Comparison of Different Signal Peptides for the Efficient Secretion of the Sweet-Tasting Plant Protein Brazzein in Pichia pastoris
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
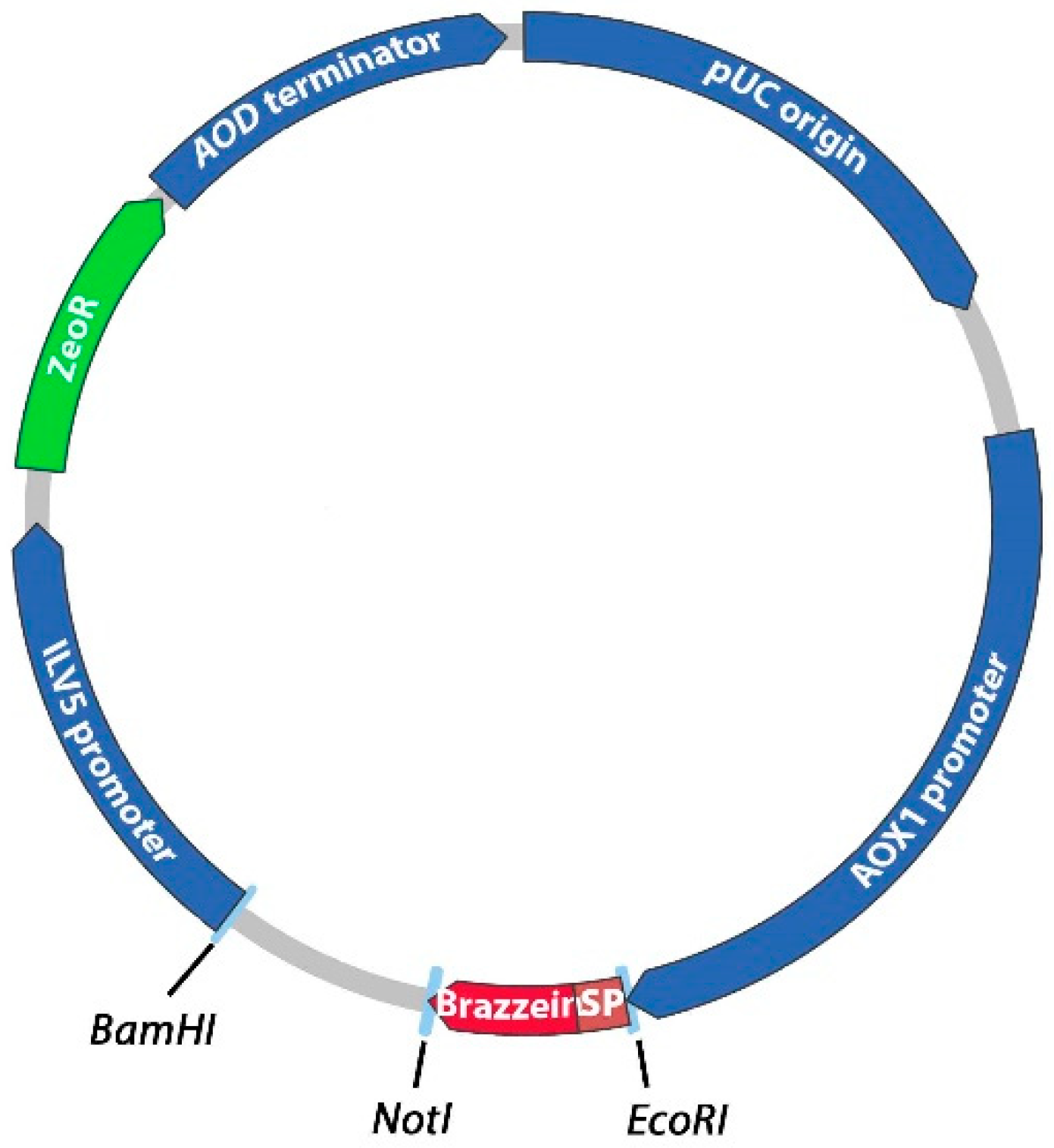
2.1. Construction of the Expression Vectors
2.2. Transformation and Culture Methods
2.3. Purification of Recombinant Brazzein
2.4. SDS-PAGE and Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.5. Functional Characterization of Brazzein Using a Functional Sweet Taste Receptor Assay
3. Results
3.1. Construction of Expression Vectors and Transformation into P. pastoris
3.2. Clones Screening for Brazzein Expression
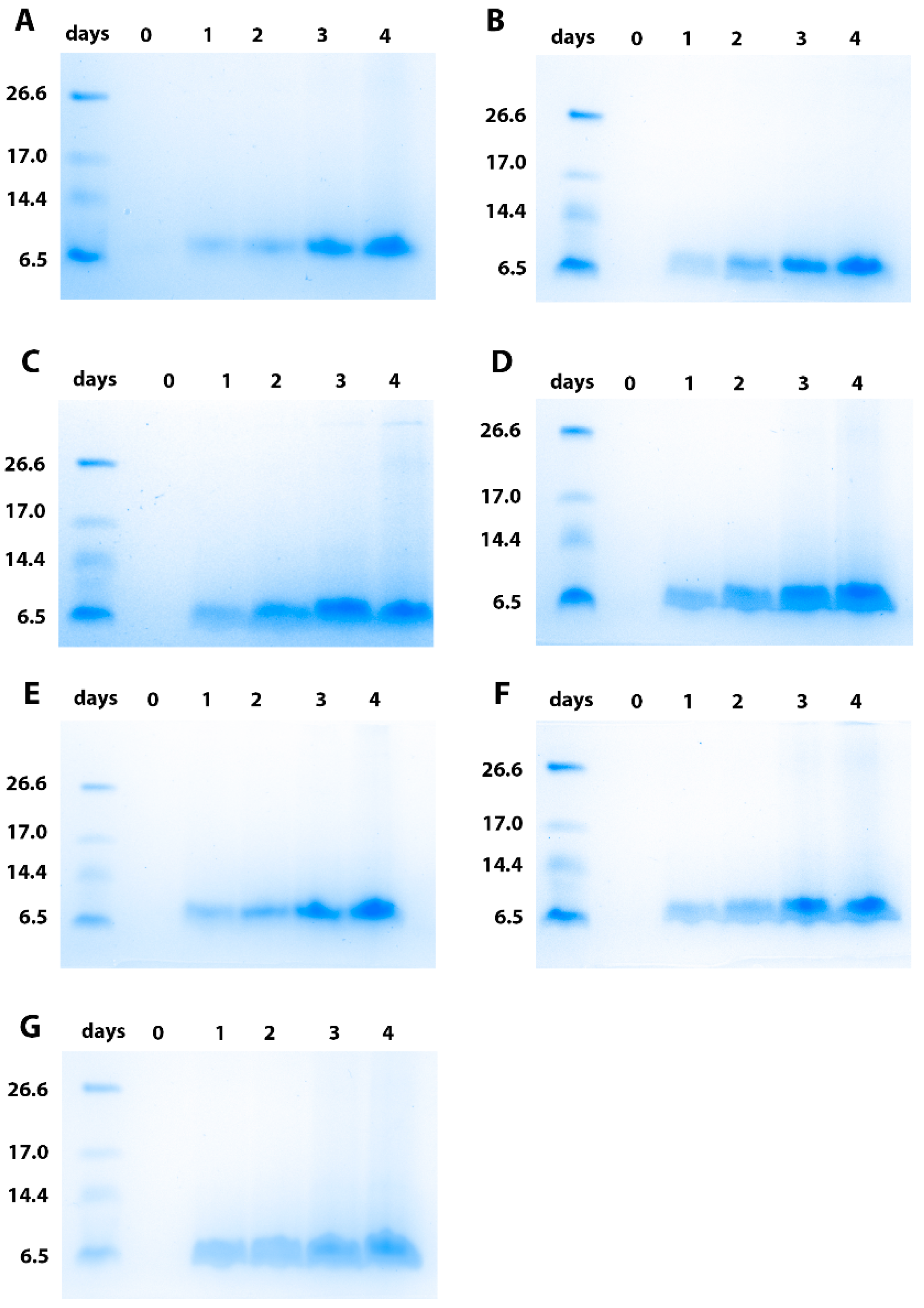
3.3. Production and Purification of the Brazzein Secreted with the Different Constructs
3.4. Activation of the Sweet Taste Receptor by Recombinant Brazzein
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neiers, F.; Naumer, C.; Krohn, M.; Briand, L. The recent development of a sweet-tasting brazzein and its potential industrial applications. In Sweeteners; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; p. 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, D.; Hellekant, G. Brazzein, a new high-potency thermostable sweet protein from Pentadiplandra brazzeana B. FEBS Lett. 1994, 355, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assadi-Porter, F.M.; Aceti, D.J.; Cheng, H.; Markley, J.L. Efficient production of recombinant brazzein, a small, heat-stable, sweet-tasting protein of plant origin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 376, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, N.; Roudnitzky, N.; Brockhoff, A.; Belloir, C.; Maison, M.; Thomas-Danguin, T.; Meyerhof, W.; Briand, L. Efficient production and characterization of the sweet-tasting brazzein secreted by the yeast Pichia pastoris. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9807–9814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, J.E.; Abildgaard, F.; Dzakula, Z.; Ming, D.; Hellekant, G.; Markley, J.L. Solution structure of the thermostable sweet-tasting protein brazzein. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Hongo, N.; Kameda, Y.; Yamamura, A.; Sasaki, H.; Lee, W.C.; Ishikawa, K.; Suzuki, E.; Tanokura, M. The structure of brazzein, a sweet-tasting protein from the wild African plant Pentadiplandra brazzeana. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 2013, 69, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi-Porter, F.M.; Maillet, E.L.; Radek, J.T.; Quijada, J.; Markley, J.L.; Max, M. Key amino acid residues involved in multi-point binding interactions between brazzein, a sweet protein, and the T1R2-T1R3 human sweet receptor. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 398, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Z.; Danilova, V.; Assadi-Porter, F.M.; Aceti, D.J.; Markley, J.L.; Hellekant, G. Critical regions for the sweetness of brazzein. FEBS Lett. 2003, 544, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singarapu, K.K.; Tonelli, M.; Markley, J.L.; Assadi-Porter, F.M. Structure-function relationships of brazzein variants with altered interactions with the human sweet taste receptor. Protein Sci. 2016, 25, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghanavatian, P.; Khalifeh, K.; Jafarian, V. Structural features and activity of Brazzein and its mutants upon substitution of a surfaced exposed alanine. Biochimie 2016, 131, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; Cha, J.E.; Jo, H.J.; Kong, K.H. Multiple mutations of the critical amino acid residues for the sweetness of the sweet-tasting protein, brazzein. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1370–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlec, A.; Strukelj, B. Large increase in brazzein expression achieved by changing the plasmid/strain combination of the NICE system in Lactococcus lactis. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, L. Removal of the N-terminal methionine improves the sweetness of the recombinant expressed sweet-tasting protein brazzein and its mutants in Escherichia coli. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 2020, e13354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; Hellekant, G.; Yan, W. Expression of sweet protein brazzein by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chem. Senses 1995, 20, 701. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi-Nasab, A.; Shahpiri, A. Expression of Brazzein, a Small Sweet-Tasting Protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: An Introduction for Production of Sweet Yeasts. Protein. Pept. Lett. 2020, 27, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Park, S.W.; Lee, S.J.; Kong, K.H. Optimized production and quantification of the tryptophan-deficient sweet-tasting protein brazzein in Kluyveromyces lactis. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamphear, B.J.; Barker, D.K.; Brooks, C.A.; Delaney, D.E.; Lane, J.R.; Beifuss, K.; Love, R.; Thompson, K.; Mayor, J.; Clough, R.; et al. Expression of the sweet protein brazzein in maize for production of a new commercial sweetener. Plant. Biotechnol. J. 2005, 3, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Li, L.; Lu, N.; Zheng, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, B. Expression of a high sweetness and heat-resistant mutant of sweet-tasting protein, monellin, in Pichia pastoris with a constitutive GAPDH promoter and modified N-terminus. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 1941–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, R.D.; Lebhar, H.; Hornung, S.; Thordarson, P.; Marquis, C.P. An improved process for the production of highly purified recombinant thaumatin tagged-variants. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, N.; Kaneko, R.; Wada, R.; Mehta, A.; Tamaki, S.; Tsuruta, T.; Fujita, Y.; Masuda, T.; Kitabatake, N. Cloning of the thaumatin I cDNA and characterization of recombinant thaumatin I secreted by Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, N.; Masuda, T.; Kitabatake, N. Effects of pre- and pro-sequence of thaumatin on the secretion by Pichia pastoris. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 363, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Ueno, Y.; Kitabatake, N. High yield secretion of the sweet-tasting protein lysozyme from the yeast Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 39, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigoillot, M.; Brockhoff, A.; Lescop, E.; Poirier, N.; Meyerhof, W.; Briand, L. Optimization of the production of gurmarin, a sweet-taste-suppressing protein, secreted by the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aw, R.; McKay, P.F.; Shattock, R.J.; Polizzi, K.M. A systematic analysis of the expression of the anti-HIV VRC01 antibody in Pichia pastoris through signal peptide optimization. Protein Expr. Purif. 2018, 149, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrero, J.J.; Casler, J.C.; Valero, F.; Ferrer, P.; Glick, B.S. An improved secretion signal enhances the secretion of model proteins from Pichia pastoris. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briand, L.; Perez, V.; Huet, J.C.; Danty, E.; Masson, C.; Pernollet, J.C. Optimization of the production of a honeybee odorant-binding protein by Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 1999, 15, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naatsaari, L.; Mistlberger, B.; Ruth, C.; Hajek, T.; Hartner, F.S.; Glieder, A. Deletion of the Pichia pastoris KU70 homologue facilitates platform strain generation for gene expression and synthetic biology. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villalobos, A.; Ness, J.E.; Gustafsson, C.; Minshull, J.; Govindarajan, S. Gene Designer: A synthetic biology tool for constructing artificial DNA segments. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paifer, E.; Margolles, E.; Cremata, J.; Montesino, R.; Herrera, L.; Delgado, J.M. Efficient expression and secretion of recombinant alpha amylase in Pichia pastoris using two different signal sequences. Yeast 1994, 10, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, C.; Ye, Y.; Lin, Y. Endogenous signal peptides efficiently mediate the secretion of recombinant proteins in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massahi, A.; Calik, P. In-silico determination of Pichia pastoris signal peptides for extracellular recombinant protein production. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 364, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, C.; Tanaka, M.; Muraki, M.; Harata, K.; Suzuki, K.; Jigami, Y. Human lysozyme secretion increased by alpha-factor pro-sequence in Pichia pastoris. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, R.; Chen, J.; Chen, J. Secreted expression of human lysozyme in the yeast Pichia pastoris under the direction of the signal peptide from human serum albumin. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2008, 51, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuberl, A.; Schneider, J.; Thallinger, G.G.; Anderl, I.; Wibberg, D.; Hajek, T.; Jaenicke, S.; Brinkrolf, K.; Goesmann, A.; Szczepanowski, R.; et al. High-quality genome sequence of Pichia pastoris CBS7435. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 154, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raliou, M.; Grauso, M.; Hoffmann, B.; Schlegel-Le-Poupon, C.; Nespoulous, C.; Debat, H.; Belloir, C.; Wiencis, A.; Sigoillot, M.; Bano, S.P.; et al. Human genetic polymorphisms in T1R1 and T1R3 taste receptor subunits affect their function. Chem. Senses 2011, 36, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerboom, J.; Chen, T.W.; Wardill, T.J.; Tian, L.; Marvin, J.S.; Mutlu, S.; Calderon, N.C.; Esposti, F.; Borghuis, B.G.; Sun, X.R.; et al. Optimization of a GCaMP calcium indicator for neural activity imaging. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 13819–13840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Chen, X.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Gu, L.; Liu, J.R.; Liu, J. A cell-based functional assay using a green fluorescent protein-based calcium indicator dCys-GCaMP. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cregg, J.M.; Vedvick, T.S.; Raschke, W.C. Recent advances in the expression of foreign genes in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology 1993, 11, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschopp, J.F.; Brust, P.F.; Cregg, J.M.; Stillman, C.A.; Gingeras, T.R. Expression of the lacZ gene from two methanol-regulated promoters in Pichia pastoris. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 3859–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Construct Name | Signal Peptide | Organism | Sequence: Signal Peptide | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pAF-bra | α-mating factor | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | * | [4] |
