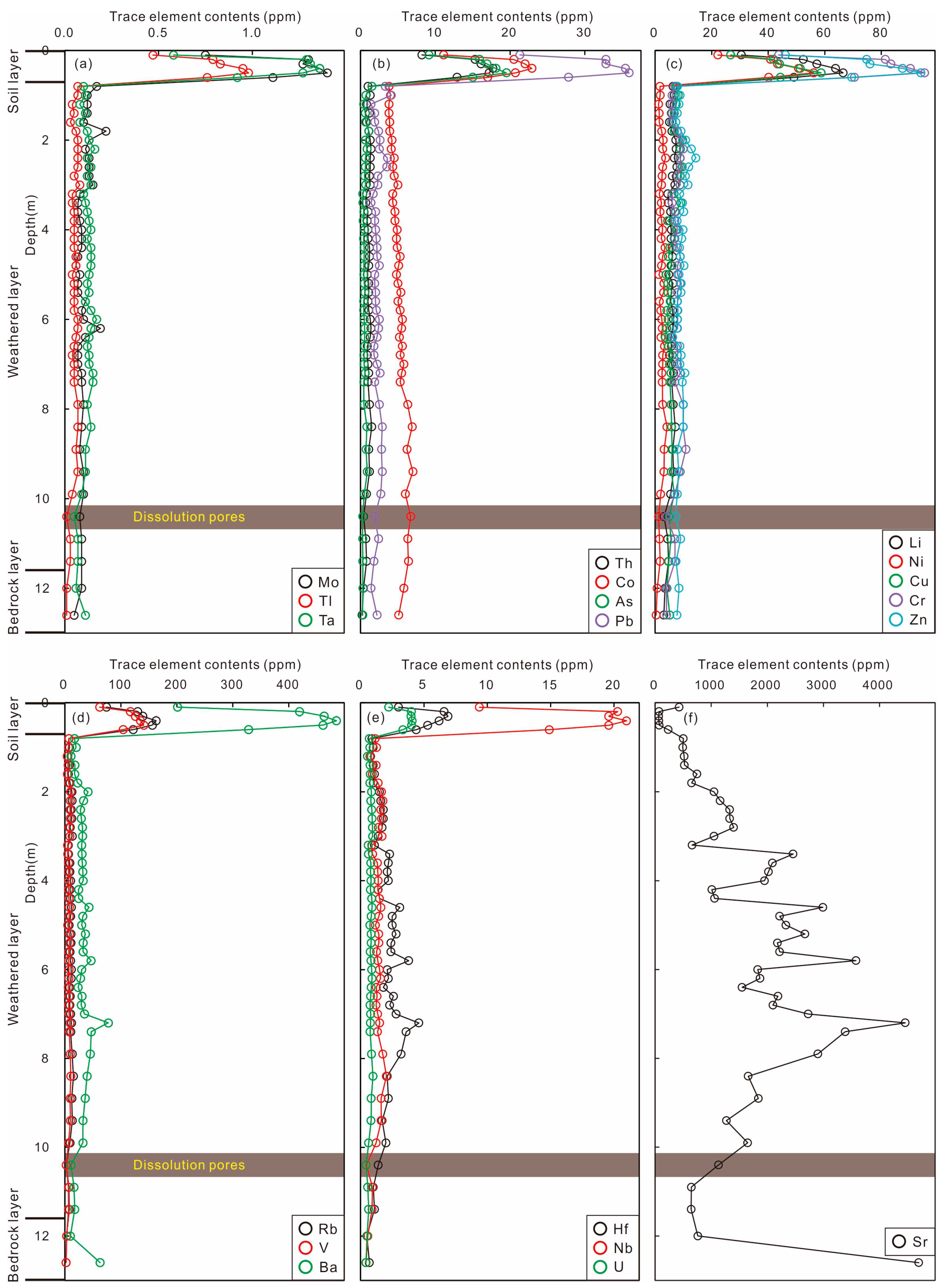
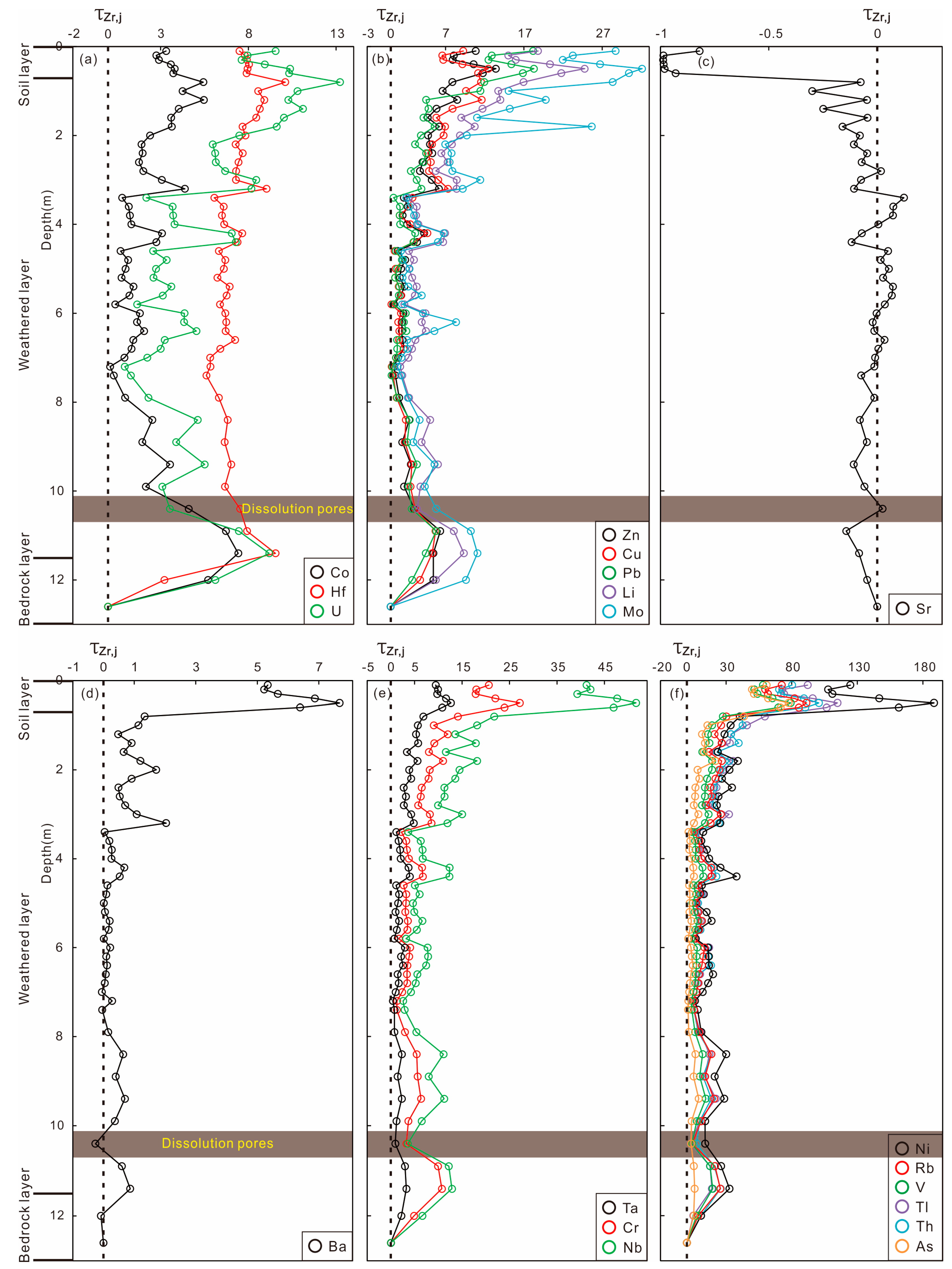
4.4. Whole-Rock Trace Elements in Weathering Profile
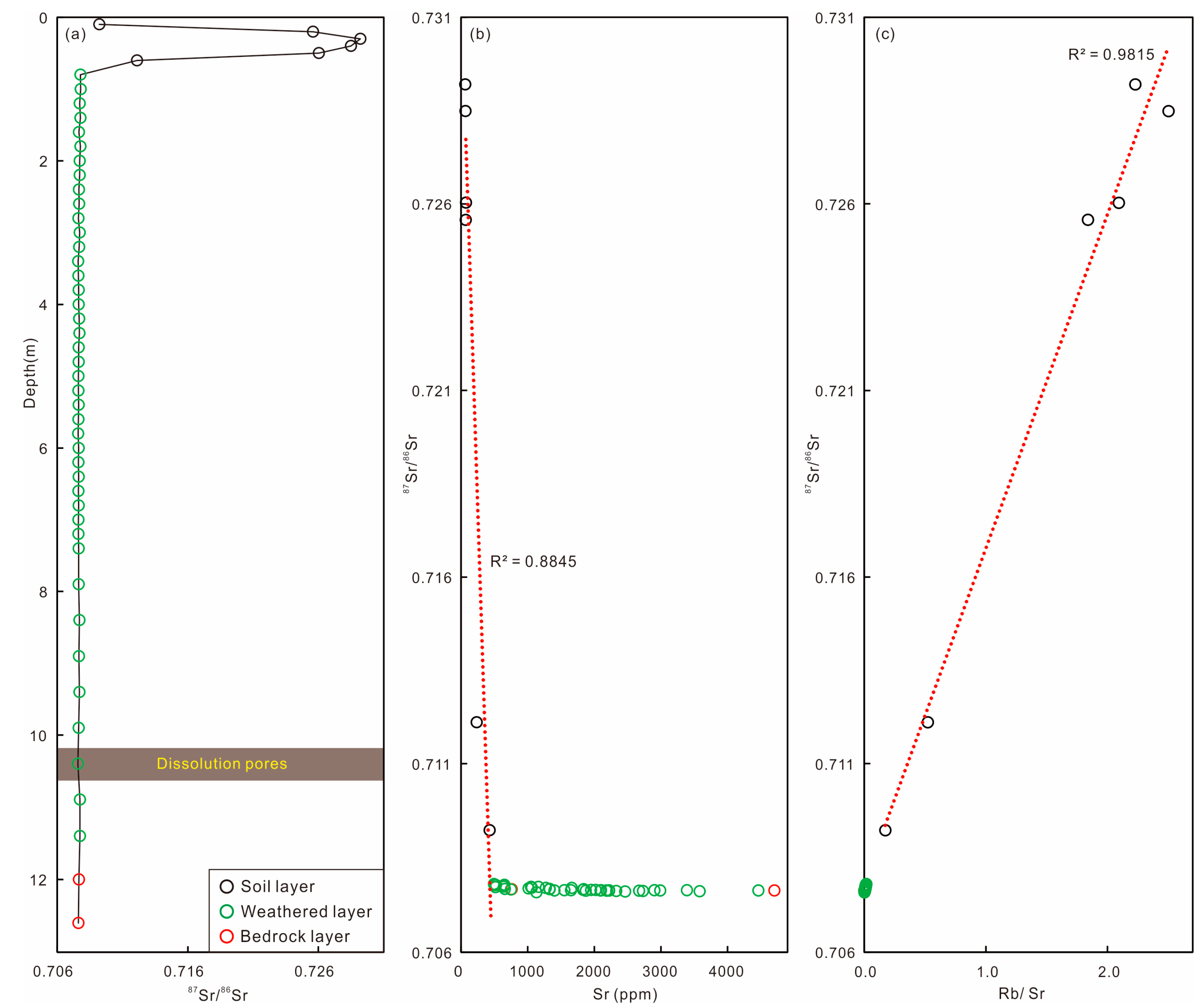
4.5. Whole-Rock Sr Isotopes in Weathering Profile
5. Discussion
5.1. Chemical Weathering Intensity and Trends
5.2. Elemental Mobilization and Redistribution
5.3. Pedogenesis Model of Weathering Shimen Limestone
5.4. Implications for Weathering Geochemistry in Carbonate Systems
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brantley, S.L.; Goldhaber, M.B.; Ragnarsdottir, K.V. Crossing disciplines and scales to understand the critical zone. Elements 2007, 3, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneville, S.; Morgan, D.J.; Schmalenberger, A.; Bray, A.; Brown, A.; Banwart, S.A.; Benning, L.G. Tree-mycorrhiza symbiosis accelerate mineral weathering: Evidences from nanometer-scale elemental fluxes at the hypha–mineral interface. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 6988–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigira, M.; Oyama, T. Mechanism and effect of chemical weathering of sedimentary rocks. Eng. Geol. 2000, 55, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frings, P.J.; Buss, H.L. The Central Role of Weathering in the Geosciences. Elements 2019, 15, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algeo, T.J.; Hong, H.L.; Wang, C.W. The chemical index of alteration (CIA) and interpretation of ACNK diagrams. Chem. Geol. 2025, 671, 122474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Li, X.S.; Han, Z.Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Yang, D.Y. Chemical weathering intensity and element migration features of the Xiashu loess profile in Zhenjiang, Jiangsu Province. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.F.; Bullen, T.D.; Schulz, M.S.; Blum, A.E.; Huntington, T.G.; Peters, N.E. Differential rates of feldspar weathering in granitic regoliths. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 847–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H.G. Residual clay deposits on basement rocks: The impact of climate and the geological setting on supergene argillitization in the Bohemian Massif (Central Europe) and across the globe. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 165, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Wang, Z.B.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.X.; Cai, J.G. Heavy mineral compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze River) sediments and their provenance-tracing implication. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 35, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, N.; Jiang, S.; Ali, S.H.; Naz, A.F.; Tariq, M. Effect of Diagenetic Processes and Depositional Facies on Reservoir Quality of the Eocene Carbonate Sequence (Sakesar Limestone) in the Central Salt Range, Pakistan. J. Earth Sci. 2025, 36, 1129–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Wan, D.