Design and Analysis of a Lower Limb Rehabilitation Training Component for Bedridden Stroke Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
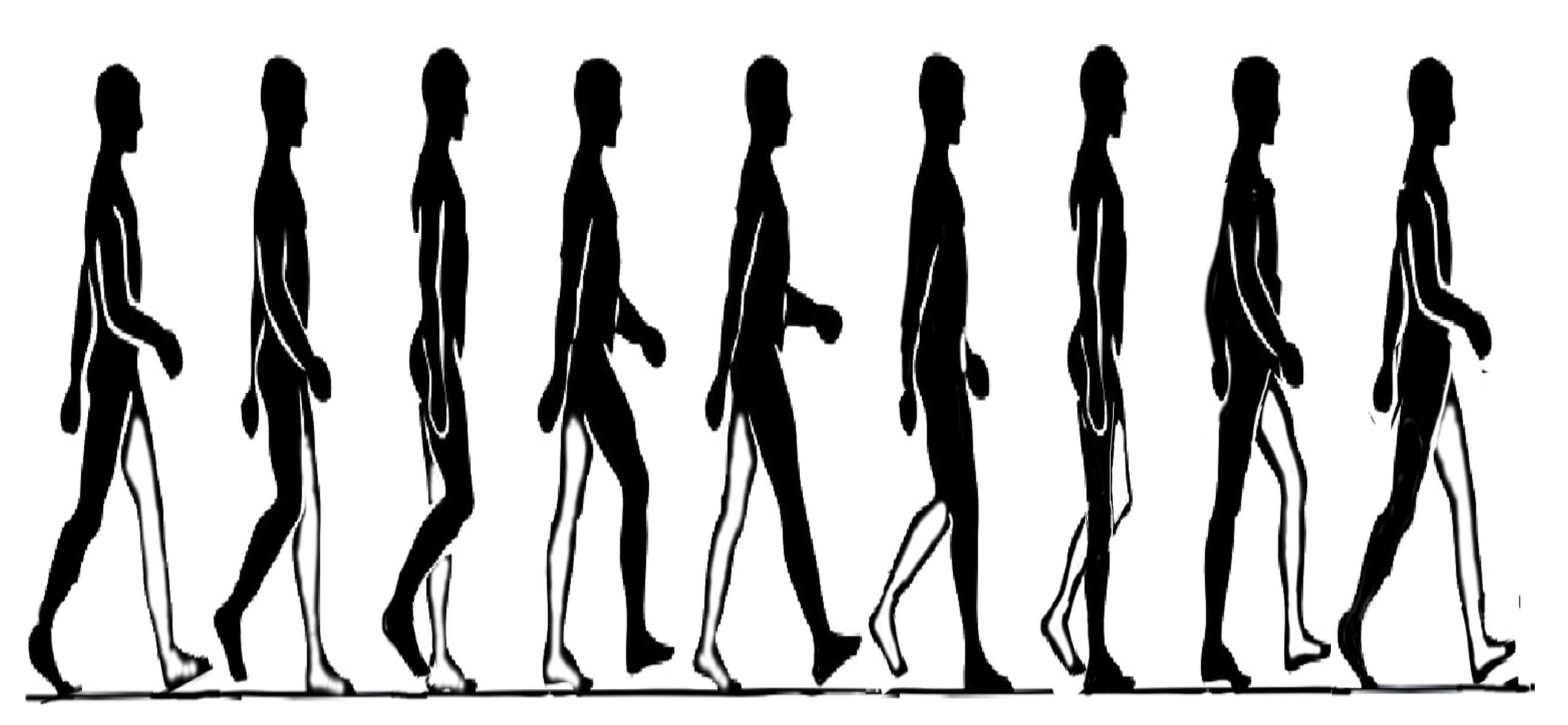
2.1. Motion Analysis of Human Lower Limb during Walking
2.2. Mechanism Design and Analysis of Lower Limb Rehabilitation Module
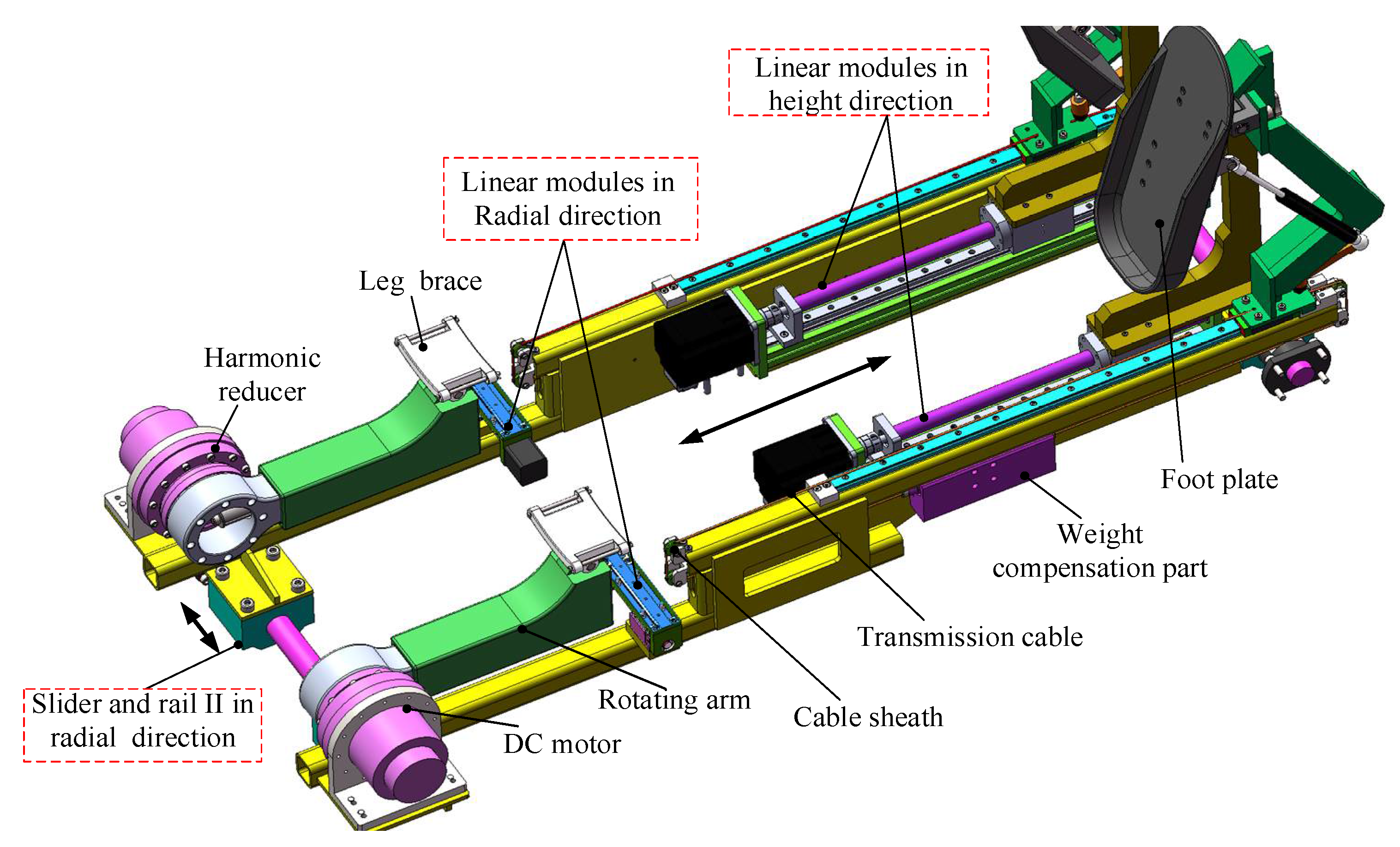
2.2.1. Mechanism Design of Lower Limb Rehabilitation Module
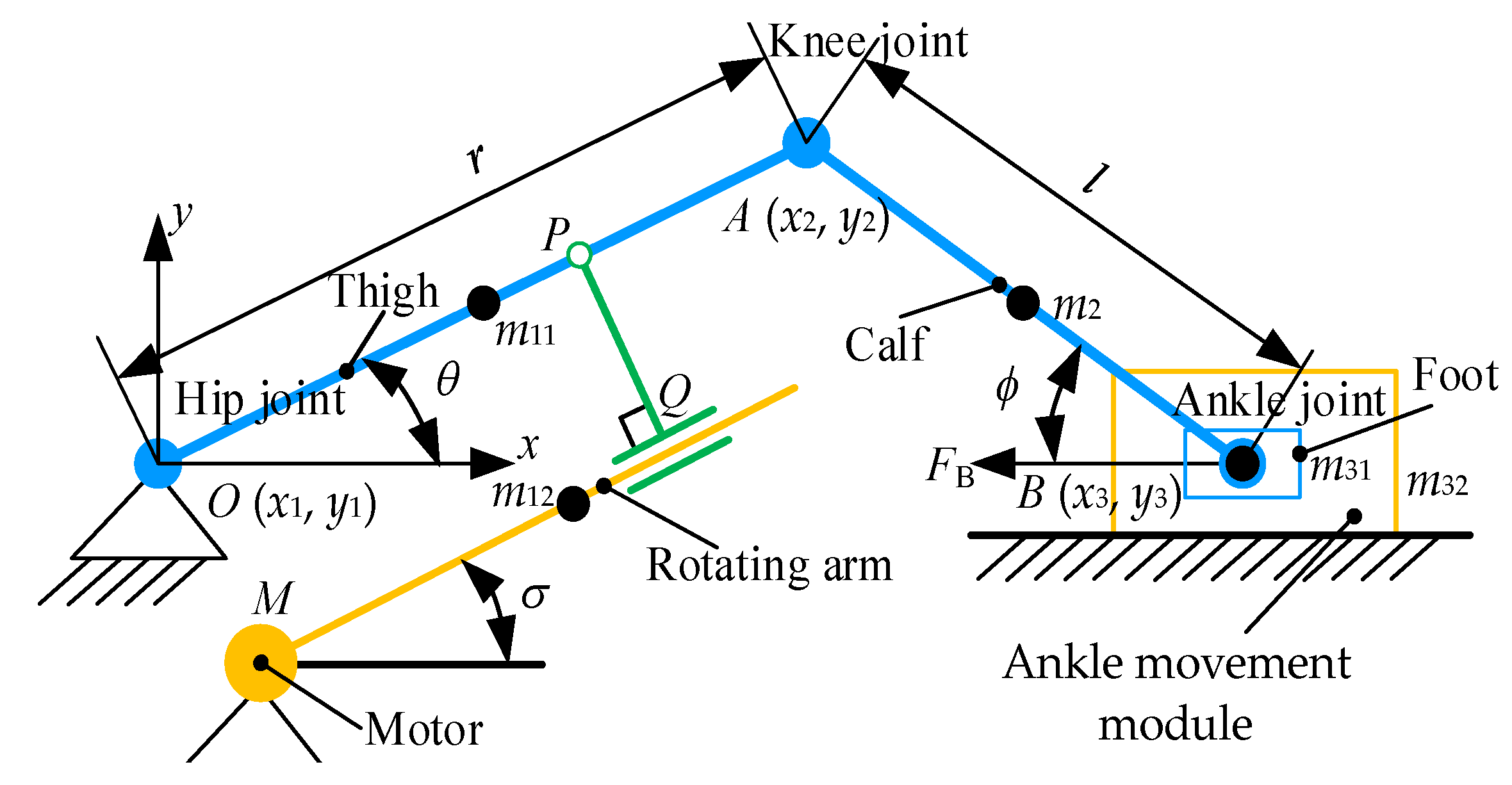
2.2.2. Analysis of Human–Machine Simplified Linkage Model
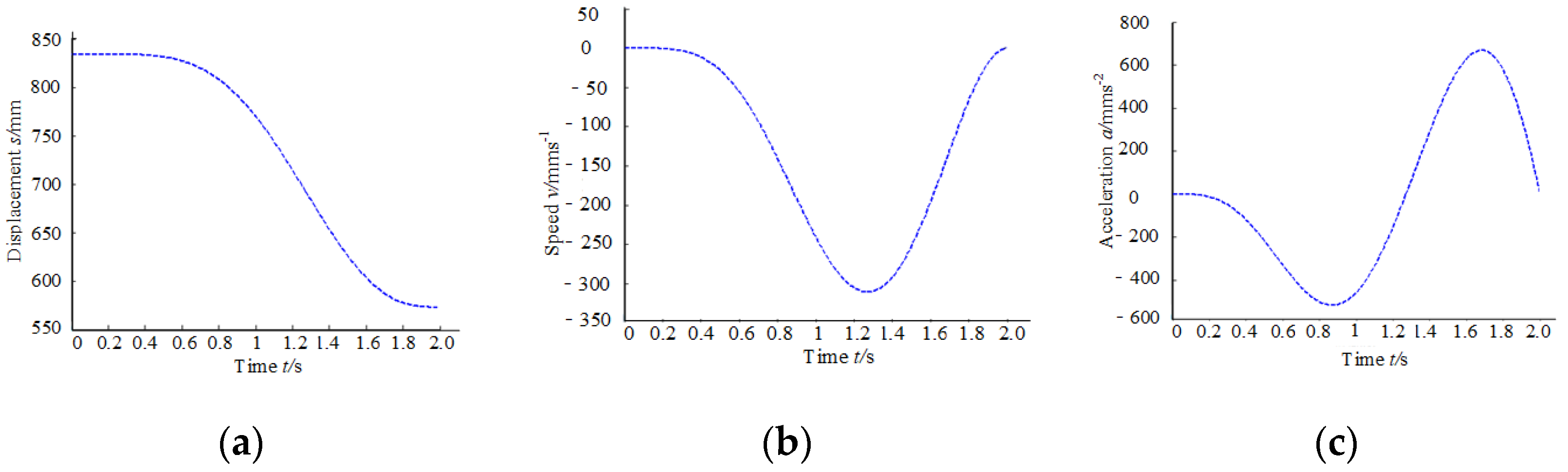
2.2.3. Design and Analysis of Speed and Acceleration of Human–Machine Linkage Model
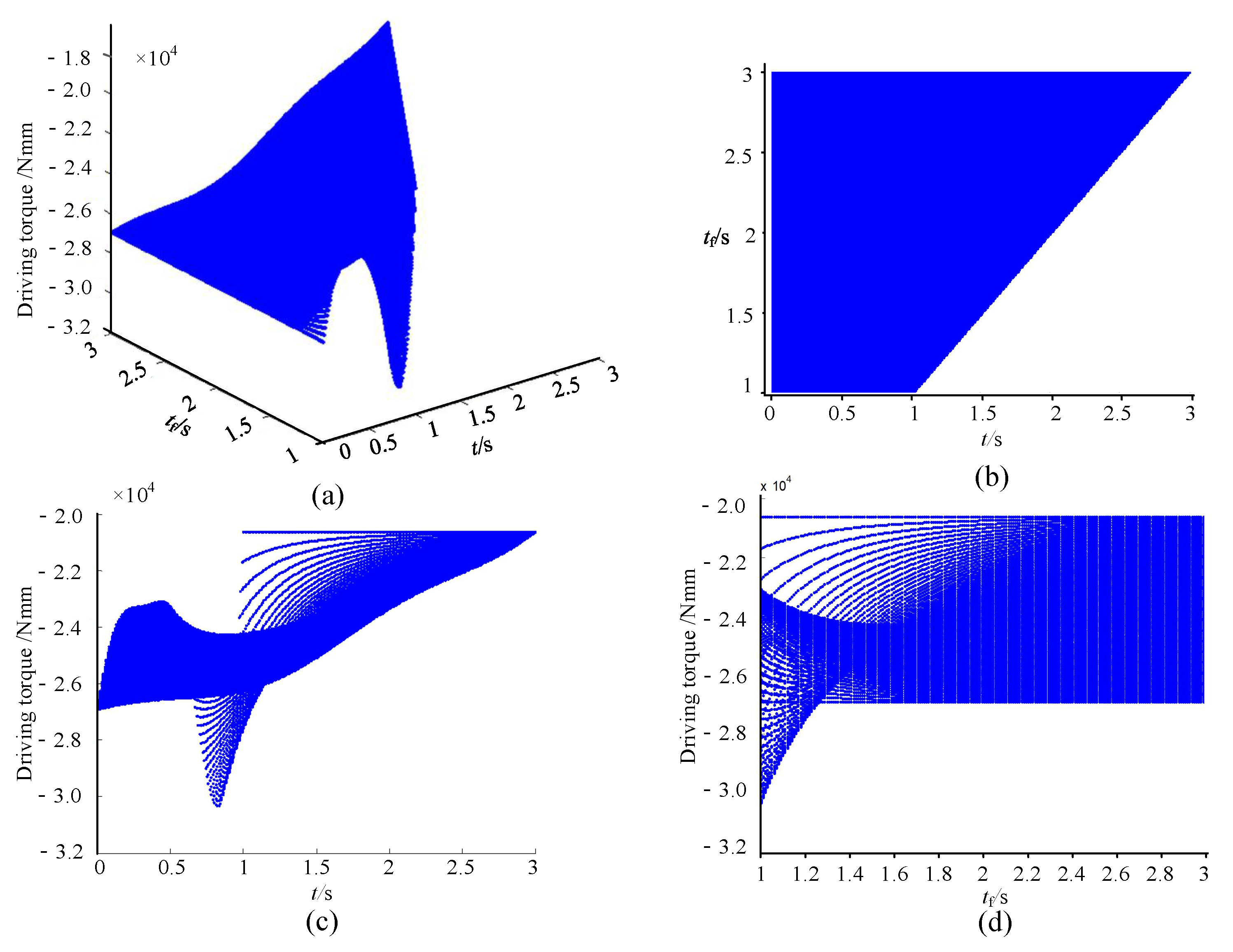
2.2.4. Dynamic Analysis of Lower Limb Rehabilitation Module
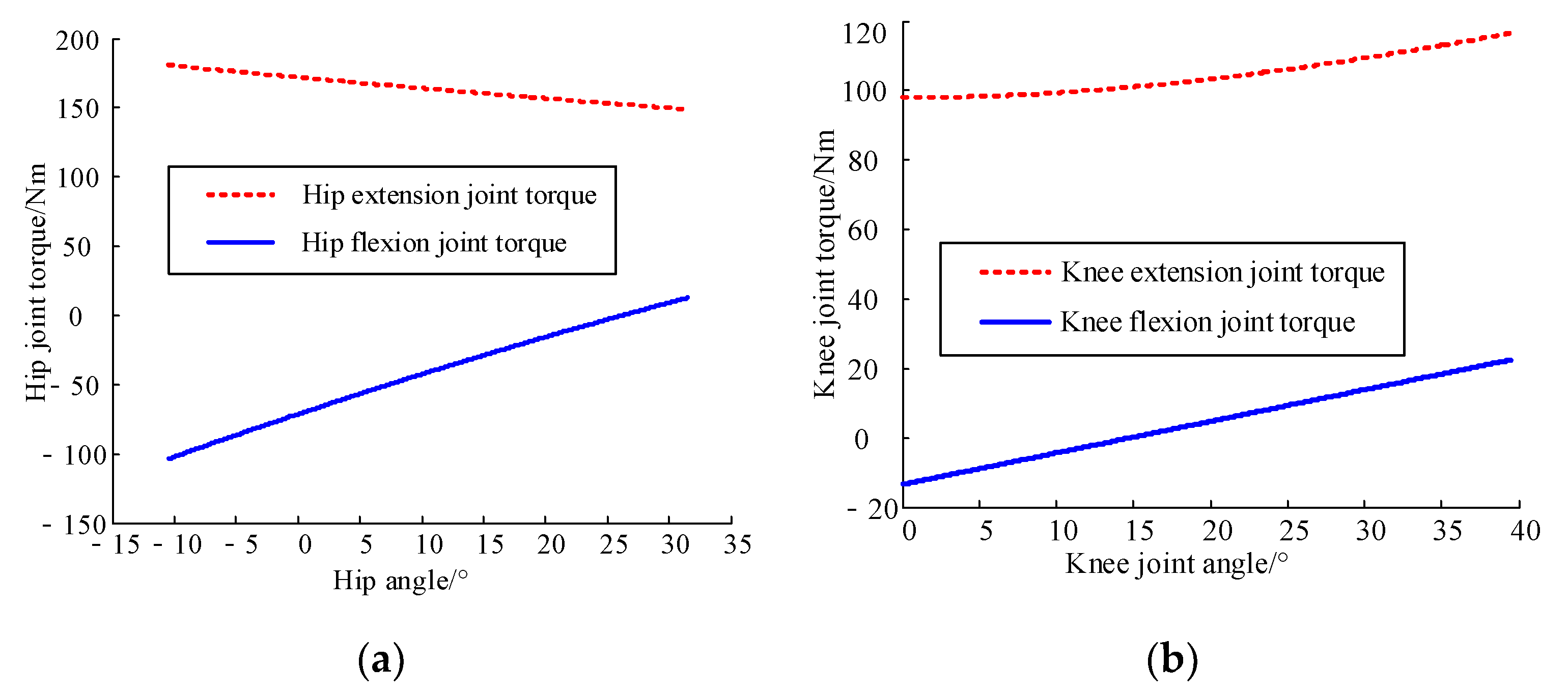
2.2.5. Analysis of the Static Moment Safety Protection of Human–Machine Linkage Model
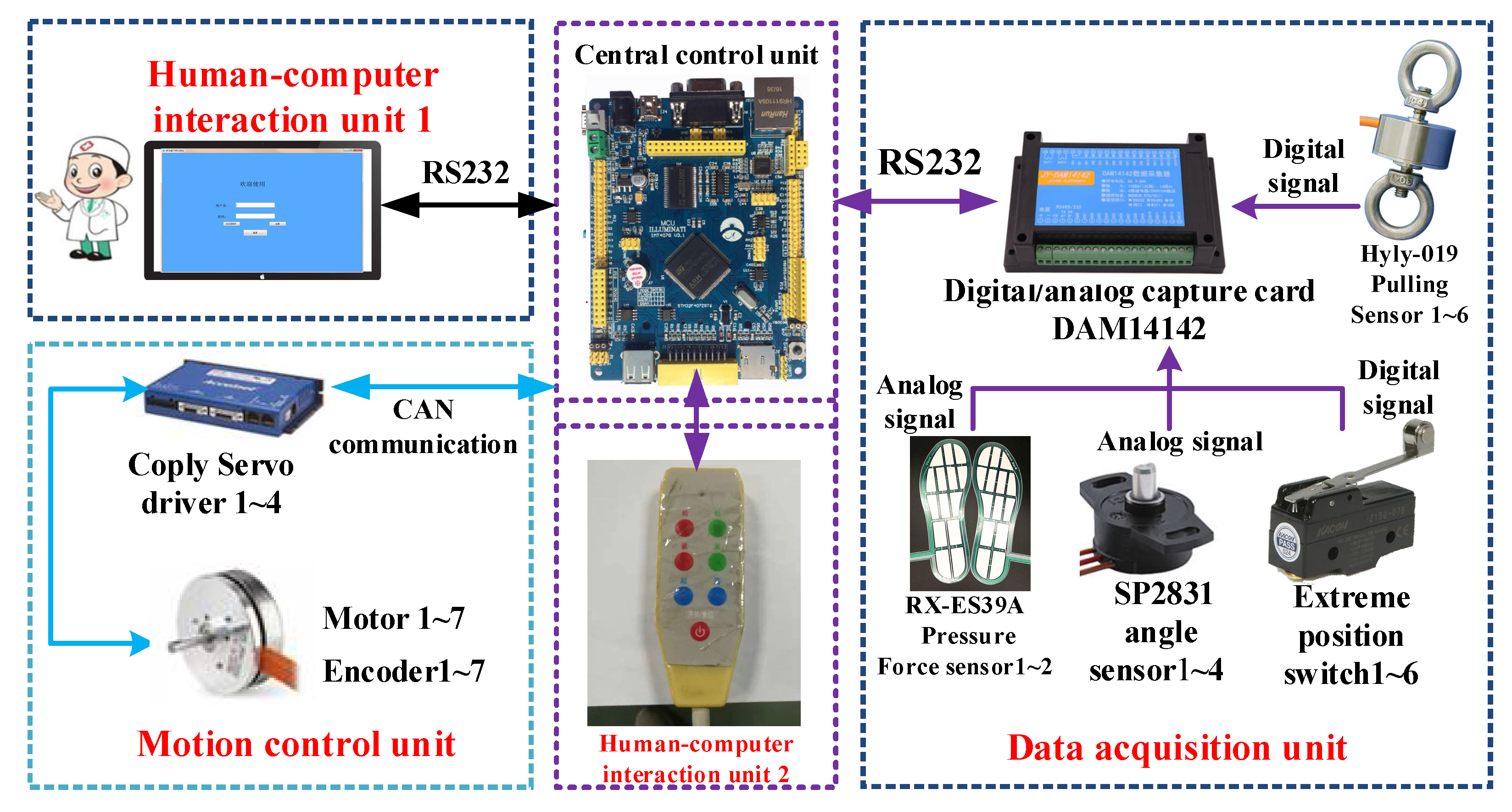
2.2.6. Active Training Control System of the Proposed Mechanism
3. Results
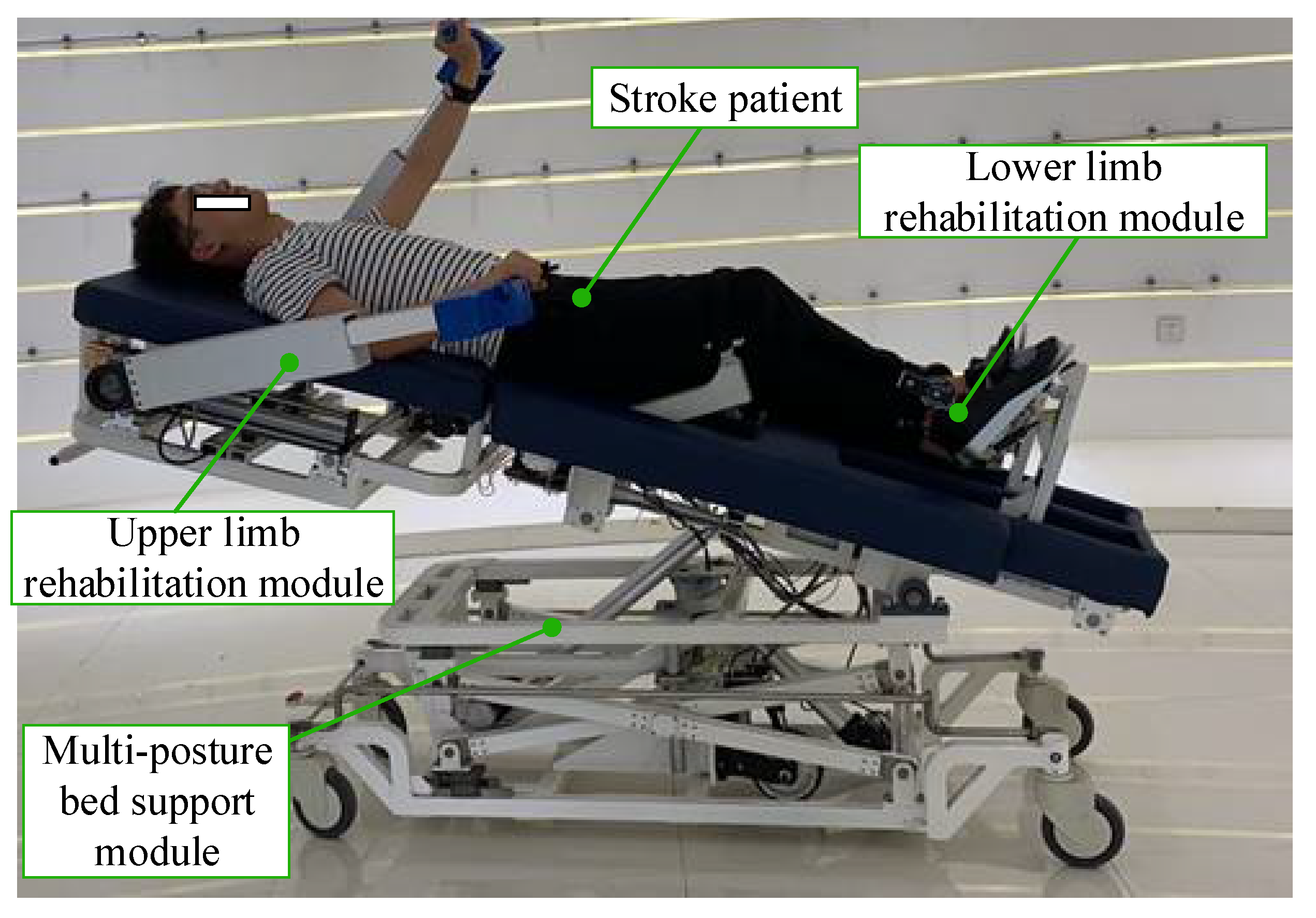
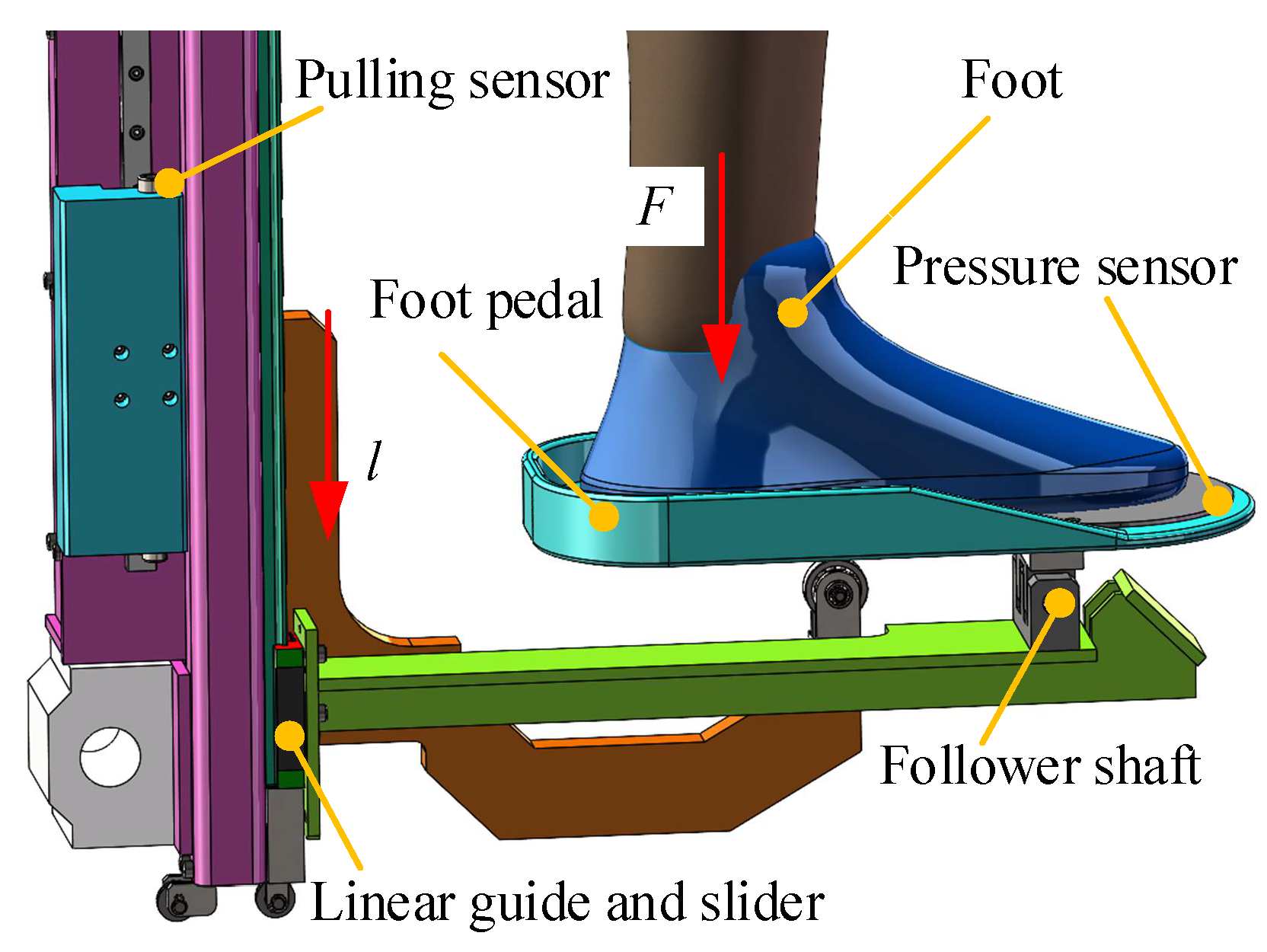
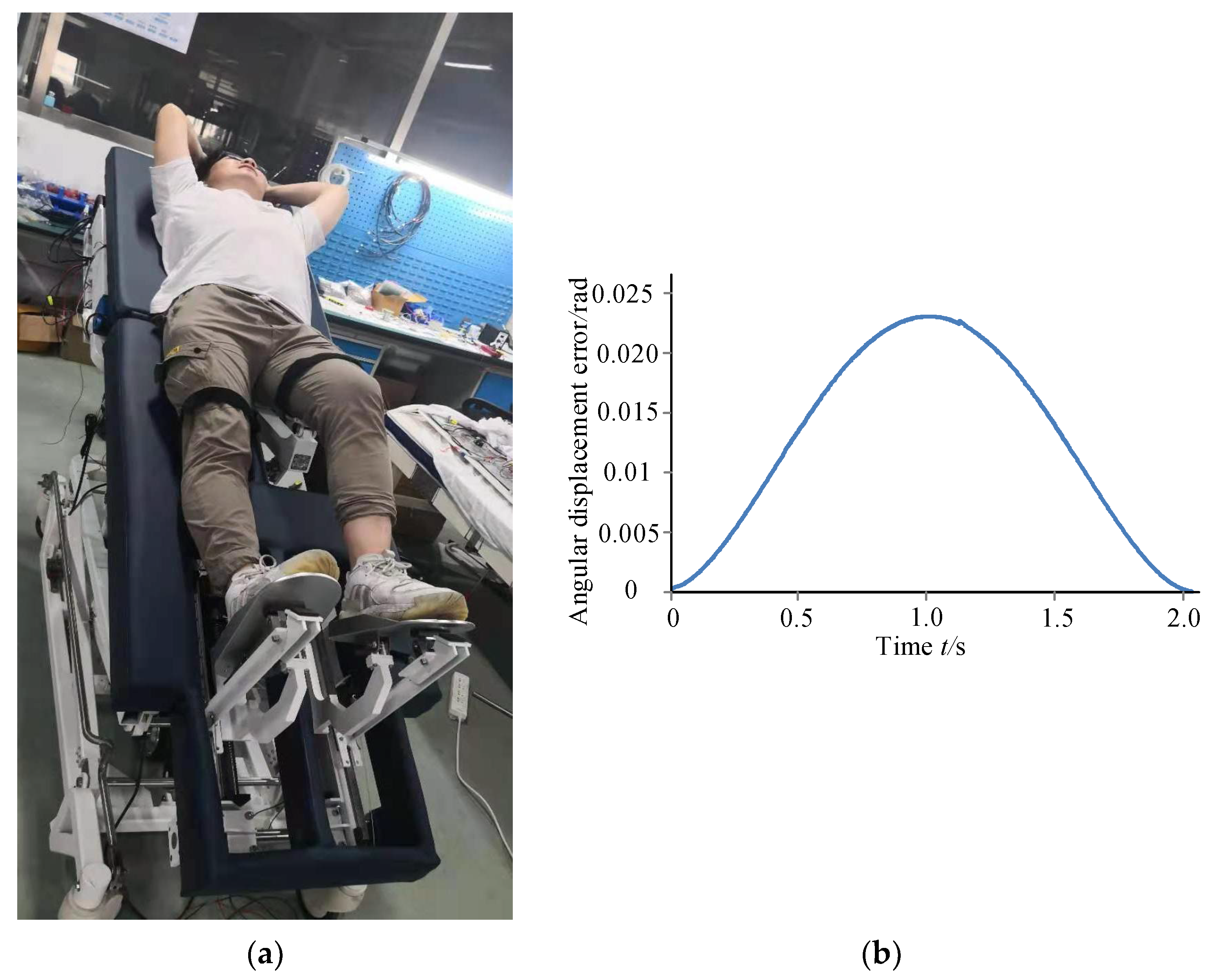
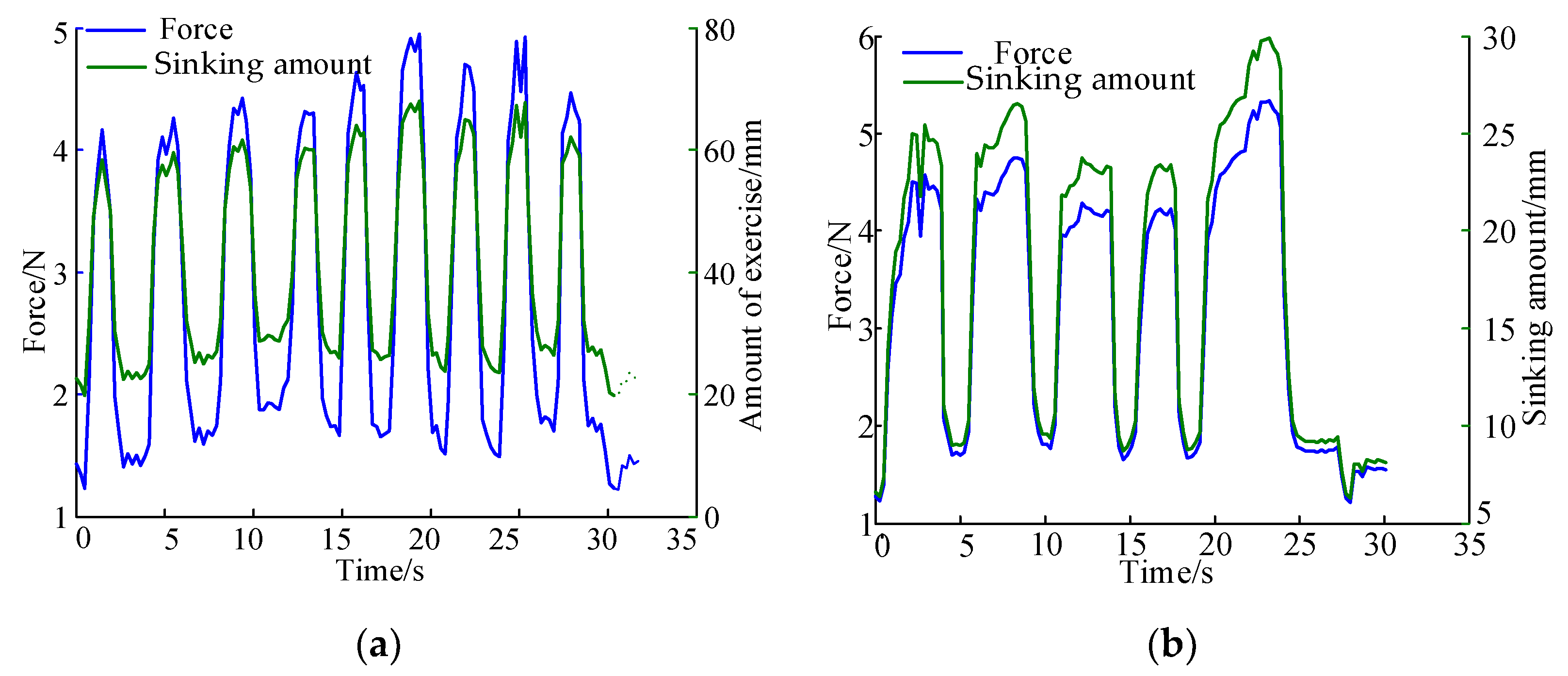
Rehabilitation Robot Experimental Platform Construction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Su, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Sang, L.; Feng, Y.; Niu, J. Design and evaluation of a novel person transfer assist system. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 14306–14318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.H.; Takeda, Y. Geometric design and prototyping of a (2-RRU)-URR parallel mechanism for thumb rehabilitation therapy. Machines 2021, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassert, R.; Dietz, V. Rehabilitation robots for the treatment of sensorimotor deficits: A neurophysiological perspective. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayr, A.; Quirbach, E.; Picelli, A.; Kofler, M.; Smania, N.; Saltuari, L. Early robot-assisted gait retraining in non-ambulatory patients with stroke: A single blind randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 54, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.D.; Wang, J.H.; Peng, B.; Xu, Y.M. Brief report on stroke prevention and treatment in China. Chin. J. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 17, 272–281. [Google Scholar]
- Doost, M.Y.; Herman, B.; Denis, A.; Sapin, J.; Galinski, D.; Riga, A.; Laloux, P.; Bihin, B.; Vandermeeren, Y. Bimanual motor skill learning and robotic assistance for chronic hemiparetic stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar]
- Birouaș, F.I.; Țarcă, R.C.; Dzitac, S.; Dzitac, I. Preliminary results in testing of a novel asymmetric underactuated robotic hand exoskeleton for motor impairment rehabilitation. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sconza, C.; Negrini, F.; Di Matteo, B.; Borboni, A.; Boccia, G.; Petrikonis, I.; Stankevičius, E.; Casale, R. Robot-Assisted Gait Training in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Randomized Controlled Crossover Trial. Medicina 2021, 57, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, E.R.; Moudgal, R.; Lang, K.; Hyacinth, H.I.; Awosika, O.O.; Kissela, B.M.; Feng, W. Early rehabilitation after stroke: A narrative review. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 30, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Onofrio, G.; Fiorini, L.; Hoshino, H.; Matsumori, A.; Okabe, Y.; Tsukamoto, M.; Limosani, R.; Vitanza, A.; Greco, F.; Greco, A.; et al. Assistive robots for socialization in elderly people: Results pertaining to the needs of the users. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 1313–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Ceccarelli, M. Analysis of a wearable robotic system for ankle rehabilitation. Machines 2020, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzarane, R.A.; Klimstra, M.; Lewis, A.; Hundza, S.R.; Zehr, E.P. Interlimb coupling from the arms to legs is differentially specified for populations of motor units comprising the compound h-reflex