Genetic Model of the Luhai Sandstone-Type Uranium Deposit in the Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia
Abstract
1. Introduction
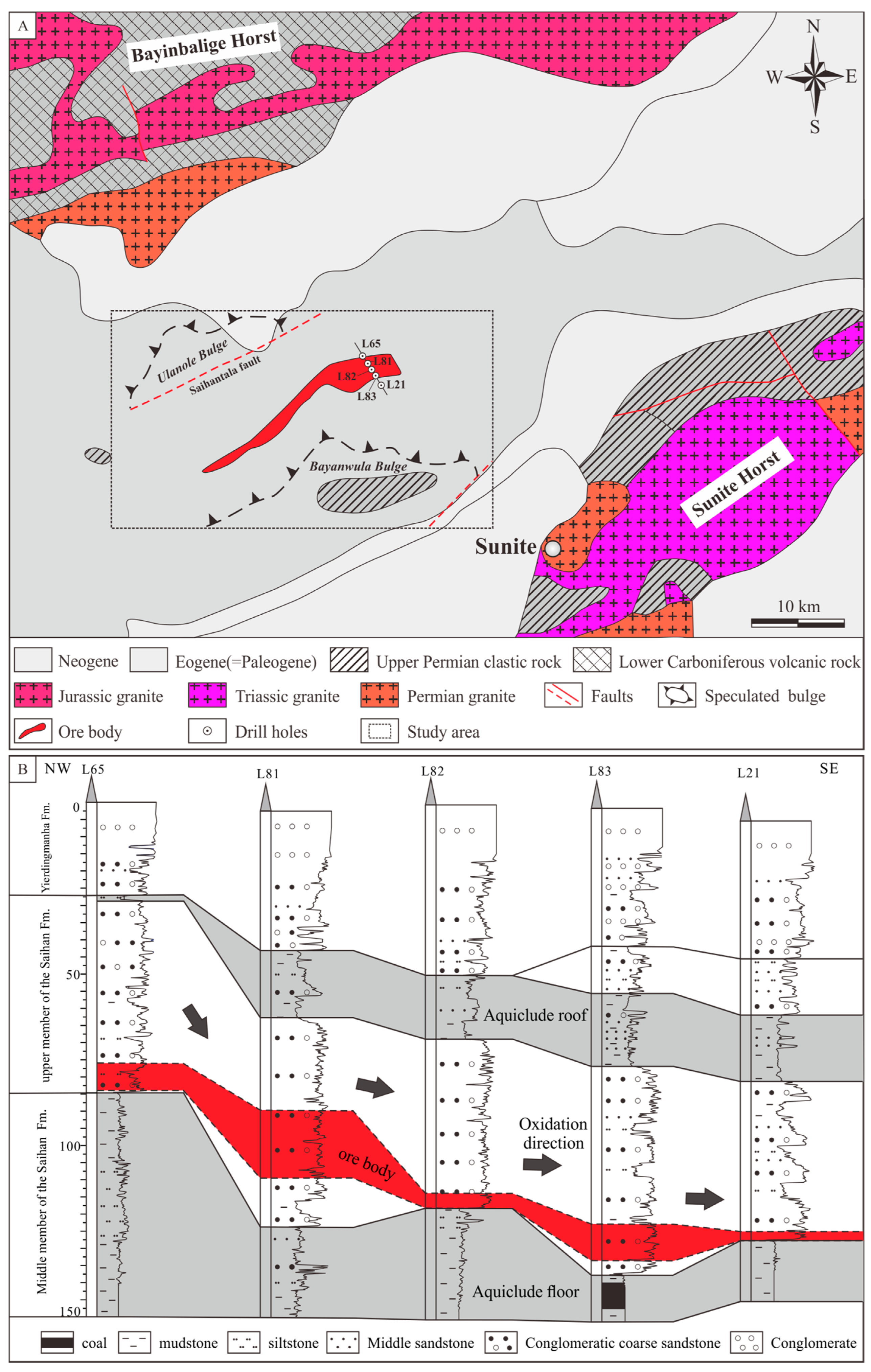
2. Geology Setting
2.1. Erlian Basin
2.2. Luhai Deposit
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Characteristics of Host Rocks and Uranium Ore
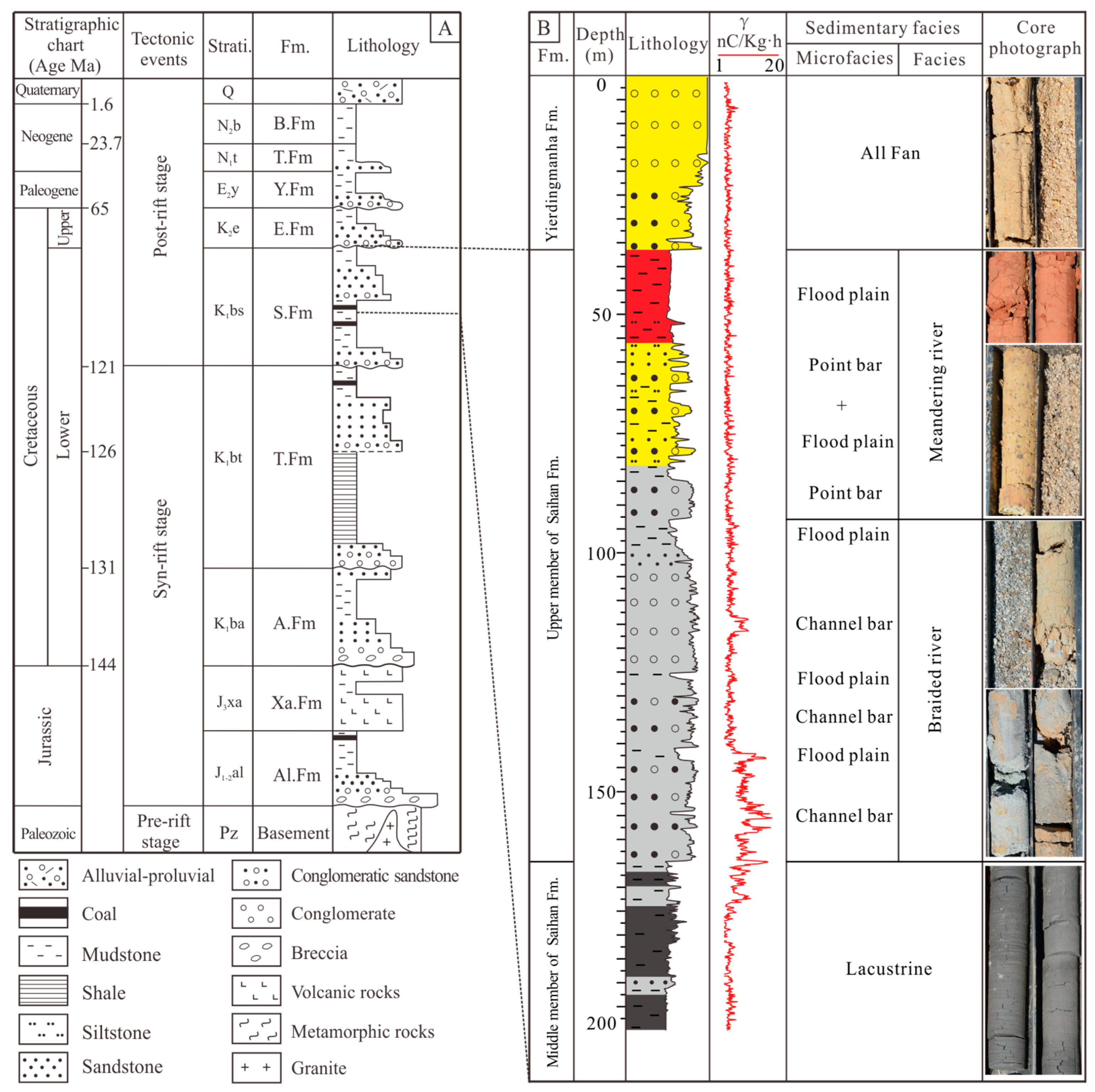
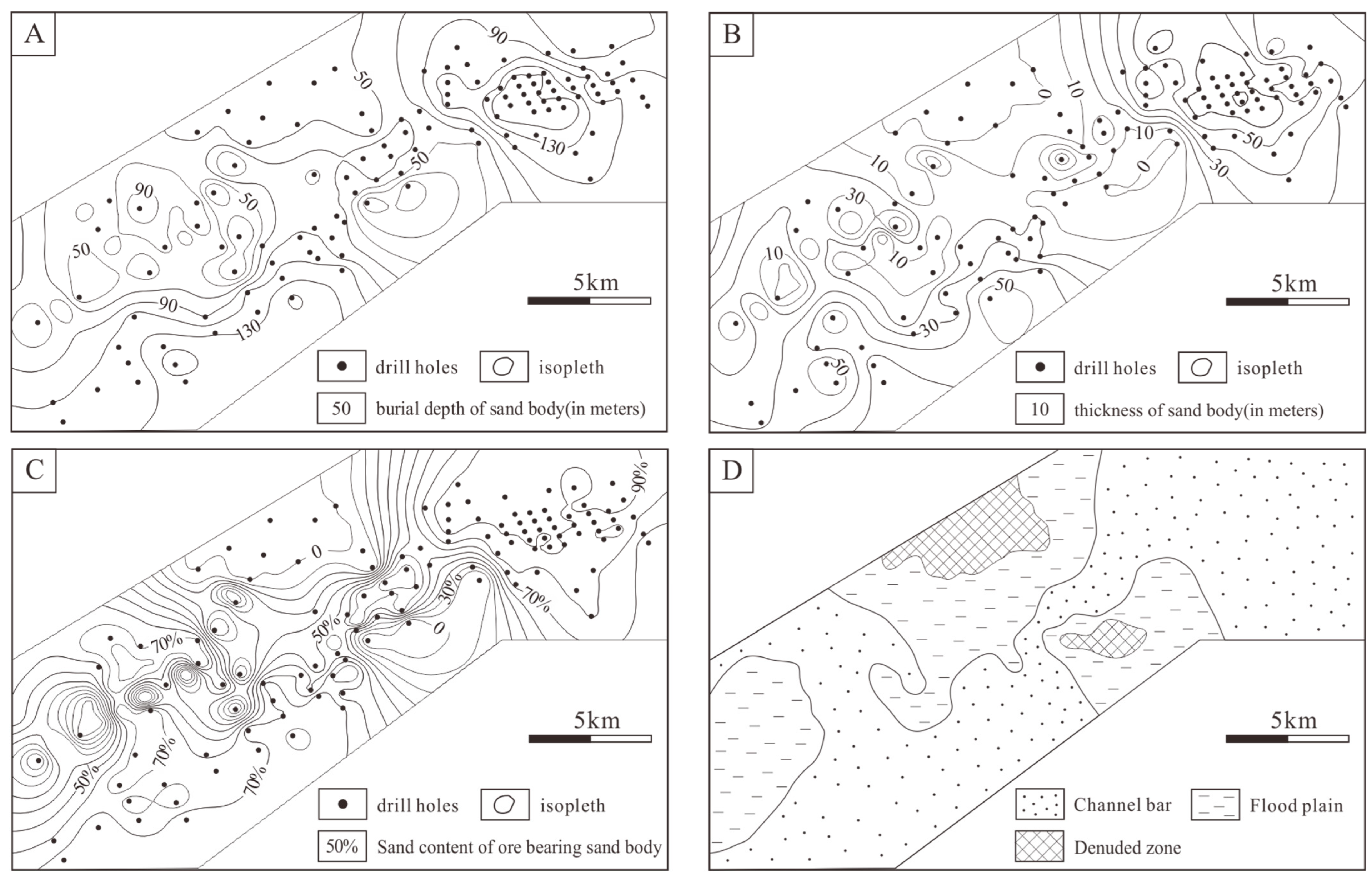
4.1.1. Sedimentary Features of the Saihan Formation
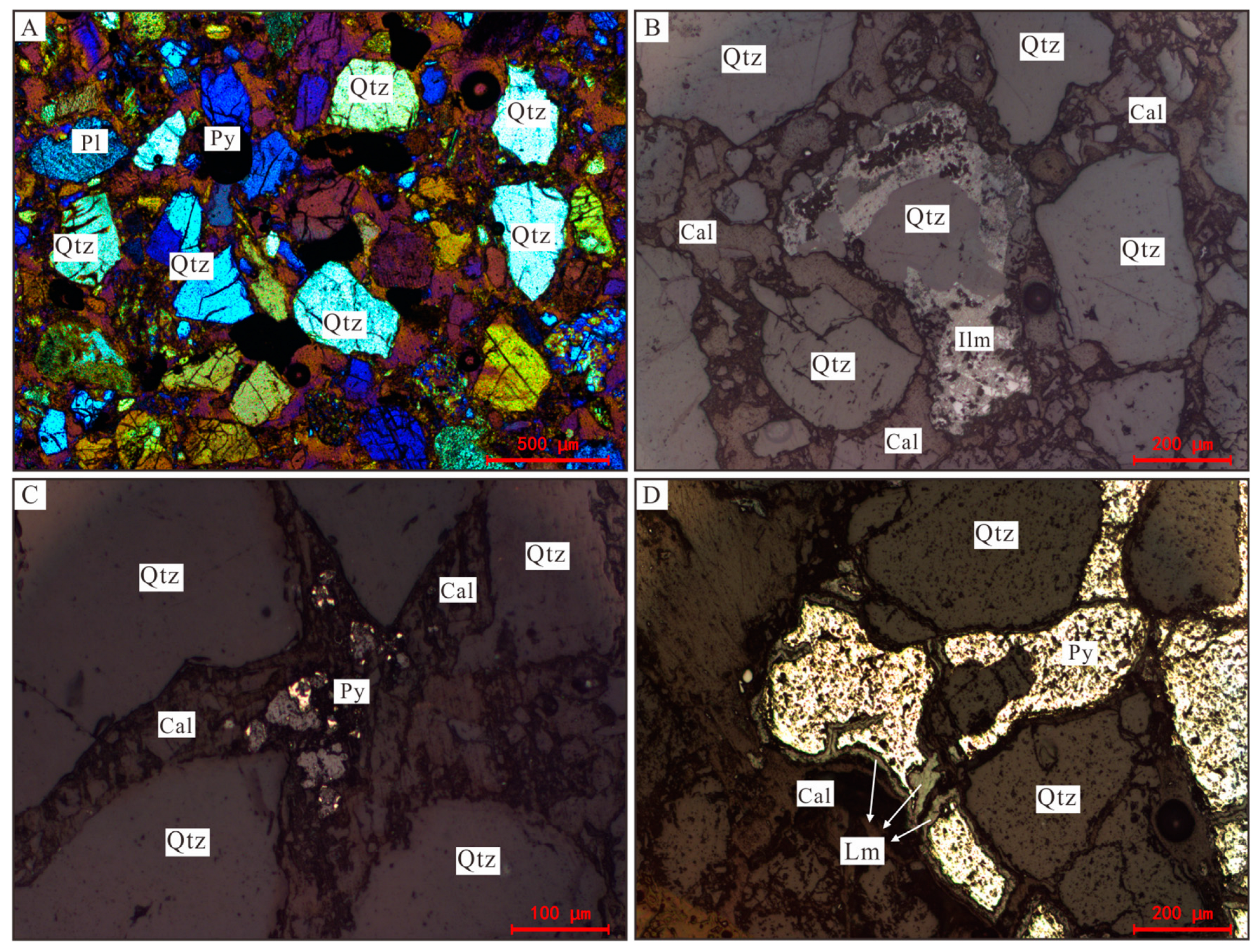
4.1.2. Petrological Characteristics of the Saihan Formation
4.1.3. Mineralogical and Geochemical in Different Color Facies
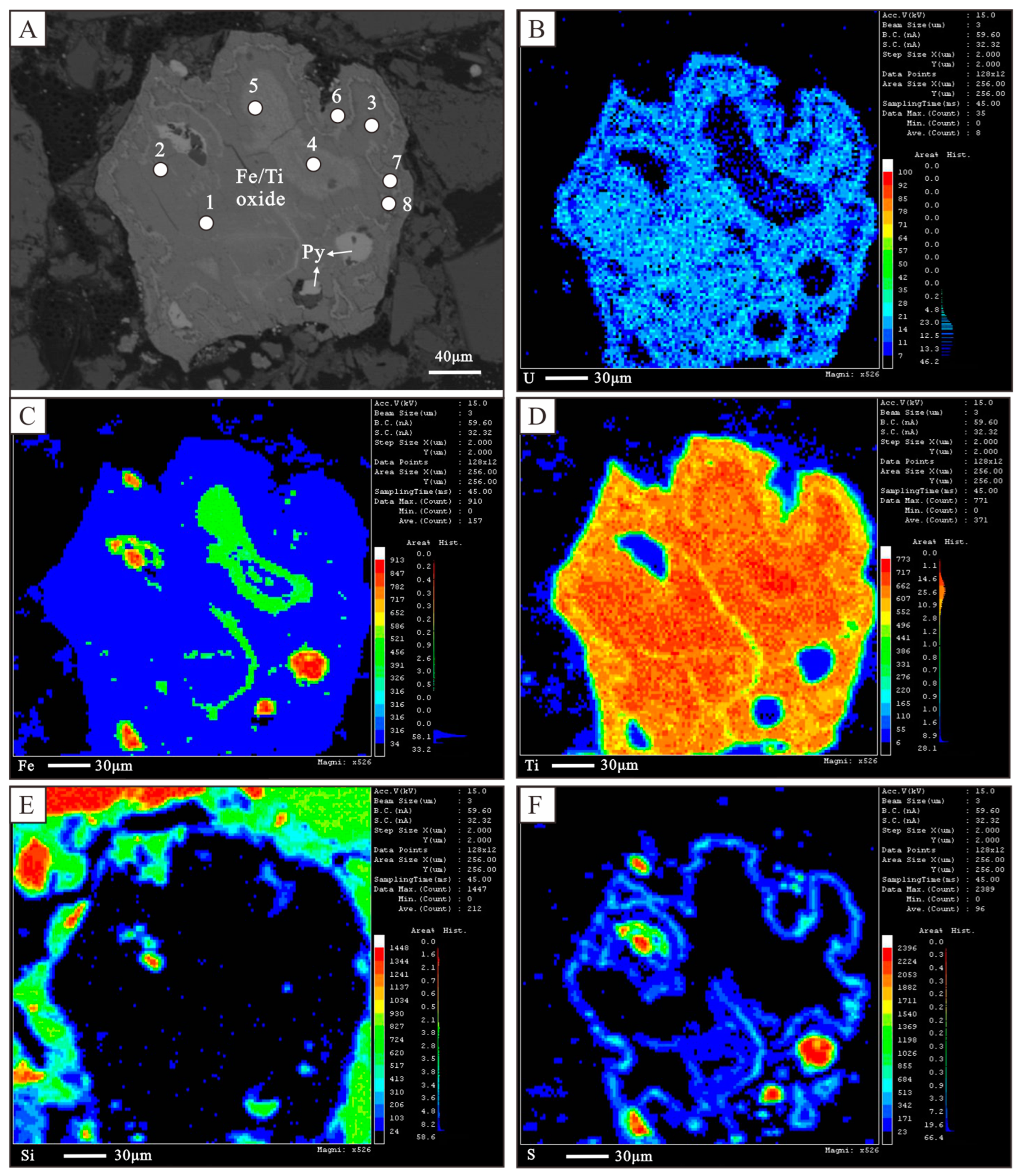
4.2. Occurrence Forms of Uranium
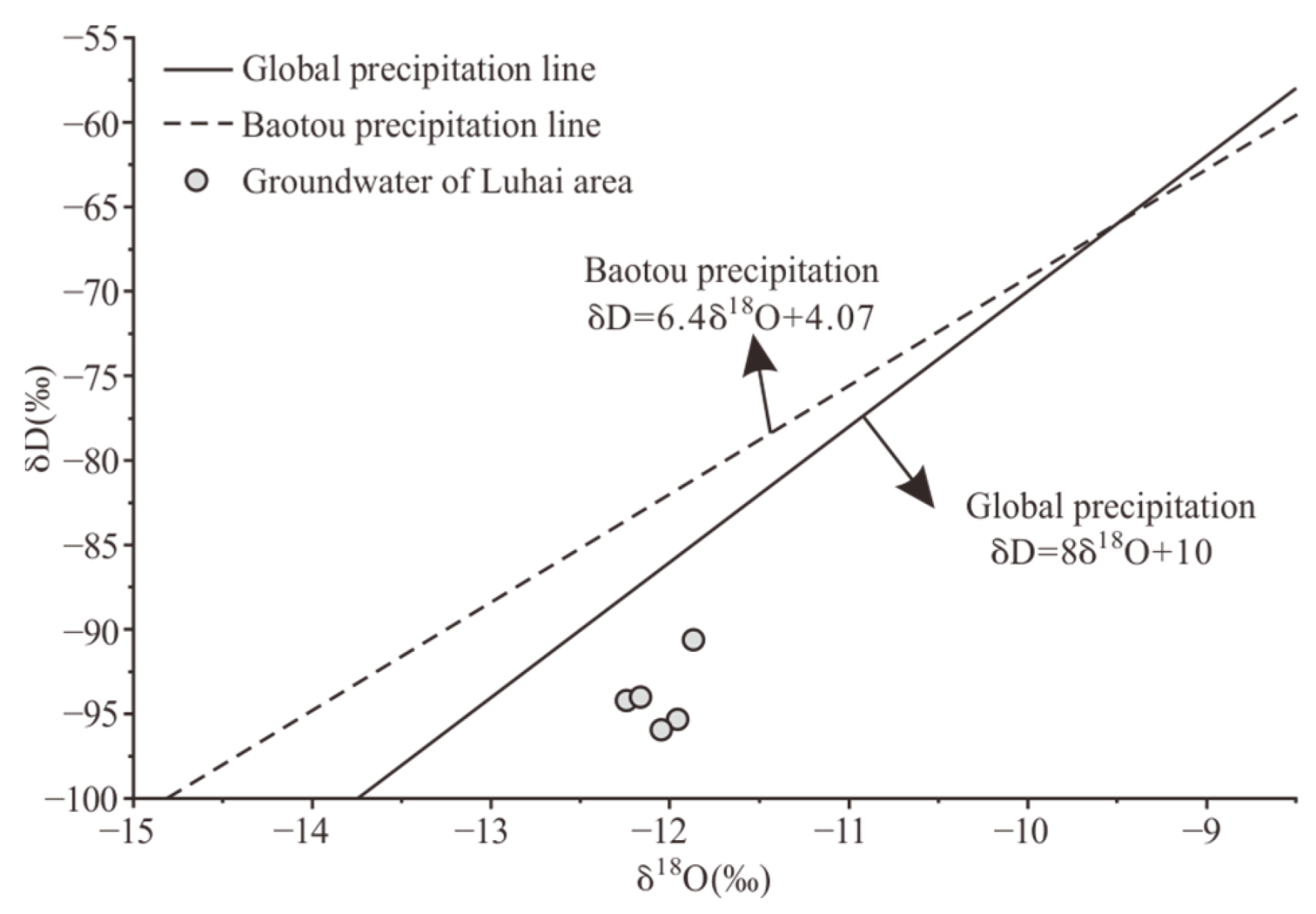
4.3. Characteristics of Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes in Groundwater
4.4. Characteristics of Carbon and Oxygen Isotopes of Carbonate Cements
4.5. Geochemical Characteristics of Hydrocarbon Gases
5. Discussion
5.1. Sedimentary Facies of the Saihan Formation
5.2. Oxidizing Fluids
5.2.1. Source of Ore-Forming Fluids
5.2.2. Migration of Oxidizing Fluids
5.2.3. Role of the Mudstone Partition
5.3. Reducing Agents
5.4. Uranium Mineralization
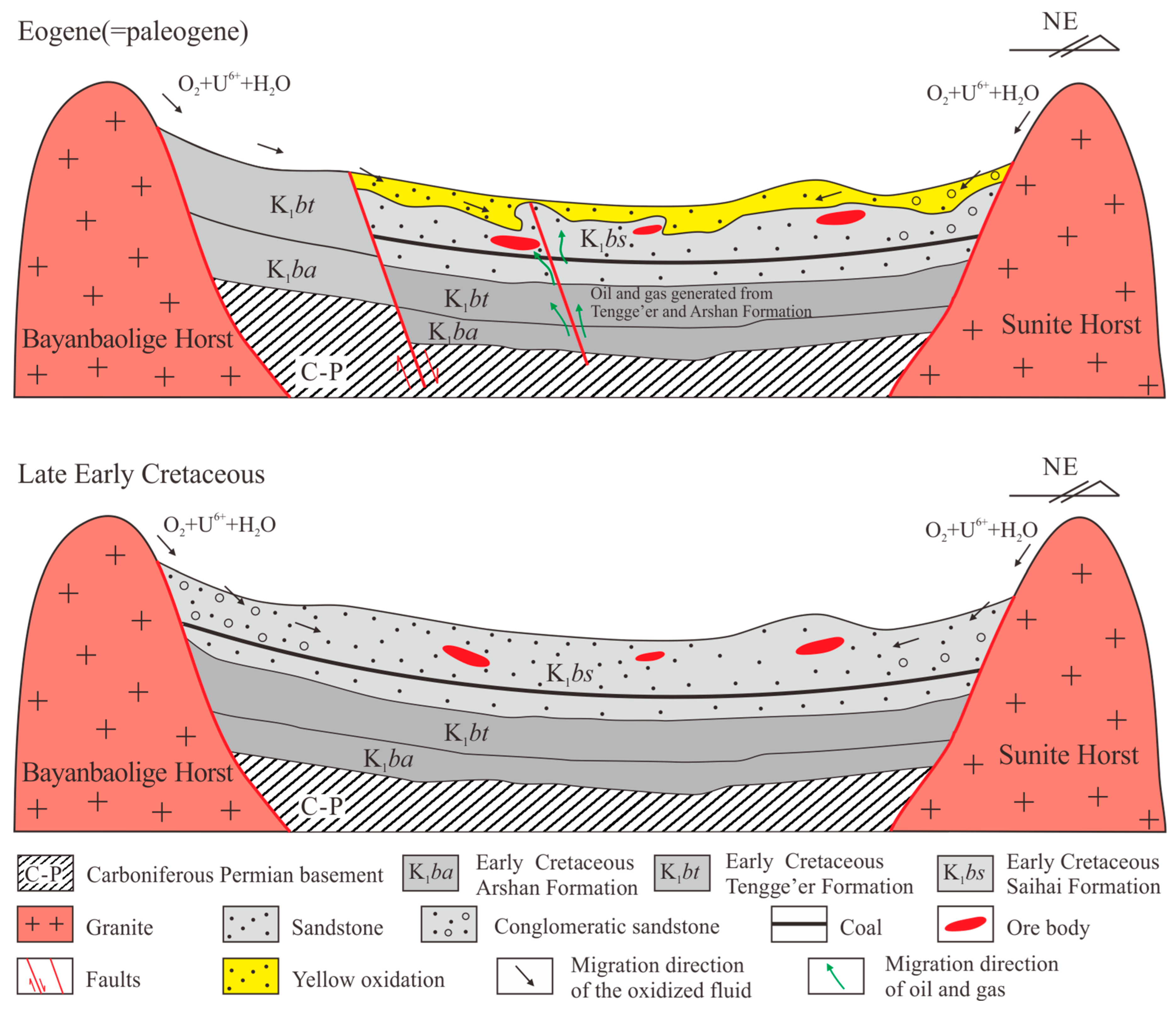
5.5. Uranium Ore Genetic Model
- During the sedimentation period of the upper member of the Saihan Formation, the sedimentary system in the Luhai area transformed into a terrestrial fluvial facies, forming a typical river valley landform. The horst areas on both sides of the basin provided abundant provenance and uranium sources [23,32,48]. The uranium-rich parent rocks were weathered and eroded, and then transported and deposited in the thick and stable sand bodies in the ancient river channels. During the early burial–diagenesis stage, the rock fragments were altered, and uranium was pre-enriched in iron–titanium oxides.
- From the late Early Cretaceous to the early Paleogene, a long-term sedimentary hiatus formed in the Luhai area [25]. The differential uplift structure lifted the top strata of the Saihan Formation to the surface or near-surface [19], enabling the oxidation of supergene fluids to reach them. Surface water, carrying a large amount of uranium, infiltrated vertically along the sandstone. After entering the permeable sandy conglomerate layer in the upper member of the Saihan Formation, it migrated laterally and underwent large-scale inter-layer oxidation. Uranium was enriched under the reduction of organic matter in the underlying dark mudstone of the sandstone. With the continuous effect of compressional tectonics, the Saihantala Fault on the north side of the Luhai area became more active. Deep brine and oil and gas began to migrate upward to the shallow part of the basin along the fault and mixed with the oxygen-and uranium-containing fluids from the surface, resulting in the superimposed enrichment of uranium.
6. Conclusions
- The braided channel sandstone in the upper member of the Saihan Formation provides favorable permeable ore-hosting rocks for the formation of sandstone-type uranium mineralization. The distribution of uranium ore bodies is controlled by channel lag deposits, while the floodplain deposits, which are interbedded with the ore-hosting sandstone, act as reducing traps.
