Kinematic Analysis of a Gear-Driven Rotary Planting Mechanism for a Six-Row Self-Propelled Onion Transplanter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overall Structure and Working Principle of Onion Transplanter
2.2. Vector-Loop Modeling of the Rotary Planting Mechanism
2.2.1. Position Analysis
2.2.2. Velocity and Acceleration
2.2.3. Simulation of the Rotary Planting Mechanism
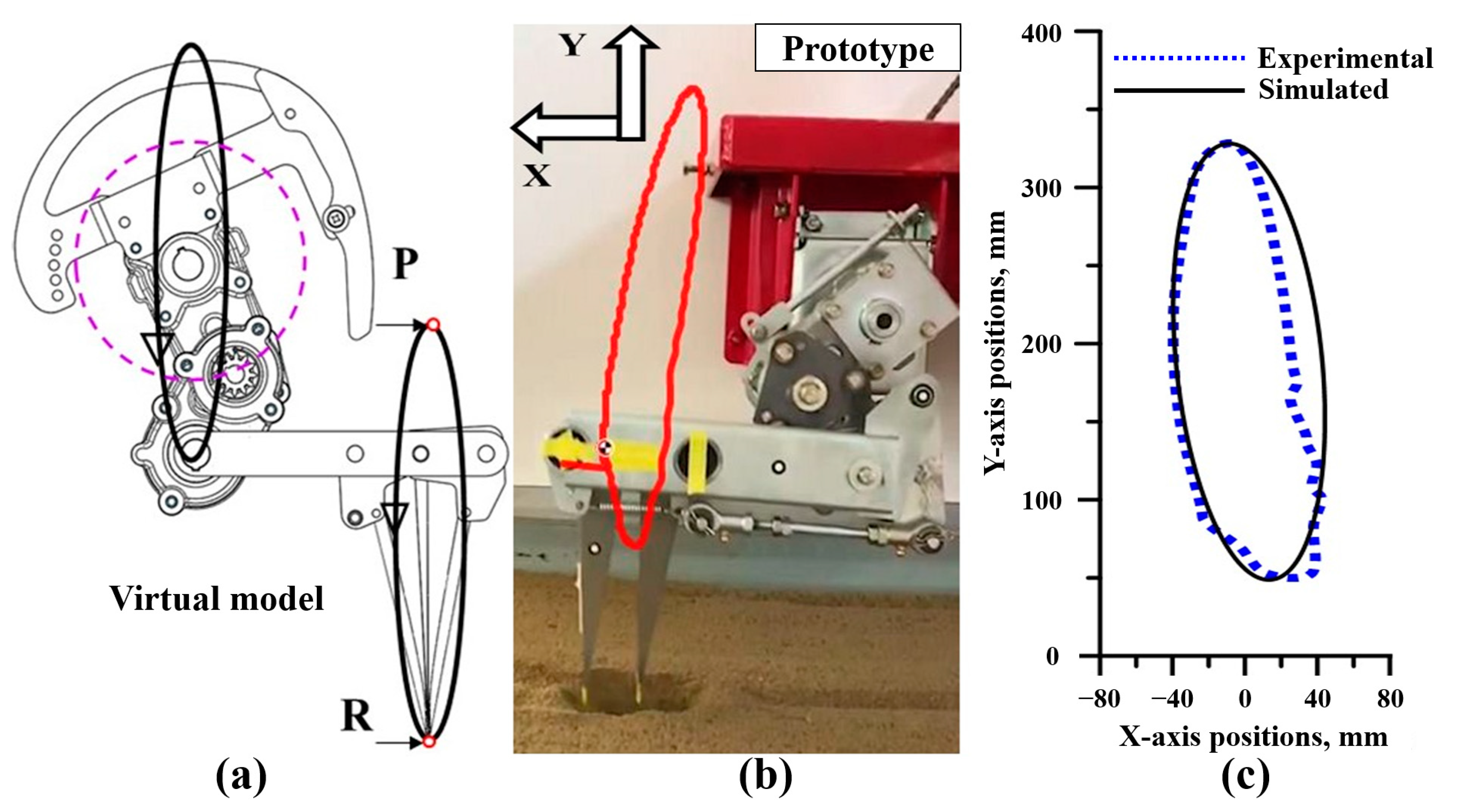
2.3. Validation of Planting Mechanism
3. Results and Discussion
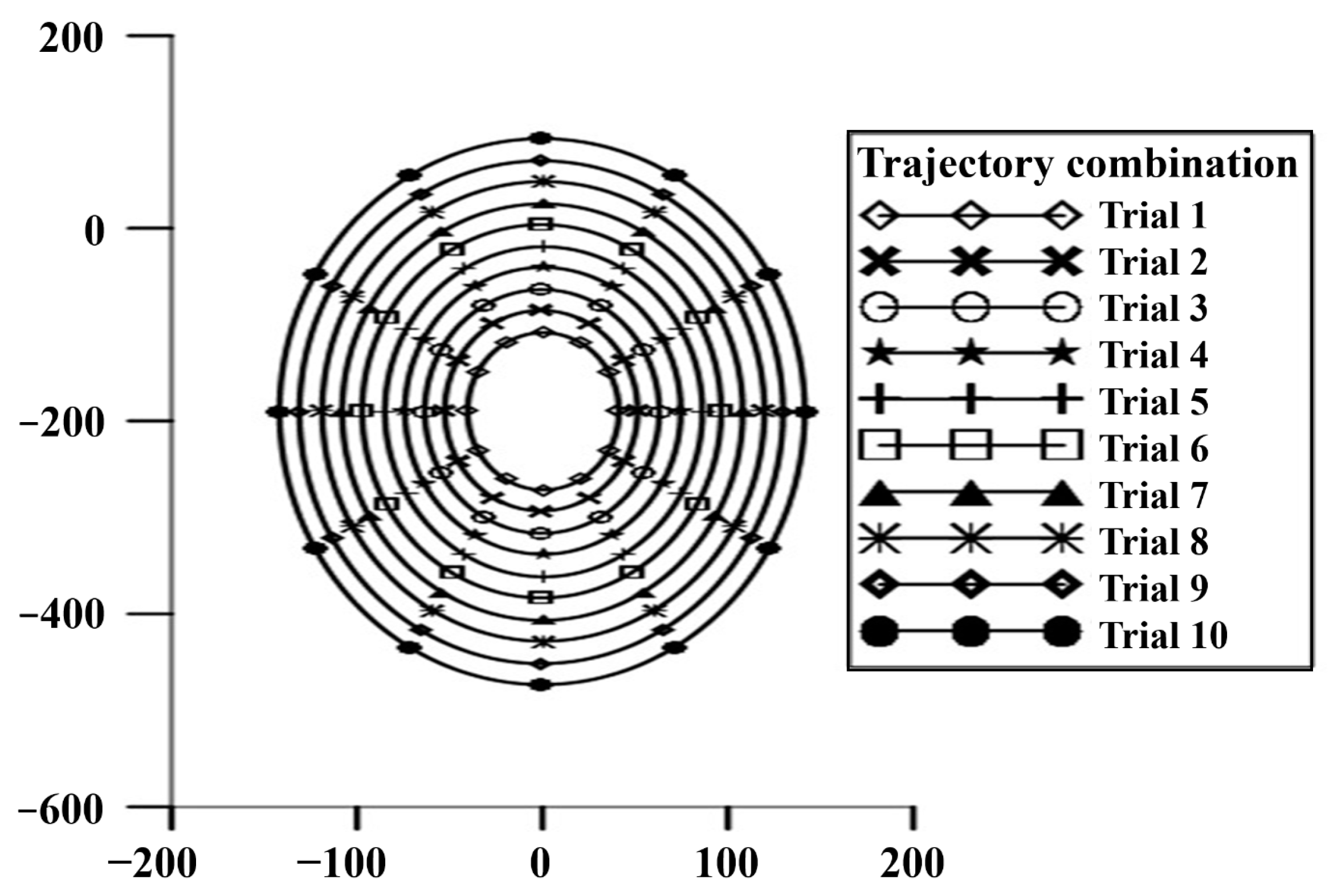
3.1. Working Trajectory of the Dibbling Mechanism
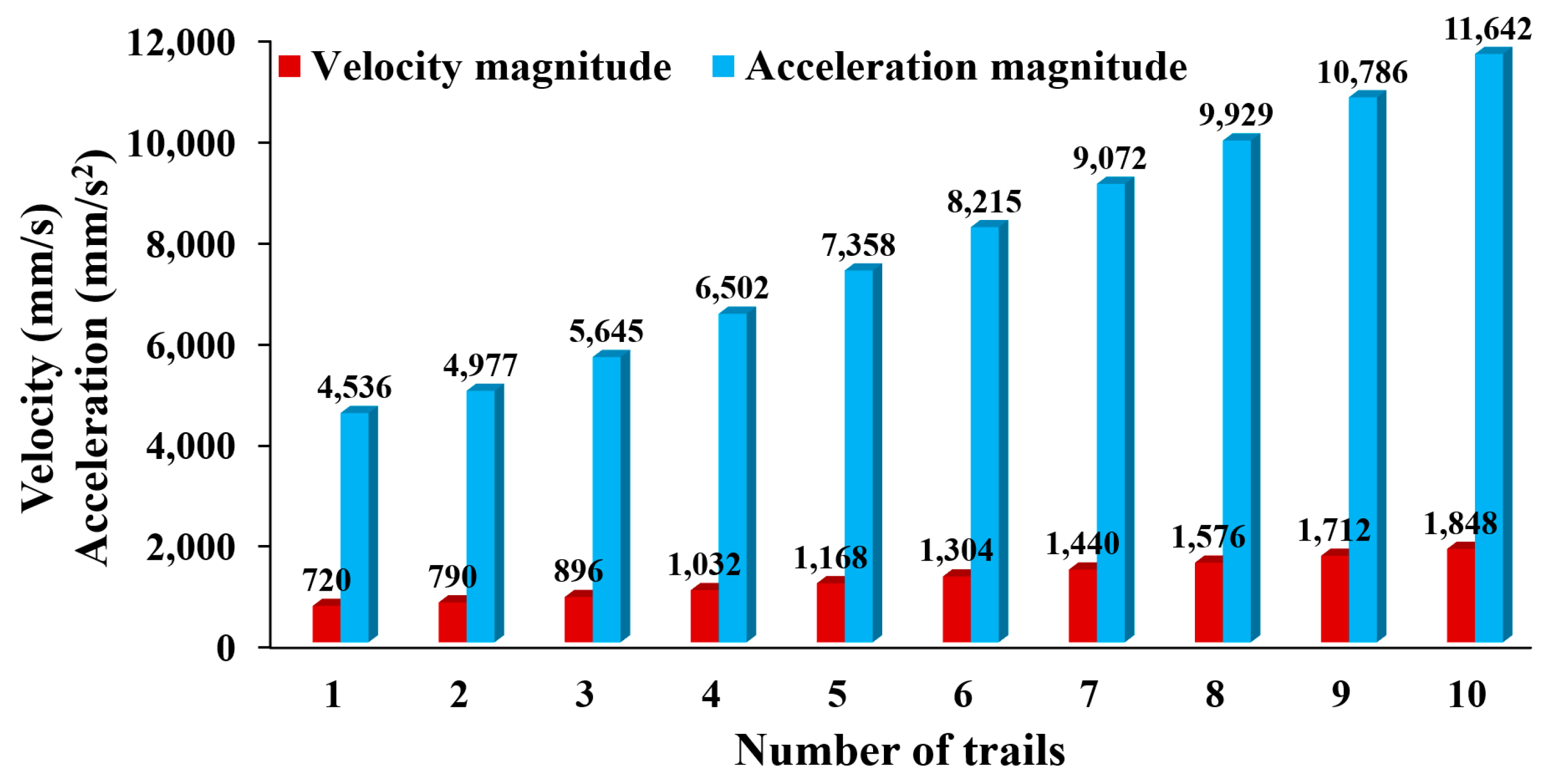
3.2. Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of the Planting Mechanism
3.3. Motion Analysis Based on Velocity and Acceleration
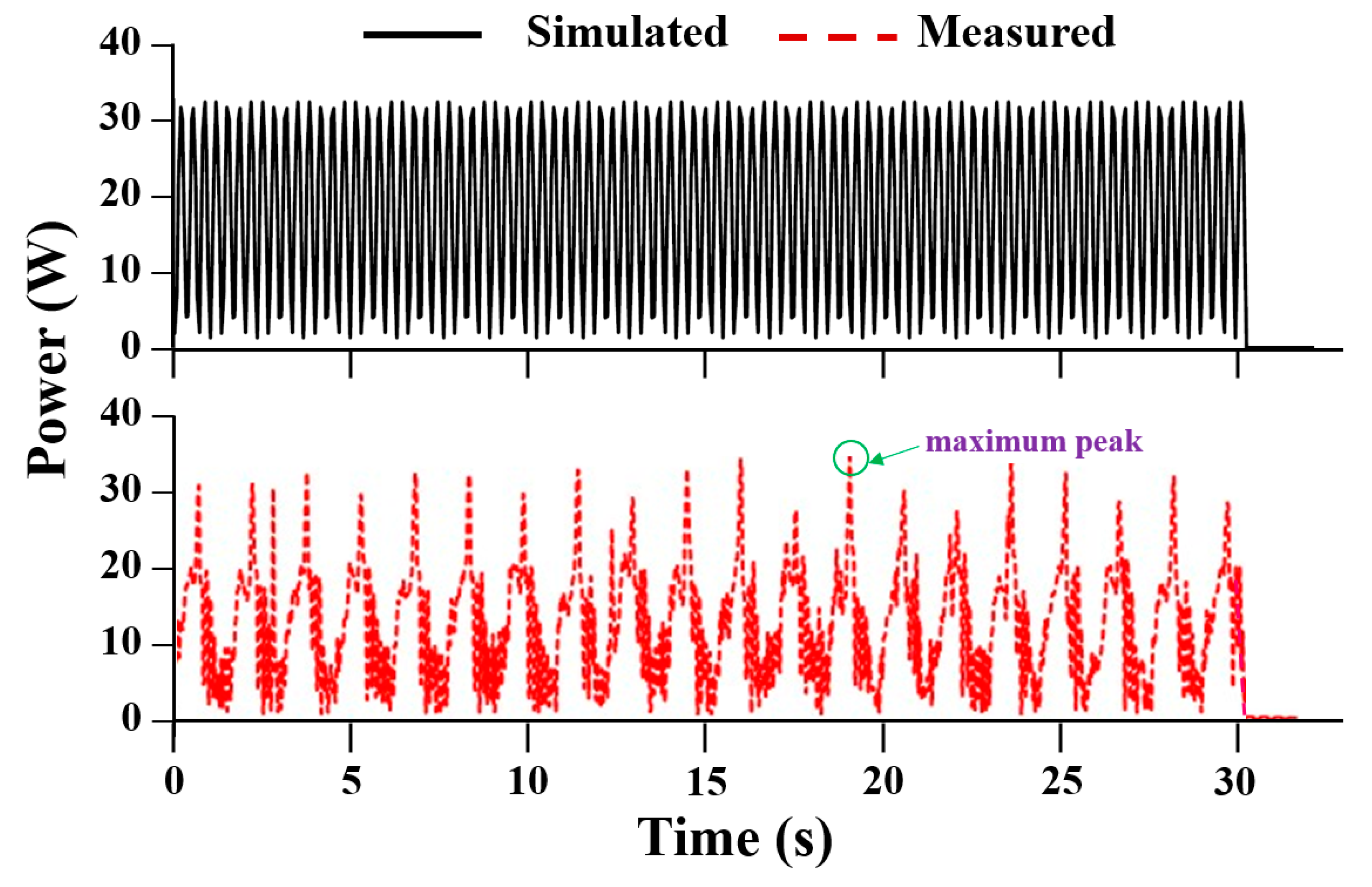
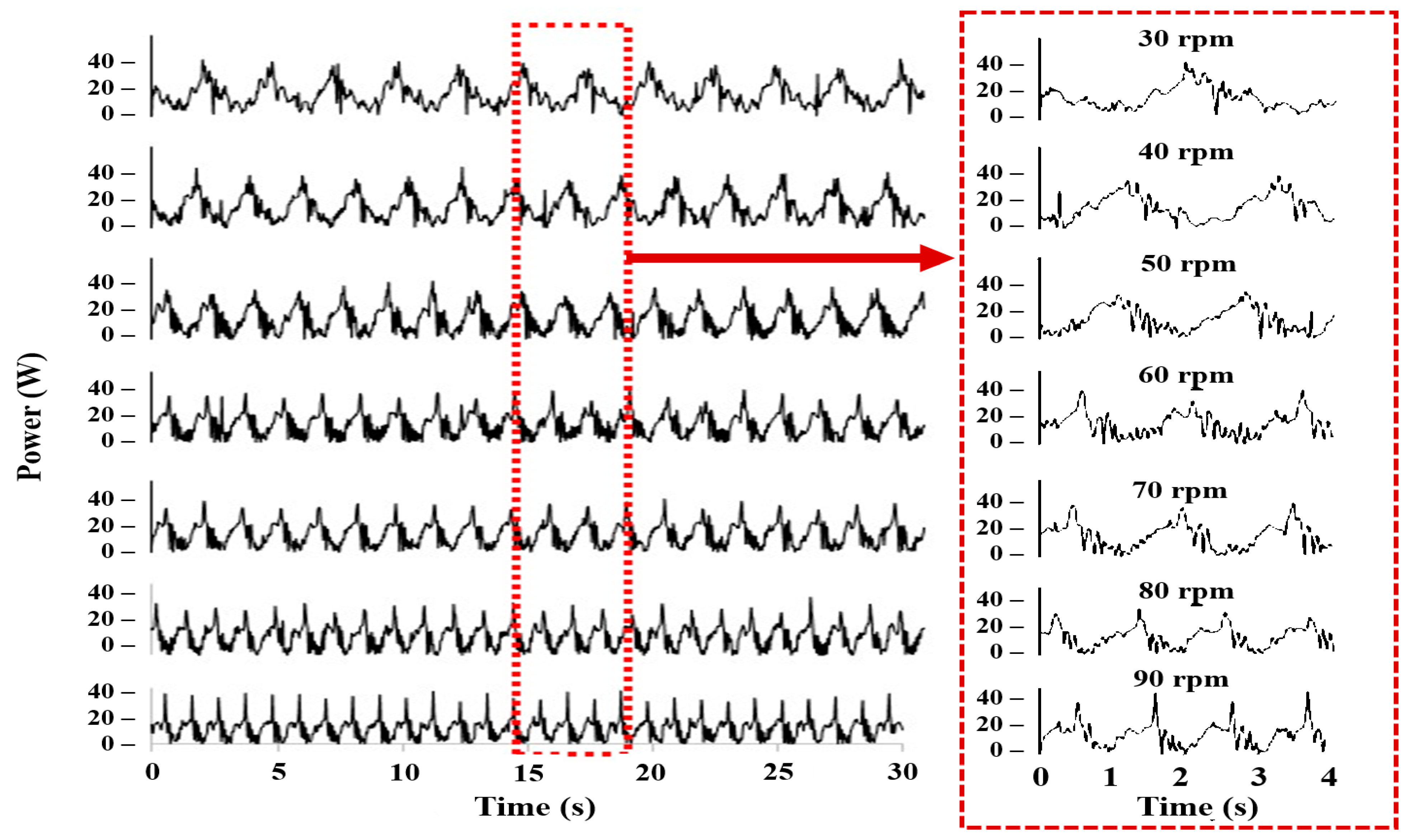
3.4. Power Requirement of the Planting Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, K.; Mahato, N.; Nile, S.H.; Lee, E.T.; Lee, Y.R. Economical and environmentally-friendly approaches for usage of onion (Allium cepa L.) waste. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3354–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sami, R.; Elhakem, A.; Alharbi, M.; Almatrafi, M.; Benajiba, N.; Ahmed Mohamed, T.; Fikry, M.; Helal, M. In-vitro evaluation of the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of volatile compounds and minerals in five different onion varieties. Separations 2021, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanci, F. A comprehensive overview of onion production: Worldwide and Turkey. J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2018, 11, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- KOSTAT. Production Volume of Onions in South Korea from 2009 to 2020. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/958845/south-korea-onion-production/ (accessed on 3 March 2021).
