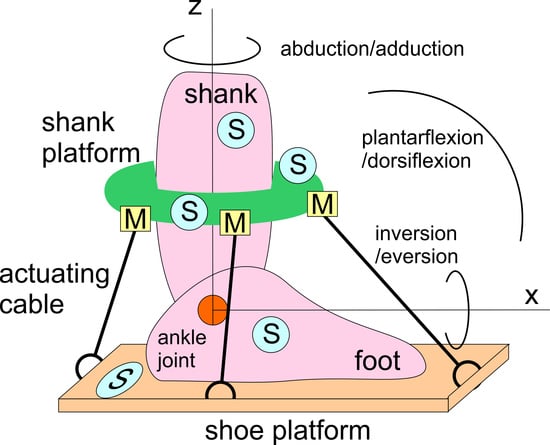
Analysis of a Wearable Robotic System for Ankle Rehabilitation †
Abstract
Share and Cite
Russo, M.; Ceccarelli, M. Analysis of a Wearable Robotic System for Ankle Rehabilitation. Machines 2020, 8, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8030048
Russo M, Ceccarelli M. Analysis of a Wearable Robotic System for Ankle Rehabilitation. Machines. 2020; 8(3):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Matteo, and Marco Ceccarelli. 2020. "Analysis of a Wearable Robotic System for Ankle Rehabilitation" Machines 8, no. 3: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8030048
APA StyleRusso, M., & Ceccarelli, M. (2020). Analysis of a Wearable Robotic System for Ankle Rehabilitation. Machines, 8(3), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines8030048