The Habitability of the Galactic Bulge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
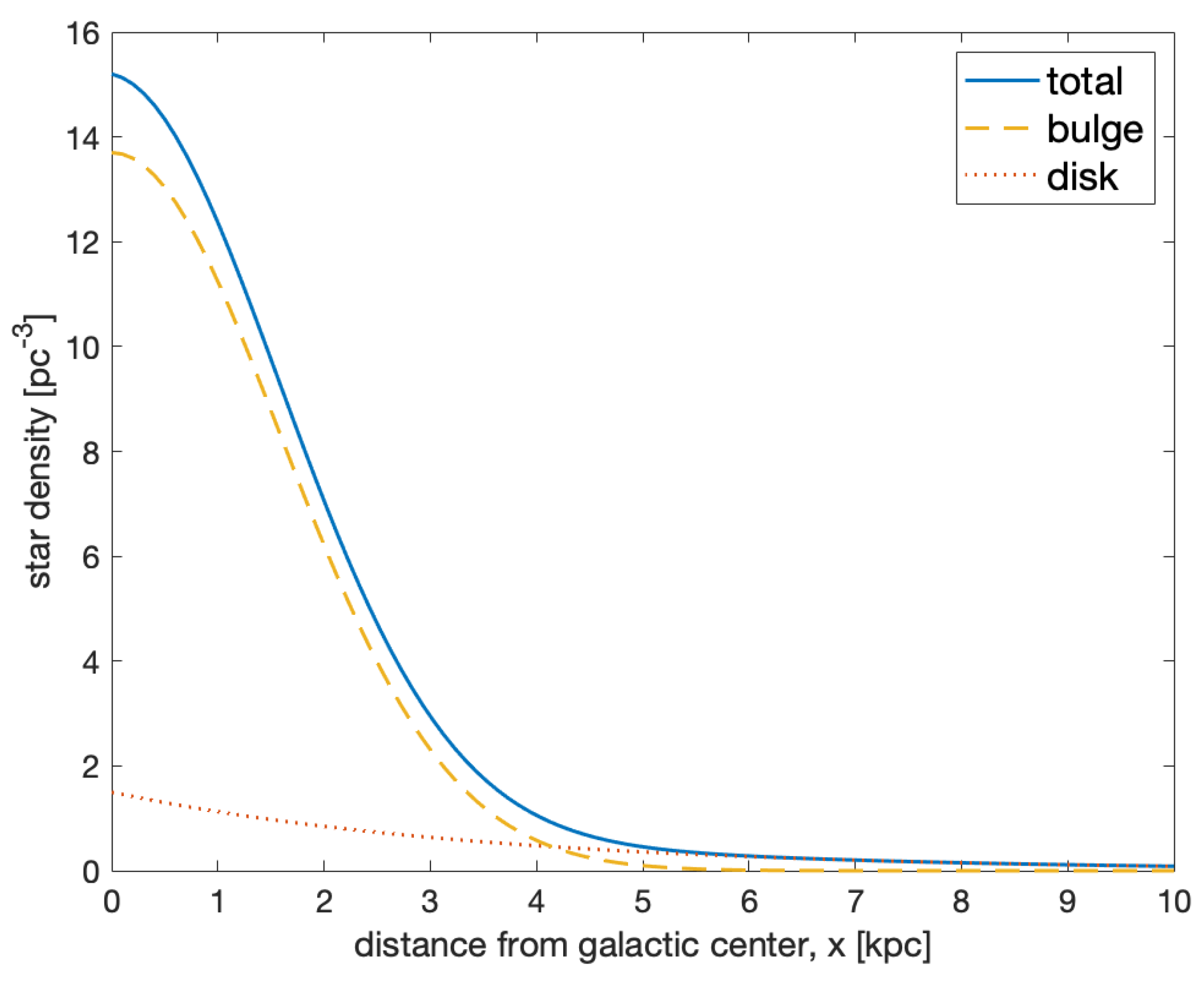
2. Planets in the Galactic Bulge
2.1. Metallicity
2.2. Orbital Stability and Encounters
2.3. Planets Around the Central Black Hole
3. The Radiation Environment in the Bulge
3.1. The Supermassive Black Hole
3.2. Supernovae Explosions
4. Transfer of Biological Material
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGN | Active Galactic Nucleus |
| GHZ | Galactic Habitable Zone |
| ESO | European Southern Observatory |
| SMBH | Supermassive black hole |
| SN | Supernova(e) |
| SWEEPS | Sagittarius Window Eclipsing Extrasolar Planet Search |
| WFIRST | Wide Field Infrared Survey Telescope (now Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope) |
References
- Kasting, J.F.; Whitmire, D.P.; Reynolds, R.T. Habitable Zones around Main Sequence Stars. Icarus 1993, 101, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, G.; Brownlee, D.; Ward, P. The Galactic Habitable Zone: Galactic Chemical Evolution. Icarus 2001, 152, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lineweaver, C.H.; Fenner, Y.; Gibson, B.K. The Galactic Habitable Zone and the Age Distribution of Complex Life in the Milky Way. Science 2004, 303, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prantzos, N. On the “galactic habitable zone”. Space Sci. Rev. 2008, 135, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgan, D.; Dayal, P.; Cockell, C.; Libeskind, N. Evaluating galactic habitability using high-resolution cosmological simulations of galaxy formation. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2017, 16, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vukotić, B.; Steinhauser, D.; Martinez-Aviles, G.; Ćirković, M.M.; Micic, M.; Schindler, S. “Grandeur in this view of life”: N-body simulation models of the Galactic habitable zone. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 3512–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gowanlock, M.G.; Morrison, I.S. The Habitability of Our Evolving Galaxy. In Habitability of the Universe Before Earth; Gordon, R., Sharov, A.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 149–171. [Google Scholar]
- Gowanlock, M.G.; Patton, D.R.; McConnell, S.M. A model of habitability within the Milky Way galaxy. Astrobiology 2011, 11, 855–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrison, I.S.; Gowanlock, M.G. Extending Galactic Habitable Zone Modeling to Include the Emergence of Intelligent Life. Astrobiology 2015, 15, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balbi, A.; Tombesi, F. The habitability of the Milky Way during the active phase of its central supermassive black hole. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.C.; Loeb, A. Evaporation of planetary atmospheres due to XUV illumination by quasars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 479, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wisłocka, A.M.; Kovačević, A.B.; Balbi, A. Comparative analysis of the influence of Sgr A* and nearby active galactic nuclei on the mass loss of known exoplanets. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 624, A71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Forbes, J.C.; Loeb, A. Habitable Evaporated Cores and the Occurrence of Panspermia Near the Galactic Center. Astrophys. J. 2018, 855, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingam, M.; Ginsburg, I.; Bialy, S. Active Galactic Nuclei: Boon or Bane for Biota? Astrophys. J. 2019, 877, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahu, K.C.; Casertano, S.; Bond, H.E.; Valenti, J.; Smith, T.E.; Minniti, D.; Zoccali, M.; Livio, M.; Panagia, N.; Piskunov, N.; et al. Transiting extrasolar planetary candidates in the Galactic bulge. Nature 2006, 443, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, K.C.; Casertano, S.; Valenti, J.; Bond, H.E.; Brown, T.M.; Smith, T.E.; Clarkson, W.; Minniti, D.; Zoccali, M.; Livio, M.; et