Resonant Actuation Based on Dynamic Characteristics of Bistable Laminates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling
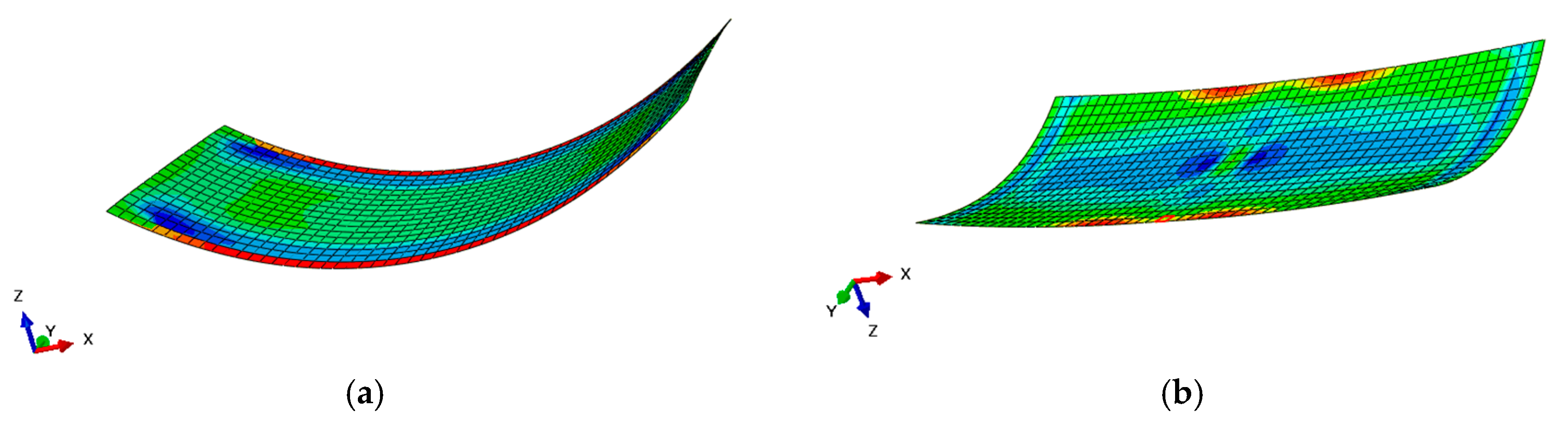
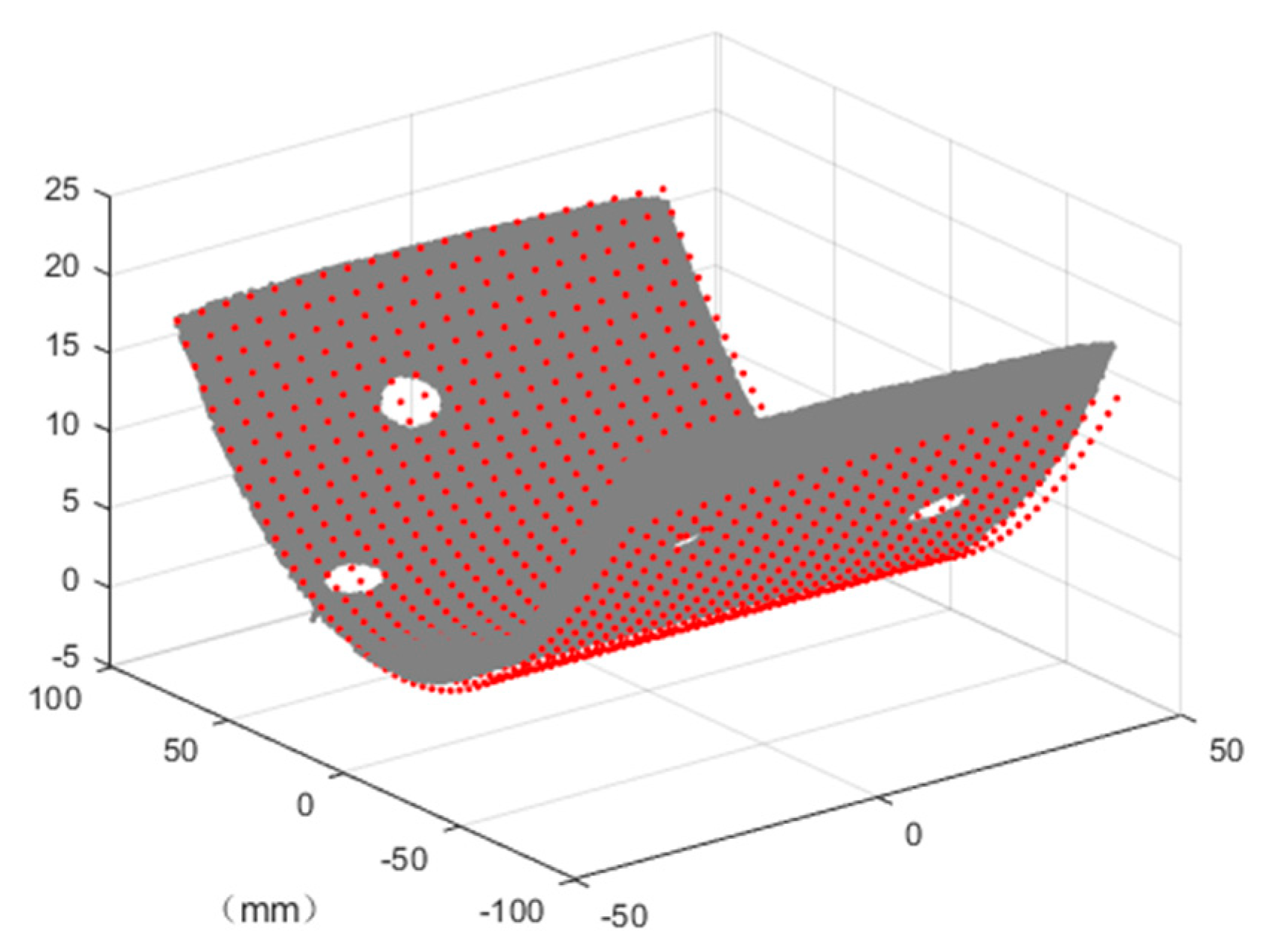
2.1. The Finite Element Model
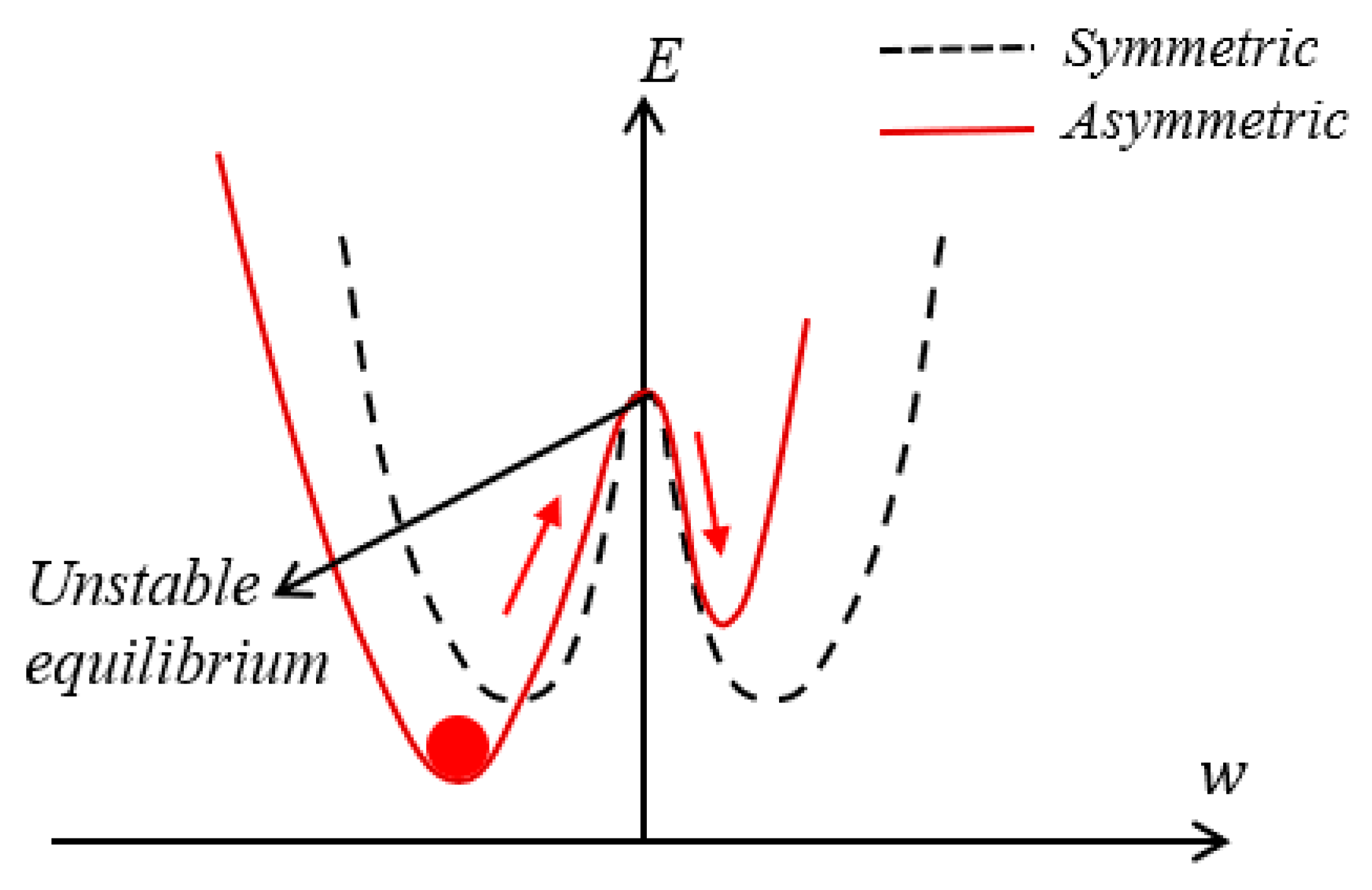
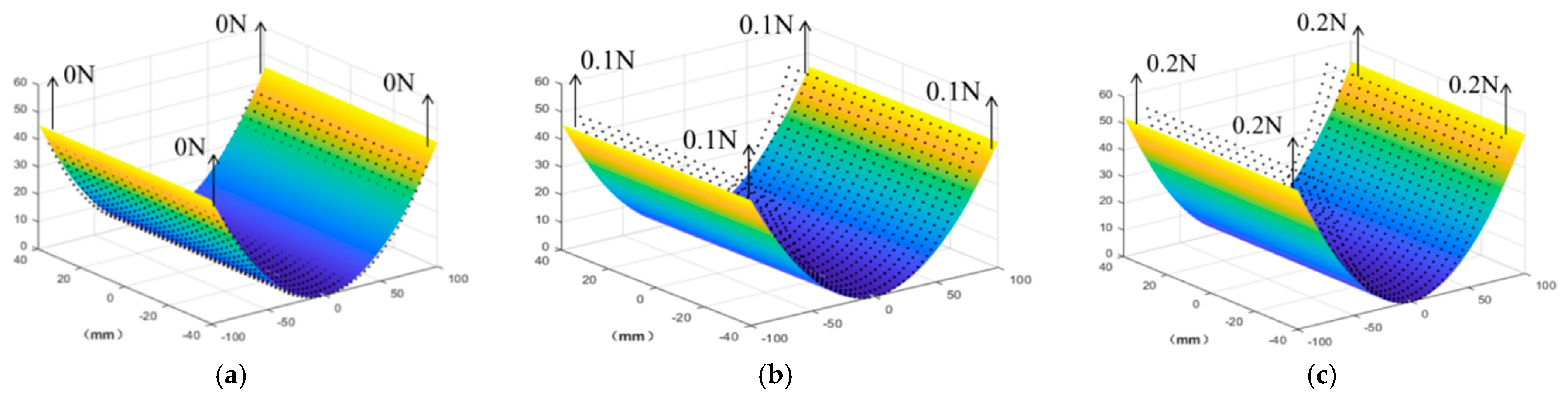
2.2. The Static Behaviour of the Analytical Model
2.3. The Dynamic Behaviour of the Analytical Model
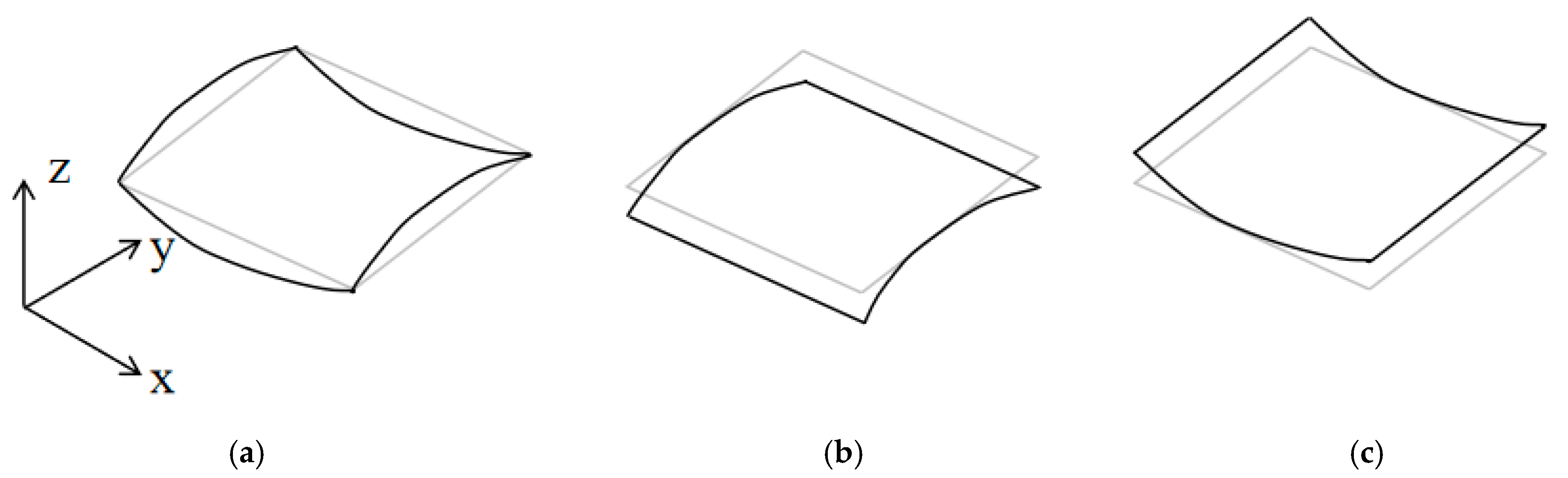
2.4. Prediction of Stable Configuration
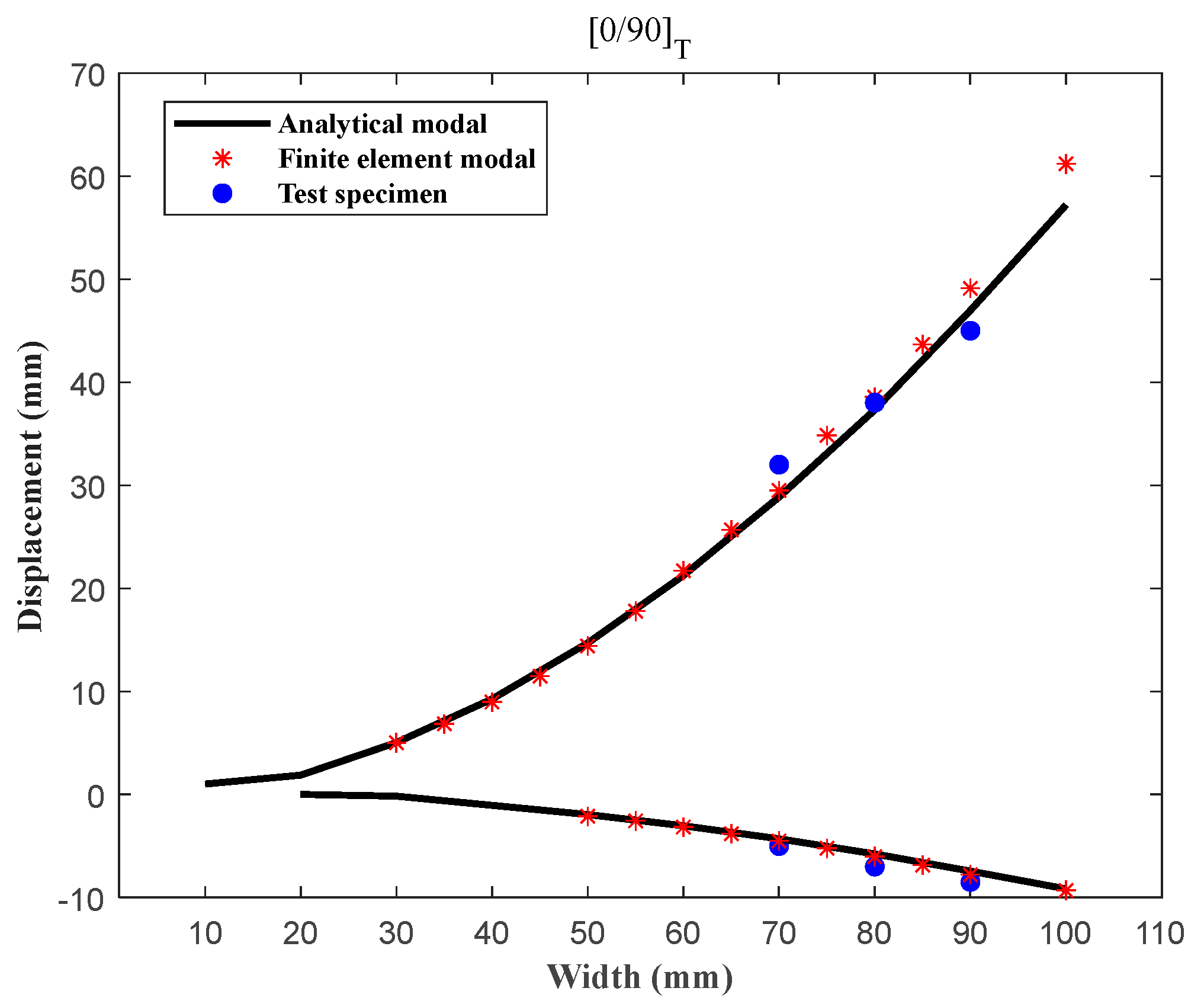
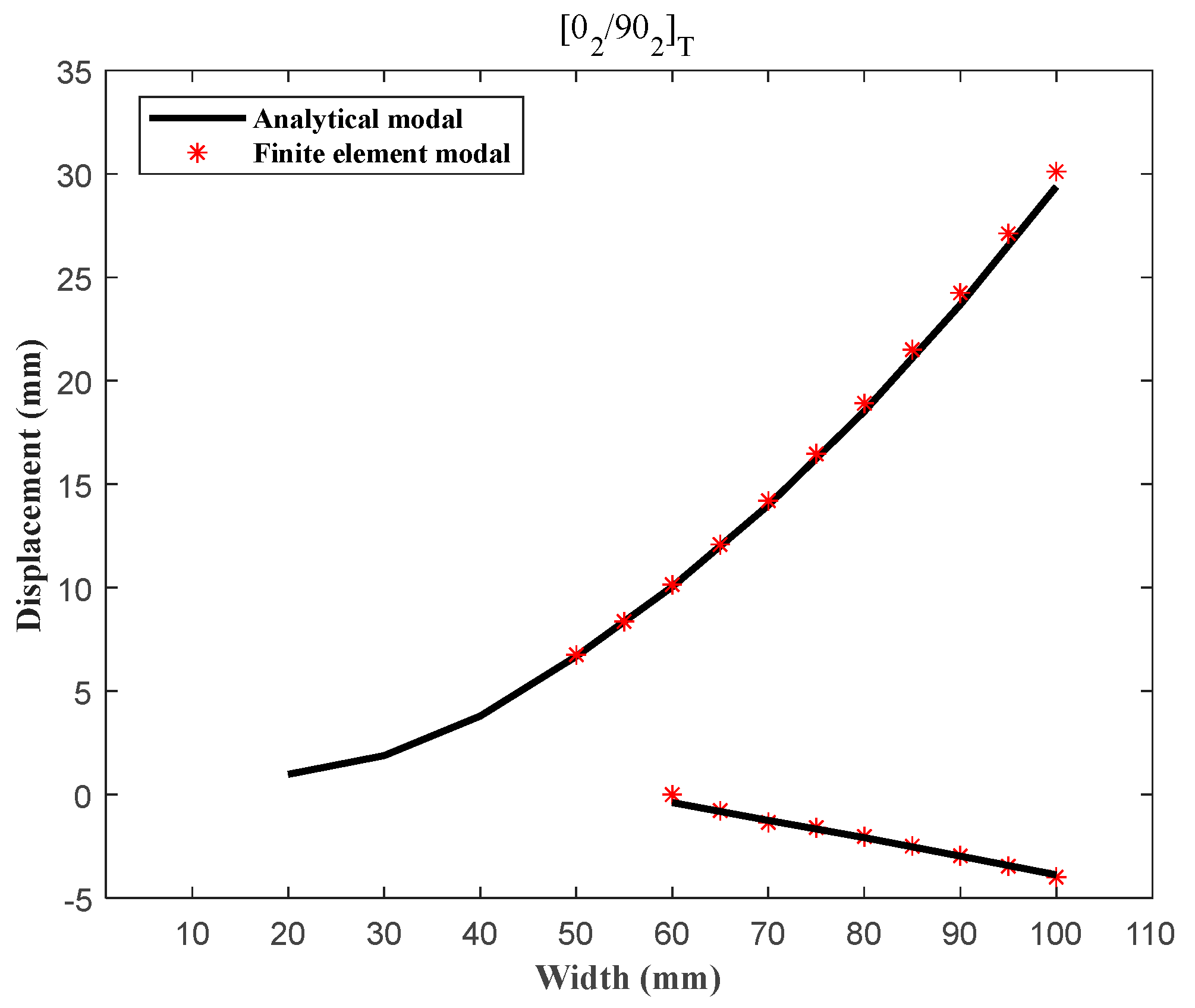
2.5. Geometric Parameter Analysis of Bistable Unsymmetric Laminates
3. Kinetic Analysis
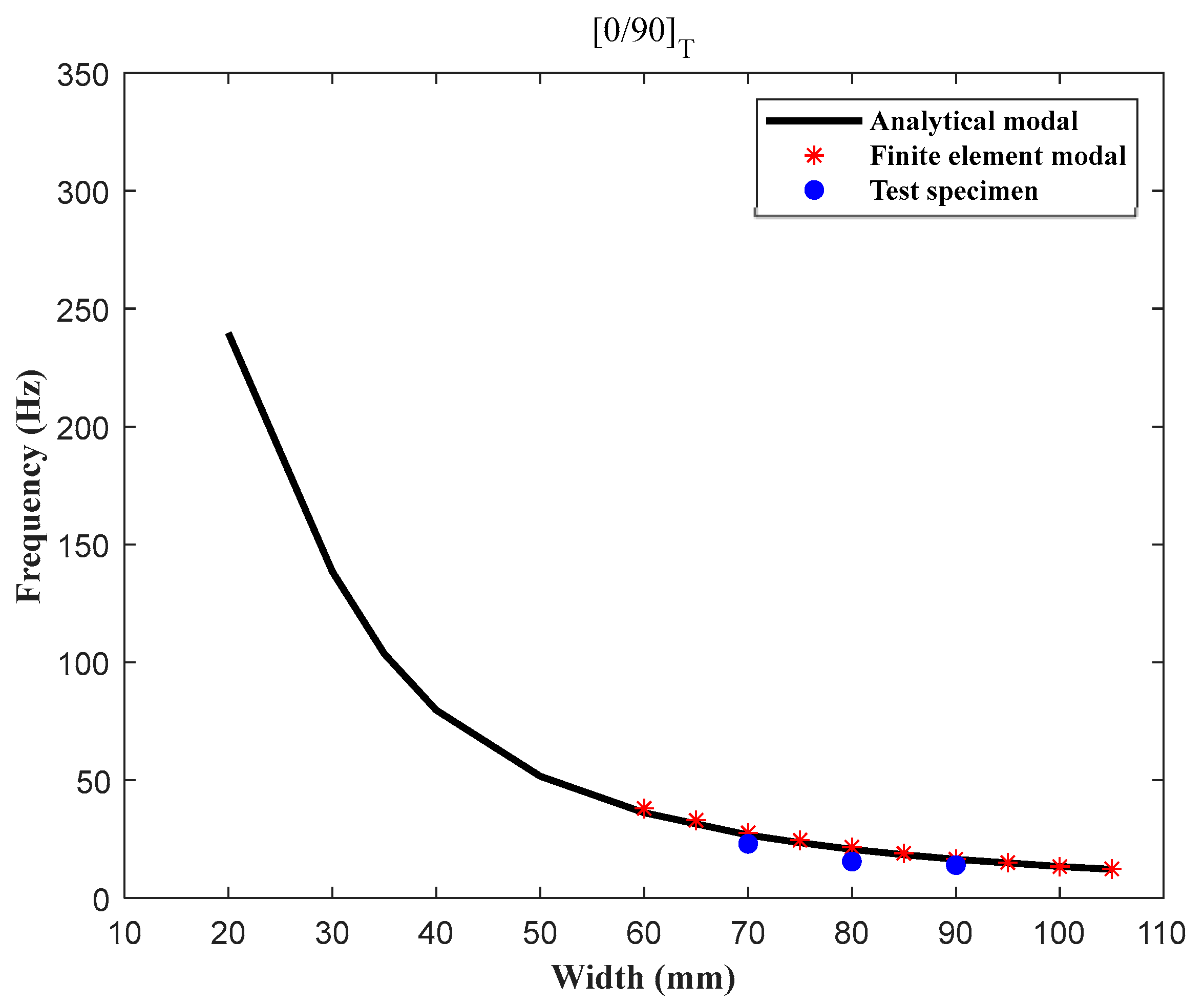
3.1. Fundamental Frequency Analysis
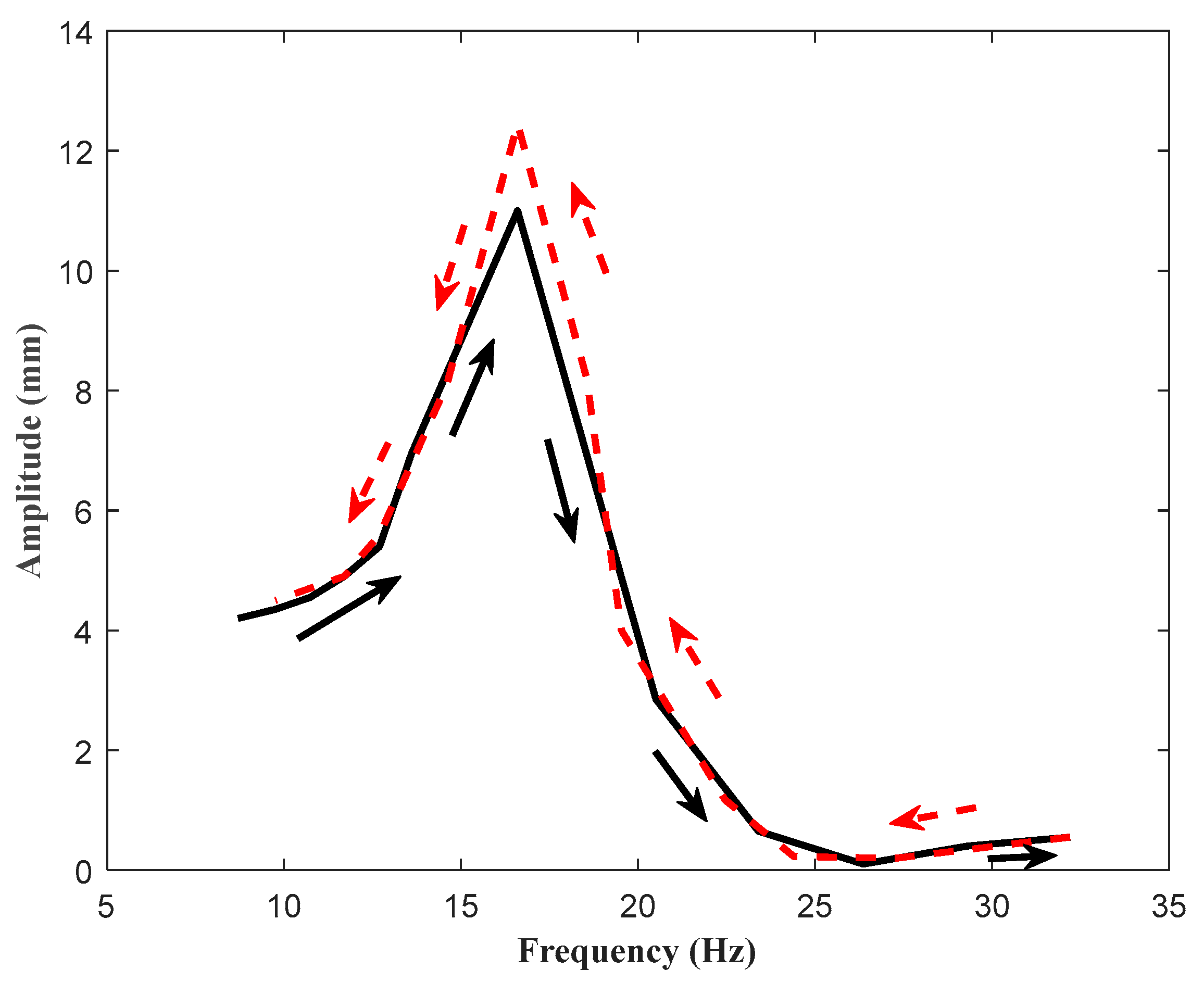
3.2. Frequency Sweep Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Shaw, A.D.; Wang, C.; Gu, H.; Amoozgar, M.R.; Friswell, M.I. Aeroelastic model and analysis of an active camber morphing wing. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Padilla, J.R.; Boston, D.M.; Boddapati, K.; Arrieta, A.F. Topology Optimization and Experimental Validation of a Selectively Stiff Multistable Morphing Wing Section. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2022 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, S.; Riley, K.S.; Arrieta, A.F. Multistable bioinspired origami with reprogrammable self-folding. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chi, Y.; Sun, J.; Huang, T.H.; Maghsoudi, O.H.; Spence, A.; Zhao, J.; Su, H.; Yin, J. Leveraging elastic instabilities for amplified performance: Spine-inspired high-speed and high-force soft robots. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.J.; Inman, D.J. A multifunctional bistable laminate: Snap-through morphing enabled by broadband energy harvesting. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 2528–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.J.; Inman, D.J. Electromechanical modelling of a bistable plate with macro fiber composites under nonlinear vibrations. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 446, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.G.; Seffen, K.A. On the shape of bistable creased strips. Thin-Walled Struct. 2018, 124, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemenschneider, J.; Pohl, M.; Ungurán, R.; Petrović, V.; Kühn, M.; Haldar, A.; Madhusoodanan, H.; Jansen, E.; Rolfes, R. Smart trailing edges for wind turbines. In Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 51944, p. V001T04A001. [Google Scholar]
- Hyer, M.W. Some observations on the cured shape of thin unsymmetric laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1981, 15, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyer, M.W. Calculations of the Room-Temperature Shapes of Unsymmetric Laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1981, 15, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyer, M.W. The Room-Temperature Shapes of Four-Layer Unsymmetric Cross-Ply Laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1982, 16, 318–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, W.J.; Hong, C.S. Effect of residual shear strain on the cured shape of unsymmetric cross-ply thin laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1990, 38, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, C.G.; Weaver, P.M.; Arrieta, A.F. Dynamic analysis of bi-stable composite plates. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 322, 987–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dano, M.L.; Hyer, M.W. Thermally-induced deformation behavior of unsymmetric laminates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1998, 35, 2101–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dano, M.L.; Hyer, M.W. Snap-through of unsymmetric fiber-reinforced composite laminates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2002, 39, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Kim, M.H.; Choi, H.S.; Chung, C.H.; Ahn, K.J.; Eom, Y.S. A study on the room-temperature curvature shapes of unsymmetric laminates including slippage effects. J. Compos. Mater. 1998, 32, 460–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etches, J.; Potter, K.; Weaver, P.; Bond, I. Environmental effects on thermally induced multistability in unsymmetric composite laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliotti, M.; Jacquemin, F.; Molimard, J.; Vautrin, A. Transient and cyclical hygrothermoelastic stress in laminated composite plates: Modelling and experimental assessment. Mech. Mater. 