Comprehensive Recovery Technology for Te, Au, and Ag from a Telluride-Type Refractory Gold Mine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Experimental Sample and Experimental Reagents
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Analytical Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mineralogical Analysis
3.2. Study on Flotation Efficiency
3.2.1. Influence of Ore Particle Size on the Recovery of Te, Au, and Ag
3.2.2. Effect of Pulp pH on the Recovery of Te, Au, and Ag
3.2.3. Effect of Collector Types on the Recovery of Te, Au, and Ag
3.2.4. Effect of Collector Dosage on the Recovery of Te, Au, and Ag
3.2.5. Effect of Slurry Pulp Density on the Recovery of Te, Au and Ag
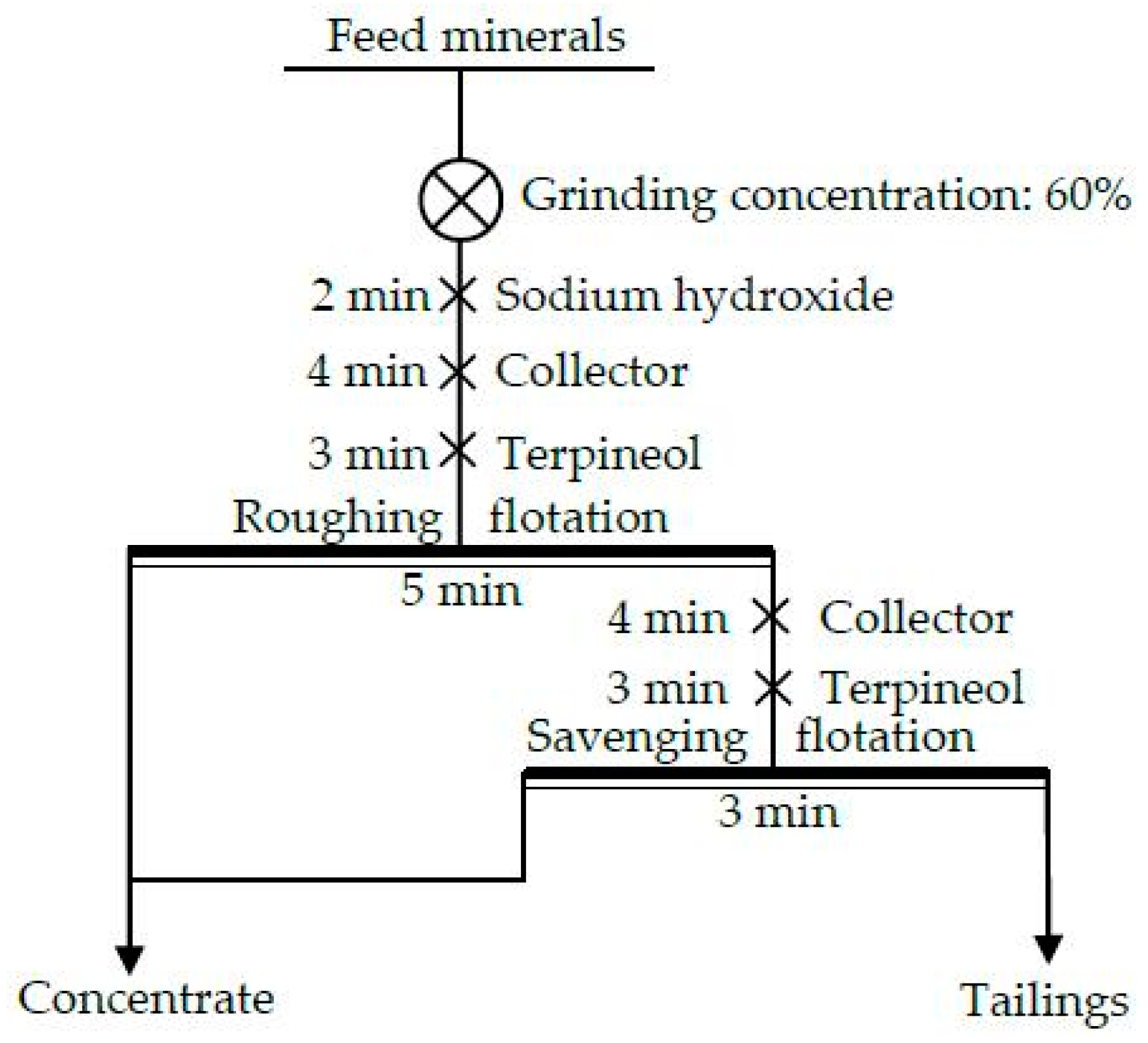
3.2.6. The Closed-Circuit Flotation Test
3.3. Industrial Tests
3.4. Flotation Product Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.L.; Huang, J.R.; Wang, H.; Pan, L.; Wei, X.W. Formation of single-crystal tellurium nanowires and nanotubes via hydrothermal recrystallization and their gas sensing properties at room temperature. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 2457–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, K.T.; Madden, S.J.; Barry, L.D.; Bulla, D. Stoichiometric low loss tellurium oxide thin films for photonic applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 7997–8003. [Google Scholar]
- Goksin, K.; Graedel, T.E. Global anthropogenic tellurium cycles for 1940–2010. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 76, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chris, C.; Anja-Verena, M. Structures, properties, and potential applications of rare earth-noble metal tellurides. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 274, 243–258. [Google Scholar]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Tellurium, its resourcefulness and recovery. JOM 2011, 63, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Lei, Y. Recovery of tellurium from high tellurium bearing materials by alkaline pressure leaching process: Thermodynamic evaluation and experimental study. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 139, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, T.; Abe, K.; Takeuchi, H. Recovery of tellurium from decopperizing leach solution of copper refinery slimes by a fixed bed reactor. Hydrometallurgy 1992, 29, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidele, M.M.; Gamini, S. Extraction of tellurium from lead and copper bearing feed materials and interim metallurgical products—A short review. Miner. Eng. 2018, 115, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.Y.; Ren, F.G.; Li, Z.H. Sulfur and Lead Isotopes of Telluride-type Deposit in Xiong’er Group and Discussing on the Mineralization. Henan Geol. 1995, 4, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.M.; Yang, D.W. Analysis of the Characteristics of Gold and Antimony Minerals in the Gold Deposits of the Xiaojinling Zhongcheng Ore Belt. Technol. Enterp. 