Investigation of Cell Concentration Change and Cell Aggregation Due to Cell Sedimentation during Inkjet-Based Bioprinting of Cell-Laden Bioink
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioink Preparation
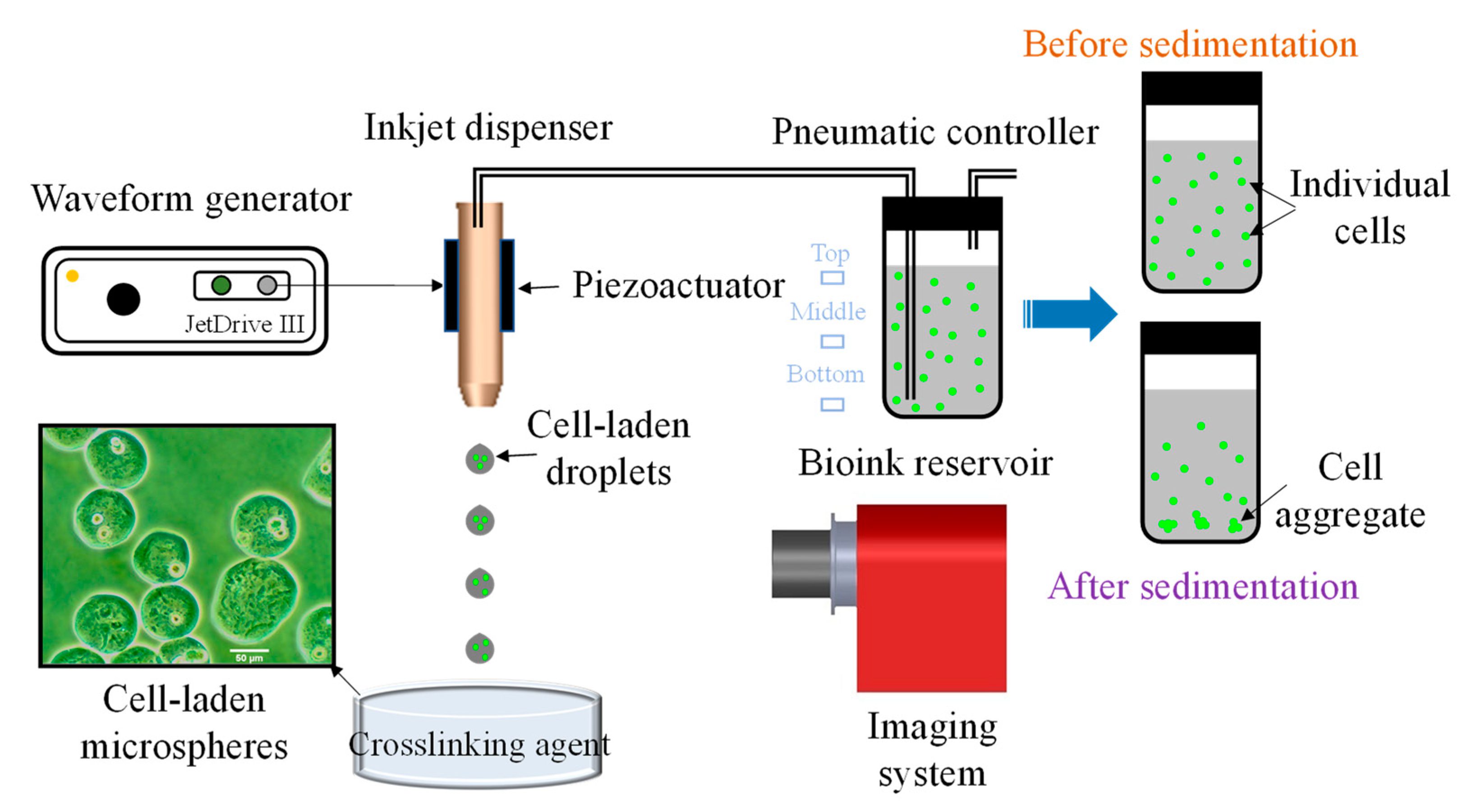
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Cell Aggregation Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
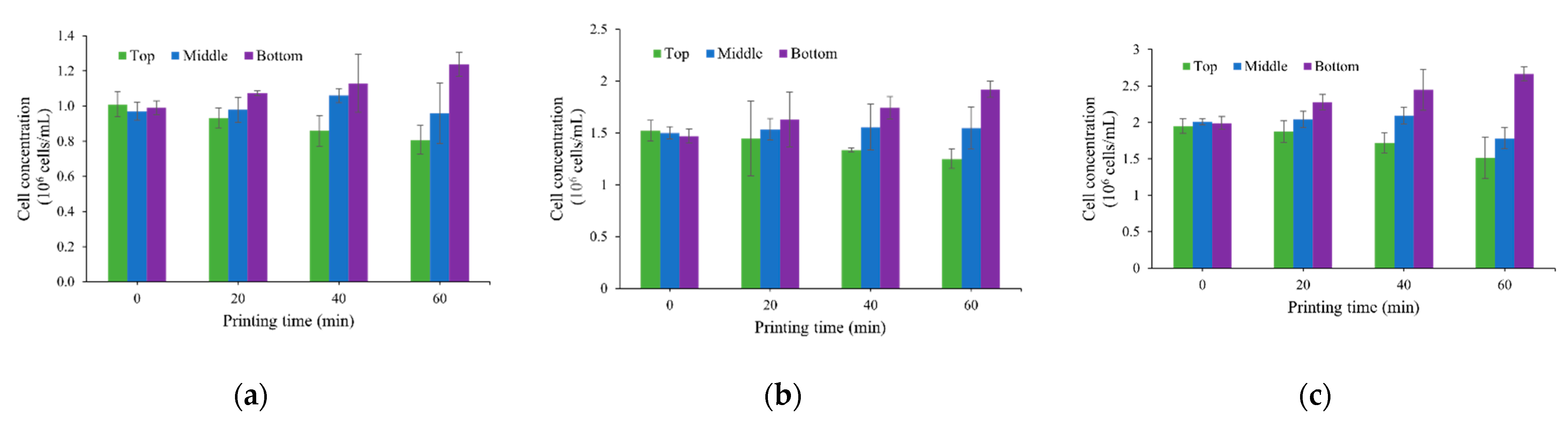
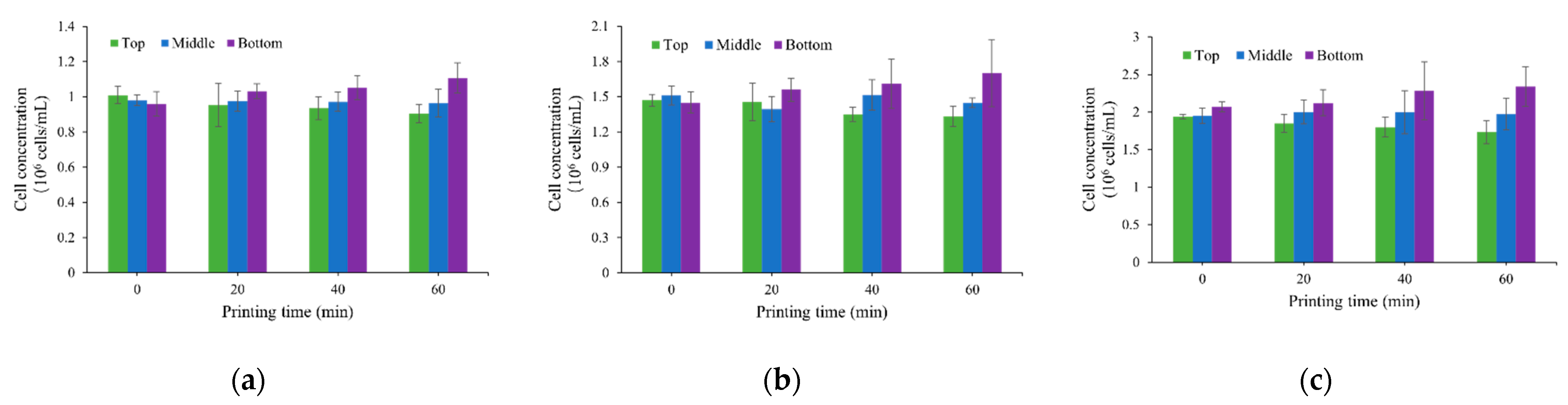
3.1. Cell Concentration Change Due to Cell Sedimentation
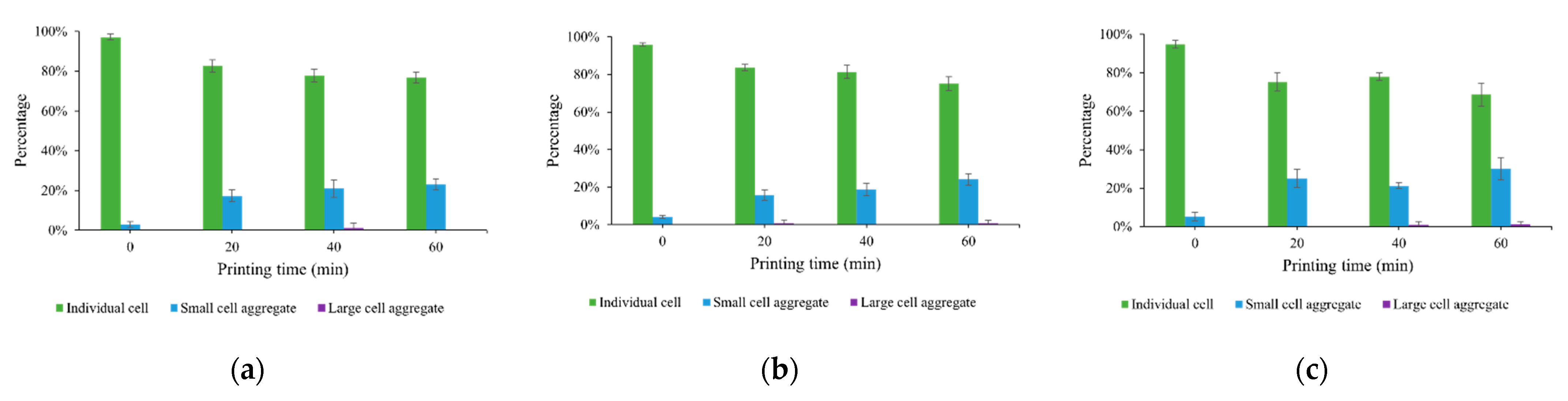
3.2. Cell Aggregation Due to Cell Sedimentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, S.V.; Atala, A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Luo, Y.; Ma, L.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.; Xue, Q.; Yang, H.; Cui, Z. 3D bioprinting: An emerging technology full of opportunities and challenges. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2018, 1, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor-Ozkerim, P.S.; Inci, I.; Zhang, Y.S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Dokmeci, M.R. Bioinks for 3D bioprinting: An overview. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 915–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, S.; Guvendiren, M. Recent advances in bioink design for 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2017, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Lee, J.M.; Yeong, W.Y. Smart hydrogels for 3D bioprinting. Int. J. Bioprint. 2015, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Melo, B.A.; Jodat, Y.A.; Cruz, E.M.; Benincasa, J.C.; Shin, S.R.; Porcionatto, M.A. Strategies to use fibrinogen as bioink for 3D bioprinting fibrin-based soft and hard tissues. Acta Biomater. 2020, 117, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Hudson, A.; Shiwarski, D.; Tashman, J.; Hinton, T.; Yerneni, S.; Bliley, J.; Campbell, P.; Feinberg, A. 3D bioprinting of collagen to rebuild components of the human heart. Science 2019, 365, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Chimene, D.; Garza, J.E.; Gaharwar, A.K.; Alge, D.L. Clickable PEG hydrogel microspheres as building blocks for 3D bioprinting. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, L.K.; Huebner, P.; Fisher, M.B.; Spang, J.T.; Starly, B.; Shirwaiker, R.A. 3D-bioprinting of polylactic acid (PLA) nanofiber–alginate hydrogel bioink containing human adipose-derived stem cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1732–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garreta, E.; Oria, R.; Tarantino, C.; Pla-Roca, M.; Prado, P.; Fernandez-Aviles, F.; Campistol, J.M.; Samitier, J.; Montserrat, N. Tissue engineering by decellularization and 3D bioprinting. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaebel, R.; Ma, N.; Liu, J.; Guan, J.; Koch, L.; Klopsch, C.; Gruene, M.; Toelk, A.; Wang, W.; Mark, P. Patterning human stem cells and endothelial cells with laser printing for cardiac regeneration. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9218–9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubo, N.; Garcia, M.; Del Canizo, J.F.; Velasco, D.; Jorcano, J.L. 3D bioprinting of functional human skin: Production and in vivo analysis. Biofabrication 2016, 9, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, B.; Hockaday, L.A.; Kang, K.H.; Butcher, J.T. 3D bioprinting of heterogeneous aortic valve conduits with alginate/gelatin hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 101, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Chen, M.; Fan, X.; Zhou, H. Recent advances in bioprinting techniques: Approaches, applications and future prospects. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, M.; Kobayashi, A.; Takagi, F.; Watanabe, A.; Hiruma, Y.; Ohuchi, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Horie, M.; Morita, I.; Takatani, S. Biocompatible inkjet printing technique for designed seeding of individual living cells. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbolat, I.T.; Hospodiuk, M. Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, R.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, W.; Chrisey, D.B.; Huang, Y. Study of gelatin as an effective energy absorbing layer for laser bioprinting. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 024103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Abdulla, R.; Parker, B.; Samanipour, R.; Ghosh, S.; Kim, K. A simple and high-resolution stereolithography-based 3D bioprinting system using visible light crosslinkable bioinks. Biofabrication 2015, 7, 045009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudapati, H.; Dey, M.; Ozbolat, I. A comprehensive review on droplet-based bioprinting: Past, present and future. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Pei, B.; Chen, J.; Zhou, D.