2007, 39, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissner, E.; Stavsky, Y. Bending and stretching of certain types of heterogeneous aeolotropic elastic plates. J. Appl. Mech. 1961, 28, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, J.M.; Leissa, A.W. Analysis of heterogeneous anisotropic plates. J. Appl. Mech. 1969, 36, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, M.; Mitura, A.; Romeo, F.; Warminski, J. Nonlinear dynamics of bistable composite cantilever shells: An experimental and modelling study. J. Sound Vib. 2022, 526, 116779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, M.; Vidoli, S.; Vincenti, A. Bistability of orthotropic shells with clamped boundary conditions: An analysis by the polar method. Compos. Struct. 2018, 194, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidoli, S. Discrete approximations of the Föppl–von Kármán shell model: From coarse to more refined models. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, M.; Vincenti, A.; Vidoli, S. A class of morphing shell structures satisfying clamped boundary conditions. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2016, 82, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancey, K.S. Viscoelastically prestressed polymeric matrix composites: An overview. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2016, 35, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ge, C.; Fancey, K.S. Snap-through behaviour of a bistable structure based on viscoelastically generated prestress. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 114, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürdal, Z.; Tatting, B.F.; Wu, C.K. Variable stiffness composite panels: Effects of stiffness variation on the in-plane and buckling response. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, A.; Reinoso, J.; Jansen, E.; Rolfes, R. Snap-through of bistable configurations generated from variable stiffness composites. In Multiscale Modeling of Heterogeneous Structures; Springer: Cham, Swtizerland, 2018; pp. 61–82. [Google Scholar]
- Haldar, A.; Reinoso, J.; Jansen, E.; Rolfes, R. Thermally induced multistable configurations of variable stiffness composite plates: Semi-analytical and finite element investigation. Compos. Struct. 2018, 183, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillara, V.S.C.; Dapino, M.J. Bistable morphing composites with selectively pre-stressed laminae. In Proceedings of the Behavior and Mechanics of Multifunctional Materials and Composites 2017, SPIE, Portland, OR, USA, 1 May 2017; Volume 10165, pp. 198–212. [Google Scholar]
- Chillara, V.S.C.; Dapino, M.J. Stability considerations and actuation requirements in bistable laminated composites. Compos. Struct. 2018, 184, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Q.; Li, L.; Kitipornchai, S.; Wang, C.M.; Zhu, H.P. Bi-stable analyses of laminated FGM shells. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2012, 12, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; He, X.; Wu, H.; Bao, Y.; Chai, G. The bistable behaviors of carbon-fiber/epoxy anti-symmetric composite shells. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 47, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.R.; Wilkie, W.K.; Bryant, R.G. Investigation of self-resetting active multistable laminates. J. Aircr. 