Removal of Chloride Ions from Mg(OH)2 Using NaOH with Ethanol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Chloride Measurement
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
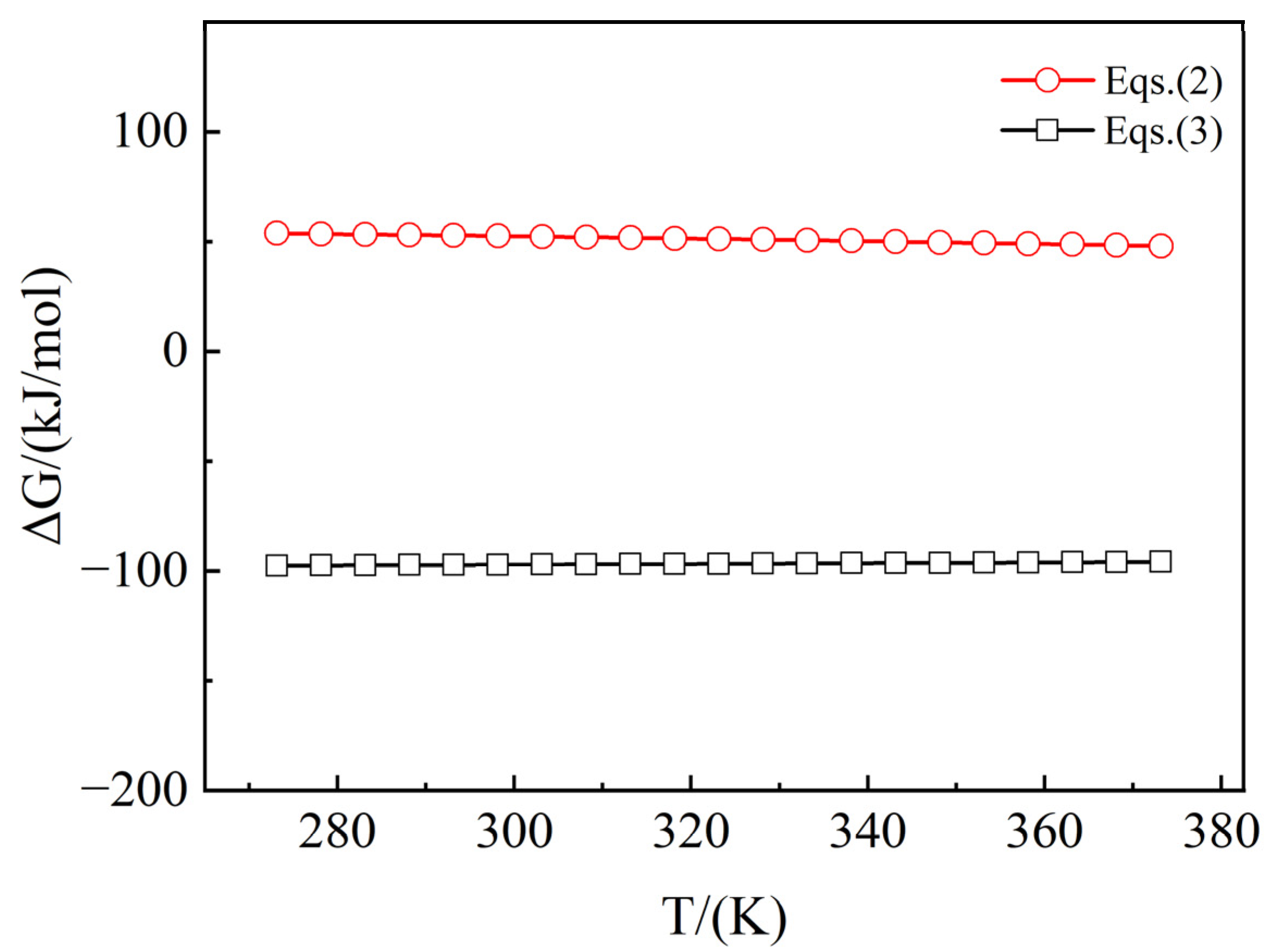
3.1. The Cl− Ion in Mg(OH)2 and Thermodynamic Analysis
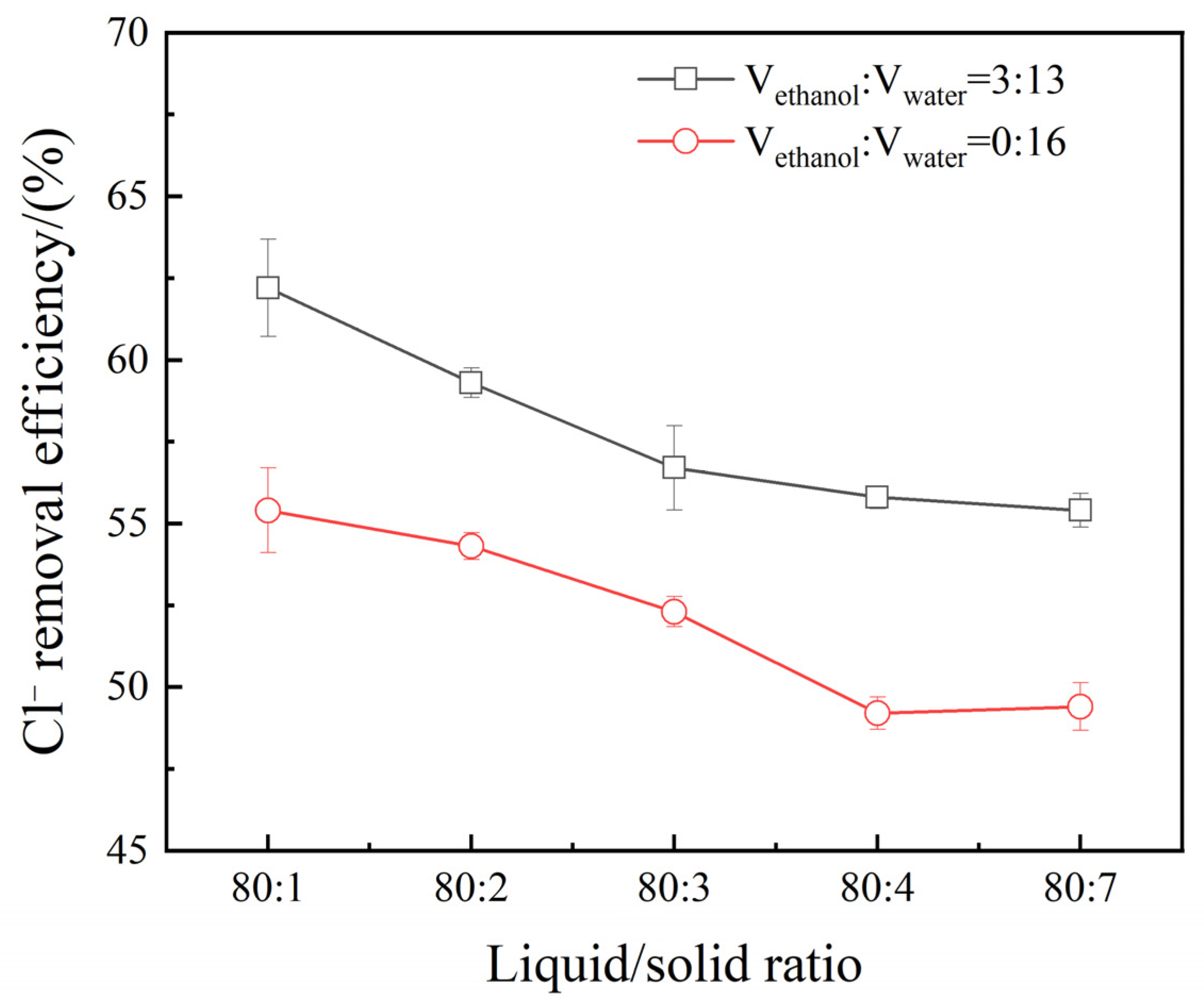
3.2. Effect of Liquid/Solid Ratio
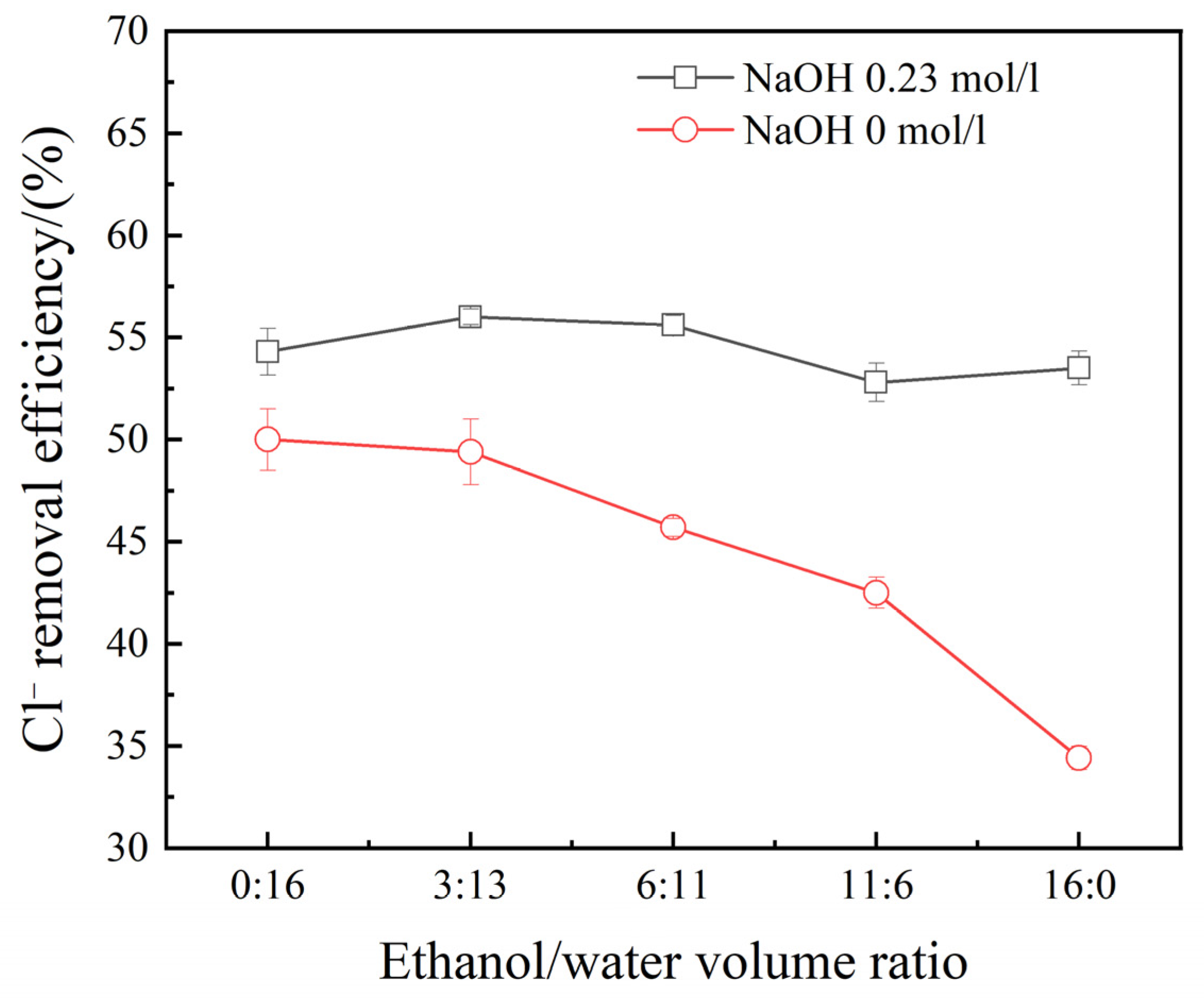
3.3. Effect of Ethanol Concentration
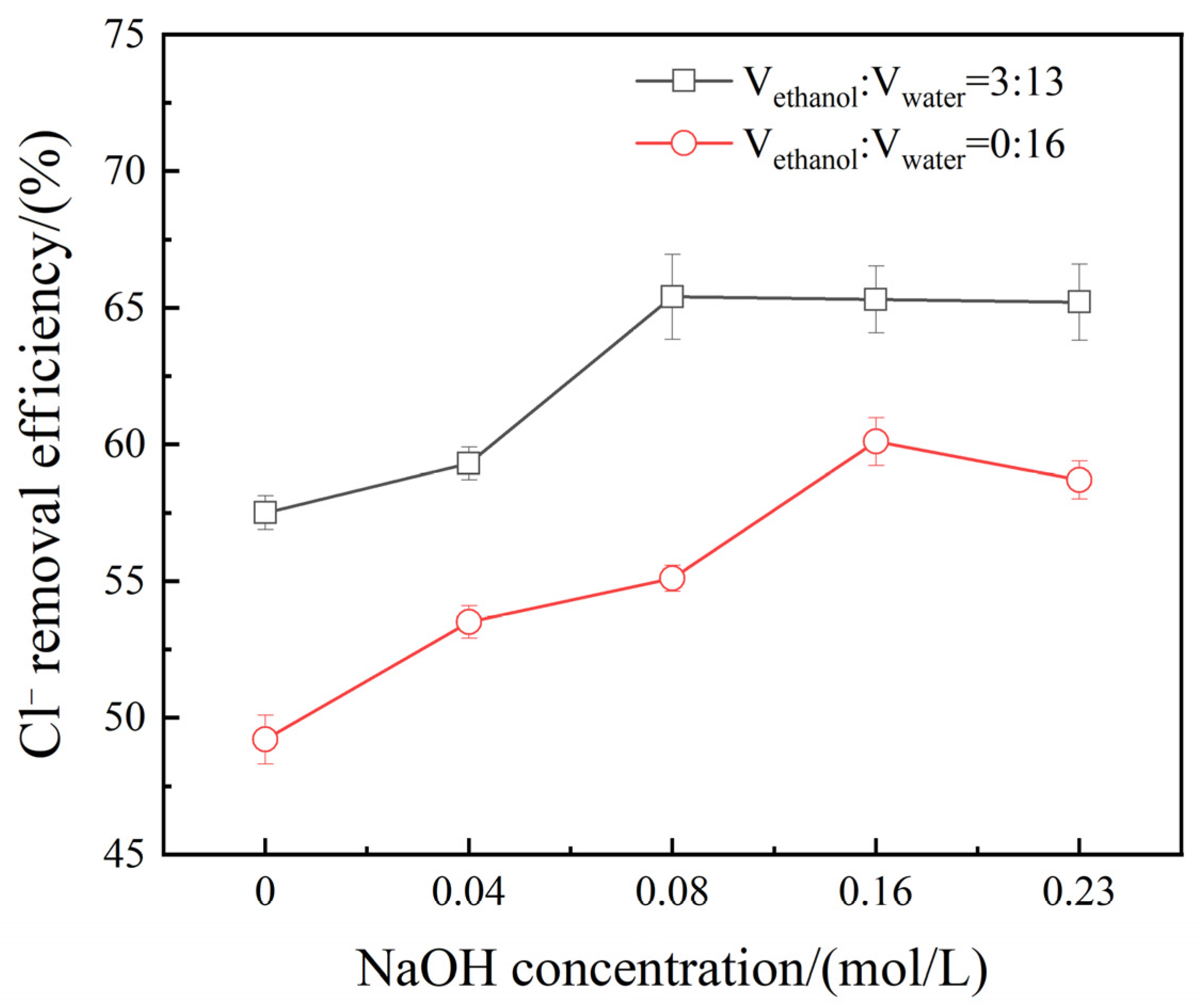
3.4. Effect of NaOH Concentration
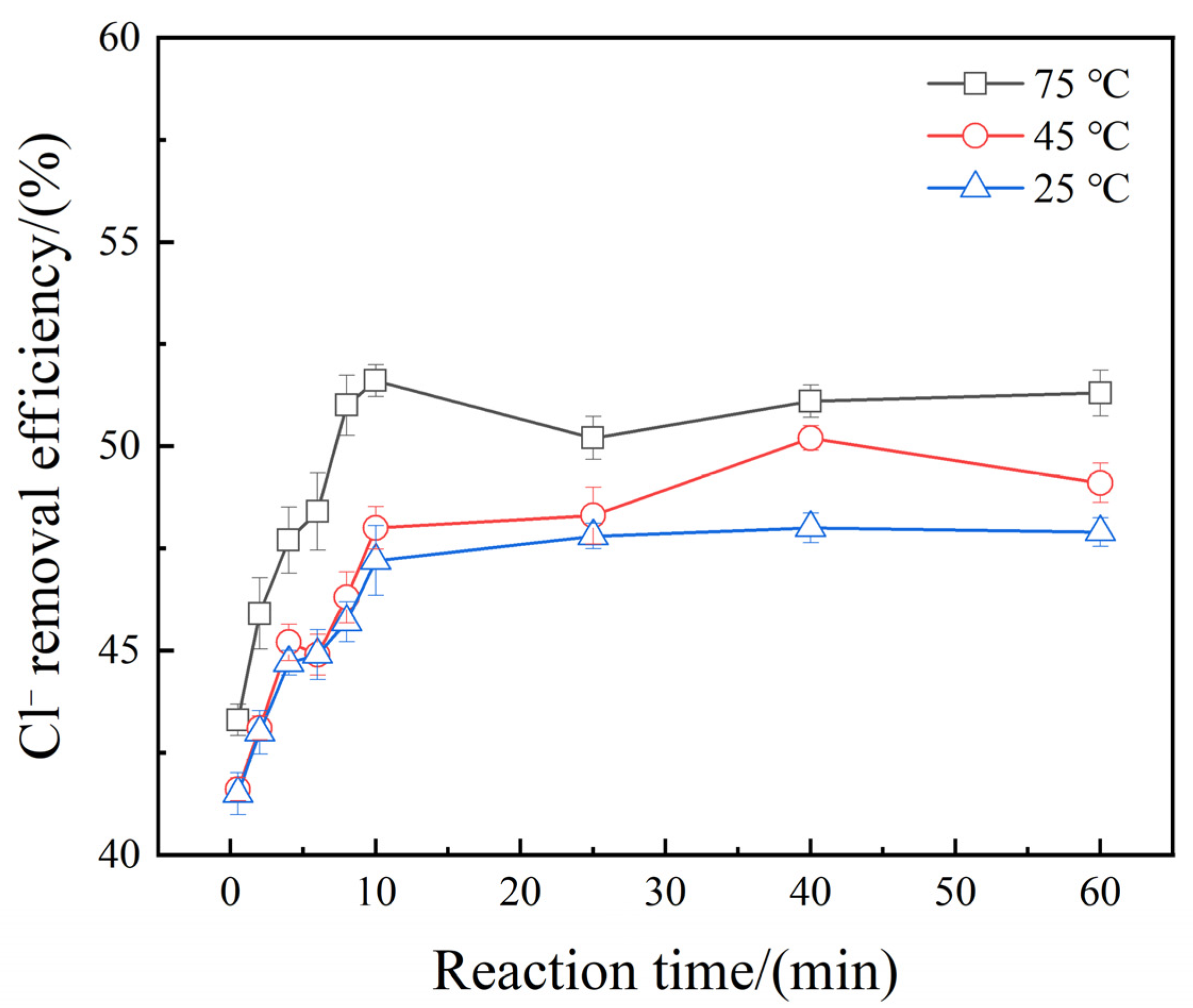
3.5. Effect of Reaction Time
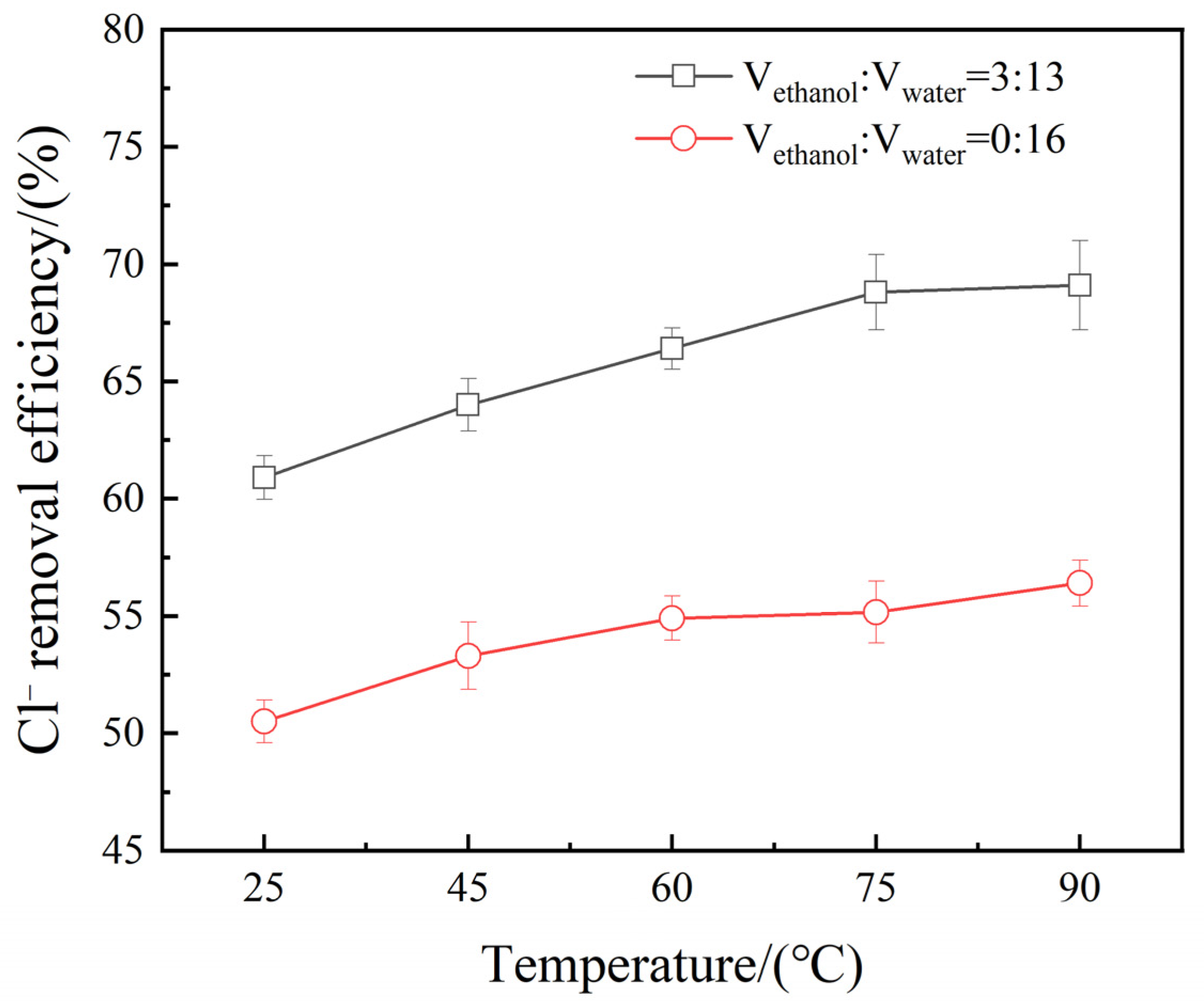
3.6. Effect of Reaction Temperature
3.7. Kinetic Analysis
3.8. Calculation of Apparent Activation Energy
4. Mechanism of Chloride Removal Process with NaOH and Ethanol
4.1. Particle Size Distribution Analysis
4.2. Electrochemical Property of Mg(OH)2
4.3. Chloride Removal Mechanism
5. Summary and Conclusions
- The addition of NaOH to the aqueous solution improves the dispersion of Mg(OH)2 particles, and the removal of Cl− by NaOH is primarily governed by internal diffusion.
- Ethanol adsorbs to the surface of magnesium hydroxide, which decreases surface energy and reduces the system’s polarity, thereby facilitating chloride ion removal.
- The chloride removal rate reached 68.9% and Cl− content in Mg(OH)2 decreased to 0.14% under optimized conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, W.; Li, H. Research on preparation of magnesium hydroxide using magnesium oxide of salt lake. Metal Mine 2007, 373, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Luo, X.; Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; An, D.; Li, J. Preparation and characterization of microporous magnesia-based refractory. Int. J. Appl. Ceramic Technol. 2020, 17, 2629–2637. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, D.; Song, X. Research status of modification process of magnesium hydroxide flame retardant. J. Salt Sci. Chem. Ind. 2019, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhan, Y.; Lin, J.; Qiu, B.; Xu, W.; Yu, Y.; Huang, L. Efficiency of magnesium hydroxide capping and amendment to control phosphorus release from sediments. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Idris, M.S.; Shanmugan, S.; Devarajan, M.; Maryam, W. Heat transfer enhancement in light-emitting diode packaging employing different molar concentration of magnesium oxide thin films as a heat spreader. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 9527–9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Huo, Y.; Li, C.; Kannan, M.B.; Chen, X.; Guan, S.; Zeng, R.; Ma, Q. Corrosion resistance of nano-structured magnesium hydroxide coating on magnesium alloy AZ31: Influence of EDTA. Rare Metals 2019, 38, 520–531. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, W.; Choi, B.J.; Han, J.H. Growth characteristics and film properties of plasma-enhanced and thermal atomic-layer deposited magnesium oxide thin films prepared using bis(ethyl-cyclopentadienyl) magnesium precursor. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 10115–10120. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Ye, J.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, S.; Shi, L.; Zhong, J.; Ning, G. Highly effective antibacterial activity of lithium-doped magnesium oxide particles synthesized by the microwave-assisted hydrothermal route. Powder Technol. 2020, 371, 130–141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Ni, W.; Zang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yan, Y. Magnesium oxide anchored into a hollow carbon sphere realizes synergistic adsorption and activation of CO2 for electrochemical reduction. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 6062–6065. [Google Scholar]
- Calderón, D.J.; DeAlba-Montero, I.; Ruiz, F.; Echeverría, F. Effect of synthesis variables on the characteristics of magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles and evaluation of the fluorescence of functionalised Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 025008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Yu, J. Effect of particle size on thermal decomposition kinetics of micron magnesium hydroxide. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2021, 21, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Pang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z. Technological progress in the development of magnesium resources in salt lakes and planning and ideas for the development of the magnesium industry. Qinghai Sci. Technol. 2010, 17, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Miller, J.D.; Cheng, F.; Cheng, H. Potash flotation practice for carnallite resources in the Qinghai Province, PRC. Min. Eng. 2014, 66–68, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Xu, H.; Shi, X.; Yang, X. Fractional crystallization for extracting lithium from Cha’erhan tail brine. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, T.; Cheng, Y. Deposition of MgO film by pyrolysis of bischofite through RF thermal plasma process. CIESC J. 2014, 65, 4191–4196. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z. A review on the technologies of high-purity magnesia production from brine. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2016, 35, 3251–3257. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Xu, H.; Shi, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, X. Improved lime method to prepare high-purity magnesium hydroxide and light magnesia from bischofite. JOM 2019, 71, 4674–4680. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Cheng, H.; Cui, X. Development history and present status of salt lake resources in China. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2011, 43, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, X. Preparation of high-purity light magnesia from sulfate salt subtype salt lake brine. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2011, 8, 2204–2208. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Song, X.; Zhang, D. Synthesis of magnesium hydroxide from waste bischofite by reaction crystallization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 33, 298–300. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Han, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, X. Novel alkaline method for the preparation of low-chromium magnesia. JOM 2020, 72, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, J.; Xu, H. Preparation and melting process of fused magnesia. J. Salt Chem. Ind. 2016, 45, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, F.; Jiang, B.; Song, J.; Wang, S. Several thoughts on accelerating the development of magnesium-based structural and functional materials in salt lakes. Qinghai Sci. Technol. 