Indexing Exoplanets with Physical Conditions Potentially Suitable for Rock-Dependent Extremophiles
Abstract
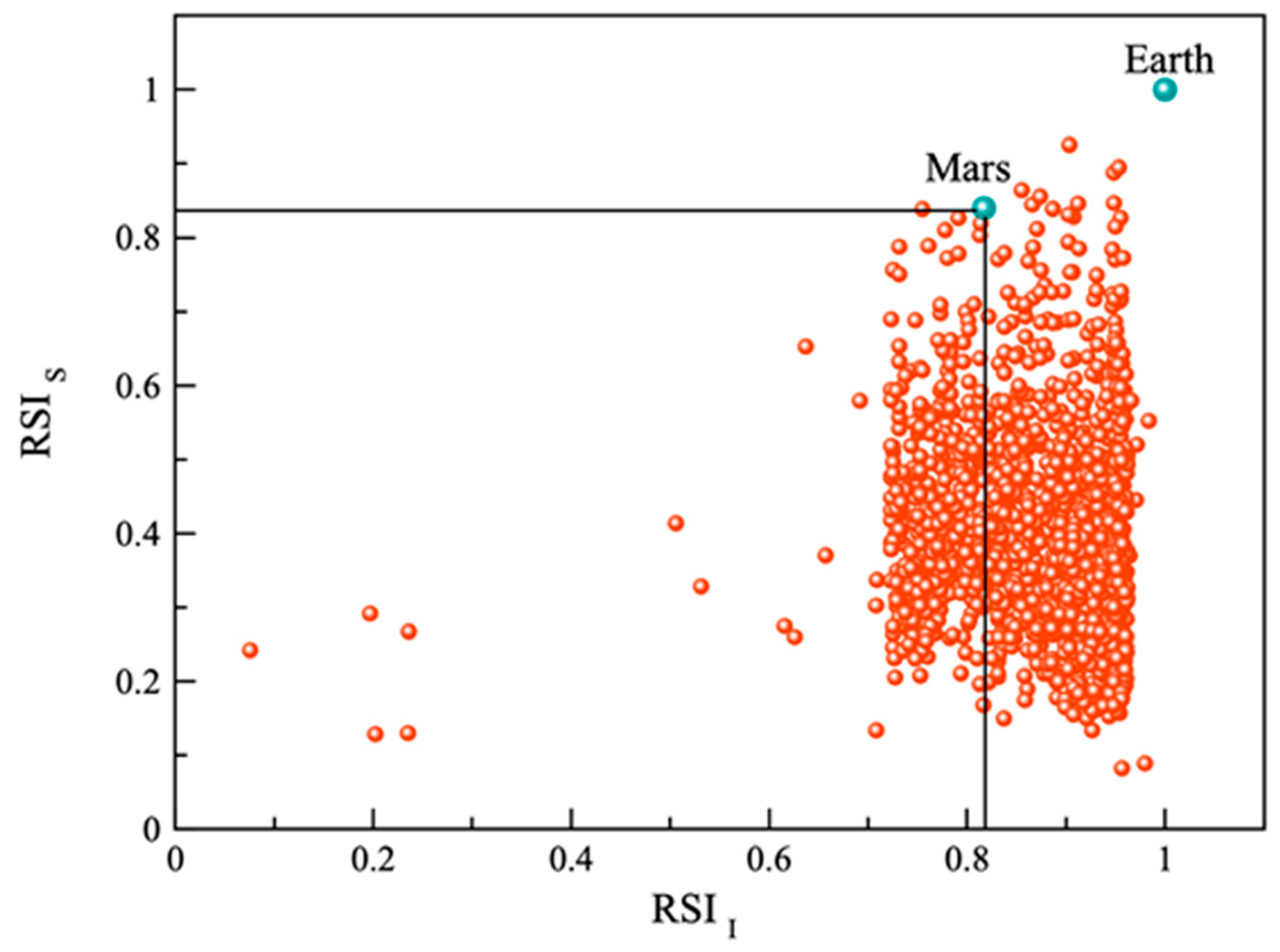
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Planetary Habitability Laboratory, PHL-EC@UPR Arecibo. 2017. Available online: http://phl.upr.edu/projects/habitable-exoplanets-catalog/data/database (accessed on 26 June 2018).