2007, 44, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufenbach, W.; Gude, M.; Kroll, L. Design of multistable composites for application in adaptive structures. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 2201–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dano, M.L.; Hyer, M.W. SMA-induced snap-through of unsymmetric fiber-reinforced composite laminates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2003, 40, 5949–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Hao, L.; Nie, R.; Qiu, J. Nonlinear dynamics of shape memory alloys actuated bistable beams. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 055009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Hao, L.; Nie, R.; Qiu, J. Exploiting the instability of Smart Structure for Reconfiguring. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 064102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brampton, C.J.; Bowen, C.R.; Buschhorn, S.T.; Lee, J.; Pickering, S.G.; Wardle, B.L.; Kim, H.A. Actuation of bistable laminates by conductive polymer nanocomposites for use in thermal-mechanical aerosurface de-icing systems. In Proceedings of the 55th AIAA/ASMe/ASCE/AHS/SC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, National Harbor, MD, USA, 13–17 January 2014; p. 0105. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Dai, F.; Du, S. The morphing bi-stable glass fiber–reinforced polymer laminates actuated by embedded electrothermal alloy. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, A.F.; Neild, S.A.; Wagg, D.J. Nonlinear dynamic response and modeling of a bi-stable composite plate for applications to adaptive structures. Nonlinear Dyn. 2009, 58, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senba, A.; Ikeda, T.; Ueda, T. A two-way morphing actuation of bi-stable composites with piezoelectric fibers. In Proceedings of the 51st AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference 18th AIAA/ASME/AHS Adaptive Structures Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–15 April 2010; p. 2744. [Google Scholar]
- Arrieta, A.F.; Bilgen, O.; Friswell, M.I.; Hagedorn, P. Dynamic control for morphing of bi-stable composites. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2013, 24, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.Z.; Wu, M.Q. Theory and experiment of nonlinear vibrations and dynamic snap-through phenomena for bi-stable asymmetric laminated composite square panels under foundation excitation. Compos. Struct. 2019, 225, 111140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, J.E. Approximate solutions for unsymmetrically laminated plates. J. Compos. Mater. 1969, 3, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
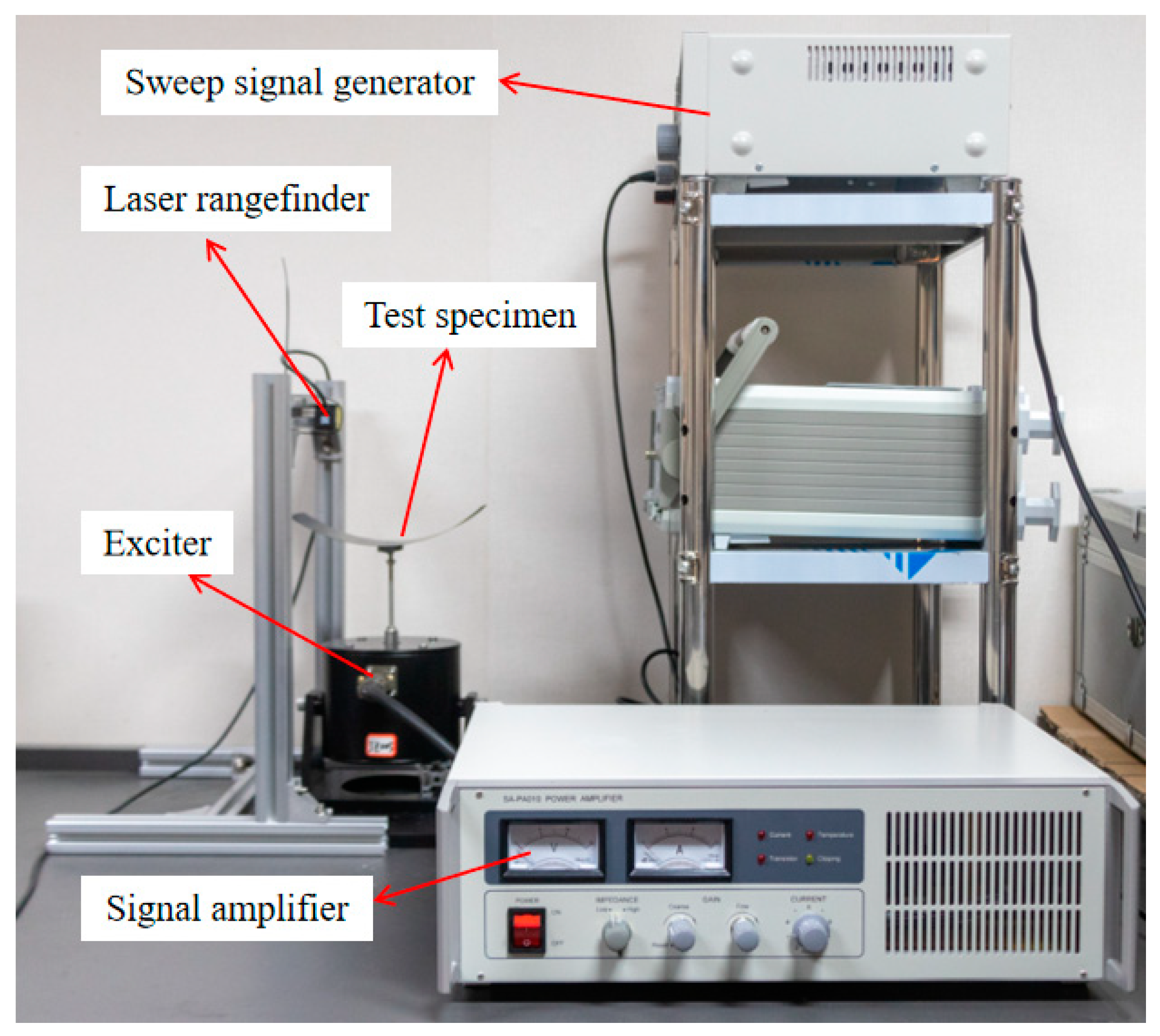

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Axial tensile modulus E1/GPa | 124.9 |
| Transversal tensile modulus E2/GPa | 7.9 |
| Shear modulus G12/GPa | 5.6 |
| Shear modulus G23/GPa | 5.6 |
| Poisson’s ratio ν12 | 0.3 |
| Longitudinal thermal expansion coefficient α1/°C−1 | 4 × 10−7 |