2016, 29, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Dong, X. Preparation and properties of superfine Mg(OH)2 flame retardant. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2006, 2, 488–492. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Li, X.; Chen, B. A Method for Producing High-Purity Magnesia Using Salt Lake Bischofite as Raw Material. Chinese Patent CN125229C, 25 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J. Study on the forms of chlorine in the preparation of industrial grade magnesium hydroxide and magnesium oxide from salt lake brine. J. Salt Lake Res. 2021, 29, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Jia, M.; Huo, J. The effect of Cl− on corrosion behavior of copper in bitter and brackish solution. J. Beijing Univ. Chem. Technol. 2000, 27, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Lu, S.; Yu, X.; Xu, W.; Chen, L. Analysis on corrosion of black-chromium-plated plastics applied to automotive interiors during salt spray test. Electroplat. Finish. 2022, 41, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Hou, B.; Liu, N.; Du, Z.; Lu, J. The aging and pollution behavior of microplastics in tap water supply system subjected to residual chlorine exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gan, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Z. Analysis of the failure cases of chloride ion corrosion in PCBA. Electron. Product Reliab. Environ. Test. 2022, 40, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.M.; Chen, Z.Y.; Luo, H.F.; Teng, Z.; Zhao, Y.L.; Ling, Z.C. Corrosion resistances of metallic materials in environments containing chloride ions: A review. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 377–410. [Google Scholar]
- HG/T 4531-2013; Magnesium Hydroxide for Flame Retardant. Chemical Industry Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2013.
