Investigation of Genetic Variations of IL6 and IL6R as Potential Prognostic and Pharmacogenetics Biomarkers: Implications for COVID-19 and Neuroinflammatory Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bravo-Merodio, L.; Williams, J.A.; Gkoutos, G.V.; Acharjee, A. Omics biomarker identification pipeline for translational medicine. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cascella, R.; Strafella, C.; Longo, G.; Maccarone, M.; Borgiani, P.; Sangiuolo, F.; Novelli, G.; Giardina, E. Pharmacogenomics of multifactorial diseases: A focus on psoriatic arthritis. Pharmacogenomics 2016, 17, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocchi, L.; Cascella, R.; Zampatti, S.; Pirazzoli, A.; Novelli, G.; Giardina, E. The Pharmacogenomic HLA Biomarker Associated to Adverse Abacavir Reactions: Comparative Analysis of Different Genotyping Methods. Curr. Genom. 2012, 13, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Docampo, E.; Giardina, E.; Riveira-Muñoz, E.; de Cid, R.; Escaramís, G.; Perricone, C.; Fernández-Sueiro, J.L.; Maymó, J.; González-Gay, M.A.; Blanco, F.J.; et al. Deletion of LCE3C and LCE3B is a susceptibility factor for psoriatic arthritis: A study in Spanish and Italian populations and meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1860–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardina, E.; Capon, F.; De Rosa, M.C.; Mango, R.; Zambruno, R.; Orecchia, A.; Chimenti, S.; Giardina, B.; Novelli, G. Characterization of the loricrin (LOR) gene as a positional candidate for the PSORS4 psoriasis susceptibility locus. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2004, 68, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermali, M.; Khalsa, R.K.; Pillai, K.; Ismail, Z.; Harky, A. The role of biomarkers in diagnosis of COVID-19—A systematic review. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strafella, C.; Caputo, V.; Termine, A.; Barati, S.; Gambardella, S.; Borgiani, P.; Caltagirone, C.; Novelli, G.; Giardina, E.; Cascella, R. Analysis of ACE2 Genetic Variability among Populations Highlights a Possible Link with COVID-19-Related Neurological Complications. Genes 2020, 11, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Sa, A.C.; Madsen, H.; Brown, J.R. Shared Molecular Signatures Across Neurodegenerative Diseases and Herpes Virus Infections Highlights Potential Mechanisms for Maladaptive Innate Immune Responses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochocka, M.; Zwolińska, K.; Leszek, J. The Infectious Etiology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strafella, C.; Caputo, V.; Galota, M.R.; Zampatti, S.; Marella, G.; Mauriello, S.; Cascella, R.; Giardina, E. Application of Precision Medicine in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garbers, C.; Heink, S.; Korn, T.