Enigmatic Histamine Receptor H4 for Potential Treatment of Multiple Inflammatory, Autoimmune, and Related Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
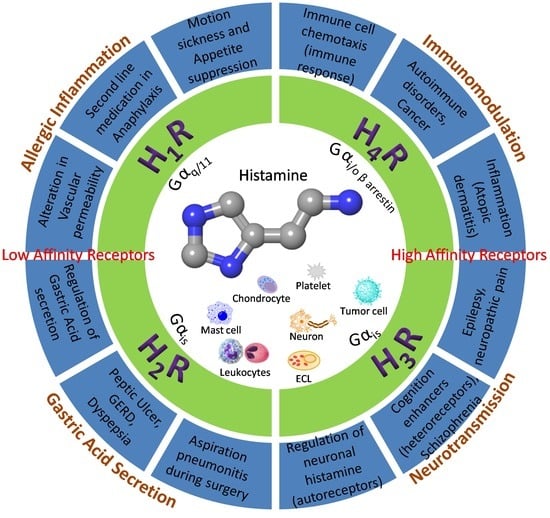
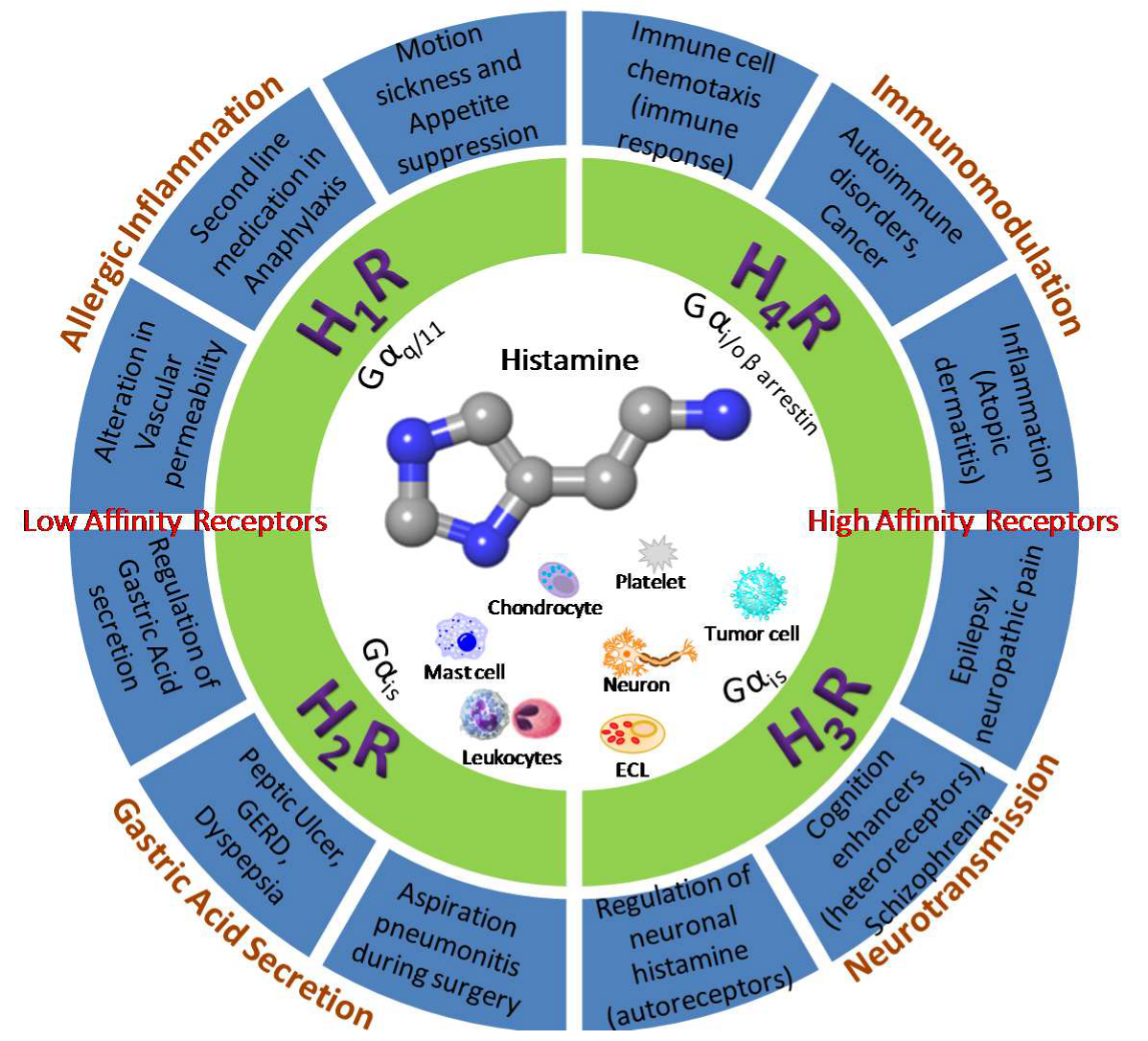
2. The Histamine Receptors—Localization and Function
3. Species Differences of H4R
4. The Pharmacological Effects of H4R Ligands
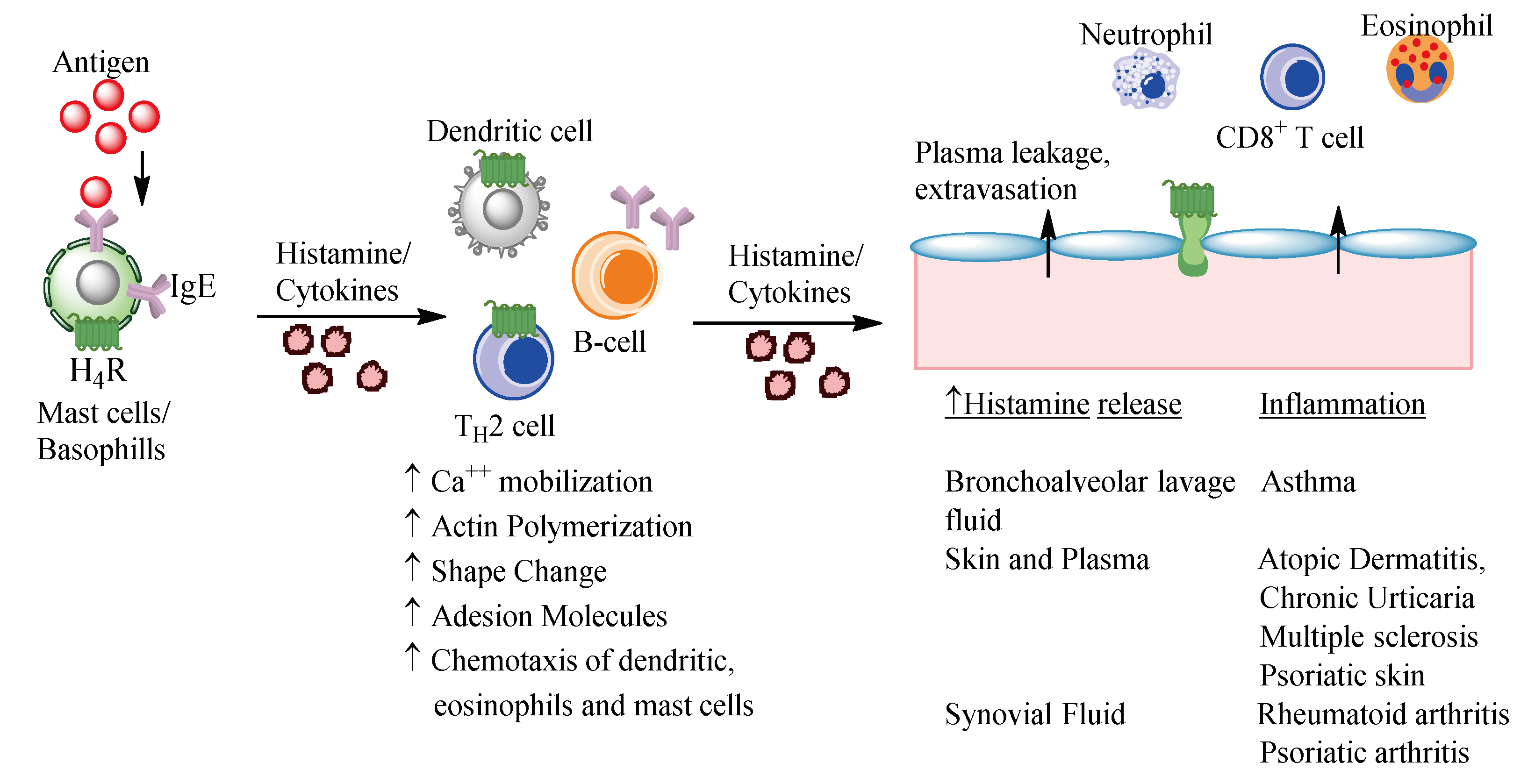
4.1. Allergic Diseases
4.2. Asthma
4.3. Diabetes
4.4. Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Diseases
4.5. Autoimmune Diseases
5. Clinical Trials of Drug Candidates Targeting H4R
6. Challenges and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obara, I.; Telezhkin, V.; Alrashdi, I.; Chazot, P.L. Histamine, histamine receptors, and neuropathic pain relief. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 580–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, J.; Falkenberg, K.; Olesen, J. Histamine and migraine revisited: Mechanisms and possible drug targets. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chazot, P.L.; Johnston, L.; McAuley, E.; Bonner, S. Histamine and Delirium: Current Opinion. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Sgambellone, S.; Lanzi, C.; Nardini, P.; Pini, A.; Moroni, F.; Masini, E.; Lucarini, L. Effects of PARP-1 Deficiency and Histamine H4 Receptor Inhibition in an Inflammatory Model of Lung Fibrosis in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fan, Y.; Lai, Y.; Han, T.; Li, Z.; Zhou, P.; Pan, P.; Wang, W.; Hu, D.; Liu, X.; et al. Coronavirus infections and immune responses. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula, P.; Chazot, P.L.; Cowart, M.; Gutzmer, R.; Leurs, R.; Liu, W.L.; Stark, H.; Thurmond, R.L.; Haas, H.L. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. XCVIII. Histamine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 601–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corrêa, M.F.; Fernandes, J.P.d.S. Histamine H4 receptor ligands: Future applications and state of art. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 85, 461–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, M.; Borriello, F.; Granata, F.; Annunziato, L.; Marone, G. Histamine receptors and antihistamines: From discovery to clinical applications. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2014, 100, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowden, J.M.; Yu, F.; Banie, H.; Farahani, M.; Ling, P.; Nguyen, S.; Riley, J.P.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, J.; Dunford, P.J.; et al. The histamine H4 receptor mediates inflammation and Th17 responses in preclinical models of arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jemima, E.A.; Prema, A.; Thangam, E.B. Functional characterization of histamine H4 receptor on human mast cells. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 62, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.H.; Seifert, R. The histamine H4-receptor and the central and peripheral nervous system: A critical analysis of the literature. Neuropharmacology 2016, 106, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, B.; Stark, H. Cherry-picked ligands at histamine receptor subtypes. Neuropharmacology 2016, 106, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, H.L.; Panula, P.P. Histamine receptors. Neuropharmacology 2016, 106, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Qu, C.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Activation of microglia by histamine and substance P. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliszek, M.; Speckmann, V.; Schacht, D.; von Lehe, M.; Stark, H.; Schlicker, E. A search for functional histamine H4 receptors in the human, guinea pig and mouse brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2015, 388, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipek, S. Molecular switches in GPCRs. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 55, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, D.; Wu, M.; Guo, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhong, L.; Cai, X.; Dai, A.; Jang, W.; Shakhnovich, E.I.; et al. Common activation mechanism of class A GPCRs. eLife 2019, 8, e50279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Weinstein, H. Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G protein-coupled receptors. Methods Neurosci. 1995, 25, 366–428. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Michalovich, D.; Wu, H.