Design and Performance Investigation of a Vehicle Drive System with a 12/10 Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Motor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of the FSPM Drive System
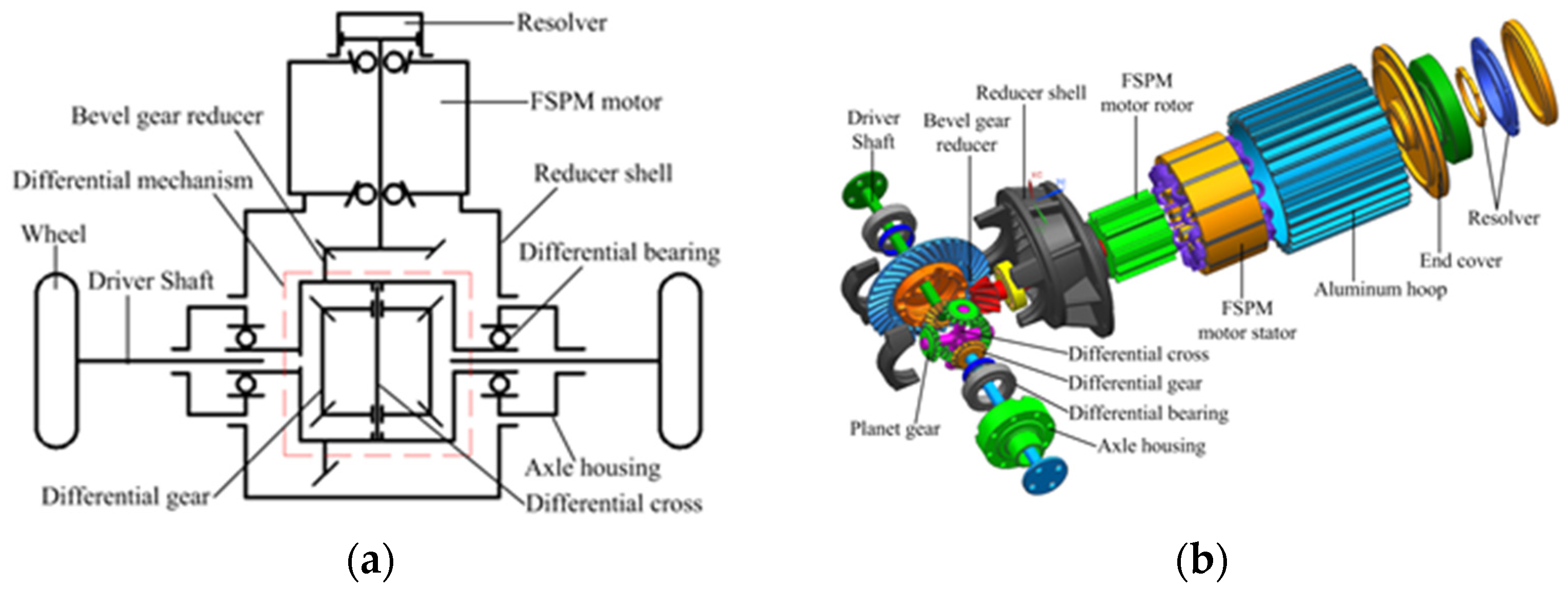
2.1. Fundamental Structure
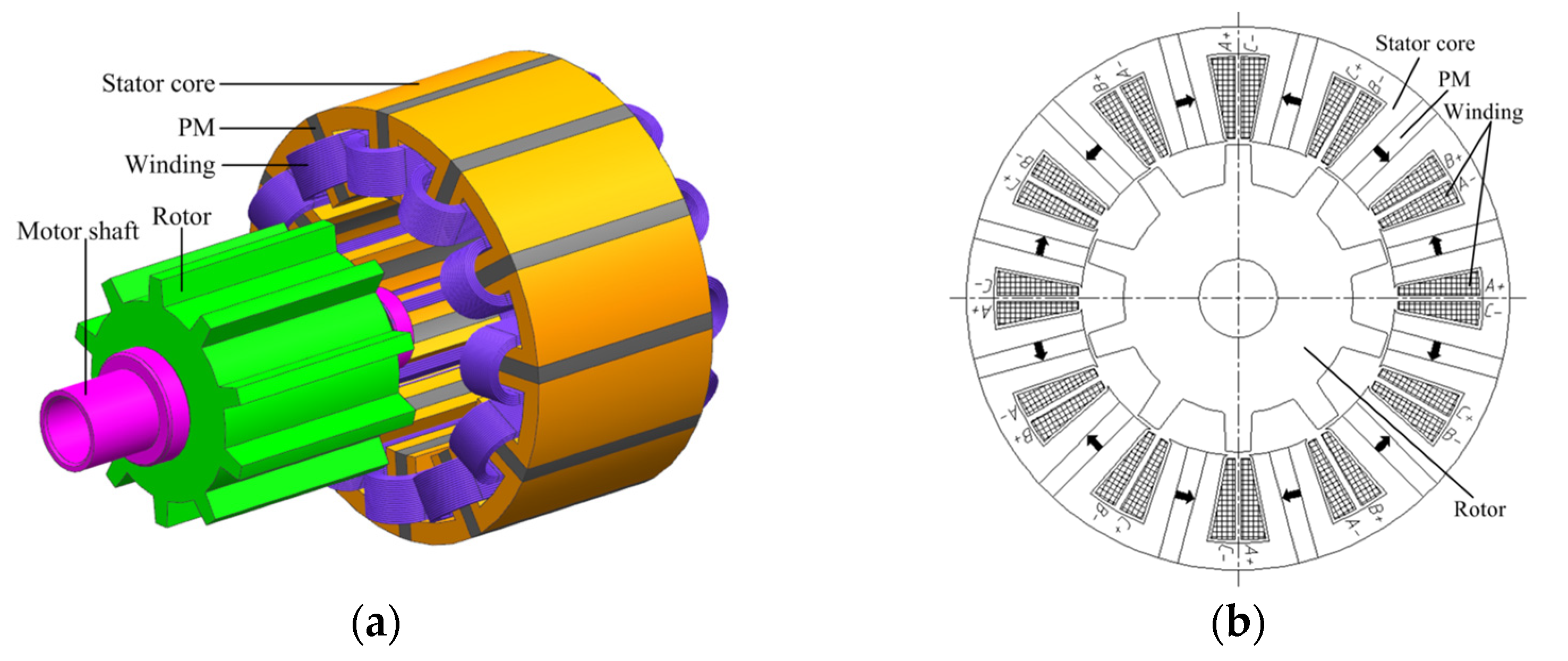
2.2. FSPM Motor
3. Optimization Method of the FSPM Motor
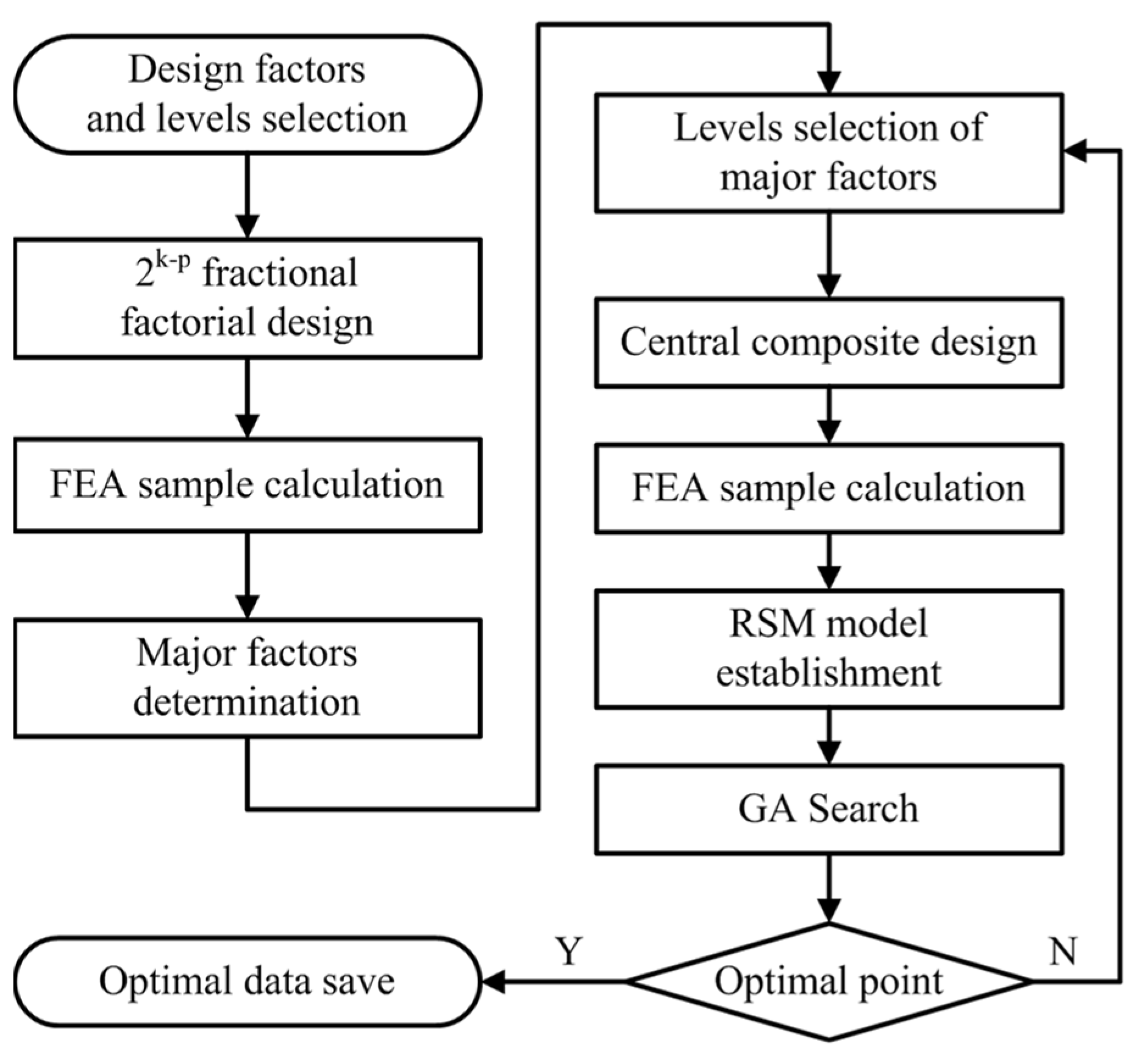
3.1. Optimization Process
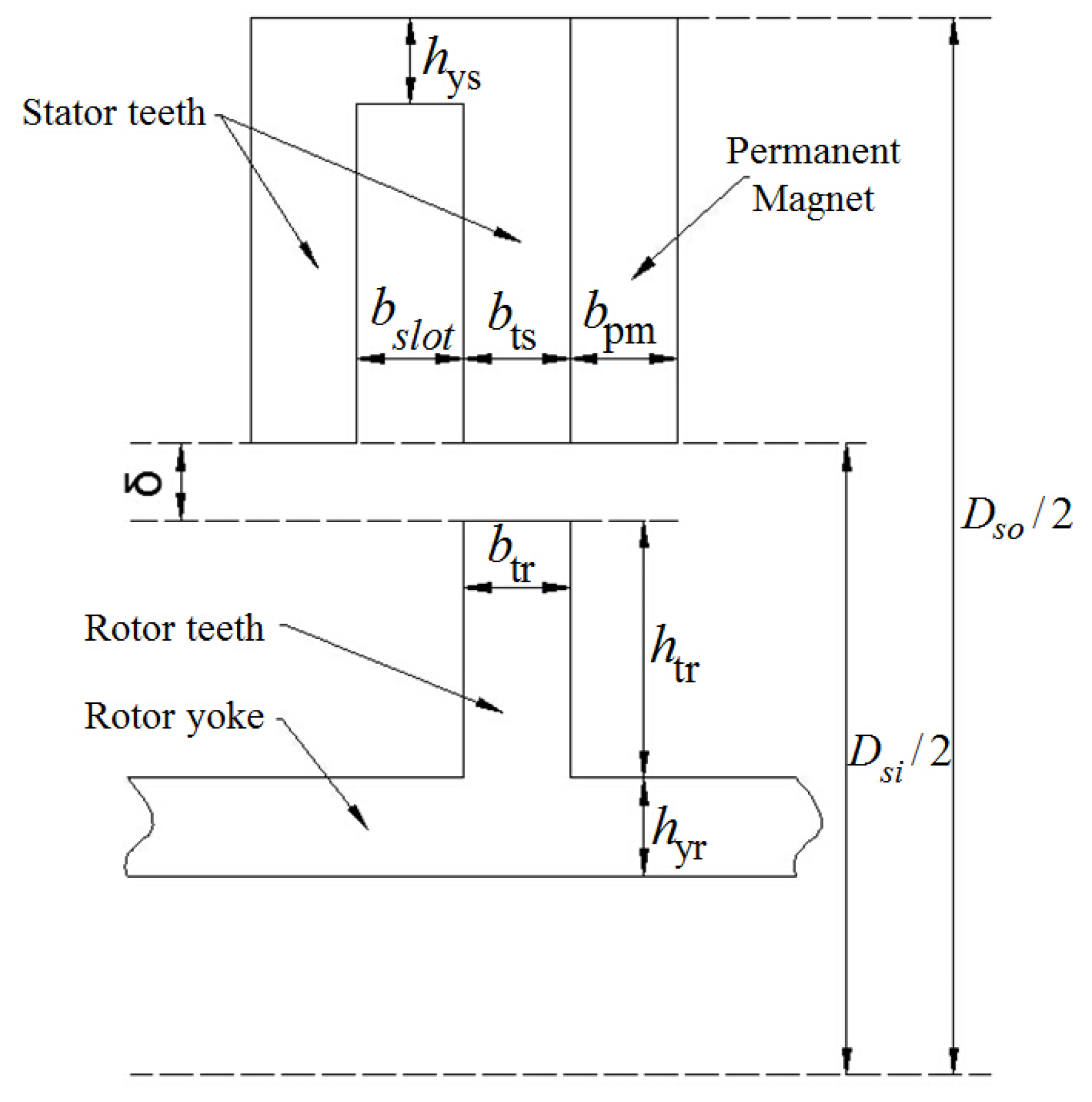
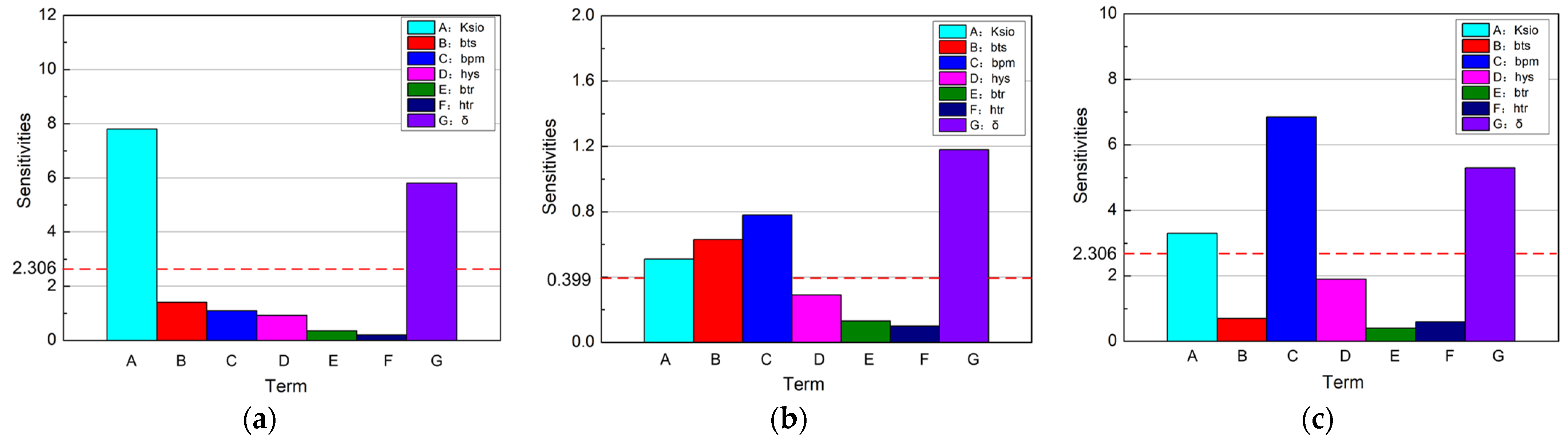
3.2. Major Impact Factors
3.3. RSM Model
3.4. GA Optimization
4. Experimental Investigation
4.1. Prototype and Testing Bench
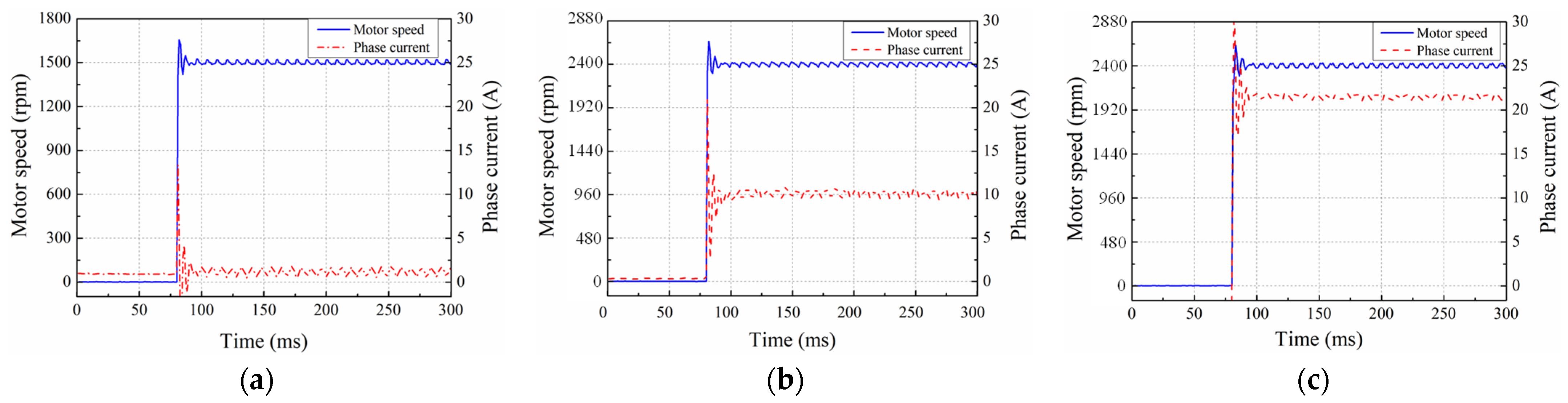
4.2. Driving Capacity
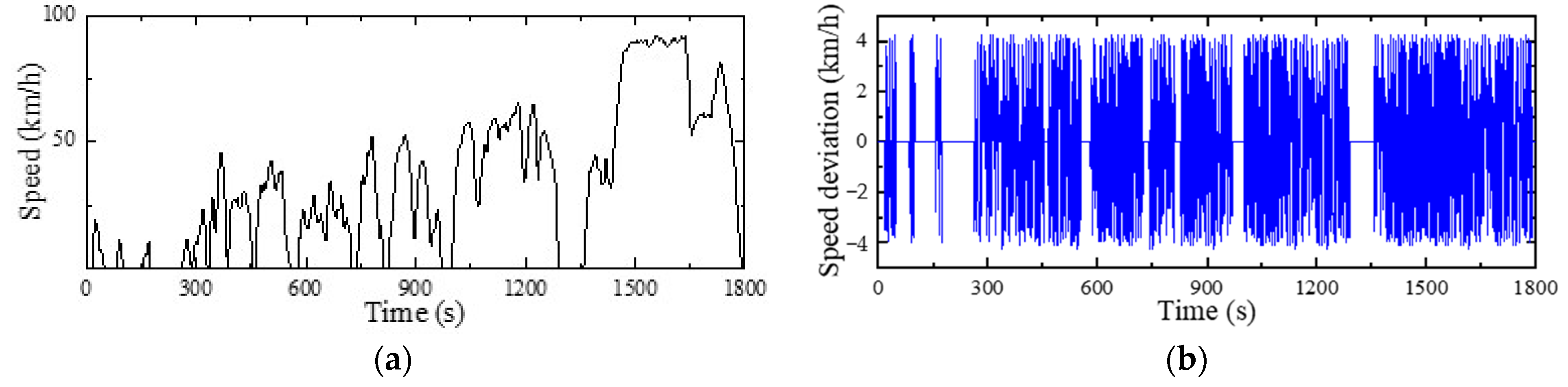
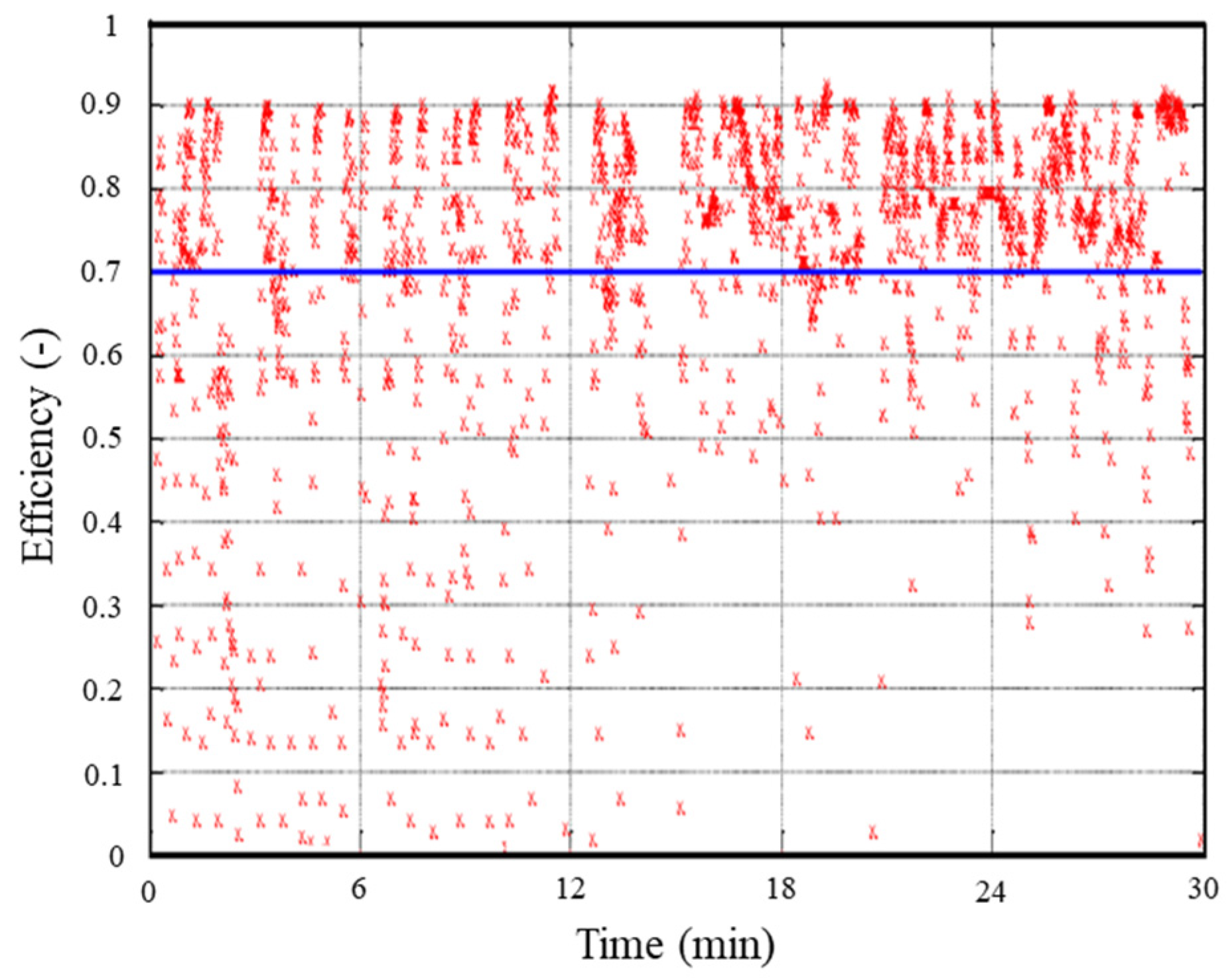
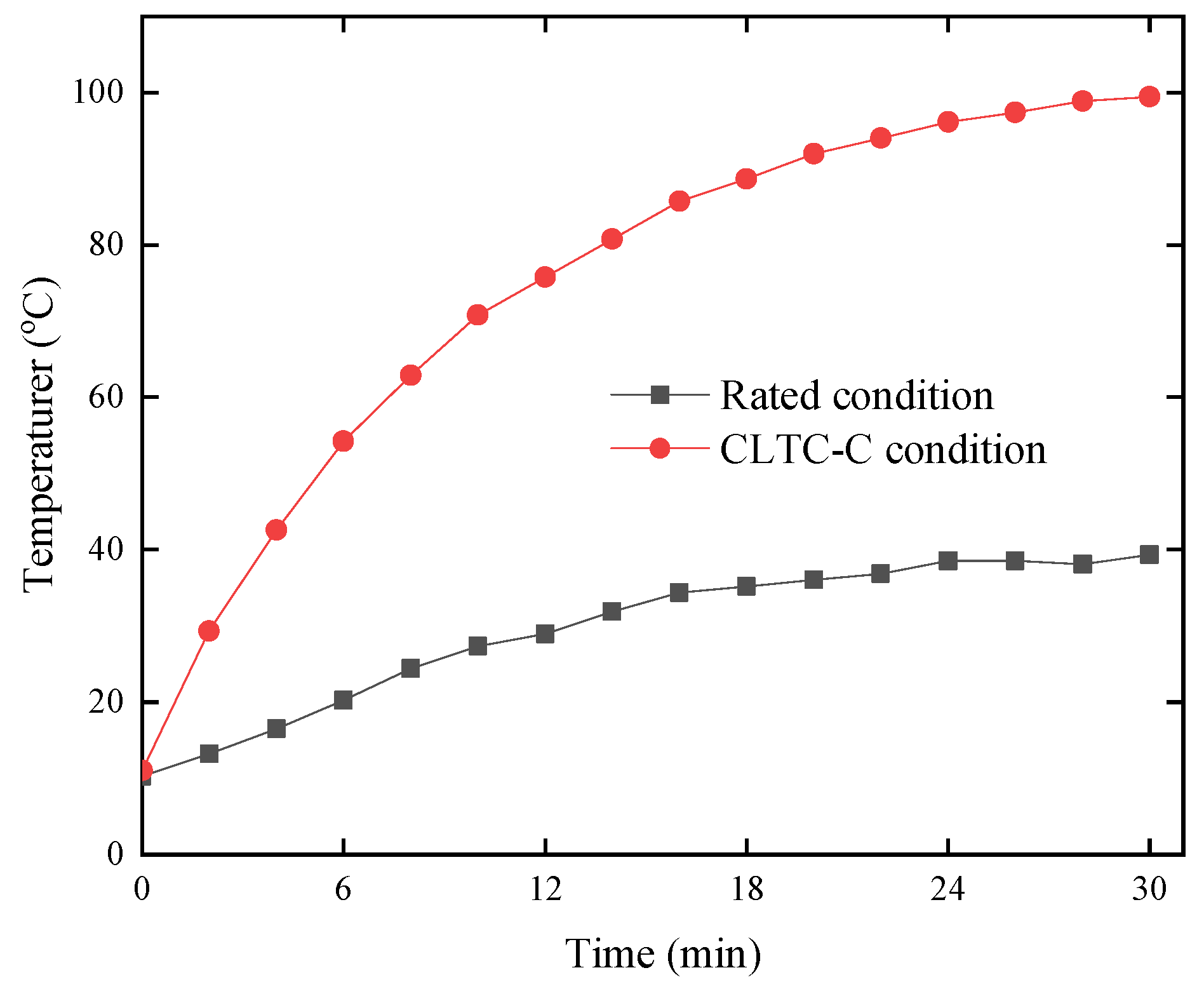
4.3. Operating Test with Driving Cycle
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, C.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Cao, W. Design consideration of fractional slot concentrated winding interior permanent magnet synchronous motor for EV and HEV applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 64116–64126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havel, A.; Sobek, M.; Stepanec, L.; Strossa, J. Optimization