- Rasool, K.; Islam, M.N.; Ali, M.; Jang, B.E.; Khan, N.A.; Chowdhury, M.; Chung, S.O.; Kwon, H.J. Onion transplanting mechanisms: A review. Precis. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 196. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Wang, X.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, R.; Ma, W. Design and test of key parts on automatic transplanter for flower seedling. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dihingia, P.C.; Prasanna Kumar, G.; Sarma, P.K. Development of a hopper-type planting device for a walk-behind hand-tractor-powered vegetable transplanter. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 41, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khadatkar, A.; Mathur, S.; Gaikwad, B. Automation in transplanting: A smart way of vegetable cultivation. Curr. Sci. 2018, 115, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Zeng, G.; Deng, B.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Yu, G. Design and tests of a rotary plug seedling pick-up mechanism for vegetable automatic transplanter. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ye, J.; Chu, M.; Dai, L.; Chen, J. Automatic scallion seedling feeding mechanism with an asymmetrical high-order transmission gear train. Chin. J. Mech. 2020, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Shim, S.B.; Nam, J.S. Optimization of main link lengths of transplanting device of semi-automatic vegetable transplanter. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manilla, R.; Shaw, L. A high-speed dibbling transplanter. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 904–0908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.; Harrison, D.; Zuhoski, P.B., Jr. Computer Operated Automatic Seedling Plant Transplanting Machine. United States Patent U.S. 4,947,579A, 14 August 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.; Geng, D.; Wang, Z. Study on block seedling transplanter with belt feeding mechanism. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2000, 31, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, D.; Kim, C.; Kwak, T.; Cho, S. Development of walking type Chinese cabbage Transplanter. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2005, 30, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.P.; Raheman, H. Development of a walk-behind type hand tractor powered vegetable transplanter for paper pot seedlings. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 110, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Mao, H.; Hu, J.; Kumi, F. Development of a riding-type fully automatic transplanter for vegetable plug seedlings. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 17, e0205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.S.; Okyere, F.G.; Jo, J.M.; Kim, H.T. A study on improving the performance of the planting device of a vegetable transplanter. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 43, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, G.; Ran, Y.; Yu, H. Kinematic modeling and machining precision analysis of multi-axis CNC machine tools based on screw theory. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 140, 538–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, K.; Ali, M.; Chowdhury, M.; Kwon, H.; Swe, K.M.; Chung, S.O. Theoretical analysis of velocity, acceleration and torque calculation of a five-bar onion transplanting mechanism. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 012019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Mao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Du, X. Kinematic analysis of rotary transplanting mechanism for wide-narrow row pot seedlings. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 475–485. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.Z.; Islam, M.N.; Ali, M.; Kabir, M.S.N.; Park, T.; Kang, T.G.; Park, K.S.; Chung, S.O. Kinematic analysis of a hopper-type dibbling mechanism for a 2.6 kW two-row pepper transplanter. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 2605–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Ali, M.; Chowdhury, M.; Kabir, M.S.N.; Park, T.; Kim, Y.J.; Chung, S.O. Kinematic analysis of a clamp-type picking device for an automatic pepper transplanter. Agriculture 2020, 10, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cao, W.; Tian, D.; Tang, H.; Zhao, H. Kinematic analysis and experiment of planetary five-bar planting mechanism for zero-speed transplanting on mulch film. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2016, 9, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Howard, I. Finite element analysis of high contact ratio spur gears in mesh. J. Trib. 2005, 127, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, M.J. Design and Analysis of Mechanisms: A Planar Approach; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.Z. Design of a Gear Driven Hopper Type Dibbling Mechanism for a 2.7 kW Two-Row Pepper Transplanter. Master’s Thesis, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, N. Structural Analysis of a Clamp-Type Picking Mechanism for a 2.7 kW Automatic Pepper Transplanter. Master’s Thesis, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Mao, H.; Hu, J.; Tian, K. Development of a doorframe-typed swinging seedling pick-up device for automatic field transplantation. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paraforos, D.S.; Griepentrog, H.W.; Vougioukas, S.G. Methodology for designing accelerated structural durability tests on agricultural machinery. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 149, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuria, J.; Kihiu, J. Prediction of overall efficiency in multistage gear trains. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2011, 5, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
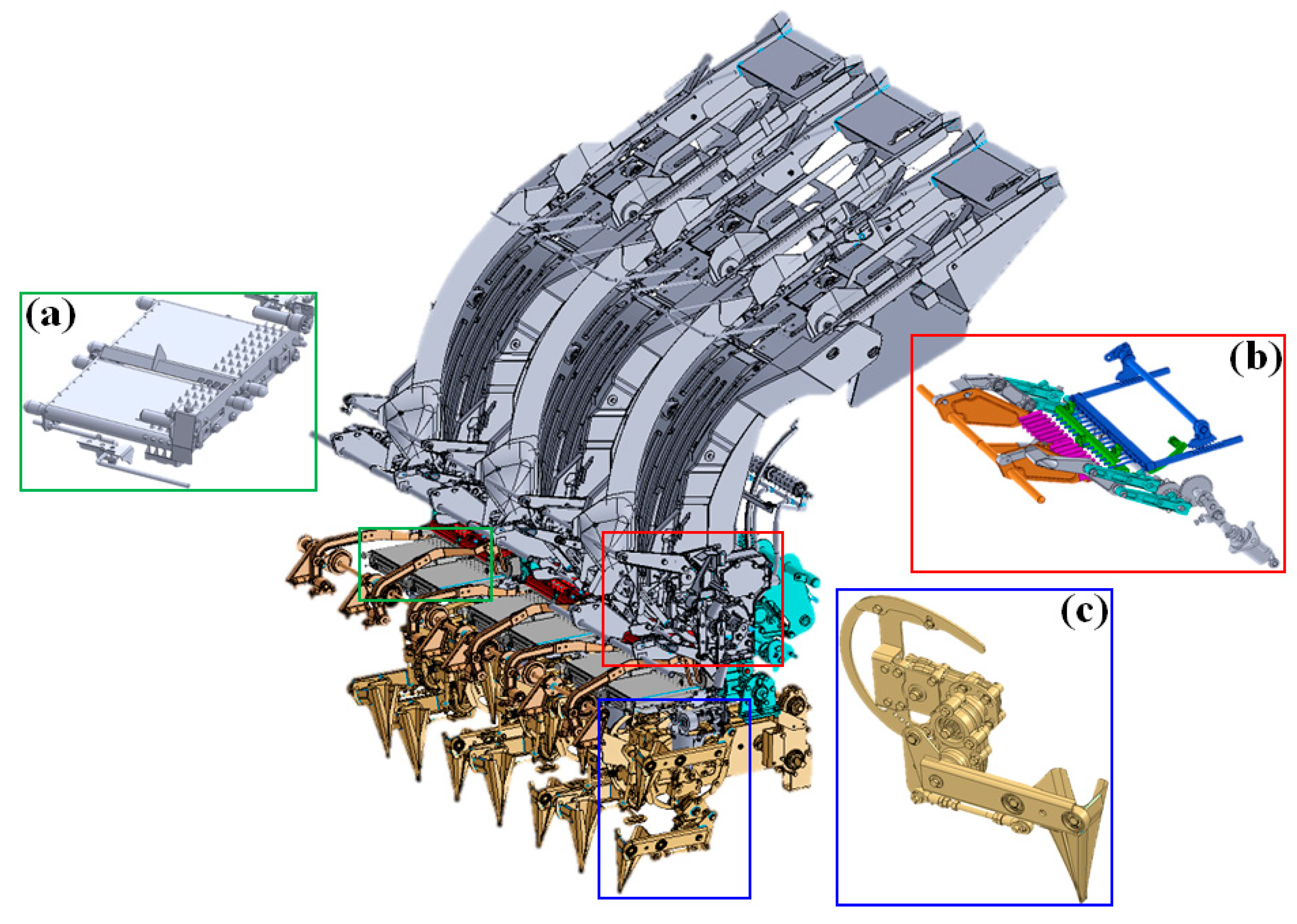
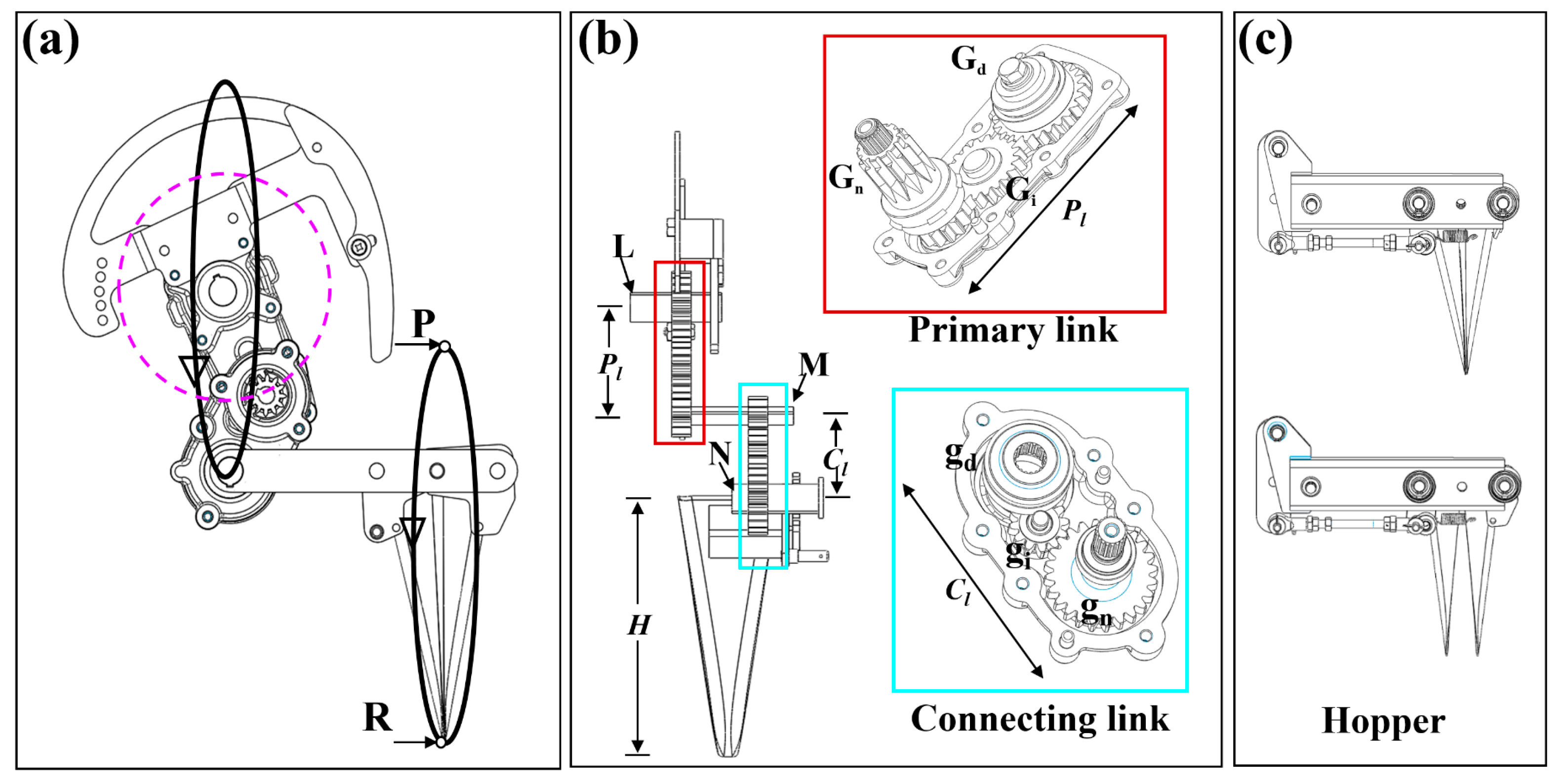
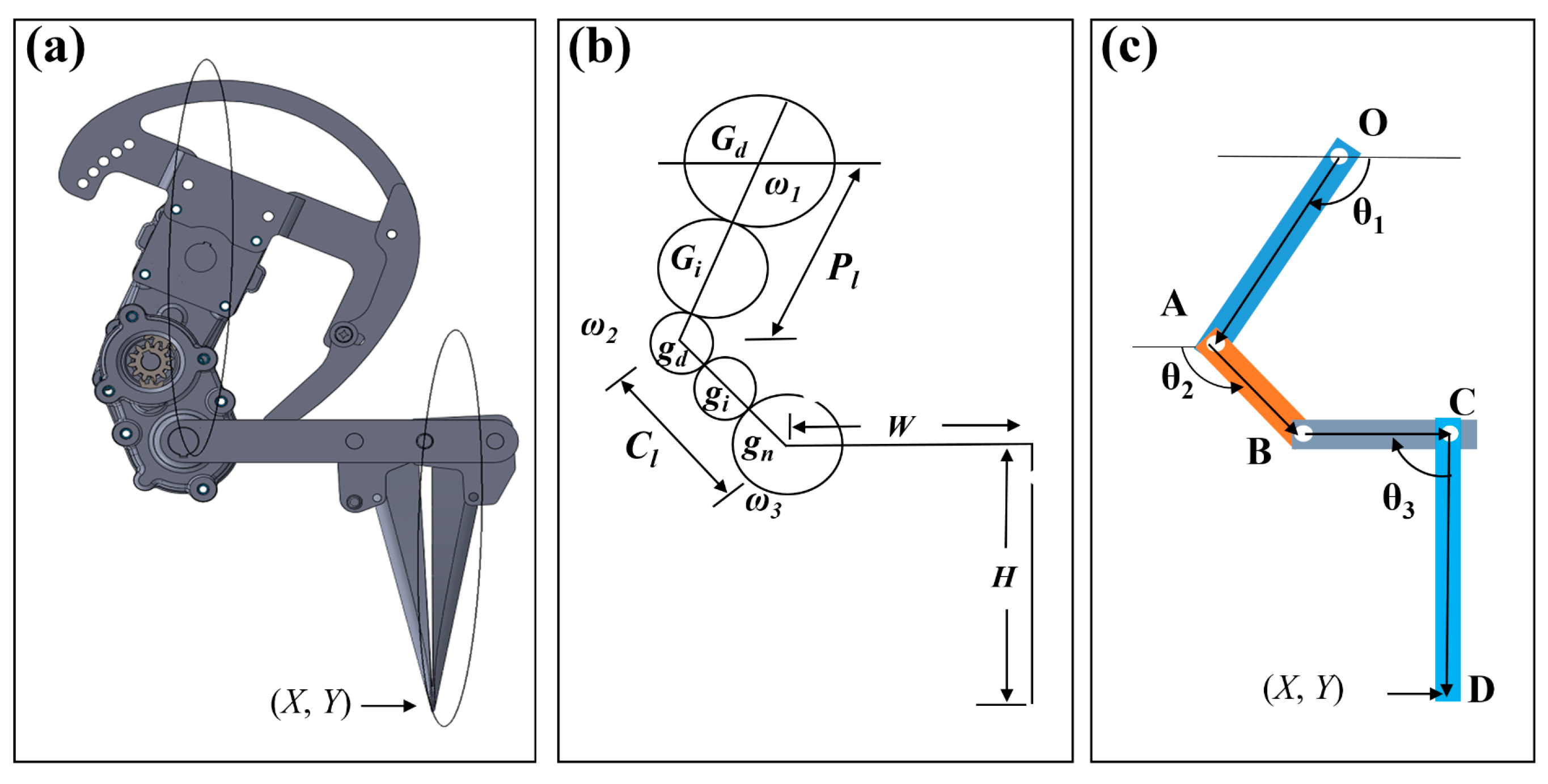
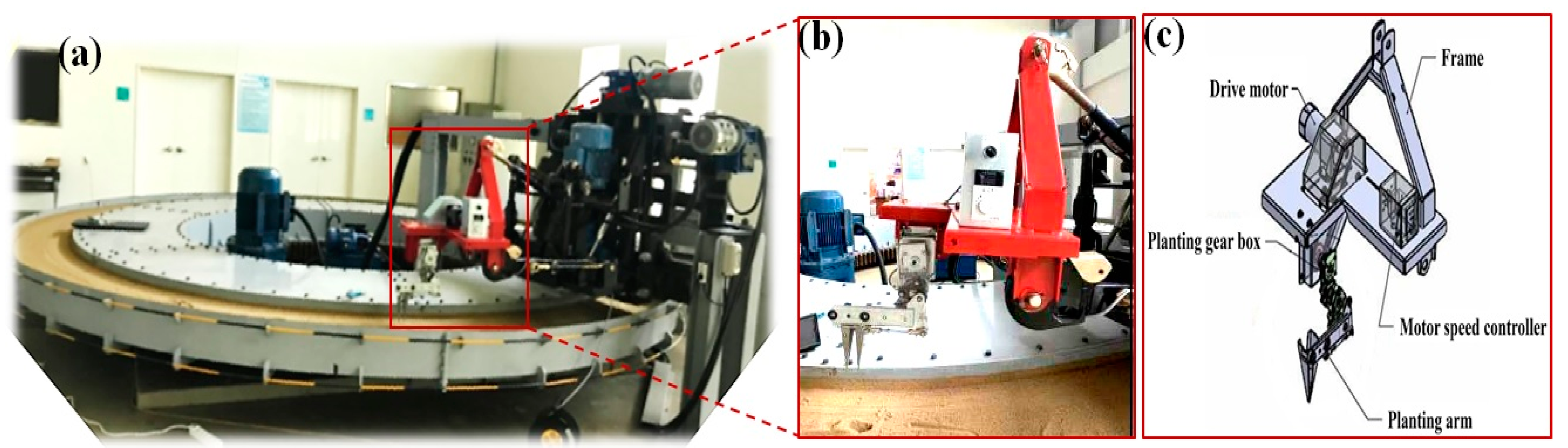



| Notation | Definitions and Measurement Units |
|---|---|
| Pl | Primary arm length, mm |
| Cl | Connecting arm length, mm |
| H | Dibbling hopper length, mm |
| Gd | Driver gear of the primary arm |
| Gi | Idler gear of the primary arm |
| Gn | Driven gear of the primary arm |
| gd | Driver gear of the connecting arm |
| gi | Idler gear of the connecting arm |
| gn | Driven gear of the connecting arm |
| T1 | Number of teeth on driver gear |
| T2 | Number of teeth on driven gear |
| d1 | Diameter of the driver gear |
| d2 | Diameter of the driven gear |
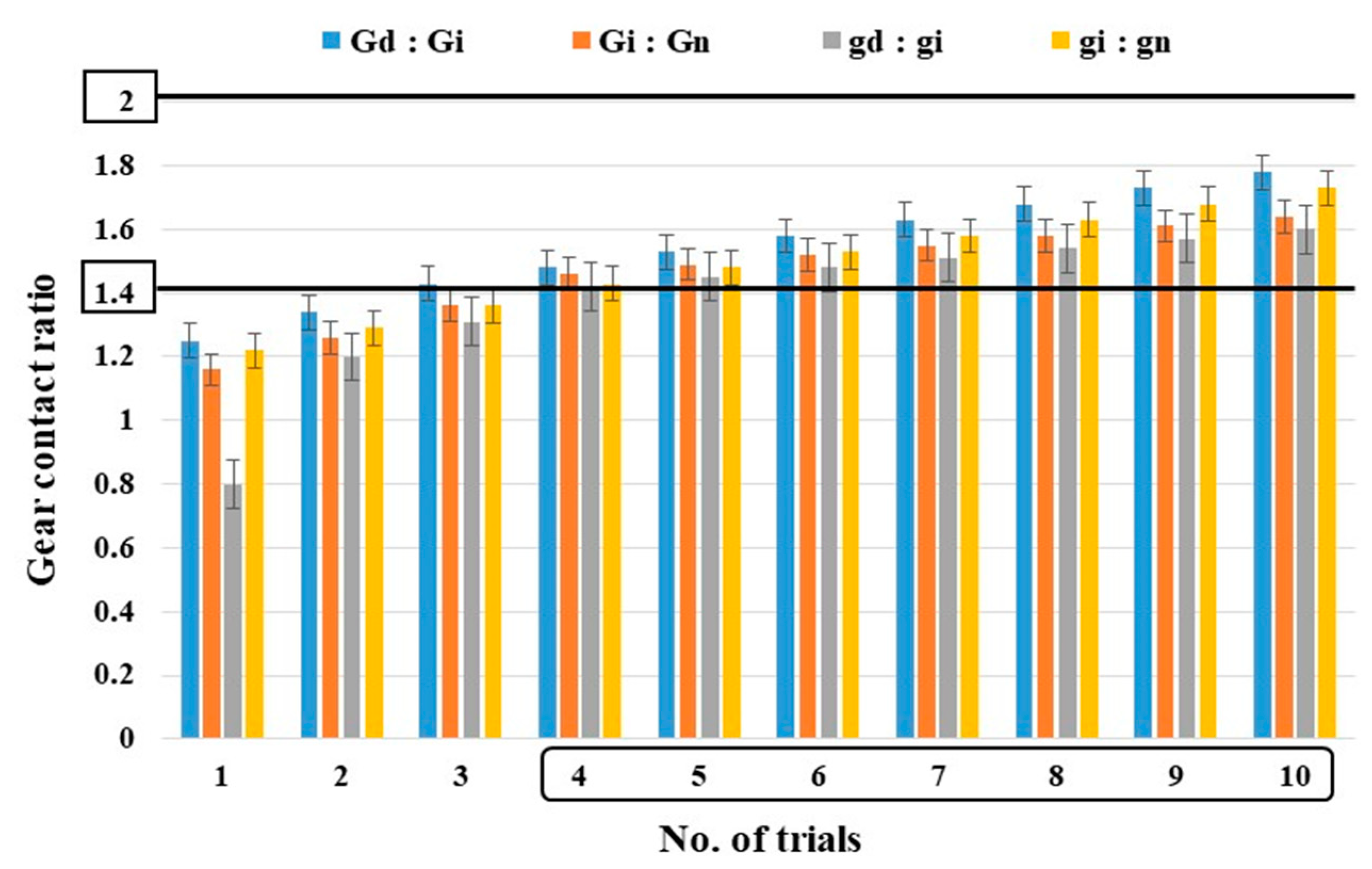
| CR | Contact ratio of two meshing gear, numeral |
| ω1 | Angular velocity of the primary arm, rad/s |
| ω2 | Angular velocity of the connecting arm, rad/s |