-L.; Tan, K.B.; Dytko, G.M.; Mannan, I.J.; Boyce, R.; Alston, J.; Tierney, L.A.; Li, X.; et al. Cloning, Expression, and Pharmacological Characterization of a Novel Human Histamine Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.S. Construction of a sequence motif characteristic of aminergic G protein–coupled receptors. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, M.; Shachaf, N.; Basile, L.; Milardi, D.; Zeidan, M.; Raiyn, J.; Guccione, S.; Rayan, A. Sequential application of ligand and structure based modeling approaches to index chemicals for their hH4R antagonism. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, R.; Noszal, B.; Racz, A.; Falus, A.; Eros, D.; Keseru, G.M. Binding mode analysis and enrichment studies on homology models of the human histamine H4 receptor. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.D.; de Graaf, C.; Jiang, W.; Sadek, P.; McGovern, P.M.; Istyastono, E.P.; Bakker, R.A.; de Esch, I.J.; Thurmond, R.L.; Leurs, R. Molecular determinants of ligand binding to H4R species variants. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhne, S.; Kooistra, A.J.; Bosma, R.; Bortolato, A.; Wijtmans, M.; Vischer, H.F.; Mason, J.S.; de Graaf, C.; de Esch, I.J.; Leurs, R. Identification of Ligand Binding Hot Spots of the Histamine H1 Receptor following Structure-Based Fragment Optimization. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 9047–9061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, X.-J.; Jiang, X.; Wilson, S.J.; Hofstra, C.L.; Blevitt, J.; Pyati, J.; Li, X.; Chai, W.; Carruthers, N. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a fourth histamine receptor (H4) expressed in bone marrow. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istyastono, E.P.; Kooistra, A.J.; Vischer, H.F.; Kuijer, M.; Roumen, L.; Nijmeijer, S.; Smits, R.A.; de Esch, I.J.P.; Leurs, R.; de Graaf, C. Structure-based virtual screening for fragment-like ligands of the G protein-coupled histamine H4 receptor. Med. Chem. Comm. 2015, 6, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultes, S.; Kooistra, A.J.; Vischer, H.F.; Nijmeijer, S.; Haaksma, E.E.J.; Leurs, R.; de Esch, I.J.P.; de Graaf, C. Combinatorial Consensus Scoring for Ligand-Based Virtual Fragment Screening: A Comparative Case Study for Serotonin 5-HT3A, Histamine H1, and Histamine H4 Receptors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 1030–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Q.; Kodithuwakku, N.D.; Yuan, X.; He, G.; Chen, M.; Xu, S.; Wu, Y. Anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory properties of a potent histamine H1 receptor antagonist, desloratadine citrate disodium injection, and its anti-inflammatory mechanism on EA.hy926 endothelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 754, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangam, E.B.; Jemima, E.A.; Singh, H.; Baig, M.S.; Khan, M.; Mathias, C.B.; Church, M.K.; Saluja, R. The Role of Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Mast Cell-Mediated Allergy and Inflammation: The Hunt for New Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shim, Y.K.; Kim, N. The Effect of H2 Receptor Antagonist in Acid Inhibition and Its Clinical Efficacy. Korean J. Gastroenterol. Taehan Sohwagi Hakhoe Chi 2017, 70, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Wering, H.M.; Benninga, M.A. Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonist in the Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, A.; Yoshikawa, T.; Miura, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Naganuma, F.; Shibuya, K.; Iida, T.; Harada, R.; Okamura, N.; Watanabe, T.; et al. Mechanism of the histamine H(3) receptor-mediated increase in exploratory locomotor activity and anxiety-like behaviours in mice. Neuropharmacology 2014, 81, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarskog, L.F.; Lowy, M.T.; Grove, R.A.; Keefe, R.S.; Horrigan, J.P.; Ball, M.P.; Breier, A.; Buchanan, R.W.; Carter, C.S.; Csernansky, J.G.; et al. A Phase II study of a histamine H (3) receptor antagonist GSK239512 for cognitive impairment in stable schizophrenia subjects on antipsychotic therapy. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 164, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadek, B.; Saad, A.; Latacz, G.; Kuder, K.; Olejarz, A.; Karcz, T.; Stark, H.; Kiec-Kononowicz, K. Non-imidazole-based histamine H3 receptor antagonists with anticnvulsant activity in different seizure models in male adult rats. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 3879–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sadek, B.; Saad, A.; Subramanian, D.; Shafiullah, M.; Lazewska, D.; Kiec-Kononowiczc, K. Anticonvulsant and procognitive properties of the non-imidazole histamine H3 receptor antagonist DL77 in male adult rats. Neuropharmacology 2016, 106, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, B.; Schwed, J.S.; Subramanian, D.; Weizel, L.; Walter, M.; Adem, A.; Stark, H. Non-imidazole histamine H3 receptor ligands incorporating antiepileptic moieties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 77, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, N.; Khan, N.; Ojha, S.K.; Lazewska, D.; Kiec-Kononowicz, K.; Sadek, B. The Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist DL77 Ameliorates MK801-Induced Memory Deficits in Rats. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.L. Histamine H4 receptor antagonists for the treatment of inflammatory disorders. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, M.F.; Varela, M.T.; Balbino, A.M.; Torrecilhas, A.C.; Landgraf, R.G.; Troncone, L.R.P.; Fernandes, J.P.d.S. 1-[(2,3-Dihydro-1-benzofuran-2-yl) methyl] piperazines as novel anti-inflammatory compounds: Synthesis and evaluation on H3R/H4R. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 90, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterle, H.A.; Nicoud, M.B.; Massari, N.A.; Táquez Delgado, M.A.; Herrero Ducloux, M.V.; Cremaschi, G.A.; Medina, V.A. Immunomodulatory role of histamine H4 receptor in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazewska, D.; Mogilski, S.; Hagenow, S.; Kuder, K.; Gluch-Lutwin, M.; Siwek, A.; Wiecek, M.; Kaleta, M.; Seibel, U.; Buschauer, A.; et al. Alkyl derivatives of 1,3,5-triazine as histamine H4 receptor ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, A.; Gola, J.; Kraszewska, K.; Mussur, M.; Kobos, J.; Mazurek, U.; Stark, H.; Fogel, W.A. Experimental autoimmune myocarditis in rats and therapeutic histamine H1–H4 receptor inhibition. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 69, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.P.; Christopoulos, A.; Davenport, A.P.; Kelly, E.; Marrion, N.V.; Peters, J.A.; Faccenda, E.; Harding, S.D.; Pawson, A.J.; Sharman, J.L. The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2017/18: G protein-coupled receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, S17–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiligada, E.; Ennis, M. Histamine pharmacology: From Sir Henry Dale to the 21st century. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wifling, D.; Bernhardt, G.; Dove, S.; Buschauer, A. The Extracellular Loop 2 (ECL2) of the Human Histamine H4 Receptor Substantially Contributes to Ligand Binding and Constitutive Activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wifling, D.; Löffel, K.; Nordemann, U.; Strasser, A.; Bernhardt, G.; Dove, S.; Seifert, R.; Buschauer, A. Molecular determinants for the high constitutive activity of the human histamine H4 receptor: Functional studies on orthologues and mutants. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UniProt Database. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/ (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Clustal Omega Service. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/ (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Nakamura, T.; Itadani, H.; Hidaka, Y.; Ohta, M.; Tanaka, K. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a New Human Histamine Receptor, HH4R. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurmond, R.L.; Venable, J.; Savall, B.; La, D.; Snook, S.; Dunford, P.J.; Edwards, J.P. Clinical Development of Histamine H4 Receptor Antagonists. In Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Health and Disease; Hattori, Y., Seifert, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 301–320. [Google Scholar]
- Thurmond, R.L. The histamine H4 receptor: From orphan to the clinic. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiteren, A.; De Man, J.G.; Pelckmans, P.A.; De Winter, B.Y. Histamine H(4) receptors in the gastrointestinal tract. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehling, S.; Rossbach, K.; Dunston, S.M.; Stark, H.; Baumer, W. Allergic inflammation is augmented via histamine H4 receptor activation: The role of natural killer cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2016, 83, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosicki, M.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. Human eosinophils potential pharmacological model applied in human histamine H4 receptor research. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 2087–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedetto, A.; Yoshida, T.; Fridy, S.; Park, J.E.; Kuo, I.H.; Beck, L.A. Histamine and Skin Barrier: Are Histamine Antagonists Useful for the Prevention or Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis? J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levoin, N.; Labeeuw, O.; Billot, X.; Calmels, T.; Danvy, D.; Krief, S.; Berrebi-Bertrand, I.; Lecomte, J.M.; Schwartz, J.C.; Capet, M. Discovery of nanomolar ligands with novel scaffolds for the histamine H4 receptor by virtual screening. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labeeuw, O.; Levoin, N.; Billot, X.; Danvy, D.; Calmels, T.; Krief, S.; Ligneau, X.; Berrebi-Bertrand, I.; Robert, P.; Lecomte, J.M.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of a 2-benzothiazolylphenylmethyl ether class of histamine H4 receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5263–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohsawa, Y.; Hirasawa, N. The Role of Histamine H1 and H4 Receptors in Atopic Dermatitis: From Basic Research to Clinical Study. Allergol. Int. 2014, 63, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savall, B.M.; Chavez, F.; Tays, K.; Dunford, P.J.; Cowden, J.M.; Hack, M.D.; Wolin, R.L.; Thurmond, R.L.; Edwards, J.P. Discovery and SAR of 6-alkyl-2,4-diaminopyrimidines as histamine H(4) receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 2429–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigbu, D.I.; Coyne, A.M. Update and clinical utility of alcaftadine ophthalmic solution 0.25% in the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2015, 9, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLaurin, E.B.; Marsico, N.P.; Ackerman, S.L.; Ciolino, J.B.; Williams, J.M.; Villanueva, L.; Hollander, D.A. Ocular itch relief with alcaftadine 0.25% versus olopatadine 0.2% in allergic conjunctivitis: Pooled analysis of two multicenter randomized clinical trials. Adv. Ther. 2014, 31, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grzybowska-Kowalczyk, A.; Maslinska, D.; Wojciechowska, M.; Szukiewicz, D.; Wojtecka-Lukasik, E.; Paradowska, A.; Maldyk, P.; Maslinski, S. Expression of histamine H4 receptor in human osteoarthritic synovial tissue. Inflamm. Res. 2008, 57 (Suppl. 1), S63–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybowska-Kowalczyk, A.; Wojtecka-Lukasik, E.; Maslinska, D.; Gujski, M.; Maslinski, S. Human and clinical aspects of histamine. Inflamm. Res. 2007, 56 (Suppl. 1), S59–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzodkiewicz, P.; Wojtecka-Łukasik, E.; Maśliński, S. Role of histamine in rheumatoid diseases. Reumatol. Rheumatol. 2010, 48, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Shao, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, Q.; Yang, H.; Hu, X.; Chen, B.; Peng, X.; Wu, Q.; et al. Copy number variations of the human histamine H4 receptor gene are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiteren, A.; De Man, J.G.; Ruyssers, N.E.; Moreels, T.G.; Pelckmans, P.A.; De Winter, B.Y. Histamine H4 and H1 receptors contribute to postinflammatory visceral hypersensitivity. Gut 2014, 63, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, C.; Tufvesson, E.; Diamant, Z.; Bjermer, L. Revisiting the role of the mast cell in asthma. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2016, 22, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, L.; Brightling, C.E. Eosinophilic airway inflammation: Role in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2016, 7, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Metcalfe, D.D.; Pawankar, R.; Ackerman, S.J.; Akin, C.; Clayton, F.; Falcone, F.H.; Gleich, G.J.; Irani, A.M.; Johansson, M.W.; Klion, A.D.; et al. Biomarkers of the involvement of mast cells, basophils and eosinophils in asthma and allergic diseases. World Allergy Organ. J. 2016, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grosicki, M.; Wójcik, T.; Chlopicki, S.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K. In vitro study of histamine and histamine receptor ligands influence on the adhesion of purified human eosinophils to endothelium. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 777, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.C.; Pini, A.; Lucarini, L.; Lanzi, C.; Veglia, E.; Thurmond, R.L.; Stark, H.; Masini, E. Prevention of bleomycin-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice by naproxen and JNJ7777120 treatment. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 351, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thurmond, R.L.; Chen, B.; Dunford, P.J.; Greenspan, A.J.; Karlsson, L.; La, D.; Ward, P.; Xu, X.L. Clinical and preclinical characterization of the histamine H(4) receptor antagonist JNJ-39758979. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 349, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, C.; Munder, A.; Glage, S.; Wedekind, D.; Schenk, H.; Seifert, R.; Neumann, D. The histamine H4-receptor (H4R) regulates eosinophilic inflammation in ovalbumin-induced experimental allergic asthma in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.; Albrecht, M.; Behrens, B.; Jirmo, A.; Behrens, G.; Hartwig, C.; Neumann, D.; Raap, U.; Bahre, H.; Herrick, C.; et al. Delineating the role of histamine-1- and -4-receptors in a mouse model of Th2-dependent antigen-specific skin inflammation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veglia, E.; Grange, C.; Pini, A.; Moggio, A.; Lanzi, C.; Camussi, G.; Chazot, P.L.; Rosa, A.C. Histamine receptor expression in human renal tubules: A comparative pharmacological evaluation. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, A.C.; Grange, C.; Pini, A.; Katebe, M.; Benetti, E.; Collino, M.; Miglio, G.; Bani, D.; Camussi, G.; Chazot, P. Overexpression of histamine H4 receptors in the kidney of diabetic rat. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 62, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pini, A.; Grange, C.; Veglia, E.; Argenziano, M.; Cavalli, R.; Guasti, D.; Calosi, L.; Ghè, C.; Solarino, R.; Thurmond, R.L.; et al. Histamine H4 receptor antagonism prevents the progression of diabetic nephropathy in male DBA2/J mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Homberg, J.R.; Fang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Meng, X.; Shen, J.; Luan, Y.; Liao, P.; Swaab, D.F.; et al. Histamine-4 receptor antagonist JNJ7777120 inhibits pro-inflammatory microglia and prevents the progression of Parkinson-like pathology and behaviour in a rat model. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2019, 76, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuutinen, S.; Panula, P. Histamine in neurotransmission and brain diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 709, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhurst, A.D.; Roberts, J.C.; Lee, J.; Chen, C.P.; Brown, S.H.; Roman, S.; Lai, M.K. Characterization of histamine H3 receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease brain and amyloid over-expressing TASTPM mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patnaik, R.; Sharma, A.; Skaper, S.D.; Muresanu, D.F.; Lafuente, J.V.; Castellani, R.J.; Nozari, A.; Sharma, H.S. Histamine H3 Inverse Agonist BF 2649 or Antagonist with Partial H4 Agonist Activity Clobenpropit Reduces Amyloid Beta Peptide-Induced Brain Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Bao, A.M.; Swaab, D.F. The human histaminergic system in neuropsychiatric disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Kim, B.M.; Lee, K.A.; Lee, S.H.; Firestein, G.S.; Kim, H.R. Histamine and Histamine H4 Receptor Promotes Osteoclastogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd-Allah, A.R.; Ahmad, S.F.; Alrashidi, I.; Abdel-Hamied, H.E.; Zoheir, K.M.; Ashour, A.E.; Bakheet, S.A.; Attia, S.M. Involvement of histamine 4 receptor in the pathogenesis and progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunol. 2014, 26, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massari, N.A.; Medina, V.A.; Lamas, D.J.M.; Cricco, G.P.; Croci, M.; Sambuco, L.; Bergoc, R.M.; Rivera, E.S. Role of H4 receptor in histamine-mediated responses in human melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2011, 21, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, V.A.; Brenzoni, P.G.; Lamas, D.J.; Massari, N.; Mondillo, C.; Nunez, M.A.; Pignataro, O.; Rivera, E.S. Role of histamine H4 receptor in breast cancer cell proliferation. Front. Biosci. 2011, 3, 1042–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cricco, G.P.; Mohamad, N.A.; Sambuco, L.A.; Genre, F.; Croci, M.; Gutiérrez, A.S.; Medina, V.; Bergoc, R.; Rivera, E.; Martin, G. Histamine regulates pancreatic carcinoma cell growth through H3 and H4 receptors. Inflamm. Res. 2008, 57, 23–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boer, K.; Helinger, E.; Helinger, A.; Pocza, P.; Pos, Z.; Demeter, P.; Baranyai, Z.; Dede, K.; Darvas, Z.; Falus, A. Decreased expression of histamine H1 and H4 receptors suggests disturbance of local regulation in human colorectal tumours by histamine. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 87, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saligrama, N.; Noubade, R.; Case, L.K.; del Rio, R.; Teuscher, C. Combinatorial roles for histamine H1-H2 and H3-H4 receptors in autoimmune inflammatory disease of the central nervous system. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werfel, T. Novel systemic drugs in treatment of atopic dermatitis: Results from phase II and phase III studies published in 2017/2018. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 18, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attali, P.; Gomeni, R.; Wersinger, E.; Poli, S.; Venail, F. The effects of SENS-111, a new H4R antagonist, on vertigo induced by caloric test in healthy volunteers (HV) is related to plasma concentrations. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Synovial Biopsy Study of JNJ-38518168 in Participants with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Despite Methotrexate Therapy (TERMINATED), Database Entry NCT01862224. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 24 May 2013).
- A Dose Range Finding Study of JNJ-38518168 in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis in Spite of Treatment with Methotrexate (TERMINATED), Database Entry NCT01679951. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 6 September 2012).
- A Study of JNJ-38518168 in Symptomatic Adult Participants with Uncontrolled, Persistent Asthma (COMPLETED), Database Entry NCT01823016. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 4 April 2013).
- Riddy, D.M.; Cook, A.E.; Diepenhorst, N.A.; Bosnyak, S.; Brady, R.; la Cour, C.M.; Mocaer, E.; Summers, R.J.; Charman, W.N.; Sexton, P.M. Isoform-specific biased agonism of histamine H3 receptor agonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 91, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmeier, A.; Greenspan, A.; Xu, X.; Silkoff, P.; Barnathan, E.; Loza, M.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, B.; Chen, B.; Thurmond, R. Phase 2a, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre, parallel-group study of an H4R-antagonist (JNJ-39758979) in adults with uncontrolled asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmeier, A.; Francke, K.; Chen, B.; Dunford, P.J.; Greenspan, A.J.; Xia, Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, B.; Thurmond, R.L. The histamine H(4) receptor antagonist, JNJ 39758979, is effective in reducing histamine-induced pruritus in a randomized clinical study in healthy subjects. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 350, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, R.; Keseru, G.M. Novel histamine H4 receptor ligands and their potential therapeutic applications: An update. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2014, 24, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Dose Range Finding Study of JNJ-39758979 in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Currently Treated with Methotrexate (WITHDRAWN), Database Entry NCT01480388. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 28 November 2011).
- Study of JNJ-39758979 in Symptomatic Adult Patients with Uncontrolled Asthma (WITHDRAWN), Database Entry NCT01493882. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 16 December 2011).
- Murata, Y.; Song, M.; Kikuchi, H.; Hisamichi, K.; Xu, X.L.; Greenspan, A.; Kato, M.; Chiou, C.F.; Kato, T.; Guzzo, C. Phase 2a, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, parallel-group study of a H4R-antagonist (JNJ-39758979) in Japanese adults with moderate atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 2015, 42, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Study to Determine the Efficacy of ZPL-3893787 in Subjects with Atopic Dermatitis (COMPLETED), Database Entry NCT02424253. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 23 April 2015).
- A Study to Determine the Efficacy of ZPL-3893787 in Subjects with Plaque Psoriasis (COMPLETED), Database Entry NCT02618616. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 1 December 2015).
- A Study to Assess the Safety and Efficacy of ZPL389 in Patients with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis (RECRUITING), Database Entry NCT03517566. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 7 May 2018).
- A Study to Assess the Safety and Efficacy of ZPL389 with TCS/TCI in Atopic Dermatitis Patients (ZESTExt) (RECRUITING), Database Entry NCT03948334. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 13 May 2019).
- Efficacy of SENS-111 in Patients Suffering From Acute Unilateral Vestibulopathy (RECRUITING), Database Entry NCT03110458. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 12 April 2017).