- HG/T 3607-2007; Magnesium Hydroxide for Industrial Use. Chemical Industry Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2007.
- HG/T 3821-2006; Nano-Powder of Magnesium Hydroxide. Chemical Industry Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Liu, Z.; Yan, D.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, Z.; Li, N.; Chen, A.; Jiao, L.; Li, Y. A Method for Preparing Flame Retardant Magnesium Hydroxide by Wet Dechlorination of Industrial Grade Magnesium Hydroxide. Chinese Patent CN114804163A, 29 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, Z. A Preparation Method for Reducing the Chloride Content of Magnesium Hydroxide. Chinese Patent CN108190924B, 22 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Li, C.; Liu, S. Removal of chlorine from magnesium hydroxide by precipitation-separation method. Sea-Lake Salt Chem. Ind. 2005, 35, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Di, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, N. Preparation of flake-like magnesium hydroxide by diaphragm electrodeposition method and its influence factors. J. Northeast. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2017, 38, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Lai, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Weng, C.; Ding, X. A Preparation Method for Low-Chlorine Content Flake Magnesium Hydroxide. Chinese Patent CN114717579A, 8 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Manoli, F.; Dalas, E. Spontaneous precipitation of calcium carbonate in the presence of ethanol, isopropanol, and diethyleneglycol. J. Cryst. Growth 2000, 218, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.J.; Hua, X.; Han, Q.F.; Yang, X.J.; Lu, L.D.; Wang, X. Preparation of lamellar magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles via precipitation method. Powder Technol. 2009, 191, 227–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, R.; Brunner, J.G.; Kunze, J.; Schmuki, P.; Virtanen, S. A novel approach for the formation of Mg(OH)2/MgO nanowhiskers on magnesium: Rapid anodization in chloride containing solutions. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 288–292. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Yu, Q.; Huang, C.