Impulsive Linearly Implicit Euler Method for the SIR Epidemic Model with Pulse Vaccination Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Exact Solution of Impulsive SIR
3. ILIEM for Impulsive SIR
3.1. Advantages of ILIELM
3.2. Global Attractivity of Disease-Free Periodic Solution of ILIEM
4. Numerical Experiments
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. 1927, 115, 700–721. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.M.; May, R.M. Infectious Diseases of Humans: Dynamics and Control; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.E.; Zhou, Y.C.; Wu, J.H. Modeling and Dynamics of Infectious Diseases; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brauer, F.; Castillo-Chavez, C.; Feng, Z. Mathematical Models in Epidemiology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Agur, Z.; Cojocaru, L.; Mazor, G.; Anderson, R.M.; Danon, Y.L. Pulse mass measles vaccination across age cohorts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11698–11702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulgin, B.; Stone, L.; Agur, Z. Pulse vaccination strategy in the SIR epidemic model. Bull. Math. Biol. 1998, 60, 1123–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, L.; Shulgin, B.; Agur, Z. Theoretical examination of the pulse vaccination policy in the SIR epidemic model. Math. Comput. Model. 2000, 31, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.Y.; Xiao, Y.N.; Clancy, D. New modelling approach concerning integrated disease control and cost-effectivity. Nonlinear Anal. 2005, 63, 439–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Chen, L.; Nieto, J.J.; Torres, A. Analysis of a delayed epidemic model with pulse vaccination and saturation incidence. Vaccine 2006, 24, 6037–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.J.; Teng, Z.D.; Xie, D.H. Analysis of a delayed SIR epidemic model with pulse vaccination. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 40, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Huo, H.F.; Sun, X.K.; Fu, Q. The differential susceptibility SIR epidemic model with time delay and pulse vaccination. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2010, 34, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Smith, H.L.; Wang, L. Global dynamics of an SEIR epidemic model with vertical transmission. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2001, 62, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanakul, C.; Chaiya, I. Amathematical model for predicting and controlling COVID-19 transmission with impulsive vaccination. AIMS Math. 2014, 9, 6281–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, J.P.M.; Rodrigues, A.A. Pulse vaccination in a SIR model: Global dynamics, bifurcations and seasonality. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2024, 139, 108272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannelli, M.; Milner, F.A.; Pugliese, A. Analytical and numerical results for the agestructured SIS epidemic model with mixed inter-intracohort transmission. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 1992, 23, 662–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.W.; Zuo, T.Q.; Chen, Z.J. Numerical analysis of linearly implicit Euler–Riemann method for nonlinear Gurtin-MacCamy model. Appl. Numer. Math. 2021, 163, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Z.; Yang, Z.W.; Liu, S.Q. Numerical threshold of linearly implicit Euler method for nonlinear infection-age SIR models. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 2023, 28, 70–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.X.; Chen, Z.J.; Yang, Z.W. Numerical representations of global epidemic threshold for nonlinear infection-age SIR models. MaThemat. Comput. Simul. 2023, 204, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainov, D.D.; Simeonov, P.S. Systems with Impulsive Effect: Stability, Theory and Applications; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Bainov, D.D.; Simeonov, P.S. Impulsive Differential Equations: Asymptotic Properties of the Solutions; World Scientific: Singapore, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.E.; Zhou, Y.C.; Li, C.Z. Qualitative and Stability Methods for Ordinary Differential Equations; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hairer, E.; Nørsett, S.P.; Wanner, G. Solving Ordinary Differential Equations I: Nonstiff Problems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L. Convergence, consistency and zero stability of impulsive one-step numerical methods. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 423, 127017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchia, M.; Ishiwata, E. Dynamics of a discretized SIR epidemic model with pulse vaccinationand time delay. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2011, 236, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
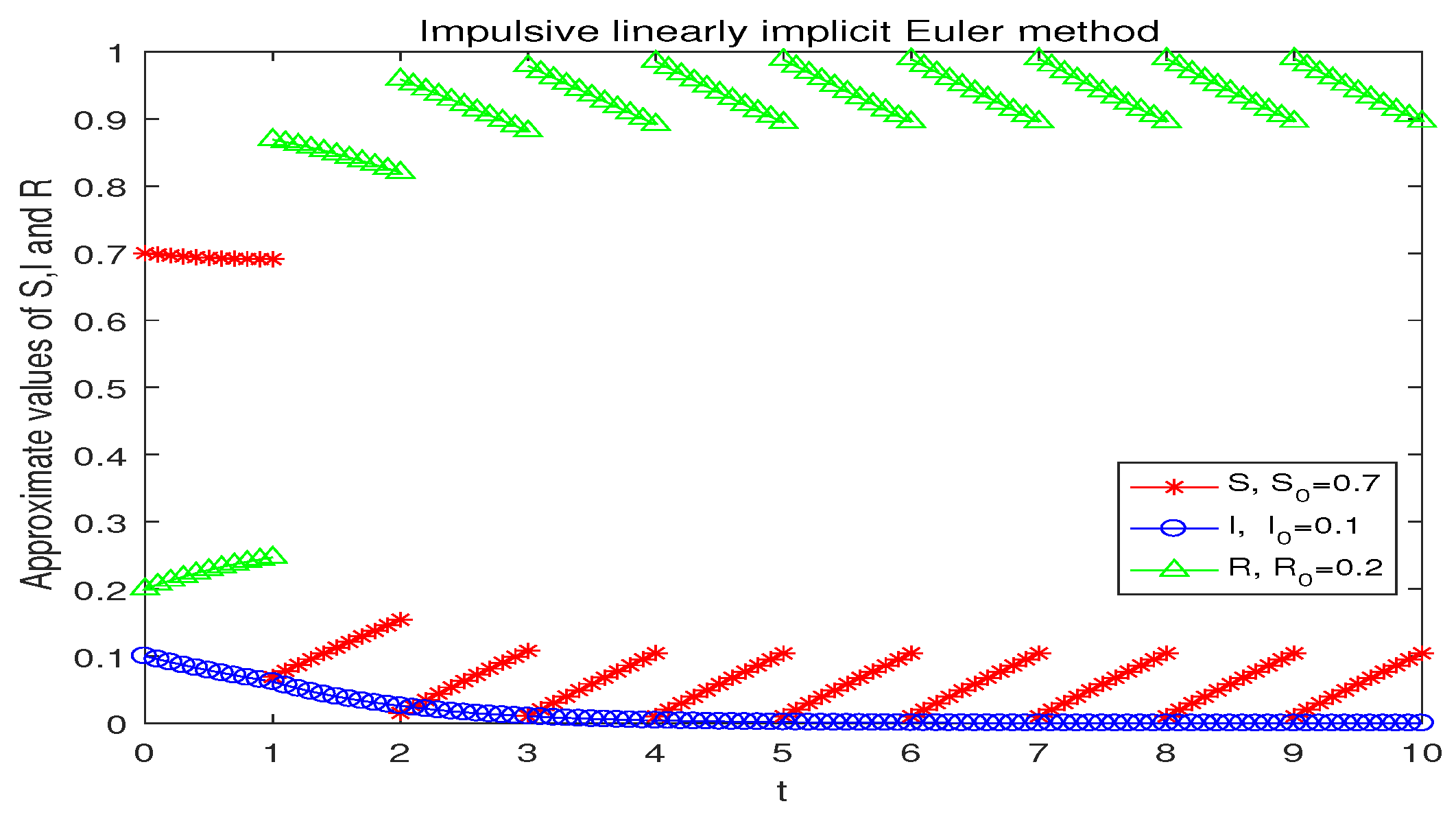
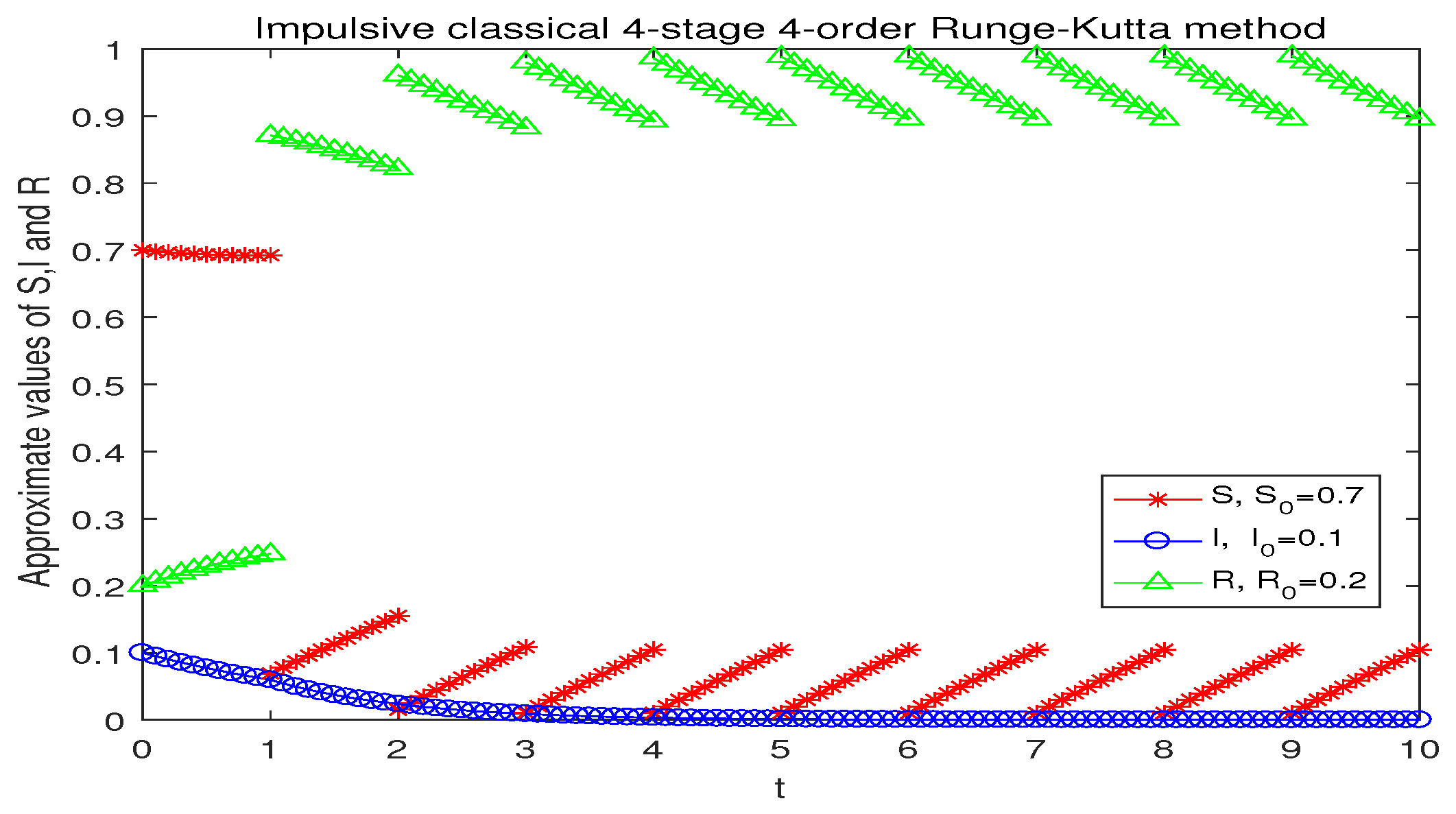

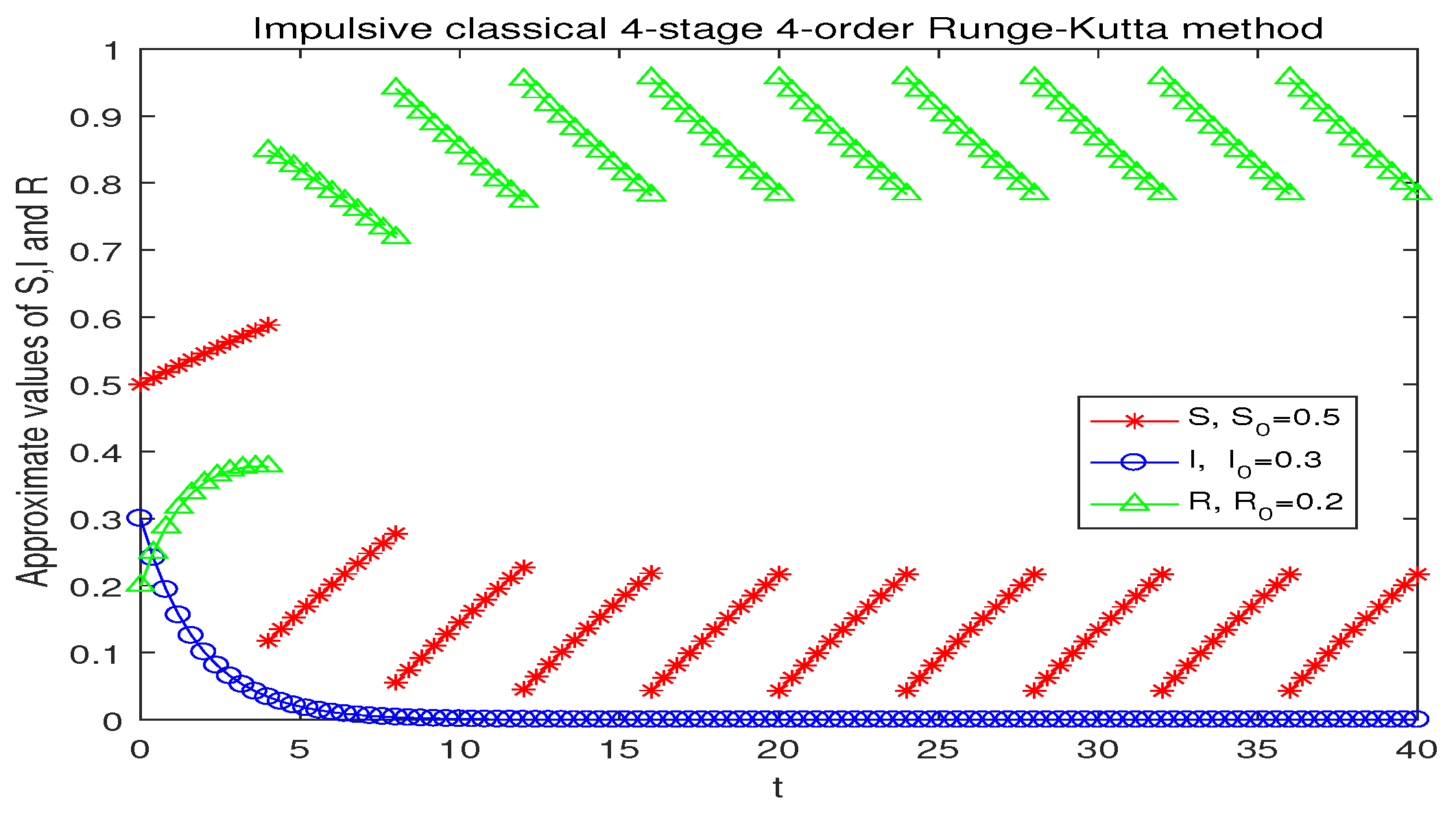
| h | ILIEM | IEEM | IIEM | ICRKM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 6.57948689 × | 6.30555457 × | 6.26634906 × | 5.37914547 × |
| 0.05 | 3.27534435 × | 3.14709001 × | 3.13734221 × | 3.28104266 × |