- Rosethorne, E.M.; Charlton, S.J. Agonist-biased signaling at the histamine H4 receptor: JNJ7777120 recruits β-arrestin without activating G proteins. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, A.; Wittmann, H.J.; Buschauer, A.; Schneider, E.H.; Seifert, R. Species-dependent activities of G-protein-coupled receptor ligands: Lessons from histamine receptor orthologs. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, R.; Strasser, A.; Schneider, E.H.; Neumann, D.; Dove, S.; Buschauer, A. Molecular and cellular analysis of human histamine receptor subtypes. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monczor, F.; Fernandez, N. Current knowledge and perspectives on histamine H1 and H2 receptor pharmacology: Functional selectivity, receptor crosstalk, and repositioning of classic histaminergic ligands. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenakin, T. Signaling bias in drug discovery. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiligada, E.; Ishii, M.; Riccardi, C.; Spedding, M.; Simon, H.U.; Teixeira, M.M.; Landys Chovel Cuervo, M.; Holgate, S.T.; Levi-Schaffer, F. The expanding role of immunopharmacology: IUPHAR Review 16. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4217–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riccardi, C.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Tiligada, E. Immunopharmacology and Inflammation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]


| Species | Scientific Name | UniProt ID | Similarity to hH4R | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Human | Homo sapiens | Q9H3N8 | - |
| 2 | Chimpanzee | Pan troglodytes | H2QED2 | 99% |
| 3 | Gorilla | Gorilla | G3QS38 | 98% |
| 4 | Pygmy chimpanzee | Pan paniscus | A0A2R9BQY6 | 98% |
| 5 | Orangutan | Pongo abelii | H2NW27 | 98% |
| 6 | Crab-eating macaque | Macaca fascicularis | Q3V8G8 | 94% |
| 7 | Pig-tailed macaque | Macaca nemestrina | A0A2K6D1G7 | 94% |
| 8 | Rhesus macaque | Macaca mulatta | G7NKH9 | 94% |
| 9 | Olive baboon | Papio anubis | A0A096NGN9 | 94% |
| 10 | Drill | Mandrillus leucophaeus | A0A2K5YBZ5 | 94% |
| 11 | Angolan colobus | Colobus angolensis palliatus | A0A2K5HHL6 | 93% |
| 12 | Sooty mangabey | Cercocebus atys | A0A2K5LQL7 | 93% |
| 13 | Black snub-based monkey | Rhinopithecus bieti | A0A2K6MXG3 | 93% |
| 14 | Golden snub-based monkey | Rhinopithecus roxellana | A0A2K6RWF0 | 93% |
| 15 | Green monkey | Chlorocebus sabaeus | A0A0D9RYY4 | 90% |
| 16 | Ma’s Night monkey | Aotus nancymaae | A0A2K5CHI5 | 90% |
| 17 | Cebus capucinus imitator | Cebus capucinus imitator | A0A2K5RKQ4 | 90% |
| 18 | White-tufted-ear marmoset | Callithrix jacchus | F7IT43 | 89% |
| 19 | Squirrel monkey | Saimiri boliviensis | A0A2K6TG45 | 88% |
| 20 | Philippine tarsier | Tarsius syrichta | A0A1U7UM57 | 78% |
| 21 | Small-eared galago | Otolemur garnettii | H0WYC8 | 73% |
| 22 | Thirteen-lined ground squirrel | Ictidomys tridecemlineatus | I3MG71 | 72% |
| 23 | Dog | Canis lupus familiaris | J9P1C3 | 71% |
| 24 | Golden hamster | Mesocricetus auratus | A0A1U7Q7T1 | 71% |
| 25 | Grizzly bear | Ursus arctos horribilis | A0A3Q7WBT8 | 70% |
| 26 | Polar bear | Ursus maritimus | A0A384C2G0 | 70% |
| 27 | Pig | Sus scrofa | Q8WNV9 (Pig 1) | 70% |
| 28 | A0A5G2QV28 (Pig 2) | 10% | ||
| 29 | Red fox | Vulpes vulpes | A0A3Q7SYT7 | 70% |
| 30 | Black flying fox | Pteropus alecto | L5K5C7 | 69% |
| 31 | African elephant | Loxodonta africana | G3STF1 | 69% |
| 32 | Giant panda | Ailuropoda melanoleuca | G1M6D3 | 69% |
| 33 | Chinese hamster | Cricetulus griseus | A0A3L7I1V9 | 69% |
| 34 | Horse | Equus caballus | F6Z8L3 | 69% |
| 35 | Sea cow | Trichechus manatus latirostris | A0A2Y9E7N3 | 69% |
| 36 | Rabbit | Oryctolagus cuniculus | G1TKW6 | 68% |
| 37 | Iberian lynx | Lynx pardinus | A0A485N8M7 | 68% |
| 38 | Cat | Felis catus | M3WE71 | 68% |
| 39 | Pacific walrus | Odobenus rosmarus divergens | A0A2U3WW63 | 68% |
| 40 | Rat | Rattus norvegicus | Q91ZY1 | 68% |
| 41 | Kangaroo rat | Dipodomys ordii | A0A1S3F272 | 68% |
| 42 | Hawaiian monk seal | Neomonachus schauinslandi | A0A2Y9GRV4 | 68% |
| 43 | Northern fur seal | Callorhinus ursinus | A0A3Q7Q9W4 | 67% |
| 44 | Sea otter | Enhydra lutris kenyoni | A0A2Y9ITU9 | 67% |
| 45 | Hedgehog | Erinaceus europaeus | A0A1S3A2Y6 | 67% |