- The metallogenesis of the Luhai sandstone-type uranium deposit is characterized by superimposed polygenetic oxidation–reduction mineralization. Oxygen- and uranium-containing groundwater migrated laterally to the deep along the edges of paleochannel and erosion windows and reacted or mixed with reducing substances in the strata, such as oil and gas, leading to the unloading of ore-forming elements and the formation of uranium ore bodies.
- A genetic model related to the uranium metallogenesis in the paleochannel of the Luhai area has been established. Stable fluvial facies sedimentation in the context of a depression-type basin has formed favorable uranium reservoirs. The tectonic inversion in the late sedimentation stage was conducive to the redox reaction between surface water and deep reducing substances (fluids) and the formation of ore through fluid mixing. This model plays an important guiding role in the search for paleochannel sandstone-type uranium deposits in other areas of the Erlian Basin.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cumberland, S.; Douglas, G.; Grice, K.; Moreau, J. Uranium mobility in organic matter-rich sediments: A review of geologicaland geochemical processes. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 1, 160–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, J.; Guo, H.; Miao, P.; Jin, R.; Tang, C.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G. Uranium occurrence state in the Tarangaole area of the Ordos Basin, China: Implications for enrichment and mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115, 103034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaireth, S.; Mckay, A.; Lambert, I. Association of large sandstone uranium deposits with hydrocarbons. AusGeo News 2008, 89, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, R.S.; Teng, X.M. Large scale sandstone-type uranium mineralization in northern China. North China Geol. 2022, 45, 42–57, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Nuclear Energy Agency and the International Atomic Energy Agency. Uranium 2023: Resources, Production and Demand; IAEA-OECD/NEA: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.Q. Important breakthrough in exploration of in-situ leachable sandstone-type uranium deposit at south margin of Ili Basin. Xinjiang Geol. 2002, 20, 106–109, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, H.M.; Zhang, F.X.; Xu, G.Z.; Shan, G.F.; Qi, Y.L. Hydrogeologic characteristics and metallogenesis of the Shihongtan sandstone-type uranium deposit in Turpan-Hami Basin. Geol. Rev. 2005, 51, 257–263, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.B.; Li, Z.Y.; Fang, X.H.; Xie, Q.L. Metalogenetic characteristics of No.2081 uranium deposit in the north Ordos Basin. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2006, 26, 349–355, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.D.; Xu, G.Z.; Lin, J.R.; Peng, Y.B.; Wang, G. The implication of six kinds of new sands tone-type uranium deposits to uranium resources tential in North China. Geol. China 2010, 37, 1434–1449, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Nie, F.J.; Li, M.G.; Deng, J.Z.; Yan, Z.B.; Zhang, C.Y.; Jiang, M.Z.; Yang, J.X.; Kuang, W.Z.; Kang, S.H.; Shen, K.F. Multiple type uranium deposit assemblage and uranium exploration in Erlian rift Basin, Inner Mongolia. Miner. Depos. 