| ω3 | Angular velocity of the dibbling hopper, rad/s |
| α | Pressure angle of the spur gears, degree |
| p | Consumed power by the dibbling mechanism, kW |
| m | Total mass of the dibbling mechanism, g |
| am | Magnitude of acceleration of the dibbling hopper, mm/s2 |
| vm | Magnitude of velocity of the dibbling hopper, mm/s |
| No. of Links | Gears | Gear Trains | Gear Train Ratio | Gear Ration = Driver: Driven | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Driver | Idler | Driven | ||||
| Primary link | Gd:Gi:Gn | A | 2:1.8:1.4 | 1:0.7 | ||
| B | 2:1.6:1.2 | 1:0.6 | ||||
| C | 2:1.2:1 | 1:0.5 | ||||
| Connecting link | gd:gi:gn | D | 1:1:2 | 1:2 | ||
| E | 1:1.5:1.8 | 1:1.8 | ||||
| F | 1:2:1.6 | 1:1.6 | ||||
| Fixed Parameters | Variables |
|---|---|
| Forward speed | Primary and secondary links lengths |
| Planting depth | Gear diameters |
| Planting interval | Gear ratios |
| Rotating speed No. of teeth |
| Gear Trains | Trial Combinations | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-D | A-E | A-F | B-D | B-E | B-F | C-D | C-E | C-F | |
| Ratio | 1.4:1 | 1.26:1 | 1.12:1 | 1.2:1 | 1.08:1 | 0.96:1 | 1:1 | 0.9:1 | 0.8:1 |
| Trials | Primary Link (Pl) | Connecting Link (Cl) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Driver | Idler | Driven | Driver | Idler | Driven | |
| Nd | Ni | Nn | nd | ni | nn | |
| 1 | 16 | 12 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| 2 | 20 | 16 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 20 |
| 3 | 24 | 20 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 24 |
| 4 | 28 | 24 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 28 |
| 5 | 32 | 28 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 32 |
