Integrated Smart Warehouse and Manufacturing Management with Demand Forecasting in Small-Scale Cyclical Industries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Digital Twins and Smart Warehouse Management
2.2. Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization
3. Methodology
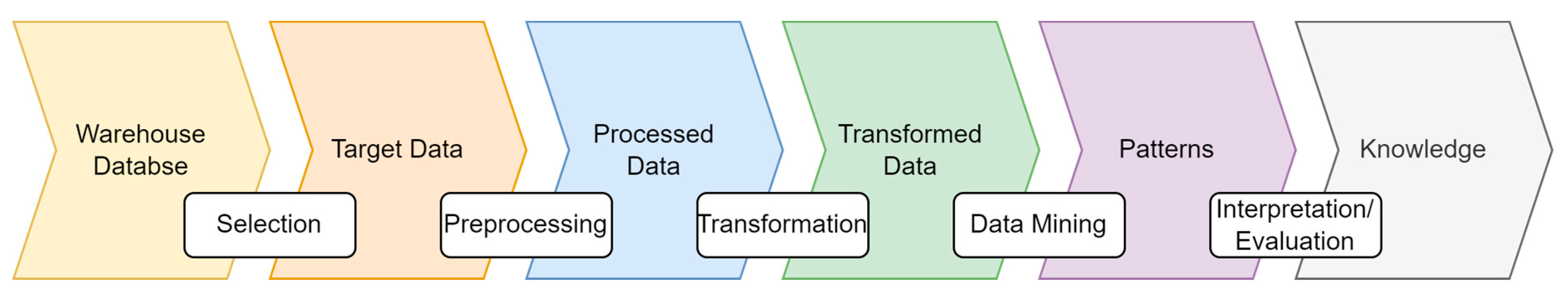
3.1. Data Acquisition and Preparation
3.2. Roulette Genetic Algorithm
- The maximum number of generations is exceeded;
- Or, the average change in the fitness value is less than the other options.
3.3. Inventory Optimization
3.4. Proposed Digital Twin in Smart Warehouse
4. Results
4.1. Roulette GA Settings
- Population size: 1000.
- Constraint-dependent mutation function.
- Constraint-dependent crossover function.
- Crossover fraction: 0.2.
- Stopping criteria generation: 1000.
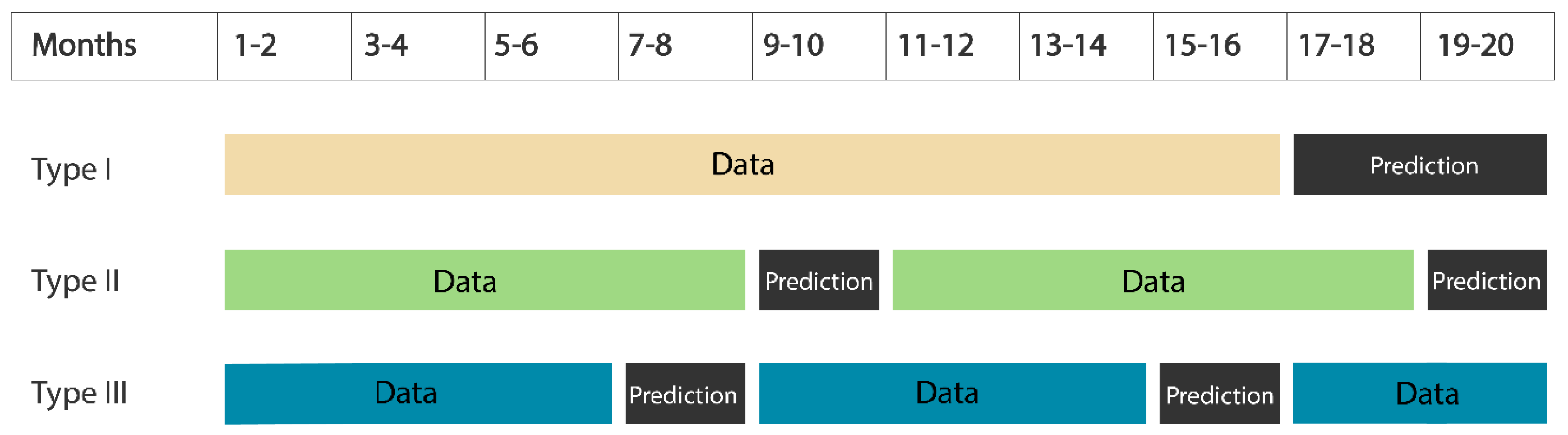
4.2. Demand Forecasting
4.3. Inventory Optimization
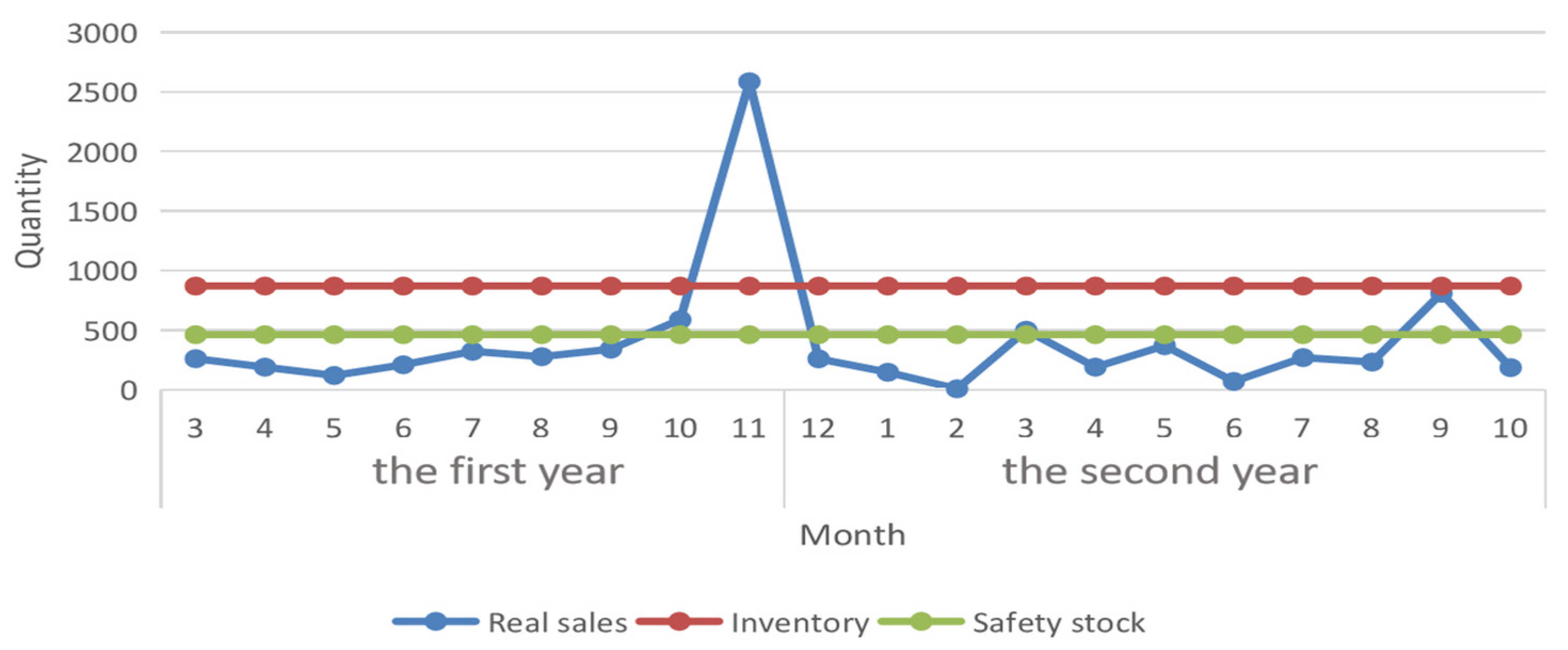
4.3.1. Safety Stock Statistical Model
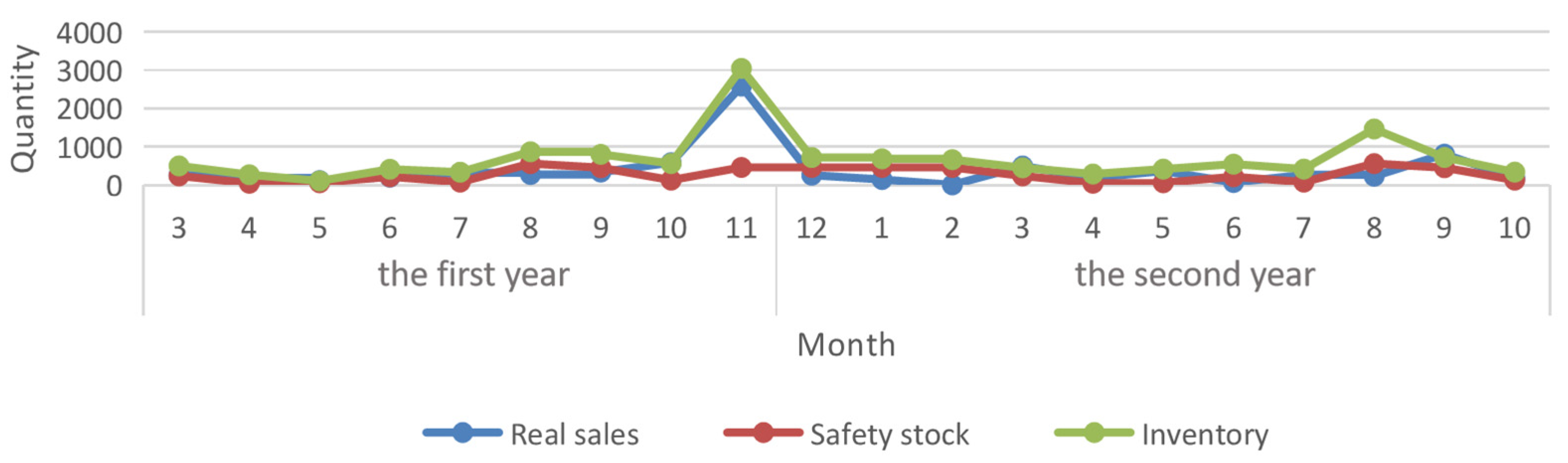
4.3.2. Dynamic Safety Stock Level Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Y.; Lin, B. Time-varying effects of cyclical fluctuations in China’s energy industry on the macro economy and carbon emissions. Energy 2018, 155, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobetz, W.; Menzel, C.; Schröder, H. Systematic risk behavior in cyclical industries: The case of shipping. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2016, 88, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chau, K.; Hong, L.; Ip, Y.; Yan, W. Financial Innovation in Digital Payment with WeChat towards Electronic Business Success. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 16, 1844–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesha, H.R.; Aithal, P. Integrated Inventory Management Control Framework. Int. J. Manag. Technol. Soc. Sci. IJMTS 2020, 5, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Jiang, W. A new belief Markov chain model and its application in inventory prediction. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 2800–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talib, F.; Asjad, M.; Attri, R.; Siddiquee, A.N.; Khan, Z.A. A road map for the implementation of integrated JIT-lean practices in Indian manufacturing industries using the best-worst method approach. J. Ind. Prod. Eng. 2020, 37, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Luo, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Genetic algorithm combined with BP neural network in hospital drug inventory management system. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 1981–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrzad, B.M.; Alidoosti, Z. A realistic perish ability inventory management for location-inventory-routing problem based on Genetic Algorithm. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. Stud. 2018, 5, 106–121. [Google Scholar]