during “reduced” human locomotion. Exp. Brain Res. 2011, 208, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susanto, S.; Simorangkir, I.T.; Analia, R.; Pamungkas, D.S.; Soebhakti, H.; Sani, A.; Caesarendra, W. Real-time identification of knee joint walking gait as preliminary signal for developing lower limb exoskeleton. Electronics 2021, 10, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, R.; Shushtari, M.; Arami, A. An Adaptive assistance controller to optimize the exoskeleton contribution in rehabilitation. Robotics 2021, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzlin, B.; Bergmann, L.; Li, Y.; Ji, L.; Leonhardt, S.; Ngo, C. Design and first operation of an active lower limb exoskeleton with parallel elastic actuation. Actuators 2021, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kammen, K.; Reinders-Messelink, H.A.; Elsinghorst, A.L.; Wesselink, C.F.; Meeuwisse-de Vries, B.; van der Woude, L.H.; Boonstra, A.M.; den Otter, R. Amplitude and stride-to-stride variability of muscle activity during Lokomat guided walking and treadmill walking in children with cerebral palsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2021, 29, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.; Koyama, S.; Sakurai, H.; Teranishi, T.; Kanada, Y.; Tanabe, S. Wearable robotic exoskeleton for gait reconstruction in patients with spinal cord injury: A literature review. J. Orthop. Transl. 