| pAA-bra | α-amylase | Aspergillus niger | MVAWWSLFLYGLQVAAPALA | [29] |
| pAE-bra | Exg1p | Pichia pastoris | MNLYLITLLFASLCSA | [30] |
| pAI-bra | Inulinase | Kluyveromyces maxianus | MKFAYSLLLPLAGVSA | [31] |
| pAL-bra | Lysozyme | Gallus gallus | MLGKNDPMCLVLVLLGLTALLGICQG | [32] |
| pAS-bra | Serum albumin | Homo sapiens | MKWVTFISLLFLFSSAYS | [33] |
| pAV-bra | Invertase | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | MLLQAFLFLLAGFAAKISA | [32] |
| Construct Name and Clone Used for the Production | Purified Brazzein (mg/Liter of Culture) |
|---|---|
| pAF-bra #33 Mut+ | 323 |
| pAA-bra #45 Mut+ | 283 |
| pAE-bra #11 Muts | 72 |
| pAI-bra #49 Mut+ | 44 |
| pAL-bra #10 Mut+ | 345 |
| pAS-bra #7 Muts | 49 |
| pAV-bra #10 Muts | 206 |
| Construct Used for the Production | Measured Mass (Da) | Mass Differences (Da) |
|---|---|---|
| pAF-bra | 6362 ± 1 | 0 |
| pAA-bra | 6375 ± 1 | +13 |
| pAE-bra | 6362 ± 1 | 0 |
| pAI-bra | 6361 ± 1 | 0 |
| pAL-bra | 6375 ± 1 | +13 |
| pAS-bra | 6362 ± 1 | 0 |
| pAV-bra | 6308 ± 1 | −52 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neiers, F.; Belloir, C.; Poirier, N.; Naumer, C.; Krohn, M.; Briand, L. Comparison of Different Signal Peptides for the Efficient Secretion of the Sweet-Tasting Plant Protein Brazzein in Pichia pastoris. Life 2021, 11, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010046
Neiers F, Belloir C, Poirier N, Naumer C, Krohn M, Briand L. Comparison of Different Signal Peptides for the Efficient Secretion of the Sweet-Tasting Plant Protein Brazzein in Pichia pastoris. Life. 2021; 11(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeiers, Fabrice, Christine Belloir, Nicolas Poirier, Christian Naumer, Michael Krohn, and Loïc Briand. 2021. "Comparison of Different Signal Peptides for the Efficient Secretion of the Sweet-Tasting Plant Protein Brazzein in Pichia pastoris" Life 11, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010046
APA StyleNeiers, F., Belloir, C., Poirier, N., Naumer, C., Krohn, M., & Briand, L. (2021). Comparison of Different Signal Peptides for the Efficient Secretion of the Sweet-Tasting Plant Protein Brazzein in Pichia pastoris. Life, 11(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010046