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, W.; Xu, T. Inkjet bioprinting of biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10793–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Casillas, J.; Xu, C. Effects of printing conditions on cell distribution within microspheres during inkjet-based bioprinting. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 095055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.E.; Gough, J.E.; Derby, B. Delivery of human fibroblast cells by piezoelectric drop-on-demand inkjet printing. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, R.E.; Derby, B. Inkjet printing biomaterials for tissue engineering: Bioprinting. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 430–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C. Sedimentation study of bioink containing living cells. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 114901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendekie, Z.B.; Bacchin, P. Colloidal jamming dynamics in microchannel bottlenecks. Langmuir 2016, 32, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chahal, D.; Ahmadi, A.; Cheung, K.C. Improving piezoelectric cell printing accuracy and reliability through neutral buoyancy of suspensions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2932–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsa, S.; Gupta, M.; Loizeau, F.; Cheung, K.C. Effects of surfactant and gentle agitation on inkjet dispensing of living cells. Biofabrication 2010, 2, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.; Xiong, R.; Chrisey, D.B.; Huang, Y. Effects of living cells on the bioink printability during laser printing. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 034120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, J.; Roy, A.; Das, A.; Ghosh, M.; Thomas, S.; Sinha, A.; Kim, J.; Saha, P. Effects of processing parameters of 3D bioprinting on the cellular activity of bioinks. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2000179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, M.E.; Seshadri, V.; Burg, T.; Booth, B.W.; Burg, K.J.; Groff, R.E. Cell settling effects on a thermal inkjet bioprinter. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 3609–3612. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.; Sudau, K.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, S.J.; Willenbacher, N. Optimization of experimental parameters to suppress nozzle clogging in inkjet printing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 13195–13204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringeisen, B.R.; Othon, C.M.; Barron, J.A.; Young, D.; Spargo, B.J. Jet-based methods to print living cells. Biotechnol. J. Healthc. Nutr. Technol. 