2014, 4, 121–122. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.; Feng, S.; Zhang, S.; Gan, Q. Simulation study on the dynamic ventilation control of single head roadway in high altitude mine based on thermal comfort. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.L. Study on Mineral Processing Technology of a High Sulphur Refractory Tetradymite in Sichuan Province; Master. Gen. Res. Inst. Nonferrous Met: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Shu, C.; Wang, C.L.; Rao, X.Y. Beneficiation of a Refractory and Low-grade Joseite Ore in Sichuan. Multipurp. Util. Miner. Resour. 2018, 3, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.H. Gold and silver extraction technology. Metall. Ind. Press 2005, 3, 289. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, S. Treatment of gold-telluride ores. Dev. Miner. Process. 2005, 15, 973–984. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, C.T.; Dunne, R.C. The flotation of gold bearing ores—A review. Miner. Eng. 1994, 7, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Ren, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L. Effect of sodium oleate on the adsorption morphology and mechanism of nanobubbles on the mica surface. Langmuir 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Sun, C.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Chen, F.W. Effect of alkyl structure on the flotation performance of xanthate collectors. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 2014, 36, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Srdjan, M.B. Handbook of Flotation Reagents Chemistry, Theory and Practice Flotation of Sulfide Ores; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.L.; Zhang, C.Q.; Shen, Z.L. The Chemical Principle of Ethyl Thio Carbamate; Central South University of Technology Press: Changsha, China, 1987; pp. 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Jiao, F.; Liu, W.; Qin, W.; Xu, T.; Xue, K.; Zhang, T. Innovative methodology for comprehensive utilization of spent MgO-Cr2O3 bricks: Copper flotation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5503–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Mineral Composition | Chemical Formula | Dissemination Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Natural gold | Au | <0.038 |
| Calaverite | AuTe2 | <0.038 |
| Hessite | Ag2Te | <0.038 |
| Altaite | PbTe | 0.008–0.09 |
| Antamokite | Ag3AuTe2 | 0.006–0.09 |
| Pyrite | FeS2 | 0.048–2 |
| Galena | PbS | 0.037–2 |
| Chalcopyrite | CuFeS2 | 0.016–1 |
| Bornite | Cu5FeS4 | - |
| Sphalerite | ZnS | - |
| Pyrrhotite | Fe1-xS | - |
| Quartz | SiO2 | >0.005 |