2015, 4, 711–729, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.Q.; Wu, L.Q.; Peng, Y.B.; Rong, H.; Ji, D.M.; Miao, A.S.; Li, H.L. Sedimen-tary-tectonic setting of the deposition-type uranium deposits forming in the Paleo-Asian tectonic domain, North China. Earth Sci. Front. 2015, 34, 189–205, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jin, R.S.; Yu, R.A.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.X.; Teng, X.M.; Wang, S.B.; Si, Q.H.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, T.F. Paleo-environmental constraints on uranium mineralization in the Ordos Basin: Evidence from the color zoning of U-bearing rock series. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 104, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.S.; Jin, R.S.; Li, J.G.; Zhao, H.L.; Chen, L.L.; Chen, Y.; Si, Q.H. The first discovery of a large sandstone-type uranium deposit in aeolian depositional environment. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Liu, W.S.; Li, W.T.; Li, X.D.; Qin, M.K.; Cai, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; He, S.; Wu, Q.B.; Qiu, L.F.; et al. ExudativemetallogenyoftheHadatusandstone-type uranium deposit in the ErlianBasin, Inner Mongolia. Geol. China 2022, 49, 1009–1047, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Ao, C.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Miao, P.; Si, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Yu, R.; Chen, Y. Occurrence and mechanism of uranium enrichment with a unique eolian sedimental environment in the Pengyang uranium deposit, Ordos Basin. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 141, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Qin, M.K.; He, Z.B. Spatiotemporal distribution of uranium, oil and coal, and uranium metallogenic processes in Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia. World Nucl. Geosci. 2009, 26, 25–30, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.S.; Kang, S.H.; Jia, L.C.; Peng, C. Characteristics of paleo-valley sandstone-type uranium mineralizationin the Middle of Erlian Basin. Uranium Geol. 2013, 29, 328–335, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.S.; Kang, S.H.; Zhao, X.Q.; Zhang, Z.N. Mineralization mechanism and exploratio of paleo-channel type uranium deposit in central Erlian basin. Uranium Geol. 2015, 31, 164–175, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.S.; Zhao, X.Q.; Kang, S.H.; Shi, Q.P.; Zhang, Z.N. Inversion structure and its relationshipwith sandstone type uranium metallization in Erlian Basin. Uranium Geol. 2018, 34, 81–89, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bonnetti, C.; Malartre, F.; Huault, V.; Cuney, M.; Bourlange, S.; Liu, X.; Peng, Y. Sedimentology, Stratigraphy and Palynological Occurrences of the Late Cretaceous Erlian Formation, Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia, People’s Republic of China. Creta Ceous Res. 2014, 48, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Yang, J.X.; Liu, W.S.; Zhao, X.Q.; Qiao, P.; Du, P.F.; Lv, Y.H. Mineralization characteristic sandpotential of paleo-valley type uranium deposition central Erlian Basin, InnerMongolia. UraniumGeology 2017, 33, 206–214, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.Z.; Hu, H.; Wu, Z.J.