Design and Performance Evaluation of a Novel Slave System for Endovascular Tele-Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Related Work
1.2. Our Contribution
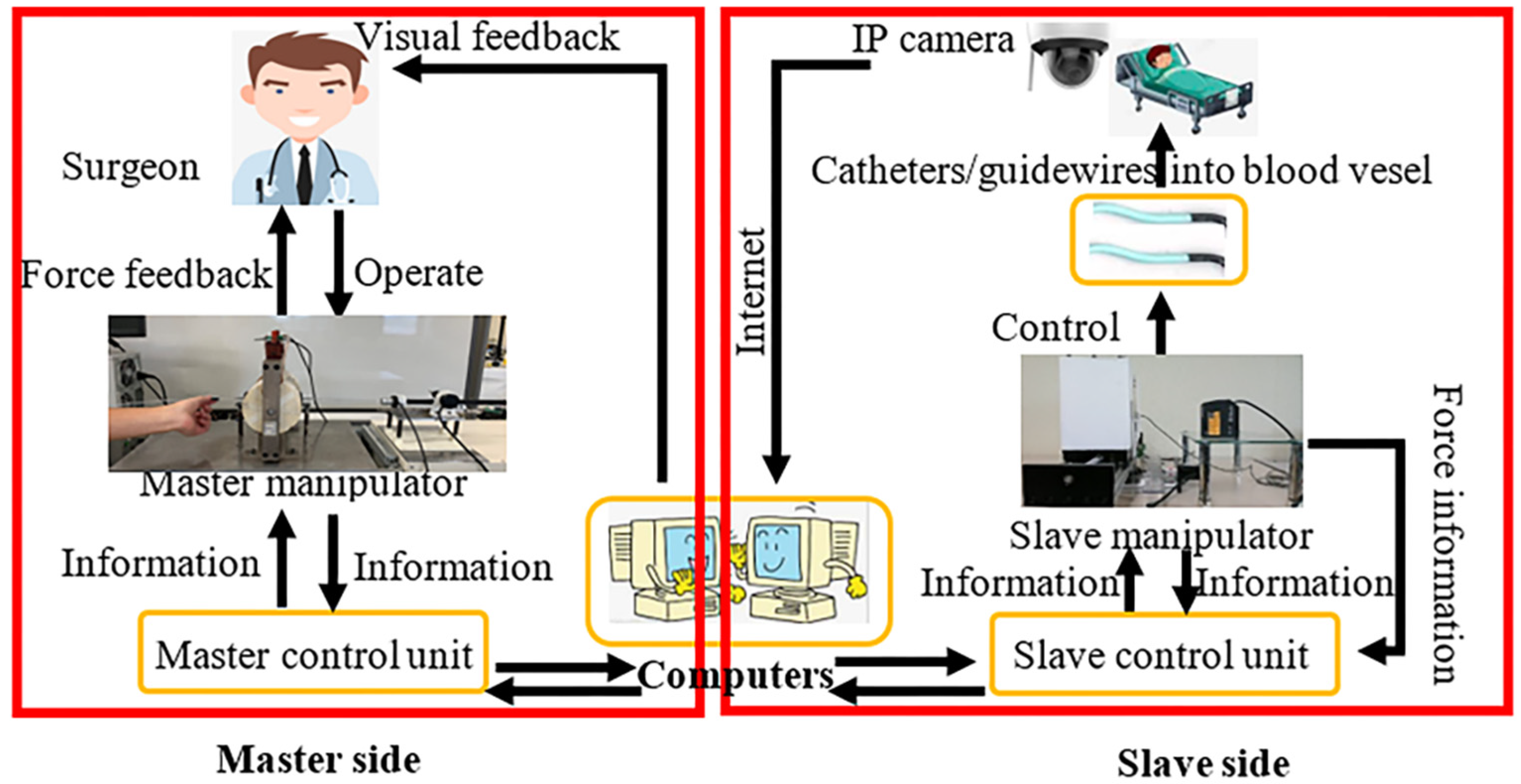
2. Our Robotic System
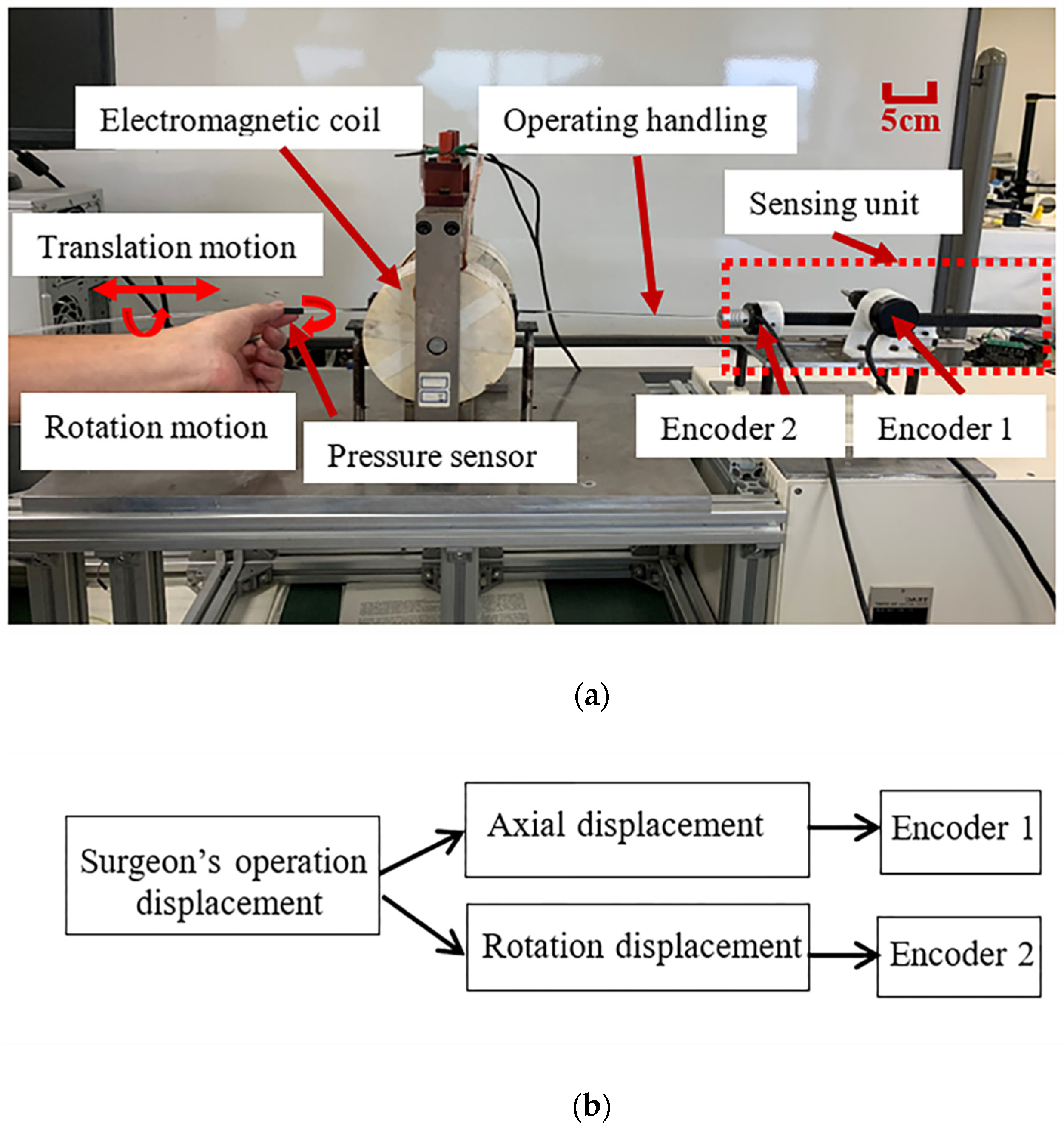
2.1. Introduction of the Master System
- Recording the radial and axial displacement information of the surgeon’s hand when the surgeon is operating the operating handling device;
- Providing the surgeon with axial and radial force feedback;
- Following the operating habits of traditional surgeons.