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6: Designing specific therapeutics for a complex cytokine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Kamimura, D.; Hirano, T. Pleiotropy and Specificity: Insights from the Interleukin 6 Family of Cytokines. Immunity 2019, 50, 812–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salvi, R.; Patankar, P. Emerging pharmacotherapies for COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulhaq, Z.S.; Soraya, G.V. Interleukin-6 as a potential biomarker of COVID-19 progression. Med. Mal. Infect. 2020, 50, 382–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redenšek, S.; Flisar, D.; Kojović, M.; Kramberger, M.G.; Georgiev, D.; Pirtošek, Z.; Trošt, M.; Dolžan, V. Genetic variability of inflammation and oxidative stress genes does not play a major role in the occurrence of adverse events of dopaminergic treatment in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mun, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Jang, W.C. Genetic polymorphisms of interleukin genes and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease: An update meta-analysis. Meta Gene. 2016, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.; Humphries, S.E. IL-6 polymorphisms: A useful genetic tool for inflammation research? J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1413–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, T.; Zabaneh, D.; Gaunt, T.; Swerdlow, D.I.; Shah, S.; Talmud, P.J.; Day, I.N.; Whittaker, J.; Holmes, M.V.; Sofat, R.; et al. Gene-centric analysis identifies variants associated with interleukin-6 levels and shared pathways with other inflammation markers. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunningham, F.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Allen, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Boddu, S.; et al. Ensembl 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D745–D751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- 1000 Genomes Project Consortium; Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Garrison, E.P.; Kang, H.M.; Korbel, J.O.; Marchini, J.L.; McCarthy, S.; McVean, G.A.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, B.J.; Grunwald, N.J. VCFR: A package to manipulate and visualize variant call format data in R. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravasio, V.; Ritelli, M.; Legati, A.; Giacopuzzi, E. GARFIELD-NGS: Genomic variants filtering by deep learning models in NGS. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3038–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Stephenson, J.D.; Sillitoe, I.; Orengo, C.A.; Thornton, J.M. VarSite: Disease variants and protein structure. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desmet, F.O.; Hamroun, D.; Lalande, M.; Collod-Béroud, G.; Claustres, M.; Béroud, C. Human splicing finder: An online bioinformatics tool to predict splicing signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 8, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emilsson, V.; Ilkov, M.; Lamb, J.R.; Finkel, N.; Gudmundsson, E.F.; Pitts, R.; Hoover, H.