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, J.; Zhu, P. Preparation of mesoporous spherical magnesium hydroxide particles via the static self-assembled method. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1175, 858–864. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Jiang, L.; Wen, T.; Yuan, L.; Yu, J. Structure–property relations of recrystallized products from magnesium chloride ethanol solution: Aiming at recycling magnesium resources from nature. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 60, 553–561. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, L.; Wu, H.; Jin, Y. Review of the preparation technology of flame retardant type magnesium hydroxide. Sea-Lake Salt Chem. Ind. 2001, 30, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhai, X.; Tang, J. Research on the control of chlorine content in high-purity magnesium oxide. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 1993, 2, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Green, J. Calcination of precipitated Mg(OH)2 to active MgO in the production of refractory and chemical grade MgO. J. Mater. Sci. 1983, 18, 637–651. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Yang, Y.; Tang, J. Determination of the state of impurity chlorine in Mg(OH)2 by study of carbonation kinetics. Chem. Reagents 1996, 3, 144–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Song, L.; Bai, W. Preliminary mechanism research of high-magnesium scaling during continuous production process of magnesium hydroxide. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2019, 51, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Dan, J.; Li, H.; Qi, Y.; Hong, C.; Qiao, X. Preparation of Fibrous Magnesium Hydroxide from Basic Magnesium Chloride in Ethanol Solution. J. Shihezi Univ. Nat. Sci. 2015, 33, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, S. Adsorption mechanism of polymer dechlorination agent to chloride ion in water. Environ. Prot. Chem. Ind. 2018, 2, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Tan, F.; Chen, Y.; Yin, J.; Yuan, X.; Liao, M.; Liu, H. Leaching Kinetics of Co and Ni from Waste Aerospace Magnetic Materials. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2023, 47, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar]