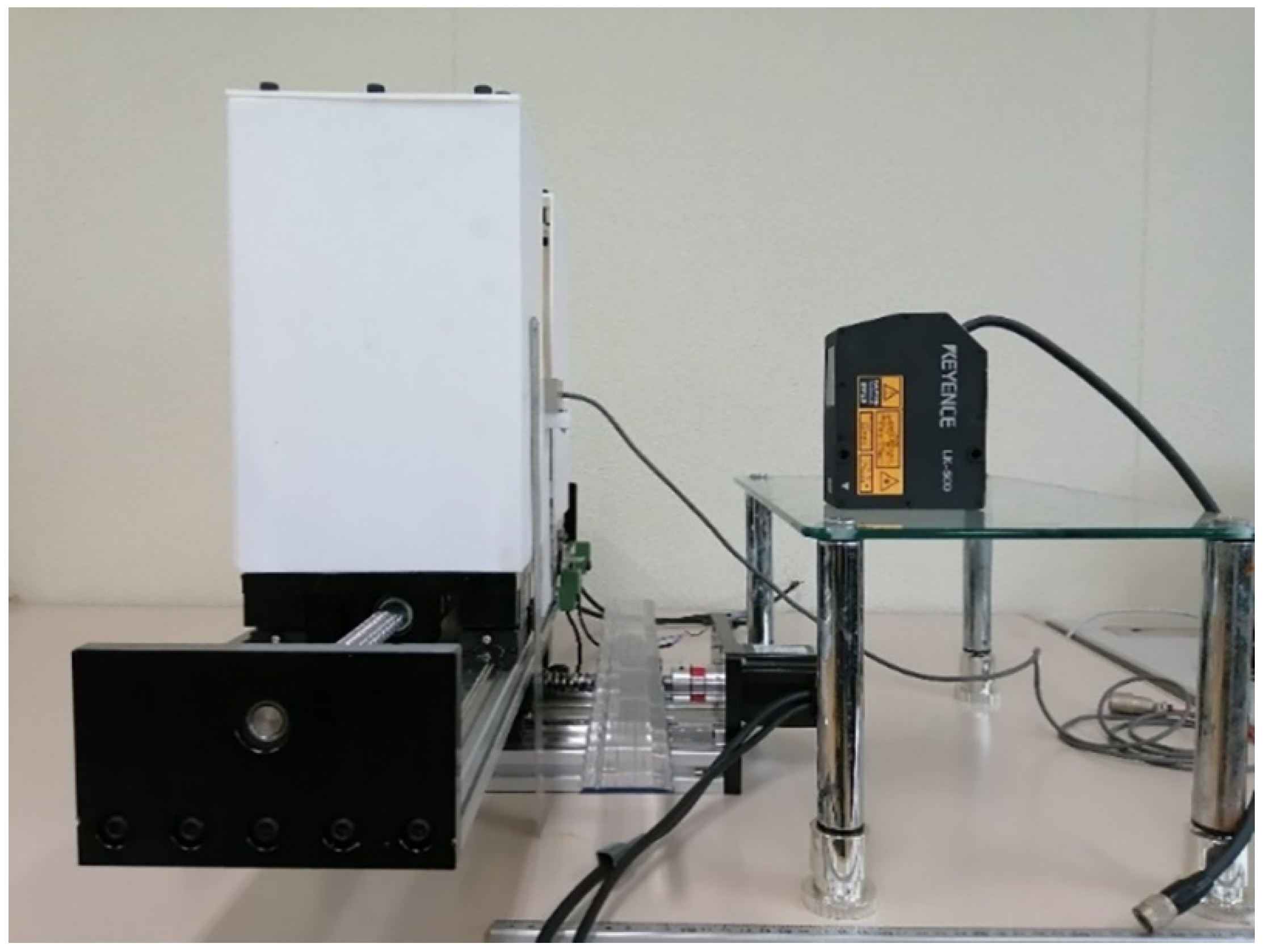
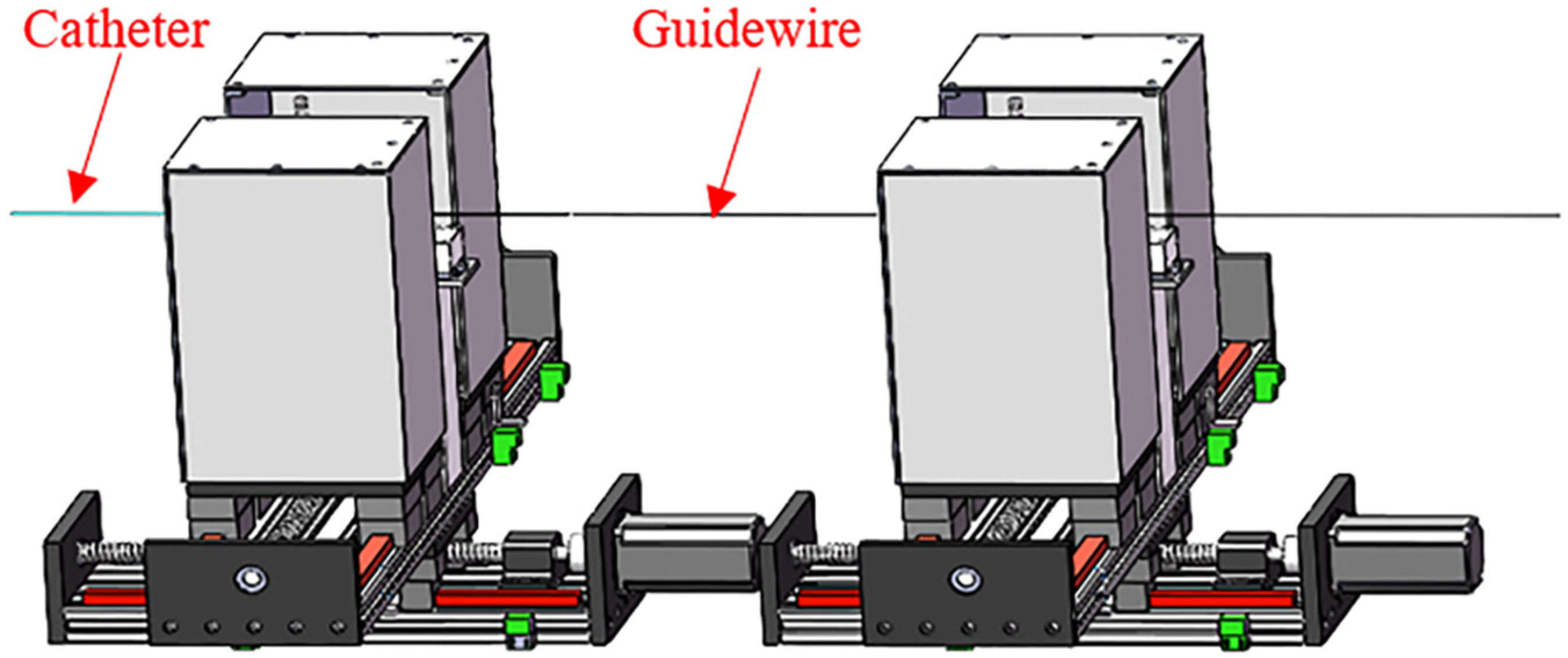
2.2. Overview of the Slave System
3. Design of the Slave System
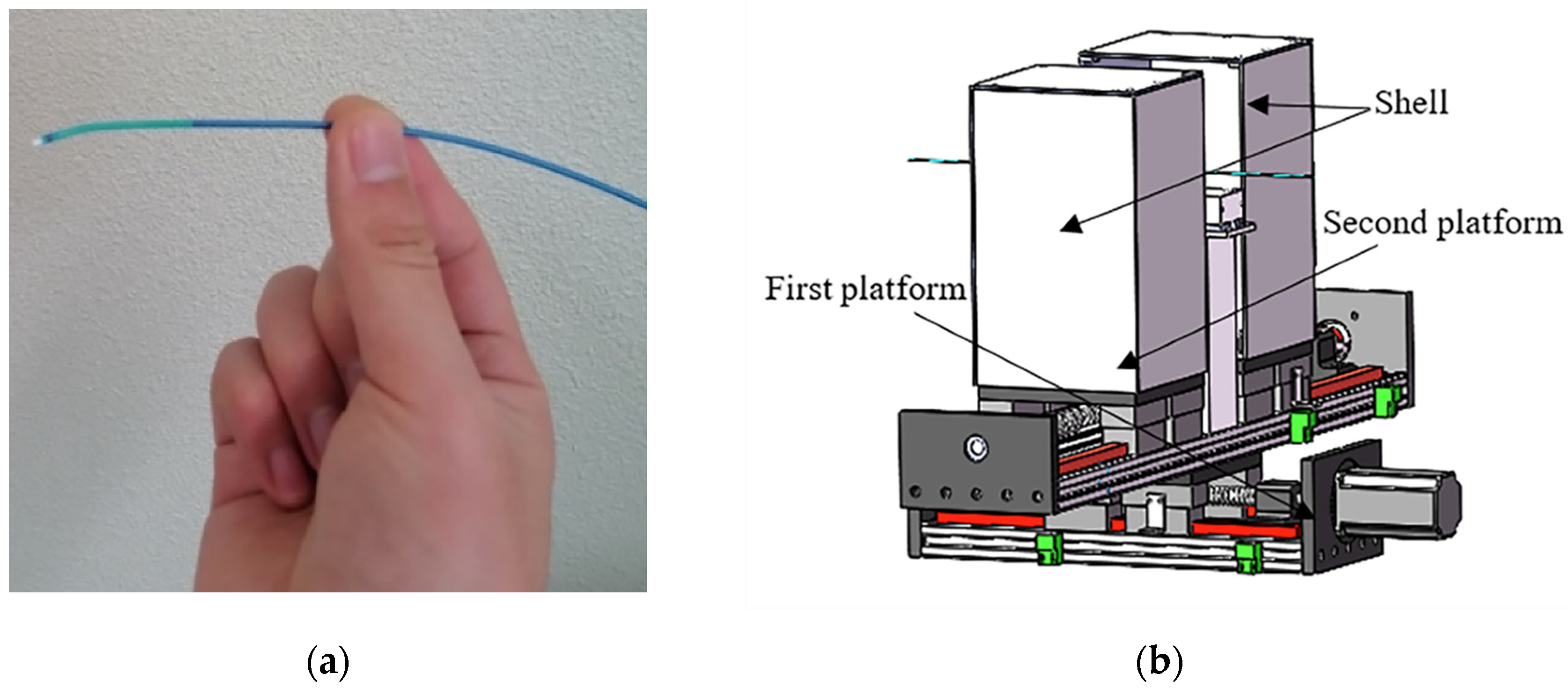
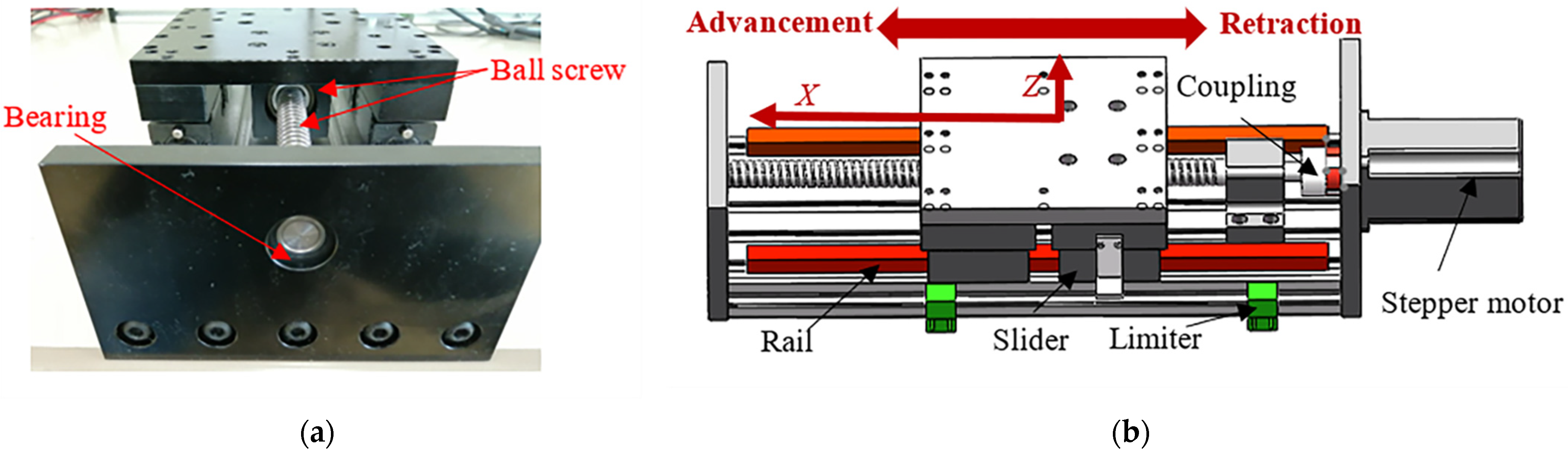
3.1. Design of the FP
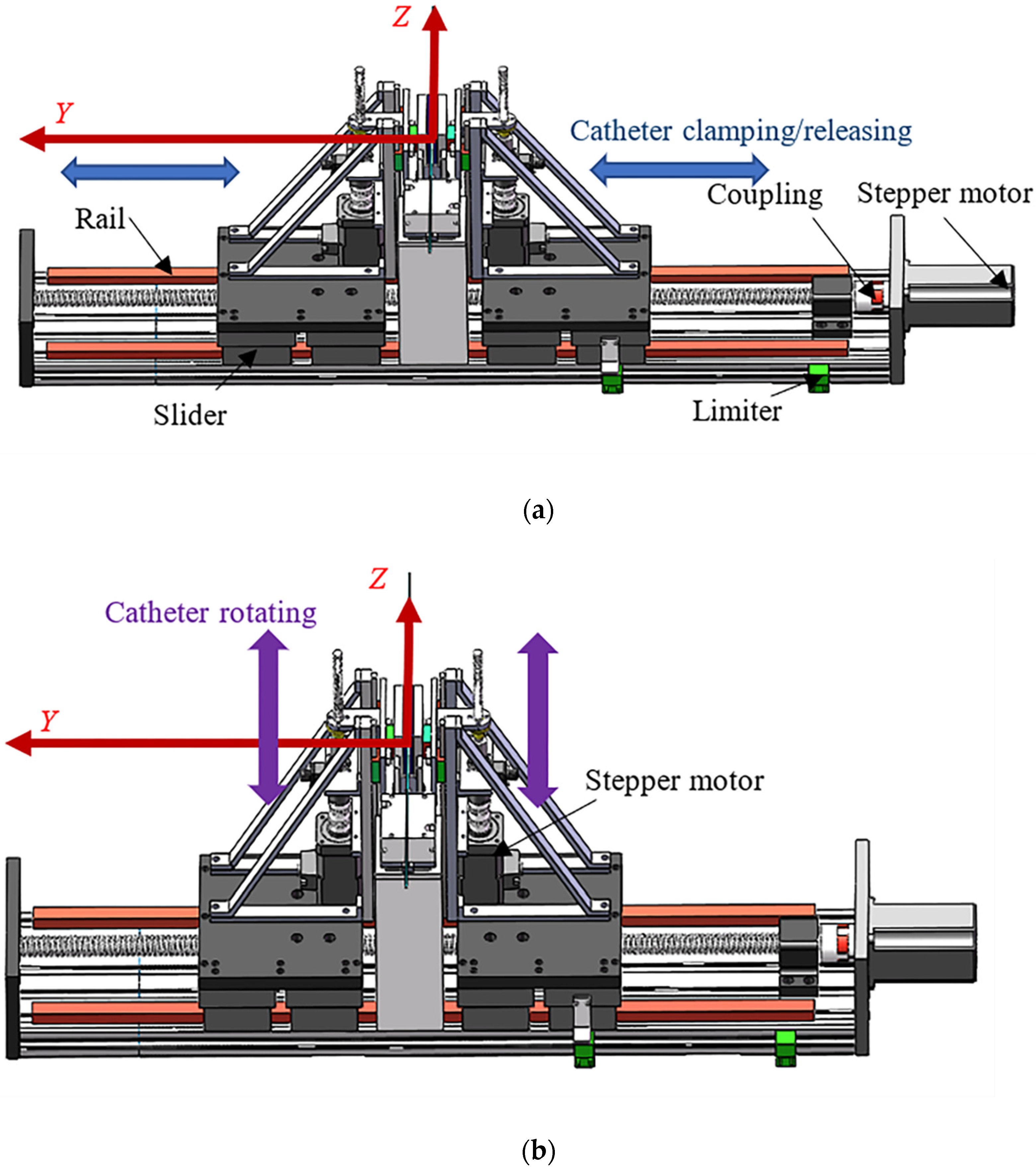
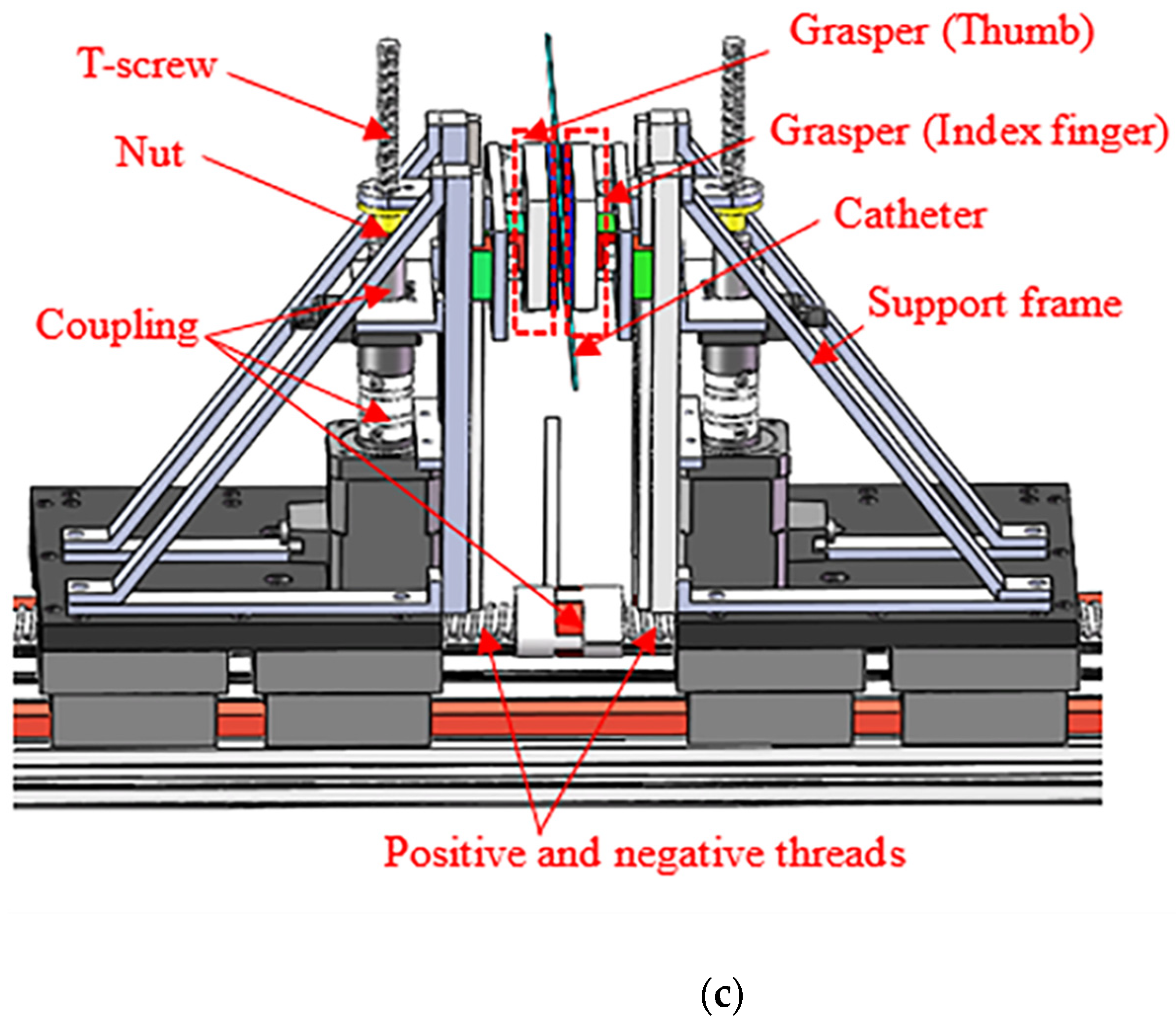
3.2. Design of the SP
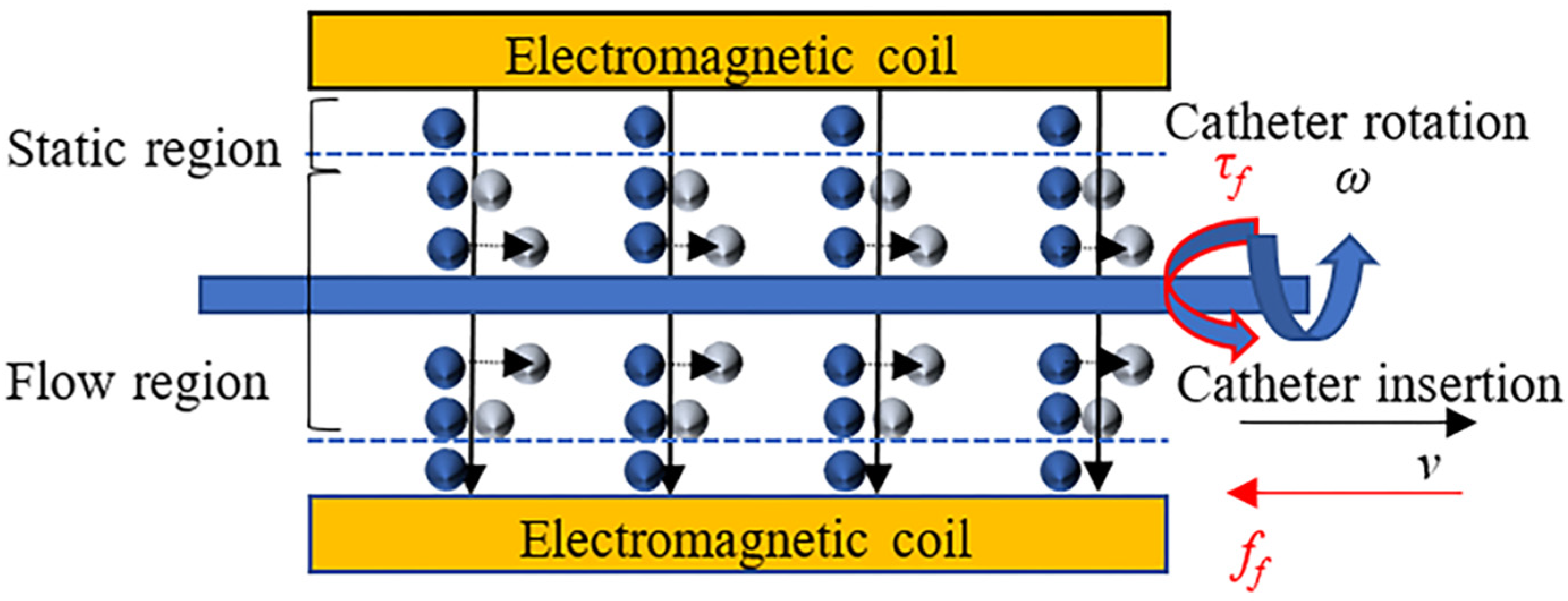
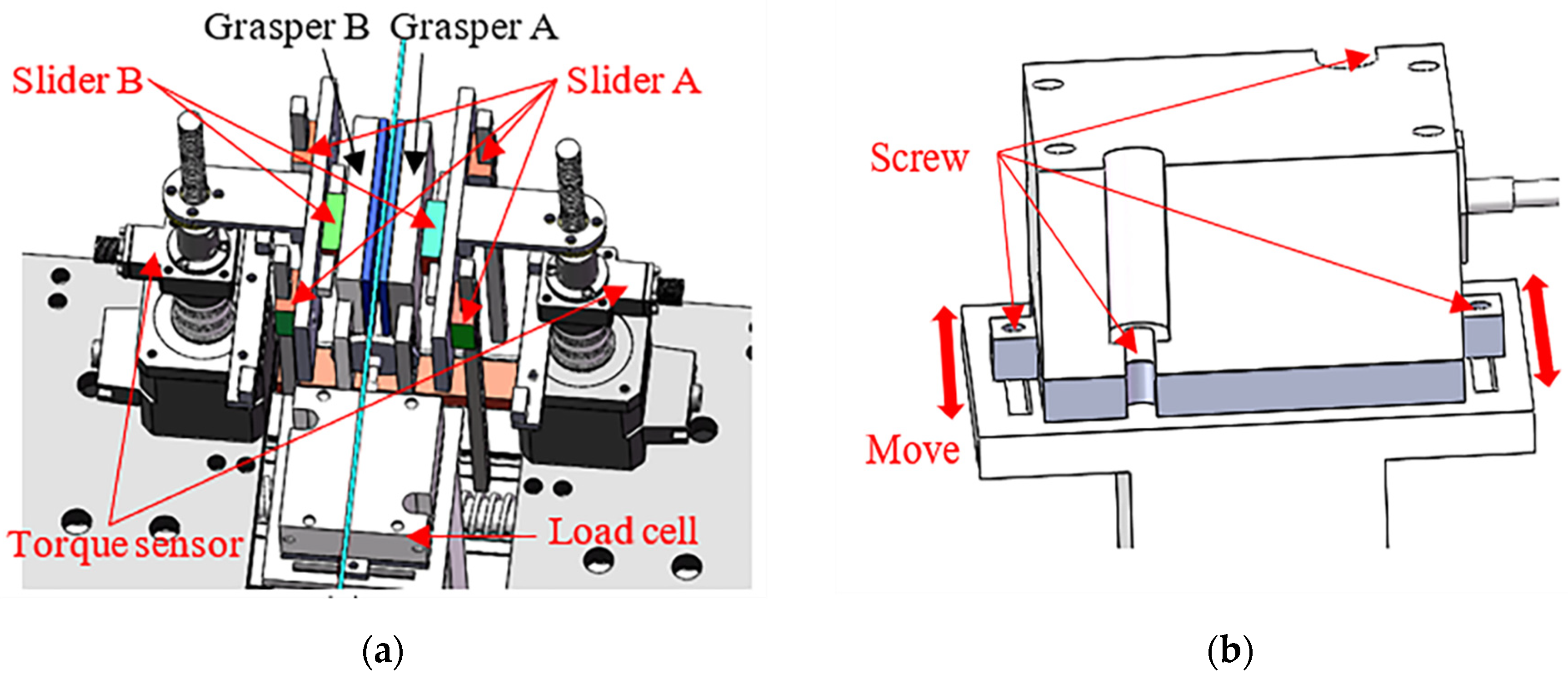
3.3. Design of the Force Detection Structure
3.4. Reciprocating Manipulation
4. Experimental Design and Results
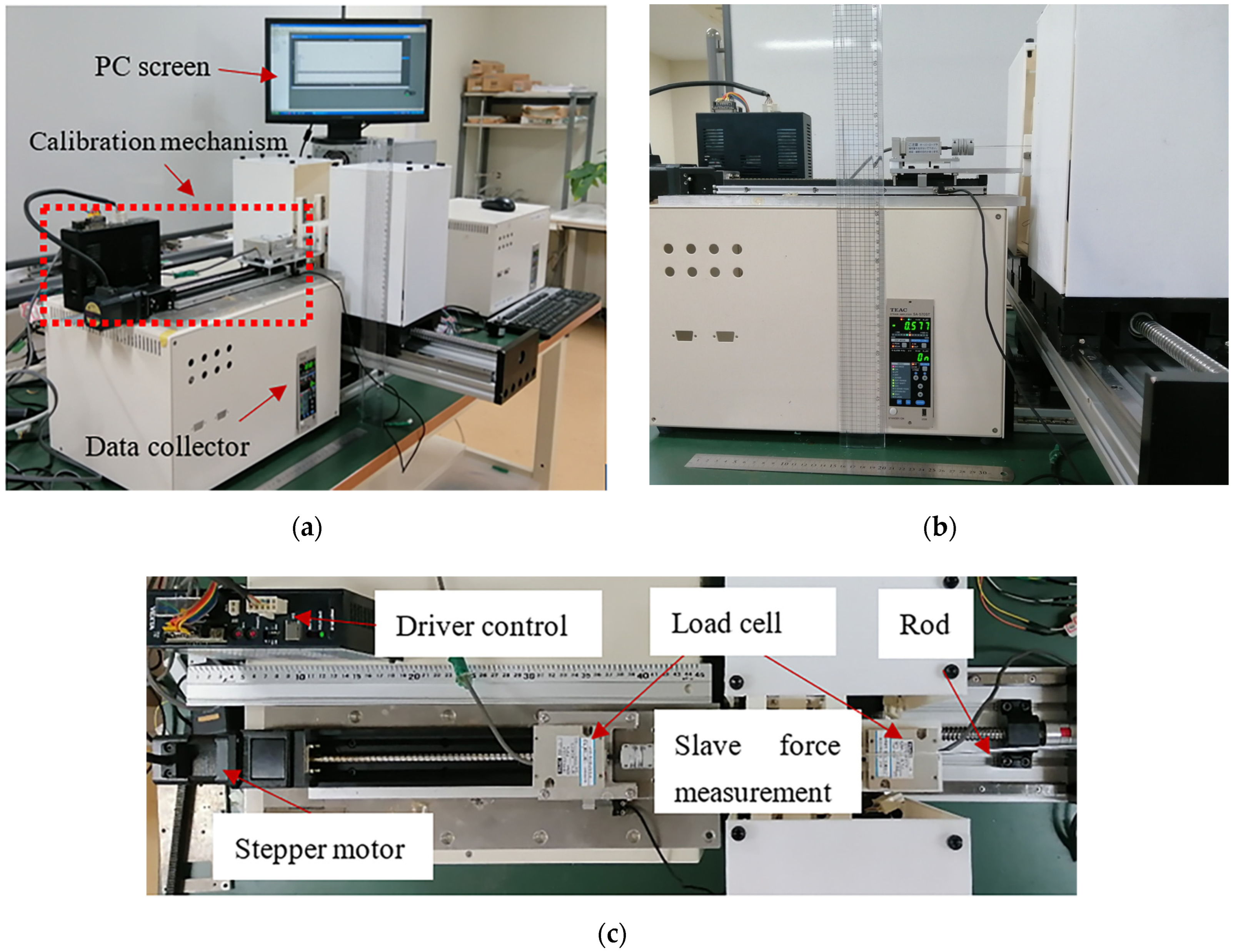
4.1. Axial Force Calibration Experiment on the Slave Side
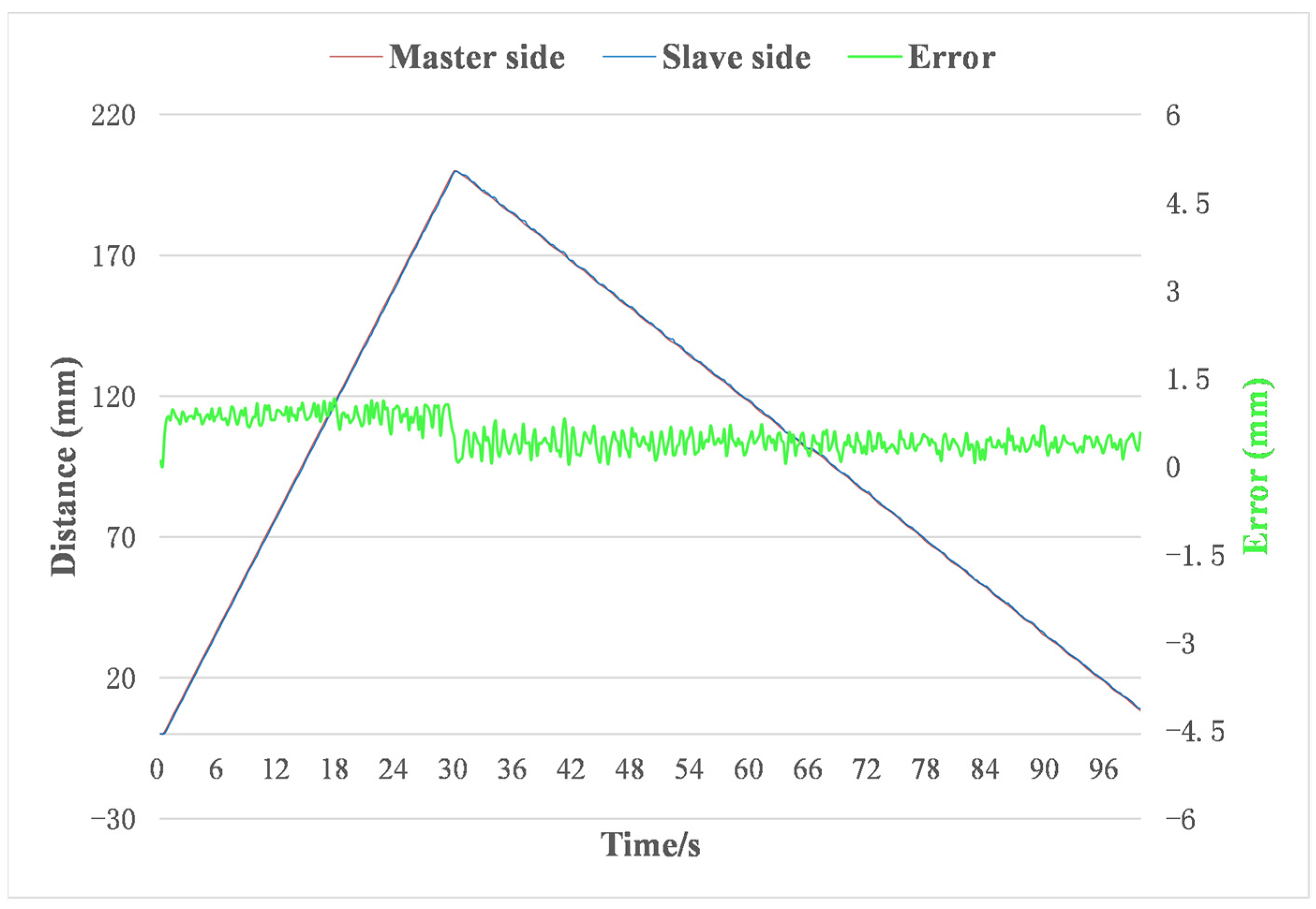
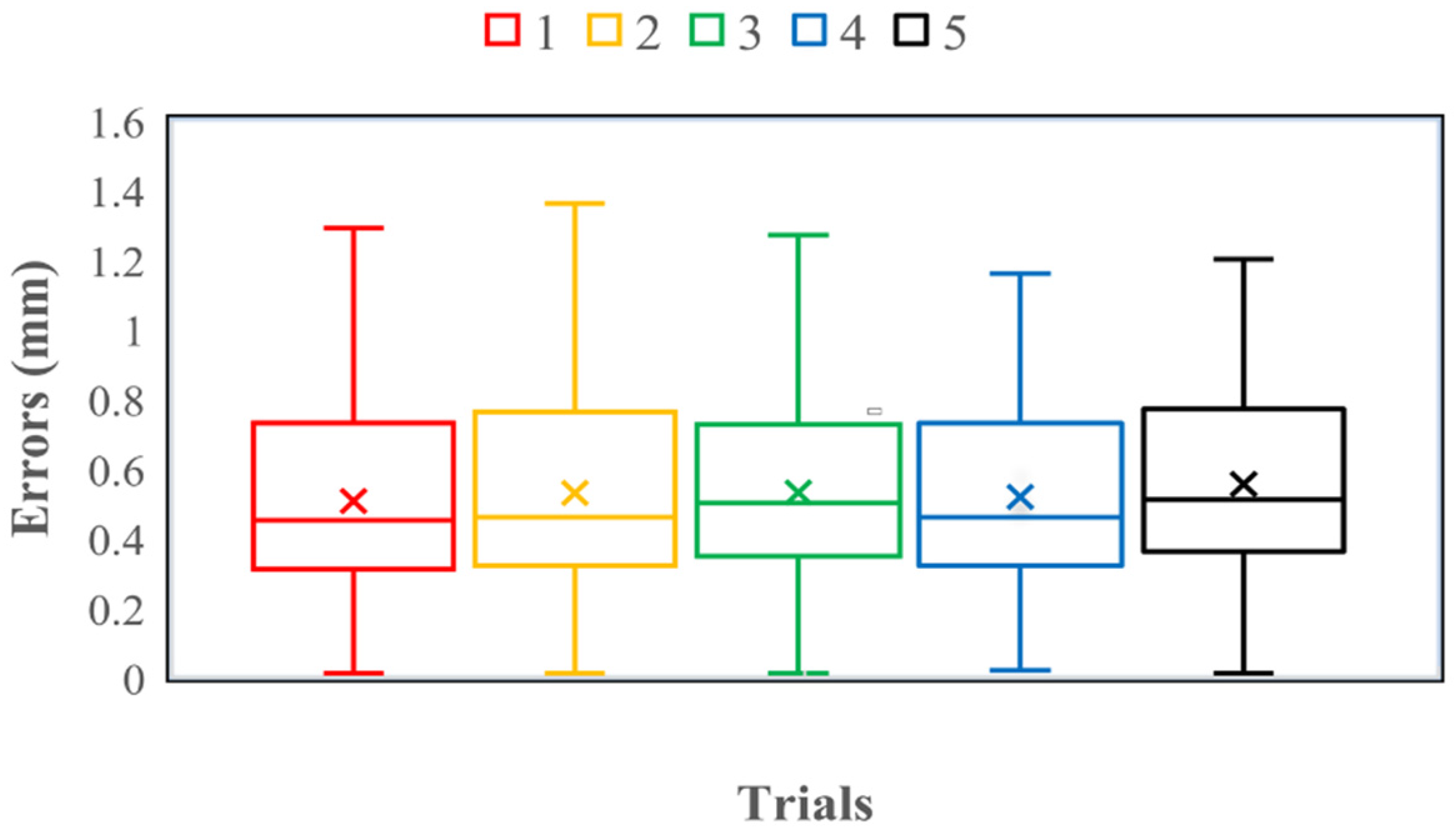
4.2. Master–Slave Linear Tracking Test
4.3. Glass Tube Test
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. World Health Statistics 2020: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240005105 (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Hu, J.; Albadawi, H.; Chong, B.W.; Delpolyi, A.R.; Sheth, R.A.; Khademhosseini, A.; Oklu, R. Advances in biomaterials and technologies for vascular embolization. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, R.W.; Ducruet, A.F.; McDougall, C.G.; Albuquerque, F.C. Endovascular advances for brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 2014, 74, S74–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Wei, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, L.; Cheng, Y.; Li, M.; et al. Endovascular Metal Devices for the Treatment of Cerebrovascular Diseases. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubicz, B.; Collignon, L.; Raphaeli, G.; Pruvo, J.P.; Bruneau, M.; De Witte, O.; Leclerc, X. Flow-diverter stent for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: A prospective study in 29 patients with 34 aneurysms. Stroke 2010, 41, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roguin, A.; Goldstein, J.; Bar, O.; Goldstein, J.A. Brain and neck tumors among physicians performing interventional procedures. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 111, 1368–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vano, E.; Kleiman, N.J.; Duran, A.; Romano-Miller, M.; Rehani, M.M. Radiation-associated lens opacities in catheterization personnel: Results of a survey and direct assessments. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, L.W.; Tra, Y.; Garratt, K.N.; Powell, W.; Lopez, G.; Chambers, C.; Goldstein, J.A. Occupational health hazards of interventional cardiologists in the current decade: Results of the 2014 SCAI membership survey. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 86, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.; Ko, K.; Tsang, J.; Chan, Y.C. Robotic endovascular surgery. Asian Cardiovasc. Thorac. Ann. 2014, 22, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, G.; Metzger, D.C.; Caputo, R.P.; Delgado, J.A.; Marshall, J.J.; Vetrovec, G.W.; Reisman, M.; Waksman, R.; Granada, J.F.; Novacl, V.; et al. Safety and feasibility of robotic percutaneous coronary intervention: PRECISE (Percutaneous Robotically-Enhanced Coronary Intervention) study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 1596–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.M.; Shah, S.C.; Soni, Y.Y.; Radadiya, R.C.; Patel, G.A.; Tiwari, P.O.; Pancholy, S.B. Comparison of robotic percutaneous coronary intervention with traditional percutaneous coronary intervention: A propensity score–matched analysis of a large cohort. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 13, e008888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaza, L.; Virk, H.U.H.; Janzer, S.; Janzer, S.; George, J.C. Robotic-assisted percutaneous coronary intervention in a COVID-19 patient. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 97, E343–E345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaman, C.B.; Kaneko, N.; Meyers, P.M.; Tateshima, S. A review of robotic interventional neuroradiology. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Reis, J.E.; Soullié, P.; Battaglia, A.; Petitmangin, G.; Hoyland, P.; Josseaume, L.; Chillou, C.d.; Odille, F.; Felblinger, J. Electrocardiogram Acquisition during Remote Magnetic Catheter Navigation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 47, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riga, C.V.; Bicknell, C.D.; Hamady, M.S.; Cheshire, N.J.W. Evaluation of robotic endovascular catheters for arch vessel cannulation. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 54, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwein, A.; Kramer, B.; Chinnadurai, P.; Virmani, N.; Walker, S.; O’Malley, M.; Lumsden, A.B.; Bismuth, J. Electromagnetic tracking of flexible robotic catheters enables “assisted navigation” and brings automation to endovascular navigation in an in vitro study. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, E.M.; Frumkin, W.; Ng, G.A.; Neelagaru, S.; Abi-Samra, F.M.; Lee, J.; Giudici, M.; Gohn, D.; Winkle, R.A.; Sussman, J.; et al. First experience with a novel robotic remote catheter system: Amigo (TM) mapping trial. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2013, 37, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datino, T.; Arenal, A.; Ruiz-Hernández, P.M.; Pelliza, M.; Hernández-Hernández, J.; González-Torrecilla, E.; Atienza, F.; Ávila, P.; Fernández-Avilés, F. Arrhythmia ablation using the Amigo robotic remote catheter system versus manual ablation: One year follow-up results. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 202, 877–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, P.; Blacker, S.J.; Kottenstette, N.; Saber, O.; Sokhanvar, S. Robotic-assisted percutaneous coronary intervention. In Handbook of Robotic and Image-Guided Surgery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 341–362. [Google Scholar]
- Cercenelli, L.; Bortolani, B.; Marcelli, E. CathROB: A Highly Compact and Versatile Remote Catheter Navigation System. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2017, 2017, 2712453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigo Remote Catheter System. Available online: https://catheterrobotics.com/images/AmigoBrochure.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Wang, H.; Chang, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, H.; Hou, C.; Lu, H. Research on a Novel Vascular Interventional Surgery Robot and Control Method Based on Precise Delivery. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 26568–26582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.S.; Woo, J.H.; Won, J.Y.; Yi, B.J. In Vivo Usability Test of Vascular Intervention Robotic System Controlled by Two Types of Master Devices. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundrat, D.; Dagnino, G.; Kwok, T.; Abdelaziz, M.; Chi, W.; Nguyen, A.; Riga, C.; Yang, G. An MR-Safe Endovascular Robotic Platform: Design, Control, and Ex-Vivo Evaluation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 3110–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Guo, S.; Bao, X. An Isomorphic Interactive Device for the Interventional Surgical Robot after In Vivo Study. Micromachines 2022, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.; Moon, Y.; Choi, J. A Vascular Intervention Assist Device Using Bi-Motional Roller Cartridge Structure and Clinical Evaluation. Biosensors 2021, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Guo, S.; Guo, Y.; Yang, C.; Shi, L.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y. Multilevel Operation Strategy of a Vascular Interventional Robot System for Surgical Safety in Teleoperation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 38, 2238–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Guo, S.; Guo, J.; Shi, P.; Tamiya, T.; Hirata, H. Development of a Tactile Sensing Robot-Assisted System for Vascular Interventional Surgery. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 12284–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Guo, S. Evaluation of a Clamping Mechanism for Vascular Interventional Surgery Robotic System. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Takamatsu, Japan, 8–11 August 2021; pp. 1044–1049. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, S.; Guo, S.; Tamiya, T. A Magnetorheological Fluids-Based Robot-Assisted Catheter/Guidewire Surgery System for Endovascular Catheterization. Micromachines 2021, 12, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Guo, S.; Xiao, N.; Tamiya, T.; Hirata, H.; Ishihara, H. Safety operation consciousness realization of a MR fluids-based novel haptic interface for teleoperated catheter minimally invasive neurosurgery. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 21, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhan, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. An MR Fluid based Master Manipulator of the Vascular Intervention Robot with Haptic Feedback. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Takamatsu, Japan, 8–11 August 2021; pp. 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hibbeler, R.C. Statics and Mechanics of Materials, 5th ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2017; pp. 418–419. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, L.A. Kinesthetic Sensing, in Human and Machine Haptics; Cutkosky, M., Howe, R., Salisbury, K., Srinivasan, M., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Cao, L.; Miyasaka, M.; Phee, S.J. A Frictional Contact-Pattern-Based Model for Inserting a Flexible Shaft Into Curved Channels. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






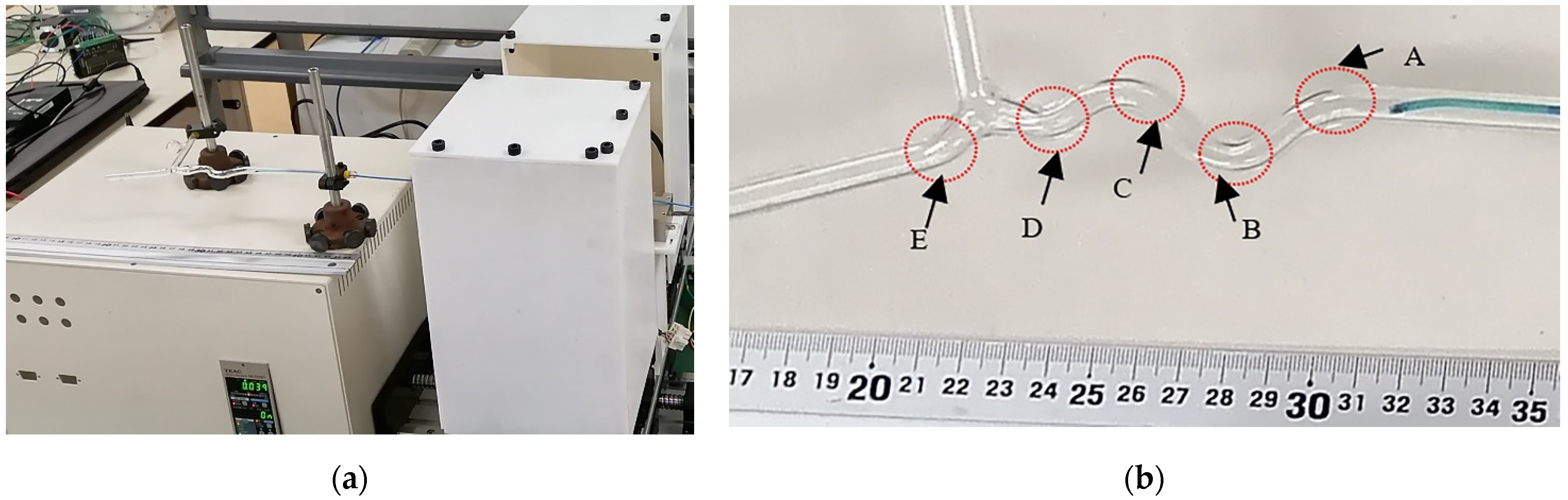
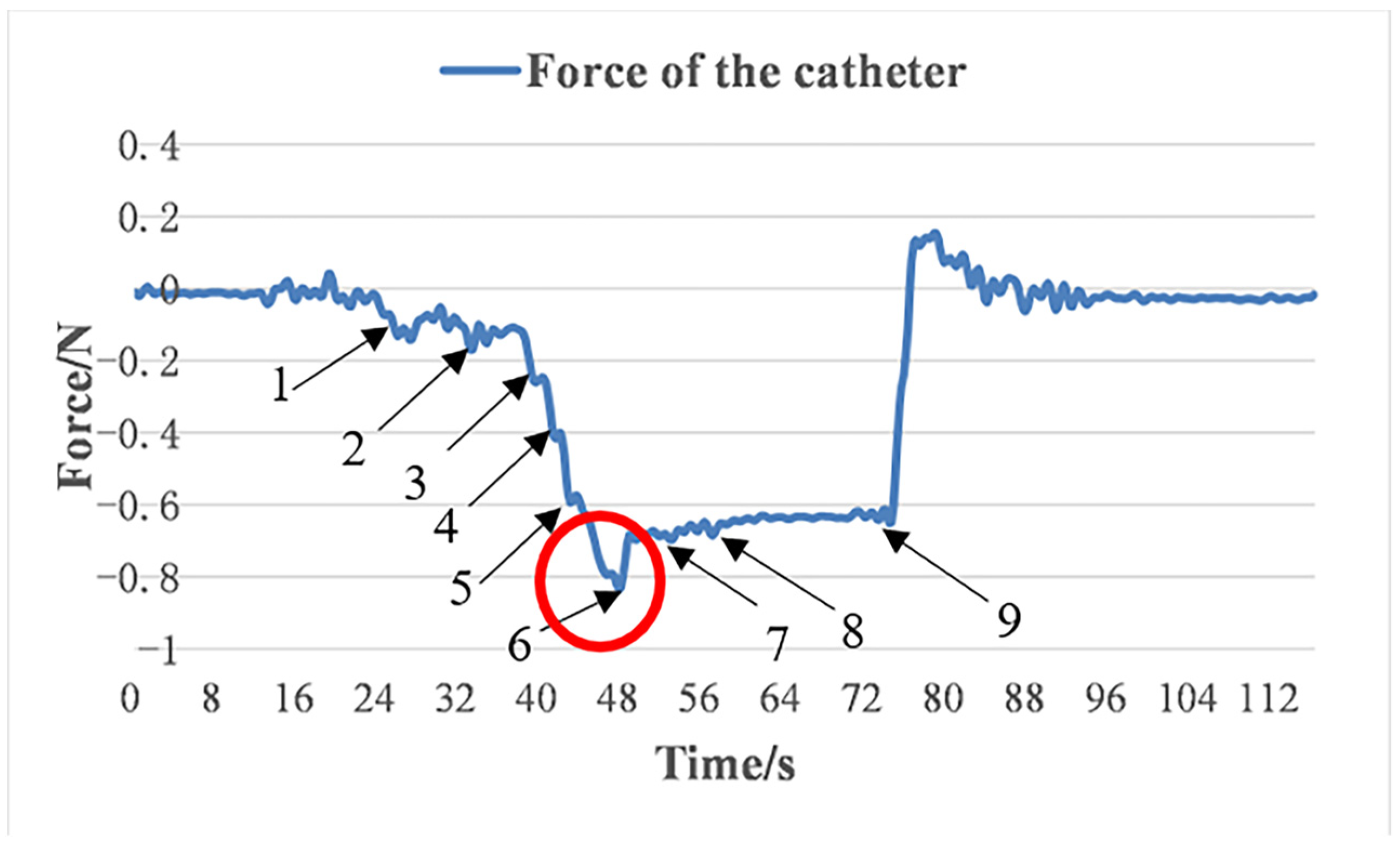

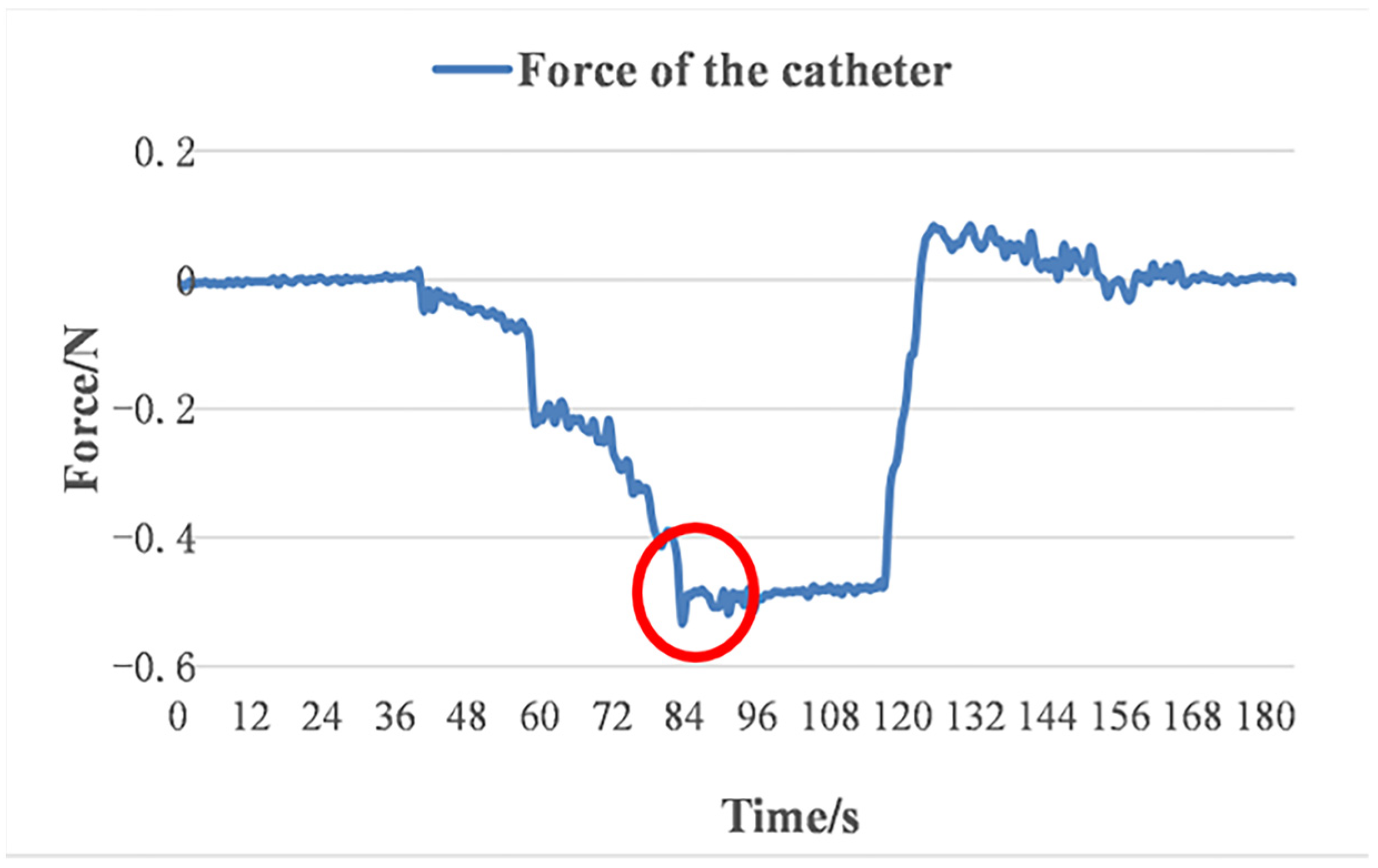

| System (Company) | Technology | Clinical Needs | Features | Main Shortcomings | Visual Feedback | Force Feedback |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Niobe (Stereotaxis) | Magnetic | RF ablation | Dedicated large magnets; dedicated magnetic catheter with a soft tip | Requires specially designed catheter and a room dedicated to the magnets; complexity of the overall system set-up | Yes | No |
| Sensi/Magellan (Hansen Medical) | Electromechanical | RF ablation/vascular procedures | Remote catheter control with dedicated steerable sheaths | Require specially designed sheaths | Yes | No |