- Chau, K.-Y.; Tang, Y.M.; Liu, X.; Ip, Y.-K.; Tao, Y. Investigation of critical success factors for improving supply chain quality management in manufacturing. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2021, 15, 1418–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, G.; Tang, Y.M.; Tsang, K.Y.; Tang, V.; Chau, K.Y. A blockchain-based system to enhance aircraft parts traceability and trackability for inventory management. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 179, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, K.L.; Ho, G.T.S.; Tang, Y.M.; Ip, W.H. Inventory classification system in space mission component replenishment using multi-attribute fuzzy ABC classification. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2021, 121, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejesh, S.B.S.; Neeraja, S. Warehouse inventory management system using IoT and open source framework. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 3817–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binos, T.; Bruno, V.; Adamopoulos, A. Intelligent agent based framework to augment warehouse management systems for dynamic demand environments. Australas. J. Inf. Syst. 2021, 25, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.M.; Chau, K.Y.; Xu, D.; Liu, X. Consumer perceptions to support IoT based smart parcel locker logistics in China. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2021, 62, 102659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weißhuhn, S.; Hoberg, K. Designing smart replenishment systems: Internet-of-Things technology for vendor-managed inventory at end consumers. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 295, 949–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Lin, P.; Guo, D.; Huang, G.Q. Towards zero-warehousing smart manufacturing from zero-inventory just-in-time production. Robot. Comput. -Integr. Manuf. 2020, 64, 101932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Geest, M.; Tekinerdogan, B.; Catal, C. Design of a reference architecture for developing smart warehouses in industry 4.0. Comput. Ind. 2021, 124, 103343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, K.-L.; Tang, Y.-M.; Ip, W.-H.; Kuo, W.-T. A systematic review of product design for space instrument innovation, reliability, and manufacturing. Machines 2021, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chau, K.-Y.; Li, W.; Wan, T. Forecasting economic recession through share price in the logistics industry with artificial intelligence (AI). Computation 2020, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Tao, F.; Hu, T.; Answer, N.; Liu, A.; Wei, Y.; Wang, L.; Nee, A.Y.C. Enabling technologies and tools for digital twin. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fang, S.; Dong, H.; Xu, C. Review of digital twin about concepts, technologies, and industrial applications. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Leng, J.; Yan, D.; Zhang, D.; Wei, L.; Yu, A.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Digital twin-based designing of the configuration, motion, control, and optimization model of a flow-type smart manufacturing system. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Qiu, X.; Jing, G.; Tang, J.; Zhu, Y. Digital twin-based decision making paradigm of raise boring method. J. Intell. Manuf. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Yan, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, G.; Wei, L.; Zhang, D.; Yu, A.; Chen, X. Digital twin-driven joint optimisation of packing and storage assignment in large-scale automated high-rise warehouse product-service system. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2021, 34, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A. A digital supply chain twin for managing the disruption risks and resilience in the era of Industry 4.0. Prod. Plan. Control. 2020, 32, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Tolk, A.; Pyles, A.; Van Balen, N.; Bergollo, K. Digital twin modeling, co-simulation and cyber use-case inclusion methodology for IoT systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), National Harbor, MD, USA, 8–11 December 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abideen, A.; Mohamad, F.B. Improving the performance of a Malaysian pharmaceutical warehouse supply chain by integrating value stream mapping and discrete event simulation. J. Model. Manag. 2020, 16, 70–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafian, A.; Pettersen, O.-G.; Kuntze, K.N.; Franke, J.; Alfnes, E.; Henriksen, K.F.; Spone, J. Full-scale discrete event simulation of an automated modular conveyor system for warehouse logistics. In Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Advances in Production Management Systems, Austin, TX, USA, 1–5 September 2019; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.Y. Improving warehouse responsiveness by job priority management: A European distribution centre field study. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 139, 105564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, N.; Ierapetritou, M. Supply chain management using an optimization driven simulation approach. AIChE J. 2013, 59, 4612–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Blanco-Novoa, O.; Froiz-Míguez, I.; Fraga-Lamas, P. Towards an autonomous industry 4.0 warehouse: A UAV and blockchain-based system for inventory and traceability applications in big data-driven supply chain management. Sensors 2019, 19, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M. Using data driven simulation to build inventory model. In Proceedings of the 2008 Winter Simulation Conference, Miami, FL, USA, 7–10 December 2008; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Loaiza, J.H.; Cloutier, R.J. Analyzing the implementation of a digital twin manufacturing system: Using a systems thinking approach. Systems 2022, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, C.W. Demand-Driven Forecasting: A Structured Approach to Forecasting; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Darmanyan, A.; Rogachev, A. Modeling and forecasting seasonal and cyclical events using retrospective data. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 217, 06007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Michalewicz, Z. Genetic Algorithms + Data Structures = Evolution Programs; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.-B.; Chang, J. Combined forecasting of regional logistics demand optimized by genetic algorithm. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2014, 4, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liang, C.