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F. Silicon isotope compositions of dissolved silicon and suspended matter in the Yangtze River, China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.W.; Jian, X.; Zhang, W.; Fu, H.J.; Zhang, S. Behavioral differences between weathering and pedogenesis in a subtropical humid granitic terrain: Implications for chemical weathering intensity evaluation. Catena 2021, 203, 105368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Ji, H.B.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zhou, D.Q.; Zhen, L.P.; Li, T.Y. Preliminary study on weathering and pedogenesis of carbonate rocks. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 1999, 42, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, A.; Martínez, E.; Pettinari, G.; Herrero, S. Weathering profiles in granites, Sierra Norte (Córdoba, Argentina). J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2005, 19, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Xu, Z.F.; Liang, C.S.; Li, L.B.; Feng, J.Y. Elemental and strontium isotopic geochemistry of the soil profiles developed on limestone and sandstone in karstic terrain on Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China: Implications for chemical weathering and parent materials. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 67–68, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabski, M.; Badura, I.; Kycko, M.; Grabarczyk, A.; Matlakowska, R.; Otto, J.C. The Development of Limestone Weathering Rind in a Proglacial Environment of the Hallstätter Glacier. Minerals 2023, 13, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graustein, W.C. 87Sr/86Sr ratios measure the sources and flow of strontium in terrestrial ecosystems. Stable Isot. Ecol. Res. 1989, 68, 491–512. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, S.X.; Wu, X.Y.; Sun, C.W.; Liao, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.N. Mineralogy and geochemistry of three weathered Lower Cambrian black shale profiles in Northeast Chongqing, China. Geosci. J. 2016, 20, 793–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Ling, S.X.; Wu, X.Y.; Li, X.N.; Liao, X. Investigations on mineralogy and geochemistry of a black shale profile on the northern Yangtze platform, China: Weathering fate of rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) and its implications. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 126, 104897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Zhou, J.C.; Qiu, J.S.; Zhang, W.L.; Liu, X.M.; Zhang, G.L. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Neoproterozoic igneous rocks from Northern Guangxi, South China: Implications for tectonic evolution. Precambrian Res. 2006, 145, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, S.Y.; Chen, L.M.; Zhou, S.H.; Kang, J. Textural and compositional zoning in plagioclase phenocrysts: Implications for magma chamber processes in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province, SW China. Acta Geochim. 