2021, 28, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, T.; Vladareanuv, V.; Li, Q.; Zhao, C. Teaching training method of a lower limb rehabilitation robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Vladareanu, L.; Chen, Z.; Jin, D. New motion intention acquisition method of lower limb rehabilitation robot based on static torque sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Yadav, R.A.; Aafreen; Yadav, S. Effect of robotic tilt table on rehabilitation outcome in right side versus left side hemiplegia. Int. J. Yogic Hum. Mov. Sports Sci. 2018, 3, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Xie, Q.; Yang, G.Y.; Xie, L. Development and feasibility assessment of a rotational orthosis for walking with arm swing. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, T.W. Comparisons between Locomat and Walkbot robotic gait training regarding balance and lower extremity function among non-ambulatory chronic acquired brain injury survivors. Medicine 2021, 100, e25125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurich-Schuler, T.; Gut, A.; Labruyere, R. The FreeD module for the Lokomat facilitates a physiological movement pattern in healthy people—A proof of concept study. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Li, L.; Shin, S.Y.; Deshpande, A.D.; Sulzer, J. Kinematic comparison of single degree-of-freedom robotic gait trainers. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 159, 104258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Vladareanuv, V.; Du, Y. Mechanical design and trajectory planning of a lower limb rehabilitation robot with a variable workspace. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Tian, Y.; Lin, M.; Yan, H.; Niu, J.; Sun, L. Adaptive direct teaching control with variable load of the lower limb rehabilitation robot (LLR-II). Machines 2021, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daunoraviciene, K.; Adomaviciene, A.; Svirskis, D.; Griškevičius, J.; Juocevicius, A. Necessity of early-stage verticalization in patients with brain and spinal cord injuries: Preliminary study. Technol. Health Care 2018, 26, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, C. Design of Multi-Step Synergy Rehabilitation Model Based on Flexbot Rehabilitation Robot Platform. Master’s Thesis, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China, 19 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhang, D.; Lu, H. Research on the lower limb gait rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Tianjin, China, 3–6 August 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, C.S.; Bi, S.; Xie, Y.J.; YU, Z.Z.; Qin, Y.; Wu, Y.M.; Lu, Y.H. Relationship between walking speed and step length and walking rate in hemiparetic stroke patients. Chin. J. Clin. Rehabil. 