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, M.H. Sedimentary Features of Saihan Formation and Its Controlling on Uranium Mineralization in Zhunshan Area, Manit Depression. Coal Geol. China 2017, 29, 16–22, 35, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.Z.; Wu, Z.J.; Sima, X.Z.; Yu, R.A.; Li, J.G.; Hu, H.; Jiang, Z. Metallogenic model of uranium with source supply from the south and the north in Manite depression of Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia. Coal Geol. Explor. 2018, 46, 1–10, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Han, X.Z.; Hu, H.; Wu, Z.J.; Li, Z.N.; Lai, Q.; Guo, P. Geological Characteristics and Ore-Forming Process of the Engeriy in Large Sandstone-Type Uranium Deposit in the Manite Depression, Erlian Basin. Geotecton. Metallog. 2020, 44, 742–753, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.B.; Li, X.D.; Liu, W.S. Metallogenic Types and Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of Uranium Deposits in Erlian Basin. Uranium Geol. 2021, 37, 1013–1026, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Yang, J.X.; Peng, Y.B.; Kang, S.H.; Qiao, P.; Lu, C.; Zhang, F. Study of Structure and Formation in Uranium-Bearing Paleo-Valley and Typical Metallogenic Models in Eastern Part of Erlian Basin. Miner. Depos. 2017, 36, 126–142, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Peng, Y.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Jiao, Y.Q.; Yang, J.X.; Chen, F.Z.; Sheng, K.F.; Li, R.L. Sedimentary Backgrounds of Sandstone-type Uranium Deposits in Western Manite Depression of Erlian Basin. Uranium Geol. 2013, 29, 336–342, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Nie, F.J.; Li, M.G.; Yan, Z.B.; Xia, F.; Zhang, C.Y.; Yang, J.X.; Kang, S.H.; Shen, K.F. Segmentation of the target layer Saihan Formation and sandstone-type uranium mineralization in Erlian Basin. Geol. Bull. China 2015, 34, 1952–1963, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Peng, Y.B.; Kang, S.H.; Qin, Y.W. Depositional Characteristics and Uranium Metallogenic Fluid Dynam ics of Uranium Bearing Paleovalley of the Saihan Formation in Basaiqi, Erlian Basin. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2018, 37, 316–325, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.A.; Wu, Z.J.; Sima, X.Z.; Han, X.Z.; Li, Z.N.; Wen, S.B.; Tu, J.R. Geochronology and Geological Significance of Sandstone Detrital Zircons from Saihantala Formation in Southern Manite Depression, Erlian Basin. Earth Sci. 2020, 45, 1609–1621, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.X.; Zhao, L.J.; Yu, R.A.; Tang, C. Rock geochemistry characteristics and geological significance of sandstone-type uranium deposits in Luhai area, ErlianBasin. North China Geol. 2024, 47, 36–45, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.J.; Xu, Z.L.; Tang, C.; Jin, R.S.; Duan, M.; Wei, J.L.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, C. Provenance Characteristics of Uranium-Bearing Sediments of Upper Saihan Formation and Its Implications for Sandstone-Type Uranium Mineralization in Manite Depression.Erlian Basin. Earth Sci. 2024, 49, 3589–3609, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Khain, E.V.; Bibikova, E.V.; Kröner, A.; Zhuravlev, D.Z.; Sklyarov, E.V.; Fedotova, A.A. Kravchenko-Berezhnoy I R. The most ancient ophiolite of the Central Asian fold belt: U-Pb and Pb-Pb zircon ages for the Dunzhugur Complex, Eastern Sayan, Siberia, and geodynamic implications. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2002, 199, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Tamaki, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, J. Late Mesozoic and Cenozoic rifting and its dynamic setting in eastern China and adjacent areas. Tectonophysics 2002, 344, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, N.; Augier, R.; Gumiaux, C.; Monié, P.; Chen, Y.; Faure, M.; Zhu, R. Timing, duration and role of magmatism in wide rift systems:Insights from the Jiaodong Peninsula (China, East Asia). Gondwana Res. 2013, 24, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Chang, L. Fault linkage patterns and their control on the formation of the petroleum systems of the Erlian basin, eastern China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2003, 20, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Qin, M.; Li, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, A.; Shen, K. Late Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectono-sedimentary evolution and sandstone-hosted uranium mineralization of the Erlian basin. In Proceedings of the Mineral Deposit Research, Meeting the Global Challenge, 8th Biennial SGA Meeting, Beijing, China, 18–21 August 2005; Chapter 3−27. pp. 320–322. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnetti, C.; Cuney, M.; Michels, R.; Truche, L.; Malartre, F.; Liu, X.D.; Yang, J.X. The Multiple Roles of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Fe-Ti Oxides in the Genesis of the Bayinwula Roll Front-Type Uranium Deposit, Erlian Basin, NE China. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 1059–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Lin, J.Q.; Wilde, S.A.; Sun, D.Y.; Yang, J.H. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 233, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Sun, F.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z.; Zhao, A.; Pang, Q.; Li, G. Discovery of the early Paleozoic post-collisional granites in northern margin of the Erguna massif and its geological significance. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2005, 50, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.F.; Zhou, X.H.; Zhang, L.C.; Wang, F. Geochronological framework of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing’an Range, NE China, and their geodynamic implications. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2010, 39, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.B.; Wilde, S.A.; Zhang, X.Z.; Ren, S.M.; Zheng, C.Q. Early Paleozoic metamorphic rocks of the Erguna block in the Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Evidence for the timing of magmatic and metamorphic events and their tectonic implications. Tectonophysics 2010, 12, 50–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Windley, B.F.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Huang, B.; Han, C.; Yuan, C.; Sun, M.; Chen, H. A tale of amalgamation of three Permo-Triassic collage systems in Central Asia: Oroclines, sutures, and terminal accretion. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 43, 477–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.E.; Sun, M.; Shu, C.T.; Yuan, C.; Jiang, Y.D.; Zhang, L.; Cai, K.D. Evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt along the Siberian margin from Neoproterozoic-Early Paleozoic accretion to Devonian trench retreat and acomparison with Phanerozoic eastern Australia. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 198, 10295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuza, A.V.; Yin, A. Balkatach hypothesis: A new model for the evolution of the Pacific, Tethyan, and Paleo-Asian oceanic domains. Geosphere 2017, 13, 1664–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnetti, C.; Cuney, M.; Malartre, F.; Michels, R.; Liu, X.D.; Peng, Y.B. The Nuheting deposit, Erlian Basin, NE China: Synsedimentary to diagenetic uranium mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 69, 118–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.L. Geochronology of Uranium Mineralization in China; China Atomic Energy Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 1–300. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bonnetti, C.; Cuney, M.; Bourlange, S.; Deloule, E.; Poujol, M.; Liu, X.; Peng, Y.B.; Yang, J.X. Primary uranium sources for sedimentary-hosted uranium deposits in NE China: Insight from basement igneous rocks of the Erlian Basin. Miner. Depos. 2017, 52, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, H.Z.; Kuan, Q.M. High resolution sequence stratigraphic character and sandstone type uranium ore formation: A case from Saihan Formation in Bayinwula area, Erlian basin. World Nucl. Geosci. 2006, 23, 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, F.J.; Chen, A.P.; Hu, Q.; Shen, K.; Qin, M.; Li, M.; Jiang, M. Discussion on the early Cretaceous sandstone-type uranium deposits, Erlian basin, Inner Mongolia. J. Stratigr. 2007, 31, 272–279, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Nie, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W. Discussion on age and paleogeographical environment of ore bearing strata for sandstone-type uranium deposits in Bayanwula area, Erlian basin. Uranium Geol. 2008, 24, 151–154, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, T.P. Present Status and Prospect of Analytical Techniques and Reference Materials for Stable Isotopes. Rock Miner. Anal. 2002, 21, 291–300, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, R.L.; Goldhaber, M.B. Origin of a south Texas roll-type uranium deposit:I. alteration of iron-titanium oxide minerals. Econ. Geol. 1978, 73, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, H.L.; Liu, F.L.; Wei, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.Y. The variations of stable isotopes (δD and δ18O) in the precipitation in Baotou area. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2013, 27, 157–162, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cuney, M.; Mercadier, J.; Bonnetti, C. Classification of sandstone-related uranium deposits. J. Earth Sci. 2022, 33, 236–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cai, C.; Jin, R.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Wei, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, B. Mineralogical and geochemical evidence for biogenic and petroleum-related uranium mineralization in the Qianjiadian deposit, NE China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 101, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, G.H.; Cole, D.R.; Giordano, T.H. Palaeoclimate controls on stable oxygen and carbon isotopes in the caliche of the Abo Formation (Permian), southcentral, New Mexico, USA. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1991, 61, 458–472. [Google Scholar]
