Study on Single-Phase BLDC Motor Design through Drive IC Integration Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Considerations in the Design of a Single-Phase BLDC Motor
2.1. Torque Equation for a Single-Phase BLDC Motor
2.2. Single-Phase Drive IC Integration Analysis
2.3. The Asymmetric Air Gap Structure of a Single-Phase BLDC Motor
3. Designing a Single-Phase BLDC Motor That Meets the Target Performance
3.1. Comparison of Single-Phase BLDC Motor Types
3.2. Derivation of the Target Performance-Satisfying Model for an C-Type Single-Phase BLDC Motor
3.3. Derivation of the Target Performance-Satisfying Model for an External Rotor Single-Phase BLDC Motor
4. Selection of a Single-Phase BLDC Motor That Meets the Target Performance and Validation through the Production of a Prototype Motor
4.1. Selection of the Final Motor, Considering the Cost, for Both the C-Type and External Rotor Single-Phase BLDC Motors
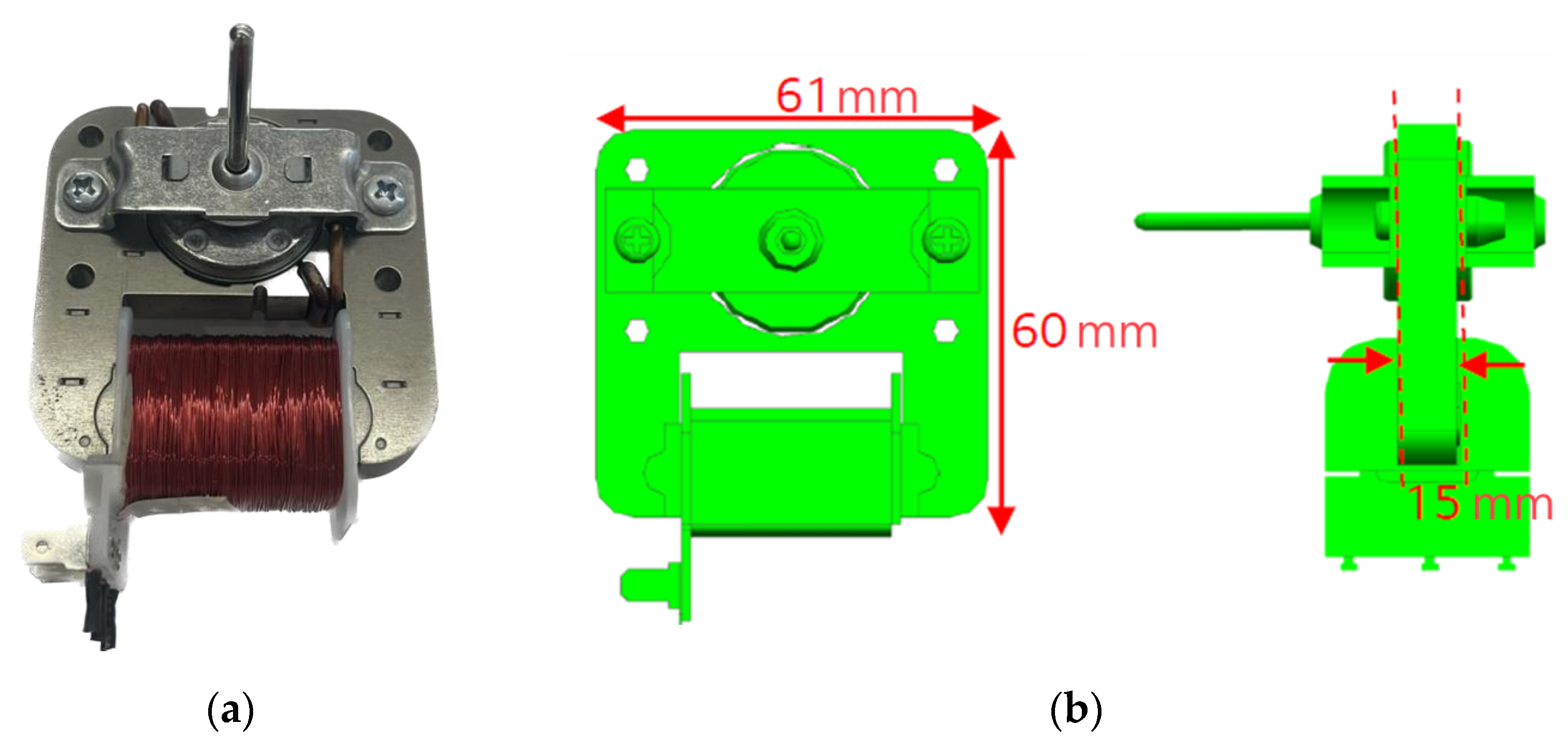
4.2. Prototype Motor Production and Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ojaghi, M.; Daliri, S. Analytic Model for Performance Study and Computer-Aided Design of Single-Phase Shaded-Pole Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 32, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Singh, B. Design and Development of Energy Efficient Single Phase Induction Motor For Ceiling Fan Using Taguchi’s Orthogonal Arrays. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 3562–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Kar, N.C. Analysis of End-Winding Thermal Effects in a Totally Enclosed Fan-Cooled Induction Motor With a Die Cast Copper Rotor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 3098–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavagnino, A.; Lazzari, M.; Profumo, F.; Tenconi, A. A comparison between the axial flux and the radial flux structures for PM synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, W. Loss Calculation and Thermal Analysis of Surface-Mounted PM Motor and Interior PM Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8112604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-J.; Hwang, S.-M.; Kim, K.-T.; Jung, W.-B.; Kim, C.-U. Comparison of dynamic responses for IPM and SPM motors by considering mechanical and magnetic coupling. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 2818–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Huang, Y.; Jin, L.; Lin, H. Comparative Study of Surface-Mounted and Interior Permanent-Magnet Motors for High-Speed Applications. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 5200304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Analysis of a Novel Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Motor With Hybrid Magnets for Low Cost and Low Torque Pulsation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 8104804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Feng, Z.J. Cogging Torque in Cost-Effective Surface-Mounted Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhu, Z.; Eastham, F.; Wang, Y.; Bin, H.; Wu, D.; Gong, L.; Chen, J. Permanent Magnet Machines for High-Speed Applications. World Electr. Veh. J. 2022, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wu, T. Analysis and design of surface permanent magnet synchronous motor and generator. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2019, 3, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Chiu, C.