| 6 | 36 | 32 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 36 |
| 7 | 40 | 36 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 40 |
| 8 | 44 | 40 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 44 |
| 9 | 48 | 44 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 48 |
| 10 | 52 | 48 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 52 |
| Trial | Primary Link Lengths (mm) | Connecting Link Lengths (mm) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gd | Nd | Gi | Ni | Gn | Nn | Pl | gd | nd | gi | ni | gn | nn | Cl | |
| 1 | 32 | 16 | 24 | 12 | 16 | 8 | 48 | 16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 32 | 16 | 40 |
| 2 | 40 | 20 | 32 | 16 | 20 | 10 | 62 | 20 | 10 | 20 | 10 | 40 | 20 | 50 |
| 3 | 48 | 24 | 40 | 20 | 24 | 12 | 76 | 24 | 12 | 24 | 12 | 48 | 24 | 60 |
| 4 | 56 | 28 | 48 | 24 | 28 | 14 | 90 | 28 | 14 | 28 | 14 | 56 | 28 | 70 |
| 5 | 64 | 32 | 56 | 28 | 32 | 16 | 104 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 16 | 64 | 32 | 80 |
| 6 | 72 | 36 | 64 | 32 | 36 | 18 | 118 | 36 | 18 | 36 | 18 | 72 | 36 | 90 |
| 7 | 80 | 40 | 72 | 36 | 40 | 20 | 132 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 80 | 40 | 100 |
| 8 | 88 | 44 | 80 | 40 | 44 | 22 | 146 | 44 | 22 | 44 | 22 | 88 | 44 | 110 |
| 9 | 96 | 48 | 88 | 44 | 48 | 24 | 160 | 48 | 24 | 48 | 24 | 96 | 48 | 120 |
| 10 | 104 | 52 | 96 | 48 | 52 | 26 | 174 | 52 | 26 | 52 | 26 | 104 | 52 | 130 |
| Direction | Velocity | Acceleration | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation (mm/s) | Experiment (mm/s) | Simulation (mm/s) | Experiment (mm/s) | |
| X-component | ±126.64 | +130.34 to −149.25 | ±811.64 | +802.62 to −1026.25 |
| Y-component | ±913.65 | ±980.36 to −1184.71 | ±5484.67 | +7135.27 to −7069.76 |