of Permanent Magnet Parameters in Axial Flux Rotary Converter for HEV Drive. Energies 2022, 15, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Jing, F. Study on the 12-10 flux switching integrated-starter-generator for hybrid electric vehicle application. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. D J. Automob. Eng. 2018, 232, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Credo, A.; Fabri, G.; Villani, M.; Popesscu, M. Adopting the topology optimization in the design of high-speed synchronous reluctance motors for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 5429–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.R.; Son, J.C.; Lim, D.K. Optimal design of IPMSM for fuel cell electric vehicles using autotuning elliptical niching genetic algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 117405–117412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Schofield, N. An induction machine design with parameter optimization for a 120-kW electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electr. 2020, 6, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargos, P.H.; Caetano, R.E. A performance study of a high-torque induction motor designed for light electric vehicles applications. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, Y.U.; Asfani, D.A.; Negara, I.M.Y.; Aziz, M.; Yuniarto, M.N. Technology Review of Electric Motor for Hybrid-Electric Vehicle. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), Auckland, New Zealand, 7–10 December 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muduli, U.R.; Beig, A.R.; Jaafari, K.; Alsawalhi, J.Y.; Behera, R.K. Interrupt-free operation of dual-motor four-wheel drive electric vehicle under inverter failure. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electr. 2020, 7, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, A.; Gu, C.; Bozhko, S.; Gerada, C. Performance Enhancement of Direct Torque-Controlled Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with a Flexible Switching Table. Energies 2020, 13, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyota, K.; Chiba, A. Design of switched reluctance motor competitive to 60 kW IPMSM in third generation hybrid electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 48, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Takemoto, M.; Ogasawara, S.; Ogawa, T.; Arita, H.; Daikoku, A. Development of a Consequent-Pole-PM-Type Axial-Gap Motor With DC Field Winding. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 4363–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yu, W.; Hua, W.; Cao, R.; Qiu, H.; Guo, A. The Design and Optimization of an Interior, Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Applied in an Electric Traction Vehicle Requiring a Low Torque Ripple. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.C. A novel calculation method on the current information of vector inverter for interior permanent magnet synchronous motor for electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.S. Design and Research of Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Direct Drive Hub Motor. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Precision Machinery and Manufacturing Technology (ICPMMT), Taiwan, China, 24–26 May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Fan, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S. Review on Torque Distribution Scheme of Four-Wheel In-Wheel Motor Electric Vehicle. Machines 2022, 10, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Wu, Y.; Feng, J.; Yang, K.; Jia, X.; Ma, C. Lightweight design of the in-wheel motor considering the coupled electromagnetic-thermal effect. Mech. Based Des. Struct. 2022, 50, 935–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Katsuyama, E.; Sugiura, H.; Ono, E.; Yamamoto, M. Direct yaw moment control and power consumption of in-wheel motor vehicle in steady-state turning. Vehicle Syst. Dyn. 2017, 55, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ge, B.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Influence of Control and Structure Parameters on the Starting Performance of a 12/8 Pole Switched Reluctance Motor. Energies 2020, 13, 3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howey, B.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A. Design of an External-Rotor Direct Drive E-Bike Switched Reluctance Motor. IEEE Trans. Ven. Technol. 2020, 69, 2552–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Jing, F. The numerical analysis and experimental study of flux switching motor/generator in HEV applications. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 52, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liang, J.; Zhao, Y. Optimization design and direct torque control of a flux concentrating axial flux permanent magnet motor for direct drive system. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2014, 42, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Zhang, T.; Lu, Q. Design and analysis of an outer-rotor-permanent-magnet flux-switching machine for electric vehicle applications. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercon. 2019, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnikjoo, S.A.; Asadi, F.; Abbaszadeh, K.; Abdollahi, S.E. Effect of rotor topology on the performance of counter-rotating double-sided flux switching permanent magnet generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Conver. 2022, 37, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Chau, K.T.; Lee, C.H.; Wang, H. A double-rotor flux-switching permanent-magnet motor for electric vehicles with magnetic differential. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelhassan, M.O.E.; Raminosoa, T.; Goodman, A.; Lillo, L.; Gerada, C. Stator-flux-oriented fault-tolerant control of flux-switching permanent-magnet motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 2997–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Sixel, W.; Sarlioglu, B. Design and testing of low pole dual-stator flux-switching permanent magnet machine for electric vehicle applications. IEEE T Ven. Technol. 2019, 69, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohoori, A.; Vahedi, A.; Noroozi, M.A. Design study of FSPM generator with novel outer rotor configuration for small wind turbine application. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), Krakow, Poland, 10–12 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, W.; Cheng, M.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Design of flux-switching permanent magnet machine considering the limitation of inverter and flux-weakening capability. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual Meeting of the IEEE Industry-Applications-Society (IAS), Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hendershot, J.R.; Miller, T.J.E. Design of Brushless Permanent-Magnet Machines; Motor Design Books LLC: Venice, FL, USA, 2010; p. 163. [Google Scholar]
- Hanselman, D.C. Brushless Permanent Magnet Motor Design; Magna Physics Publishing: Lebanon, OH, USA, 2003; p. 124. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmouditabar, F.; Vahedi, A. Optimum Design of FSPM Motor for Small Water Pump Application Considering Irreversible Demagnetization. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 2021, 45, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 38146.1-2019; China Automotive Test Cycle-Part 1: Light-Duty Vehicles. Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2019.