- Hoefs, J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Eiler, J.M.; Schiano, P.; Kitchen, N.; Stolper, E.M. Oxygen-isotope evidence for recycled crust in the sources of mid-ocean-ridge basalts. Nature 2000, 403, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, Z. Principles of Stable Isotope Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Chen, J.F. Geochemical Characteristics of Stable Isotopes; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000. (in Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Qin, M.K.; Fan, H.H.; Liu, W.S.; Kang, S.H.; Zhang, Z.L.; Zhou, F.; Cai, Y.; Shi, Q.P. Relationship between Uranium Mineralization and Hydrocarbon Fluids Characteristics in Paleo-channel Uranium Deposits of Central Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2019, 40, 405–416, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]

| Petrogeochemical Types | Rock Color | Fe3+/Fe2+ | Organic Carbon (10−2) | Stotal (10−2) | S2− (10−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Zone (45 samples) | Yellow, brown, red, purplish red, etc. | 2.59 | 0.10 | 0.076 | 0.009 |
| Reduction Zone (54 samples) | Light gray, gray, dark gray, greenish gray, etc. | 0.78 | 0.23 | 0.221 | 0.031 |
| Measurement Point | Test Number | Results (wB/%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgO | SiO2 | P2O5 | ThO2 | UO2 | CaO | TiO2 | V2O5 | Cr2O3 | MnO | FeO | CoO | Total | ||
| 1 | WT18B1 | 0.05 | 1.21 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 1.20 | 0.19 | 71.89 | 0.76 | 0.08 | 1.48 | 10.83 | 0.05 | 88.01 |
| 2 | WT18B2 | 0.04 | 0.95 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.84 | 0.14 | 70.36 | 0.69 | 0.02 | 1.00 | 13.09 | 0.04 | 87.35 |
| 3 | WT18B3 | 0.05 | 1.03 | 0.18 | 0.00 | 0.87 | 0.15 | 69.77 | 0.66 | 1.66 | 0.79 | 11.86 | 0.06 | 87.06 |
| 4 | WT18B4 | 0.02 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 0.12 | 73.46 | 0.62 | 0.09 | 1.41 | 14.83 | 0.06 | 92.07 |
| 5 | WT18B5 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 57.18 | 0.44 | 0.05 | 2.93 | 29.88 | 0.05 | 90.86 |
| 6 | WT18B6 | 0.00 | 1.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 59.84 | 0.52 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 20.41 | 0.05 | 82.44 |
| 7 | WT18B7 | 0.01 | 1.08 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 56.89 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.33 | 20.42 | 0.02 | 79.61 |
| 8 | WT18B8 | 0.00 | 0.90 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 56.20 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 0.26 | 21.75 | 0.04 | 79.86 |
| No. | Serial Number | Well Depth (m) | Sampling Horizon | δD V-SMOW (‰) | δ18O V-SMOW (‰) | T (T.U) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SDS30 | 110 | K1bs | −93.98 | −12.16 | <1.0 |
| 2 | SDS23 | 38 | K1bs | −94.18 | −12.24 | <1.0 |
| 3 | SZK01 | 126 | K1bs | −94.07 | −12.15 | <1.0 |
| 4 | SDS87 | 90 | K1bs | −90.68 | −11.87 | <1.0 |
| 5 | SZK02 | 156 | K1bs | −95.34 | −11.96 | <1.0 |
| No. | Sample No. | Lithology Description | Measuring Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ13CV-PDB (%) | δ18OV-PDB (%) | δ18OV-SOW (%) | |||
| 1 | 2019TY1 | Gray gravel-bearing coarse sandstone | −6.6 | −20.0 | 10.3 |
| 2 | 2019TY2 | Gray gravel-bearing coarse sandstone | −4.8 | −18.5 | 11.8 |