| 46 | European domestic ferret | Mustela putorius furo | M3Y4H4 | 67% |
| 47 | Mouse | Mus musculus | Q91ZY2 (Mouse 1) | 67% |
| 48 | B2ZGH2 (Mouse 2) | 66% | ||
| 49 | Goat | Capra hircus | A0A452DKI0 | 65% |
| 50 | Sheep | Ovis aries | W5PBL0 | 65% |
| 51 | Sperm whale | Physeter macrocephalus | A0A2Y9F727 | 65% |
| 52 | Hybrid cattle | Bos indicus*Bos taurus | A0A4W2DVG0 | 64% |
| 53 | Yak | Bos mutus | L8IEJ5 | 64% |
| 54 | Bovine | Bos taurus | E1BBS2 | 64% |
| 55 | Guinea pig | Cavia porcellus | Q91ZY3 | 63% |
| 56 | Black bear | Ursus americanus | A0A452QKW6 | 62% |
| 57 | Yangtze river dolphin | Lipotes vexillifer | A0A340YGS9 | 61% |
| 58 | American mink | Neovison vison | U6CNR7 | 61% |
| 59 | Beluga whale | Delphinapterus leucas | A0A2Y9PB56 | 59% |
| 60 | Yangtze finless porpoise | Neophocaena asiaeorientalis | A0A341CIF8 | 59% |
| 61 | European red deer | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus | A0A212C702 | 59% |
| 62 | Indo-pacific humpbacked dolphin | Sousa chinensis | A0A484GQ08 | 57% |
| 63 | Narwhal | Monodon monoceros | A0A4U1FGC1 | 56% |
| 64 | Wolverine | Gulo gulo | A0A3P4RYS2 | 55% |
| 65 | Atlantic bottle-nosed dolphin | Tursiops truncatus | A0A2U3V3K5 | 54% |
| 66 | Gray short-tailed opossum | Monodelphis domestica | F6QB56 | 47% |
| 67 | North-Pacific minke whale | Balaenoptera acutorostrata scammoni | A0A452C640 | 46% |
| 68 | Tasmanian devil | Sarcophilus harrisii | G3X3P1 | 45% |
| 69 | Weddell seal | Leptonychotes weddellii | A0A2U3YB28 | 42% |
| 70 | White-tailed sea-eagle | Haliaeetus albicilla | A0A091PX74 | 42% |
| 71 | Trogon | Apaloderma vittatum | A0A091NQC4 | 41% |
| 72 | Cuckoo | Cuculus canorus | A0A091G9T7 | 40% |
| 73 | Turbot | Scophthalmus maximus | A0A2U9BJT1 (Turbot 1) | 36% |
| 74 | A0A2U9C3Q1 (Turbot 2) | 36% | ||
| 75 | Channel catfish | Ictalurus punctatus | A0A2D0RQW6 | 36% |
| 76 | Chinese tree shrew | Tupaia chinensis | L8YD15 | 35% |
| 77 | Rifleman | Acanthisitta chloris | A0A091MN56 | 31% |
| 78 | Scallop | Mizuhopecten yessoensis | A0A210PRL2 (Scallop 1) | 26% |
| 79 | A0A210PS14 (Scallop 2) | 22% | ||
| 80 | Oyster | Crassostrea gigas | K1PU39 | 24% |
| 81 | Coral | Stylophora pistillata | A0A2B4RTL0 (Coral 1) | 17% |
| 82 | A0A2B4RX53 (Coral 2) | 14% | ||
| 83 | Sea cucumber | Stichopus japonicus | A0A2G8KHM7 (Sea cucumber 1) | 15% |
| 84 | A0A2G8L2L5 (Sea cucumber 2) | 13% | ||
| 85 | A0A2G8JXR8 (Sea cucumber 3) | 20% |
| Compound | Clinical Indications | Phase | Status | ClinicalTrials.Gov Database Entry | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
JNJ38518168 (Toreforant) | RA | 2 | T | NCT01862224 | [92] |
| RA | 2 | T | NCT01679951 | [93] | |
| Asthma | 2 | C | NCT01823016 | [94] | |
| Psoriasis | 2 | C | NCT02295865 | [95] | |
JNJ39758979 | RA | 2 | W | NCT01480388 | [99] |
| Asthma | 2 | W | NCT01493882 | [100] | |
| ZPL3893787 (Adriforant/PF3893787/ZPL389)  | AD | 2 | C | NCT02424253 | [102] |
| Psoriasis | 2 | C | NCT02618616 | [103] | |
| AD | 2 | R | NCT03517566 | [104] | |
| AD | 2 | R | NCT03948334 | [105] | |
SENS-111 (Seliforant) | Unilateral Vestibulopathy | 2 | R | NCT03110458 | [106] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mehta, P.; Miszta, P.; Rzodkiewicz, P.; Michalak, O.; Krzeczyński, P.; Filipek, S. Enigmatic Histamine Receptor H4 for Potential Treatment of Multiple Inflammatory, Autoimmune, and Related Diseases. Life 2020, 10, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10040050
Mehta P, Miszta P, Rzodkiewicz P, Michalak O, Krzeczyński P, Filipek S. Enigmatic Histamine Receptor H4 for Potential Treatment of Multiple Inflammatory, Autoimmune, and Related Diseases. Life. 2020; 10(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleMehta, Pakhuri, Przemysław Miszta, Przemysław Rzodkiewicz, Olga Michalak, Piotr Krzeczyński, and Sławomir Filipek. 2020. "Enigmatic Histamine Receptor H4 for Potential Treatment of Multiple Inflammatory, Autoimmune, and Related Diseases" Life 10, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10040050
APA StyleMehta, P., Miszta, P., Rzodkiewicz, P., Michalak, O., Krzeczyński, P., & Filipek, S. (2020). Enigmatic Histamine Receptor H4 for Potential Treatment of Multiple Inflammatory, Autoimmune, and Related Diseases. Life, 10(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10040050