| 0.025 | 1.63436238 × | 1.57223011 × | 1.56979647 × | 2.05065166 × |
| 0.0125 | 8.16423855 × | 7.85798926 × | 7.85190685 × | 1.28165730 × |
| Ratio | 0.49877817 | 0.49949288 | 0.50040328 | 0.06199036 |
| h | ILIEM | IEEM | IIEM | ICRKM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | 0.00262953 | 0.00229213 | 0.00255089 | 5.35118642 × |
| 0.2 | 0.00128341 | 0.00117865 | 0.00124397 | 3.05181855 × |
| 0.1 | 6.33713258 × | 5.97552229 × | 6.13920780 × | 1.81923606 × |
| 0.05 | 3.14845822 × | 3.00831601 × | 3.04926145 × | 1.08122410 × |
| Ratio | 0.49286547 | 0.50817288 | 0.49259289 | 0.05866777 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.-L.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Chen, L.-K.; Liu, S.-S. Impulsive Linearly Implicit Euler Method for the SIR Epidemic Model with Pulse Vaccination Strategy. Axioms 2024, 13, 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms13120854
Zhang G-L, Zhu Z-Y, Chen L-K, Liu S-S. Impulsive Linearly Implicit Euler Method for the SIR Epidemic Model with Pulse Vaccination Strategy. Axioms. 2024; 13(12):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms13120854
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Gui-Lai, Zhi-Yong Zhu, Lei-Ke Chen, and Song-Shu Liu. 2024. "Impulsive Linearly Implicit Euler Method for the SIR Epidemic Model with Pulse Vaccination Strategy" Axioms 13, no. 12: 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms13120854
APA StyleZhang, G.-L., Zhu, Z.-Y., Chen, L.-K., & Liu, S.-S. (2024). Impulsive Linearly Implicit Euler Method for the SIR Epidemic Model with Pulse Vaccination Strategy. Axioms, 13(12), 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms13120854