| Parameter | Power Requirement (W) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 rpm | 40 rpm | 50 rpm | 60 rpm | 70 rpm | 80 rpm | 90 rpm | |
| Max. | 12.3 | 20.8 | 27.5 | 35.4 | 44.8 | 52 | 65.7 |
| Min. | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.29 |
| Avg. | 0.92 ± 0.43 | 1.23 ± 0.68 | 2.54 ± 0.88 | 5.41 ± 0.74 | 6.33 ± 0.32 | 7.23 ± 0.91 | 8.16 ± 0.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reza, M.N.; Islam, M.N.; Chowdhury, M.; Ali, M.; Islam, S.; Kiraga, S.; Lim, S.-J.; Choi, I.-S.; Chung, S.-O. Kinematic Analysis of a Gear-Driven Rotary Planting Mechanism for a Six-Row Self-Propelled Onion Transplanter. Machines 2021, 9, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9090183
Reza MN, Islam MN, Chowdhury M, Ali M, Islam S, Kiraga S, Lim S-J, Choi I-S, Chung S-O. Kinematic Analysis of a Gear-Driven Rotary Planting Mechanism for a Six-Row Self-Propelled Onion Transplanter. Machines. 2021; 9(9):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9090183
Chicago/Turabian StyleReza, Md Nasim, Md Nafiul Islam, Milon Chowdhury, Mohammod Ali, Sumaiya Islam, Shafik Kiraga, Seung-Jin Lim, Il-Su Choi, and Sun-Ok Chung. 2021. "Kinematic Analysis of a Gear-Driven Rotary Planting Mechanism for a Six-Row Self-Propelled Onion Transplanter" Machines 9, no. 9: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9090183
APA StyleReza, M. N., Islam, M. N., Chowdhury, M., Ali, M., Islam, S., Kiraga, S., Lim, S.-J., Choi, I.-S., & Chung, S.-O. (2021). Kinematic Analysis of a Gear-Driven Rotary Planting Mechanism for a Six-Row Self-Propelled Onion Transplanter. Machines, 9(9), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9090183