2003, 7, 1108–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.L. A Journey from Robot to Digital Human: Mathematical Principles and Applications with MATLAB Programming, 1st ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 435–445. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, J.Y.; Reece, A.R. Prediction of rigid wheel performance based on the analysis of soil-wheel stresses: Part II. Performance of driven rigid wheels. J. Terramech. 1967, 4, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Stride (cm) | Step Width (cm) | Step Frequency (min−1) | Step Height (cm) | Hip Joint Range (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | 45–90 | 5–10 | 90–125 | 5–10 | −20–120 |
| Volunteer | Gender | Age | Height | Thigh Length | Calf Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xu | Man | 26 | 1720 (mm) | 492 (mm) | 398 (mm) |
| Sandy Soil Environment | k1 | k2 | n |
|---|---|---|---|
| Harder | 0 | 6.27 | 0.95 |
| Softer | 0 | 0.90 | 1.15 |
| Product Name | Training Joints | Range of Motion | Human Height Adjustment | Human Fat and Thin Shape Adjustment | Manufacturing Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROWAS [20] | Hip, knee and ankle | Large | Yes | Yes | High |
| Flexbot [27] | Hip, knee and ankle | Large | Yes | Yes | High |
| The proposed robot | Hip, knee and ankle | Large | Yes | Yes | Low |
| Erigo [26] | Hip, knee and ankle | Small | Yes | No | Low |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Niu, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H. Design and Analysis of a Lower Limb Rehabilitation Training Component for Bedridden Stroke Patients. Machines 2021, 9, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9100224
Wang X, Feng Y, Zhang J, Li Y, Niu J, Yang Y, Wang H. Design and Analysis of a Lower Limb Rehabilitation Training Component for Bedridden Stroke Patients. Machines. 2021; 9(10):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9100224
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xusheng, Yongfei Feng, Jiazhong Zhang, Yungui Li, Jianye Niu, Yandong Yang, and Hongbo Wang. 2021. "Design and Analysis of a Lower Limb Rehabilitation Training Component for Bedridden Stroke Patients" Machines 9, no. 10: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9100224
APA StyleWang, X., Feng, Y., Zhang, J., Li, Y., Niu, J., Yang, Y., & Wang, H. (2021). Design and Analysis of a Lower Limb Rehabilitation Training Component for Bedridden Stroke Patients. Machines, 9(10), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9100224









