Exploring the Impact of Passive Ankle Exoskeletons on Lower-Limb Neuromechanics during Walking on Sloped Surfaces: Implications for Device Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Overview
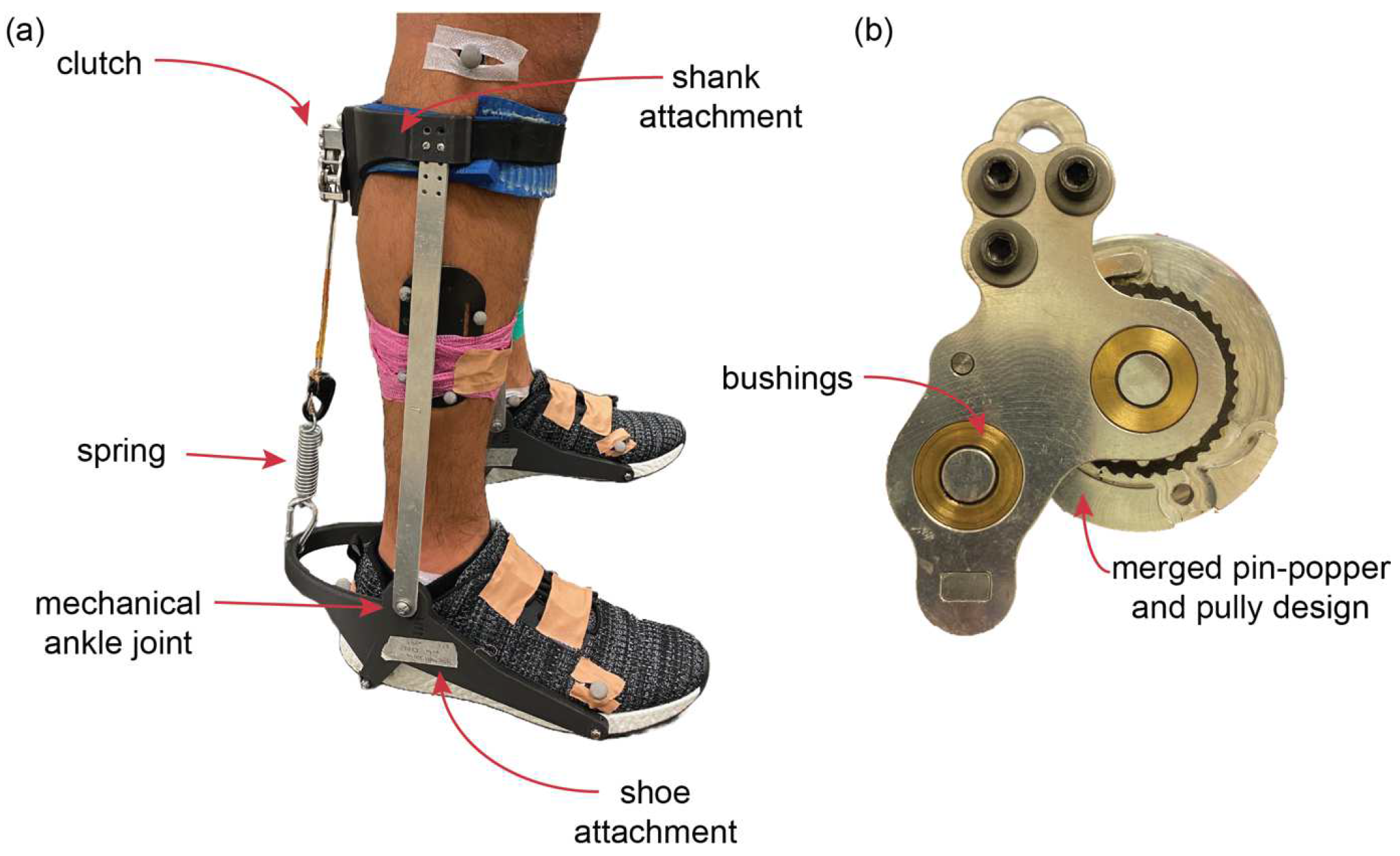
2.2. Passive Ankle Exoskeleton Design
2.3. Joint-Level Kinematics, Kinetics, and Mechanical Energetics
2.4. Muscle Activation
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
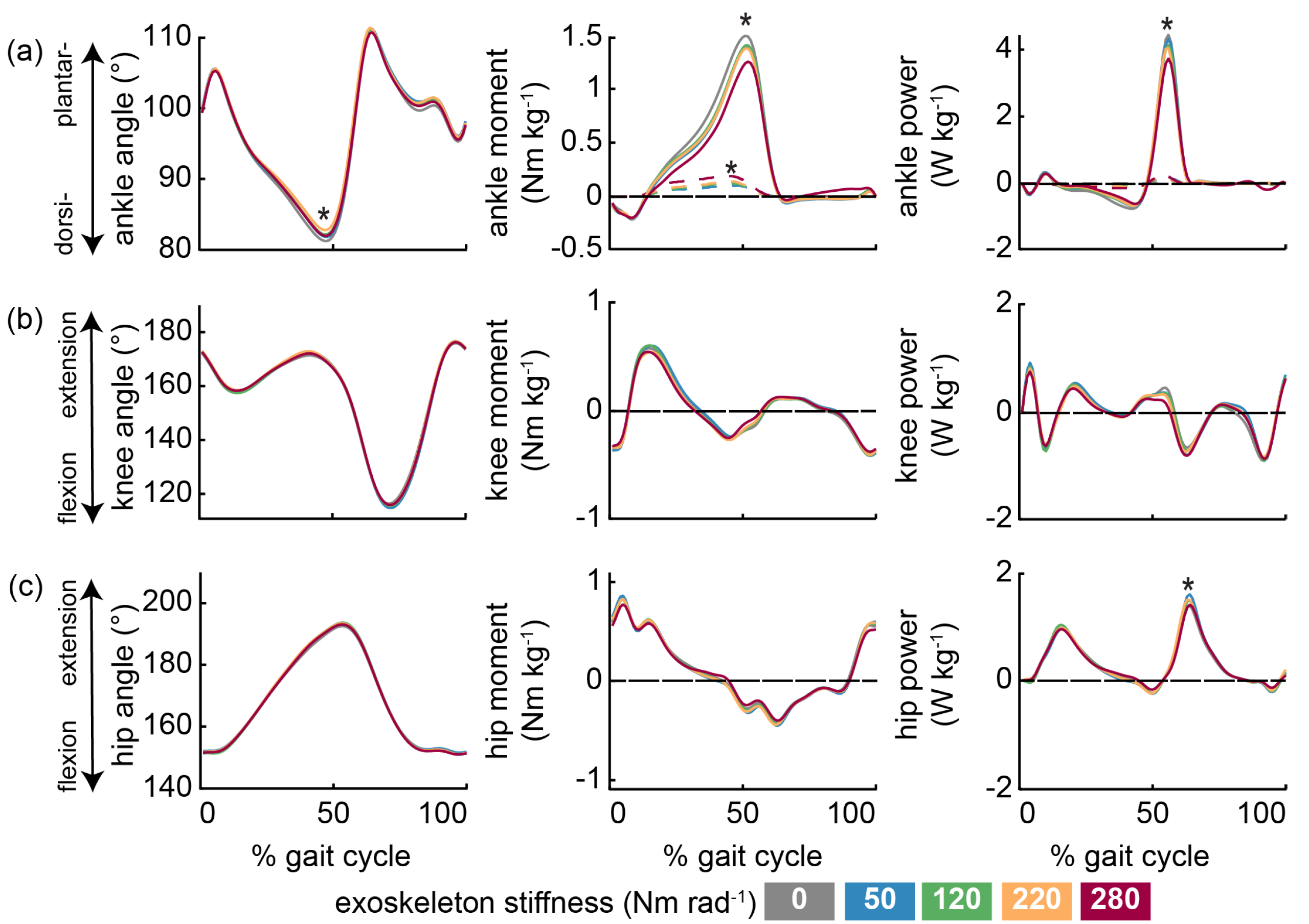
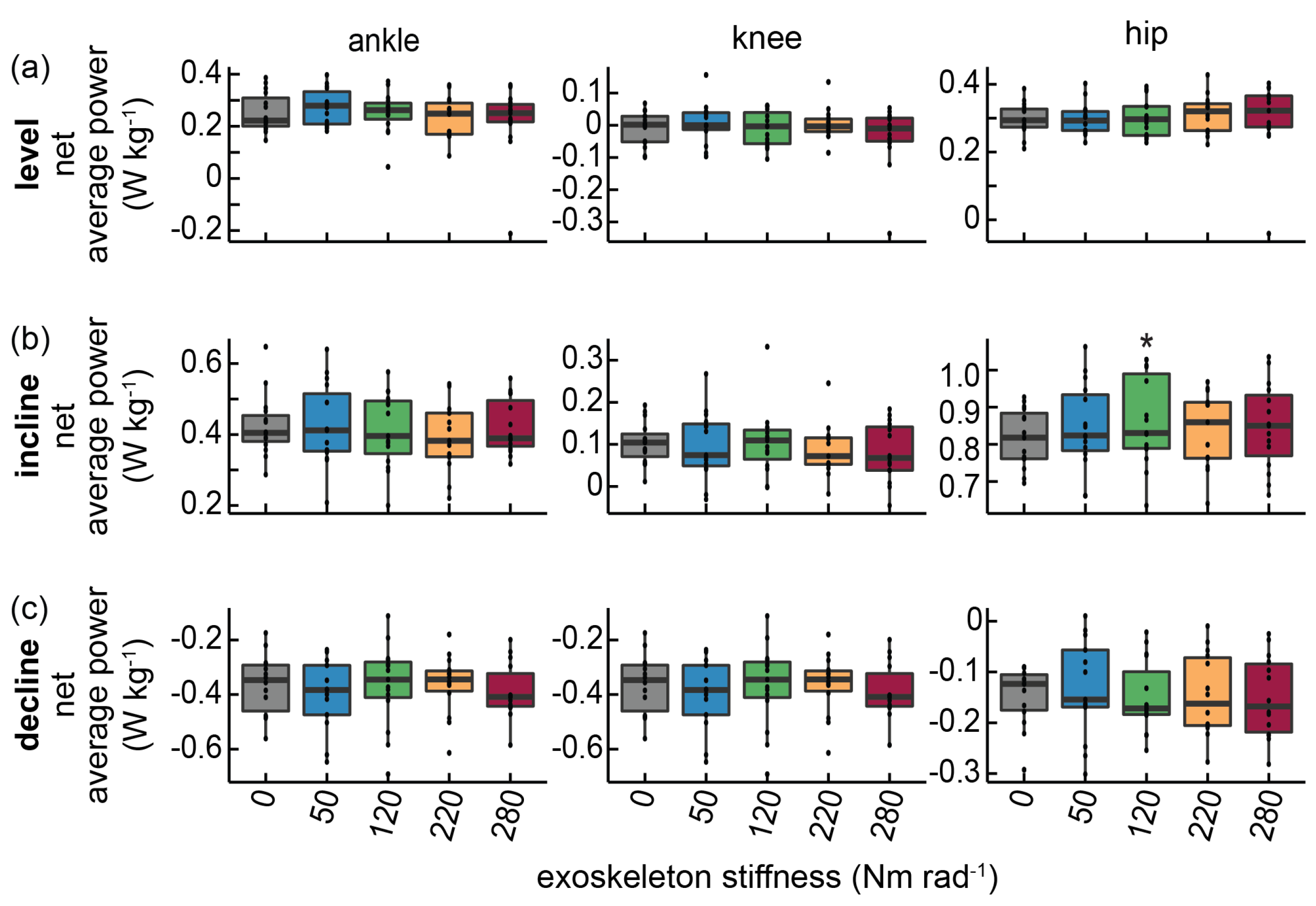
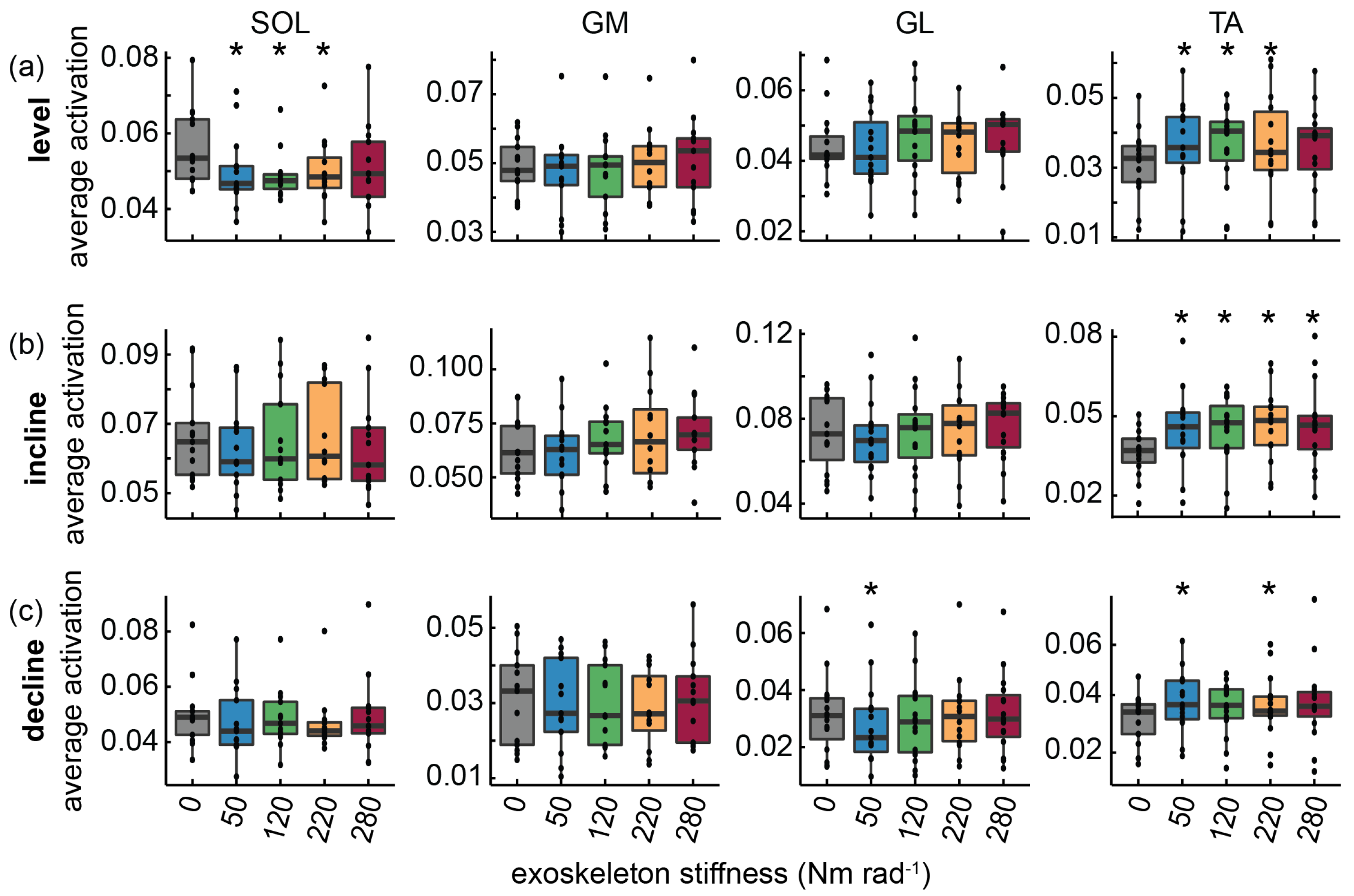
3.1. Level Walking
3.2. Incline Walking
3.3. Decline Walking
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zelik, K.E.; Huang, T.-W.P.; Adamczyk, P.G.; Kuo, A.D. The role of series ankle elasticity in bipedal walking. J. Theor. Biol. 2014, 346, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, T.J.; Punith, L.K.; Sawicki, G.S. Humans falling in holes: Adaptations in lower-limb joint mechanics in response to a rapid change in substrate height during human hopping. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcolm, P.; Derave, W.; Galle, S.; De Clercq, D. A Simple Exoskeleton That Assists Plantarflexion Can Reduce the Metabolic Cost of Human Walking. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galle, S.; Malcolm, P.; Derave, W.; De Clercq, D. Uphill walking with a simple exoskeleton: Plantarflexion assistance leads to proximal adaptations. Gait Posture 2015, 41, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.H.; Wiggin, M.B.; Sawicki, G.S. Reducing the energy cost of human walking using an unpowered exoskeleton. Nature 2015, 522, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawicki, G.S.; Lewis, C.L.; Ferris, D.P. It Pays to Have a Spring in Your Step. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2009, 37, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, D.J.; Sawicki, G. The mechanics and energetics of human walking and running: A joint level perspective. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuckols, R.W.; Sawicki, G.S. Impact of elastic ankle exoskeleton stiffness on neuromechanics and energetics of human walking across multiple speeds. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, J.A.; Granata, K.P.; Mitros, M.R.; Byrne, E.M.; Marsh, A.P. Effect of augmented plantarflexion power on preferred walking speed and economy in young and older adults. Gait Posture 2007, 25, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, G.S.; Ferris, D.P. Powered ankle exoskeletons reveal the metabolic cost of plantar flexor mechanical work during walking with longer steps at constant step frequency. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, L.M.; Rouse, E.J.; Herr, H.M. Autonomous exoskeleton reduces metabolic cost of human walking during load carriage. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, S.; Malcolm, P.; Collins, S.H.; De Clercq, D. Reducing the metabolic cost of walking with an ankle exoskeleton: Interaction between actuation timing and power. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Xiong, C.; Wang, T.; Zhou, T.; Liang, J.; Li, Y. Modulating Energy Among Foot-Ankle Complex With an Unpowered Exoskeleton Improves Human Walking Economy. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yandell, M.B.; Tacca, J.R.; Zelik, K.E. Design of a Low Profile, Unpowered Ankle Exoskeleton That Fits under Clothes: Overcoming Practical Barriers to Widespread Societal Adoption. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuckols, R.W.; Dick, T.J.; Beck, O.N.; Sawicki, G.S. Ultrasound imaging links soleus muscle neuromechanics and energetics during human walking with elastic ankle exoskeletons. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, O.N.; Punith, L.K.; Nuckols, R.W.; Sawicki, G.S. Exoskeletons Improve Locomotion Economy by Reducing Active Muscle Volume. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2019, 47, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuckols, R.W.; Takahashi, K.Z.; Farris, D.J.; Mizrachi, S.; Riemer, R.; Sawicki, G.S. Mechanics of walking and running up and downhill: A joint-level perspective to guide design of lower-limb exoskeletons. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, N.; Strutzenberger, G.; Ameshofer, L.M.; Schwameder, H. Lower limb joint work and joint work contribution during downhill and uphill walking at different inclinations. J. Biomech. 2017, 61, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, B.A.; Philius, S.A.; Nuckols, R.W.; McCall, J.; Young, A.J.; Sawicki, G.S. Neuromechanics and Energetics of Walking with an Ankle Exoskeleton Using Neuromuscular-Model Based Control: A Parameter Study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 615358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggin, M.B.; Sawicki, G.S.; Collins, S.H. An exoskeleton using controlled energy storage and release to aid ankle propulsion. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, J.L.; Lichtwark, G.A.; Sawicki, G.S.; Dick, T.J.M. The influence of elastic ankle exoskeletons on lower limb mechanical energetics during unexpected perturbations. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2023, 10, 221133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, T.J.M.; Clemente, C.J.; Punith, L.K.; Sawicki, G.S. Series elasticity facilitates safe plantar flexor muscle-tendon shock absorption during perturbed human hopping. Proc. R. Soc. B 2021, 288, 20210201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopal, A.; Dembia, C.L.; DeMers, M.S.; Delp, D.D.; Hicks, J.L.; Delp, S.L. Full-Body Musculoskeletal Model for Muscle-Driven Simulation of Human Gait. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 2068–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delp, S.L.; Anderson, F.C.; Arnold, A.S.; Loan, P.; Habib, A.; John, C.T.; Guendelman, E.; Thelen, D.G. OpenSim: Open-Source Software to Create and Analyze Dynamic Simulations of Movement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; Heisterk, S.; VanWilligen, B.; Ranke, J.; R Core Team. Nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models; Version 3.1-163; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- João, F.; Veloso, A.; Cabral, S.; Moniz-Pereira, V.; Kepple, T. Synergistic interaction between ankle and knee during hopping revealed through induced acceleration analysis. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2014, 33, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawicki, G.S.; Ferris, D.P. Mechanics and energetics of incline walking with robotic ankle exoskeletons. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, D.J.; Sawicki, G. Linking the mechanics and energetics of hopping with elastic ankle exoskeletons. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2012, 113, 1862–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudie, K.; Billing, D.; Garofolini, A.; Karakolis, T.; LaFiandra, M. The need for a paradigm shift in the development of military exoskeletons. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2021, 22, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williamson, J.L.; Lichtwark, G.A.; Dick, T.J.M. Exploring the Impact of Passive Ankle Exoskeletons on Lower-Limb Neuromechanics during Walking on Sloped Surfaces: Implications for Device Design. Machines 2023, 11, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11121071
Williamson JL, Lichtwark GA, Dick TJM. Exploring the Impact of Passive Ankle Exoskeletons on Lower-Limb Neuromechanics during Walking on Sloped Surfaces: Implications for Device Design. Machines. 2023; 11(12):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11121071
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliamson, James L., Glen A. Lichtwark, and Taylor J. M. Dick. 2023. "Exploring the Impact of Passive Ankle Exoskeletons on Lower-Limb Neuromechanics during Walking on Sloped Surfaces: Implications for Device Design" Machines 11, no. 12: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11121071
APA StyleWilliamson, J. L., Lichtwark, G. A., & Dick, T. J. M. (2023). Exploring the Impact of Passive Ankle Exoskeletons on Lower-Limb Neuromechanics during Walking on Sloped Surfaces: Implications for Device Design. Machines, 11(12), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11121071