| Amigo (Catheter Precision) | Electromechanical | RF ablation | Remote manipulation of standard tip steerable EP catheters | Encumbrance of the system: larger size (101 × 137 × 112 cm); heavier weight (32 kg) [21] | Yes | No |
| CorPath (Corindus) | Electromechanical | Percutaneous coronary interventions | Remote manipulation of the standard guide catheter, guidewire, and balloon/stent catheters | Requires a dedicated single-use cassette to maneuver the interventional devices; using joysticks to control the motion of the intervention devices is not intuitive | Yes | No |
| Trials | Average (mm) | Variance (mm) | Maximum (mm) | Minimum (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.51 | 0.08 | 1.29 | 0.01 |
| 2 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 1.36 | 0.01 |
| 3 | 0.53 | 0.07 | 1.27 | 0.01 |
| 4 | 0.52 | 0.07 | 1.16 | 0.02 |
| 5 | 0.55 | 0.08 | 1.20 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, C.; Guo, S.; Kawanishi, M. Design and Performance Evaluation of a Novel Slave System for Endovascular Tele-Surgery. Machines 2022, 10, 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10090795
Shi C, Guo S, Kawanishi M. Design and Performance Evaluation of a Novel Slave System for Endovascular Tele-Surgery. Machines. 2022; 10(9):795. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10090795
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Chaochao, Shuxiang Guo, and Masahiko Kawanishi. 2022. "Design and Performance Evaluation of a Novel Slave System for Endovascular Tele-Surgery" Machines 10, no. 9: 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10090795
APA StyleShi, C., Guo, S., & Kawanishi, M. (2022). Design and Performance Evaluation of a Novel Slave System for Endovascular Tele-Surgery. Machines, 10(9), 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10090795