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Horman, S.R.; Aspelund, T.; et al. Co-regulatory networks of human serum proteins link genetics to disease. Science 2018, 361, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, R.C.; Freitag, D.F.; Cutler, A.J.; Howson, J.M.; Rainbow, D.B.; Smyth, D.J.; Kaptoge, S.; Clarke, P.; Boreham, C.; Coulson, R.M.; et al. Functional IL6R 358Ala allele impairs classical IL-6 receptor signaling and influences risk of diverse inflammatory diseases. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbers, C.; Monhasery, N.; Aparicio-Siegmund, S.; Lokau, J.; Baran, P.; Nowell, M.A.; Jones, S.A.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. The interleukin-6 receptor Asp358Ala single nucleotide polymorphism rs2228145 confers increased proteolytic conversion rates by ADAM proteases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wosiski-Kuhn, M.; Robinson, M.; Strupe, J.; Arounleut, P.; Martin, M.; Caress, J.; Cartwright, M.; Bowser, R.; Cudkowicz, M.; Langefeld, C.; et al. IL6 receptor358Ala variant and trans-signaling are disease modifiers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 6, e631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haddick, P.C.; Larson, J.L.; Rathore, N.; Bhangale, T.R.; Phung, Q.T.; Srinivasan, K.; Hansen, D.V.; Lill, J.R.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Haines, J.; et al. A Common Variant of IL-6R is Associated with Elevated IL-6 Pathway Activity in Alzheimer’s Disease Brains. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 56, 1037–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rafiq, S.; Frayling, T.M.; Murray, A.; Hurst, A.; Stevens, K.; Weedon, M.N.; Henley, W.; Ferrucci, L.; Bandinelli, S.; Corsi, A.M.; et al. A common variant of the interleukin 6 receptor (IL-6r) gene increases IL-6r and IL-6 levels, without other inflammatory effects. Genes Immun. 2007, 8, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Q. Unique epidemiological and clinical features of the emerging 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) implicate special control measures. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akhmerov, A.; Marbán, E. COVID-19 and the Heart. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, F.S. Liver injury in COVID-19: Management and challenges. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 428–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, S.A.; Schattenberg, J.M. Liver injury in COVID-19: The current evidence. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Bai, W.Z.; Hashikawa, T. The neuroinvasive potential of SARS-CoV2 may play a role in the respiratory failure of COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.; Kremer, S.; Merdji, H.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Schenck, M.; Kummerlen, C.; Collange, O.; Boulay, C.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Ohana, M.; et al. Neurologic Features in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2268–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pero, A.; Ng, S.; Cai, D. COVID-19: A Perspective from Clinical Neurology and Neuroscience. Neuroscientist 2020, 26, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzolla, A.P.; Lovero, R.; Lo Muzio, L.; Testa, N.F.; Schirinzi, A.; Palmieri, G.; Pozzessere, P.; Procacci, V.; Di Comite, M.; Ciavarella, D.; et al. Taste and Smell Disorders in COVID-19 Patients: Role of Interleukin-6. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 2774–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caronna, E.; Ballvé, A.; Llauradó, A.; Gallardo, V.J.; María Ariton, D.; Lallana, S.; Maza, S.L.; Gadea, M.O.; Quibus, L.; Restrepo, J.L.; et al. Headache: A striking prodromal and persistent symptom, predictive of COVID-19 clinical evolution. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 1410–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadian, S.; Glick, L.R.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Thomas, J.; Chiarella, J.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Zhou, J.; Odio, C.; Vijayakumar, P.; Geng, B.; et al. Acute encephalopathy with elevated CSF inflammatory markers as the initial presentation of COVID-19. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schett, G. Physiological effects of modulating the interleukin-6 axis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neveu, W.A.; Allard, J.L.; Raymond, D.M.; Bourassa, L.M.; Burns, S.M.; Bunn, J.Y.; Irvin, C.G.; Kaminsky, D.A.; Rincon, M. Elevation of IL-6 in the allergic asthmatic airway is independent of inflammation but associates with loss of central airway function. Respir. Res. 2010, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okiyama, N.; Sugihara, T.; Iwakura, Y.; Yokozeki, H.; Miyasaka, N.; Kohsaka, H. Therapeutic effects of interleukin-6 blockade in a murine model of polymyositis that does not require interleukin-17A. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2505–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, I.L.; Erta, M.; Lim, S.L.; Frausto, R.; May, U.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J.; Hidalgo, J. Trans-signaling is a dominant mechanism for the pathogenic actions of interleukin-6 in the brain. J. Neuro. Sci. 2014, 34, 2503–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choy, E.H.; De Benedetti, F.; Takeuchi, T.; Hashizume, M.; John, M.R.; Kishimoto, T. Translating IL-6 biology into effective treatments. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G.Q. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: Interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, D.; Li, J. Tocilizumab treatment in COVID-19: A single center experience. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
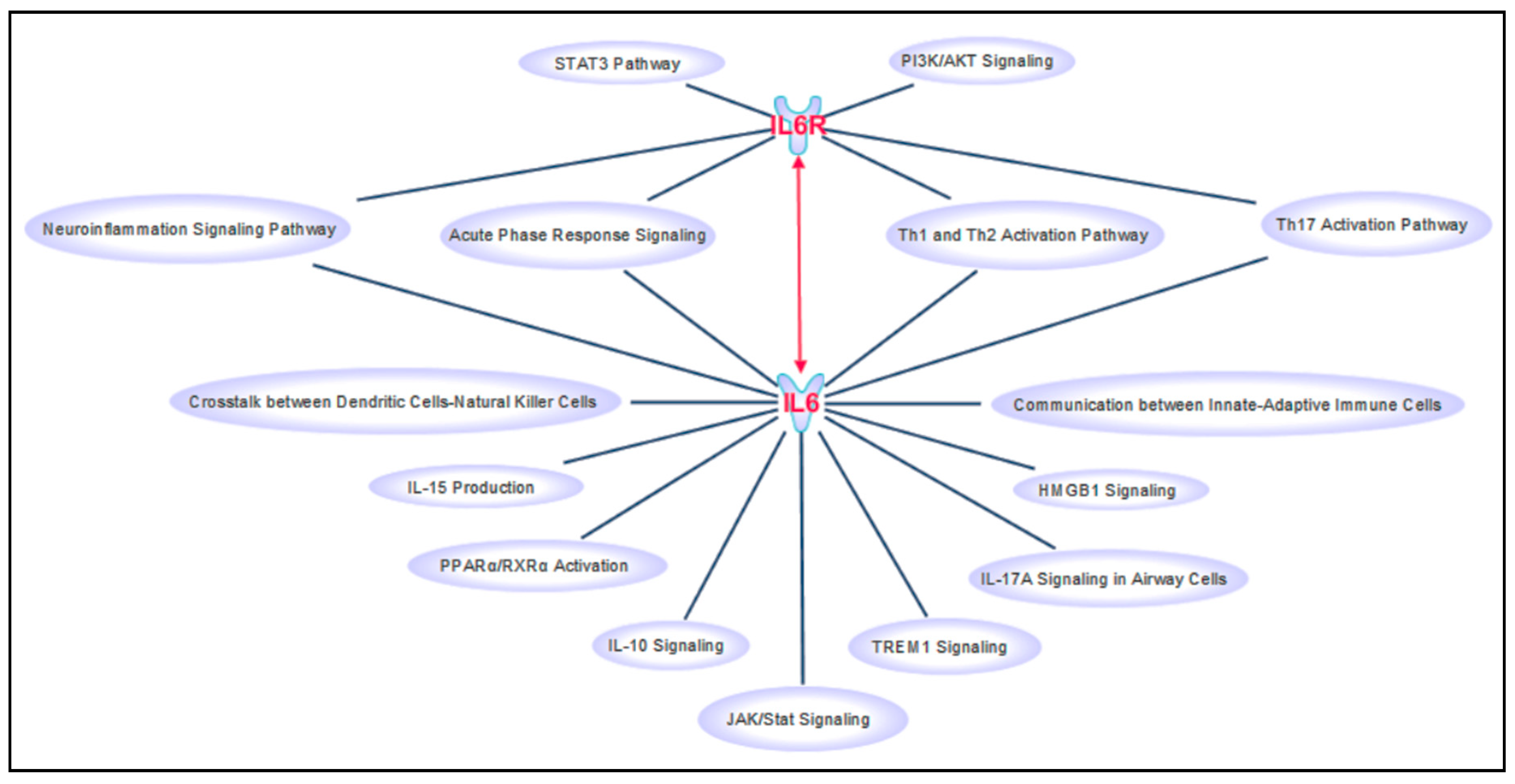
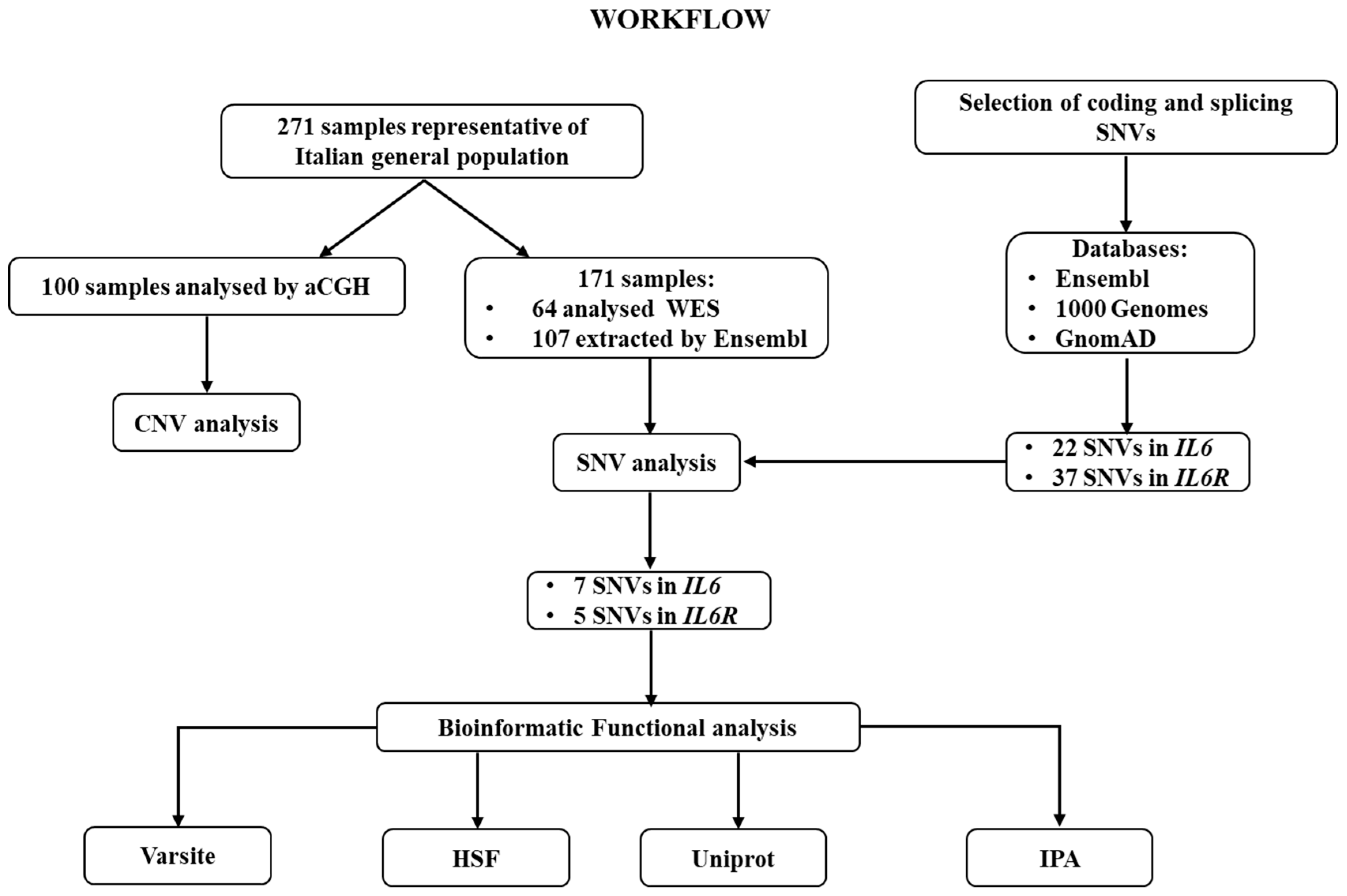

| Gene | Genomic Location | SNV | N Cod | Allele Counts (Frequencies) | Ex | P Cod | Structural Impact of AA Change (Varsite) | Impact on Splicing (HSF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL6 (7p15.3) | 7:22767134 | rs142759801 | c.91 C > A | C: 341 (0.997) A: 1 (0.003) * | 2 | p.P31T | low impact on protein structure | alteration of an ESE site |
| 7:22767226 | rs140764737 | c.183 C > T | C: 341 (0.997) T: 1 (0.003) * | 2 | p.L61= | NA | alteration of an ESE site, creation of an ESS site | |