| 3 | 2019TY3 | Gray gravel-bearing coarse sandstone | −5.8 | −18.6 | 11.7 |
| 4 | 2019TY4 | Gray gravel-bearing coarse sandstone | −3.3 | −17.5 | 12.9 |
| 5 | 2019TY5 | Gray gravel-bearing coarse sandstone | −3.7 | −16.7 | 13.7 |
| 6 | 2019TY6 | Yellowish-green siltstone | −0.6 | −15.0 | 15.4 |
| 7 | 2019TY7 | Gray medium-grained sandstone | −4.4 | −15.3 | 15.1 |
| 8 | 2019TY8 | Gray coarse sandstone | −4.8 | −11.5 | 19.0 |
| 9 | 2019TY9 | Gray gravel-bearing coarse sandstone | −4.5 | −16.6 | 13.8 |
| 10 | 2019TY10 | Gray siltstone | −3.4 | −14.9 | 15.5 |
| 11 | 2019TY11 | Gray coarse sandstone | −6.4 | −24.0 | 6.2 |
| 12 | 2019TY12 | Gray medium-grained sandstone | −6.3 | −17.1 | 13.2 |
| No. | Original Sample Number | Summary of Measuring Results (μL/kg) | C1/∑C | C1/C2+ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | iC4 | nC4 | iC5 | nC5 | Total Hydrocarbons (∑C) | ||||
| 1 | 2019TY1 | 0.20 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.67 |
| 2 | 2019TY2 | 0.32 | 0.09 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.66 | 0.48 | 0.94 |
| 3 | 2019TY3 | 0.33 | 0.08 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.66 | 0.50 | 1.00 |
| 4 | 2019TY4 | 0.29 | 0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.59 | 0.49 | 0.97 |
| 5 | 2019TY5 | 0.25 | 0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.83 |
| 6 | 2019TY6 | 0.32 | 0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.62 | 0.52 | 1.07 |
| 7 | 2019TY7 | 0.36 | 0.08 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.69 | 0.52 | 1.09 |
| 8 | 2019TY8 | 0.43 | 0.12 | 0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.80 | 0.54 | 1.16 |
| 9 | 2019TY9 | 0.40 | 0.09 | 0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.74 | 0.54 | 1.18 |
| 10 | 2019TY10 | 0.41 | 0.10 | 0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.76 | 0.54 | 1.17 |
| 11 | 2019TY11 | 0.35 | 0.10 | 0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.70 | 0.50 | 1.00 |
| 12 | 2019TY12 | 0.21 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.51 | 0.41 | 0.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, C.; Xu, Z.; Duan, M.; Meng, L.; Liu, H.; Wei, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, L. Genetic Model of the Luhai Sandstone-Type Uranium Deposit in the Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia. Minerals 2025, 15, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030294
Tang C, Xu Z, Duan M, Meng L, Liu H, Wei J, Zhang C, Zhao L. Genetic Model of the Luhai Sandstone-Type Uranium Deposit in the Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia. Minerals. 2025; 15(3):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030294
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Chao, Zenglian Xu, Ming Duan, Lishan Meng, Huajian Liu, Jialin Wei, Chao Zhang, and Lijun Zhao. 2025. "Genetic Model of the Luhai Sandstone-Type Uranium Deposit in the Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia" Minerals 15, no. 3: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030294
APA StyleTang, C., Xu, Z., Duan, M., Meng, L., Liu, H., Wei, J., Zhang, C., & Zhao, L. (2025). Genetic Model of the Luhai Sandstone-Type Uranium Deposit in the Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia. Minerals, 15(3), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030294