al. Planets in the Galactic Bulge: Results from the SWEEPS Project. Extrem. Sol. Syst. ASP Conf. Ser. 2007, 398, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson, W.; Sahu, K.; Anderson, J.; Smith, T.E.; Brown, T.M.; Rich, R.M.; Casertano, S.; Bond, H.E.; Livio, M.; Minniti, D.; et al. Stellar Proper Motions in the Galactic Bulge from Deep Hubble Space Telescope ACS WFC Photometry. Astrophys. J. 2008, 684, 1110–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagakane, M.; Sumi, T.; Koshimoto, N.; Bennett, D.P.; Bond, I.A.; Rattenbury, N.; Suzuki, D.; Abe, F.; Asakura, Y.; Barry, R.; et al. MOA-2012-BLG-505Lb: A Super-Earth-mass Planet That Probably Resides in the Galactic Bulge. Astron. J. 2017, 154, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, V.; Beaulieu, J.-P.; Gould, A.; Bennett, D.P.; Yee, J.C.; Fukui, A.; Gaudi, B.S.; Sumi, T.; Udalski, A. MOA-2011-BLG-293LB: First Microlensing Planet Possibly In The Habitable Zone. Astrophys. J. 2013, 780, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassan, A.; Kubas, D.; Beaulieu, J.-P.; Dominik, M.; Horne, K.; Greenhill, J.; Wambsganss, J.; Menzies, J.; Williams, A.; Jørgensen, U.G.; et al. One or more bound planets per Milky Way star from microlensing observations. Nature 2012, 481, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penny, M.T.; Henderson, C.B.; Clanton, C. Is the Galactic Bulge Devoid of Planets? Astrophys. J. 2016, 830, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penny, M.T.; Kerins, E.; Rattenbury, N.; Beaulieu, J.P.; Robin, A.C.; Mao, S.; Batista, V.; Calchi Novati, S.; Cassan, A.; Fouqúe, P.; et al. ExELS: An exoplanet legacy science proposal for the ESA euclid mission—I. Cold exoplanets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 434, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montet, B.T.; Yee, J.C.; Penny, M.T. Measuring the galactic distribution of transiting planets with WFIRST. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2017, 129, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Udalski, A.; Novati, S.C.; Chung, S.-J.; Jung, Y.K.; Ryu, Y.-H.; Shin, I.-G.; Gould, A.; Lee, C.-U.; Albrow, M.D.; et al. Toward a Galactic Distribution of Planets. I. Methodology and Planet Sensitivities of the 2015 High-cadence Spitzer Microlens Sample. Astron. J. 2017, 154, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, O.A.; Gadotti, D. The milky way bulge: Observed properties and a comparison to external galaxies. In Galactic Bulges. Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 418, pp. 199–232. [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson, W.I.; Sahu, K.C.; Anderson, J.; Rich, R.M.; Smith, T.E.; Brown, T.M.; Bond, H.E.; Livio, M.; Minniti, D.; Renzini, A.; et al. The first detection of blue straggler stars in the Milky Way bulge. Astrophys. J. 2011, 735, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, J.L.; Li, H. The first planets: The critical metallicity for planet formation. Astrophys. J. 2012, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchhave, L.A.; Latham, D.W.; Johansen, A.; Bizzarro, M.; Torres, G.; Rowe, J.F.; Batalha, N.M.; Borucki, W.J.; Brugamyer, E.; Caldwell, C.; et al. An abundance of small exoplanets around stars with a wide range of metallicities. Nature 2012, 486, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchhave, L.A.; Bizzarro, M.; Latham, D.W.; Sasselov, D.; Cochran, W.D.; Endl, M.; Isaacson, H.; Juncher, D.; Marcy, G.W. Three regimes of extrasolar planet radius inferred from host star metallicities. Nature 2014, 509, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchhave, L.A.; Latham, D.W. The Metallicities of Stars with and Without Transiting Planets. Astrophys. J. 2015, 808, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Fischer, D.A. Revealing a universal planet-metallicity correlation for planets of different solar-type stars. Astron. J. 2015, 149, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoccali, M.; Renzini, A.; Ortolani, S.; Greggio, L.; Saviane, I.; Cassisi, S.; Rejkuba, M.; Barbuy, B.; Rich, R.M.; Bica, E. Age and metallicity distribution of the Galactic bulge from extensive optical and near-IR stellar photometry. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 399, 931–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, V.; Lecureur, A.; Gómez, A.; Zoccali, M.; Schultheis, M.; Babusiaux, C.; Royer, F.; Barbuy, B.; Arenou, F.; Minniti, D.; et al. The metallicity distribution of bulge clump giants in Baade’s window. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 534, A80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojas-Arriagada, A.; Recio-Blanco, A.; Hill, V.; De Laverny, P.; Schultheis, M.; Babusiaux, C.; Zoccali, M.; Minniti, D.; Gonzalez, O.A.; Feltzing, S.; et al. The Gaia -ESO Survey: Metallicity and kinematic trends in the Milky Way bulge. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 569, A103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Juan Ovelar, M.; Kruijssen, J.M.D.; Bressert, E.; Testi, L.; Bastian, N.; Cánovas, H. Can habitable planets form in clustered environments? Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 546, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojnordi-Arbab, B.; Rahvar, S. Dangerous stellar encounters with an Earth-like planet in the Milky Way galaxy. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.10595. [Google Scholar]
- Sloan, D.; Batista, R.A.; Loeb, A. The Resilience of Life to Astrophysical Events. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTier, M.A.S.; Kipping, D.M.; Johnston, K. 8 in 10 Stars in the Milky Way Bulge Experience Stellar Encounters Within 1000 AU in a Gigayear. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 495, 2105–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trani, A.A.; Mapelli, M.; Spera, M.; Bressan, A. Dynamics of tidally captured planets in the Galactic Center. Mem. Della Soc. Astron. Ital. J. Ital. Astron. Soc. 2016, 87, 705–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davari, N.; Capuzzo-Dolcetta, R.; Spurzem, R. Interaction of stars hosting planets with Sgr A* black hole. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2019, 14, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davari, N.; Capuzzo-Dolcetta, R. Dynamical properties of binary stars hosting planets in the Galactic Center. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.03738. [Google Scholar]
- Iorio, L. What Would Happen if We Were About 1 pc Away from a Supermassive Black Hole? Astrophys. J. 2020, 889, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbot, D.S.; Switzer, E.R. The steppenwolf: A proposal for a habitable planet in interstellar space. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 735, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lingam, M.; Loeb, A. Subsurface exolife. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2019, 18, 112–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonucci, R. Unified models for active galactic nuclei and quasars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 31, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, H. Revisiting the Unified Model of Active Galactic Nuclei. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 53, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wada, K.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Kokubo, E. Planet Formation around Supermassive Black Holes in the Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2019, 886, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakala, P.; Docekal, J.; Turonova, Z. Habitable Zones around Almost Extremely Spinning Black Holes (Black Sun Revisited). Astrophys. J. 2020, 889, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piran, T.; Jimenez, R. Possible role of gamma ray bursts on life extinction in the universe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 231102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gowanlock, M.G. Astrobiological Effects of Gamma-Ray Bursts in the Milky Way Galaxy. Astrophys. J. 2016, 832, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lingam, M.; Loeb, A. Colloquium: Physical constraints for the evolution of life on exoplanets. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2019, 91, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gehrels, N.; Laird, C.M.; Jackman, C.H.; Cannizzo, J.K.; Mattson, B.J.; Chen, W. Ozone Depletion from Nearby Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2003, 585, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melott, A.L.; Thomas, B.C. Astrophysical ionizing radiation and Earth: A brief review and census of intermittent intense sources. Astrobiology 2011, 11, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, A.C.; Reylé, C.; Derrière, S.; Picaud, S. A synthetic view on structure and evolution of the Milky Way. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 409, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingam, M.; Loeb, A. Risks for Life on Habitable Planets from Superflares of Their Host Stars. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melosh, H.J. The rocky road to panspermia. Nature 1988, 332, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesson, P.S. Panspermia, Past and Present: Astrophysical and Biophysical Conditions for the Dissemination of Life in Space. Space Sci. Rev. 2010, 156, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meech, K.J.; Weryk, R.; Micheli, M.; Kleyna, J.T.; Hainaut, O.R.; Jedicke, R.; Wainscoat, R.J.; Chambers, K.C.; Keane, J.V.; Petric, A.; et al. A brief visit from a red and extremely elongated interstellar asteroid. Nature 2017, 552, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsburg, I.; Lingam, M.; Loeb, A. Galactic Panspermia. Astrophys. J. 2018, 868, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melosh, H.J. Exchange of meteorites (and life?) between stellar systems. Astrobiology 2003, 3, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adams, F.C.; Spergel, D.N. Lithospanspermia in Star-Forming clusters. Astrobiology 2005, 5, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belbruno, E.; Moro-Martín, A.; Malhotra, R.; Savransky, D. Chaotic Exchange of Solid Material Between Planetary Systems: Implications for Lithopanspermia. Astrobiology 2012, 12, 754–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lingam, M.; Loeb, A. Enhanced interplanetary panspermia in the TRAPPIST-1 system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6689–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lingam, M.; Loeb, A. Implications of Captured Interstellar Objects for Panspermia and Extraterrestrial Life. Astron. J. 2018, 156, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brayard, A.; Krumenacker, L.J.; Botting, J.P.; Jenks, J.F.; Bylund, K.G.; Fara, E.; Vennin, E.; Olivier, N.; Goudemand, N.; Saucède, T.; et al. Unexpected Early Triassic marine ecosystem and the rise of the Modern evolutionary fauna. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balbi, A.; Hami, M.; Kovačević, A. The Habitability of the Galactic Bulge. Life 2020, 10, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10080132
Balbi A, Hami M, Kovačević A. The Habitability of the Galactic Bulge. Life. 2020; 10(8):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10080132
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalbi, Amedeo, Maryam Hami, and Andjelka Kovačević. 2020. "The Habitability of the Galactic Bulge" Life 10, no. 8: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10080132
APA StyleBalbi, A., Hami, M., & Kovačević, A. (2020). The Habitability of the Galactic Bulge. Life, 10(8), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10080132