- Safitri, N.; Mubarok, M.Z.; Winarko, R.; Tanlega, Z. Recovery of nickel and cobalt as MHP from limonitic ore leaching solution: Kinetics analysis and precipitate characterization. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1964, 020030. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yu, P.; Xu, H.; Shi, X. Preparation of rod-like magnesium hydroxide from brine. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2014, 45, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Luo, C.; Zou, L.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X. Effect of brine-ammonia reverse precipitation on crystal growth of magnesium hydroxide. Nonferrous Met. Sci. Eng. 2023, 14, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
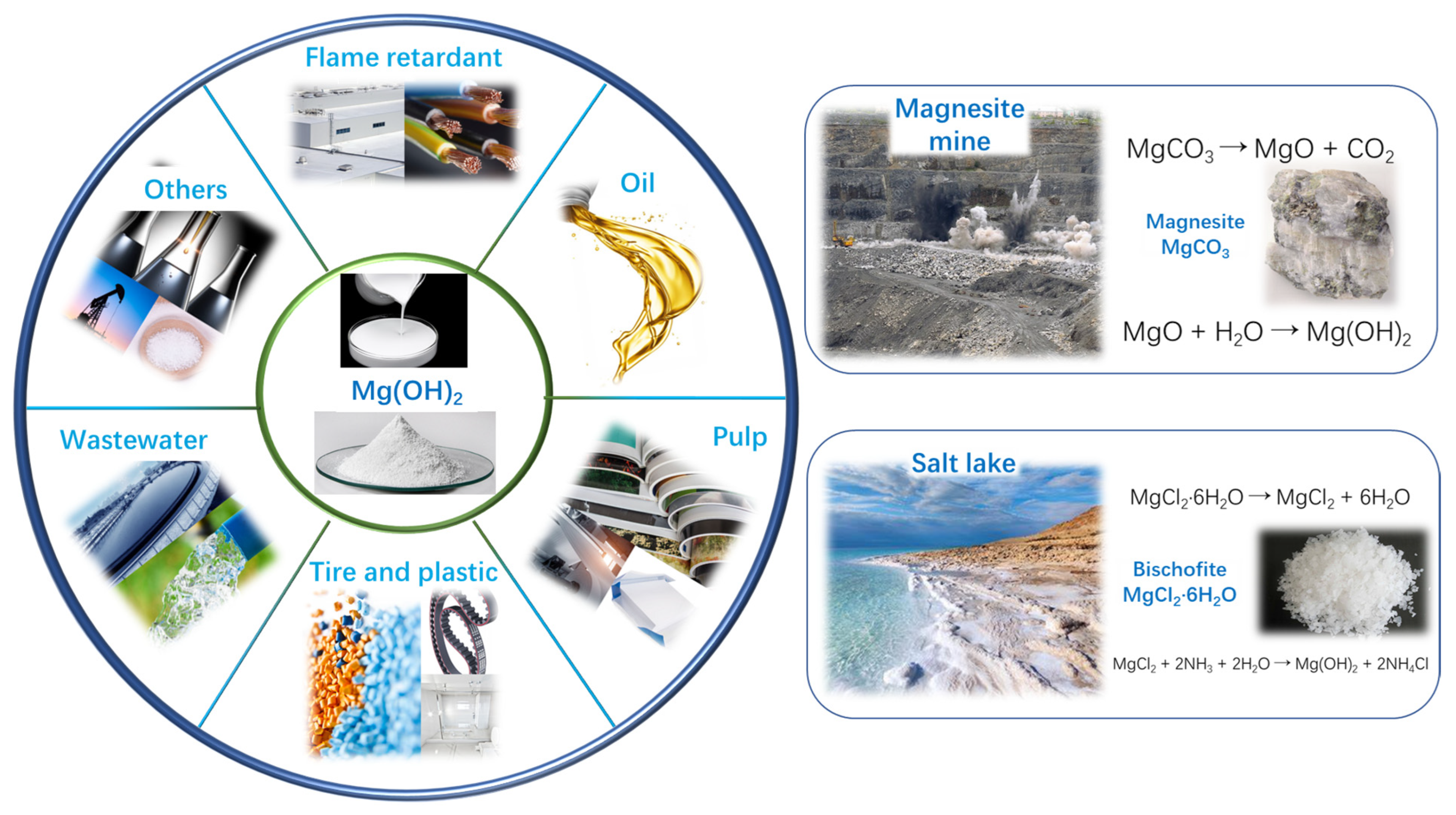
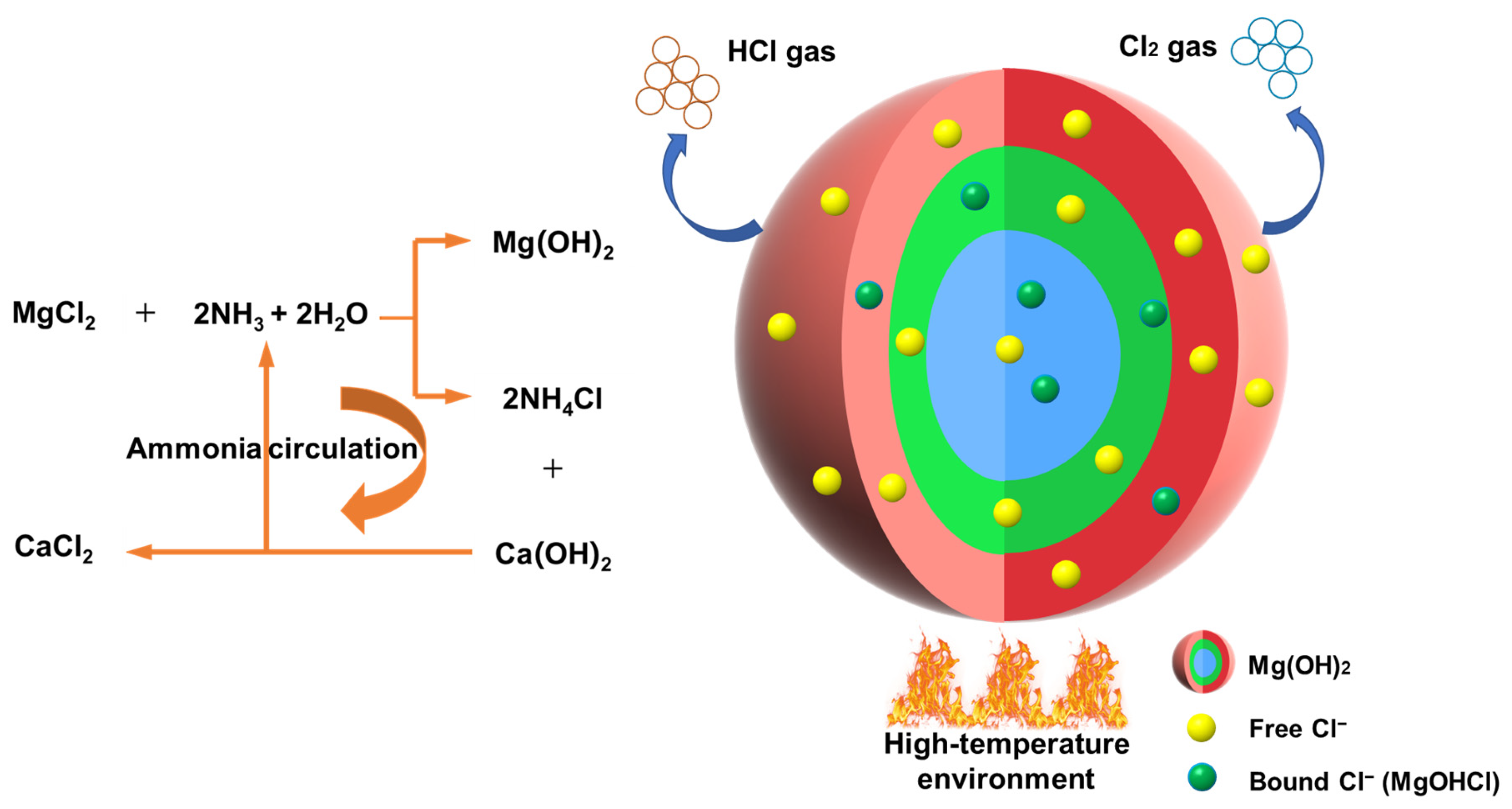




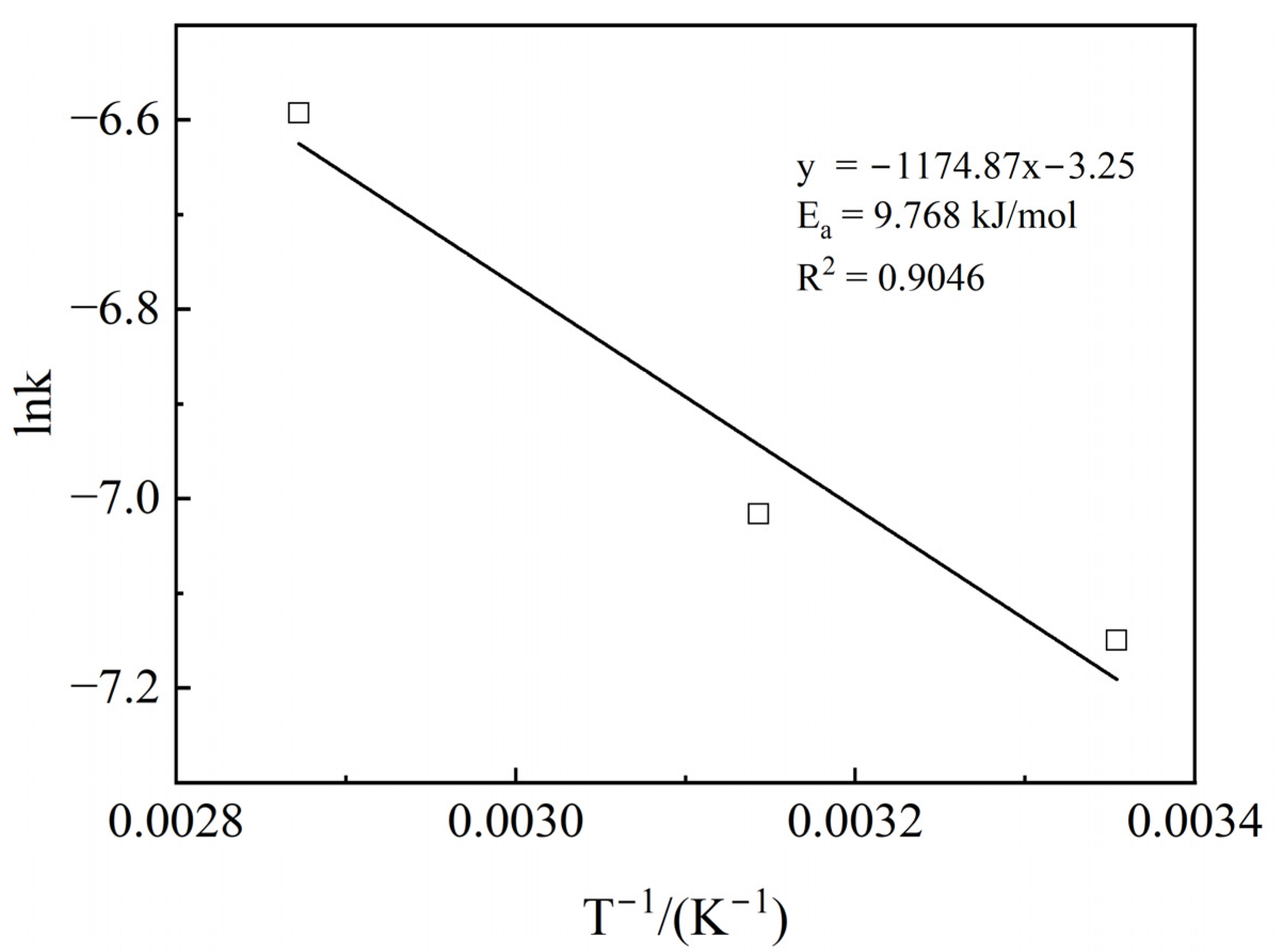
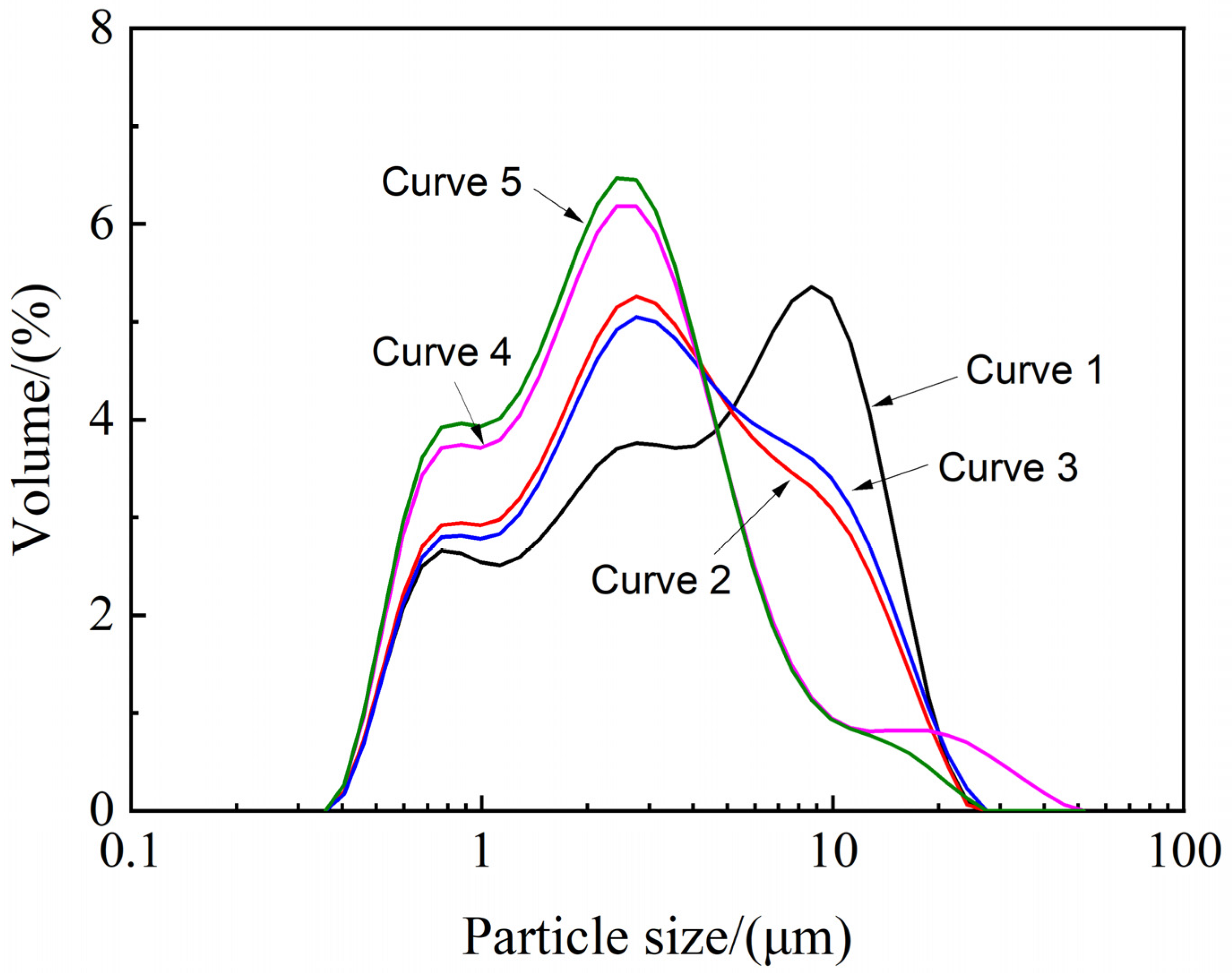

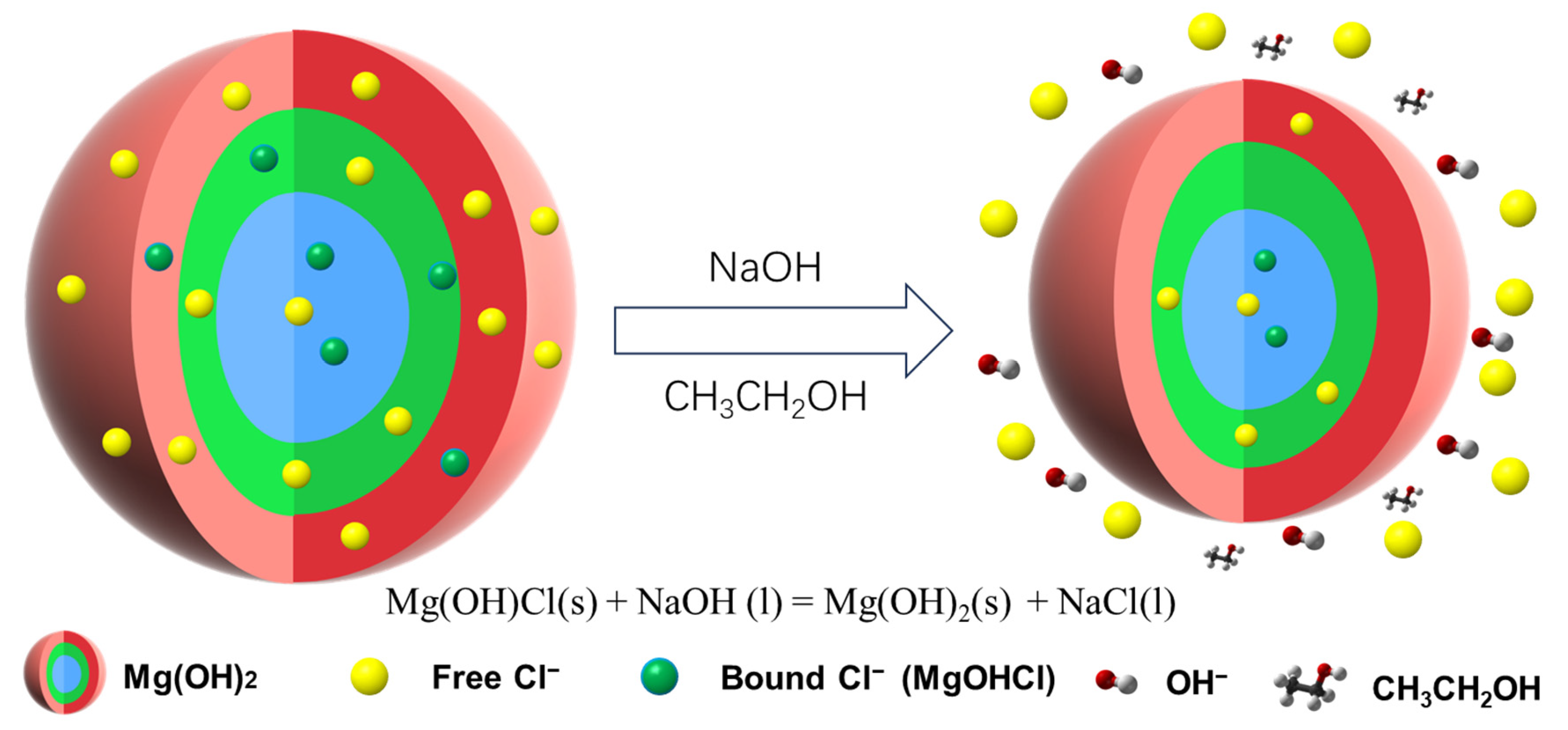
| Application Area | Product Model | Cl−% | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flame retardant | MC-1-2 | 0.08% | HG/T 4531-2013 [32] |
| MC-2-15 | 0.15% | ||
| Industrial use | I | 0.10% | HG/T 3607-2007 [33] |
| II/III-1 | 0.40% | ||
| II/III-2 | 0.50% | ||
| Nano-powder | I | 0.40% | HG/T 3821-2006 [34] |
| II | 0.50% |
| Author | Method | Initial Cl−% | Final Cl−% | Chloride Removal Efficiency, % | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu et al. [35] | Ball milling and strong alkalis under hydrothermal conditions | 0.5% | 0.01% | 98 | Chloride removal efficiency high | High energy input and strong alkalis |
| Wang et al. [36] | Washing with ammonia | 0.8% | 0.2% | 75 | Short flowsheet with less energy consumption | Ammonia-containing wastewater treatment |
| Song et al. [26] | Water washing | 0.34% | 0.33% | 3 | Short flowsheet with less energy consumption | Water recycling and low removal efficiency |
| 0.42% | 0.3% | 29 | ||||
| Wu et al. [37] | Flocculant | - | 4.5% | - | Short flowsheet | Chlorine content high |
| Jiang et al. [39] | Electrodeposition | - | 0.03% | - | Chlorine level low | Needs to be applied in magnesium hydroxide slurry |
| Contents | HCl Insoluble | Water | Cl− | CaO | Fe2O3 | Loss on Ignition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Index | ≥99% | ≤0.05% | ≤0.5% | ≤0.6% | ≤0.02% | ≤0.01% | ≥30% |
| Reaction Equations | Δ-T(kJ/mol) | Eqs. |
|---|---|---|