-L.; Jhang, Y.-R.; Tang, Z.-H.; Liang, R.-H. A Driver for the Single-Phase Brushless DC Fan Motor With Hybrid Winding Structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 4369–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, W.; Sarlioglu, B. Torque Ripple Minimization Control Technique of High-Speed Single-Phase Brushless DC Motor for Electric Turbocharger. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 10357–10365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkl, S.; Muetze, A.; Schoener, G. Design Constraints of Small Single-Phase Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Drives for Fan Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3178–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazil, M.; Rajagopal, K.R. Nonlinear Dynamic Modeling of a Single-Phase Permanent-Magnet Brushless DC Motor Using 2-D Static Finite-Element Results. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H. Electric Motor Control DC, AC, and BLDC Motors; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 275–335. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, H.; Blaabjerg, F. Analysis and Mitigation of Dead-Time Harmonics in the Single-Phase Full-Bridge PWM Converter With Repetitive Controllers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 5343–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazil, M.; Rajagopal, K.R. A Novel Air-Gap Profile of Single-Phase Permanent-Magnet Brushless DC Motor for Starting Torque Improvement and Cogging Torque Reduction. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 3928–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-U.; Cho, J.-H.; Kim, D.-K. Cogging Torque Reduction of Single-Phase Brushless DC Motor With a Tapered Air-Gap Using Optimizing Notch Size and Position. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 4455–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.-I.; Yang, B.-Y.; Park, S.-C.; Jin, Y.-S. Novel topology of unequal air gap in a single-phase brushless DC motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 3723–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, Y.; Hwang, H.; Cho, J.; Kim, C.; Kim, J.; Hwang, S.-H.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, C. Investigation of Systematic Efficiency in a High-Speed Single-Phase Brushless DC Motor Using Multi-Physics Analysis for a Vacuum Cleaner. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 8203606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.; Huang, S.; Lipo, T. Torque quality and comparison of internal and external rotor axial flux surface-magnet disc machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


























| Parameter | Symmetrical Air-Gap | Asymmetrical Air-Gap | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torque | 25.8 | 23.2 | mNm |
| Parameter | C-Type Single Phase BLDC Motor | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Poles | 2 | - |
| Slots | 2 | - |
| Rated Speed | 2950 | rpm |
| Rated Power | 5 | W |
| Rated Torque | 15 | mNm |
| Stack Length | 11.2 | mm |
| Fill Factor | 50 | % |
| Current Density | 8 | |
| 1.7 | Ohm | |
| Current Limit | 1.5 | A |
| Maximum Outer Size | 61 × 60 | mm |
| Core Material | 35PN440 | - |
| Permanent Magnet Material | HMG-12L (Nd-Bonded) | - |
| Coil Material | Copper | - |