2023, 42, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Gao, R.; Su, J.B.; Liu, M.; Li, J.H. A possible buried Paleoproterozoic collisional orogen beneath central South China: Evidence from seismic-reflection profiling. Precambrian Res. 2015, 264, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; He, D.F. Deep Duplex Thrust in the Sangzhi-Shimen Tectonic Belt, in the West Hunan and Hubei Areas. J. Earth Sci. 2020, 31, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Guan, C.G.; Zhou, C.M.; Xiao, S.H. Acanthomorphic acritarchs of the Doushantuo Formation from an upper slope section in northwestern Hunan Province, South China, with implications for early–middle Ediacaran biostratigraphy. Precambrian Res. 2017, 298, 512–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, X.L. Diagenesis and Porosity of the Cambrian-Ordovician Carbonate Shoal Facies at Yangjiaping, Shimen, Hunan. Acta Geol. Sin. 2000, 74, 29–45. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Fang, J.; Xu, W.; Shi, P.J. Analysis of dry/wet conditions using the standardized precipitation index and its potential usefulness for drought/flood monitoring in Hunan Province, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Liu, J.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A. Seasonal variations in arsenic mobility and bacterial diversity: The case study of Huangshui Creek, Shimen Realgar Mine, Hunan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 142353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, C.R.; Snyder, R.L. RIR-Measurement and Use in Quantitative XRD. Powder Diffr. 1988, 3, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Mungall, J.E.; Georgatou, A.A.; Wang, H.; Dong, Y.H.; Shi, G.Y.; Chen, L.; Chu, F.Y.; Li, X.H. Magmatic sulfide oxidation drives crustal PGE mobilization: Implications for hydrothermal PGE mineralization. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2024, 378, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Huang, X.L.; Xu, Y.G.; He, P.L. Magmatic Processes Associated with Oceanic Crustal Accretion at Slow-spreading Ridges: Evidence from Plagioclase in Mid-ocean Ridge Basalts from the South China Sea. J. Petrol. 2019, 60, 1135–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.M.; Wang, X.T.; Yang, S.X.; Guo, Y.Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Xi, M. Divergent response of blue carbon components to wetland types and hydrological effects in typical estuarine wetlands of Jiaozhou Bay, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, J.; Gregoire, D.C. Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Talanta 2000, 51, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Qi, L.; Fan, H.F.; Yin, R.S. An optimized protocol for high precision measurement of 87Sr/86Sr using a Neptune Plus multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer: Evaluation of different cone combinations for Sr isotope determination. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 4089–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautz, C.Q.; Martin, C.E. Chemical and physical weathering in New Zealand’s Southern Alps monitored by bedload sediment major element composition. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 1715–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.Z.; Jia, W.L.; Li, J.; Yin, L.; Wang, S.S.; Wu, J.X.; Song, J.Z.; Peng, P.A. Geochemistry and molybdenum isotopes of the basal Datangpo Formation: Implications for ocean-redox conditions and organic matter accumulation during the Cryogenian interglaciation. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 563, 110169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W. Mobility and fractionation of rare earth elements during weathering of a granodiorite. Nature 1979, 279, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.R.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Cui, L.F.; Liu, C.Q. The influence of climate and topography on chemical weathering of granitic regoliths in the monsoon region of China. Acta Geochim. 2018, 37, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 1982, 299, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnois, L. The CIW index: A new chemical index of weathering. Sediment. Geol. 1988, 55, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.V.M.W.; Sousa, J.E.S.; Santos, J.C.B.; Filho, J.C.A.; Corrêa, M.M.; Sousa, M.G.; Fracetto, F.J.C.; Fracetto, G.G.M.; Araujo, J.K.S.; Freire, G.A.P.; et al. Weathering of gneiss saprolites and formation of Planosols under semiarid climate (NE Brazil). J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2023, 123, 104206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.; Lowe, D.R.; Cullers, R.L. The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 2919–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M. Weathering and Global Denudation. J. Geol. 1993, 101, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, S.L.; White, A.F. Approaches to Modeling Weathered Regolith. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2009, 70, 435–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazilevskaya, E.; Lebedeva, M.; Pavich, M.; Rother, G.; Parkinson, D.Y.; Cole, D.; Brantley, S.L. Where fast weathering creates thin regolith and slow weathering creates thick regolith. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bétard, F.; Caner, L.; Gunnell, Y.; Bourgeon, G. Illite neoformation in plagioclase during weathering: Evidence from semi-arid Northeast Brazil. Geoderma 2009, 152, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J.; Weijden, C.H.V.D.; Woittiez, J.R.W. Chemical processes affecting the mobility of major, minor and trace elements during weathering of granitic rocks. Chem. Geol. 1988, 68, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derry, L.A.; Chadwick, O.A. Contributions from Earth’s Atmosphere to Soil. Elements 2007, 3, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Li, G.J.; Rao, W.B.; Ji, J.F. Isotopic evidences for provenance of east Asian dust. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4424–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.B. Carbonate minerals in the global carbon cycle. Chem. Geol. 2017, 449, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.T.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Vicca, S.; Goll, D.S.; Li, G.C.; Lin, L.X.; Chen, H.; Bi, B.Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, C.L.; et al. Enhanced silicate weathering accelerates forest carbon sequestration by stimulating the soil mineral carbon pump. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, T.; White, A.; Blum, A.; Harden, J.; Schulz, M. Chemical weathering of a soil chronosequence on granitoid alluvium: II. Mineralogic and isotopic constraints on the behavior of strontium. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Xu, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.J.; Yin, M.H.; Zhu, W.B.; Guo, S.W.; Huang, X.K.; Kan, L.; Wu, G.B.; Luo, Y.; et al. Relationship between the genesis of Changlinggang alkaline rocks and uranium mineralization in the 414U-Th deposit, Jianshui County, Yunnan Province, China. Ore Energy Resour. Geol. 2024, 16, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswami, S.; Trivedi, J.R.; Sarin, M.M.; Ramesh, R.; Sharma, K.K. Strontium isotopes and rubidium in the Ganga-Brahmaputra river system: Weathering in the Himalaya, fluxes to the Bay of Bengal and contributions to the evolution of oceanic 87Sr/86Sr. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1992, 109, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, G.L.; Sullivan, P.L. Dust, impure calcite, and phytoliths: Modeled alternative sources of chemical weathering solutes in shallow groundwater. Chem. Geol. 2018, 527, 118871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Ma, J.L.; Wang, Z.B.; Zhang, L.; He, X.Y.; Zhu, G.H.; Zeng, T.; Wei, G.J. Rubidium isotope fractionation during chemical weathering of granite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2021, 313, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.L.; Deng, Y.S.; Duan, X.Q.; Cai, C.F.; Ding, S.W. Variations in weathering characteristics of soil profiles and response of the Atterberg limits in the granite hilly area of South China. Catena 2022, 215, 106325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, Z.M.; Ngwenya, B.T.; Parsons, I. Mobility and fractionation of REEs during deep weathering of geochemically contrasting granites in a tropical setting, Malaysia. Chem. Geol. 2013, 349–350, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Chen, J.T.; Lang, X.G.; Fang, H.; Ning, M.; Ma, H.R.; Hu, L. Carbonate sedimentary geochemistry: Influence of sedimentary processes and benthic flux. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2025, 68, 2094–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Heaney, P.J.; Reis, F.D.A.A.; Brantley, S.L. Deep abiotic weathering of pyrite. Science 2020, 370, eabb8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimhall, G.H.; Lewis, C.J.; Ford, C.; Bratt, J.; Taylor, G.; Warin, O. Quantitative geochemical approach to pedogenesis: Importance of parent material reduction, volumetric expansion, and eolian influx in lateritization. Geoderma 1991, 51, 51–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, K.; Pustovoytov, K.; Kuzyakov, Y. Pedogenic carbonates: Forms and formation processes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 157, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Anton, A.; Raven, J.A.; Beaumont, N.; Connolly, R.M.; Friess, D.A.; Kelleway, J.J.; Kennedy, H.; Kuwae, T.; Lavery, P.S. The future of Blue Carbon science. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, Z.W.; Wu, B.J.; Wang, W.H. Effects of Zn2+ on Limestone Weathering and Carbon Sink in the Chaotian River Basin, Guilin, China. Land 2024, 13, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, K.Y.; Zhu, X.Q.; Tang, H.S.; Du, S.J.; Gu, J. Geology and geochemistry of the Xiaoshanba bauxite deposit, Central Guizhou Province, SW China: Implications for the behavior of trace and rare earth elements. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 190, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damu, D.N.A.; Lee, A.G.J.; Chai, S.Y.W.; Ngu, L.H. Accelerated weathering of construction-grade limestone for CO2 absorption. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2024, 14, 1049–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuyns, V.; Claes, H.; Geris, P.; Maquil, R.; Swennen, R. Mineralogical and geochemical characterization of Mo-rich black shales in the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 206, 106351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, R.; Jin, L.; Prush, V.; Paul, J.; Ebersole, C.; Fornadel, A.; Williams, J.Z.; Brantley, S. Cu isotopes and concentrations during weathering of black shale of the Marcellus Formation, Huntingdon County, Pennsylvania (USA). Chem. Geol. 2012, 304–305, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidzang, F.N.; Sababa, E.; Teutsong, T. Niobium–tantalum oxide minerals in alluvial placer deposits from the Ngoura area, East-Cameroon. Acta Geochim. 2021, 40, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, I.A.; Stepanov, A.S.; Jiang, S.Y.; Zhimulev, F.I.; Gurevich, D.V.; Polonyankin, A.A.; Lavrenchuk, A.V.; Kotlyarov, A. Platinum-group elements geochemistry of chromite from Kondyor ultramafic intrusion, Siberia: Re-evaluation of factors controlling PGE content of intrusive chromite. Chem. Geol. 2025, 691, 122871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Song, Z.L.; Tu, X.L.; Xiao, M.L.; Wu, F.C.; Lv, H.Z. Release of heavy metals during weathering of the Lower Cambrian Black Shales in western Hunan, China. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L. Trace elements in ferromanganese concretions, gibbsite spots, and the surrounding terra rossa overlying dolomite: Their mobilization, redistribution and fractionation. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 108, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Hong, H.L.; Ji, K.P.; Li, F.; Wang, X.H. New insight into biotite weathering in the subtropic Tongcheng granite regolith, Hubei Province, South China. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 224, 106518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.N.; Chi, Y.P.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Sun, L.; Wu, P.; Wei, Z.Y. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Granite Weathering Profile: A Case Study of a High Latitude Area in Northeastern China. Minerals 2024, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shen, Q.H.; Sun, X.M. Isotopic and Geochemical Signatures of Dolostones and Their Implications for Carbonate Incipient Weathering Processes in the Datangpo Region, Guizhou, China. Minerals 2025, 15, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, O.; Siegesmund, S.; Licha, T.; Török, Á. Geochemical and mineralogical composition of black weathering crusts on limestones from seven different European countries. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuyse, A.; Breemen, N.V. Quantitative aspects of weathering and neoformation in selected Costa Rican volcanic soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, G.L.; Roberts, J.A.; Blair, J.M.; Townsend, M.A.; Fowle, D.A.; Beisner, K.R. Increasing shallow groundwater CO2 and limestone weathering, Konza Prairie, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 5581–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engon, T.C.; Abane, M.A.A.; Zame, P.Z.; Ekomane, E.; Bekoa, E.; Mvogo, K.; Bitom, D. Morphological, physico-chemical and geochemical characterization of two weathering profiles developed on limestone from the Mintom Formation in the tropical humid zone of Cameroon. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 131, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Luo, J.; Liao, F.; Xu, X.; Li, A.; Chen, L.; Zhao, T.; Long, T.; Li, S.; Li, H. Mineralogical and Geochemical Evolution During Limestone Weathering and Pedogenesis in Shimen, Hunan Province, South China. Minerals 2025, 15, 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111109
Chen Q, Luo J, Liao F, Xu X, Li A, Chen L, Zhao T, Long T, Li S, Li H. Mineralogical and Geochemical Evolution During Limestone Weathering and Pedogenesis in Shimen, Hunan Province, South China. Minerals. 2025; 15(11):1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111109
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qi, Jianlan Luo, Fengchu Liao, Xuesheng Xu, Aili Li, Liran Chen, Tuo Zhao, Tingmao Long, Suxin Li, and Huan Li. 2025. "Mineralogical and Geochemical Evolution During Limestone Weathering and Pedogenesis in Shimen, Hunan Province, South China" Minerals 15, no. 11: 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111109
APA StyleChen, Q., Luo, J., Liao, F., Xu, X., Li, A., Chen, L., Zhao, T., Long, T., Li, S., & Li, H. (2025). Mineralogical and Geochemical Evolution During Limestone Weathering and Pedogenesis in Shimen, Hunan Province, South China. Minerals, 15(11), 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111109