2006, 1, 930–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, A.; Levato, R.; D’Este, M.; Piluso, S.; Eglin, D.; Malda, J. Printability and shape fidelity of bioinks in 3D bioprinting. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 11028–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axpe, E.; Oyen, M.L. Applications of alginate-based bioinks in 3D bioprinting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Song, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C. Ligament flow during drop-on-demand inkjet printing of bioink containing living cells. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 124904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chai, W.; Huang, Y.; Markwald, R.R. Scaffold-free inkjet printing of three-dimensional zigzag cellular tubes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 3152–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Ogale, A.; Fu, J.; Markwald, R.R. Study of droplet formation process during drop-on-demand inkjetting of living cell-laden bioink. Langmuir 2014, 30, 9130–9138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C. Cell sedimentation during 3D bioprinting: A mini review. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Martinez Salazar, D.M.; Xu, C. Investigation of Cell Concentration Change and Cell Aggregation Due to Cell Sedimentation during Inkjet-Based Bioprinting of Cell-Laden Bioink. Machines 2022, 10, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10050315
Xu H, Martinez Salazar DM, Xu C. Investigation of Cell Concentration Change and Cell Aggregation Due to Cell Sedimentation during Inkjet-Based Bioprinting of Cell-Laden Bioink. Machines. 2022; 10(5):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10050315
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Heqi, Dulce Maria Martinez Salazar, and Changxue Xu. 2022. "Investigation of Cell Concentration Change and Cell Aggregation Due to Cell Sedimentation during Inkjet-Based Bioprinting of Cell-Laden Bioink" Machines 10, no. 5: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10050315
APA StyleXu, H., Martinez Salazar, D. M., & Xu, C. (2022). Investigation of Cell Concentration Change and Cell Aggregation Due to Cell Sedimentation during Inkjet-Based Bioprinting of Cell-Laden Bioink. Machines, 10(5), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10050315