| Parameter | C-Type Basic Design Model | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power | 6.3 | W |
| Torque | 19.3 | mNm |
| Number of Turns | 495 | - |
| Current | 0.486 | A |
| Copper Loss | 2.1 | W |
| Iron Loss | 0.164 | W |
| Efficiency | 75.5 | % |
| Parameter | C-Type Single Phase BLDC Motor | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power | 5.1 | W |
| Torque | 16.5 | mNm |
| Number of Turns | 184 | - |
| Current | 1.25 | A |
| Copper Loss | 1.86 | W |
| Iron Loss | 0.31 | W |
| Efficiency | 68.3 | % |
| Parameter | External Rotor Type Single Phase BLDC Motor | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Poles | 2 | - |
| Slots | 2 | - |
| Rated Speed | 2950 | rpm |
| Rated Output | 5 | W |
| Rated Torque | 15 | mNm |
| Stack Length | 11.2 | mm |
| Fill Factor | 50 | % |
| Current Density | 8 | |
| 0.71 | Ohm | |
| Current Limit | 1.8 | A |
| Maximum Outer Diameter | 39 | mm |
| Core Material | 35PN440 | - |
| Permanent Magnet Material | HMG-4 (Nd-Bonded Magnet) HMG-12L (Nd-Bonded Magnet) | - |
| Coil Material | Copper | - |
| Material | Residual Magnetic Flux Density | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| HMG-4 | 0.47 | T |
| HMG-12L | 0.75 |
| Parameter | External Rotor Type Single Phase BLDC Motor | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power | 4.7 | W |
| Torque | 15.2 | mNm |
| Number of Turns | 216 | - |
| Current | 1.3 | A |
| Copper Loss | 1.67 | W |
| Iron Loss | 0.215 | W |
| Efficiency | 69.3 | % |
| Parameter | External Rotor Single Phase BLDC Motor | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power | 4.8 | W |
| Torque | 15.6 | mNm |
| Number of Turns | 228 | - |
| Current | 1.66 | A |
| Copper Loss | 2.51 | W |
| Iron Loss | 0.192 | W |
| Efficiency | 62.4 | % |
| Parameter | C-Type Single Phase BLDC Motor | Outer Rotor Single Phase BLDC Motor | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stator Core (35PN440) | 0.123 | 0.025 | kg |
| Rotor Core (35PN440) | 0.017 | 0.011 | |
| Magnet(HMG-12L/HMG-4) | 0.009 | 0.012 | |
| Coil (Copper) | 0.015 | 0.017 | |
| Stator Core (35PN440) | 209.4 | 42.1 | KRW |
| Rotor Core (35PN440) | 29.3 | 18.5 | |
| Magnet (HMG-12L/HMG-4) | 57.6 | 59.4 | |
| Coil (Copper) | 145.3 | 160.5 | |
| Sum | 441.6 | 280.4 |
| Parameter | FEA | Test | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power | 4.8 | 4.7 | W |
| Torque | 15.6 | 15.0 | mNm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-S.; Jo, N.-R.; Pyo, H.-J.; Jung, D.-H.; Kim, W.-H. Study on Single-Phase BLDC Motor Design through Drive IC Integration Analysis. Machines 2023, 11, 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11111003
Lee Y-S, Jo N-R, Pyo H-J, Jung D-H, Kim W-H. Study on Single-Phase BLDC Motor Design through Drive IC Integration Analysis. Machines. 2023; 11(11):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11111003
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ye-Seo, Na-Rim Jo, Hyun-Jo Pyo, Dong-Hoon Jung, and Won-Ho Kim. 2023. "Study on Single-Phase BLDC Motor Design through Drive IC Integration Analysis" Machines 11, no. 11: 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11111003
APA StyleLee, Y.-S., Jo, N.-R., Pyo, H.-J., Jung, D.-H., & Kim, W.-H. (2023). Study on Single-Phase BLDC Motor Design through Drive IC Integration Analysis. Machines, 11(11), 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11111003