| 2Mg(OH)Cl(s) = Mg(OH)2(s) + MgCl2(l) | Δ = −0.05748T + 69.65166 | (2) |
| Mg(OH)Cl(s) + NaOH(l) = Mg(OH)2(s) + NaCl(l) | Δ = 0.01675T − 102.15172 | (3) |
| Kinetic Control Steps | Spherical Unreacted Shrinkage Nuclei Model | Plate-Like Unreacted Shrinkage Nuclei Model |
|---|---|---|
| External diffusion control | ||
| Surface chemical reaction control | ||
| Solid film diffusion control |
| Models | Control Equation | T/°C | k/10−3 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | 75 | 4.35 | 0.95296 | |
| 45 | 3.04 | 0.92542 | ||
| 25 | 2.69 | 0.93143 | ||
| 75 | 1.37 | 0.95908 | ||
| 45 | 0.89 | 0.92738 | ||
| 25 | 0.78 | 0.93596 | ||
| Plate-like | 75 | 8.45 | 0.94825 | |
| 45 | 6.14 | 0.92380 | ||
| 25 | 5.45 | 0.92853 | ||
| 75 | 8.08 | 0.95576 | ||
| 45 | 5.50 | 0.92655 | ||
| 25 | 4.84 | 0.93381 |
| Curve 1. Raw Mg(OH)2 | Curve 2. Water | Curve 3. Ethanol | Curve 4. NaOH | Curve 5. Ethanol/NaOH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median particle diameter (μm) | 4.43 ± 0.02 | 3.17 ± 0.03 | 3.37 ± 0.02 | 2.47 ± 0.01 | 2.34 ± 0.03 |
| Specific surface area (m2/kg) | 2502 ± 2 | 2832 ± 4 | 2731 ± 3 | 3364 ± 6 | 3510 ± 5 |
| Sample b: Water | Sample c: Ethanol | Sample d: NaOH | Sample e: Ethanol/NaOH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeta potential | 9.14 ± 0.03 | 17.30 ± 0.05 | −3.39 ± 0.07 | −13.00 ± 0.08 |
| pH | 7.55 ± 0.04 | 8.19 ± 0.03 | 11.2 ± 0.02 | 11.34 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Sun, W.; Alam, S. Removal of Chloride Ions from Mg(OH)2 Using NaOH with Ethanol. Minerals 2025, 15, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040364
Zhao Y, Cheng J, Liu W, Li J, Wu F, Sun W, Alam S. Removal of Chloride Ions from Mg(OH)2 Using NaOH with Ethanol. Minerals. 2025; 15(4):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040364
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yujie, Junfeng Cheng, Weiping Liu, Jinhui Li, Fang Wu, Wei Sun, and Shafiq Alam. 2025. "Removal of Chloride Ions from Mg(OH)2 Using NaOH with Ethanol" Minerals 15, no. 4: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040364
APA StyleZhao, Y., Cheng, J., Liu, W., Li, J., Wu, F., Sun, W., & Alam, S. (2025). Removal of Chloride Ions from Mg(OH)2 Using NaOH with Ethanol. Minerals, 15(4), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040364