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Phase number m | 3 |
| Rated voltage Voe | 330 V |
| Rated current Aoe | 15 A |
| Rated power Poe | 7.5 kW |
| Rated speed ne | 2400 rpm |
| Rated torque Te | 30 N·m |
| Maximum speed nmax | 4000 rpm |
| Maximum torque Tmax | 65 N·m |
| Bevel gear reduction ratio | 4.2 |
| Tire diameter | 0.56 m |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Stator outer diameter, Dso | 166 mm |
| Stator inner diameter, Dsi | 96 mm |
| Stator axial length, La | 80 mm |
| Air gap length, δ | 1.2 mm |
| Phase number, m | 3 |
| Stator pole number, Ps | 12 |
| Rotor pole number, Pr | 10 |
| Number of turns per phase, Nk | 180 |
| Stator Slot open width, bslot | 7.5 Mech. degree |
| Stator tooth width, bts | 7.5 Mech. degree |
| Permanent magnet width, bpm | 7.5 Mech. degree |
| Stator yoke height, hys | 8.2 mm |
| Rotor tooth width, btr | 12 Mech. degree |
| Rotor tooth height, htr | 12 mm |
| Level | Ksio | bts (°) | bpm (°) | hys (mm) | btr (°) | htr (mm) | δ (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0.55 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 8.2 | 9 | 12 | 1.2 |
| +1 | 0.65 | 8.5 | 8.5 | 9.2 | 12 | 15 | 1.5 |
| Level | Ksio | bts (°) | bpm (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −α | 0.516 | 4.977 | 4.818 |
| −1 | 0.550 | 6.000 | 5.500 |
| 0 | 0.600 | 7.500 | 6.500 |
| +1 | 0.650 | 9.000 | 7.500 |
| +α | 0.684 | 10.020 | 8.182 |
| Part | Materials | Trademark | Material Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator | Silicon steel sheet | 35DW540 | The thickness of the monolithic piece is 0.35 mm |
| The iron loss value is 5.4 W/kg (A peak magnetic inductance of 1.5 T and a sinusoidal waveform at a frequency of 50 Hz) | |||
| Rotor | Carbon structural steel | 20# | The tensile strength is 355–500 MPa |
| The elongation is greater than or equal to 24% | |||
| Permanent magnets | NdFeB | 35SH | The remanence is 1.2 T |
| The coercivity is 890,000 A/m | |||
| The maximum operating temperature is 150 °C | |||
| The maximum energy product is 275,000 J/m3 | |||
| Winding | Copper | 1UEW | The line diameter is 1.5 mm |
| The conductivity is 580,000,000 S/m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, Y.; Shi, G.; Guo, H.; Yang, N.; Zhu, C.; Cui, M. Design and Performance Investigation of a Vehicle Drive System with a 12/10 Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Motor. Machines 2022, 10, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121216
Chi Y, Shi G, Guo H, Yang N, Zhu C, Cui M. Design and Performance Investigation of a Vehicle Drive System with a 12/10 Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Motor. Machines. 2022; 10(12):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121216
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Yada, Guangyuan Shi, Haorong Guo, Nan Yang, Chengcheng Zhu, and Minchao Cui. 2022. "Design and Performance Investigation of a Vehicle Drive System with a 12/10 Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Motor" Machines 10, no. 12: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121216
APA StyleChi, Y., Shi, G., Guo, H., Yang, N., Zhu, C., & Cui, M. (2022). Design and Performance Investigation of a Vehicle Drive System with a 12/10 Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Motor. Machines, 10(12), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10121216