| 7:22768336 | rs190436077 | c.235 G > C | G: 341 (0.997) C: 1 (0.003) * | 3 | p.E79Q | potential impact on protein structure | alteration of an ESE site | |
| 7:22768350 | rs142164099 | c.249 G > A | G: 341 (0.997) A: 1 (0.003) * | 3 | p.E83= | NA | no predicted impact | |
| 7:22769154 | rs148171375 | c.346 A > T | A: 341 (0.997) T: 1 (0.003) * | 4 | p.I116F | low impact on protein structure | no predicted impact | |
| 7:22771039 | rs13306435 | c.486 T > A | T: 339 (0.991) A: 3 (0.009) * | 5 | p.D162E | potential impact on protein structure | no predicted impact | |
| 7:22771156 | rs2069849 | c.603 C > T | C: 339 (0.991) A: 3 (0.009) * | 5 | p.F201= | NA | no predicted impact | |
| IL6R (1q21.3) | 1:154401679 | rs2228144 | c.93 G > A | G: 281 (0.822) A: 61 (0.178) * | 2 | p.A31= | NA | no predicted impact |
| 1:154401796 | rs2229237 | c.210 C > T | C: 338 (0.988) T: 4 (0.012) * | 2 | p.H70= | NA | alteration of an ESE site, creation of an ESS site | |
| 1:154426970 | rs2228145 | c.1073 A > C | A: 230 (0.673) C: 112 (0.327) * | 9 | p.D358A | potential impact on protein structure | alteration of an ESE site, creation of an ESS site | |
| 1:154427032 | rs28730735 | c.1135 C > T | C: 340 (0.994) T: 2 (0.006) * | 9 | p.L379F | low impact on protein structure | alteration of an ESE site, creation of an ESS site | |
| 1:154437719 | rs143810642 | c.1270 C > T | C: 340 (0.994) T: 2 (0.006) * | 10 | p.L424F | low impact on protein structure | alteration of an ESE site, creation of an ESS site |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strafella, C.; Caputo, V.; Termine, A.; Barati, S.; Caltagirone, C.; Giardina, E.; Cascella, R. Investigation of Genetic Variations of IL6 and IL6R as Potential Prognostic and Pharmacogenetics Biomarkers: Implications for COVID-19 and Neuroinflammatory Disorders. Life 2020, 10, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10120351
Strafella C, Caputo V, Termine A, Barati S, Caltagirone C, Giardina E, Cascella R. Investigation of Genetic Variations of IL6 and IL6R as Potential Prognostic and Pharmacogenetics Biomarkers: Implications for COVID-19 and Neuroinflammatory Disorders. Life. 2020; 10(12):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10120351
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrafella, Claudia, Valerio Caputo, Andrea Termine, Shila Barati, Carlo Caltagirone, Emiliano Giardina, and Raffaella Cascella. 2020. "Investigation of Genetic Variations of IL6 and IL6R as Potential Prognostic and Pharmacogenetics Biomarkers: Implications for COVID-19 and Neuroinflammatory Disorders" Life 10, no. 12: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10120351
APA StyleStrafella, C., Caputo, V., Termine, A., Barati, S., Caltagirone, C., Giardina, E., & Cascella, R. (2020). Investigation of Genetic Variations of IL6 and IL6R as Potential Prognostic and Pharmacogenetics Biomarkers: Implications for COVID-19 and Neuroinflammatory Disorders. Life, 10(12), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10120351