| Transverse thermal expansion coefficient α2/°C−1 | 1.8 × 10−5 |
| The thickness of layer t/mm | 0.15 |
| Applied Force (N) | Analytical Model (mm) | Finite Element Model (mm) | Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 38.5675 | 37.3187 | 3.99% |
| 0.1 | 45.3683 | 46.6199 | 2.68% |
| 0.2 | 52.2781 | 53.3966 | 2.09% |
| Width (mm) | Analytical Model (Hz) | Finite Element Model (Hz) | Test Specimen (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | 26.77 | 27.6 | 23 |
| 80 | 20.649 | 21.5 | 15.5 |
| 90 | 16.4 | 16.5 | 14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pan, D.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Q. Resonant Actuation Based on Dynamic Characteristics of Bistable Laminates. Machines 2023, 11, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030318
Liu Y, Zhang J, Pan D, Wu Z, Wang Q. Resonant Actuation Based on Dynamic Characteristics of Bistable Laminates. Machines. 2023; 11(3):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030318
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuting, Jiaying Zhang, Diankun Pan, Zhangming Wu, and Qingyun Wang. 2023. "Resonant Actuation Based on Dynamic Characteristics of Bistable Laminates" Machines 11, no. 3: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030318
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhang, J., Pan, D., Wu, Z., & Wang, Q. (2023). Resonant Actuation Based on Dynamic Characteristics of Bistable Laminates. Machines, 11(3), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030318