- Schulze-Makuch, D.; Mndez, A.; Fairén, A.G.; von Paris, P.; Turse, C.; Boyer, G.; Davila, A.F.; António, M.R.; Catling, D.; Irwin, L.N. A two-tiered approach to assessing the habitability of exoplanets. Astrobiology 2011, 11, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonova, M.; Murthy, J.; Shchekinov, Y.M. Age aspects of habitability. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2016, 15, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashyap, J.M.; Gudennavar, S.B.; Doshi, U.; Safonova, M. Indexing of exoplanets in search for potential habitability: Application to Mars-like worlds. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2017, 362, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, J.M.; Roszkowska, M.; Kaczmarek, Ł. Tardigrade indexing approach on exoplanets. Life Sci. Space Res. 2018, 19, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rampelotto, P.H. Resistance of microorganisms to extreme environmental conditions and its contribution to Astrobiology. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1602–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McSorley, R. Adaptations of nematodes to environmental extremes. Fla. Entomol. 2003, 86, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, P. The limits and frontiers of desiccation-tolerant life. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2005, 45, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.R.; Dirk Schulze-Makuch, D. Adaptations to environmental extremes by multicellular organisms. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2007, 6, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, R.; Rizzo, A.M.; Altiero, T.; Rebecchi, L. What can we learn from the toughest animals of the Earth? Water bears (tardigrades) as multicellular model organisms in order to perform scientific preparations for lunar exploration. Planet. Space Sci. 2012, 74, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckbach, J. Survey of algae in extreme environments. In The Algae World. Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology; Sahoo, D., Seckbach, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 26, pp. 307–315. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, R.A. Adaptation of lichens to extreme conditions. In Plant Adaptation Strategies in Changing Environment; Shukla, V., Kumar, S., Kumar, N., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Onofri, S.; de la Torre, R.; de Vera, J.P.; Ott, S.; Zucconi, L.; Selbmann, L.; Scalzi, G.; Venkateswaran, K.J.; Rabbow, E.; Sánchez Iñigo, F.J.; et al. Survival of rock-colonizing organisms after 1.5 years in outer space. Astrobiology 2012, 12, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbmann, L.; Pacelli, C.; Zucconi, L.; Dadachova, E.; Moeller, R.; de Vera, J.P.; Onofri, S. Resistance of an Antarctic cryptoendolithic black fungus to radiation gives new insights of astrobiological relevance. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, T.H.; Ryan, B.D.; Gries, C.; Bugartz, F. Acarospora. In Lichen Flora of the Greater Sonoran Desert Region; Arizona State University: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cumbers, J.; Rothschild, L.J. Salt tolerance and polyphyly in the cyanobacterium Chroococcidiopsis (Pleurocapsales). J. Phycol. 2014, 50, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolda, A.; Petrić, I.; Mucko, M.; Gottstein, S.; Žutinić, P.; Goreta, G.; Ternjej, I.; Rubinić, J.; Radišić, M.; Udovič, M.G. How environment selects: Resilience and survival of microbial mat community within intermittent karst spring Krčić (Croatia). Ecohydrology 2018, 12, e2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzchos, J.; DiRuggiero, J.; Vítek, P.; Artieda, O.; Souza-Egipsy, V.; Škaloud, P.; Michel Tisza, M.; Davila, A.F.; Vílchez, C.; Garbayo, I.; et al. Adaptation strategies of endolithic chlorophototrophs to survive the hyperarid and extreme solar radiation environment of the Atacama Desert. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verseux, C.; Baqué, M.; Lehto, K.; de Vera, J.-P.P.; Rothschild, L.J.; Billi, D. Sustainable life support on Mars—The potential roles of cyanobacteria. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2015, 15, 65–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cockell, C.S.; Schuerger, A.C.; Billi, D.; Friedmann, E.I.; Panitz, C. Effects of a simulated Martian UV flux on the cyanobacterium, Chroococcidiopsis sp. 029. Astrobiology 2005, 5, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cockell, C.S.; Rettberg, P.; Rabbow, E.; Olson-Francis, K. Exposure of phototrophs to 548 days in low Earth orbit: Microbial selection pressures in outer space and on early Earth. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1671–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Billi, D. Damage escape and repair in dried Chroococcidiopsis spp. from hot and cold deserts exposed to simulated space and Martian conditions. Astrobiology 2011, 11, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqué, M.; de Vera, J.; Rettberg, P.; Billi, D. The BOSS and BIOMEX space experiments on the EXPOSE-R2 mission: Endurance of the desert cyanobacterium Chroococcidiopsis under simulated space vacuum, Martian atmosphere, UVC radiation and temperature extremes. Acta Astronaut. 2013, 91, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero-Longo, S.E.; Accattino, E.; Matteucci, E.; Borghi, A.; Piervittori, R. Weakening of gneiss surfaces colonized by endolithic lichens in the temperate climate area of northwest Italy, 2015. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2015, 40, 2000–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azua-Bustos, A.; Urrejola, C.; Vicuña, R. Life at the dry edge: Microorganisms of the Atacama Desert. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2939–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scalzi, G.; Selbmann, L.; Zucconi, L.; Rabbow, E.; Horneck, G.; Albertano, P.; Onofri, S. LIFE experiment: Isolation of cryptoendolithic organisms from Antarctic colonized sandstone exposed to space and simulated Mars conditions on the international space station. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2012, 42, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, C.P. Requirements and limits for life in the context of exoplanets. PNAS 2014, 111, 12628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kashyap, J.M. “RSI”, Mendeley Data; 2019. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.17632/xp4wy9px6n.1 (accessed on 26 January 2020).
- de Vera, J.P.; Alawi, M.; Backhaus, T.; Baqué, M.; Billi, D.; Böttger, U.; Berger, T.; Bohmeier, M.; Cockell, C.; Demets, R.; et al. Limits of life and the habitability of Mars: The ESA space experiment BIOMEX on the ISS. Astrobiology 2019, 19, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deleuil, M.; Fridlund, M. CoRoT: The first space-based transit survey to explore the close-in planet population. In Handbook of Exoplanets; Deeg, H., Belmonte, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, F. Electric and magnetic effects of cosmic rays. Phys. Rev. 1942, 61, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billi, D.; Friedmann, H.; Caiola, O. Ionizing-radiation resistance in the desiccation-tolerant cyanobacterium Chroococcidiopsis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Planetary Property | Reference Values for RSI | Weight Exponents for RSI |
|---|---|---|
| Mean radius | 1 EU | 0.57 |
| Bulk density | 1 EU | 1.07 |
| Escape velocity | 1 EU | 0.70 |
| Surface temperature | 288 K | 2.26 |
| Surface pressure | 1 EU | 0.022 |
| Revolution | 1 Earth year | 0.7 |
| Planet | R (EU) | ρ (EU) | T (K) | Ve (EU) | P (EU) | Rev (Days) | RSII | RSIS | RSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earth | 1.00 | 1.00 | 288 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Mars | 0.532 | 0.713 | 218 | 0.45 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.82 |
| Proxima Cen.-b | 1.12 | 0.9 | 263.9 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 0.59 | 0.75 |
| GJ 667Cc | 1.4 | 0.99 | 286.4 | 1.39 | 2.7 | 0.24 | 0.92 | 0.66 | 0.78 |
| Kepler-296e | 1.48 | 1.03 | 306.6 | 1.07 | 1.1 | 0.27 | 0.93 | 0.68 | 0.79 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kashyap Jagadeesh, M.; Rao Valluri, S.; Kari, V.; Kubska, K.; Kaczmarek, Ł. Indexing Exoplanets with Physical Conditions Potentially Suitable for Rock-Dependent Extremophiles. Life 2020, 10, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10020010
Kashyap Jagadeesh M, Rao Valluri S, Kari V, Kubska K, Kaczmarek Ł. Indexing Exoplanets with Physical Conditions Potentially Suitable for Rock-Dependent Extremophiles. Life. 2020; 10(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleKashyap Jagadeesh, Madhu, Sagarika Rao Valluri, Vani Kari, Katarzyna Kubska, and Łukasz Kaczmarek. 2020. "Indexing Exoplanets with Physical Conditions Potentially Suitable for Rock-Dependent Extremophiles" Life 10, no. 2: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10020010
APA StyleKashyap Jagadeesh, M., Rao Valluri, S., Kari, V., Kubska, K., & Kaczmarek, Ł. (2020). Indexing Exoplanets with Physical Conditions Potentially Suitable for Rock-Dependent Extremophiles. Life, 10(2), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10020010