-Y.; Hong, W.-C.; Gu, D.-X. Forecasting holiday daily tourist flow based on seasonal support vector regression with adaptive genetic algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 26, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermpinis, G.; Stasinakis, C.; Theofilatos, K.; Karathanasopoulos, A. Modeling, forecasting and trading the EUR exchange rates with hybrid rolling genetic algorithms—Support vector regression forecast combinations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 247, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakhuja, S.; Jain, V.; Kumar, S.; Chandra, C.; Ghildayal, S.K. Genetic algorithm based fuzzy time series tourism demand forecast model. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2016, 116, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Chin, K.S.; Wang, L.; Qu, G.; Tsui, K.L. Modified genetic algorithm-based feature selection combined with pre-trained deep neural network for demand forecasting in outpatient department. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 82, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Sarker, B.R. Integrated production-inventory and pricing decisions for a single-manufacturer multi-retailer system of deteriorating items under JIT delivery policy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 89, 2099–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isen, E.; Boran, S. A novel approach based on combining ANFIS, genetic algorithm and fuzzy c-means methods for multiple criteria inventory classification. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 3229–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, A.; Kundu, S.; Sannigrahi, T.; Goyal, S.K. An application of tournament genetic algorithm in a marketing oriented economic production lot-size model for deteriorating items. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2009, 119, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-B.; Yoo, J.-S.; Park, H.-S. A genetic algorithm for the vendor-managed inventory routing problem with lost sales. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 53, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadeh, A.; Elahi, S.; Farahani, M.H.; Nasirian, B. A genetic algorithm-Taguchi based approach to inventory routing problem of a single perishable product with transshipment. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 104, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiassat, A.; Diabat, A.; Rahwan, I. A genetic algorithm approach for location-inventory-routing problem with perishable products. J. Manuf. Syst. 2017, 42, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezig, E.K.; Cao, L.; Stonebraker, M.; Simonini, G.; Tao, W.; Madden, S.; Ouzzani, M.; Tang, N.; Elmagarmid, A.K. Data civilizer 2.0: A holistic framework for data preparation and analytics. Proc. VLDB Endow. 2019, 12, 1954–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodak, G.; Kwaśnicki, W. Genetic Algorithms in Seasonal Demand Forecasting; Wroclaw University of Technology: Wrocław, Poland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.K.H. A review of applications of genetic algorithms in operations management. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 76, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beşkirli, M. Solving continuous optimization problems using the tree seed algorithm developed with the roulette wheel strategy. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 170, 114579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammano, A.; Teekeng, W. A modified genetic algorithm with fuzzy roulette wheel selection for job-shop scheduling problems. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2015, 44, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunaud, B.; Laínez-Aguirre, J.M.; Pinto, J.M.; Grossmann, I.E. Inventory policies and safety stock optimization for supply chain planning. AIChE J. 2019, 65, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radasanu, A.C. Inventory management, service level and safety stock. J. Public Adm. Financ. Law 2016, 09, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Yadollahi, E.; Aghezzaf, E.H.; Raa, B. Managing inventory and service levels in a safety stock-based inventory routing system with stochastic retailer demands. Appl. Stoch. Models Bus. Ind. 2017, 33, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferbar Tratar, L. Minimising inventory costs by properly choosing the level of safety stock. Econ. Bus. Rev. 2009, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inegbedion, H.; Eze, S.; Asaleye, A.; Lawal, A. Inventory management and organisational efficiency. J. Soc. Sci. Res. 2019, 5, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Methods | Strengths (Similarity) | Strengths (Similarity) | Weakness (Similarity) | Weaknesses (Difference) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The moving average (MA) |
| N/A |
|
|
| Simple exponential smoothing (SES) |
| N/A | ||
| Holt’s two-parameter |
|
|
|
|
| Holt–Winters method |
|
|
| Error | Type I | Type II | Type III |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. error | 78.90 | 56.80 | 44.20 |
| RMSE | 120.72 | 91.76 | 103.98 |
| % error | 19.59 | 22.18 | 10.62 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Y.-M.; Ho, G.T.S.; Lau, Y.-Y.; Tsui, S.-Y. Integrated Smart Warehouse and Manufacturing Management with Demand Forecasting in Small-Scale Cyclical Industries. Machines 2022, 10, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10060472
Tang Y-M, Ho GTS, Lau Y-Y, Tsui S-Y. Integrated Smart Warehouse and Manufacturing Management with Demand Forecasting in Small-Scale Cyclical Industries. Machines. 2022; 10(6):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10060472
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Yuk-Ming, George To Sum Ho, Yui-Yip Lau, and Shuk-Ying Tsui. 2022. "Integrated Smart Warehouse and Manufacturing Management with Demand Forecasting in Small-Scale Cyclical Industries" Machines 10, no. 6: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10060472
APA StyleTang, Y.-M., Ho, G. T. S., Lau, Y.-Y., & Tsui, S.-Y. (2022). Integrated Smart Warehouse and Manufacturing Management with Demand Forecasting in Small-Scale Cyclical Industries. Machines, 10(6), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10060472