| Component | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe | Mn | MgO | CaO | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 74.92 | 0.28 | 6.38 | 2.35 | 0.076 | 1.06 | 1.71 | 3.76 |
| Component | Na2O | Cu | Pb | Zn | S | Au* | Ag* | Te * |
| Content (%) | 0.84 | 0.013 | 0.1 | 0.03 | 2.76 | 5.30 | 5.70 | 14.80 |
| Collector Type | Yield (%) | Grade (g/t) | Recovery (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | Ag | Te | Au | Ag | Te | ||
| Butyl xanthate | 6.91 | 72.27 | 76.70 | 195.5 | 93.88 | 93.28 | 91.95 |
| Sodium isoamyl xanthate | 7.27 | 70.28 | 72.03 | 190.31 | 95.33 | 94.64 | 92.73 |
| Ammonium dibutyl dithiophosphate | 14.18 | 29.62 | 37.88 | 94.73 | 80.32 | 94.57 | 90.88 |
| Ethyl thiocarbamate | 7.45 | 53.39 | 70.03 | 186.65 | 71.66 | 95.27 | 95.31 |
| Sodium isoamyl xanthate and ethyl thiocarbamate (1:1) | 7.37 | 68.34 | 73.45 | 190.93 | 95.03 | 94.98 | 95.08 |
| Product | Yield (%) | Grade (g/t) | Recovery (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | Ag | Te | Au | Ag | Te | ||
| Concentrates | 5.82 | 89.30 | 93.00 | 242.95 | 97.18 | 94.96 | 95.54 |
| Final tailings | 94.18 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.70 | 2.82 | 5.04 | 4.46 |
| Feed minerals | 100.00 | 5.30 | 5.70 | 14.80 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Mineral Composition | Chemical Formula | Content (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrite | FeS2 | 84.34 |
| Galena | PbS | 1.20 |
| Pyrrhotite | Fe1 − xS | 1.45 |
| Muscovite | (K,Na)(Al,Fe)2(Si,Al)4O10(OH)2 | 13.01 |
| Mineral Composition | Chemical Formula | Content (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Quartz | SiO2 | 24.87 |
| Muscovite | (K,Na)(Al,Fe)2(Si,Al)4O10(OH)2 | 30.94 |
| Plagioclase | (Na,Ca)(Al1.02Si2.98O8) | 10.82 |
| Calcite | (Mg0.03Ca0.97)(CO3) | 6.38 |
| Potash feldspar | KAl2(Si3Al)O10(OH,F)2 | 26.98 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, W.; Wang, G.; Wang, Q.; Dong, P.; Cao, H.; Zhang, K. Comprehensive Recovery Technology for Te, Au, and Ag from a Telluride-Type Refractory Gold Mine. Minerals 2019, 9, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9100597
Yang W, Wang G, Wang Q, Dong P, Cao H, Zhang K. Comprehensive Recovery Technology for Te, Au, and Ag from a Telluride-Type Refractory Gold Mine. Minerals. 2019; 9(10):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9100597
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Wei, Gang Wang, Qian Wang, Ping Dong, Huan Cao, and Kai Zhang. 2019. "Comprehensive Recovery Technology for Te, Au, and Ag from a Telluride-Type Refractory Gold Mine" Minerals 9, no. 10: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9100597
APA StyleYang, W., Wang, G., Wang, Q., Dong, P., Cao, H., & Zhang, K. (2019). Comprehensive Recovery Technology for Te, Au, and Ag from a Telluride-Type Refractory Gold Mine. Minerals, 9(10), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9100597




